# Objective
Fix#7447.
The `SystemParam` derive uses the wrong lifetimes for ignored fields.
## Solution
Use type inference instead of explicitly naming the types of ignored fields. This allows the compiler to automatically use the correct lifetime.
# Objective
- Fix panic_when_hierachy_cycle test hanging
- The problem is that the scope only awaits one task at a time in get_results. In stageless this task is the multithreaded executor. That tasks hangs when a system panics and cannot make anymore progress. This wasn't a problem before because the executor was spawned after all the system tasks had been spawned. But in stageless the executor is spawned before all the system tasks are spawned.
## Solution
- We can catch unwind on each system and close the finish channel if one panics. This then causes the receiver end of the finish channel to panic too.
- this might have a small perf impact, but when running many_foxes it seems to be within the noise. So less than 40us.
## Other possible solutions
- It might be possible to fairly poll all the tasks in get_results in the scope. If we could do that then the scope could panic whenever one of tasks panics. It would require a data structure that we could both poll the futures through a shared ref and also push to it. I tried FuturesUnordered, but it requires an exclusive ref to poll it.
- The catch unwind could be moved onto when we create the tasks for scope instead. We would then need something like a oneshot async channel to inform get_results if a task panics.
# Objective
Ability to use `ReflectComponent` methods in dynamic type contexts with no access to `&World`.
This problem occurred to me when wanting to apply reflected types to an entity where the `&World` reference was already consumed by query iterator leaving only `EntityMut`.
## Solution
- Remove redundant `EntityMut` or `EntityRef` lookup from `World` and `Entity` in favor of taking `EntityMut` directly in `ReflectComponentFns`.
- Added `RefectComponent::contains` to determine without panic whether `apply` can be used.
## Changelog
- Changed function signatures of `ReflectComponent` methods, `apply`, `remove`, `contains`, and `reflect`.
## Migration Guide
- Call `World::entity` before calling into the changed `ReflectComponent` methods, most likely user already has a `EntityRef` or `EntityMut` which was being queried redundantly.
# Objective
- Trying to move some of the fixes from https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/7267 to make that one easier to review
- The MainThreadExecutor is how the render world runs nonsend systems on the main thread for pipelined rendering.
- The multithread executor for stageless wasn't using the MainThreadExecutor.
- MainThreadExecutor was declared in the old executor_parallel module that is getting deleted.
- The way the MainThreadExecutor was getting passed to the scope was actually unsound as the resource could be dropped from the World while the schedule was running
## Solution
- Move MainThreadExecutor to the new multithreaded_executor's file.
- Make the multithreaded executor use the MainThreadExecutor
- Clone the MainThreadExecutor onto the stack and pass that ref in
## Changelog
- Move MainThreadExecutor for stageless migration.
# Objective
- After the multithreaded executor finishes running all the systems, we apply the buffers for any system that hasn't applied it's buffers. This is a courtesy apply for users who forget to order their systems before a apply_system_buffers. When checking stageless, it was found that this apply_system_buffers was running on the executor thread instead of the world's thread. This is a problem because anything with world access should be able to access nonsend resources.
## Solution
- Move the final apply_system_buffers outside of the executor and outside of the scope, so it runs on the same thread that schedule.run is called on.
# Objective
In CSS Flexbox width and height are auto by default, whereas in Bevy their default is `Size::Undefined`.
This means that, unlike in CSS, if you elide a height or width value for a node it will be given zero length (unless it has an explicitly sized child node). This has misled users into falsely assuming that they have to explicitly set a value for both height and width all the time.
relevant issue: #7120
## Solution
Change the `Size` `width` and `height` default values to `Val::Auto`
## Changelog
* Changed the `Size` `width` and `height` default values to `Val::Auto`
## Migration Guide
The default values for `Size` `width` and `height` have been changed from `Val::Undefined` to `Val::Auto`.
It's unlikely to cause any issues with existing code.
# Objective
- The stageless executor keeps track of systems that have run, but have not applied their system buffers. The bitset for that was being cloned into apply_system_buffers and cleared in that function, but we need to clear the original version instead of the cloned version
## Solution
- move the clear out of the apply_system_buffers function.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
Clearing the reader doesn't require iterating the events. Updating the `last_event_count` of the reader is enough.
I rewrote part of the documentation as some of it was incorrect or harder to understand than necessary.
## Changelog
Added `ManualEventReader::clear()`
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
# Objective
During testing, I observed that the `FrameCount` resource (`bevy_core`) was being incremented by `FrameCountPlugin` non-deterministically, during update, subject to the whims of the execution order.
The effect was that the counter could and did change while a frame was still in flight, while user-systems were still executing.
## Solution
I have delayed the incrementing of the `FrameCount` resource to `CoreStage::Last`. The resource was described in the documentation as "*a count of rendered frames*" and, after my change, it actually will match that description.
## Changes
- `CoreStage::Last` was chosen so that the counter will be `0` during all earlier stages of the very first execution of the schedule.
- Documentation added declaring *when* the counter is incremented.
- Hint added, directing users towards `u32::wrapping_sub()` because integer overflow is reasonable to expect.
## Note
Even though this change might have a short time-to-live in light of the upcoming *Stageless* changes, I think this is worthwhile – at least as an in-code reminder that this counter should behave predictably.
# Objective
- Resolve a Fixme to remove the `Default` impl for `HandleType`, once Reflection no longer requires it.
- Presumebly this Comment was made before the `FromReflect` Derive used the `#[reflect(Default)]`, to substitute for the requirment that a ignored field has a `Default`.
## Solution
- Just remove the `Default` derive and comment.
## Objective
A common easy to miss mistake is to write something like:
``` rust
Size::new(Val::Percent(100.), Val::Px(100.));
```
`UiRect` has the `left`, `right`, `all`, `vertical`, etc constructor functions, `Size` is used a lot more frequently but lacks anything similar.
## Solution
Implement `all`, `width` and `height` functions for `Size`.
## Changelog
* Added `all`, `width` and `height` functions to `Size`.
# Problem
The field is called `background_color` but it is also used to hold the colors of text glyphs and images.
It's mildly confusing and longer to type than just `color`.
## Solution
Rename `background_color` to `color`.
## Changelog
* Renamed the `background_color` field of `ExtractedUiNode` to `color`.
## Migration Guide
* The `background_color` field of `ExtractedUiNode` is now named `color`.
# Objective
- Fixes#7430.
## Solution
- Changed fields of `ArrayIter` to be private.
- Add a constructor `new` to `ArrayIter`.
- Replace normal struct creation with `new`.
---
## Changelog
- Add a constructor `new` to `ArrayIter`.
Co-authored-by: Elbert Ronnie <103196773+elbertronnie@users.noreply.github.com>
## Objective
Remove `QueuedText`.
`QueuedText` isn't useful. It's exposed in the `bevy_ui` public interface but can't be used for anything because its `entities` field is private.
## Solution
Remove the `QueuedText` struct and use a `Local<Vec<Entity>` in its place.
## Changelog
* Removed `QueuedText`
# Objective
- Bevy should not have any "internal" execution order ambiguities. These clutter the output of user-facing error reporting, and can result in nasty, nondetermistic, very difficult to solve bugs.
- Verifying this currently involves repeated non-trivial manual work.
## Solution
- [x] add an example to quickly check this
- ~~[ ] ensure that this example panics if there are any unresolved ambiguities~~
- ~~[ ] run the example in CI 😈~~
There's one tricky ambiguity left, between UI and animation. I don't have the tools to fix this without system set configuration, so the remaining work is going to be left to #7267 or another PR after that.
```
2023-01-27T18:38:42.989405Z INFO bevy_ecs::schedule::ambiguity_detection: Execution order ambiguities detected, you might want to add an explicit dependency relation between some of these systems:
* Parallel systems:
-- "bevy_animation::animation_player" and "bevy_ui::flex::flex_node_system"
conflicts: ["bevy_transform::components::transform::Transform"]
```
## Changelog
Resolved internal execution order ambiguities for:
1. Transform propagation (ignored, we need smarter filter checking).
2. Gamepad processing (fixed).
3. bevy_winit's window handling (fixed).
4. Cascaded shadow maps and perspectives (fixed).
Also fixed a desynchronized state bug that could occur when the `Window` component is removed and then added to the same entity in a single frame.
# Objective
- Fix a bug causing performance to drop over time because the GPU fog buffer was endlessly growing
## Solution
- Clear the fog buffer every frame before populating it
# Objective
- Fix `post_processing` and `shader_prepass` examples as they fail when compiling shaders due to missing shader defs
- Fixes#6799
- Fixes#6996
- Fixes#7375
- Supercedes #6997
- Supercedes #7380
## Solution
- The prepass was broken due to a missing `MAX_CASCADES_PER_LIGHT` shader def. Add it.
- The shader used in the `post_processing` example is applied to a 2D mesh, so use the correct mesh2d_view_bindings shader import.
# Objective
- Trying to make it easier to have a more user friendly debugging name for when you want to print out an entity.
## Solution
- Add a new `WorldQuery` struct `DebugName` to format the `Name` if the entity has one, otherwise formats the `Entity` id.
This means we can do this and get more descriptive errors without much more effort:
```rust
fn my_system(moving: Query<(DebugName, &mut Position, &Velocity)>) {
for (name, mut position, velocity) in &mut moving {
position += velocity;
if position.is_nan() {
error!("{:?} has an invalid position state", name);
}
}
}
```
---
## Changelog
- Added `DebugName` world query for more human friendly debug names of entities.
# Objective
In simple cases we might want to derive the `ExtractComponent` trait.
This adds symmetry to the existing `ExtractResource` derive.
## Solution
Add an implementation of `#[derive(ExtractComponent)]`.
The implementation is adapted from the existing `ExtractResource` derive macro.
Additionally, there is an attribute called `extract_component_filter`. This allows specifying a query filter type used when extracting.
If not specified, no filter (equal to `()`) is used.
So:
```rust
#[derive(Component, Clone, ExtractComponent)]
#[extract_component_filter(With<Fuel>)]
pub struct Car {
pub wheels: usize,
}
```
would expand to (a bit cleaned up here):
```rust
impl ExtractComponent for Car
{
type Query = &'static Self;
type Filter = With<Fuel>;
type Out = Self;
fn extract_component(item: QueryItem<'_, Self::Query>) -> Option<Self::Out> {
Some(item.clone())
}
}
```
---
## Changelog
- Added the ability to `#[derive(ExtractComponent)]` with an optional filter.
# Objective
- Fixes#4592
## Solution
- Implement `SrgbColorSpace` for `u8` via `f32`
- Convert KTX2 R8 and R8G8 non-linear sRGB to wgpu `R8Unorm` and `Rg8Unorm` as non-linear sRGB are not supported by wgpu for these formats
- Convert KTX2 R8G8B8 formats to `Rgba8Unorm` and `Rgba8UnormSrgb` by adding an alpha channel as the Rgb variants don't exist in wgpu
---
## Changelog
- Added: Support for KTX2 `R8_SRGB`, `R8_UNORM`, `R8G8_SRGB`, `R8G8_UNORM`, `R8G8B8_SRGB`, `R8G8B8_UNORM` formats by converting to supported wgpu formats as appropriate
# Objective
Add a `FromReflect` derive to the `Aabb` type, like all other math types, so we can reflect `Vec<Aabb>`.
## Solution
Just add it :)
---
## Changelog
### Added
- Implemented `FromReflect` for `Aabb`.
# Objective
Update Bevy to wgpu 0.15.
## Changelog
- Update to wgpu 0.15, wgpu-hal 0.15.1, and naga 0.11
- Users can now use the [DirectX Shader Compiler](https://github.com/microsoft/DirectXShaderCompiler) (DXC) on Windows with DX12 for faster shader compilation and ShaderModel 6.0+ support (requires `dxcompiler.dll` and `dxil.dll`, which are included in DXC downloads from [here](https://github.com/microsoft/DirectXShaderCompiler/releases/latest))
## Migration Guide
### WGSL Top-Level `let` is now `const`
All top level constants are now declared with `const`, catching up with the wgsl spec.
`let` is no longer allowed at the global scope, only within functions.
```diff
-let SOME_CONSTANT = 12.0;
+const SOME_CONSTANT = 12.0;
```
#### `TextureDescriptor` and `SurfaceConfiguration` now requires a `view_formats` field
The new `view_formats` field in the `TextureDescriptor` is used to specify a list of formats the texture can be re-interpreted to in a texture view. Currently only changing srgb-ness is allowed (ex. `Rgba8Unorm` <=> `Rgba8UnormSrgb`). You should set `view_formats` to `&[]` (empty) unless you have a specific reason not to.
#### The DirectX Shader Compiler (DXC) is now supported on DX12
DXC is now the default shader compiler when using the DX12 backend. DXC is Microsoft's replacement for their legacy FXC compiler, and is faster, less buggy, and allows for modern shader features to be used (ShaderModel 6.0+). DXC requires `dxcompiler.dll` and `dxil.dll` to be available, otherwise it will log a warning and fall back to FXC.
You can get `dxcompiler.dll` and `dxil.dll` by downloading the latest release from [Microsoft's DirectXShaderCompiler github repo](https://github.com/microsoft/DirectXShaderCompiler/releases/latest) and copying them into your project's root directory. These must be included when you distribute your Bevy game/app/etc if you plan on supporting the DX12 backend and are using DXC.
`WgpuSettings` now has a `dx12_shader_compiler` field which can be used to choose between either FXC or DXC (if you pass None for the paths for DXC, it will check for the .dlls in the working directory).
# Objective
- Fix#7315
- Add IME support
## Solution
- Add two new fields to `Window`, to control if IME is enabled and the candidate box position
This allows the use of dead keys which are needed in French, or the full IME experience to type using Pinyin
I also added a basic general text input example that can handle IME input.
https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/8672791/213941353-5ed73a73-5dd1-4e66-a7d6-a69b49694c52.mp4
<img width="1392" alt="image" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/418473/203873533-44c029af-13b7-4740-8ea3-af96bd5867c9.png">
<img width="1392" alt="image" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/418473/203873549-36be7a23-b341-42a2-8a9f-ceea8ac7a2b8.png">
# Objective
- Add support for the “classic” distance fog effect, as well as a more advanced atmospheric fog effect.
## Solution
This PR:
- Introduces a new `FogSettings` component that controls distance fog per-camera.
- Adds support for three widely used “traditional” fog falloff modes: `Linear`, `Exponential` and `ExponentialSquared`, as well as a more advanced `Atmospheric` fog;
- Adds support for directional light influence over fog color;
- Extracts fog via `ExtractComponent`, then uses a prepare system that sets up a new dynamic uniform struct (`Fog`), similar to other mesh view types;
- Renders fog in PBR material shader, as a final adjustment to the `output_color`, after PBR is computed (but before tone mapping);
- Adds a new `StandardMaterial` flag to enable fog; (`fog_enabled`)
- Adds convenience methods for easier artistic control when creating non-linear fog types;
- Adds documentation around fog.
---
## Changelog
### Added
- Added support for distance-based fog effects for PBR materials, controllable per-camera via the new `FogSettings` component;
- Added `FogFalloff` enum for selecting between three widely used “traditional” fog falloff modes: `Linear`, `Exponential` and `ExponentialSquared`, as well as a more advanced `Atmospheric` fog;
# Objective
Found while working on #7385.
The struct `EntityMut` has the safety invariant that it's cached `EntityLocation` must always accurately specify where the entity is stored. Thus, any time its location might be invalidated (such as by calling `EntityMut::world_mut` and moving archetypes), the cached location *must* be updated by calling `EntityMut::update_location`.
The method `world_scope` encapsulates this pattern in safe API by requiring world mutations to be done in a closure, after which `update_location` will automatically be called. However, this method has a soundness hole: if a panic occurs within the closure, then `update_location` will never get called. If the panic is caught in an outer scope, then the `EntityMut` will be left with an outdated location, which is undefined behavior.
An example of this can be seen in the unit test `entity_mut_world_scope_panic`, which has been added to this PR as a regression test. Without the other changes in this PR, that test will invoke undefined behavior in safe code.
## Solution
Call `EntityMut::update_location()` from within a `Drop` impl, which ensures that it will get executed even if `EntityMut::world_scope` unwinds.
# Objective
I recently had an issue, where I have a struct:
```
struct Property {
inner: T
}
```
that I use as a wrapper for internal purposes.
I don't want to update my struct definition to
```
struct Property<T: Reflect>{
inner: T
}
```
because I still want to be able to build `Property<T>` for types `T` that are not `Reflect`. (and also because I don't want to update my whole code base with `<T: Reflect>` bounds)
I still wanted to have reflection on it (for `bevy_inspector_egui`), but adding `derive(Reflect)` fails with the error:
`T cannot be sent between threads safely. T needs to implement Sync.`
I believe that `bevy_reflect` should adopt the model of other derives in the case of generics, which is to add the `Reflect` implementation only if the generics also implement `Reflect`. (That is the behaviour of other macros such as `derive(Clone)` or `derive(Debug)`.
It's also the current behavior of `derive(FromReflect)`.
Basically doing something like:
```
impl<T> Reflect for Foo<T>
where T: Reflect
```
## Solution
- I updated the derive macros for `Structs` and `TupleStructs` to add extra `where` bounds.
- Every type that is reflected will need a `T: Reflect` bound
- Ignored types will need a `T: 'static + Send + Sync` bound. Here's the reason. For cases like this:
```
#[derive(Reflect)]
struct Foo<T, U>{
a: T
#[reflect(ignore)]
b: U
}
```
I had to add the bound `'static + Send + Sync` to ignored generics like `U`.
The reason is that we want `Foo<T, U>` to be `Reflect: 'static + Send + Sync`, so `Foo<T, U>` must be able to implement those auto-traits. `Foo<T, U>` will only implement those auto-traits if every generic type implements them, including ignored types.
This means that the previously compile-fail case now compiles:
```
#[derive(Reflect)]
struct Foo<'a> {
#[reflect(ignore)]
value: &'a str,
}
```
But `Foo<'a>` will only be useable in the cases where `'a: 'static` and panic if we don't have `'a: 'static`, which is what we want (nice bonus from this PR ;) )
---
## Changelog
> This section is optional. If this was a trivial fix, or has no externally-visible impact, you can delete this section.
### Added
Possibility to add `derive(Reflect)` to structs and enums that contain generic types, like so:
```
#[derive(Reflect)]
struct Foo<T>{
a: T
}
```
Reflection will only be available if the generic type T also implements `Reflect`.
(previously, this would just return a compiler error)
# Objective
The function `EntityMut::world_scope` is a safe abstraction that allows you to temporarily get mutable access to the underlying `World` of an `EntityMut`. This function is purely stateful, meaning it is not easily possible to return a value from it.
## Solution
Allow returning a computed value from the closure. This is similar to how `World::resource_scope` works.
---
## Changelog
- The function `EntityMut::world_scope` now allows returning a value from the immediately-computed closure.
# Objective
## Use Case
A render node which calls `post_process_write()` on a `ViewTarget` multiple times during a single run of the node means both main textures of this view target is accessed.
If the source texture (which alternate between main textures **a** and **b**) is accessed in a shader during those iterations it means that those textures have to be bound using bind groups.
Preparing bind groups for both main textures ahead of time is desired, which means having access to the _other_ main texture is needed.
## Solution
Add a method on `ViewTarget` for accessing the other main texture.
---
## Changelog
### Added
- `main_texture_other` API on `ViewTarget`
# Objective
There's no period at the end of the first line of the `Name` documentation, and this messes up the grammar of the summary rustdoc creates:
```
↓
Component used to identify an entity. Stores a hash for faster comparisons The hash is eagerly re-computed upon each update to the name.
```
## Solution
I added it.
# Objective
I found several words in code and docs are incorrect. This should be fixed.
## Solution
- Fix several minor typos
Co-authored-by: Chris Ohk <utilforever@gmail.com>
alternative to #5922, implements #5956
builds on top of https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/6402
# Objective
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/5956 goes into more detail, but the TLDR is:
- bevy systems ensure disjoint accesses to resources and components, and for that to work there are methods `World::get_resource_unchecked_mut(&self)`, ..., `EntityRef::get_mut_unchecked(&self)` etc.
- we don't have these unchecked methods for `by_id` variants, so third-party crate authors cannot build their own safe disjoint-access abstractions with these
- having `_unchecked_mut` methods is not great, because in their presence safe code can accidentally violate subtle invariants. Having to go through `world.as_unsafe_world_cell().unsafe_method()` forces you to stop and think about what you want to write in your `// SAFETY` comment.
The alternative is to keep exposing `_unchecked_mut` variants for every operation that we want third-party crates to build upon, but we'd prefer to avoid using these methods alltogether: https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/5922#issuecomment-1241954543
Also, this is something that **cannot be implemented outside of bevy**, so having either this PR or #5922 as an escape hatch with lots of discouraging comments would be great.
## Solution
- add `UnsafeWorldCell` with `unsafe fn get_resource(&self)`, `unsafe fn get_resource_mut(&self)`
- add `fn World::as_unsafe_world_cell(&mut self) -> UnsafeWorldCell<'_>` (and `as_unsafe_world_cell_readonly(&self)`)
- add `UnsafeWorldCellEntityRef` with `unsafe fn get`, `unsafe fn get_mut` and the other utilities on `EntityRef` (no methods for spawning, despawning, insertion)
- use the `UnsafeWorldCell` abstraction in `ReflectComponent`, `ReflectResource` and `ReflectAsset`, so these APIs are easier to reason about
- remove `World::get_resource_mut_unchecked`, `EntityRef::get_mut_unchecked` and use `unsafe { world.as_unsafe_world_cell().get_mut() }` and `unsafe { world.as_unsafe_world_cell().get_entity(entity)?.get_mut() }` instead
This PR does **not** make use of `UnsafeWorldCell` for anywhere else in `bevy_ecs` such as `SystemParam` or `Query`. That is a much larger change, and I am convinced that having `UnsafeWorldCell` is already useful for third-party crates.
Implemented API:
```rust
struct World { .. }
impl World {
fn as_unsafe_world_cell(&self) -> UnsafeWorldCell<'_>;
}
struct UnsafeWorldCell<'w>(&'w World);
impl<'w> UnsafeWorldCell {
unsafe fn world(&self) -> &World;
fn get_entity(&self) -> UnsafeWorldCellEntityRef<'w>; // returns 'w which is `'self` of the `World::as_unsafe_world_cell(&'w self)`
unsafe fn get_resource<T>(&self) -> Option<&'w T>;
unsafe fn get_resource_by_id(&self, ComponentId) -> Option<&'w T>;
unsafe fn get_resource_mut<T>(&self) -> Option<Mut<'w, T>>;
unsafe fn get_resource_mut_by_id(&self) -> Option<MutUntyped<'w>>;
unsafe fn get_non_send_resource<T>(&self) -> Option<&'w T>;
unsafe fn get_non_send_resource_mut<T>(&self) -> Option<Mut<'w, T>>>;
// not included: remove, remove_resource, despawn, anything that might change archetypes
}
struct UnsafeWorldCellEntityRef<'w> { .. }
impl UnsafeWorldCellEntityRef<'w> {
unsafe fn get<T>(&self, Entity) -> Option<&'w T>;
unsafe fn get_by_id(&self, Entity, ComponentId) -> Option<Ptr<'w>>;
unsafe fn get_mut<T>(&self, Entity) -> Option<Mut<'w, T>>;
unsafe fn get_mut_by_id(&self, Entity, ComponentId) -> Option<MutUntyped<'w>>;
unsafe fn get_change_ticks<T>(&self, Entity) -> Option<Mut<'w, T>>;
// fn id, archetype, contains, contains_id, containts_type_id
}
```
<details>
<summary>UnsafeWorldCell docs</summary>
Variant of the [`World`] where resource and component accesses takes a `&World`, and the responsibility to avoid
aliasing violations are given to the caller instead of being checked at compile-time by rust's unique XOR shared rule.
### Rationale
In rust, having a `&mut World` means that there are absolutely no other references to the safe world alive at the same time,
without exceptions. Not even unsafe code can change this.
But there are situations where careful shared mutable access through a type is possible and safe. For this, rust provides the [`UnsafeCell`](std::cell::UnsafeCell)
escape hatch, which allows you to get a `*mut T` from a `&UnsafeCell<T>` and around which safe abstractions can be built.
Access to resources and components can be done uniquely using [`World::resource_mut`] and [`World::entity_mut`], and shared using [`World::resource`] and [`World::entity`].
These methods use lifetimes to check at compile time that no aliasing rules are being broken.
This alone is not enough to implement bevy systems where multiple systems can access *disjoint* parts of the world concurrently. For this, bevy stores all values of
resources and components (and [`ComponentTicks`](crate::component::ComponentTicks)) in [`UnsafeCell`](std::cell::UnsafeCell)s, and carefully validates disjoint access patterns using
APIs like [`System::component_access`](crate::system::System::component_access).
A system then can be executed using [`System::run_unsafe`](crate::system::System::run_unsafe) with a `&World` and use methods with interior mutability to access resource values.
access resource values.
### Example Usage
[`UnsafeWorldCell`] can be used as a building block for writing APIs that safely allow disjoint access into the world.
In the following example, the world is split into a resource access half and a component access half, where each one can
safely hand out mutable references.
```rust
use bevy_ecs::world::World;
use bevy_ecs::change_detection::Mut;
use bevy_ecs::system::Resource;
use bevy_ecs::world::unsafe_world_cell_world::UnsafeWorldCell;
// INVARIANT: existance of this struct means that users of it are the only ones being able to access resources in the world
struct OnlyResourceAccessWorld<'w>(UnsafeWorldCell<'w>);
// INVARIANT: existance of this struct means that users of it are the only ones being able to access components in the world
struct OnlyComponentAccessWorld<'w>(UnsafeWorldCell<'w>);
impl<'w> OnlyResourceAccessWorld<'w> {
fn get_resource_mut<T: Resource>(&mut self) -> Option<Mut<'w, T>> {
// SAFETY: resource access is allowed through this UnsafeWorldCell
unsafe { self.0.get_resource_mut::<T>() }
}
}
// impl<'w> OnlyComponentAccessWorld<'w> {
// ...
// }
// the two interior mutable worlds borrow from the `&mut World`, so it cannot be accessed while they are live
fn split_world_access(world: &mut World) -> (OnlyResourceAccessWorld<'_>, OnlyComponentAccessWorld<'_>) {
let resource_access = OnlyResourceAccessWorld(unsafe { world.as_unsafe_world_cell() });
let component_access = OnlyComponentAccessWorld(unsafe { world.as_unsafe_world_cell() });
(resource_access, component_access)
}
```
</details>
# Objective
Prevent things from breaking tomorrow when rust 1.67 is released.
## Solution
Fix a few `uninlined_format_args` lints in recently introduced code.
# Objective
Fixes#6952
## Solution
- Request WGPU capabilities `SAMPLED_TEXTURE_AND_STORAGE_BUFFER_ARRAY_NON_UNIFORM_INDEXING`, `SAMPLER_NON_UNIFORM_INDEXING` and `UNIFORM_BUFFER_AND_STORAGE_TEXTURE_ARRAY_NON_UNIFORM_INDEXING` when corresponding features are enabled.
- Add an example (`shaders/texture_binding_array`) illustrating (and testing) the use of non-uniform indexed textures and samplers.
## Changelog
- Added new capabilities for shader validation.
- Added example `shaders/texture_binding_array`.
Co-authored-by: Robert Swain <robert.swain@gmail.com>
# Objective
Implements cascaded shadow maps for directional lights, which produces better quality shadows without needing excessively large shadow maps.
Fixes#3629
Before
After
## Solution
Rather than rendering a single shadow map for directional light, the view frustum is divided into a series of cascades, each of which gets its own shadow map. The correct cascade is then sampled for shadow determination.
---
## Changelog
Directional lights now use cascaded shadow maps for improved shadow quality.
## Migration Guide
You no longer have to manually specify a `shadow_projection` for a directional light, and these settings should be removed. If customization of how cascaded shadow maps work is desired, modify the `CascadeShadowConfig` component instead.
# Objective
Fixes#7286. Both `App::add_sub_app` and `App::insert_sub_app` are rather redundant. Before 0.10 is shipped, one of them should be removed.
## Solution
Remove `App::add_sub_app` to prefer `App::insert_sub_app`.
Also hid away `SubApp::extract` since that can be a footgun if someone mutates it for whatever reason. Willing to revert this change if there are objections.
Perhaps we should make `SubApp: Deref<Target=App>`? Might change if we decide to move `!Send` resources into it.
---
## Changelog
Added: `SubApp::new`
Removed: `App::add_sub_app`
## Migration Guide
`App::add_sub_app` has been removed in favor of `App::insert_sub_app`. Use `SubApp::new` and insert it via `App::add_sub_app`
Old:
```rust
let mut sub_app = App::new()
// Build subapp here
app.add_sub_app(MySubAppLabel, sub_app);
```
New:
```rust
let mut sub_app = App::new()
// Build subapp here
app.insert_sub_app(MySubAppLabel, SubApp::new(sub_app, extract_fn));
```
# Objective
- The functions added to utils.wgsl by the prepass assume that mesh_view_bindings are present, which isn't always the case
- Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/7353
## Solution
- Move these functions to their own `prepass_utils.wgsl` file
Co-authored-by: IceSentry <IceSentry@users.noreply.github.com>
# Problem
The `upsert_leaf` method creates a new `MeasureFunc` and, if required, a new leaf node, but then it only adds the new `MeasureFunc` to existing leaf nodes.
## Solution
Add the `MeasureFunc` to new leaf nodes as well.
# Objective
`add_system(system)` without any `.in_set` configuration should land in `CoreSet::Update`.
We check that the sets are empty, but for systems there is always the `SystemTypeset`.
## Solution
- instead of `is_empty()`, check that the only set it the `SystemTypeSet`
# Objective
The naming of the two plugin groups `DefaultPlugins` and `MinimalPlugins` suggests that one is a super-set of the other but this is not the case. Instead, the two plugin groups are intended for very different purposes.
Closes: https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/7173
## Solution
This merge request adds doc. comments that compensate for this and try save the user from confusion.
1. `DefaultPlugins` and `MinimalPlugins` intentions are described.
2. A strong emphasis on embracing `DefaultPlugins` as a whole but controlling what it contains with *Cargo* *features* is added – this is because the ordering in `DefaultPlugins` appears to be important so preventing users with "minimalist" foibles (That's Me!) from recreating the code seems worthwhile.
3. Notes are added explaining the confusing fact that `MinimalPlugins` contains `ScheduleRunnerPlugin` (which is very "important"-sounding) but `DefaultPlugins` does not.
# Objective
Help users understand how to write code that runs when the app is exiting.
See:
- #7067 (Partial resolution)
## Solution
Added documentation to `AppExit` class that mentions using the `Drop` trait for code that needs to run on program exit, as well as linking to the caveat about `App::run()` not being guaranteed to return.
# Objective
`bevy_ecs/system_param.rs` contains many seemingly-arbitrary struct definitions which serve as compile tests.
## Solution
Add a comment to each one, linking the issue or PR that motivated its addition.
# Objective
> ℹ️ **This is an adoption of #4081 by @james7132**
Fixes#4080.
Provide a way to pre-parse reflection paths so as to avoid having to parse at each call to `GetPath::path` (or similar method).
## Solution
Adds the `ParsedPath` struct (named `FieldPath` in the original PR) that parses and caches the sequence of accesses to a reflected element. This is functionally similar to the `GetPath` trait, but removes the need to parse an unchanged path more than once.
### Additional Changes
Included in this PR from the original is cleaner code as well as the introduction of a new pathing operation: field access by index. This allows struct and struct variant fields to be accessed in a more performant (albeit more fragile) way if needed. This operation is faster due to not having to perform string matching. As an example, if we wanted the third field on a struct, we'd write `#2`—where `#` denotes indexed access and `2` denotes the desired field index.
This PR also contains improved documentation for `GetPath` and friends, including renaming some of the methods to be more clear to the end-user with a reduced risk of getting them mixed up.
### Future Work
There are a few things that could be done as a separate PR (order doesn't matter— they could be followup PRs or done in parallel). These are:
- [x] ~~Add support for `Tuple`. Currently, we hint that they work but they do not.~~ See #7324
- [ ] Cleanup `ReflectPathError`. I think it would be nicer to give `ReflectPathError` two variants: `ReflectPathError::ParseError` and `ReflectPathError::AccessError`, with all current variants placed within one of those two. It's not obvious when one might expect to receive one type of error over the other, so we can help by explicitly categorizing them.
---
## Changelog
- Cleaned up `GetPath` logic
- Added `ParsedPath` for cached reflection paths
- Added new reflection path syntax: struct field access by index (example syntax: `foo#1`)
- Renamed methods on `GetPath`:
- `path` -> `reflect_path`
- `path_mut` -> `reflect_path_mut`
- `get_path` -> `path`
- `get_path_mut` -> `path_mut`
## Migration Guide
`GetPath` methods have been renamed according to the following:
- `path` -> `reflect_path`
- `path_mut` -> `reflect_path_mut`
- `get_path` -> `path`
- `get_path_mut` -> `path_mut`
Co-authored-by: Gino Valente <gino.valente.code@gmail.com>
# Objective
On wasm, bevy applications currently prevent any of the normal browser hotkeys from working normally (Ctrl+R, F12, F5, Ctrl+F5, tab, etc.).
Some of those events you may want to override, perhaps you can hold the tab key for showing in-game stats?
However, if you want to make a well-behaved game, you probably don't want to needlessly prevent that behavior unless you have a good reason.
Secondary motivation: Also, consider the workaround presented here to get audio working: https://developer.chrome.com/blog/web-audio-autoplay/#moving-forward ; It won't work (for keydown events) if we stop event propagation.
## Solution
- Winit has a field that allows it to not stop event propagation, expose it on the window settings to allow the user to choose the desired behavior. Default to `true` for backwards compatibility.
---
## Changelog
- Added `Window::prevent_default_event_handling` . This allows bevy apps to not override default browser behavior on hotkeys like F5, F12, Ctrl+R etc.
# Problemo
Some code in #5911 and #5454 does not compile with dynamic linking enabled.
The code is behind a feature gate to prevent dynamically linked builds from breaking, but it's not quite set up correctly.
## Solution
Forward the `dynamic` feature flag to the `bevy_diagnostic` crate and gate the code behind it.
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
# Objective
Fixes#5675. Replace `toml` with `toml_edit`
## Solution
Replace `toml` with `toml_edit`. This conveniently also removes the `serde` dependency from `bevy_macro_utils`, which may speed up cold compilation by removing the serde bottleneck from most of the macro crates in the engine.
# Objective
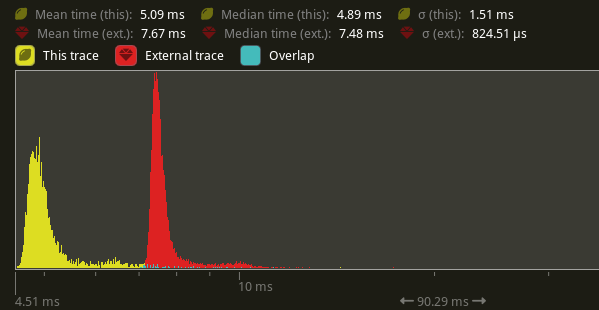
Speed up `prepare_uinodes`. The color `[f32; 4]` is being computed separately for every vertex in the UI, even though the color is the same for all 6 verticies.
## Solution
Avoid recomputing the color and cache it for all 6 verticies.
## Performance
On `many_buttons`, this shaved off 33% of the time in `prepare_uinodes` (7.67ms -> 5.09ms) on my local machine.
# Objective
`RenderContext`, the core abstraction for running the render graph, currently only supports recording one `CommandBuffer` across the entire render graph. This means the entire buffer must be recorded sequentially, usually via the render graph itself. This prevents parallelization and forces users to only encode their commands in the render graph.
## Solution
Allow `RenderContext` to store a `Vec<CommandBuffer>` that it progressively appends to. By default, the context will not have a command encoder, but will create one as soon as either `begin_tracked_render_pass` or the `command_encoder` accesor is first called. `RenderContext::add_command_buffer` allows users to interrupt the current command encoder, flush it to the vec, append a user-provided `CommandBuffer` and reset the command encoder to start a new buffer. Users or the render graph will call `RenderContext::finish` to retrieve the series of buffers for submitting to the queue.
This allows users to encode their own `CommandBuffer`s outside of the render graph, potentially in different threads, and store them in components or resources.
Ideally, in the future, the core pipeline passes can run in `RenderStage::Render` systems and end up saving the completed command buffers to either `Commands` or a field in `RenderPhase`.
## Alternatives
The alternative is to use to use wgpu's `RenderBundle`s, which can achieve similar results; however it's not universally available (no OpenGL, WebGL, and DX11).
---
## Changelog
Added: `RenderContext::new`
Added: `RenderContext::add_command_buffer`
Added: `RenderContext::finish`
Changed: `RenderContext::render_device` is now private. Use the accessor `RenderContext::render_device()` instead.
Changed: `RenderContext::command_encoder` is now private. Use the accessor `RenderContext::command_encoder()` instead.
Changed: `RenderContext` now supports adding external `CommandBuffer`s for inclusion into the render graphs. These buffers can be encoded outside of the render graph (i.e. in a system).
## Migration Guide
`RenderContext`'s fields are now private. Use the accessors on `RenderContext` instead, and construct it with `RenderContext::new`.
# Objective
- This PR adds support for blend modes to the PBR `StandardMaterial`.
<img width="1392" alt="Screenshot 2022-11-18 at 20 00 56" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/418473/202820627-0636219a-a1e5-437a-b08b-b08c6856bf9c.png">
<img width="1392" alt="Screenshot 2022-11-18 at 20 01 01" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/418473/202820615-c8d43301-9a57-49c4-bd21-4ae343c3e9ec.png">
## Solution
- The existing `AlphaMode` enum is extended, adding three more modes: `AlphaMode::Premultiplied`, `AlphaMode::Add` and `AlphaMode::Multiply`;
- All new modes are rendered in the existing `Transparent3d` phase;
- The existing mesh flags for alpha mode are reorganized for a more compact/efficient representation, and new values are added;
- `MeshPipelineKey::TRANSPARENT_MAIN_PASS` is refactored into `MeshPipelineKey::BLEND_BITS`.
- `AlphaMode::Opaque` and `AlphaMode::Mask(f32)` share a single opaque pipeline key: `MeshPipelineKey::BLEND_OPAQUE`;
- `Blend`, `Premultiplied` and `Add` share a single premultiplied alpha pipeline key, `MeshPipelineKey::BLEND_PREMULTIPLIED_ALPHA`. In the shader, color values are premultiplied accordingly (or not) depending on the blend mode to produce the three different results after PBR/tone mapping/dithering;
- `Multiply` uses its own independent pipeline key, `MeshPipelineKey::BLEND_MULTIPLY`;
- Example and documentation are provided.
---
## Changelog
### Added
- Added support for additive and multiplicative blend modes in the PBR `StandardMaterial`, via `AlphaMode::Add` and `AlphaMode::Multiply`;
- Added support for premultiplied alpha in the PBR `StandardMaterial`, via `AlphaMode::Premultiplied`;
# Objective
Currently, Text always uses the default linebreaking behaviour in glyph_brush_layout `BuiltInLineBreaker::Unicode` which breaks lines at word boundaries. However, glyph_brush_layout also supports breaking lines at any character by setting the linebreaker to `BuiltInLineBreaker::AnyChar`. Having text wrap character-by-character instead of at word boundaries is desirable in some cases - consider that consoles/terminals usually wrap this way.
As a side note, the default Unicode linebreaker does not seem to handle emergency cases, where there is no word boundary on a line to break at. In that case, the text runs out of bounds. Issue #1867 shows an example of this.
## Solution
Basically just copies how TextAlignment is exposed, but for a new enum TextLineBreakBehaviour.
This PR exposes glyph_brush_layout's two simple linebreaking options (Unicode, AnyChar) to users of Text via the enum TextLineBreakBehaviour (which just translates those 2 aforementioned options), plus a method 'with_linebreak_behaviour' on Text and TextBundle.
## Changelog
Added `Text::with_linebreak_behaviour`
Added `TextBundle::with_linebreak_behaviour`
`TextPipeline::queue_text` and `GlyphBrush::compute_glyphs` now need a TextLineBreakBehaviour argument, in order to pass through the new field.
Modified the `text2d` example to show both linebreaking behaviours.
## Example
Here's what the modified example looks like

# Objective
- Fixes#7294
## Solution
- Do not trigger change detection when setting the cursor position from winit
When moving the cursor continuously, Winit sends events:
- CursorMoved(0)
- CursorMoved(1)
- => start of Bevy schedule execution
- CursorMoved(2)
- CursorMoved(3)
- <= End of Bevy schedule execution
if Bevy schedule runs after the event 1, events 2 and 3 would happen during the execution but would be read only on the next system run. During the execution, the system would detect a change on cursor position, and send back an order to winit to move it back to 1, so event 2 and 3 would be ignored. By bypassing change detection when setting the cursor from winit event, it doesn't trigger sending back that change to winit out of order.
# Objective
- `Components::resource_id` doesn't exist. Like `Components::component_id` but for resources.
## Solution
- Created `Components::resource_id` and added some docs.
---
## Changelog
- Added `Components::resource_id`.
- Changed `World::init_resource` to return the generated `ComponentId`.
- Changed `World::init_non_send_resource` to return the generated `ComponentId`.
# Objective
- Fixes#7288
- Do not expose access directly to cursor position as it is the physical position, ignoring scale
## Solution
- Make cursor position private
- Expose getter/setter on the window to have access to the scale
# Objective
Fixes#6931
Continues #6954 by squashing `Msaa` to a flat enum
Helps out #7215
# Solution
```
pub enum Msaa {
Off = 1,
#[default]
Sample4 = 4,
}
```
# Changelog
- Modified
- `Msaa` is now enum
- Defaults to 4 samples
- Uses `.samples()` method to get the sample number as `u32`
# Migration Guide
```
let multi = Msaa { samples: 4 }
// is now
let multi = Msaa::Sample4
multi.samples
// is now
multi.samples()
```
Co-authored-by: Sjael <jakeobrien44@gmail.com>
After #6503, bevy_render uses the `send_blocking` method introduced in async-channel 1.7, but depended only on ^1.4.
I saw this after pulling main without running cargo update.
# Objective
- Fix minimum dependency version of async-channel
## Solution
- Bump async-channel version constraint to ^1.8, which is currently the latest version.
NOTE: Both bevy_ecs and bevy_tasks also depend on async-channel but they didn't use any newer features.
# Objective
Fixes#3184. Fixes#6640. Fixes#4798. Using `Query::par_for_each(_mut)` currently requires a `batch_size` parameter, which affects how it chunks up large archetypes and tables into smaller chunks to run in parallel. Tuning this value is difficult, as the performance characteristics entirely depends on the state of the `World` it's being run on. Typically, users will just use a flat constant and just tune it by hand until it performs well in some benchmarks. However, this is both error prone and risks overfitting the tuning on that benchmark.
This PR proposes a naive automatic batch-size computation based on the current state of the `World`.
## Background
`Query::par_for_each(_mut)` schedules a new Task for every archetype or table that it matches. Archetypes/tables larger than the batch size are chunked into smaller tasks. Assuming every entity matched by the query has an identical workload, this makes the worst case scenario involve using a batch size equal to the size of the largest matched archetype or table. Conversely, a batch size of `max {archetype, table} size / thread count * COUNT_PER_THREAD` is likely the sweetspot where the overhead of scheduling tasks is minimized, at least not without grouping small archetypes/tables together.
There is also likely a strict minimum batch size below which the overhead of scheduling these tasks is heavier than running the entire thing single-threaded.
## Solution
- [x] Remove the `batch_size` from `Query(State)::par_for_each` and friends.
- [x] Add a check to compute `batch_size = max {archeytpe/table} size / thread count * COUNT_PER_THREAD`
- [x] ~~Panic if thread count is 0.~~ Defer to `for_each` if the thread count is 1 or less.
- [x] Early return if there is no matched table/archetype.
- [x] Add override option for users have queries that strongly violate the initial assumption that all iterated entities have an equal workload.
---
## Changelog
Changed: `Query::par_for_each(_mut)` has been changed to `Query::par_iter(_mut)` and will now automatically try to produce a batch size for callers based on the current `World` state.
## Migration Guide
The `batch_size` parameter for `Query(State)::par_for_each(_mut)` has been removed. These calls will automatically compute a batch size for you. Remove these parameters from all calls to these functions.
Before:
```rust
fn parallel_system(query: Query<&MyComponent>) {
query.par_for_each(32, |comp| {
...
});
}
```
After:
```rust
fn parallel_system(query: Query<&MyComponent>) {
query.par_iter().for_each(|comp| {
...
});
}
```
Co-authored-by: Arnav Choubey <56453634+x-52@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Robert Swain <robert.swain@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Corey Farwell <coreyf@rwell.org>
Co-authored-by: Aevyrie <aevyrie@gmail.com>
## Problem
`extract_uinodes` checks if an image is loaded for nodes without images
## Solution
Move the image loading skip check so that it is only performed for nodes with a `UiImage` component.
# Objective
- Implement pipelined rendering
- Fixes#5082
- Fixes#4718
## User Facing Description
Bevy now implements piplelined rendering! Pipelined rendering allows the app logic and rendering logic to run on different threads leading to large gains in performance.

*tracy capture of many_foxes example*
To use pipelined rendering, you just need to add the `PipelinedRenderingPlugin`. If you're using `DefaultPlugins` then it will automatically be added for you on all platforms except wasm. Bevy does not currently support multithreading on wasm which is needed for this feature to work. If you aren't using `DefaultPlugins` you can add the plugin manually.
```rust
use bevy::prelude::*;
use bevy::render::pipelined_rendering::PipelinedRenderingPlugin;
fn main() {
App::new()
// whatever other plugins you need
.add_plugin(RenderPlugin)
// needs to be added after RenderPlugin
.add_plugin(PipelinedRenderingPlugin)
.run();
}
```
If for some reason pipelined rendering needs to be removed. You can also disable the plugin the normal way.
```rust
use bevy::prelude::*;
use bevy::render::pipelined_rendering::PipelinedRenderingPlugin;
fn main() {
App::new.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins.build().disable::<PipelinedRenderingPlugin>());
}
```
### A setup function was added to plugins
A optional plugin lifecycle function was added to the `Plugin trait`. This function is called after all plugins have been built, but before the app runner is called. This allows for some final setup to be done. In the case of pipelined rendering, the function removes the sub app from the main app and sends it to the render thread.
```rust
struct MyPlugin;
impl Plugin for MyPlugin {
fn build(&self, app: &mut App) {
}
// optional function
fn setup(&self, app: &mut App) {
// do some final setup before runner is called
}
}
```
### A Stage for Frame Pacing
In the `RenderExtractApp` there is a stage labelled `BeforeIoAfterRenderStart` that systems can be added to. The specific use case for this stage is for a frame pacing system that can delay the start of main app processing in render bound apps to reduce input latency i.e. "frame pacing". This is not currently built into bevy, but exists as `bevy`
```text
|-------------------------------------------------------------------|
| | BeforeIoAfterRenderStart | winit events | main schedule |
| extract |---------------------------------------------------------|
| | extract commands | rendering schedule |
|-------------------------------------------------------------------|
```
### Small API additions
* `Schedule::remove_stage`
* `App::insert_sub_app`
* `App::remove_sub_app`
* `TaskPool::scope_with_executor`
## Problems and Solutions
### Moving render app to another thread
Most of the hard bits for this were done with the render redo. This PR just sends the render app back and forth through channels which seems to work ok. I originally experimented with using a scope to run the render task. It was cuter, but that approach didn't allow render to start before i/o processing. So I switched to using channels. There is much complexity in the coordination that needs to be done, but it's worth it. By moving rendering during i/o processing the frame times should be much more consistent in render bound apps. See https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/4691.
### Unsoundness with Sending World with NonSend resources
Dropping !Send things on threads other than the thread they were spawned on is considered unsound. The render world doesn't have any nonsend resources. So if we tell the users to "pretty please don't spawn nonsend resource on the render world", we can avoid this problem.
More seriously there is this https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/6534 pr, which patches the unsoundness by aborting the app if a nonsend resource is dropped on the wrong thread. ~~That PR should probably be merged before this one.~~ For a longer term solution we have this discussion going https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/discussions/6552.
### NonSend Systems in render world
The render world doesn't have any !Send resources, but it does have a non send system. While Window is Send, winit does have some API's that can only be accessed on the main thread. `prepare_windows` in the render schedule thus needs to be scheduled on the main thread. Currently we run nonsend systems by running them on the thread the TaskPool::scope runs on. When we move render to another thread this no longer works.
To fix this, a new `scope_with_executor` method was added that takes a optional `TheadExecutor` that can only be ticked on the thread it was initialized on. The render world then holds a `MainThreadExecutor` resource which can be passed to the scope in the parallel executor that it uses to spawn it's non send systems on.
### Scopes executors between render and main should not share tasks
Since the render world and the app world share the `ComputeTaskPool`. Because `scope` has executors for the ComputeTaskPool a system from the main world could run on the render thread or a render system could run on the main thread. This can cause performance problems because it can delay a stage from finishing. See https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/6503#issuecomment-1309791442 for more details.
To avoid this problem, `TaskPool::scope` has been changed to not tick the ComputeTaskPool when it's used by the parallel executor. In the future when we move closer to the 1 thread to 1 logical core model we may want to overprovide threads, because the render and main app threads don't do much when executing the schedule.
## Performance
My machine is Windows 11, AMD Ryzen 5600x, RX 6600
### Examples
#### This PR with pipelining vs Main
> Note that these were run on an older version of main and the performance profile has probably changed due to optimizations
Seeing a perf gain from 29% on many lights to 7% on many sprites.
<html>
<body>
<!--StartFragment--><google-sheets-html-origin>
| percent | | | Diff | | | Main | | | PR | |
-- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | --
tracy frame time | mean | median | sigma | mean | median | sigma | mean | median | sigma | mean | median | sigma
many foxes | 27.01% | 27.34% | -47.09% | 1.58 | 1.55 | -1.78 | 5.85 | 5.67 | 3.78 | 4.27 | 4.12 | 5.56
many lights | 29.35% | 29.94% | -10.84% | 3.02 | 3.03 | -0.57 | 10.29 | 10.12 | 5.26 | 7.27 | 7.09 | 5.83
many animated sprites | 13.97% | 15.69% | 14.20% | 3.79 | 4.17 | 1.41 | 27.12 | 26.57 | 9.93 | 23.33 | 22.4 | 8.52
3d scene | 25.79% | 26.78% | 7.46% | 0.49 | 0.49 | 0.15 | 1.9 | 1.83 | 2.01 | 1.41 | 1.34 | 1.86
many cubes | 11.97% | 11.28% | 14.51% | 1.93 | 1.78 | 1.31 | 16.13 | 15.78 | 9.03 | 14.2 | 14 | 7.72
many sprites | 7.14% | 9.42% | -85.42% | 1.72 | 2.23 | -6.15 | 24.09 | 23.68 | 7.2 | 22.37 | 21.45 | 13.35
<!--EndFragment-->
</body>
</html>
#### This PR with pipelining disabled vs Main
Mostly regressions here. I don't think this should be a problem as users that are disabling pipelined rendering are probably running single threaded and not using the parallel executor. The regression is probably mostly due to the switch to use `async_executor::run` instead of `try_tick` and also having one less thread to run systems on. I'll do a writeup on why switching to `run` causes regressions, so we can try to eventually fix it. Using try_tick causes issues when pipeline rendering is enable as seen [here](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/6503#issuecomment-1380803518)
<html>
<body>
<!--StartFragment--><google-sheets-html-origin>
| percent | | | Diff | | | Main | | | PR no pipelining | |
-- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | --
tracy frame time | mean | median | sigma | mean | median | sigma | mean | median | sigma | mean | median | sigma
many foxes | -3.72% | -4.42% | -1.07% | -0.21 | -0.24 | -0.04 | 5.64 | 5.43 | 3.74 | 5.85 | 5.67 | 3.78
many lights | 0.29% | -0.30% | 4.75% | 0.03 | -0.03 | 0.25 | 10.29 | 10.12 | 5.26 | 10.26 | 10.15 | 5.01
many animated sprites | 0.22% | 1.81% | -2.72% | 0.06 | 0.48 | -0.27 | 27.12 | 26.57 | 9.93 | 27.06 | 26.09 | 10.2
3d scene | -15.79% | -14.75% | -31.34% | -0.3 | -0.27 | -0.63 | 1.9 | 1.83 | 2.01 | 2.2 | 2.1 | 2.64
many cubes | -2.85% | -3.30% | 0.00% | -0.46 | -0.52 | 0 | 16.13 | 15.78 | 9.03 | 16.59 | 16.3 | 9.03
many sprites | 2.49% | 2.41% | 0.69% | 0.6 | 0.57 | 0.05 | 24.09 | 23.68 | 7.2 | 23.49 | 23.11 | 7.15
<!--EndFragment-->
</body>
</html>
### Benchmarks
Mostly the same except empty_systems has got a touch slower. The maybe_pipelining+1 column has the compute task pool with an extra thread over default added. This is because pipelining loses one thread over main to execute systems on, since the main thread no longer runs normal systems.
<details>
<summary>Click Me</summary>
```text
group main maybe-pipelining+1
----- ------------------------- ------------------
busy_systems/01x_entities_03_systems 1.07 30.7±1.32µs ? ?/sec 1.00 28.6±1.35µs ? ?/sec
busy_systems/01x_entities_06_systems 1.10 52.1±1.10µs ? ?/sec 1.00 47.2±1.08µs ? ?/sec
busy_systems/01x_entities_09_systems 1.00 74.6±1.36µs ? ?/sec 1.00 75.0±1.93µs ? ?/sec
busy_systems/01x_entities_12_systems 1.03 100.6±6.68µs ? ?/sec 1.00 98.0±1.46µs ? ?/sec
busy_systems/01x_entities_15_systems 1.11 128.5±3.53µs ? ?/sec 1.00 115.5±1.02µs ? ?/sec
busy_systems/02x_entities_03_systems 1.16 50.4±2.56µs ? ?/sec 1.00 43.5±3.00µs ? ?/sec
busy_systems/02x_entities_06_systems 1.00 87.1±1.27µs ? ?/sec 1.05 91.5±7.15µs ? ?/sec
busy_systems/02x_entities_09_systems 1.04 139.9±6.37µs ? ?/sec 1.00 134.0±1.06µs ? ?/sec
busy_systems/02x_entities_12_systems 1.05 179.2±3.47µs ? ?/sec 1.00 170.1±3.17µs ? ?/sec
busy_systems/02x_entities_15_systems 1.01 219.6±3.75µs ? ?/sec 1.00 218.1±2.55µs ? ?/sec
busy_systems/03x_entities_03_systems 1.10 70.6±2.33µs ? ?/sec 1.00 64.3±0.69µs ? ?/sec
busy_systems/03x_entities_06_systems 1.02 130.2±3.11µs ? ?/sec 1.00 128.0±1.34µs ? ?/sec
busy_systems/03x_entities_09_systems 1.00 195.0±10.11µs ? ?/sec 1.00 194.8±1.41µs ? ?/sec
busy_systems/03x_entities_12_systems 1.01 261.7±4.05µs ? ?/sec 1.00 259.8±4.11µs ? ?/sec
busy_systems/03x_entities_15_systems 1.00 318.0±3.04µs ? ?/sec 1.06 338.3±20.25µs ? ?/sec
busy_systems/04x_entities_03_systems 1.00 82.9±0.63µs ? ?/sec 1.02 84.3±0.63µs ? ?/sec
busy_systems/04x_entities_06_systems 1.01 181.7±3.65µs ? ?/sec 1.00 179.8±1.76µs ? ?/sec
busy_systems/04x_entities_09_systems 1.04 265.0±4.68µs ? ?/sec 1.00 255.3±1.98µs ? ?/sec
busy_systems/04x_entities_12_systems 1.00 335.9±3.00µs ? ?/sec 1.05 352.6±15.84µs ? ?/sec
busy_systems/04x_entities_15_systems 1.00 418.6±10.26µs ? ?/sec 1.08 450.2±39.58µs ? ?/sec
busy_systems/05x_entities_03_systems 1.07 114.3±0.95µs ? ?/sec 1.00 106.9±1.52µs ? ?/sec
busy_systems/05x_entities_06_systems 1.08 229.8±2.90µs ? ?/sec 1.00 212.3±4.18µs ? ?/sec
busy_systems/05x_entities_09_systems 1.03 329.3±1.99µs ? ?/sec 1.00 319.2±2.43µs ? ?/sec
busy_systems/05x_entities_12_systems 1.06 454.7±6.77µs ? ?/sec 1.00 430.1±3.58µs ? ?/sec
busy_systems/05x_entities_15_systems 1.03 554.6±6.15µs ? ?/sec 1.00 538.4±23.87µs ? ?/sec
contrived/01x_entities_03_systems 1.00 14.0±0.15µs ? ?/sec 1.08 15.1±0.21µs ? ?/sec
contrived/01x_entities_06_systems 1.04 28.5±0.37µs ? ?/sec 1.00 27.4±0.44µs ? ?/sec
contrived/01x_entities_09_systems 1.00 41.5±4.38µs ? ?/sec 1.02 42.2±2.24µs ? ?/sec
contrived/01x_entities_12_systems 1.06 55.9±1.49µs ? ?/sec 1.00 52.6±1.36µs ? ?/sec
contrived/01x_entities_15_systems 1.02 68.0±2.00µs ? ?/sec 1.00 66.5±0.78µs ? ?/sec
contrived/02x_entities_03_systems 1.03 25.2±0.38µs ? ?/sec 1.00 24.6±0.52µs ? ?/sec
contrived/02x_entities_06_systems 1.00 46.3±0.49µs ? ?/sec 1.04 48.1±4.13µs ? ?/sec
contrived/02x_entities_09_systems 1.02 70.4±0.99µs ? ?/sec 1.00 68.8±1.04µs ? ?/sec
contrived/02x_entities_12_systems 1.06 96.8±1.49µs ? ?/sec 1.00 91.5±0.93µs ? ?/sec
contrived/02x_entities_15_systems 1.02 116.2±0.95µs ? ?/sec 1.00 114.2±1.42µs ? ?/sec
contrived/03x_entities_03_systems 1.00 33.2±0.38µs ? ?/sec 1.01 33.6±0.45µs ? ?/sec
contrived/03x_entities_06_systems 1.00 62.4±0.73µs ? ?/sec 1.01 63.3±1.05µs ? ?/sec
contrived/03x_entities_09_systems 1.02 96.4±0.85µs ? ?/sec 1.00 94.8±3.02µs ? ?/sec
contrived/03x_entities_12_systems 1.01 126.3±4.67µs ? ?/sec 1.00 125.6±2.27µs ? ?/sec
contrived/03x_entities_15_systems 1.03 160.2±9.37µs ? ?/sec 1.00 156.0±1.53µs ? ?/sec
contrived/04x_entities_03_systems 1.02 41.4±3.39µs ? ?/sec 1.00 40.5±0.52µs ? ?/sec
contrived/04x_entities_06_systems 1.00 78.9±1.61µs ? ?/sec 1.02 80.3±1.06µs ? ?/sec
contrived/04x_entities_09_systems 1.02 121.8±3.97µs ? ?/sec 1.00 119.2±1.46µs ? ?/sec
contrived/04x_entities_12_systems 1.00 157.8±1.48µs ? ?/sec 1.01 160.1±1.72µs ? ?/sec
contrived/04x_entities_15_systems 1.00 197.9±1.47µs ? ?/sec 1.08 214.2±34.61µs ? ?/sec
contrived/05x_entities_03_systems 1.00 49.1±0.33µs ? ?/sec 1.01 49.7±0.75µs ? ?/sec
contrived/05x_entities_06_systems 1.00 95.0±0.93µs ? ?/sec 1.00 94.6±0.94µs ? ?/sec
contrived/05x_entities_09_systems 1.01 143.2±1.68µs ? ?/sec 1.00 142.2±2.00µs ? ?/sec
contrived/05x_entities_12_systems 1.00 191.8±2.03µs ? ?/sec 1.01 192.7±7.88µs ? ?/sec
contrived/05x_entities_15_systems 1.02 239.7±3.71µs ? ?/sec 1.00 235.8±4.11µs ? ?/sec
empty_systems/000_systems 1.01 47.8±0.67ns ? ?/sec 1.00 47.5±2.02ns ? ?/sec
empty_systems/001_systems 1.00 1743.2±126.14ns ? ?/sec 1.01 1761.1±70.10ns ? ?/sec
empty_systems/002_systems 1.01 2.2±0.04µs ? ?/sec 1.00 2.2±0.02µs ? ?/sec
empty_systems/003_systems 1.02 2.7±0.09µs ? ?/sec 1.00 2.7±0.16µs ? ?/sec
empty_systems/004_systems 1.00 3.1±0.11µs ? ?/sec 1.00 3.1±0.24µs ? ?/sec
empty_systems/005_systems 1.00 3.5±0.05µs ? ?/sec 1.11 3.9±0.70µs ? ?/sec
empty_systems/010_systems 1.00 5.5±0.12µs ? ?/sec 1.03 5.7±0.17µs ? ?/sec
empty_systems/015_systems 1.00 7.9±0.19µs ? ?/sec 1.06 8.4±0.16µs ? ?/sec
empty_systems/020_systems 1.00 10.4±1.25µs ? ?/sec 1.02 10.6±0.18µs ? ?/sec
empty_systems/025_systems 1.00 12.4±0.39µs ? ?/sec 1.14 14.1±1.07µs ? ?/sec
empty_systems/030_systems 1.00 15.1±0.39µs ? ?/sec 1.05 15.8±0.62µs ? ?/sec
empty_systems/035_systems 1.00 16.9±0.47µs ? ?/sec 1.07 18.0±0.37µs ? ?/sec
empty_systems/040_systems 1.00 19.3±0.41µs ? ?/sec 1.05 20.3±0.39µs ? ?/sec
empty_systems/045_systems 1.00 22.4±1.67µs ? ?/sec 1.02 22.9±0.51µs ? ?/sec
empty_systems/050_systems 1.00 24.4±1.67µs ? ?/sec 1.01 24.7±0.40µs ? ?/sec
empty_systems/055_systems 1.05 28.6±5.27µs ? ?/sec 1.00 27.2±0.70µs ? ?/sec
empty_systems/060_systems 1.02 29.9±1.64µs ? ?/sec 1.00 29.3±0.66µs ? ?/sec
empty_systems/065_systems 1.02 32.7±3.15µs ? ?/sec 1.00 32.1±0.98µs ? ?/sec
empty_systems/070_systems 1.00 33.0±1.42µs ? ?/sec 1.03 34.1±1.44µs ? ?/sec
empty_systems/075_systems 1.00 34.8±0.89µs ? ?/sec 1.04 36.2±0.70µs ? ?/sec
empty_systems/080_systems 1.00 37.0±1.82µs ? ?/sec 1.05 38.7±1.37µs ? ?/sec
empty_systems/085_systems 1.00 38.7±0.76µs ? ?/sec 1.05 40.8±0.83µs ? ?/sec
empty_systems/090_systems 1.00 41.5±1.09µs ? ?/sec 1.04 43.2±0.82µs ? ?/sec
empty_systems/095_systems 1.00 43.6±1.10µs ? ?/sec 1.04 45.2±0.99µs ? ?/sec
empty_systems/100_systems 1.00 46.7±2.27µs ? ?/sec 1.03 48.1±1.25µs ? ?/sec
```
</details>
## Migration Guide
### App `runner` and SubApp `extract` functions are now required to be Send
This was changed to enable pipelined rendering. If this breaks your use case please report it as these new bounds might be able to be relaxed.
## ToDo
* [x] redo benchmarking
* [x] reinvestigate the perf of the try_tick -> run change for task pool scope
# Objective
- Add a configurable prepass
- A depth prepass is useful for various shader effects and to reduce overdraw. It can be expansive depending on the scene so it's important to be able to disable it if you don't need any effects that uses it or don't suffer from excessive overdraw.
- The goal is to eventually use it for things like TAA, Ambient Occlusion, SSR and various other techniques that can benefit from having a prepass.
## Solution
The prepass node is inserted before the main pass. It runs for each `Camera3d` with a prepass component (`DepthPrepass`, `NormalPrepass`). The presence of one of those components is used to determine which textures are generated in the prepass. When any prepass is enabled, the depth buffer generated will be used by the main pass to reduce overdraw.
The prepass runs for each `Material` created with the `MaterialPlugin::prepass_enabled` option set to `true`. You can overload the shader used by the prepass by using `Material::prepass_vertex_shader()` and/or `Material::prepass_fragment_shader()`. It will also use the `Material::specialize()` for more advanced use cases. It is enabled by default on all materials.
The prepass works on opaque materials and materials using an alpha mask. Transparent materials are ignored.
The `StandardMaterial` overloads the prepass fragment shader to support alpha mask and normal maps.
---
## Changelog
- Add a new `PrepassNode` that runs before the main pass
- Add a `PrepassPlugin` to extract/prepare/queue the necessary data
- Add a `DepthPrepass` and `NormalPrepass` component to control which textures will be created by the prepass and available in later passes.
- Add a new `prepass_enabled` flag to the `MaterialPlugin` that will control if a material uses the prepass or not.
- Add a new `prepass_enabled` flag to the `PbrPlugin` to control if the StandardMaterial uses the prepass. Currently defaults to false.
- Add `Material::prepass_vertex_shader()` and `Material::prepass_fragment_shader()` to control the prepass from the `Material`
## Notes
In bevy's sample 3d scene, the performance is actually worse when enabling the prepass, but on more complex scenes the performance is generally better. I would like more testing on this, but @DGriffin91 has reported a very noticeable improvements in some scenes.
The prepass is also used by @JMS55 for TAA and GTAO
discord thread: <https://discord.com/channels/691052431525675048/1011624228627419187>
This PR was built on top of the work of multiple people
Co-Authored-By: @superdump
Co-Authored-By: @robtfm
Co-Authored-By: @JMS55
Co-authored-by: Charles <IceSentry@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: JMS55 <47158642+JMS55@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
- Safety comments for the `CommandQueue` type are quite sparse and very imprecise. Sometimes, they are right for the wrong reasons or use circular reasoning.
## Solution
- Document previously-implicit safety invariants.
- Rewrite safety comments to actually reflect the specific invariants of each operation.
- Use `OwningPtr` instead of raw pointers, to encode an invariant in the type system instead of via comments.
- Use typed pointer methods when possible to increase reliability.
---
## Changelog
+ Added the function `OwningPtr::read_unaligned`.
# Objective
Fix https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/4530
- Make it easier to open/close/modify windows by setting them up as `Entity`s with a `Window` component.
- Make multiple windows very simple to set up. (just add a `Window` component to an entity and it should open)
## Solution
- Move all properties of window descriptor to ~components~ a component.
- Replace `WindowId` with `Entity`.
- ~Use change detection for components to update backend rather than events/commands. (The `CursorMoved`/`WindowResized`/... events are kept for user convenience.~
Check each field individually to see what we need to update, events are still kept for user convenience.
---
## Changelog
- `WindowDescriptor` renamed to `Window`.
- Width/height consolidated into a `WindowResolution` component.
- Requesting maximization/minimization is done on the [`Window::state`] field.
- `WindowId` is now `Entity`.
## Migration Guide
- Replace `WindowDescriptor` with `Window`.
- Change `width` and `height` fields in a `WindowResolution`, either by doing
```rust
WindowResolution::new(width, height) // Explicitly
// or using From<_> for tuples for convenience
(1920., 1080.).into()
```
- Replace any `WindowCommand` code to just modify the `Window`'s fields directly and creating/closing windows is now by spawning/despawning an entity with a `Window` component like so:
```rust
let window = commands.spawn(Window { ... }).id(); // open window
commands.entity(window).despawn(); // close window
```
## Unresolved
- ~How do we tell when a window is minimized by a user?~
~Currently using the `Resize(0, 0)` as an indicator of minimization.~
No longer attempting to tell given how finnicky this was across platforms, now the user can only request that a window be maximized/minimized.
## Future work
- Move `exit_on_close` functionality out from windowing and into app(?)
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/5621
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/7099
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/7098
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
See:
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/7067#issuecomment-1381982285
- (This does not fully close that issue in my opinion.)
- https://discord.com/channels/691052431525675048/1063454009769340989
## Solution
This merge request adds documentation:
1. Alert users to the fact that `App::run()` might never return and code placed after it might never be executed.
2. Makes `winit::WinitSettings::return_from_run` discoverable.
3. Better explains why `winit::WinitSettings::return_from_run` is discouraged and better links to up-stream docs. on that topic.
4. Adds notes to the `app/return_after_run.rs` example which otherwise promotes a feature that carries caveats.
Furthermore, w.r.t `winit::WinitSettings::return_from_run`:
- Broken links to `winit` docs are fixed.
- Links now point to BOTH `EventLoop::run()` and `EventLoopExtRunReturn::run_return()` which are the salient up-stream pages and make more sense, taken together.
- Collateral damage: "Supported platforms" heading; disambiguation of "run" → `App::run()`; links.
## Future Work
I deliberately structured the "`run()` might not return" section under `App::run()` to allow for alternative patterns (e.g. `AppExit` event, `WindowClosed` event) to be listed or mentioned, beneath it, in the future.
# Objective
- Fixes#7260
## Solution
- #6649 used `init_non_send_resource` for `AudioOutput`, but this is before #6436 was merged.
- Use `init_resource` instead.
# Objective
Repeated calls to `init_non_send_resource` currently overwrite the old value because the wrong storage is being checked.
## Solution
Use the correct storage. Add some tests.
## Notes
Without the fix, the new test fails with
```
thread 'world::tests::init_non_send_resource_does_not_overwrite' panicked at 'assertion failed: `(left == right)`
left: `1`,
right: `0`', crates/bevy_ecs/src/world/mod.rs:2267:9
note: run with `RUST_BACKTRACE=1` environment variable to display a backtrace
test world::tests::init_non_send_resource_does_not_overwrite ... FAILED
```
This was introduced by #7174 and it seems like a fairly straightforward oopsie.
# Objective
I was reading through the bevy_ecs code, trying to understand how everything works.
I was getting a bit confused when reading the doc comment for the `new_archetype` function; it looks like it doesn't create a new archetype but instead updates some internal state in the SystemParam to facility QueryIteration.
(I still couldn't find where a new archetype was actually created)
## Solution
- Adding a doc comment with a more correct explanation.
If it's deemed correct, I can also update the doc-comment for the other `new_archetype` calls
# Objective
Speed up the render phase of rendering. An extension of #6885.
`SystemState::get` increments the `World`'s change tick atomically every time it's called. This is notably more expensive than a unsynchronized increment, even without contention. It also updates the archetypes, even when there has been nothing to update when it's called repeatedly.
## Solution
Piggyback off of #6885. Split `SystemState::validate_world_and_update_archetypes` into `SystemState::validate_world` and `SystemState::update_archetypes`, and make the later `pub`. Then create safe variants of `SystemState::get_unchecked_manual` that still validate the `World` but do not update archetypes and do not increment the change tick using `World::read_change_tick` and `World::change_tick`. Update `RenderCommandState` to call `SystemState::update_archetypes` in `Draw::prepare` and `SystemState::get_manual` in `Draw::draw`.
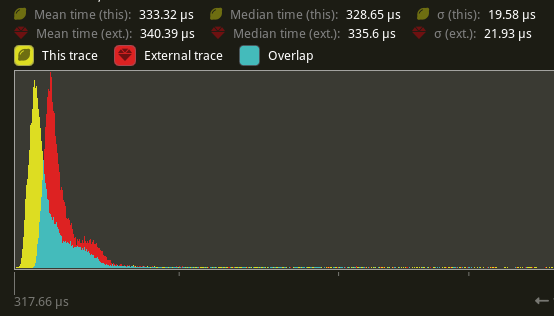
## Performance
There's a slight perf benefit (~2%) for `main_opaque_pass_3d` on `many_foxes` (340.39 us -> 333.32 us)
## Alternatives
We can change `SystemState::get` to not increment the `World`'s change tick. Though this would still put updating the archetypes and an atomic read on the hot-path.
---
## Changelog
Added: `SystemState::get_manual`
Added: `SystemState::get_manual_mut`
Added: `SystemState::update_archetypes`
# Objective
Remove the `VerticalAlign` enum.
Text's alignment field should only affect the text's internal text alignment, not its position. The only way to control a `TextBundle`'s position and bounds should be through the manipulation of the constraints in the `Style` components of the nodes in the Bevy UI's layout tree.
`Text2dBundle` should have a separate `Anchor` component that sets its position relative to its transform.
Related issues: #676, #1490, #5502, #5513, #5834, #6717, #6724, #6741, #6748
## Changelog
* Changed `TextAlignment` into an enum with `Left`, `Center`, and `Right` variants.
* Removed the `HorizontalAlign` and `VerticalAlign` types.
* Added an `Anchor` component to `Text2dBundle`
* Added `Component` derive to `Anchor`
* Use `f32::INFINITY` instead of `f32::MAX` to represent unbounded text in Text2dBounds
## Migration Guide
The `alignment` field of `Text` now only affects the text's internal alignment.
### Change `TextAlignment` to TextAlignment` which is now an enum. Replace:
* `TextAlignment::TOP_LEFT`, `TextAlignment::CENTER_LEFT`, `TextAlignment::BOTTOM_LEFT` with `TextAlignment::Left`
* `TextAlignment::TOP_CENTER`, `TextAlignment::CENTER_LEFT`, `TextAlignment::BOTTOM_CENTER` with `TextAlignment::Center`
* `TextAlignment::TOP_RIGHT`, `TextAlignment::CENTER_RIGHT`, `TextAlignment::BOTTOM_RIGHT` with `TextAlignment::Right`
### Changes for `Text2dBundle`
`Text2dBundle` has a new field 'text_anchor' that takes an `Anchor` component that controls its position relative to its transform.
# Objective
- Enabling the `debug_asset_server` feature doesn't compile when using it with `load_internal_binary_asset!()`. The issue is because it assumes the loader takes an `&'static str` as a parameter, but binary assets loader expect `&'static [u8]`.
## Solution
- Add a generic type for the loader and use a different type in `load_internal_asset` and `load_internal_binary_asset`
# Objective
- Fixes#6361
- Fixes#6362
- Fixes#6364
## Solution
- Added an example for creating a custom `Decodable` type
- Clarified the documentation on `Decodable`
- Added an `AddAudioSource` trait and implemented it for `App`
Co-authored-by: dis-da-moe <84386186+dis-da-moe@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
Fix#4647. If any child is changed, or even reordered, `Changed<Children>` is true, which causes transform propagation to propagate changes to all siblings of a changed child, even if they don't need to be.
## Solution
As `Parent` and `Children` are updated in tandem in hierarchy commands after #4800. `Changed<Parent>` is true on the child when `Changed<Children>` is true on the parent. However, unlike checking children, checking `Changed<Parent>` is only localized to the current entity and will not force propagation to the siblings.
Also took the opportunity to change propagation to use `Query::iter_many` instead of repeated `Query::get` calls. Should cut a bit of the overhead out of propagation. This means we won't panic when there isn't a `Parent` on the child, just skip over it.
The tests from #4608 still pass, so the change detection here still works just fine under this approach.
# Objective
fix bloom when used on a camera with a viewport specified
## Solution
- pass viewport into the prefilter shader, and use it to read from the correct section of the original rendered screen
- don't apply viewport for the intermediate bloom passes, only for the final blend output
# Objective
- Fixes#3158
## Solution
- clear columns
My implementation of `clear_resources` do not remove the components itself but it clears the columns that keeps the resource data. I'm not sure if the issue meant to clear all resources, even the components and component ids (which I'm not sure if it's possible)
Co-authored-by: 2ne1ugly <47616772+2ne1ugly@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
The trait `ReadOnlySystemParam` is not implemented for `Option<NonSend<>>`, even though it should be.
Follow-up to #7243. This fixes another mistake made in #6919.
## Solution
Add the missing impl.
# Objective
The trait `ReadOnlySystemParam` is implemented for `NonSendMut`, when it should not be. This mistake was made in #6919.
## Solution
Remove the incorrect impl.
# Objective
Complete the first part of the migration detailed in bevyengine/rfcs#45.
## Solution
Add all the new stuff.
### TODO
- [x] Impl tuple methods.
- [x] Impl chaining.
- [x] Port ambiguity detection.
- [x] Write docs.
- [x] ~~Write more tests.~~(will do later)
- [ ] Write changelog and examples here?
- [x] ~~Replace `petgraph`.~~ (will do later)
Co-authored-by: james7132 <contact@jamessliu.com>
Co-authored-by: Michael Hsu <mike.hsu@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Mike Hsu <mike.hsu@gmail.com>
# Objective
- We rely on the construction of `EntityRef` to be valid elsewhere in unsafe code. This construction is not checked (for performance reasons), and thus this private method must be unsafe.
- Fixes#7218.
## Solution
- Make the method unsafe.
- Add safety docs.
- Improve safety docs slightly for the sibling `EntityMut::new`.
- Add debug asserts to start to verify these assumptions in debug mode.
## Context for reviewers
I attempted to verify the `EntityLocation` more thoroughly, but this turned out to be more work than expected. I've spun that off into #7221 as a result.
# Objective
Fixes#5859
## Solution
- Add `ClearChildren` and `ReplaceChildren` commands in the `crates/bevy_hierarchy/src/child_builder.rs`
---
## Changelog
- Added `ClearChildren` and `ReplaceChildren` struct
- Added `clear_children(&mut self) -> &mut Self` and `replace_children(&mut self, children: &[Entity]) -> &mut Self` function in `BuildChildren` trait
- Changed `PushChildren` `write` function body to a `push_children ` function to reused in `ReplaceChildren`
- Added `clear_children` function
- Added `push_and_replace_children_commands` and `push_and_clear_children_commands` test
Co-authored-by: ld000 <lidong9144@163.com>
Co-authored-by: lidong63 <lidong63@meituan.com>
# Objective
- Fixes a bug where `just_pressed` and `just_released` in `Input<GamepadButton>` might behave incorrectly due calling `clear` 3 times in a single frame through these three different systems: `gamepad_button_event_system`, `gamepad_axis_event_system` and `gamepad_connection_system` in any order
## Solution
- Call `clear` only once and before all the above three systems, i.e. in `gamepad_event_system`
## Additional Info
- Discussion in Discord: https://discord.com/channels/691052431525675048/768253008416342076/1064621963693273279
# Objective
The usages of the unsafe function `byte_add` are not properly documented.
Follow-up to #7151.
## Solution
Add safety comments to each call-site.
# Objective
Currently, the `AxisSettings::new` function is unusable due to
an implementation quirk. It only allows `AxisSettings` where
the bounds that are supposed to be positive are negative!
## Solution
- We fix the bound check
- We add a test to make sure the method is usable
Seems like the error slipped through because of the relatively
verbose code style. With all those `if/else`, very long names,
range syntax, the bound check is actually hard to spot. I first
refactored a lot of code, but I left out the refactor because the
fix should be integrated independently.
---
## Changelog
- Fix `AxisSettings::new` only accepting invalid bounds
# Objective
Add useful information about cursor position relative to a UI node. Fixes#7079.
## Solution
- Added a new `RelativeCursorPosition` component
---
## Changelog
- Added
- `RelativeCursorPosition`
- an example showcasing the new component
Co-authored-by: Dawid Piotrowski <41804418+Pietrek14@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
- Allow rendering queue systems to use a `Res<PipelineCache>` even for queueing up new rendering pipelines. This is part of unblocking parallel execution queue systems.
## Solution
- Make `PipelineCache` internally mutable w.r.t to queueing new pipelines. Pipelines are no longer immediately updated into the cache state, but rather queued into a Vec. The Vec of pending new pipelines is then later processed at the same time we actually create the queued pipelines on the GPU device.
---
## Changelog
`PipelineCache` no longer requires mutable access in order to queue render / compute pipelines.
## Migration Guide
* Most usages of `resource_mut::<PipelineCache>` and `ResMut<PipelineCache>` can be changed to `resource::<PipelineCache>` and `Res<PipelineCache>` as long as they don't use any methods requiring mutability - the only public method requiring it is `process_queue`.
# Objective
- The function `BlobVec::replace_unchecked` has informal use of safety comments.
- This function does strange things with `OwningPtr` in order to get around the borrow checker.
## Solution
- Put safety comments in front of each unsafe operation. Describe the specific invariants of each operation and how they apply here.
- Added a guard type `OnDrop`, which is used to simplify ownership transfer in case of a panic.
---
## Changelog
+ Added the guard type `bevy_utils::OnDrop`.
+ Added conversions from `Ptr`, `PtrMut`, and `OwningPtr` to `NonNull<u8>`.
# Objective
Fix#5248.
## Solution
Support `In<T>` parameters and allow returning arbitrary types in exclusive systems.
---
## Changelog
- Exclusive systems may now be used with system piping.
## Migration Guide
Exclusive systems (systems that access `&mut World`) now support system piping, so the `ExclusiveSystemParamFunction` trait now has generics for the `In`put and `Out`put types.
```rust
// Before
fn my_generic_system<T, Param>(system_function: T)
where T: ExclusiveSystemParamFunction<Param>
{ ... }
// After
fn my_generic_system<T, In, Out, Param>(system_function: T)
where T: ExclusiveSystemParamFunction<In, Out, Param>
{ ... }
```
# Objective
Pipelines can be customized by wrapping an existing pipeline in a newtype and adding custom logic to its implementation of `SpecializedMeshPipeline::specialize`. To make that easier, the wrapped pipeline type needs to implement `Clone`.
For example, the current non-cloneable pipelines require wrapper pipelines to pull apart the wrapped pipeline like this:
```rust
impl FromWorld for Wireframe2dPipeline {
fn from_world(world: &mut World) -> Self {
let p = &world.resource::<Material2dPipeline<ColorMaterial>>();
Self {
mesh2d_pipeline: p.mesh2d_pipeline.clone(),
material2d_layout: p.material2d_layout.clone(),
vertex_shader: p.vertex_shader.clone(),
fragment_shader: p.fragment_shader.clone(),
}
}
}
```
## Solution
Derive or implement `Clone` on all built-in pipeline types. This is easy to do since they mostly just contain cheaply clonable reference-counted types.
---
## Changelog
Implement `Clone` for all pipeline types.
# Objective
fix error with shadow shader's spotlight direction calculation when direction.y ~= 0
fixes#7152
## Solution
same as #6167: in shadows.wgsl, clamp 1-x^2-z^2 to >= 0 so that we can safely sqrt it
# Objective
There are some utility functions for actually working with `Storages` inside `entity_ref.rs` that are used both for `EntityRef/EntityMut` and `World`, with a `// TODO: move to Storages`.
This PR moves them to private methods on `World`, because that's the safest API boundary. On `Storages` you would need to ensure that you pass `Components` from the same world.
## Solution
- move get_component[_with_type], get_ticks[_with_type], get_component_and_ticks[_with_type] to `World` (still pub(crate))
- replace `pub use entity_ref::*;` with `pub use entity_ref::{EntityRef, EntityMut}` and qualified `entity_ref::get_mut[_by_id]` in `world.rs`
- add safety comments to a bunch of methods
# Objective
* `World::init_resource` and `World::get_resource_or_insert_with` are implemented naively, and as such they perform duplicate `TypeId -> ComponentId` lookups.
* `World::get_resource_or_insert_with` contains an additional duplicate `ComponentId -> ResourceData` lookup.
* This function also contains an unnecessary panic branch, which we rely on the optimizer to be able to remove.
## Solution
Implement the functions using engine-internal code, instead of combining high-level functions. This allows computed variables to persist across different branches, instead of being recomputed.
# Objective
It is often necessary to update an entity's parent
while keeping its GlobalTransform static. Currently
it is cumbersome and error-prone (two questions in
the discord `#help` channel in the past week)
- Part 2, resolves#5475
- Builds on: #7020.
## Solution
- Added the `BuildChildrenTransformExt` trait, it is part
of `bevy::prelude` and adds the following methods to `EntityCommands`:
- `set_parent_in_place`: Change the parent of an entity and
update its `Transform` in order to preserve its `GlobalTransform` after the parent change
- `remove_parent_in_place`: Remove an entity from a hierarchy,
while preserving its `GlobalTransform`.
---
## Changelog
- Added the `BuildChildrenTransformExt` trait, it is part
of `bevy::prelude` and adds the following methods to `EntityCommands`:
- `set_parent_in_place`: Change the parent of an entity and
update its `Transform` in order to preserve its `GlobalTransform` after the parent change
- `remove_parent_in_place`: Remove an entity from a hierarchy,
while preserving its `GlobalTransform`.
Co-authored-by: Nicola Papale <nicopap@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
- While building UI, it makes more sense for most nodes to have a `FocusPolicy` of `Pass`, so that user interaction can correctly bubble
- Only `ButtonBundle` blocks by default
This change means that for someone adding children to a button, it's not needed to change the focus policy of those children to `Pass` for the button to continue to work.
---
## Changelog
- `FocusPolicy` default has changed from `FocusPolicy::Block` to `FocusPolicy::Pass`
## Migration Guide
- `FocusPolicy` default has changed from `FocusPolicy::Block` to `FocusPolicy::Pass`
# Objective
The documentation of the bevy_render crate is still pretty incomplete.
This PR follows up on #6885 and improves the documentation of the `render_phase` module.
This module contains one of our most important rendering abstractions and the current documentation is pretty confusing. This PR tries to clarify what all of these pieces are for and how they work together to form bevy`s modular rendering logic.
## Solution
### Code Reformating
- I have moved the `rangefinder` into the `render_phase` module since it is only used there.
- I have moved the `PhaseItem` (and the `BatchedPhaseItem`) from `render_phase::draw` over to `render_phase::mod`. This does not change the public-facing API since they are reexported anyway, but this change makes the relation between `RenderPhase` and `PhaseItem` clear and easier to discover.
### Documentation
- revised all documentation in the `render_phase` module
- added a module-level explanation of how `RenderPhase`s, `RenderPass`es, `PhaseItem`s, `Draw` functions, and `RenderCommands` relate to each other and how they are used
---
## Changelog
- The `rangefinder` module has been moved into the `render_phase` module.
## Migration Guide
- The `rangefinder` module has been moved into the `render_phase` module.
```rust
//old
use bevy::render::rangefinder::*;
// new
use bevy::render::render_phase::rangefinder::*;
```
# Objective
Following #6681, both `TableRow` and `TableId` are now part of `EntityLocation`. However, the safety invariant on `EntityLocation` requires that all of the constituent fields are `repr(transprent)` or `repr(C)` and the bit pattern of all 1s must be valid. This is not true for `TableRow` and `TableId` currently.
## Solution
Mark `TableRow` and `TableId` to satisfy the safety requirement. Add safety comments on `ArchetypeId`, `ArchetypeRow`, `TableId` and `TableRow`.
# Objective
Improve safety testing when using `bevy_ptr` types. This is a follow-up to #7113.
## Solution
Add a debug-only assertion that pointers are aligned when casting to a concrete type. This should very quickly catch any unsoundness from unaligned pointers, even without miri. However, this can have a large negative perf impact on debug builds.
---
## Changelog
Added: `Ptr::deref` will now panic in debug builds if the pointer is not aligned.
Added: `PtrMut::deref_mut` will now panic in debug builds if the pointer is not aligned.
Added: `OwningPtr::read` will now panic in debug builds if the pointer is not aligned.
Added: `OwningPtr::drop_as` will now panic in debug builds if the pointer is not aligned.
# Objective
- It can be useful for third party crates to work independently on how bevy is imported
## Solution
- Expose an helper to get a subcrate path for macros
# Objective
- There is a warning when building in release:
```
warning: unused import: `bevy_ecs::system::Local`
--> crates/bevy_render/src/extract_resource.rs:5:5
|
5 | use bevy_ecs::system::Local;
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
= note: `#[warn(unused_imports)]` on by default
```
- It's used 59751d6e33/crates/bevy_render/src/extract_resource.rs (L47)
- Fix it
## Solution
- Gate the import
- repeat of #5320
# Objective
`MutUntyped` is a struct that stores a `PtrMut` alongside change tick metadata. Working with this type is cumbersome, and has few benefits over storing the pointer and change ticks separately.
Related: #6430 (title is out of date)
## Solution
Add a convenience method for transforming an untyped change detection pointer into its typed counterpart.
---
## Changelog
- Added the method `MutUntyped::with_type`.
As mentioned in https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/6530. It allows to not create a new constant and simply having it to show up in the documentation when someone is looking for "transparent" (case insensitive) in rustdoc search.
cc @alice-i-cecile
# Objective
Enums are now reflectable, but are not accessible via reflection paths.
This would allow us to do things like:
```rust
#[derive(Reflect)]
struct MyStruct {
data: MyEnum
}
#[derive(Reflect)]
struct MyEnum {
Foo(u32, u32),
Bar(bool)
}
let x = MyStruct {
data: MyEnum::Foo(123),
};
assert_eq!(*x.get_path::<u32>("data.1").unwrap(), 123);
```
## Solution
Added support for enums in reflection paths.
##### Note
This uses a simple approach of just getting the field with the given accessor. It does not do matching or anything else to ensure the enum is the intended variant. This means that the variant must be known ahead of time or matched outside the reflection path (i.e. path to variant, perform manual match, and continue pathing).
---
## Changelog
- Added support for enums in reflection paths
# Objective
There are times where we want to simply take an owned `dyn Reflect` and cast it to a type `T`.
Currently, this involves doing:
```rust
let value = value.take::<T>().unwrap_or_else(|value| {
T::from_reflect(&*value).unwrap_or_else(|| {
panic!(
"expected value of type {} to convert to type {}.",
value.type_name(),
std::any::type_name::<T>()
)
})
});
```
This is a common operation that could be easily be simplified.
## Solution
Add the `FromReflect::take_from_reflect` method. This first tries to `take` the value, calling `from_reflect` iff that fails.
```rust
let value = T::take_from_reflect(value).unwrap_or_else(|value| {
panic!(
"expected value of type {} to convert to type {}.",
value.type_name(),
std::any::type_name::<T>()
)
});
```
Based on suggestion from @soqb on [Discord](https://discord.com/channels/691052431525675048/1002362493634629796/1041046880316043374).
---
## Changelog
- Add `FromReflect::take_from_reflect` method
# Objective
- Fixes#7066
## Solution
- Split the ChangeDetection trait into ChangeDetection and ChangeDetectionMut
- Added Ref as equivalent to &T with change detection
---
## Changelog
- Support for Ref which allow inspecting change detection flags in an immutable way
## Migration Guide
- While bevy prelude includes both ChangeDetection and ChangeDetectionMut any code explicitly referencing ChangeDetection might need to be updated to ChangeDetectionMut or both. Specifically any reading logic requires ChangeDetection while writes requires ChangeDetectionMut.
use bevy_ecs::change_detection::DetectChanges -> use bevy_ecs::change_detection::{DetectChanges, DetectChangesMut}
- Previously Res had methods to access change detection `is_changed` and `is_added` those methods have been moved to the `DetectChanges` trait. If you are including bevy prelude you will have access to these types otherwise you will need to `use bevy_ecs::change_detection::DetectChanges` to continue using them.
# Objective
The types in the `bevy_ptr` accidentally did not document anything relating to alignment. This is unsound as many methods rely on the pointer being correctly aligned.
## Solution
This PR introduces new safety invariants on the `$ptr::new`, `$ptr::byte_offset` and `$ptr::byte_add` methods requiring them to keep the pointer aligned. This is consistent with the documentation of these pointer types which document them as being "type erased borrows".
As it was pointed out (by @JoJoJet in #7117) that working with unaligned pointers can be useful (for example our commands abstraction which does not try to align anything properly, see #7039) this PR also introduces a default type parameter to all the pointer types that specifies whether it has alignment requirements or not. I could not find any code in `bevy_ecs` that would need unaligned pointers right now so this is going unused.
---
## Changelog
- Correctly document alignment requirements on `bevy_ptr` types.
- Support variants of `bevy_ptr` types that do not require being correctly aligned for the pointee type.
## Migration Guide
- Safety invariants on `bevy_ptr` types' `new` `byte_add` and `byte_offset` methods have been changed. All callers should re-audit for soundness.
# Objective
- Spawn tasks from other threads onto an async executor, but limit those tasks to run on a specific thread.
- This is a continuation of trying to break up some of the changes in pipelined rendering.
- Eventually this will be used to allow `NonSend` systems to run on the main thread in pipelined rendering #6503 and also to solve #6552.
- For this specific PR this allows for us to store a thread executor in a thread local, rather than recreating a scope executor for every scope which should save on a little work.
## Solution
- We create a Executor that does a runtime check for what thread it's on before creating a !Send ticker. The ticker is the only way for the executor to make progress.
---
## Changelog
- create a ThreadExecutor that can only be ticked on one thread.
`Query`'s fields being `pub(crate)` means that the struct can be constructed via safe code from anywhere in `bevy_ecs` . This is Not Good since it is intended that all construction of this type goes through `Query::new` which is an `unsafe fn` letting various `Query` methods rely on those invariants holding even though they can be trivially bypassed.
This has no user facing impact
# Objective
It is possible to manually update `GlobalTransform`.
The engine actually assumes this is not possible.
For example, `propagate_transform` does not update children
of an `Entity` which **`GlobalTransform`** changed,
leading to unexpected behaviors.
A `GlobalTransform` set by the user may also be blindly
overwritten by the propagation system.
## Solution
- Remove `translation_mut`
- Explain to users that they shouldn't manually update the `GlobalTransform`
- Remove `global_vs_local.rs` example, since it misleads users
in believing that it is a valid use-case to manually update the
`GlobalTransform`
---
## Changelog
- Remove `GlobalTransform::translation_mut`
## Migration Guide
`GlobalTransform::translation_mut` has been removed without alternative,
if you were relying on this, update the `Transform` instead. If the given entity
had children or parent, you may need to remove its parent to make its transform
independent (in which case the new `Commands::set_parent_in_place` and
`Commands::remove_parent_in_place` may be of interest)
Bevy may add in the future a way to toggle transform propagation on
an entity basis.
# Objective
- Fix#7103.
- The issue is caused because I forgot to add a where clause to a generated struct in #7056.
## Solution
- Add the where clause.
`Query` relies on the `World` it stores being the same as the world used for creating the `QueryState` it stores. If they are not the same then everything is very unsound. This was not actually being checked anywhere, `Query::new` did not have a safety invariant or even an assertion that the `WorldId`'s are the same.
This shouldn't have any user facing impact unless we have really messed up in bevy and have unsoundness elsewhere (in which case we would now get a panic instead of being unsound).
# Objective
- In some cases, you need a `Mut<T>` pointer, but you only have a mutable reference to one. There is no easy way of converting `&'a mut Mut<'_, T>` -> `Mut<'a, T>` outside of the engine.
### Example (Before)
```rust
fn do_with_mut<T>(val: Mut<T>) { ... }
for x: Mut<T> in &mut query {
// The function expects a `Mut<T>`, so `x` gets moved here.
do_with_mut(x);
// Error: use of moved value.
do_a_thing(&x);
}
```
## Solution
- Add the function `reborrow`, which performs the mapping. This is analogous to `PtrMut::reborrow`.
### Example (After)
```rust
fn do_with_mut<T>(val: Mut<T>) { ... }
for x: Mut<T> in &mut query {
// We reborrow `x`, so the original does not get moved.
do_with_mut(x.reborrow());
// Works fine.
do_a_thing(&x);
}
```
---
## Changelog
- Added the method `reborrow` to `Mut`, `ResMut`, `NonSendMut`, and `MutUntyped`.
# Objective
This a follow-up to #6894, see https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/6894#discussion_r1045203113
The goal is to avoid cloning any string when getting a `&TypeRegistration` corresponding to a string which is being deserialized. As a bonus code duplication is also reduced.
## Solution
The manual deserialization of a string and lookup into the type registry has been moved into a separate `TypeRegistrationDeserializer` type, which implements `DeserializeSeed` with a `Visitor` that accepts any string with `visit_str`, even ones that may not live longer than that function call.
`BorrowedStr` has been removed since it's no longer used.
---
## Changelog
- The type `TypeRegistrationDeserializer` has been added, which simplifies getting a `&TypeRegistration` while deserializing a string.
# Objective
- Fix the name of function parameter name in docs
## Solution
- Change `f` to `sub_app_runner`
---
It confused me a bit when I was reading the docs in the autocomplete hint.
Hesitated about filing a PR since it's just a one single word change in the comment.
Is this the right process to change these docs?
# Objective
The type `Local<T>` unnecessarily has the bound `T: Sync` when the local is used in an exclusive system.
## Solution
Lift the bound.
---
## Changelog
Removed the bound `T: Sync` from `Local<T>` when used as an `ExclusiveSystemParam`.
# Objective
Fixes#3310. Fixes#6282. Fixes#6278. Fixes#3666.
## Solution
Split out `!Send` resources into `NonSendResources`. Add a `origin_thread_id` to all `!Send` Resources, check it on dropping `NonSendResourceData`, if there's a mismatch, panic. Moved all of the checks that `MainThreadValidator` would do into `NonSendResources` instead.
All `!Send` resources now individually track which thread they were inserted from. This is validated against for every access, mutation, and drop that could be done against the value.
A regression test using an altered version of the example from #3310 has been added.
This is a stopgap solution for the current status quo. A full solution may involve fully removing `!Send` resources/components from `World`, which will likely require a much more thorough design on how to handle the existing in-engine and ecosystem use cases.
This PR also introduces another breaking change:
```rust
use bevy_ecs::prelude::*;
#[derive(Resource)]
struct Resource(u32);
fn main() {
let mut world = World::new();
world.insert_resource(Resource(1));
world.insert_non_send_resource(Resource(2));
let res = world.get_resource_mut::<Resource>().unwrap();
assert_eq!(res.0, 2);
}
```
This code will run correctly on 0.9.1 but not with this PR, since NonSend resources and normal resources have become actual distinct concepts storage wise.
## Changelog
Changed: Fix soundness bug with `World: Send`. Dropping a `World` that contains a `!Send` resource on the wrong thread will now panic.
## Migration Guide
Normal resources and `NonSend` resources no longer share the same backing storage. If `R: Resource`, then `NonSend<R>` and `Res<R>` will return different instances from each other. If you are using both `Res<T>` and `NonSend<T>` (or their mutable variants), to fetch the same resources, it's strongly advised to use `Res<T>`.
# Objective
- Fixes#7061
## Solution
- Add and implement `insert` and `remove` methods for `List`.
---
## Changelog
- Added `insert` and `remove` methods to `List`.
- Changed the `push` and `pop` methods on `List` to have default implementations.
## Migration Guide
- Manual implementors of `List` need to implement the new methods `insert` and `remove` and
consider whether to use the new default implementation of `push` and `pop`.
Co-authored-by: radiish <thesethskigamer@gmail.com>
# Objective
Speed up the render phase for rendering.
## Solution
- Follow up #6988 and make the internals of atomic IDs `NonZeroU32`. This niches the `Option`s of the IDs in draw state, which reduces the size and branching behavior when evaluating for equality.
- Require `&RenderDevice` to get the device's `Limits` when initializing a `TrackedRenderPass` to preallocate the bind groups and vertex buffer state in `DrawState`, this removes the branch on needing to resize those `Vec`s.
## Performance
This produces a similar speed up akin to that of #6885. This shows an approximate 6% speed up in `main_opaque_pass_3d` on `many_foxes` (408.79 us -> 388us). This should be orthogonal to the gains seen there.
---
## Changelog
Added: `RenderContext::begin_tracked_render_pass`.
Changed: `TrackedRenderPass` now requires a `&RenderDevice` on construction.
Removed: `bevy_render::render_phase::DrawState`. It was not usable in any form outside of `bevy_render`.
## Migration Guide
TODO
# Objective
- This pulls out some of the changes to Plugin setup and sub apps from #6503 to make that PR easier to review.
- Separate the extract stage from running the sub app's schedule to allow for them to be run on separate threads in the future
- Fixes#6990
## Solution
- add a run method to `SubApp` that runs the schedule
- change the name of `sub_app_runner` to extract to make it clear that this function is only for extracting data between the main app and the sub app
- remove the extract stage from the sub app schedule so it can be run separately. This is done by adding a `setup` method to the `Plugin` trait that runs after all plugin build methods run. This is required to allow the extract stage to be removed from the schedule after all the plugins have added their systems to the stage. We will also need the setup method for pipelined rendering to setup the render thread. See e3267965e1/crates/bevy_render/src/pipelined_rendering.rs (L57-L98)
## Changelog
- Separate SubApp Extract stage from running the sub app schedule.
## Migration Guide
### SubApp `runner` has conceptually been changed to an `extract` function.
The `runner` no longer is in charge of running the sub app schedule. It's only concern is now moving data between the main world and the sub app. The `sub_app.app.schedule` is now run for you after the provided function is called.
```rust
// before
fn main() {
let sub_app = App::empty();
sub_app.add_stage(MyStage, SystemStage::parallel());
App::new().add_sub_app(MySubApp, sub_app, move |main_world, sub_app| {
extract(app_world, render_app);
render_app.app.schedule.run();
});
}
// after
fn main() {
let sub_app = App::empty();
sub_app.add_stage(MyStage, SystemStage::parallel());
App::new().add_sub_app(MySubApp, sub_app, move |main_world, sub_app| {
extract(app_world, render_app);
// schedule is automatically called for you after extract is run
});
}
```
# Objective
- Remove redundant gamepad events
- Simplify consuming gamepad events.
- Refactor: Separate handling of gamepad events into multiple systems.
## Solution
- Removed `GamepadEventRaw`, and `GamepadEventType`.
- Added bespoke `GamepadConnectionEvent`, `GamepadAxisChangedEvent`, and `GamepadButtonChangedEvent`.
- Refactored `gamepad_event_system`.
- Added `gamepad_button_event_system`, `gamepad_axis_event_system`, and `gamepad_connection_system`, which update the `Input` and `Axis` resources using their corresponding event type.
Gamepad events are now handled in their own systems and have their own types.
This allows for querying for gamepad events without having to match on `GamepadEventType` and makes creating handlers for specific gamepad event types, like a `GamepadConnectionEvent` or `GamepadButtonChangedEvent` possible.
We remove `GamepadEventRaw` by filtering the gamepad events, using `GamepadSettings`, _at the source_, in `bevy_gilrs`. This way we can create `GamepadEvent`s directly and avoid creating `GamepadEventRaw` which do not pass the user defined filters.
We expose ordered `GamepadEvent`s and we can respond to individual gamepad event types.
## Migration Guide
- Replace `GamepadEvent` and `GamepadEventRaw` types with their specific gamepad event type.
# Objective
- Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/discussions/6338
This PR allows for smooth transitions between different animations.
## Solution
- This PR uses very simple linear blending of animations.
- When starting a new animation, you can give it a duration, and throughout that duration, the previous and the new animation are being linearly blended, until only the new animation is running.
- I'm aware of https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/pull/49 and https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/pull/51, which are more complete solutions to this problem, but they seem still far from being implemented. Until they're ready, this PR allows for the most basic use case of blending, i.e. smoothly transitioning between different animations.
## Migration Guide
- no bc breaking changes
# Objective
- Storage buffers are useful and not currently supported by the `AsBindGroup` derive which means you need to expand the macro if you need a storage buffer
## Solution
- Add a new `#[storage]` attribute to the derive `AsBindGroup` macro.
- Support and optional `read_only` parameter that defaults to false when not present.
- Support visibility parameters like the texture and sampler attributes.
---
## Changelog
- Add a new `#[storage(index)]` attribute to the derive `AsBindGroup` macro.
Co-authored-by: IceSentry <IceSentry@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
- Avoid slower than necessary first frame after spawning many entities due to them not having `Aabb`s and so being marked visible
- Avoids unnecessarily large system and VRAM allocations as a consequence
## Solution
- I noticed when debugging the `many_cubes` stress test in Xcode that the `MeshUniform` binding was much larger than it needed to be. I realised that this was because initially, all mesh entities are marked as being visible because they don't have `Aabb`s because `calculate_bounds` is being run in `PostUpdate` and there are no system commands applications before executing the visibility check systems that need the `Aabb`s. The solution then is to run the `calculate_bounds` system just before the previous system commands are applied which is at the end of the `Update` stage.
Spiritual successor to #5205.
Actual successor to #6865.
# Objective
Currently, system params are defined using three traits: `SystemParam`, `ReadOnlySystemParam`, `SystemParamState`. The behavior for each param is specified by the `SystemParamState` trait, while `SystemParam` simply defers to the state.
Splitting the traits in this way makes it easier to implement within macros, but it increases the cognitive load. Worst of all, this approach requires each `MySystemParam` to have a public `MySystemParamState` type associated with it.
## Solution
* Merge the trait `SystemParamState` into `SystemParam`.
* Remove all trivial `SystemParam` state types.
* `OptionNonSendMutState<T>`: you will not be missed.
---
- [x] Fix/resolve the remaining test failure.
## Changelog
* Removed the trait `SystemParamState`, merging its functionality into `SystemParam`.
## Migration Guide
**Note**: this should replace the migration guide for #6865.
This is relative to Bevy 0.9, not main.
The traits `SystemParamState` and `SystemParamFetch` have been removed, and their functionality has been transferred to `SystemParam`.
```rust
// Before (0.9)
impl SystemParam for MyParam<'_, '_> {
type State = MyParamState;
}
unsafe impl SystemParamState for MyParamState {
fn init(world: &mut World, system_meta: &mut SystemMeta) -> Self { ... }
}
unsafe impl<'w, 's> SystemParamFetch<'w, 's> for MyParamState {
type Item = MyParam<'w, 's>;
fn get_param(&mut self, ...) -> Self::Item;
}
unsafe impl ReadOnlySystemParamFetch for MyParamState { }
// After (0.10)
unsafe impl SystemParam for MyParam<'_, '_> {
type State = MyParamState;
type Item<'w, 's> = MyParam<'w, 's>;
fn init_state(world: &mut World, system_meta: &mut SystemMeta) -> Self::State { ... }
fn get_param<'w, 's>(state: &mut Self::State, ...) -> Self::Item<'w, 's>;
}
unsafe impl ReadOnlySystemParam for MyParam<'_, '_> { }
```
The trait `ReadOnlySystemParamFetch` has been replaced with `ReadOnlySystemParam`.
```rust
// Before
unsafe impl ReadOnlySystemParamFetch for MyParamState {}
// After
unsafe impl ReadOnlySystemParam for MyParam<'_, '_> {}
```
# Objective
- The doctest for `Mut::map_unchanged` uses a fake function `set_if_not_equal` to demonstrate usage.
- Now that #6853 has been merged, we can use `Mut::set_if_neq` directly instead of mocking it.
(github made me type out a message for the commit which looked like it was for the pr, sorry)
# Objective
- Add a way to get all of the input devices of an `Axis`, primarily useful for looping through them
## Solution
- Adds `Axis<T>::devices()` which returns a `FixedSizeIterator<Item = &T>`
- Adds a (probably unneeded) `test_axis_devices` test because tests are cool.
---
## Changelog
- Added `Axis<T>::devices()` method
## Migration Guide
Not a breaking change.