# Objective
- `#![warn(missing_docs)]` was added to bevy_asset in #3536
- A method was not documented when targeting wasm
## Solution
- Add documentation for it
# Objective
Some generic types like `Option<T>`, `Vec<T>` and `HashMap<K, V>` implement `Reflect` when where their generic types `T`/`K`/`V` implement `Serialize + for<'de> Deserialize<'de>`.
This is so that in their `GetTypeRegistration` impl they can insert the `ReflectSerialize` and `ReflectDeserialize` type data structs.
This has the annoying side effect that if your struct contains a `Option<NonSerdeStruct>` you won't be able to derive reflect (https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/4054).
## Solution
- remove the `Serialize + Deserialize` bounds on wrapper types
- this means that `ReflectSerialize` and `ReflectDeserialize` will no longer be inserted even for `.register::<Option<DoesImplSerde>>()`
- add `register_type_data<T, D>` shorthand for `registry.get_mut(T).insert(D::from_type<T>())`
- require users to register their specific generic types **and the serde types** separately like
```rust
.register_type::<Option<String>>()
.register_type_data::<Option<String>, ReflectSerialize>()
.register_type_data::<Option<String>, ReflectDeserialize>()
```
I believe this is the best we can do for extensibility and convenience without specialization.
## Changelog
- `.register_type` for generic types like `Option<T>`, `Vec<T>`, `HashMap<K, V>` will no longer insert `ReflectSerialize` and `ReflectDeserialize` type data. Instead you need to register it separately for concrete generic types like so:
```rust
.register_type::<Option<String>>()
.register_type_data::<Option<String>, ReflectSerialize>()
.register_type_data::<Option<String>, ReflectDeserialize>()
```
TODO: more docs and tweaks to the scene example to demonstrate registering generic types.
# Objective
- wgpu 0.13 has validation to ensure that the width and height specified for a texture are both multiples of the respective block width and block height. This means validation fails for compressed textures with say a 4x4 block size, but non-modulo-4 image width/height.
## Solution
- Using `Extent3d`'s `physical_size()` method in the `dds` loader. It takes a `TextureFormat` argument and ensures the resolution is correct.
---
## Changelog
- Fixes: Validation failure for compressed textures stored in `dds` where the width/height are not a multiple of the block dimensions.
# Objective
the bevy pbr shader doesn't handle at all normal maps
if a mesh doesn't have backed tangents. This is a pitfall
(that I fell into) and needs to be documented.
# Solution
Document the behavior. (Also document a few other
`StandardMaterial` fields)
## Changelog
* Add documentation to `emissive`, `normal_map_texture` and `occlusion_texture` fields of `StandardMaterial`.
# Objective
I've found there is a duplicated line, probably left after some copy paste.
## Solution
- removed it
---
Co-authored-by: adsick <vadimgangsta73@gmail.com>
# Objective
UI nodes can be hidden by setting their `Visibility` property. Since #5310 was merged, this is now ergonomic to use, as visibility is now inherited.
However, UI nodes still receive (and store) interactions when hidden, resulting in surprising hidden state (and an inability to otherwise disable UI nodes.
## Solution
Fixes#5360.
I've updated the `ui_focus_system` to accomplish this in a minimally intrusive way, and updated the docs to match.
**NOTE:** I have not added automated tests to verify this behavior, as we do not currently have a good testing paradigm for `bevy_ui`. I'm not thrilled with that by any means, but I'm not sure fixing it is within scope.
## Paths not taken
### Separate `Disabled` component
This is a much larger and more controversial change, and not well-scoped to UI.
Furthermore, it is extremely rare that you want hidden UI elements to function: the most common cases are for things like changing tabs, collapsing elements or so on.
Splitting this behavior would be more complex, and substantially violate user expectations.
### A separate limbo world
Mentioned in the linked issue. Super cool, but all of the problems of the `Disabled` component solution with a whole new RFC-worth of complexity.
### Using change detection to reduce the amount of redundant work
Adds a lot of complexity for questionable performance gains. Likely involves a complete refactor of the entire system.
We simply don't have the tests or benchmarks here to justify this.
## Changelog
- UI nodes are now always in an `Interaction::None` state while they are hidden (via the `ComputedVisibility` component).
# Objective
- Fixes#5293
- UI nodes with a rotation that made the top left corner lower than the top right corner (z rotations greater than π/4) were culled
## Solution
- Do not cull nodes with a rotation, but don't do proper culling in this case
As a reminder, changing rotation and scale of UI nodes is not recommended as it won't impact layout. This is a quick fix but doesn't handle properly rotations and scale in clipping/culling. This would need a lot more work as mentioned here: c2b332f98a/crates/bevy_ui/src/render/mod.rs (L404-L405)
# Objective
I noticed while working on #5366 that the documentation for label types wasn't working correctly. Having experimented with this for a few weeks, I believe that generating docs in macros is more effort than it's worth.
## Solution
Add more boilerplate, copy-paste and edit the docs across types. This also lets us add custom doctests for specific types. Also, we don't need `concat_idents` as a dependency anymore.
# Objective
- Migrate changes from #3503.
## Solution
- Document `Size` and `UiRect`.
- I also removed the type alias from the `size_ops` test since it's unnecessary.
## Follow Up
After this change is merged I'd follow up with removing the generics from `Size` and `UiRect` since `Val` should be extensible enough. This was also discussed and decided on in #3503. let me know if this is not needed or wanted anymore!
# Objective
I want to use the `deno_runtime` crate in my game, but it has a conflict with the version of the `notify` crate that Bevy depends on.
## Solution
Updates the version of the `notify` crate the Bevy depends on.
If users try to implement a custom asset loader, they must manually import anyhow::error as it's used by the asset loader trait but not exported.
2b93ab5812/examples/asset/custom_asset.rs (L25)Fixes#3138
Co-authored-by: sark <sarkahn@hotmail.com>
# Objective
Creating UI elements is very boilerplate-y with lots of indentation.
This PR aims to reduce boilerplate around creating text elements.
## Changelog
* Renamed `Text::with_section` to `from_section`.
It no longer takes a `TextAlignment` as argument, as the vast majority of cases left it `Default::default()`.
* Added `Text::from_sections` which creates a `Text` from a list of `TextSections`.
Reduces line-count and reduces indentation by one level.
* Added `Text::with_alignment`.
A builder style method for setting the `TextAlignment` of a `Text`.
* Added `TextSection::new`.
Does not reduce line count, but reduces character count and made it easier to read. No more `.to_string()` calls!
* Added `TextSection::from_style` which creates an empty `TextSection` with a style.
No more empty strings! Reduces indentation.
* Added `TextAlignment::CENTER` and friends.
* Added methods to `TextBundle`. `from_section`, `from_sections`, `with_text_alignment` and `with_style`.
## Note for reviewers.
Because of the nature of these changes I recommend setting diff view to 'split'.
~~Look for the book icon~~ cog in the top-left of the Files changed tab.
Have fun reviewing ❤️
<sup> >:D </sup>
## Migration Guide
`Text::with_section` was renamed to `from_section` and no longer takes a `TextAlignment` as argument.
Use `with_alignment` to set the alignment instead.
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Fix some small errors in the documentation of the `OwningPtr` struct.
## Solution
- Change comments with 4 slashes `////` to doc comments with 3 slashes `///`.
- Fix typos.
# Objective
Update the `calculate_bounds` system to update `Aabb`s
for entities who've either:
- gotten a new mesh
- had their mesh mutated
Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/4294.
## Solution
There are two commits here to address the two issues above:
### Commit 1
**This Commit**
Updates the `calculate_bounds` system to operate not only on entities
without `Aabb`s but also on entities whose `Handle<Mesh>` has changed.
**Why?**
So if an entity gets a new mesh, its associated `Aabb` is properly
recalculated.
**Questions**
- This type is getting pretty gnarly - should I extract some types?
- This system is public - should I add some quick docs while I'm here?
### Commit 2
**This Commit**
Updates `calculate_bounds` to update `Aabb`s of entities whose meshes
have been directly mutated.
**Why?**
So if an entity's mesh gets updated, its associated `Aabb` is properly
recalculated.
**Questions**
- I think we should be using `ahash`. Do we want to do that with a
direct `hashbrown` dependency or an `ahash` dependency that we
configure the `HashMap` with?
- There is an edge case of duplicates with `Vec<Entity>` in the
`HashMap`. If an entity gets its mesh handle changed and changed back
again it'll be added to the list twice. Do we want to use a `HashSet`
to avoid that? Or do a check in the list first (assuming iterating
over the `Vec` is faster and this edge case is rare)?
- There is an edge case where, if an entity gets a new mesh handle and
then its old mesh is updated, we'll update the entity's `Aabb` to the
new geometry of the _old_ mesh. Do we want to remove items from the
`Local<HashMap>` when handles change? Does the `Changed` event give us
the old mesh handle? If not we might need to have a
`HashMap<Entity, Handle<Mesh>>` or something so we can unlink entities
from mesh handles when the handle changes.
- I did the `zip()` with the two `HashMap` gets assuming those would
be faster than calculating the Aabb of the mesh (otherwise we could do
`meshes.get(mesh_handle).and_then(Mesh::compute_aabb).zip(entity_mesh_map...)`
or something). Is that assumption way off?
## Testing
I originally tried testing this with `bevy_mod_raycast` as mentioned in the
original issue but it seemed to work (maybe they are currently manually
updating the Aabbs?). I then tried doing it in 2D but it looks like
`Handle<Mesh>` is just for 3D. So I took [this example](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/main/examples/3d/pbr.rs)
and added some systems to mutate/assign meshes:
<details>
<summary>Test Script</summary>
```rust
use bevy::prelude::*;
use bevy::render:📷:ScalingMode;
use bevy::render::primitives::Aabb;
/// Make sure we only mutate one mesh once.
#[derive(Eq, PartialEq, Clone, Debug, Default)]
struct MutateMeshState(bool);
/// Let's have a few global meshes that we can cycle between.
/// This way we can be assigned a new mesh, mutate the old one, and then get the old one assigned.
#[derive(Eq, PartialEq, Clone, Debug, Default)]
struct Meshes(Vec<Handle<Mesh>>);
fn main() {
App::new()
.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins)
.init_resource::<MutateMeshState>()
.init_resource::<Meshes>()
.add_startup_system(setup)
.add_system(assign_new_mesh)
.add_system(show_aabbs.after(assign_new_mesh))
.add_system(mutate_meshes.after(show_aabbs))
.run();
}
fn setup(
mut commands: Commands,
mut meshes: ResMut<Assets<Mesh>>,
mut global_meshes: ResMut<Meshes>,
mut materials: ResMut<Assets<StandardMaterial>>,
) {
let m1 = meshes.add(Mesh::from(shape::Icosphere::default()));
let m2 = meshes.add(Mesh::from(shape::Icosphere {
radius: 0.90,
..Default::default()
}));
let m3 = meshes.add(Mesh::from(shape::Icosphere {
radius: 0.80,
..Default::default()
}));
global_meshes.0.push(m1.clone());
global_meshes.0.push(m2);
global_meshes.0.push(m3);
// add entities to the world
// sphere
commands.spawn_bundle(PbrBundle {
mesh: m1,
material: materials.add(StandardMaterial {
base_color: Color::hex("ffd891").unwrap(),
..default()
}),
..default()
});
// new 3d camera
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle {
projection: OrthographicProjection {
scale: 3.0,
scaling_mode: ScalingMode::FixedVertical(1.0),
..default()
}
.into(),
..default()
});
// old 3d camera
// commands.spawn_bundle(OrthographicCameraBundle {
// transform: Transform::from_xyz(0.0, 0.0, 8.0).looking_at(Vec3::default(), Vec3::Y),
// orthographic_projection: OrthographicProjection {
// scale: 0.01,
// ..default()
// },
// ..OrthographicCameraBundle::new_3d()
// });
}
fn show_aabbs(query: Query<(Entity, &Handle<Mesh>, &Aabb)>) {
for thing in query.iter() {
println!("{thing:?}");
}
}
/// For testing the second part - mutating a mesh.
///
/// Without the fix we should see this mutate an old mesh and it affects the new mesh that the
/// entity currently has.
/// With the fix, the mutation doesn't affect anything until the entity is reassigned the old mesh.
fn mutate_meshes(
mut meshes: ResMut<Assets<Mesh>>,
time: Res<Time>,
global_meshes: Res<Meshes>,
mut mutate_mesh_state: ResMut<MutateMeshState>,
) {
let mutated = mutate_mesh_state.0;
if time.seconds_since_startup() > 4.5 && !mutated {
println!("Mutating {:?}", global_meshes.0[0]);
let m = meshes.get_mut(&global_meshes.0[0]).unwrap();
let mut p = m.attribute(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION).unwrap().clone();
use bevy::render::mesh::VertexAttributeValues;
match &mut p {
VertexAttributeValues::Float32x3(v) => {
v[0] = [10.0, 10.0, 10.0];
}
_ => unreachable!(),
}
m.insert_attribute(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION, p);
mutate_mesh_state.0 = true;
}
}
/// For testing the first part - assigning a new handle.
fn assign_new_mesh(
mut query: Query<&mut Handle<Mesh>, With<Aabb>>,
time: Res<Time>,
global_meshes: Res<Meshes>,
) {
let s = time.seconds_since_startup() as usize;
let idx = s % global_meshes.0.len();
for mut handle in query.iter_mut() {
*handle = global_meshes.0[idx].clone_weak();
}
}
```
</details>
## Changelog
### Fixed
Entity `Aabb`s not updating when meshes are mutated or re-assigned.
# Objective
- Allows conversion of mutable queries to immutable queries.
- Fixes#4606
## Solution
- Add `to_readonly` method on `Query`, which uses `QueryState::as_readonly`
- `AsRef` is not feasible because creation of new queries is needed.
---
## Changelog
### Added
- Allows conversion of mutable queries to immutable queries using `Query::to_readonly`.
# Objective
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/4447 adds functions that can fetch resources/components as `*const ()` ptr by providing the `ComponentId`. This alone is not enough for them to be usable safely with reflection, because there is no general way to go from the raw pointer to a `&dyn Reflect` which is the pointer + a pointer to the VTable of the `Reflect` impl.
By adding a `ReflectFromPtr` type that is included in the type type registration when deriving `Reflect`, safe functions can be implemented in scripting languages that don't assume a type layout and can access the component data via reflection:
```rust
#[derive(Reflect)]
struct StringResource {
value: String
}
```
```lua
local res_id = world:resource_id_by_name("example::StringResource")
local res = world:resource(res_id)
print(res.value)
```
## Solution
1. add a `ReflectFromPtr` type with a `FromType<T: Reflect>` implementation and the following methods:
- ` pub unsafe fn as_reflect_ptr<'a>(&self, val: Ptr<'a>) -> &'a dyn Reflect`
- ` pub unsafe fn as_reflect_ptr_mut<'a>(&self, val: PtrMut<'a>) -> &'a mud dyn Reflect`
Safety requirements of the methods are that you need to check that the `ReflectFromPtr` was constructed for the correct type.
2. add that type to the `TypeRegistration` in the `GetTypeRegistration` impl generated by `#[derive(Reflect)]`.
This is different to other reflected traits because it doesn't need `#[reflect(ReflectReflectFromPtr)]` which IMO should be there by default.
Co-authored-by: Jakob Hellermann <hellermann@sipgate.de>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
after #5355, three methods were added on world:
* `send_event`
* `send_event_batch`
* `send_default_event`
rename `send_default_event` to `send_event_default` for better discoverability
# Objective
- Provide better compile-time errors and diagnostics.
- Add more options to allow more textures types and sampler types.
- Update array_texture example to use upgraded AsBindGroup derive macro.
## Solution
Split out the parsing of the inner struct/field attributes (the inside part of a `#[foo(...)]` attribute) for better clarity
Parse the binding index for all inner attributes, as it is part of all attributes (`#[foo(0, ...)`), then allow each attribute implementer to parse the rest of the attribute metadata as needed. This should make it very trivial to extend/change if needed in the future.
Replaced invocations of `panic!` with the `syn::Error` type, providing fine-grained errors that retains span information. This provides much nicer compile-time errors, and even better IDE errors.
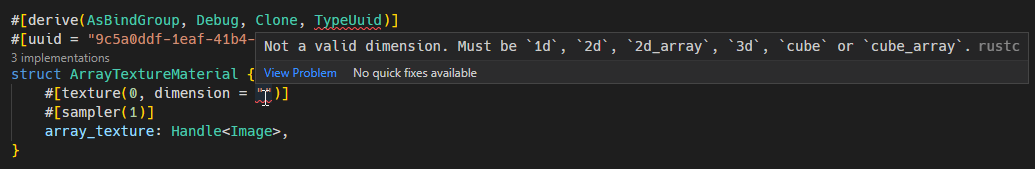
Updated the array_texture example to demonstrate the new changes.
## New AsBindGroup attribute options
### `#[texture(u32, ...)]`
Where `...` is an optional list of arguments.
| Arguments | Values | Default |
|-------------- |---------------------------------------------------------------- | ----------- |
| dimension = "..." | `"1d"`, `"2d"`, `"2d_array"`, `"3d"`, `"cube"`, `"cube_array"` | `"2d"` |
| sample_type = "..." | `"float"`, `"depth"`, `"s_int"` or `"u_int"` | `"float"` |
| filterable = ... | `true`, `false` | `true` |
| multisampled = ... | `true`, `false` | `false` |
| visibility(...) | `all`, `none`, or a list-combination of `vertex`, `fragment`, `compute` | `vertex`, `fragment` |
Example: `#[texture(0, dimension = "2d_array", visibility(vertex, fragment))]`
### `#[sampler(u32, ...)]`
Where `...` is an optional list of arguments.
| Arguments | Values | Default |
|----------- |--------------------------------------------------- | ----------- |
| sampler_type = "..." | `"filtering"`, `"non_filtering"`, `"comparison"`. | `"filtering"` |
| visibility(...) | `all`, `none`, or a list-combination of `vertex`, `fragment`, `compute` | `vertex`, `fragment` |
Example: `#[sampler(0, sampler_type = "filtering", visibility(vertex, fragment)]`
## Changelog
- Added more options to `#[texture(...)]` and `#[sampler(...)]` attributes, supporting more kinds of materials. See above for details.
- Upgraded IDE and compile-time error messages.
- Updated array_texture example using the new options.
# Objective
- With access to `World`, it's not obvious how to send an event.
- This is especially useful if you are writing a `Command` that needs to send an `Event`.
- `Events` are a first-class construct in bevy, even though they are just `Resources` under the hood. Their methods should be discoverable.
## Solution
- Provide a simple helpers to send events through `Res<Events<T>>`.
---
## Changelog
> `send_event`, `send_default_event`, and `send_event_batch` methods added to `World`.
# Objective
Fixes#5362
## Solution
Add the attribute `#[label(ignore_fields)]` for `*Label` types.
```rust
#[derive(SystemLabel)]
pub enum MyLabel {
One,
// Previously this was not allowed since labels cannot contain data.
#[system_label(ignore_fields)]
Two(PhantomData<usize>),
}
```
## Notes
This label makes it possible for equality to behave differently depending on whether or not you are treating the type as a label. For example:
```rust
#[derive(SystemLabel, PartialEq, Eq)]
#[system_label(ignore_fields)]
pub struct Foo(usize);
```
If you compare it as a label, it will ignore the wrapped fields as the user requested. But if you compare it as a `Foo`, the derive will incorrectly compare the inner fields. I see a few solutions
1. Do nothing. This is technically intended behavior, but I think we should do our best to prevent footguns.
2. Generate impls of `PartialEq` and `Eq` along with the `#[derive(Label)]` macros. This is a breaking change as it requires all users to remove these derives from their types.
3. Only allow `PhantomData` to be used with `ignore_fields` -- seems needlessly prescriptive.
---
## Changelog
* Added the `ignore_fields` attribute to the derive macros for `*Label` types.
* Added an example showing off different forms of the derive macro.
<!--
## Migration Guide
> This section is optional. If there are no breaking changes, you can delete this section.
- If this PR is a breaking change (relative to the last release of Bevy), describe how a user might need to migrate their code to support these changes
- Simply adding new functionality is not a breaking change.
- Fixing behavior that was definitely a bug, rather than a questionable design choice is not a breaking change.
-->
# Objective
remove `QF` generics from a bunch of types and methods on query related items. this has a few benefits:
- simplifies type signatures `fn iter(&self) -> QueryIter<'_, 's, Q::ReadOnly, F::ReadOnly>` is (imo) conceptually simpler than `fn iter(&self) -> QueryIter<'_, 's, Q, ROQueryFetch<'_, Q>, F>`
- `Fetch` is mostly an implementation detail but previously we had to expose it on every `iter` `get` etc method
- Allows us to potentially in the future simplify the `WorldQuery` trait hierarchy by removing the `Fetch` trait
## Solution
remove the `QF` generic and add a way to (unsafely) turn `&QueryState<Q1, F1>` into `&QueryState<Q2, F2>`
---
## Changelog/Migration Guide
The `QF` generic was removed from various `Query` iterator types and some methods, you should update your code to use the type of the corresponding worldquery of the fetch type that was being used, or call `as_readonly`/`as_nop` to convert a querystate to the appropriate type. For example:
`.get_single_unchecked_manual::<ROQueryFetch<Q>>(..)` -> `.as_readonly().get_single_unchecked_manual(..)`
`my_field: QueryIter<'w, 's, Q, ROQueryFetch<'w, Q>, F>` -> `my_field: QueryIter<'w, 's, Q::ReadOnly, F::ReadOnly>`
# Objective
- Help user when they need to add both a `TransformBundle` and a `VisibilityBundle`
## Solution
- Add a `SpatialBundle` adding all components
# Objective
[This unwrap()](de484c1e41/crates/bevy_pbr/src/pbr_material.rs (L195)) in pbr_material.rs will be hit if a StandardMaterial normal_map image has not finished loading, resulting in an error message that is hard to debug.
## Solution
~~This PR improves the error message including a potential indication of why the unwrap() could have panic'd by using expect() instead of unwrap().~~
This PR removes the panic by only proceeding if the image is found.
---
## Changelog
Don't panic when StandardMaterial normal_map images have not finished loading.
# Objective
- Fixes #5338
- Allow the usage of `use bevy::ui::Size` (see migration guide in #4285)
## Solution
- Remove the `use crate::Size` import so that the `pub use geometry::*` import also publicly uses the `Size` struct.
# Objective
- 0.8 is coming soon, and our mikktspace implementation is unsound - see https://github.com/gltf-rs/mikktspace/issues/26
- Best not to ship that
## Solution
- Fix the unsoundness in a minimal way
- Obviously there might be others, but it seems unlikely we have any way to know about those
# Objective
- Add capability to use `Affine3A`s for some `GlobalTransform`s. This allows affine transformations that are not possible using a single `Transform` such as shear and non-uniform scaling along an arbitrary axis.
- Related to #1755 and #2026
## Solution
- `GlobalTransform` becomes an enum wrapping either a `Transform` or an `Affine3A`.
- The API of `GlobalTransform` is minimized to avoid inefficiency, and to make it clear that operations should be performed using the underlying data types.
- using `GlobalTransform::Affine3A` disables transform propagation, because the main use is for cases that `Transform`s cannot support.
---
## Changelog
- `GlobalTransform`s can optionally support any affine transformation using an `Affine3A`.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
Port changes made to Material in #5053 to Material2d as well.
This is more or less an exact copy of the implementation in bevy_pbr; I
simply pretended the API existed, then copied stuff over until it
started building and the shapes example was working again.
# Objective
The changes in #5053 makes it possible to add custom materials with a lot less boiler plate. However, the implementation isn't shared with Material 2d as it's a kind of fork of the bevy_pbr version. It should be possible to use AsBindGroup on the 2d version as well.
## Solution
This makes the same kind of changes in Material2d in bevy_sprite.
This makes the following work:
```rust
//! Draws a circular purple bevy in the middle of the screen using a custom shader
use bevy::{
prelude::*,
reflect::TypeUuid,
render::render_resource::{AsBindGroup, ShaderRef},
sprite::{Material2d, Material2dPlugin, MaterialMesh2dBundle},
};
fn main() {
App::new()
.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins)
.add_plugin(Material2dPlugin::<CustomMaterial>::default())
.add_startup_system(setup)
.run();
}
/// set up a simple 2D scene
fn setup(
mut commands: Commands,
mut meshes: ResMut<Assets<Mesh>>,
mut materials: ResMut<Assets<CustomMaterial>>,
asset_server: Res<AssetServer>,
) {
commands.spawn_bundle(MaterialMesh2dBundle {
mesh: meshes.add(shape::Circle::new(50.).into()).into(),
material: materials.add(CustomMaterial {
color: Color::PURPLE,
color_texture: Some(asset_server.load("branding/icon.png")),
}),
transform: Transform::from_translation(Vec3::new(-100., 0., 0.)),
..default()
});
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle::default());
}
/// The Material2d trait is very configurable, but comes with sensible defaults for all methods.
/// You only need to implement functions for features that need non-default behavior. See the Material api docs for details!
impl Material2d for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"shaders/custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
// This is the struct that will be passed to your shader
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
# Objective
Fixes#4907. Fixes#838. Fixes#5089.
Supersedes #5146. Supersedes #2087. Supersedes #865. Supersedes #5114
Visibility is currently entirely local. Set a parent entity to be invisible, and the children are still visible. This makes it hard for users to hide entire hierarchies of entities.
Additionally, the semantics of `Visibility` vs `ComputedVisibility` are inconsistent across entity types. 3D meshes use `ComputedVisibility` as the "definitive" visibility component, with `Visibility` being just one data source. Sprites just use `Visibility`, which means they can't feed off of `ComputedVisibility` data, such as culling information, RenderLayers, and (added in this pr) visibility inheritance information.
## Solution
Splits `ComputedVisibilty::is_visible` into `ComputedVisibilty::is_visible_in_view` and `ComputedVisibilty::is_visible_in_hierarchy`. For each visible entity, `is_visible_in_hierarchy` is computed by propagating visibility down the hierarchy. The `ComputedVisibility::is_visible()` function combines these two booleans for the canonical "is this entity visible" function.
Additionally, all entities that have `Visibility` now also have `ComputedVisibility`. Sprites, Lights, and UI entities now use `ComputedVisibility` when appropriate.
This means that in addition to visibility inheritance, everything using Visibility now also supports RenderLayers. Notably, Sprites (and other 2d objects) now support `RenderLayers` and work properly across multiple views.
Also note that this does increase the amount of work done per sprite. Bevymark with 100,000 sprites on `main` runs in `0.017612` seconds and this runs in `0.01902`. That is certainly a gap, but I believe the api consistency and extra functionality this buys us is worth it. See [this thread](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/5146#issuecomment-1182783452) for more info. Note that #5146 in combination with #5114 _are_ a viable alternative to this PR and _would_ perform better, but that comes at the cost of api inconsistencies and doing visibility calculations in the "wrong" place. The current visibility system does have potential for performance improvements. I would prefer to evolve that one system as a whole rather than doing custom hacks / different behaviors for each feature slice.
Here is a "split screen" example where the left camera uses RenderLayers to filter out the blue sprite.
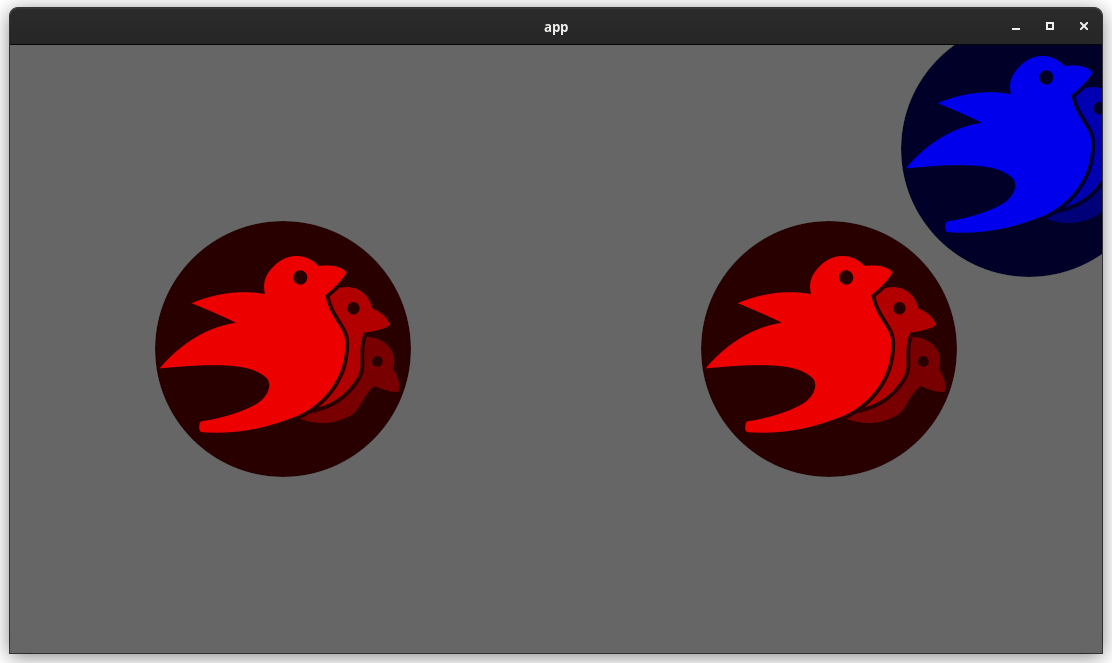

Note that this builds directly on #5146 and that @james7132 deserves the credit for the baseline visibility inheritance work. This pr moves the inherited visibility field into `ComputedVisibility`, then does the additional work of porting everything to `ComputedVisibility`. See my [comments here](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/5146#issuecomment-1182783452) for rationale.
## Follow up work
* Now that lights use ComputedVisibility, VisibleEntities now includes "visible lights" in the entity list. Functionally not a problem as we use queries to filter the list down in the desired context. But we should consider splitting this out into a separate`VisibleLights` collection for both clarity and performance reasons. And _maybe_ even consider scoping `VisibleEntities` down to `VisibleMeshes`?.
* Investigate alternative sprite rendering impls (in combination with visibility system tweaks) that avoid re-generating a per-view fixedbitset of visible entities every frame, then checking each ExtractedEntity. This is where most of the performance overhead lives. Ex: we could generate ExtractedEntities per-view using the VisibleEntities list, avoiding the need for the bitset.
* Should ComputedVisibility use bitflags under the hood? This would cut down on the size of the component, potentially speed up the `is_visible()` function, and allow us to cheaply expand ComputedVisibility with more data (ex: split out local visibility and parent visibility, add more culling classes, etc).
---
## Changelog
* ComputedVisibility now takes hierarchy visibility into account.
* 2D, UI and Light entities now use the ComputedVisibility component.
## Migration Guide
If you were previously reading `Visibility::is_visible` as the "actual visibility" for sprites or lights, use `ComputedVisibilty::is_visible()` instead:
```rust
// before (0.7)
fn system(query: Query<&Visibility>) {
for visibility in query.iter() {
if visibility.is_visible {
log!("found visible entity");
}
}
}
// after (0.8)
fn system(query: Query<&ComputedVisibility>) {
for visibility in query.iter() {
if visibility.is_visible() {
log!("found visible entity");
}
}
}
```
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
Export and register a missing type from `glam`.
Reflect impls were already present, but not registered.
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
# Objective
- There is a warning when building in release:
```
warning: unused import: `Local`
--> crates/bevy_render/src/extract_resource.rs:4:34
|
4 | use bevy_ecs::system::{Commands, Local, Res, ResMut, Resource};
| ^^^^^
|
= note: `#[warn(unused_imports)]` on by default
```
- It's used 814f8d1635/crates/bevy_render/src/extract_resource.rs (L45)
- Fix it
## Solution
- Gate the import
# Objective
- Closes#4954
- Reduce the complexity of the `{System, App, *}Label` APIs.
## Solution
For the sake of brevity I will only refer to `SystemLabel`, but everything applies to all of the other label types as well.
- Add `SystemLabelId`, a lightweight, `copy` struct.
- Convert custom types into `SystemLabelId` using the trait `SystemLabel`.
## Changelog
- String literals implement `SystemLabel` for now, but this should be changed with #4409 .
## Migration Guide
- Any previous use of `Box<dyn SystemLabel>` should be replaced with `SystemLabelId`.
- `AsSystemLabel` trait has been modified.
- No more output generics.
- Method `as_system_label` now returns `SystemLabelId`, removing an unnecessary level of indirection.
- If you *need* a label that is determined at runtime, you can use `Box::leak`. Not recommended.
## Questions for later
* Should we generate a `Debug` impl along with `#[derive(*Label)]`?
* Should we rename `as_str()`?
* Should we remove the extra derives (such as `Hash`) from builtin `*Label` types?
* Should we automatically derive types like `Clone, Copy, PartialEq, Eq`?
* More-ergonomic comparisons between `Label` and `LabelId`.
* Move `Dyn{Eq, Hash,Clone}` somewhere else.
* Some API to make interning dynamic labels easier.
* Optimize string representation
* Empty string for unit structs -- no debug info but faster comparisons
* Don't show enum types -- same tradeoffs as asbove.
This replaces `rand` with `fastrand` as the source of randomness for `HandleId::new()` in `bevy_asset`. This was the only crate with a dependency on `rand`, and now the dependency exists only as a dev-dependency.
`fastrand` was already in the dependency tree, thanks to `futures-lite`, `async-executor`, and `tempfile` to name a few.
## Changelog
Removed `rand` from dependencies in `bevy_asset` in favor of existing in-tree `fast-rand`
Add compile time check for if a system is an exclusive system. Resolves#4788
Co-authored-by: Daniel Liu <mr.picklepinosaur@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Daniel Liu <danieliu3120@gmail.com>
Following https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/5124 I decided to add the `ExactSizeIterator` impl for `QueryCombinationIter`.
Also:
- Clean up the tests for `size_hint` and `len` for both the normal `QueryIter` and `QueryCombinationIter`.
- Add tests to `QueryCombinationIter` when it shouldn't be `ExactSizeIterator`
---
## Changelog
- Added `ExactSizeIterator` implementation for `QueryCombinatonIter`
# Objective
- `.iter_combinations_*()` cannot be used on custom derived `WorldQuery`, so this fixes that
- Fixes#5284
## Solution
- `#[derive(Clone)]` on the `Fetch` of the proc macro derive.
- `#[derive(Clone)]` for `AnyOf` to satisfy tests.
Someone noted that the `rotate_around` method did not give the results they expected: [discord thread](https://discord.com/channels/691052431525675048/996497295325544479)
I tested `rotate_around` and their workaround and it seems like it was indeed incorrect.
Here is a scene with some cubes at different angles all being rotated around the center on the Y axis.
https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/29694403/178598432-407d7e80-1caf-4b17-b69b-66d9156c81e1.mp4
Interestingly, the middle cube rotates as you might expect. This threw me for a bit of a loop before I added the other cubes to the test haha.
Here is the same scene with the order multiplication of the quaternions flipped in `rotate_around`.
https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/29694403/178598446-a98026f3-524c-448b-8437-4d0d3175c6ca.mp4
That looks better :)
## Changelog
* Fixed `rotate_around` rotating the wrong way around
* Added `translate_around`. - Split out the translation code from `rotate_around`.
* Simplified/optimized `rotate_local_*` methods. - Yep, That works somehow.
<sup>Quaternions sure are wacky. Do not ask me how this works exactly, haha.</sup>
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
Generally a good idea.
I ran into this because I wanted to store `Gamepads` in a wrapper struct in https://github.com/Leafwing-Studios/leafwing-input-manager/pull/168.
This PR allows the `Debug` derive used there to continue working. I could workaround this with a custom impl, but a PR upstream seemed like the right fix.
# Objective
Improve documentation, information users of the limitations in bevy's idiomatic patterns, and suggesting alternatives for when those limitations are encountered.
## Solution
* Add documentation to `Commands` informing the user of the option of writing one-shot commands with closures.
* Add documentation to `EventWriter` regarding the limitations of event types, and suggesting alternatives using commands.
# Objective
Fixes#5304
## Solution
Instead of using a simple utility function for loading, which uses a default allocation limit of 512MB, we use a Reader object which can be configured ad hoc.
## Changelog
> This section is optional. If this was a trivial fix, or has no externally-visible impact, you can delete this section.
- Allows loading of textures larger than 512MB
# Objective
- Wireframes are currently not rendering on main because they aren't being extracted correctly
## Solution
- Extract the wireframes correctly
# Objective
When someone searches in rustdoc for `world_to_screen`, they now will
find `world_to_viewport`. The method was renamed in 0.8, it would be
nice to allow users to find the new name more easily.
---
# Objective
This PR aims to document the `bevy_asset` crate to complete coverage, while also trying to improve some bits of UX.
### Progress
- [x] Root items
- [x] `handle` module
- [x] `info` module
- [x] `path` module
- [x] `loader` module
- [x] `io` and `filesystem_watcher` module
- [x] `assets` module
- [x] `asset_server` module
- [x] `diagnostic` module
- [x] `debug_asset_server` module
- [x] Crate level documentation
- [x] Add `#![warn(missing_docs)]` lint
Coverage: 100%
## Migration Guide
- Rename `FileAssetIo::get_root_path` uses to `FileAssetIo::get_base_path`
`FileAssetIo::root_path()` is a getter for the `root_path` field, while `FileAssetIo::get_root_path` returned the parent directory of the asset root path, which was the executable's directory unless `CARGO_MANIFEST_DIR` was set. This change solves the ambiguity between the two methods.
# Objective
- Added a bunch of backticks to things that should have them, like equations, abstract variable names,
- Changed all small x, y, and z to capitals X, Y, Z.
This might be more annoying than helpful; Feel free to refuse this PR.
# Objective
- The time update is currently done in the wrong part of the schedule. For a single frame the current order of things is update input, update time (First stage), other stages, render stage (frame presentation). So when we update the time it includes the input processing of the current frame and the frame presentation of the previous frame. This is a problem when vsync is on. When input processing takes a longer amount of time for a frame, the vsync wait time gets shorter. So when these are not paired correctly we can potentially have a long input processing time added to the normal vsync wait time in the previous frame. This leads to inaccurate frame time reporting and more variance of the time than actually exists. For more details of why this is an issue see the linked issue below.
- Helps with https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/4669
- Supercedes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/4728 and https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/4735. This PR should be less controversial than those because it doesn't add to the API surface.
## Solution
- The most accurate frame time would come from hardware. We currently don't have access to that for multiple reasons, so the next best thing we can do is measure the frame time as close to frame presentation as possible. This PR gets the Instant::now() for the time immediately after frame presentation in the render system and then sends that time to the app world through a channel.
- implements suggestion from @aevyrie from here https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/4728#discussion_r872010606
## Statistics
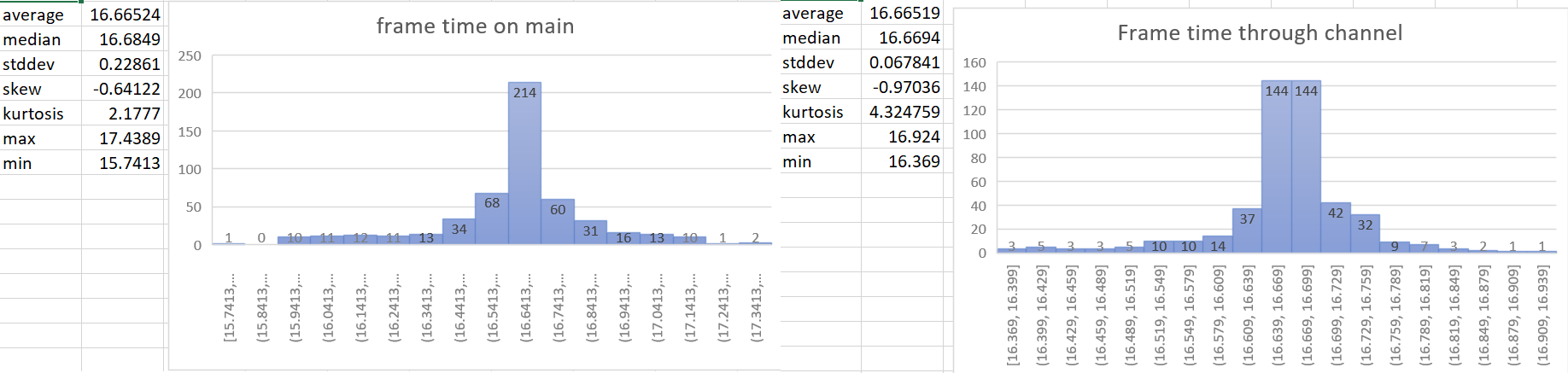
---
## Changelog
- Make frame time reporting more accurate.
## Migration Guide
`time.delta()` now reports zero for 2 frames on startup instead of 1 frame.
Remove unnecessary calls to `iter()`/`iter_mut()`.
Mainly updates the use of queries in our code, docs, and examples.
```rust
// From
for _ in list.iter() {
for _ in list.iter_mut() {
// To
for _ in &list {
for _ in &mut list {
```
We already enable the pedantic lint [clippy::explicit_iter_loop](https://rust-lang.github.io/rust-clippy/stable/) inside of Bevy. However, this only warns for a few known types from the standard library.
## Note for reviewers
As you can see the additions and deletions are exactly equal.
Maybe give it a quick skim to check I didn't sneak in a crypto miner, but you don't have to torture yourself by reading every line.
I already experienced enough pain making this PR :)
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
Resolves#5004. As suggested in the original issue, change tuple types to their corresponding vector type.
## migration guide
Changed the following fields
- `WindowCommand::SetWindowMode.resolution` from `(u32, u32)` to `UVec2`
- `WindowCommand::SetResolution.logical_resolution` from `(f32, f32)` to `Vec2`
Co-authored-by: Daniel Liu <mr.picklepinosaur@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Validate the format of the values with the expected attribute format.
- Currently, if you pass the wrong format, it will crash somewhere unrelated with a very cryptic error message, so it's really hard to debug for beginners.
## Solution
- Compare the format and panic when unexpected format is passed
## Note
- I used a separate `error!()` for a human friendly message because the panic message is very noisy and hard to parse for beginners. I don't mind changing this to only a panic if people prefer that.
- This could potentially be something that runs only in debug mode, but I don't think inserting attributes is done often enough for this to be an issue.
Co-authored-by: Charles <IceSentry@users.noreply.github.com>
Small optimization. `.collect()` from arrays generates very nice code without reallocations: https://rust.godbolt.org/z/6E6c595bq
Co-authored-by: Kornel <kornel@geekhood.net>
# Objective
Currently some TextureFormats are not supported by the Image type.
The `TextureFormat::R16Unorm` format is useful for storing heightmaps.
This small change would unblock releasing my terrain plugin on bevy 0.8.
## Solution
Added `TextureFormat::R16Unorm` support to Image.
This is an alternative (short term solution) to the large texture format issue https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/4124.
# Objective
- Slight documentation tweak to make it more clear that `FloatOrd` also implements `Hash` and `Eq`, not just `Ord`.
- I know that it does show that Hash is implemented in the docs, but I had missed it after reading the description and assuming it didn't do it, so hopefully this helps other people who might miss it like I did. :)
## Solution
- Just mention in the Hash and Eq implementation in the docstring.
# Objective
- Currently bevy_ui only checks for primary window cursor position to determine `Interaction` behavior.
- Added checks for focused window where cursor position is available.
- Fixes#5224.
## Solution
- Added checks for focused windows in `Interaction` focus system.
## Follow Up
- All windows with camera will be rendering the UI elements right now.
- We will need some way to tell which camera to render which UI.
---
Co-authored-by: fadhliazhari <44402264+fadhliazhari@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
- Enable the `axis_dpad_to_button` gilrs filter to map hats to dpad buttons on supported remotes.
- Fixes https://github.com/Leafwing-Studios/leafwing-input-manager/issues/149
- Might have fixed the confusion related to https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/3229
## Solution
- Enables the `axis_dpad_to_button` filter in `gilrs` which will use it's remote mapping information to see if there are hats mapped to dpads for that remote model. I don't really understand the logic it uses exactly, but it is usually enabled by default in gilrs and I believe it probably leads to more intuitive mapping compared to the current situation of dpad buttons being mapped to an axis.
- Removes the `GamepadAxisType::DPadX` and `GamepadAxisType::DPadY` enum variants to avoid user confusion. Those variants should never be emitted anyway, for all supported remotes.
---
## Changelog
### Changed
- Removed `GamepadAxisType::DPadX` and `GamepadAxisType::DPadY` in favor of using `GamepadButtonType::DPad[Up/Down/Left/Right]` instead.
## Migration Guide
If your game reads gamepad events or queries the axis state of `GamePadAxisType::DPadX` or `GamePadAxisType::DPadY`, then you must migrate your code to check whether or not the `GamepadButtonType::DPadUp`, `GamepadButtonType::DPadDown`, etc. buttons were pressed instead.
# Objective
`ReflectResource` and `ReflectComponent` will panic on `apply` method if there is no such component. It's not very ergonomic. And not very good for performance since I need to check if such component exists first.
## Solution
* Add `ReflectComponent::apply_or_insert` and `ReflectResource::apply_or_insert` functions.
* Rename `ReflectComponent::add` into `ReflectComponent::insert` for consistency.
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `ReflectResource::apply_or_insert` and `ReflectComponent::apply_on_insert`.
### Changed
* Rename `ReflectComponent::add` into `ReflectComponent::insert` for consistency.
* Use `ReflectComponent::apply_on_insert` in `DynamicScene` instead of manual checking.
## Migration Guide
* Rename `ReflectComponent::add` into `ReflectComponent::insert`.
# Objective
- Extracting resources currently always uses commands, which requires *at least* one additional move of the extracted value, as well as dynamic dispatch.
- Addresses https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/4402#discussion_r911634931
## Solution
- Write the resource into a `ResMut<R>` directly.
- Fall-back to commands if the resource hasn't been added yet.
## Objective
Implement absolute minimum viable product for the changes proposed in bevyengine/rfcs#53.
## Solution
- Remove public mutative access to `Parent` (Children is already publicly read-only). This includes public construction methods like `Copy`, `Clone`, and `Default`.
- Remove `PreviousParent`
- Remove `parent_update_system`
- Update all hierarchy related commands to immediately update both `Parent` and `Children` references.
## Remaining TODOs
- [ ] Update documentation for both `Parent` and `Children`. Discourage using `EntityCommands::remove`
- [x] Add `HierarchyEvent` to notify listeners of hierarchy updates. This is meant to replace listening on `PreviousParent`
## Followup
- These changes should be best moved to the hooks mentioned in #3742.
- Backing storage for both might be best moved to indexes mentioned in the same relations.
# Objective
- Currently, the `Extract` `RenderStage` is executed on the main world, with the render world available as a resource.
- However, when needing access to resources in the render world (e.g. to mutate them), the only way to do so was to get exclusive access to the whole `RenderWorld` resource.
- This meant that effectively only one extract which wrote to resources could run at a time.
- We didn't previously make `Extract`ing writing to the world a non-happy path, even though we want to discourage that.
## Solution
- Move the extract stage to run on the render world.
- Add the main world as a `MainWorld` resource.
- Add an `Extract` `SystemParam` as a convenience to access a (read only) `SystemParam` in the main world during `Extract`.
## Future work
It should be possible to avoid needing to use `get_or_spawn` for the render commands, since now the `Commands`' `Entities` matches up with the world being executed on.
We need to determine how this interacts with https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/3519
It's theoretically possible to remove the need for the `value` method on `Extract`. However, that requires slightly changing the `SystemParam` interface, which would make it more complicated. That would probably mess up the `SystemState` api too.
## Todo
I still need to add doc comments to `Extract`.
---
## Changelog
### Changed
- The `Extract` `RenderStage` now runs on the render world (instead of the main world as before).
You must use the `Extract` `SystemParam` to access the main world during the extract phase.
Resources on the render world can now be accessed using `ResMut` during extract.
### Removed
- `Commands::spawn_and_forget`. Use `Commands::get_or_spawn(e).insert_bundle(bundle)` instead
## Migration Guide
The `Extract` `RenderStage` now runs on the render world (instead of the main world as before).
You must use the `Extract` `SystemParam` to access the main world during the extract phase. `Extract` takes a single type parameter, which is any system parameter (such as `Res`, `Query` etc.). It will extract this from the main world, and returns the result of this extraction when `value` is called on it.
For example, if previously your extract system looked like:
```rust
fn extract_clouds(mut commands: Commands, clouds: Query<Entity, With<Cloud>>) {
for cloud in clouds.iter() {
commands.get_or_spawn(cloud).insert(Cloud);
}
}
```
the new version would be:
```rust
fn extract_clouds(mut commands: Commands, mut clouds: Extract<Query<Entity, With<Cloud>>>) {
for cloud in clouds.value().iter() {
commands.get_or_spawn(cloud).insert(Cloud);
}
}
```
The diff is:
```diff
--- a/src/clouds.rs
+++ b/src/clouds.rs
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
-fn extract_clouds(mut commands: Commands, clouds: Query<Entity, With<Cloud>>) {
- for cloud in clouds.iter() {
+fn extract_clouds(mut commands: Commands, mut clouds: Extract<Query<Entity, With<Cloud>>>) {
+ for cloud in clouds.value().iter() {
commands.get_or_spawn(cloud).insert(Cloud);
}
}
```
You can now also access resources from the render world using the normal system parameters during `Extract`:
```rust
fn extract_assets(mut render_assets: ResMut<MyAssets>, source_assets: Extract<Res<MyAssets>>) {
*render_assets = source_assets.clone();
}
```
Please note that all existing extract systems need to be updated to match this new style; even if they currently compile they will not run as expected. A warning will be emitted on a best-effort basis if this is not met.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
Support removing attributes from meshes. For an example use case, meshes created using the bevy::predule::shape types or loaded from external files may have attributes that are not needed for the materials they will be rendered with.
This was extracted from PR #5222.
## Solution
Implement Mesh::remove_attribute().
# Objective
Bevy requires meshes to include UV coordinates, even if the material does not use any textures, and will fail with an error `ERROR bevy_pbr::material: Mesh is missing requested attribute: Vertex_Uv (MeshVertexAttributeId(2), pipeline type: Some("bevy_pbr::material::MaterialPipeline<bevy_pbr::pbr_material::StandardMaterial>"))` otherwise. The objective of this PR is to permit this.
## Solution
This PR follows the design of #4528, which added support for per-vertex colours. It adds a shader define called VERTEX_UVS which indicates the presence of UV coordinates to the shader.
# Objective
add spotlight support
## Solution / Changelog
- add spotlight angles (inner, outer) to ``PointLight`` struct. emitted light is linearly attenuated from 100% to 0% as angle tends from inner to outer. Direction is taken from the existing transform rotation.
- add spotlight direction (vec3) and angles (f32,f32) to ``GpuPointLight`` struct (60 bytes -> 80 bytes) in ``pbr/render/lights.rs`` and ``mesh_view_bind_group.wgsl``
- reduce no-buffer-support max point light count to 204 due to above
- use spotlight data to attenuate light in ``pbr.wgsl``
- do additional cluster culling on spotlights to minimise cost in ``assign_lights_to_clusters``
- changed one of the lights in the lighting demo to a spotlight
- also added a ``spotlight`` demo - probably not justified but so reviewers can see it more easily
## notes
increasing the size of the GpuPointLight struct on my machine reduces the FPS of ``many_lights -- sphere`` from ~150fps to 140fps.
i thought this was a reasonable tradeoff, and felt better than handling spotlights separately which is possible but would mean introducing a new bind group, refactoring light-assignment code and adding new spotlight-specific code in pbr.wgsl. the FPS impact for smaller numbers of lights should be very small.
the cluster culling strategy reintroduces the cluster aabb code which was recently removed... sorry. the aabb is used to get a cluster bounding sphere, which can then be tested fairly efficiently using the strategy described at the end of https://bartwronski.com/2017/04/13/cull-that-cone/. this works well with roughly cubic clusters (where the cluster z size is close to the same as x/y size), less well for other cases like single Z slice / tiled forward rendering. In the worst case we will end up just keeping the culling of the equivalent point light.
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
# Objective
`EntityMap` lacks documentation, don't have `len()` / `is_empty` and `insert` doesn't work as in the regular HashMap`.
## Solution
* Add `len()` method.
* Return previously mapped entity from `insert()` as in the regular `HashMap`.
* Add documentation.
---
## Changelog
* Add `EntityMap::len()`.
* Return previously mapped entity from `EntityMap::insert()` as in the regular `HashMap`.
* Add documentation for `EntityMap` methods.
# Objective
It is currently hard to configure the `WindowPlugin`, as it is added as part of the `DefaultPlugins`. Ideally this should not be difficult.
## Solution
Remove the configuration from the plugin itself and put it as a `Resource`, similar to how it is done for almost all other plugins.
## Migration Guide
If you are currently configuring the behavior of the `WindowPlugin`, by constructing it manually, then you will need to instead create add the `WindowSettings` as a resource.
# Objective
In bevy 0.7, `CameraUi` was a component specifically added to cameras
that display the UI. Since camera-driven rendering was merged, it
actually does the opposite! This will make it difficult for current
users to adapt to 0.8.
## Solution
To avoid unnecessary confusion, we rename `CameraUi` into
`UiCameraConfig`.
---
## Changelog
- Rename `CameraUi` to `UiCameraConfig`
# Objective
Remove suffixes from reflect component and resource methods to closer match bevy norms.
## Solution
removed suffixes and also fixed a spelling error
---
# Objective
- Help users fix issue when their app panic when executing a command on a despawned entity
## Solution
- Add an error code and a page describing how to debug the issue
# Objective
Make it easier to create pipelines derived from the `Material2dPipeline`. Currently this is made difficult because the fields of `Material2dKey` are private.
## Solution
Make the fields public.
# Objective
- To implement `Reflect` for more glam types.
## Solution
insert `impl_reflect_struct` invocations for more glam types. I am not sure about the boolean vectors, since none of them implement `Serde::Serialize/Deserialize`, and the SIMD versions don't have public fields.
I do still think implementing reflection is useful for BVec's since then they can be incorporated into `Reflect`'ed components and set dynamically even if as a whole + it's more consistent.
## Changelog
Implemented `Reflect` for the following types
- BVec2
- BVec3
- **BVec3A** (on simd supported platforms only)
- BVec4
- **BVec4A** (on simd supported platforms only)
- Mat2
- Mat3A
- DMat2
- Affine2
- Affine3A
- DAffine2
- DAffine3
- EulerRot
# Objective
Reduce the boilerplate code needed to make draw order sorting work correctly when queuing items through new common functionality. Also fix several instances in the bevy code-base (mostly examples) where this boilerplate appears to be incorrect.
## Solution
- Moved the logic for handling back-to-front vs front-to-back draw ordering into the PhaseItems by inverting the sort key ordering of Opaque3d and AlphaMask3d. The means that all the standard 3d rendering phases measure distance in the same way. Clients of these structs no longer need to know to negate the distance.
- Added a new utility struct, ViewRangefinder3d, which encapsulates the maths needed to calculate a "distance" from an ExtractedView and a mesh's transform matrix.
- Converted all the occurrences of the distance calculations in Bevy and its examples to use ViewRangefinder3d. Several of these occurrences appear to be buggy because they don't invert the view matrix or don't negate the distance where appropriate. This leads me to the view that Bevy should expose a facility to correctly perform this calculation.
## Migration Guide
Code which creates Opaque3d, AlphaMask3d, or Transparent3d phase items _should_ use ViewRangefinder3d to calculate the distance value.
Code which manually calculated the distance for Opaque3d or AlphaMask3d phase items and correctly negated the z value will no longer depth sort correctly. However, incorrect depth sorting for these types will not impact the rendered output as sorting is only a performance optimisation when drawing with depth-testing enabled. Code which manually calculated the distance for Transparent3d phase items will continue to work as before.
# Objective
`SAFETY` comments are meant to be placed before `unsafe` blocks and should contain the reasoning of why in this case the usage of unsafe is okay. This is useful when reading the code because it makes it clear which assumptions are required for safety, and makes it easier to spot possible unsoundness holes. It also forces the code writer to think of something to write and maybe look at the safety contracts of any called unsafe methods again to double-check their correct usage.
There's a clippy lint called `undocumented_unsafe_blocks` which warns when using a block without such a comment.
## Solution
- since clippy expects `SAFETY` instead of `SAFE`, rename those
- add `SAFETY` comments in more places
- for the last remaining 3 places, add an `#[allow()]` and `// TODO` since I wasn't comfortable enough with the code to justify their safety
- add ` #![warn(clippy::undocumented_unsafe_blocks)]` to `bevy_ecs`
### Note for reviewers
The first commit only renames `SAFETY` to `SAFE` so it doesn't need a thorough review.
cb042a416e..55cef2d6fa is the diff for all other changes.
### Safety comments where I'm not too familiar with the code
774012ece5/crates/bevy_ecs/src/entity/mod.rs (L540-L546)774012ece5/crates/bevy_ecs/src/world/entity_ref.rs (L249-L252)
### Locations left undocumented with a `TODO` comment
5dde944a30/crates/bevy_ecs/src/schedule/executor_parallel.rs (L196-L199)5dde944a30/crates/bevy_ecs/src/world/entity_ref.rs (L287-L289)5dde944a30/crates/bevy_ecs/src/world/entity_ref.rs (L413-L415)
Co-authored-by: Jakob Hellermann <hellermann@sipgate.de>
# Objective
`glam` is an optional feature in `bevy_reflect` and there is a separate `mod test { #[cfg(feature = "glam")] mod glam { .. }}`.
The `reflect_downcast` test is not in that module and doesn't depend on glam, which breaks `cargo test -p bevy_reflect` without the `glam` feature.
## Solution
- Remove the glam types from the test, they're not relevant to it
# Objective
We don't have reflection for resources.
## Solution
Introduce reflection for resources.
Continues #3580 (by @Davier), related to #3576.
---
## Changelog
### Added
* Reflection on a resource type (by adding `ReflectResource`):
```rust
#[derive(Reflect)]
#[reflect(Resource)]
struct MyResourse;
```
### Changed
* Rename `ReflectComponent::add_component` into `ReflectComponent::insert_component` for consistency.
## Migration Guide
* Rename `ReflectComponent::add_component` into `ReflectComponent::insert_component`.
# Objective
This is a rebase of #3701 which is currently scheduled for 0.8 but is marked for adoption.
> Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/discussions/3609
## Solution
> - add an `insert_boxed()` method on the `Map` trait
> - implement it for `HashMap` using a new `FromReflect` generic bound
> - add a `map_apply()` helper method to implement `Map::apply()`, that inserts new values instead of ignoring them
---
## Changelog
TODO
Co-authored-by: james7132 <contact@jamessliu.com>
# Objective
- I think our codebase is hit badly by rust-lang/rust-analyzer#11410
- None of our uses of cyclic dependencies are remotely necessary
- Note that these are false positives in rust-analyzer, however it's probably easier for us to work around this
- Note also that I haven't confirmed that this is causing rust-analyzer to not work very well, but it's not a bad guess.
## Solution
- Remove our cyclic dependencies
- Import the trick from #2851 for no-op plugin groups.
# Objective
This is a common and useful type. I frequently use this when working with `Events` resource directly, typically when caching the data or manipulating the `World` directly.
This is also useful when manually configuring the cleanup strategy for events.
# Objective
Transform screen-space coordinates into world space in shaders. (My use case is for generating rays for ray tracing with the same perspective as the 3d camera).
## Solution
Add `inverse_projection` and `inverse_view_proj` fields to shader view uniform
---
## Changelog
### Added
`inverse_projection` and `inverse_view_proj` fields to shader view uniform
## Note
It'd probably be good to double-check that I did the matrix multiplication in the right order for `inverse_proj_view`. Thanks!
# Objective
- Fixes#4993
## Solution
- ~~Add `centered` property to `WindowDescriptor`~~
- Add `WindowPosition` enum
- `WindowDescriptor.position` is now `WindowPosition` instead of `Option<Vec2>`
- Add `center_window` function to `Window`
## Migration Guide
- If using `WindowDescriptor`, replace `position: None` with `position: WindowPosition::Default` and `position: Some(vec2)` with `WindowPosition::At(vec2)`.
I'm not sure if this is the best approach, so feel free to give any feedback.
Also I'm not sure how `Option`s should be handled in `bevy_winit/src/lib.rs:161`.
Also, on window creation we can't (or at least I couldn't) get `outer_size`, so this doesn't include decorations in calculations.
* Cleanup redundant code
* Use a type alias to make sure the `caster_query` and
`not_caster_query` really do the same thing and access the same things
**Objective**
Cleanup code that would otherwise be difficult to understand
**Solution**
* `extract_meshes` had two for loops which are functionally identical,
just copy-pasted code. I extracted the common code between the two
and put them into an anonymous function.
* I flattened the tuple literal for the bundle batch, it looks much
less nested and the code is much more readable as a result.
* The parameters of `extract_meshes` were also very daunting, but they
turned out to be the same query repeated twice. I extracted the query
into a type alias.
EDIT: I reworked the PR to **not do anything breaking**, and keep the old allocation behavior. Removing the memorized length was clearly a performance loss, so I kept it.
# Objective
- Enable `wgpu` profiling spans
## Solution
- `wgpu` uses the `profiling` crate to add profiling span instrumentation to their code
- `profiling` offers multiple 'backends' for profiling, including `tracing`
- When the `bevy` `trace` feature is used, add the `profiling` crate with its `profile-with-tracing` feature to enable appropriate profiling spans in `wgpu` using `tracing` which fits nicely into our infrastructure
- Bump our default `tracing` subscriber filter to `wgpu=info` from `wgpu=error` so that the profiling spans are not filtered out as they are created at the `info` level.
---
## Changelog
- Added: `tracing` profiling support for `wgpu` when using bevy's `trace` feature
- Changed: The default `tracing` filter statement for `wgpu` has been changed from the `error` level to the `info` level to not filter out the wgpu profiling spans
Removed `const_vec2`/`const_vec3`
and replaced with equivalent `.from_array`.
# Objective
Fixes#5112
## Solution
- `encase` needs to update to `glam` as well. See teoxoy/encase#4 on progress on that.
- `hexasphere` also needs to be updated, see OptimisticPeach/hexasphere#12.
# Summary
This method strips a long type name like `bevy::render:📷:PerspectiveCameraBundle` down into the bare type name (`PerspectiveCameraBundle`). This is generally useful utility method, needed by #4299 and #5121.
As a result:
- This method was moved to `bevy_utils` for easier reuse.
- The legibility and robustness of this method has been significantly improved.
- Harder test cases have been added.
This change was split out of #4299 to unblock it and make merging / reviewing the rest of those changes easier.
## Changelog
- added `bevy_utils::get_short_name`, which strips the path from a type name for convenient display.
- removed the `TypeRegistry::get_short_name` method. Use the function in `bevy_utils` instead.
The first leak:
```rust
#[test]
fn blob_vec_drop_empty_capacity() {
let item_layout = Layout:🆕:<Foo>();
let drop = drop_ptr::<Foo>;
let _ = unsafe { BlobVec::new(item_layout, Some(drop), 0) };
}
```
this is because we allocate the swap scratch in blobvec regardless of what the capacity is, but we only deallocate if capacity is > 0
The second leak:
```rust
#[test]
fn panic_while_overwriting_component() {
let helper = DropTestHelper::new();
let res = panic::catch_unwind(|| {
let mut world = World::new();
world
.spawn()
.insert(helper.make_component(true, 0))
.insert(helper.make_component(false, 1));
println!("Done inserting! Dropping world...");
});
let drop_log = helper.finish(res);
assert_eq!(
&*drop_log,
[
DropLogItem::Create(0),
DropLogItem::Create(1),
DropLogItem::Drop(0),
]
);
}
```
this is caused by us not running the drop impl on the to-be-inserted component if the drop impl of the overwritten component panics
---
managed to figure out where the leaks were by using this 10/10 command
```
cargo --quiet test --lib -- --list | sed 's/: test$//' | MIRIFLAGS="-Zmiri-disable-isolation" xargs -n1 cargo miri test --lib -- --exact
```
which runs every test one by one rather than all at once which let miri actually tell me which test had the leak 🙃
# Objective
- Nightly clippy lints should be fixed before they get stable and break CI
## Solution
- fix new clippy lints
- ignore `significant_drop_in_scrutinee` since it isn't relevant in our loop https://github.com/rust-lang/rust-clippy/issues/8987
```rust
for line in io::stdin().lines() {
...
}
```
Co-authored-by: Jakob Hellermann <hellermann@sipgate.de>
# Objective
Users often ask for help with rotations as they struggle with `Quat`s.
`Quat` is rather complex and has a ton of verbose methods.
## Solution
Add rotation helper methods to `Transform`.
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
# Objective
Fixes#5153
## Solution
Search for all enums and manually check if they have default impls that can use this new derive.
By my reckoning:
| enum | num |
|-|-|
| total | 159 |
| has default impl | 29 |
| default is unit variant | 23 |
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
# Objective
- Make Bevy work on android
## Solution
- Update android metadata and add a few more
- Set the target sdk to 31 as it will soon (in august) be the minimum sdk level for play store
- Remove the custom code to create an activity and use ndk-glue macro instead
- Delay window creation event on android
- Set the example with compatibility settings for wgpu. Those are needed for Bevy to work on my 2019 android tablet
- Add a few details on how to debug in case of failures
- Fix running the example on emulator. This was failing because of the name of the example
Bevy still doesn't work on android with this, audio features need to be disabled because of an ndk-glue version mismatch: rodio depends on 0.6.2, winit on 0.5.2. You can test with:
```
cargo apk run --release --example android_example --no-default-features --features "bevy_winit,render"
```
# Objective
CI is now failing with some changes that landed in 1.62.
## Solution
* Fix an unused lifetime by using it (we double-used the `w` lifetime).
* Update compile_fail error messages
* temporarily disable check-unused-dependencies
# Objective
- Provide a way to see the components of an entity.
- Fixes#1467
## Solution
- Add `World::inspect_entity`. It accepts an `Entity` and returns a vector of `&ComponentInfo` that the entity has.
- Add `EntityCommands::log_components`. It logs the component names of the entity. (info level)
---
## Changelog
### Added
- Ability to inspect components of an entity through `World::inspect_entity` or `EntityCommands::log_components`