# Objective
- Fix#7103.
- The issue is caused because I forgot to add a where clause to a generated struct in #7056.
## Solution
- Add the where clause.
`Query` relies on the `World` it stores being the same as the world used for creating the `QueryState` it stores. If they are not the same then everything is very unsound. This was not actually being checked anywhere, `Query::new` did not have a safety invariant or even an assertion that the `WorldId`'s are the same.
This shouldn't have any user facing impact unless we have really messed up in bevy and have unsoundness elsewhere (in which case we would now get a panic instead of being unsound).
# Objective
- In some cases, you need a `Mut<T>` pointer, but you only have a mutable reference to one. There is no easy way of converting `&'a mut Mut<'_, T>` -> `Mut<'a, T>` outside of the engine.
### Example (Before)
```rust
fn do_with_mut<T>(val: Mut<T>) { ... }
for x: Mut<T> in &mut query {
// The function expects a `Mut<T>`, so `x` gets moved here.
do_with_mut(x);
// Error: use of moved value.
do_a_thing(&x);
}
```
## Solution
- Add the function `reborrow`, which performs the mapping. This is analogous to `PtrMut::reborrow`.
### Example (After)
```rust
fn do_with_mut<T>(val: Mut<T>) { ... }
for x: Mut<T> in &mut query {
// We reborrow `x`, so the original does not get moved.
do_with_mut(x.reborrow());
// Works fine.
do_a_thing(&x);
}
```
---
## Changelog
- Added the method `reborrow` to `Mut`, `ResMut`, `NonSendMut`, and `MutUntyped`.
# Objective
The type `Local<T>` unnecessarily has the bound `T: Sync` when the local is used in an exclusive system.
## Solution
Lift the bound.
---
## Changelog
Removed the bound `T: Sync` from `Local<T>` when used as an `ExclusiveSystemParam`.
# Objective
Fixes#3310. Fixes#6282. Fixes#6278. Fixes#3666.
## Solution
Split out `!Send` resources into `NonSendResources`. Add a `origin_thread_id` to all `!Send` Resources, check it on dropping `NonSendResourceData`, if there's a mismatch, panic. Moved all of the checks that `MainThreadValidator` would do into `NonSendResources` instead.
All `!Send` resources now individually track which thread they were inserted from. This is validated against for every access, mutation, and drop that could be done against the value.
A regression test using an altered version of the example from #3310 has been added.
This is a stopgap solution for the current status quo. A full solution may involve fully removing `!Send` resources/components from `World`, which will likely require a much more thorough design on how to handle the existing in-engine and ecosystem use cases.
This PR also introduces another breaking change:
```rust
use bevy_ecs::prelude::*;
#[derive(Resource)]
struct Resource(u32);
fn main() {
let mut world = World::new();
world.insert_resource(Resource(1));
world.insert_non_send_resource(Resource(2));
let res = world.get_resource_mut::<Resource>().unwrap();
assert_eq!(res.0, 2);
}
```
This code will run correctly on 0.9.1 but not with this PR, since NonSend resources and normal resources have become actual distinct concepts storage wise.
## Changelog
Changed: Fix soundness bug with `World: Send`. Dropping a `World` that contains a `!Send` resource on the wrong thread will now panic.
## Migration Guide
Normal resources and `NonSend` resources no longer share the same backing storage. If `R: Resource`, then `NonSend<R>` and `Res<R>` will return different instances from each other. If you are using both `Res<T>` and `NonSend<T>` (or their mutable variants), to fetch the same resources, it's strongly advised to use `Res<T>`.
# Objective
- This pulls out some of the changes to Plugin setup and sub apps from #6503 to make that PR easier to review.
- Separate the extract stage from running the sub app's schedule to allow for them to be run on separate threads in the future
- Fixes#6990
## Solution
- add a run method to `SubApp` that runs the schedule
- change the name of `sub_app_runner` to extract to make it clear that this function is only for extracting data between the main app and the sub app
- remove the extract stage from the sub app schedule so it can be run separately. This is done by adding a `setup` method to the `Plugin` trait that runs after all plugin build methods run. This is required to allow the extract stage to be removed from the schedule after all the plugins have added their systems to the stage. We will also need the setup method for pipelined rendering to setup the render thread. See e3267965e1/crates/bevy_render/src/pipelined_rendering.rs (L57-L98)
## Changelog
- Separate SubApp Extract stage from running the sub app schedule.
## Migration Guide
### SubApp `runner` has conceptually been changed to an `extract` function.
The `runner` no longer is in charge of running the sub app schedule. It's only concern is now moving data between the main world and the sub app. The `sub_app.app.schedule` is now run for you after the provided function is called.
```rust
// before
fn main() {
let sub_app = App::empty();
sub_app.add_stage(MyStage, SystemStage::parallel());
App::new().add_sub_app(MySubApp, sub_app, move |main_world, sub_app| {
extract(app_world, render_app);
render_app.app.schedule.run();
});
}
// after
fn main() {
let sub_app = App::empty();
sub_app.add_stage(MyStage, SystemStage::parallel());
App::new().add_sub_app(MySubApp, sub_app, move |main_world, sub_app| {
extract(app_world, render_app);
// schedule is automatically called for you after extract is run
});
}
```
Spiritual successor to #5205.
Actual successor to #6865.
# Objective
Currently, system params are defined using three traits: `SystemParam`, `ReadOnlySystemParam`, `SystemParamState`. The behavior for each param is specified by the `SystemParamState` trait, while `SystemParam` simply defers to the state.
Splitting the traits in this way makes it easier to implement within macros, but it increases the cognitive load. Worst of all, this approach requires each `MySystemParam` to have a public `MySystemParamState` type associated with it.
## Solution
* Merge the trait `SystemParamState` into `SystemParam`.
* Remove all trivial `SystemParam` state types.
* `OptionNonSendMutState<T>`: you will not be missed.
---
- [x] Fix/resolve the remaining test failure.
## Changelog
* Removed the trait `SystemParamState`, merging its functionality into `SystemParam`.
## Migration Guide
**Note**: this should replace the migration guide for #6865.
This is relative to Bevy 0.9, not main.
The traits `SystemParamState` and `SystemParamFetch` have been removed, and their functionality has been transferred to `SystemParam`.
```rust
// Before (0.9)
impl SystemParam for MyParam<'_, '_> {
type State = MyParamState;
}
unsafe impl SystemParamState for MyParamState {
fn init(world: &mut World, system_meta: &mut SystemMeta) -> Self { ... }
}
unsafe impl<'w, 's> SystemParamFetch<'w, 's> for MyParamState {
type Item = MyParam<'w, 's>;
fn get_param(&mut self, ...) -> Self::Item;
}
unsafe impl ReadOnlySystemParamFetch for MyParamState { }
// After (0.10)
unsafe impl SystemParam for MyParam<'_, '_> {
type State = MyParamState;
type Item<'w, 's> = MyParam<'w, 's>;
fn init_state(world: &mut World, system_meta: &mut SystemMeta) -> Self::State { ... }
fn get_param<'w, 's>(state: &mut Self::State, ...) -> Self::Item<'w, 's>;
}
unsafe impl ReadOnlySystemParam for MyParam<'_, '_> { }
```
The trait `ReadOnlySystemParamFetch` has been replaced with `ReadOnlySystemParam`.
```rust
// Before
unsafe impl ReadOnlySystemParamFetch for MyParamState {}
// After
unsafe impl ReadOnlySystemParam for MyParam<'_, '_> {}
```
# Objective
- The doctest for `Mut::map_unchanged` uses a fake function `set_if_not_equal` to demonstrate usage.
- Now that #6853 has been merged, we can use `Mut::set_if_neq` directly instead of mocking it.
# Objective
`SystemParam` `Local`s documentation currently leaves out information that should be documented.
- What happens when multiple `SystemParam`s within the same system have the same `Local` type.
- What lifetime parameter is expected by `Local`.
## Solution
- Added sentences to documentation to communicate this information.
- Renamed `Local` lifetimes in code to `'s` where they previously were not. Users can get complicated incorrect suggested fixes if they pass the wrong lifetime. Some instance of the code had `'w` indicating the expected lifetime might not have been known to those that wrote the code either.
Co-authored-by: iiYese <83026177+iiYese@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
- Fix#4200
Currently, `#[derive(SystemParam)]` publicly exposes each field type, which makes it impossible to encapsulate private fields.
## Solution
Previously, the fields were leaked because they were used as an input generic type to the macro-generated `SystemParam::State` struct. That type has been changed to store its state in a field with a specific type, instead of a generic type.
---
## Changelog
- Fixed a bug that caused `#[derive(SystemParam)]` to leak the types of private fields.
# Objective
`Query::get` and other random access methods require looking up `EntityLocation` for every provided entity, then always looking up the `Archetype` to get the table ID and table row. This requires 4 total random fetches from memory: the `Entities` lookup, the `Archetype` lookup, the table row lookup, and the final fetch from table/sparse sets. If `EntityLocation` contains the table ID and table row, only the `Entities` lookup and the final storage fetch are required.
## Solution
Add `TableId` and table row to `EntityLocation`. Ensure it's updated whenever entities are moved around. To ensure `EntityMeta` does not grow bigger, both `TableId` and `ArchetypeId` have been shrunk to u32, and the archetype index and table row are stored as u32s instead of as usizes. This should shrink `EntityMeta` by 4 bytes, from 24 to 20 bytes, as there is no padding anymore due to the change in alignment.
This idea was partially concocted by @BoxyUwU.
## Performance
This should restore the `Query::get` "gains" lost to #6625 that were introduced in #4800 without being unsound, and also incorporates some of the memory usage reductions seen in #3678.
This also removes the same lookups during add/remove/spawn commands, so there may be a bit of a speedup in commands and `Entity{Ref,Mut}`.
---
## Changelog
Added: `EntityLocation::table_id`
Added: `EntityLocation::table_row`.
Changed: `World`s can now only hold a maximum of 2<sup>32</sup>- 1 archetypes.
Changed: `World`s can now only hold a maximum of 2<sup>32</sup> - 1 tables.
## Migration Guide
A `World` can only hold a maximum of 2<sup>32</sup> - 1 archetypes and tables now. If your use case requires more than this, please file an issue explaining your use case.
# Objective
Bevy uses custom `Ptr` types so the rust borrow checker can help ensure lifetimes are correct, even when types aren't known. However, these types don't benefit from the automatic lifetime coercion regular rust references enjoy
## Solution
Add a couple methods to Ptr, PtrMut, and MutUntyped to allow for easy usage of these types in more complex scenarios.
## Changelog
- Added `as_mut` and `as_ref` methods to `MutUntyped`.
- Added `shrink` and `as_ref` methods to `PtrMut`.
## Migration Guide
- `MutUntyped::into_inner` now marks things as changed.
# Objective
Resolve#6156.
The most common type of command is one that runs for a single entity. Built-in commands like this can be ergonomically added to the command queue using the `EntityCommands` struct. However, adding custom entity commands to the queue is quite cumbersome. You must first spawn an entity, store its ID in a local, then construct a command using that ID and add it to the queue. This prevents method chaining, which is the main benefit of using `EntityCommands`.
### Example (before)
```rust
struct MyCustomCommand(Entity);
impl Command for MyCustomCommand { ... }
let id = commands.spawn((...)).id();
commmands.add(MyCustomCommand(id));
```
## Solution
Add the `EntityCommand` trait, which allows directly adding per-entity commands to the `EntityCommands` struct.
### Example (after)
```rust
struct MyCustomCommand;
impl EntityCommand for MyCustomCommand { ... }
commands.spawn((...)).add(MyCustomCommand);
```
---
## Changelog
- Added the trait `EntityCommand`. This is a counterpart of `Command` for types that execute code for a single entity.
## Future Work
If we feel its necessary, we can simplify built-in commands (such as `Despawn`) to use this trait.
# Objective
Any closure with the signature `FnOnce(&mut World)` implicitly implements the trait `Command` due to a blanket implementation. However, this implementation unnecessarily has the `Sync` bound, which limits the types that can be used.
## Solution
Remove the bound.
---
## Changelog
- `Command` closures no longer need to implement the marker trait `std::marker::Sync`.
# Objective
- Be able to name the type that `ManualEventReader::iter/iter_with_id` returns and `EventReader::iter/iter_with_id` by proxy.
Currently for the purpose of https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/5719
## Solution
- Create a custom `Iterator` type.
# Objective
* Currently, the `SystemParam` derive does not support types with const generic parameters.
* If you try to use const generics, the error message is cryptic and unhelpful.
* Continuation of the work started in #6867 and #6957.
## Solution
Allow const generic parameters to be used with `#[derive(SystemParam)]`.
# Objective
Fixes#4729.
Continuation of #4854.
## Solution
Add documentation to `ParamSet` and its methods. Includes examples suggested by community members in the original PR.
Co-authored-by: Nanox19435 <50684926+Nanox19435@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: JoJoJet <21144246+JoJoJet@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
* The `SystemParam` derive internally uses tuples, which means it is constrained by the 16-field limit on `all_tuples`.
* The error message if you exceed this limit is abysmal.
* Supercedes #5965 -- this does the same thing, but is simpler.
## Solution
If any tuples have more than 16 fields, they are folded into tuples of tuples until they are under the 16-field limit.
# Objective
Currently, only named structs can be used with the `SystemParam` derive macro.
## Solution
Remove the restriction. Tuple structs and unit structs are now supported.
---
## Changelog
+ Added support for tuple structs and unit structs to the `SystemParam` derive macro.
# Objective
There is currently no way to iterate over key/value pairs inside an `EntityMap`, which makes the usage of this struct very awkward. I couldn't think of a good reason why the `iter()` function should not be exposed, considering the interface already exposes `keys()` and `values()`, so I made this PR.
## Solution
Implement `iter()` for `EntityMap` in terms of its inner map type.
# Objective
[Rust 1.66](https://blog.rust-lang.org/inside-rust/2022/12/12/1.66.0-prerelease.html) is coming in a few days, and bevy doesn't build with it.
Fix that.
## Solution
Replace output from a trybuild test, and fix a few new instances of `needless_borrow` and `unnecessary_cast` that are now caught.
## Note
Due to the trybuild test, this can't be merged until 1.66 is released.
# Objective
A separate `tracing` span for running a system's commands is created, even if the system doesn't have commands. This is adding extra measuring overhead (see #4892) where it's not needed.
## Solution
Move the span into `ParallelCommandState` and `CommandQueue`'s `SystemParamState::apply`. To get the right metadata for the span, a additional `&SystemMeta` parameter was added to `SystemParamState::apply`.
---
## Changelog
Added: `SystemMeta::name`
Changed: Systems without `Commands` and `ParallelCommands` will no longer show a "system_commands" span when profiling.
Changed: `SystemParamState::apply` now takes a `&SystemMeta` parameter in addition to the provided `&mut World`.
# Objective
Change detection can be spuriously triggered by setting a field to the same value as before. As a result, a common pattern is to write:
```rust
if *foo != value {
*foo = value;
}
```
This is confusing to read, and heavy on boilerplate.
Adopted from #5373, but untangled and rebased to current `bevy/main`.
## Solution
1. Add a method to the `DetectChanges` trait that implements this boilerplate when the appropriate trait bounds are met.
2. Document this minor footgun, and point users to it.
## Changelog
* added the `set_if_neq` method to avoid triggering change detection when the new and previous values are equal. This will work on both components and resources.
## Migration Guide
If you are manually checking if a component or resource's value is equal to its new value before setting it to avoid triggering change detection, migrate to the clearer and more convenient `set_if_neq` method.
## Context
Related to #2363 as it avoids triggering change detection, but not a complete solution (as it still requires triggering it when real changes are made).
Co-authored-by: Zoey <Dessix@Dessix.net>
# Objective
Speed up bundle insertion and spawning from a bundle.
## Solution
Use the same technique used in #6800 to remove the branch on storage type when writing components from a `Bundle` into storage.
- Add a `StorageType` argument to the closure on `Bundle::get_components`.
- Pass `C::Storage::STORAGE_TYPE` into that argument.
- Match on that argument instead of reading from a `Vec<StorageType>` in `BundleInfo`.
- Marked all implementations of `Bundle::get_components` as inline to encourage dead code elimination.
The `Vec<StorageType>` in `BundleInfo` was also removed as it's no longer needed. If users were reliant on this, they can either use the compile time constants or fetch the information from `Components`. Should save a rather negligible amount of memory.
## Performance
Microbenchmarks show a slight improvement to inserting components into existing entities, as well as spawning from a bundle. Ranging about 8-16% faster depending on the benchmark.
```
group main soft-constant-write-components
----- ---- ------------------------------
add_remove/sparse_set 1.08 1019.0±80.10µs ? ?/sec 1.00 944.6±66.86µs ? ?/sec
add_remove/table 1.07 1343.3±20.37µs ? ?/sec 1.00 1257.3±18.13µs ? ?/sec
add_remove_big/sparse_set 1.08 1132.4±263.10µs ? ?/sec 1.00 1050.8±240.74µs ? ?/sec
add_remove_big/table 1.02 2.6±0.05ms ? ?/sec 1.00 2.5±0.08ms ? ?/sec
get_or_spawn/batched 1.15 401.4±17.76µs ? ?/sec 1.00 349.3±11.26µs ? ?/sec
get_or_spawn/individual 1.13 732.1±43.35µs ? ?/sec 1.00 645.6±41.44µs ? ?/sec
insert_commands/insert 1.12 623.9±37.48µs ? ?/sec 1.00 557.4±34.99µs ? ?/sec
insert_commands/insert_batch 1.16 401.4±17.00µs ? ?/sec 1.00 347.4±12.87µs ? ?/sec
insert_simple/base 1.08 416.9±5.60µs ? ?/sec 1.00 385.2±4.14µs ? ?/sec
insert_simple/unbatched 1.06 934.5±44.58µs ? ?/sec 1.00 881.3±47.86µs ? ?/sec
spawn_commands/2000_entities 1.09 190.7±11.41µs ? ?/sec 1.00 174.7±9.15µs ? ?/sec
spawn_commands/4000_entities 1.10 386.5±25.33µs ? ?/sec 1.00 352.3±18.81µs ? ?/sec
spawn_commands/6000_entities 1.10 586.2±34.42µs ? ?/sec 1.00 535.3±27.25µs ? ?/sec
spawn_commands/8000_entities 1.08 778.5±45.15µs ? ?/sec 1.00 718.0±33.66µs ? ?/sec
spawn_world/10000_entities 1.04 1026.4±195.46µs ? ?/sec 1.00 985.8±253.37µs ? ?/sec
spawn_world/1000_entities 1.06 103.8±20.23µs ? ?/sec 1.00 97.6±18.22µs ? ?/sec
spawn_world/100_entities 1.15 11.4±4.25µs ? ?/sec 1.00 9.9±1.87µs ? ?/sec
spawn_world/10_entities 1.05 1030.8±229.78ns ? ?/sec 1.00 986.2±231.12ns ? ?/sec
spawn_world/1_entities 1.01 105.1±23.33ns ? ?/sec 1.00 104.6±31.84ns ? ?/sec
```
---
## Changelog
Changed: `Bundle::get_components` now takes a `FnMut(StorageType, OwningPtr)`. The provided storage type must be correct for the component being fetched.
# Objective
- Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/6417
## Solution
- clear_trackers was not being called on the render world. This causes the removed components vecs to continuously grow. This PR adds clear trackers to the end of RenderStage::Cleanup
## Migration Guide
The call to `clear_trackers` in `App` has been moved from the schedule to App::update for the main world and calls to `clear_trackers` have been added for sub_apps in the same function. This was due to needing stronger guarantees. If clear_trackers isn't called on a world it can lead to memory leaks in `RemovedComponents`.
# Objective
* Implementing a custom `SystemParam` by hand requires implementing three traits -- four if it is read-only.
* The trait `SystemParamFetch<'w, 's>` is a workaround from before we had generic associated types, and is no longer necessary.
## Solution
* Combine the trait `SystemParamFetch` with `SystemParamState`.
* I decided to remove the `Fetch` name and keep the `State` name, since the former was consistently conflated with the latter.
* Replace the trait `ReadOnlySystemParamFetch` with `ReadOnlySystemParam`, which simplifies trait bounds in generic code.
---
## Changelog
- Removed the trait `SystemParamFetch`, moving its functionality to `SystemParamState`.
- Replaced the trait `ReadOnlySystemParamFetch` with `ReadOnlySystemParam`.
## Migration Guide
The trait `SystemParamFetch` has been removed, and its functionality has been transferred to `SystemParamState`.
```rust
// Before
impl SystemParamState for MyParamState {
fn init(world: &mut World, system_meta: &mut SystemMeta) -> Self { ... }
}
impl<'w, 's> SystemParamFetch<'w, 's> for MyParamState {
type Item = MyParam<'w, 's>;
fn get_param(...) -> Self::Item;
}
// After
impl SystemParamState for MyParamState {
type Item<'w, 's> = MyParam<'w, 's>; // Generic associated types!
fn init(world: &mut World, system_meta: &mut SystemMeta) -> Self { ... }
fn get_param<'w, 's>(...) -> Self::Item<'w, 's>;
}
```
The trait `ReadOnlySystemParamFetch` has been replaced with `ReadOnlySystemParam`.
```rust
// Before
unsafe impl ReadOnlySystemParamFetch for MyParamState {}
// After
unsafe impl<'w, 's> ReadOnlySystemParam for MyParam<'w, 's> {}
```
# Objective
It's not clear to users how to handle `!Sync` types as components and resources in the absence of engine level support for them.
## Solution
Added a section to `Component`'s and `Resource`'s type level docs on available options for making a type `Sync` when it holds `!Sync` fields, linking `bevy_utils::synccell::SyncCell` and the currently unstable `std::sync::Exclusive`.
Also added a compile_fail doctest that illustrates how to apply `SyncCell`. These will break when/if #6572 gets merged, at which point these docs should be updated.
# Objective
Fixes#6224, add ``dbg``, ``info``, ``warn`` and ``error`` system piping adapter variants to expand #5776, which call the corresponding re-exported [bevy_log macros](https://docs.rs/bevy/latest/bevy/log/macro.info.html) when the result is an error.
## Solution
* Added ``dbg``, ``info``, ``warn`` and ``error`` system piping adapter variants to ``system_piping.rs``.
* Modified and added tests for these under examples in ``system_piping.rs``.
# Objective
#6547 accidentally broke change detection for SparseSet components by using `Ticks::from_tick_cells` with the wrong argument order.
## Solution
Use the right argument order. Add a regression test.
# Objective
Prevent future unsoundness that was seen in #6623.
## Solution
Newtype both indexes in `Archetype` and `Table` as `ArchetypeRow` and `TableRow`. This avoids weird numerical manipulation on the indices, and can be stored and treated opaquely. Also enforces the source and destination of where these indices at a type level.
---
## Changelog
Changed: `Archetype` indices and `Table` rows have been newtyped as `ArchetypeRow` and `TableRow`.
# Objective
`EntityRef::get` and friends all type erase calls to fetch the target components by using passing in the `TypeId` instead of using generics. This is forcing a lookup to `Components` to fetch the storage type. This adds an extra memory lookup and forces a runtime branch instead of allowing the compiler to optimize out the unused branch.
## Solution
Leverage `Component::Storage::STORAGE_TYPE` as a constant instead of fetching the metadata from `Components`.
## Performance
This has a near 2x speedup for all calls to `World::get`. Microbenchmark results from my local machine. `Query::get_component`, which uses `EntityRef::get` internally also show a slight speed up. This has closed the gap between `World::get` and `Query::get` for the same use case.
```
group entity-ref-generics main
----- ------------------- ----
query_get_component/50000_entities_sparse 1.00 890.6±40.42µs ? ?/sec 1.10 980.6±28.22µs ? ?/sec
query_get_component/50000_entities_table 1.00 968.5±73.73µs ? ?/sec 1.08 1048.8±31.76µs ? ?/sec
query_get_component_simple/system 1.00 703.2±4.37µs ? ?/sec 1.00 702.1±6.13µs ? ?/sec
query_get_component_simple/unchecked 1.02 855.8±8.98µs ? ?/sec 1.00 843.1±8.19µs ? ?/sec
world_get/50000_entities_sparse 1.00 202.3±3.15µs ? ?/sec 1.85 374.0±20.96µs ? ?/sec
world_get/50000_entities_table 1.00 193.0±1.78µs ? ?/sec 2.02 389.2±26.55µs ? ?/sec
world_query_get/50000_entities_sparse 1.01 162.4±2.23µs ? ?/sec 1.00 161.3±0.95µs ? ?/sec
world_query_get/50000_entities_table 1.00 199.9±0.63µs ? ?/sec 1.00 200.2±0.74µs ? ?/sec
```
This should also, by proxy, speed up the `ReflectComponent` APIs as most of those use `World::get` variants internally.
# Objective
The methods `World::change_tick` and `World::read_change_tick` lack documentation and have confusingly similar behavior.
## Solution
Add documentation and clarify the distinction between the two functions.
The PR fixes the interface of `EventReader::clear`. Currently, the method consumes the reader, which makes it unusable.
## Changelog
- `EventReader::clear` now takes a mutable reference instead of consuming the event reader.
## Migration Guide
`EventReader::clear` now takes a mutable reference instead of consuming the event reader. This means that `clear` now needs explicit mutable access to the reader variable, which previously could have been omitted in some cases:
```rust
// Old (0.9)
fn clear_events(reader: EventReader<SomeEvent>) {
reader.clear();
}
// New (0.10)
fn clear_events(mut reader: EventReader<SomeEvent>) {
reader.clear();
}
```
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Fixes#6812.
## Solution
- Replaced `World::read_change_ticks` with `World::change_ticks` within `bevy_ecs` crate in places where `World` references were mutable.
---
# Objective
Partially addresses #5504. Allow users to get an `Iterator<Item = EntityRef<'a>>` over all entities in the `World`.
## Solution
Change `World::iter_entities` to return an iterator of `EntityRef` instead of `Entity`.
Not sure how to tackle making an `Iterator<Item = EntityMut<'_>>` without being horribly unsound. Might need to wait for `LendingIterator` to stabilize so we can ensure only one of them is valid at a given time.
---
## Changelog
Changed: `World::iter_entities` now returns an iterator of `EntityRef` instead of `Entity`.
# Objective
Currently, the `SystemParam` derive forces you to declare the lifetime parameters `<'w, 's>`, even if you don't use them.
If you don't follow this structure, the error message is quite nasty.
### Example (before):
```rust
#[derive(SystemParam)]
pub struct EventWriter<'w, 's, E: Event> {
events: ResMut<'w, Events<E>>,
// The derive forces us to declare the `'s` lifetime even though we don't use it,
// so we have to add this `PhantomData` to please rustc.
#[system_param(ignore)]
_marker: PhantomData<&'s ()>,
}
```
## Solution
* Allow the user to omit either lifetime.
* Emit a descriptive error if any lifetimes used are invalid.
### Example (after):
```rust
#[derive(SystemParam)]
pub struct EventWriter<'w, E: Event> {
events: ResMut<'w, Events<E>>,
}
```
---
## Changelog
* The `SystemParam` derive is now more flexible, allowing you to omit unused lifetime parameters.
# Objective
The soundness of the ECS `World` partially relies on the correctness of the state of `Entities` stored within it. We're currently allowing users to (unsafely) mutate it, as well as readily construct it without using a `World`. While this is not strictly unsound so long as users (including `bevy_render`) safely use the APIs, it's a fairly easy path to unsoundness without much of a guard rail.
Addresses #3362 for `bevy_ecs::entity`. Incorporates the changes from #3985.
## Solution
Remove `Entities`'s `Default` implementation and force access to the type to only be through a properly constructed `World`.
Additional cleanup for other parts of `bevy_ecs::entity`:
- `Entity::index` and `Entity::generation` are no longer `pub(crate)`, opting to force the rest of bevy_ecs to use the public interface to access these values.
- `EntityMeta` is no longer `pub` and also not `pub(crate)` to attempt to cut down on updating `generation` without going through an `Entities` API. It's currently inaccessible except via the `pub(crate)` Vec on `Entities`, there was no way for an outside user to use it.
- Added `Entities::set`, an unsafe `pub(crate)` API for setting the location of an Entity (parallel to `Entities::get`) that replaces the internal case where we need to set the location of an entity when it's been spawned, moved, or despawned.
- `Entities::alloc_at_without_replacement` is only used in `World::get_or_spawn` within the first party crates, and I cannot find a public use of this API in any ecosystem crate that I've checked (via GitHub search).
- Attempted to document the few remaining undocumented public APIs in the module.
---
## Changelog
Removed: `Entities`'s `Default` implementation.
Removed: `EntityMeta`
Removed: `Entities::alloc_at_without_replacement` and `AllocAtWithoutReplacement`.
Co-authored-by: james7132 <contact@jamessliu.com>
Co-authored-by: James Liu <contact@jamessliu.com>
# Objective
Document `bevy_ecs::archetype` and and declutter the public documentation for the module by making types non-`pub`.
Addresses #3362 for `bevy_ecs::archetype`.
## Solution
- Add module level documentation.
- Add type and API level documentation for all public facing types.
- Make `ArchetypeId`, `ArchetypeGeneration`, and `ArchetypeComponentId` truly opaque IDs that are not publicly constructable.
- Make `AddBundle` non-pub, make `Edges::get_add_bundle` return a `Option<ArchetypeId>` and fork the existing function into `Edges::get_add_bundle_internal`.
- Remove `pub(crate)` on fields that have a corresponding pub accessor function.
- Removed the `Archetypes: Default` impl, opting for a `pub(crate) fn new` alternative instead.
---
## Changelog
Added: `ArchetypeGeneration` now implements `Ord` and `PartialOrd`.
Removed: `Archetypes`'s `Default` implementation.
Removed: `Archetype::new` and `Archetype::is_empty`.
Removed: `ArchetypeId::new` and `ArchetypeId::value`.
Removed: `ArchetypeGeneration::value`
Removed: `ArchetypeIdentity`.
Removed: `ArchetypeComponentId::new` and `ArchetypeComponentId::value`.
Removed: `AddBundle`. `Edges::get_add_bundle` now returns `Option<ArchetypeId>`
# Objective
- The documentation describing different ways to spawn an Entity is missing reference to "method" for "Spawn an entity with components".
## Solution
- Update the documentation to add the reference to `World::spawn`.
# Objective
One of the use-cases for the function `Entity::from_raw` is creating placeholder entity ids, which are meant to be overwritten later. If we use a constant for this instead of `from_raw`, it is more ergonomic and self-documenting.
## Solution
Add a constant that returns an entity ID with an index of `u32::MAX` and a generation of zero. Users are instructed to overwrite this value before using it.
# Objective
- Reverts #5730.
- Fixes#6173, fixes#6596.
## Solution
Remove the warning entirely.
## Changelog
You will no longer be spammed about
> Missed 31 `bevy_input:🐭:MouseMotion` events. Consider
reading from the `EventReader` more often (generally the best
solution) or calling Events::update() less frequently
(normally this is called once per frame). This problem is most
likely due to run criteria/fixed timesteps or consuming events
conditionally. See the Events documentation for
more information.
when you miss events. These warnings were often (but not always) a false positive. You can still check this manually by using `ManualEventReader::missed_events`
# Objective
Consider the test
```rust
let cell = world.cell();
let _value_a = cell.resource_mut::<A>();
let _value_b = cell.resource_mut::<A>();
```
Currently, this will roughly execute
```rust
// first call
let value = unsafe {
self.world
.get_non_send_unchecked_mut_with_id(component_id)?
};
return Some(WorldBorrowMut::new(value, archetype_component_id, self.access)))
// second call
let value = unsafe {
self.world
.get_non_send_unchecked_mut_with_id(component_id)?
};
return Some(WorldBorrowMut::new(value, archetype_component_id, self.access)))
```
where `WorldBorrowMut::new` will panic if the resource is already borrowed.
This means, that `_value_a` will be created, the access checked (OK), then `value_b` will be created, and the access checked (`panic`).
For a moment, both `_value_a` and `_value_b` existed as `&mut T` to the same location, which is insta-UB as far as I understand it.
## Solution
Flip the order so that `WorldBorrowMut::new` first checks the access, _then_ fetches creates the value. To do that, we pass a `impl FnOnce() -> Mut<T>` instead of the `Mut<T>` directly:
```rust
let get_value = || unsafe {
self.world
.get_non_send_unchecked_mut_with_id(component_id)?
};
return Some(WorldBorrowMut::new(get_value, archetype_component_id, self.access)))
```
Without this fix, piped systems containing exclusive systems fail to run, giving a runtime panic.
With this PR, running piped systems that contain exclusive systems now works.
## Explanation of the bug
This is because, unless overridden, the default implementation of `run` from the `System` trait simply calls `run_unsafe`. That is not valid for exclusive systems. They must always be called via `run`, as `run_unsafe` takes `&World` instead of `&mut World`.
Trivial reproduction example:
```rust
fn main() {
App::new()
.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins)
.add_system(exclusive.pipe(another))
.run();
}
fn exclusive(_world: &mut World) {}
fn another() {}
```
If you run this, you will get a panic 'Cannot run exclusive systems with a shared World reference' and the backtrace shows how bevy (correctly) tries to call the `run` method (because the system is exclusive), but it is the implementation from the `System` trait (because `PipeSystem` does not have its own), which calls `run_unsafe` (incorrect):
- 3: <bevy_ecs::system::system_piping::PipeSystem<SystemA,SystemB> as bevy_ecs::system::system::System>::run_unsafe
- 4: bevy_ecs::system::system::System::run
# Objective
Fixes#4884. `ComponentTicks` stores both added and changed ticks contiguously in the same 8 bytes. This is convenient when passing around both together, but causes half the bytes fetched from memory for the purposes of change detection to effectively go unused. This is inefficient when most queries (no filter, mutating *something*) only write out to the changed ticks.
## Solution
Split the storage for change detection ticks into two separate `Vec`s inside `Column`. Fetch only what is needed during iteration.
This also potentially also removes one blocker from autovectorization of dense queries.
EDIT: This is confirmed to enable autovectorization of dense queries in `for_each` and `par_for_each` where possible. Unfortunately `iter` has other blockers that prevent it.
### TODO
- [x] Microbenchmark
- [x] Check if this allows query iteration to autovectorize simple loops.
- [x] Clean up all of the spurious tuples now littered throughout the API
### Open Questions
- ~~Is `Mut::is_added` absolutely necessary? Can we not just use `Added` or `ChangeTrackers`?~~ It's optimized out if unused.
- ~~Does the fetch of the added ticks get optimized out if not used?~~ Yes it is.
---
## Changelog
Added: `Tick`, a wrapper around a single change detection tick.
Added: `Column::get_added_ticks`
Added: `Column::get_column_ticks`
Added: `SparseSet::get_added_ticks`
Added: `SparseSet::get_column_ticks`
Changed: `Column` now stores added and changed ticks separately internally.
Changed: Most APIs returning `&UnsafeCell<ComponentTicks>` now returns `TickCells` instead, which contains two separate `&UnsafeCell<Tick>` for either component ticks.
Changed: `Query::for_each(_mut)`, `Query::par_for_each(_mut)` will now leverage autovectorization to speed up query iteration where possible.
## Migration Guide
TODO
# Objective
Fix#5149
## Solution
Instead of returning the **total count** of elements in the `QueryIter` in
`size_hint`, we return the **count of remaining elements**. This
Fixes#5149 even when #5148 gets merged.
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/5149
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/5148
---
## Changelog
- Fix partially consumed `QueryIter` and `QueryCombinationIter` having invalid `size_hint`
Co-authored-by: Nicola Papale <nicopap@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
BlobVec currently relies on a scratch piece of memory allocated at initialization to make a temporary copy of a component when using `swap_remove_and_{forget/drop}`. This is potentially suboptimal as it writes to a, well-known, but random part of memory instead of using the stack.
## Solution
As the `FIXME` in the file states, replace `swap_scratch` with a call to `swap_nonoverlapping::<u8>`. The swapped last entry is returned as a `OwnedPtr`.
In theory, this should be faster as the temporary swap is allocated on the stack, `swap_nonoverlapping` allows for easier vectorization for bigger types, and the same memory is used between the swap and the returned `OwnedPtr`.
# Objective
* Enable `Res` and `Query` parameter mutual exclusion
* Required for https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/5080
The `FilteredAccessSet::get_conflicts` methods didn't work properly with
`Res` and `ResMut` parameters. Because those added their access by using
the `combined_access_mut` method and directly modifying the global
access state of the FilteredAccessSet. This caused an inconsistency,
because get_conflicts assumes that ALL added access have a corresponding
`FilteredAccess` added to the `filtered_accesses` field.
In practice, that means that SystemParam that adds their access through
the `Access` returned by `combined_access_mut` and the ones that add
their access using the `add` method lived in two different universes. As
a result, they could never be mutually exclusive.
## Solution
This commit fixes it by removing the `combined_access_mut` method. This
ensures that the `combined_access` field of FilteredAccessSet is always
updated consistently with the addition of a filter. When checking for
filtered access, it is now possible to account for `Res` and `ResMut`
invalid access. This is currently not needed, but might be in the
future.
We add the `add_unfiltered_{read,write}` methods to replace previous
usages of `combined_access_mut`.
We also add improved Debug implementations on FixedBitSet so that their
meaning is much clearer in debug output.
---
## Changelog
* Fix `Res` and `Query` parameter never being mutually exclusive.
## Migration Guide
Note: this mostly changes ECS internals, but since the API is public, it is technically breaking:
* Removed `FilteredAccessSet::combined_access_mut`
* Replace _immutable_ usage of those by `combined_access`
* For _mutable_ usages, use the new `add_unfiltered_{read,write}` methods instead of `combined_access_mut` followed by `add_{read,write}`
# Objective
Make core types in ECS smaller. The column sparse set in Tables is never updated after creation.
## Solution
Create `ImmutableSparseSet` which removes the capacity fields in the backing vec's and the APIs for inserting or removing elements. Drops the size of the sparse set by 3 usizes (24 bytes on 64-bit systems)
## Followup
~~After #4809, Archetype's component SparseSet should be replaced with it.~~ This has been done.
---
## Changelog
Removed: `Table::component_capacity`
## Migration Guide
`Table::component_capacity()` has been removed as Tables do not support adding/removing columns after construction.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
Archetype is a deceptively large type in memory. It stores metadata about which components are in which storage in multiple locations, which is only used when creating new Archetypes while moving entities.
## Solution
Remove the redundant `Box<[ComponentId]>`s and iterate over the sparse set of component metadata instead. Reduces Archetype's size by 4 usizes (32 bytes on 64-bit systems), as well as the additional allocations for holding these slices.
It'd seem like there's a downside that the origin archetype has it's component metadata iterated over twice when creating a new archetype, but this change also removes the extra `Vec<ArchetypeComponentId>` allocations when creating a new archetype which may amortize out to a net gain here. This change likely negatively impacts creating new archetypes with a large number of components, but that's a cost mitigated by the fact that these archetypal relationships are cached in Edges and is incurred only once for each edge created.
## Additional Context
There are several other in-flight PRs that shrink Archetype:
- #4800 merges the entities and rows Vecs together (shaves off 24 bytes per archetype)
- #4809 removes unique_components and moves it to it's own dedicated storage (shaves off 72 bytes per archetype)
---
## Changelog
Changed: `Archetype::table_components` and `Archetype::sparse_set_components` return iterators instead of slices. `Archetype::new` requires iterators instead of parallel slices/vecs.
## Migration Guide
Do I still need to do this? I really hope people were not relying on the public facing APIs changed here.
# Objective
In bevy 0.8 you could list all resources using `world.archetypes().resource().components()`. As far as I can tell the resource archetype has been replaced with the `Resources` storage, and it would be nice if it could be used to iterate over all resource component IDs as well.
## Solution
- add `fn Resources::iter(&self) -> impl Iterator<Item = (ComponentId, &ResourceData)>`
# Objective
Fixes#6615.
`BlobVec` does not respect alignment for zero-sized types, which results in UB whenever a ZST with alignment other than 1 is used in the world.
## Solution
Add the fn `bevy_ptr::dangling_with_align`.
---
## Changelog
+ Added the function `dangling_with_align` to `bevy_ptr`, which creates a well-aligned dangling pointer to a type whose alignment is not known at compile time.
# Objective
Fix#6548. Most of these methods were already made `const` in #5688. `Entity::to_bits` is the only one that remained.
## Solution
Make it const.
# Objective
Copy `send_event` and friends from `World` to `WorldCell`.
Clean up `bevy_winit` using `WorldCell::send_event`.
## Changelog
Added `send_event`, `send_event_default`, and `send_event_batch` to `WorldCell`.
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
* Move the despawn debug log from `World::despawn` to `EntityMut::despawn`.
* Move the despawn non-existent warning log from `Commands::despawn` to `World::despawn`.
This should make logging consistent regardless of which of the three `despawn` methods is used.
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
# Objective
When an error causes `debug_checked_unreachable` to be called, the panic message unhelpfully points to the function definition instead of the place that caused the error.
## Solution
Add the `#[track_caller]` attribute in debug mode.
`EntityMut::remove_children` does not call `self.update_location()` which is unsound.
Verified by adding the following assertion, which fails when running the tests.
```rust
let before = self.location();
self.update_location();
assert_eq!(before, self.location());
```
I also removed incorrect messages like "parent entity is not modified" and the unhelpful "Inserting a bundle in the children entities may change the parent entity's location if they were of the same archetype" which might lead people to think that's the *only* thing that can change the entity's location.
# Changelog
Added `EntityMut::world_scope`.
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
# Objective
Alternative to #6424Fixes#6226
Fixes spawning empty bundles
## Solution
Add `BundleComponentStatus` trait and implement it for `AddBundle` and a new `SpawnBundleStatus` type (which always returns an Added status). `write_components` is now generic on `BundleComponentStatus` instead of taking `AddBundle` directly. This means BundleSpawner can now avoid needing AddBundle from the Empty archetype, which means BundleSpawner no longer needs a reference to the original archetype.
In theory this cuts down on the work done in `write_components` when spawning, but I'm seeing no change in the spawn benchmarks.
# Objective
Replace `WorldQueryGats` trait with actual gats
## Solution
Replace `WorldQueryGats` trait with actual gats
---
## Changelog
- Replaced `WorldQueryGats` trait with actual gats
## Migration Guide
- Replace usage of `WorldQueryGats` assoc types with the actual gats on `WorldQuery` trait
# Objective
Right now, the `TaskPool` implementation allows panics to permanently kill worker threads upon panicking. This is currently non-recoverable without using a `std::panic::catch_unwind` in every scheduled task. This is poor ergonomics and even poorer developer experience. This is exacerbated by #2250 as these threads are global and cannot be replaced after initialization.
Removes the need for temporary fixes like #4998. Fixes#4996. Fixes#6081. Fixes#5285. Fixes#5054. Supersedes #2307.
## Solution
The current solution is to wrap `Executor::run` in `TaskPool` with a `catch_unwind`, and discarding the potential panic. This was taken straight from [smol](404c7bcc0a/src/spawn.rs (L44))'s current implementation. ~~However, this is not entirely ideal as:~~
- ~~the signaled to the awaiting task. We would need to change `Task<T>` to use `async_task::FallibleTask` internally, and even then it doesn't signal *why* it panicked, just that it did.~~ (See below).
- ~~no error is logged of any kind~~ (See below)
- ~~it's unclear if it drops other tasks in the executor~~ (it does not)
- ~~This allows the ECS parallel executor to keep chugging even though a system's task has been dropped. This inevitably leads to deadlock in the executor.~~ Assuming we don't catch the unwind in ParallelExecutor, this will naturally kill the main thread.
### Alternatives
A final solution likely will incorporate elements of any or all of the following.
#### ~~Log and Ignore~~
~~Log the panic, drop the task, keep chugging. This only addresses the discoverability of the panic. The process will continue to run, probably deadlocking the executor. tokio's detatched tasks operate in this fashion.~~
Panics already do this by default, even when caught by `catch_unwind`.
#### ~~`catch_unwind` in `ParallelExecutor`~~
~~Add another layer catching system-level panics into the `ParallelExecutor`. How the executor continues when a core dependency of many systems fails to run is up for debate.~~
`async_task::Task` bubbles up panics already, this will transitively push panics all the way to the main thread.
#### ~~Emulate/Copy `tokio::JoinHandle` with `Task<T>`~~
~~`tokio::JoinHandle<T>` bubbles up the panic from the underlying task when awaited. This can be transitively applied across other APIs that also use `Task<T>` like `Query::par_for_each` and `TaskPool::scope`, bubbling up the panic until it's either caught or it reaches the main thread.~~
`async_task::Task` bubbles up panics already, this will transitively push panics all the way to the main thread.
#### Abort on Panic
The nuclear option. Log the error, abort the entire process on any thread in the task pool panicking. Definitely avoids any additional infrastructure for passing the panic around, and might actually lead to more efficient code as any unwinding is optimized out. However gives the developer zero options for dealing with the issue, a seemingly poor choice for debuggability, and prevents graceful shutdown of the process. Potentially an option for handling very low-level task management (a la #4740). Roughly takes the shape of:
```rust
struct AbortOnPanic;
impl Drop for AbortOnPanic {
fn drop(&mut self) {
abort!();
}
}
let guard = AbortOnPanic;
// Run task
std::mem::forget(AbortOnPanic);
```
---
## Changelog
Changed: `bevy_tasks::TaskPool`'s threads will no longer terminate permanently when a task scheduled onto them panics.
Changed: `bevy_tasks::Task` and`bevy_tasks::Scope` will propagate panics in the spawned tasks/scopes to the parent thread.
This reverts commit 53d387f340.
# Objective
Reverts #6448. This didn't have the intended effect: we're now getting bevy::prelude shown in the docs again.
Co-authored-by: Alejandro Pascual <alejandro.pascual.pozo@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Right now re-exports are completely hidden in prelude docs.
- Fixes#6433
## Solution
- We could show the re-exports without inlining their documentation.
# Objective
Fixes#6059, changing all incorrect occurrences of ``id`` in the ``entity`` module to ``index``:
* struct level documentation,
* ``id`` struct field,
* ``id`` method and its documentation.
## Solution
Renaming and verifying using CI.
Co-authored-by: Edvin Kjell <43633999+Edwox@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
* Add benchmarks for `Query::get_many`.
* Speed up `Query::get_many`.
## Solution
Previously, `get_many` and `get_many_mut` used the method `array::map`, which tends to optimize very poorly. This PR replaces uses of that method with loops.
## Benchmarks
| Benchmark name | Execution time | Change from this PR |
|--------------------------------------|----------------|---------------------|
| query_get_many_2/50000_calls_table | 1.3732 ms | -24.967% |
| query_get_many_2/50000_calls_sparse | 1.3826 ms | -24.572% |
| query_get_many_5/50000_calls_table | 2.6833 ms | -30.681% |
| query_get_many_5/50000_calls_sparse | 2.9936 ms | -30.672% |
| query_get_many_10/50000_calls_table | 5.7771 ms | -36.950% |
| query_get_many_10/50000_calls_sparse | 7.4345 ms | -36.987% |
# Objective
Add documentation `#[world_query(ignore)]`. Fixes#6283.
---
I've only described it's behavior so far (which appears to be the same as with `system_param`). Is there another use-case for this besides with `PhantomData`? I could only find a single usage of this construct on GitHub, which is [here](ffcb816927/bevy/examples/ecs/custom_query_param.rs (L102)).
I was also wondering if it would make sense to add a usage example to the `custom_query_example`? 🤔 That's why it's currently still in there.
Co-authored-by: Lucas Jenß <243719+x3ro@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
Bevy still has many instances of using single-tuples `(T,)` to create a bundle. Due to #2975, this is no longer necessary.
## Solution
Search for regex `\(.+\s*,\)`. This should have found every instance.
# Objective
Fix the soundness issue outlined in #5866. In short the problem is that `query.to_readonly().get_component_mut::<T>()` can provide unsound mutable access to the component. This PR is an alternative to just removing the offending api. Given that `to_readonly` is a useful tool, I think this approach is a preferable short term solution. Long term I think theres a better solution out there, but we can find that on its own time.
## Solution
Add what amounts to a "dirty flag" that marks Queries that have been converted to their read-only variant via `to_readonly` as dirty. When this flag is set to true, `get_component_mut` will fail with an error, preventing the unsound access.
# Objective
Currently for entities we serialize only `id`. But this is not very expected behavior. For example, in networking, when the server sends its state, it contains entities and components. On the client, I create new objects and map them (using `EntityMap`) to those received from the server (to know which one matches which). And if `generation` field is missing, this mapping can be broken. Example:
1. Server sends an entity `Entity{ id: 2, generation: 1}` with components.
2. Client puts the received entity in a map and create a new entity that maps to this received entity. The new entity have different `id` and `generation`. Let's call it `Entity{ id: 12, generation: 4}`.
3. Client sends a command for `Entity{ id: 12, generation: 4}`. To do so, it maps local entity to the one from server. But `generation` field is 0 because it was omitted for serialization on the server. So it maps to `Entity{ id: 2, generation: 0}`.
4. Server receives `Entity{ id: 2, generation: 0}` which is invalid.
In my game I worked around it by [writing custom serialization](https://github.com/dollisgame/dollis/blob/master/src/core/network/entity_serde.rs) and using `serde(with = "...")`. But it feels like a bad default to me.
Using `Entity` over a custom `NetworkId` also have the following advantages:
1. Re-use `MapEntities` trait to map `Entity`s in replicated components.
2. Instead of server `Entity <-> NetworkId ` and `Entity <-> NetworkId`, we map entities only on client.
3. No need to handling uniqueness. It's a rare case, but makes things simpler. For example, I don't need to query for a resource to create an unique ID.
Closes#6143.
## Solution
Use default serde impls. If anyone want to avoid wasting memory on `generation`, they can create a new type that holds `u32`. This is what Bevy do for [DynamicEntity](https://docs.rs/bevy/latest/bevy/scene/struct.DynamicEntity.html) to serialize scenes. And I don't see any use case to serialize an entity id expect this one.
---
## Changelog
### Changed
- Entity now serializes / deserializes `generation` field.
## Migration Guide
- Entity now fully serialized. If you want to serialze only `id`, as it was before, you can create a new type that wraps `u32`.
# Objective
- fix new clippy lints before they get stable and break CI
## Solution
- run `clippy --fix` to auto-fix machine-applicable lints
- silence `clippy::should_implement_trait` for `fn HandleId::default<T: Asset>`
## Changes
- always prefer `format!("{inline}")` over `format!("{}", not_inline)`
- prefer `Box::default` (or `Box::<T>::default` if necessary) over `Box::new(T::default())`
# Objective
Clean up code surrounding fetch by pulling out the common parts into the iteration code.
## Solution
Merge `Fetch::table_fetch` and `Fetch::archetype_fetch` into a single API: `Fetch::fetch(&mut self, entity: &Entity, table_row: &usize)`. This provides everything any fetch requires to internally decide which storage to read from and get the underlying data. All of these functions are marked as `#[inline(always)]` and the arguments are passed as references to attempt to optimize out the argument that isn't being used.
External to `Fetch`, Query iteration has been changed to keep track of the table row and entity outside of fetch, which moves a lot of the expensive bookkeeping `Fetch` structs had previously done internally into the outer loop.
~~TODO: Benchmark, docs~~ Done.
---
## Changelog
Changed: `Fetch::table_fetch` and `Fetch::archetype_fetch` have been merged into a single `Fetch::fetch` function.
## Migration Guide
TODO
Co-authored-by: Brian Merchant <bhmerchang@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Saverio Miroddi <saverio.pub2@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Proactive changing of code to comply with warnings generated by beta of rustlang version of cargo clippy.
## Solution
- Code changed as recommended by `rustup update`, `rustup default beta`, `cargo run -p ci -- clippy`.
- Tested using `beta` and `stable`. No clippy warnings in either after changes made.
---
## Changelog
- Warnings fixed were: `clippy::explicit-auto-deref` (present in 11 files), `clippy::needless-borrow` (present in 2 files), and `clippy::only-used-in-recursion` (only 1 file).
# Objective
- Do not implement `Copy` or `Clone` for `Fetch` types as this is kind of sus soundness wise (it feels like cloning an `IterMut` in safe code to me). Cloning a fetch seems important to think about soundness wise when doing it so I prefer this over adding a `Clone` bound to the assoc type definition (i.e. `type Fetch: Clone`) even though that would also solve the other listed things here.
- Remove a bunch of `QueryFetch<'w, Q>: Clone` bounds from our API as now all fetches can be "cloned" for use in `iter_combinations`. This should also help avoid the type inference regression ptrification introduced where `for<'a> QueryFetch<'a, Q>: Trait` bounds misbehave since we no longer need any of those kind of higher ranked bounds (although in practice we had none anyway).
- Stop being able to "forget" to implement clone for fetches, we've had a lot of issues where either `derive(Clone)` was used instead of a manual impl (so we ended up with too tight bounds on the impl) or flat out forgot to implement Clone at all. With this change all fetches are able to be cloned for `iter_combinations` so this will no longer be possible to mess up.
On an unrelated note, while making this PR I realised we probably want safety invariants on `archetype/table_fetch` that nothing aliases the table_row/archetype_index according to the access we set.
---
## Changelog
`Clone` and `Copy` were removed from all `Fetch` types.
## Migration Guide
- Call `WorldQuery::clone_fetch` instead of `fetch.clone()`. Make sure to add safety comments :)
# Objective
I was trying to implement a collision system for my game, and believed that the iter_combinations method might be what I need. But I couldn't find a simple explanation of what a combination was in Bevy and thought it could use some more explanation.
## Solution
I added some description to the documentation that can hopefully further elaborate on what a combination is.
I also changed up the docs for the method because a combination is a different thing than a permutation but the Bevy docs seemed to use them interchangeably.
# Objective
- `QueryCombinationIter` can have sizes greater than `usize::MAX`.
- Fixes#5846
## Solution
- Only the implementation of `ExactSizeIterator` has been removed. Instead of using `query_combination.len()`, you can use `query_combination.size_hint().0` to get the same value as before.
---
## Migration Guide
- Switch to using other methods of getting the length.
# Objective
Improve ergonomics by passing on the `IntoIterator` impl of the underlying type to wrapper types.
## Solution
Implement `IntoIterator` for ECS wrapper types (Mut, Local, Res, etc.).
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Improve #3953
## Solution
- The very specific circumstances under which the render world is reset meant that the flush_as_invalid function could be replaced with one that had a noop as its init method.
- This removes a double-writing issue leading to greatly increased performance.
Running the reproduction code in the linked issue, this change nearly doubles the framerate.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
Fixes#5559
Replaces #5628
## Solution
Because the generated method from_components() creates an instance of Self my implementation requires any field type that is marked to be ignored to implement Default.
---
## Changelog
Added the possibility to ignore fields in a bundle with `#[bundle(ignore)]`. Typically used when `PhantomData` needs to be added to a `Bundle`.
# Objective
- Fix disabling features in bevy_ecs (broken by #5630)
- Add tests in CI for bevy_ecs, bevy_reflect and bevy as those crates could be use standalone
Add the following message:
```
Items are returned in the order of the list of entities.
Entities that don't match the query are skipped.
```
Additionally, the docs in `iter.rs` and `state.rs` were updated to match those in `query.rs`.
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
# Objective
At least partially addresses #6282.
Resources are currently stored as a dedicated Resource archetype (ID 1). This allows for easy code reusability, but unnecessarily adds 72 bytes (on 64-bit systems) to the struct that is only used for that one archetype. It also requires several fields to be `pub(crate)` which isn't ideal.
This should also remove one sparse-set lookup from fetching, inserting, and removing resources from a `World`.
## Solution
- Add `Resources` parallel to `Tables` and `SparseSets` and extract the functionality used by `Archetype` in it.
- Remove `unique_components` from `Archetype`
- Remove the `pub(crate)` on `Archetype::components`.
- Remove `ArchetypeId::RESOURCE`
- Remove `Archetypes::resource` and `Archetypes::resource_mut`
---
## Changelog
Added: `Resources` type to store resources.
Added: `Storages::resource`
Removed: `ArchetypeId::RESOURCE`
Removed: `Archetypes::resource` and `Archetypes::resources`
Removed: `Archetype::unique_components` and `Archetypes::unique_components_mut`
## Migration Guide
Resources have been moved to `Resources` under `Storages` in `World`. All code dependent on `Archetype::unique_components(_mut)` should access it via `world.storages().resources()` instead.
All APIs accessing the raw data of individual resources (mutable *and* read-only) have been removed as these APIs allowed for unsound unsafe code. All usages of these APIs should be changed to use `World::{get, insert, remove}_resource`.
# Objective
Speed up queries that are fragmented over many empty archetypes and tables.
## Solution
Add a early-out to check if the table or archetype is empty before iterating over it. This adds an extra branch for every archetype matched, but skips setting the archetype/table to the underlying state and any iteration over it.
This may not be worth it for the default `Query::iter` and maybe even the `Query::for_each` implementations, but this definitely avoids scheduling unnecessary tasks in the `Query::par_for_each` case.
Ideally, `matched_archetypes` should only contain archetypes where there's actually work to do, but this would add a `O(n)` flat cost to every call to `update_archetypes` that scales with the number of matched archetypes.
TODO: Benchmark
# Objective
- Fixes#6206
## Solution
- Create a constructor for creating `ReflectComponent` and `ReflectResource`
---
## Changelog
> This section is optional. If this was a trivial fix, or has no externally-visible impact, you can delete this section.
### Added
- Created constructors for `ReflectComponent` and `ReflectResource`, allowing for advanced scripting use-cases.
# Objective
There is currently no good way of getting the width (# of components) of a table outside of `bevy_ecs`.
# Solution
Added the methods `Table::{component_count, component_capacity}`
For consistency and clarity, renamed `Table::{len, capacity}` to `entity_count` and `entity_capacity`.
## Changelog
- Added the methods `Table::component_count` and `Table::component_capacity`
- Renamed `Table::len` and `Table::capacity` to `entity_count` and `entity_capacity`
## Migration Guide
Any use of `Table::len` should now be `Table::entity_count`. Any use of `Table::capacity` should now be `Table::entity_capacity`.
# Objective
- Add a way to iterate over all entities from &World
## Solution
- Added a function `iter_entities` on World which returns an iterator of `Entity` derived from the entities in the `World`'s `archetypes`
---
## Changelog
- Added a function `iter_entities` on World, allowing iterating over all entities in contexts where you only have read-only access to the World.
# Objective
> System chaining is a confusing name: it implies the ability to construct non-linear graphs, and suggests a sense of system ordering that is only incidentally true. Instead, it actually works by passing data from one system to the next, much like the pipe operator.
> In the accepted [stageless RFC](https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/blob/main/rfcs/45-stageless.md), this concept is renamed to piping, and "system chaining" is used to construct groups of systems with ordering dependencies between them.
Fixes#6225.
## Changelog
System chaining has been renamed to system piping to improve clarity (and free up the name for new ordering APIs).
## Migration Guide
The `.chain(handler_system)` method on systems is now `.pipe(handler_system)`.
The `IntoChainSystem` trait is now `IntoPipeSystem`, and the `ChainSystem` struct is now `PipeSystem`.
# Objective
- Adding Debug implementations for App, Stage, Schedule, Query, QueryState.
- Fixes#1130.
## Solution
- Implemented std::fmt::Debug for a number of structures.
---
## Changelog
Also added Debug implementations for ParallelSystemExecutor, SingleThreadedExecutor, various RunCriteria structures, SystemContainer, and SystemDescriptor.
Opinions are sure to differ as to what information to provide in a Debug implementation. Best guess was taken for this initial version for these structures.
Co-authored-by: targrub <62773321+targrub@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
When designing an API, you may wish to provide access only to a specific field of a component or resource. The current options for doing this in safe code are
* `*Mut::into_inner`, which flags a change no matter what.
* `*Mut::bypass_change_detection`, which misses all changes.
## Solution
Add the method `map_unchanged`.
### Example
```rust
// When run, zeroes the translation of every entity.
fn reset_all(mut transforms: Query<&mut Transform>) {
for transform in &mut transforms {
// We pinky promise not to modify `t` within the closure.
let translation = transform.map_unchanged(|t| &mut t.translation);
// Only reset the translation if it isn't already zero.
translation.set_if_not_equal(Vec2::ZERO);
}
}
```
---
## Changelog
+ Added the method `map_unchanged` to types `Mut<T>`, `ResMut<T>`, and `NonSendMut<T>`.
# Background
Incremental implementation of #4299. The code is heavily borrowed from that PR.
# Objective
The execution order ambiguity checker often emits false positives, since bevy is not aware of invariants upheld by the user.
## Solution
Title
---
## Changelog
+ Added methods `SystemDescriptor::ignore_all_ambiguities` and `::ambiguous_with`. These allow you to silence warnings for specific system-order ambiguities.
## Migration Guide
***Note for maintainers**: This should replace the migration guide for #5916*
Ambiguity sets have been replaced with a simpler API.
```rust
// These systems technically conflict, but we don't care which order they run in.
fn jump_on_click(mouse: Res<Input<MouseButton>>, mut transforms: Query<&mut Transform>) { ... }
fn jump_on_spacebar(keys: Res<Input<KeyCode>>, mut transforms: Query<&mut Transform>) { ... }
//
// Before
#[derive(AmbiguitySetLabel)]
struct JumpSystems;
app
.add_system(jump_on_click.in_ambiguity_set(JumpSystems))
.add_system(jump_on_spacebar.in_ambiguity_set(JumpSystems));
//
// After
app
.add_system(jump_on_click.ambiguous_with(jump_on_spacebar))
.add_system(jump_on_spacebar);
```
# Objective
Relaxes the trait bound for `World::resource_scope` to allow non-send resources. Fixes#6037.
## Solution
No big changes in code had to be made. Added a check so that the non-send resources won't be accessed from a different thread.
---
## Changelog
- `World::resource_scope` accepts non-send resources now
- `World::resource_scope` verifies non-send access if the resource is non-send
- Two new tests are added, one for valid use of `World::resource_scope` with a non-send resource, and one for invalid use (calling it from a different thread, resulting in panic)
Co-authored-by: Dawid Piotrowski <41804418+Pietrek14@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
As explained by #5960, `Commands::get_or_spawn` may return a dangling `EntityCommands` that references a non-existing entities. As explained in [this comment], it may be undesirable to make the method return an `Option`.
- Addresses #5960
- Alternative to #5961
## Solution
This PR adds a doc comment to the method to inform the user that the returned `EntityCommands` is not guaranteed to be valid. It also adds panic doc comments on appropriate `EntityCommands` methods.
[this comment]: https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/5961#issuecomment-1259870849
# Objective
- Add ability to create nested spawns. This is needed for stageless. The current executor spawns tasks for each system early and runs the system by communicating through a channel. In stageless we want to spawn the task late, so that archetypes can be updated right before the task is run. The executor is run on a separate task, so this enables the scope to be passed to the spawned executor.
- Fixes#4301
## Solution
- Instantiate a single threaded executor on the scope and use that instead of the LocalExecutor. This allows the scope to be Send, but still able to spawn tasks onto the main thread the scope is run on. This works because while systems can access nonsend data. The systems themselves are Send. Because of this change we lose the ability to spawn nonsend tasks on the scope, but I don't think this is being used anywhere. Users would still be able to use spawn_local on TaskPools.
- Steals the lifetime tricks the `std:🧵:scope` uses to allow nested spawns, but disallow scope to be passed to tasks or threads not associated with the scope.
- Change the storage for the tasks to a `ConcurrentQueue`. This is to allow a &Scope to be passed for spawning instead of a &mut Scope. `ConcurrentQueue` was chosen because it was already in our dependency tree because `async_executor` depends on it.
- removed the optimizations for 0 and 1 spawned tasks. It did improve those cases, but made the cases of more than 1 task slower.
---
## Changelog
Add ability to nest spawns
```rust
fn main() {
let pool = TaskPool::new();
pool.scope(|scope| {
scope.spawn(async move {
// calling scope.spawn from an spawn task was not possible before
scope.spawn(async move {
// do something
});
});
})
}
```
## Migration Guide
If you were using explicit lifetimes and Passing Scope you'll need to specify two lifetimes now.
```rust
fn scoped_function<'scope>(scope: &mut Scope<'scope, ()>) {}
// should become
fn scoped_function<'scope>(scope: &Scope<'_, 'scope, ()>) {}
```
`scope.spawn_local` changed to `scope.spawn_on_scope` this should cover cases where you needed to run tasks on the local thread, but does not cover spawning Nonsend Futures.
## TODO
* [x] think real hard about all the lifetimes
* [x] add doc about what 'env and 'scope mean.
* [x] manually check that the single threaded task pool still works
* [x] Get updated perf numbers
* [x] check and make sure all the transmutes are necessary
* [x] move commented out test into a compile fail test
* [x] look through the tests for scope on std and see if I should add any more tests
Co-authored-by: Michael Hsu <myhsu@benjaminelectric.com>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
Make `Res` cloneable
## Solution
Add an associated fn `clone(self: &Self) -. Self` instead of `Copy + Clone` trait impls to avoid `res.clone()` failing to clone out the underlying `T`
# Objective
The [Stageless RFC](https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/pull/45) involves allowing exclusive systems to be referenced and ordered relative to parallel systems. We've agreed that unifying systems under `System` is the right move.
This is an alternative to #4166 (see rationale in the comments I left there). Note that this builds on the learnings established there (and borrows some patterns).
## Solution
This unifies parallel and exclusive systems under the shared `System` trait, removing the old `ExclusiveSystem` trait / impls. This is accomplished by adding a new `ExclusiveFunctionSystem` impl similar to `FunctionSystem`. It is backed by `ExclusiveSystemParam`, which is similar to `SystemParam`. There is a new flattened out SystemContainer api (which cuts out a lot of trait and type complexity).
This means you can remove all cases of `exclusive_system()`:
```rust
// before
commands.add_system(some_system.exclusive_system());
// after
commands.add_system(some_system);
```
I've also implemented `ExclusiveSystemParam` for `&mut QueryState` and `&mut SystemState`, which makes this possible in exclusive systems:
```rust
fn some_exclusive_system(
world: &mut World,
transforms: &mut QueryState<&Transform>,
state: &mut SystemState<(Res<Time>, Query<&Player>)>,
) {
for transform in transforms.iter(world) {
println!("{transform:?}");
}
let (time, players) = state.get(world);
for player in players.iter() {
println!("{player:?}");
}
}
```
Note that "exclusive function systems" assume `&mut World` is present (and the first param). I think this is a fair assumption, given that the presence of `&mut World` is what defines the need for an exclusive system.
I added some targeted SystemParam `static` constraints, which removed the need for this:
``` rust
fn some_exclusive_system(state: &mut SystemState<(Res<'static, Time>, Query<&'static Player>)>) {}
```
## Related
- #2923
- #3001
- #3946
## Changelog
- `ExclusiveSystem` trait (and implementations) has been removed in favor of sharing the `System` trait.
- `ExclusiveFunctionSystem` and `ExclusiveSystemParam` were added, enabling flexible exclusive function systems
- `&mut SystemState` and `&mut QueryState` now implement `ExclusiveSystemParam`
- Exclusive and parallel System configuration is now done via a unified `SystemDescriptor`, `IntoSystemDescriptor`, and `SystemContainer` api.
## Migration Guide
Calling `.exclusive_system()` is no longer required (or supported) for converting exclusive system functions to exclusive systems:
```rust
// Old (0.8)
app.add_system(some_exclusive_system.exclusive_system());
// New (0.9)
app.add_system(some_exclusive_system);
```
Converting "normal" parallel systems to exclusive systems is done by calling the exclusive ordering apis:
```rust
// Old (0.8)
app.add_system(some_system.exclusive_system().at_end());
// New (0.9)
app.add_system(some_system.at_end());
```
Query state in exclusive systems can now be cached via ExclusiveSystemParams, which should be preferred for clarity and performance reasons:
```rust
// Old (0.8)
fn some_system(world: &mut World) {
let mut transforms = world.query::<&Transform>();
for transform in transforms.iter(world) {
}
}
// New (0.9)
fn some_system(world: &mut World, transforms: &mut QueryState<&Transform>) {
for transform in transforms.iter(world) {
}
}
```
# Objective
Now that we can consolidate Bundles and Components under a single insert (thanks to #2975 and #6039), almost 100% of world spawns now look like `world.spawn().insert((Some, Tuple, Here))`. Spawning an entity without any components is an extremely uncommon pattern, so it makes sense to give spawn the "first class" ergonomic api. This consolidated api should be made consistent across all spawn apis (such as World and Commands).
## Solution
All `spawn` apis (`World::spawn`, `Commands:;spawn`, `ChildBuilder::spawn`, and `WorldChildBuilder::spawn`) now accept a bundle as input:
```rust
// before:
commands
.spawn()
.insert((A, B, C));
world
.spawn()
.insert((A, B, C);
// after
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
world.spawn((A, B, C));
```
All existing instances of `spawn_bundle` have been deprecated in favor of the new `spawn` api. A new `spawn_empty` has been added, replacing the old `spawn` api.
By allowing `world.spawn(some_bundle)` to replace `world.spawn().insert(some_bundle)`, this opened the door to removing the initial entity allocation in the "empty" archetype / table done in `spawn()` (and subsequent move to the actual archetype in `.insert(some_bundle)`).
This improves spawn performance by over 10%:

To take this measurement, I added a new `world_spawn` benchmark.
Unfortunately, optimizing `Commands::spawn` is slightly less trivial, as Commands expose the Entity id of spawned entities prior to actually spawning. Doing the optimization would (naively) require assurances that the `spawn(some_bundle)` command is applied before all other commands involving the entity (which would not necessarily be true, if memory serves). Optimizing `Commands::spawn` this way does feel possible, but it will require careful thought (and maybe some additional checks), which deserves its own PR. For now, it has the same performance characteristics of the current `Commands::spawn_bundle` on main.
**Note that 99% of this PR is simple renames and refactors. The only code that needs careful scrutiny is the new `World::spawn()` impl, which is relatively straightforward, but it has some new unsafe code (which re-uses battle tested BundlerSpawner code path).**
---
## Changelog
- All `spawn` apis (`World::spawn`, `Commands:;spawn`, `ChildBuilder::spawn`, and `WorldChildBuilder::spawn`) now accept a bundle as input
- All instances of `spawn_bundle` have been deprecated in favor of the new `spawn` api
- World and Commands now have `spawn_empty()`, which is equivalent to the old `spawn()` behavior.
## Migration Guide
```rust
// Old (0.8):
commands
.spawn()
.insert_bundle((A, B, C));
// New (0.9)
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
// Old (0.8):
commands.spawn_bundle((A, B, C));
// New (0.9)
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
// Old (0.8):
let entity = commands.spawn().id();
// New (0.9)
let entity = commands.spawn_empty().id();
// Old (0.8)
let entity = world.spawn().id();
// New (0.9)
let entity = world.spawn_empty();
```
# Objective
- Add unit tests for ambiguity detection reporting.
- Incremental implementation of #4299.
## Solution
- Refactor ambiguity detection internals to make it testable. As a bonus, this should make it easier to extend in the future.
## Notes
* This code was copy-pasted from #4299 and modified. Credit goes to @alice-i-cecile and @afonsolage, though I'm not sure who wrote what at this point.
## Objective
Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/6063
## Solution
- Use `then_some(x)` instead of `then( || x)`.
- Updated error logs from `bevy_ecs_compile_fail_tests`.
## Migration Guide
From Rust 1.63 to 1.64, a new Clippy error was added; now one should use `then_some(x)` instead of `then( || x)`.
# Objective
Take advantage of the "impl Bundle for Component" changes in #2975 / add the follow up changes discussed there.
## Solution
- Change `insert` and `remove` to accept a Bundle instead of a Component (for both Commands and World)
- Deprecate `insert_bundle`, `remove_bundle`, and `remove_bundle_intersection`
- Add `remove_intersection`
---
## Changelog
- Change `insert` and `remove` now accept a Bundle instead of a Component (for both Commands and World)
- `insert_bundle` and `remove_bundle` are deprecated
## Migration Guide
Replace `insert_bundle` with `insert`:
```rust
// Old (0.8)
commands.spawn().insert_bundle(SomeBundle::default());
// New (0.9)
commands.spawn().insert(SomeBundle::default());
```
Replace `remove_bundle` with `remove`:
```rust
// Old (0.8)
commands.entity(some_entity).remove_bundle::<SomeBundle>();
// New (0.9)
commands.entity(some_entity).remove::<SomeBundle>();
```
Replace `remove_bundle_intersection` with `remove_intersection`:
```rust
// Old (0.8)
world.entity_mut(some_entity).remove_bundle_intersection::<SomeBundle>();
// New (0.9)
world.entity_mut(some_entity).remove_intersection::<SomeBundle>();
```
Consider consolidating as many operations as possible to improve ergonomics and cut down on archetype moves:
```rust
// Old (0.8)
commands.spawn()
.insert_bundle(SomeBundle::default())
.insert(SomeComponent);
// New (0.9) - Option 1
commands.spawn().insert((
SomeBundle::default(),
SomeComponent,
))
// New (0.9) - Option 2
commands.spawn_bundle((
SomeBundle::default(),
SomeComponent,
))
```
## Next Steps
Consider changing `spawn` to accept a bundle and deprecate `spawn_bundle`.
# Objective
The doc comments for `Command` methods are a bit inconsistent on the format, they sometimes go out of scope, and most importantly they are wrong, in the sense that they claim to perform the action described by the command, while in reality, they just push a command to perform the action.
- Follow-up of #5938.
- Related to #5913.
## Solution
- Where applicable, only stated that a `Command` is pushed.
- Added a “See also” section for similar methods.
- Added a missing “Panics” section for `Commands::entity`.
- Removed a wrong comment about `Commands::get_or_spawn` returning `None` (It does not return an option).
- Removed polluting descriptions of other items.
- Misc formatting changes.
## Future possibilities
Since the `Command` implementors (`Spawn`, `InsertBundle`, `InitResource`, ...) are public, I thought that it might be appropriate to describe the action of the command there instead of the method, and to add a `method → command struct` link to fill the gap.
If that seems too far-fetched, we may opt to make them private, if possible, or `#[doc(hidden)]`.
@BoxyUwU this is your fault.
Also cart didn't arrive in time to tell us not to do this.
# Objective
- Fix#2974
## Solution
- The first commit just does the actual change
- Follow up commits do steps to prove that this method works to unify as required, but this does not remove `insert_bundle`.
## Changelog
### Changed
Nested bundles now collapse automatically, and every `Component` now implements `Bundle`.
This means that you can combine bundles and components arbitrarily, for example:
```rust
// before:
.insert(A).insert_bundle(MyBBundle{..})
// after:
.insert_bundle((A, MyBBundle {..}))
```
Note that there will be a follow up PR that removes the current `insert` impl and renames `insert_bundle` to `insert`.
### Removed
The `bundle` attribute in `derive(Bundle)`.
## Migration guide
In `derive(Bundle)`, the `bundle` attribute has been removed. Nested bundles are not collapsed automatically. You should remove `#[bundle]` attributes.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
Fixes Issue #6005.
## Solution
Replaced WorldQuery with ReadOnlyWorldQuery on F generic in Query filters and QueryState to restrict its trait bound.
## Migration Guide
Query filter (`F`) generics are now bound by `ReadOnlyWorldQuery`, rather than `WorldQuery`. If for some reason you were requesting `Query<&A, &mut B>`, please use `Query<&A, With<B>>` instead.
# Objective
While using the ParallelExecutor, systems do not actually start until `prepare_systems` completes. In stages where there are large numbers of "empty" systems with very little work to do, this delay adds significant overhead, which can add up over many stages.
## Solution
Immediately and synchronously signal the start of systems that can run without dependencies inside `prepare_systems` instead of waiting for the first executor iteration after `prepare_systems` completes. Any system that is dependent on them still cannot run until after `prepare_systems` completes, but there are a large number of unconstrained systems in the base engine where this is a general benefit in almost every case.
## Performance
This change was tested against `many_foxes` in the default configuration. As this change is sensitive to the overhead around scheduling systems, the spans for measuring system timing, system overhead, and system commands were all commented out for these measurements.
The median stage timings between `main` and this PR are as follows:
|stage|main|this PR|
|:--|:--|:--|
|First|75.54 us|61.61 us|
|LoadAssets|51.05 us|42.32 us|
|PreUpdate|54.6 us|55.56 us|
|Update|61.89 us|51.5 us|
|PostUpdate|7.27 ms|6.71 ms|
|AssetEvents|47.82 us|35.95 us|
|Last|39.19 us|37.71 us|
|reserve_and_flush|57.83 us|48.2 us|
|Extract|1.41 ms|1.28 ms|
|Prepare|554.49 us|502.53 us|
|Queue|216.29 us|207.51 us|
|Sort|67.03 us|60.99 us|
|Render|1.73 ms|1.58 ms|
|Cleanup|33.55 us|30.76 us|
|Clear Entities|18.56 us|17.05 us|
|**full frame**|**11.9 ms**|**10.91 ms**|
For the first few stages, the benefit is small but cumulative over each. For PostUpdate in particular, this allows `parent_update` to run while prepare_systems is running, which is required for the animation and transform propagation systems, which dominate the time spent in the stage, but also frontloads the contention as the other "empty" systems are also running while `parent_update` is running. For Render, where there is just a single large exclusive system, the benefit comes from not waiting on a spuriously scheduled task on the task pool to kick off the system: it's immediately scheduled to run.
# Objective
EntityMut::world takes &mut self instead of &self I don't see any reason for this.
EntityRef is overly restrictive with fn world and could return &'w World
---
## Changelog
- EntityRef now implements Copy and Clone
- EntityRef::world is now fn(&self) -> &'w World instead of fn(&mut self) -> &World
- EntityMut::world is now fn(&self) -> &World instead of fn(&mut self) -> &World
# Objective
Currently, `Local` has a `Sync` bound. Theoretically this is unnecessary as a local can only ever be accessed from its own system, ensuring exclusive access on one thread. This PR removes this restriction.
## Solution
- By removing the `Resource` bound from `Local` and adding the new `SyncCell` threading primative, `Local` can have the `Sync` bound removed.
## Changelog
### Added
- Added `SyncCell` to `bevy_utils`
### Changed
- Removed `Resource` bound from `Local`
- `Local` is now wrapped in a `SyncCell`
## Migration Guide
- Any code relying on `Local<T>` having `T: Resource` may have to be changed, but this is unlikely.
Co-authored-by: PROMETHIA-27 <42193387+PROMETHIA-27@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
- Make people stop believing that commands are applied immediately (hopefully).
- Close#5913.
- Alternative to #5930.
## Solution
I added the clause “to perform impactful changes to the `World`” to the first line to subliminally help the reader accept the fact that some operations cannot be performed immediately without messing up everything.
Then I explicitely said that applying a command requires exclusive `World` access, and finally I proceeded to show when these commands are automatically applied.
I also added a brief paragraph about how commands can be applied manually, if they want.
---
### Further possibilities
If you agree, we can also change the text of the method documentation (in a separate PR) to stress about enqueueing an action instead of just performing it. For example, in `Commands::spawn`:
> Creates a new `Entity`
would be changed to something like:
> Issues a `Command` to spawn a new `Entity`
This may even have a greater effect, since when typing in an IDE, the docs of the method pop up and the programmer can read them on the fly.
# Objective
I wanted to run the code
```rust
let reflect_resource: ReflectResource = ...;
let value: Mut<dyn Reflect> = reflect_resource.reflect(world);
value.deref();
// ^ ERROR: deref method doesn't exist because `dyn Reflect` doesnt satisfy `: Sized`.
```
## Solution
Relax `Sized` bounds in all the methods and trait implementations for `Mut` and friends.
# Objective
This code is very disjoint, and the `stage.rs` file that it's in is already very long.
All I've done is move the code and clean up the compiler errors that result.
Followup to #5916, split out from #4299.
# Objective
Ambiguity sets are used to ignore system order ambiguities between groups of systems. However, they are not very useful: they are clunky, poorly integrated, and generally hampered by the difficulty using (or discovering) the ambiguity detector.
As a first step to the work in #4299, we're removing them.
## Migration Guide
Ambiguity sets have been removed.
# Objective
- Our existing change detection API is not flexible enough for advanced users: particularly those attempting to do rollback networking.
- This is an important use case, and with adequate warnings we can make mucking about with change ticks scary enough that users generally won't do it.
- Fixes#5633.
- Closes#2363.
## Changelog
- added `ChangeDetection::set_last_changed` to manually mutate the `last_change_ticks` field"
- the `ChangeDetection` trait now requires an `Inner` associated type, which contains the value being wrapped.
- added `ChangeDetection::bypass_change_detection`, which hands out a raw `&mut Inner`
## Migration Guide
Add the `Inner` associated type and new methods to any type that you've implemented `DetectChanges` for.
Make API users aware that the type aliases `QueryItem` and `QueryFetch` can be used instead of the more bloated alternative with `WorldQueryGats`.
Fixes#5842
# Objective
Clean up taffy nodes when the associated UI node gets removed. The current UI code will keep the taffy nodes around forever.
## Solution
Use `RemovedComponents<Node>` to iterate over nodes that are no longer valid UI nodes or that have been despawned, and remove them from taffy and the internal hash map.
## Implementation Notes
Do note that using `despawn()` instead of `despawn_recursive()` on a UI node that has children will result in a [warnings spam](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/main/crates/bevy_ui/src/flex/mod.rs#L120) since the children will not be part of a proper UI hierarchy anymore.
---
## Changelog
- Fixed memory leak when nodes are removed in bevy_ui
# Objective
- Increase consistency across documentation of `Query` methods.
- Fixes#5506
## Solution
- See #4989. This PR is derived from it. It just includes changes to the `Query` methods' docs.
# Objective
- Update `Query` docs with better terminology
- add some performance remarks (Fixes#4742)
## Solution
- See #4989. This PR is derived from it. It just includes changes to the `Query` struct docs.
# Objective
- Fixes#5850
## Solution
- As described in the issue, added a `get_entity` method on `Commands` that returns an `Option<EntityCommands>`
## Changelog
- Added the new method with a simple doc test
- I have re-used `get_entity` in `entity`, similarly to how `get_single` is used in `single` while additionally preserving the error message
- Add `#[inline]` to both functions
Entities that have commands queued to despawn system will still return commands when `get_entity` is called but that is representative of the fact that the entity is still around until those commands are flushed.
A potential `contains_entity` could also be added in this PR if desired, that would effectively be replacing Entities.contains but may be more discoverable if this is a common use case.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
I'm build a UI system for bevy. In this UI system there is a concept of a system per UI entity. I had an issue where change detection wasn't working how I would expect and it's because when a function system is ran the `last_change_tick` is updated with the latest tick(from world). In my particular case I want to "wait" to update the `last_change_tick` until after my system runs for each entity.
## Solution
Initially I thought bypassing the change detection all together would be a good fix, but on talking to some users in discord a simpler fix is to just expose `last_change_tick` to the end users. This is achieved by adding the following to the `System` trait:
```rust
/// Allows users to get the system's last change tick.
fn get_last_change_tick(&self) -> u32;
/// Allows users to set the system's last change tick.
fn set_last_change_tick(&mut self, last_change_tick: u32);
```
This causes a bit of weirdness with two implementors of `System`. `FixedTimestep` and `ChainSystem` both implement system and thus it's required that some sort of implementation be given for the new functions. I solved this by outputting a warning and not doing anything for these systems.
I think it's important to understand why I can't add the new functions only to the function system and not to the `System` trait. In my code I store the systems generically as `Box<dyn System<...>>`. I do this because I have differing parameters that are being passed in depending on the UI widget's system. As far as I can tell there isn't a way to take a system trait and cast it into a specific type without knowing what those parameters are.
In my own code this ends up looking something like:
```rust
// Runs per entity.
let old_tick = widget_system.get_last_change_tick();
should_update_children = widget_system.run((widget_tree.clone(), entity.0), world);
widget_system.set_last_change_tick(old_tick);
// later on after all the entities have been processed:
for system in context.systems.values_mut() {
system.set_last_change_tick(world.read_change_tick());
}
```
## Changelog
- Added `get_last_change_tick` and `set_last_change_tick` to `System`'s.
# Objective
- `for_each` methods inconsistently used an actual generic param or `impl Trait` change it to use `impl Trait` always, change them to be consistent
- some methods returned `'w 's` or `'_ '_`, change them to return `'_ 's`
## Solution
- Do what i just said
---
## Changelog
- `iter_unsafe` and `get_unchecked` no longer return borrows tied to `'w`
## Migration Guide
transmute the returned borrow from `iter_unsafe` and `get_unchecked` if this broke you (although preferably find a way to write your code that doesnt need to do this...)
# Objective
remove `insert_resource_with_id` because `insert_resource_by_id` exists and does almost exactly the same thing
blocked on #5587 because otherwise we will leak a resource when it's inserted
## Solution
remove the function and also add a safety invariant of to `insert_resource_by_id` that the id be valid for the world.
I didn't see any discussion in #4447 about this safety invariant being left off in favor of a panic so I'm curious if there was one or if it just seemed nicer to have less safety invariants for callers to uphold 😅
---
## Changelog
- safety invariant added to `insert_resource_by_id` requiring the id to be valid for world
## Migration Guide
- audit any calls to `insert_resource_by_id` making sure that the id is valid for the world
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
Fixes#5687
## Solution
Update the methods on the `Entity` struct to be `const`, so we can
define compile-time constants and more generally use them in a const
context.
---
## Changelog
### Added
- Most `Entity` methods are now `const fn`.
# Objective
- Reduce debugging burden when using events by telling user when they missed an event.
## Solution
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Document `QueryCombinationIter`
## Solution
- Describe the item, add usage and examples
- Copy notes about the number of query items generated from the corresponding query methods (they will be removed in #5742 ([motivation]))
## Additional notes
- Derived from #4989
[motivation]: https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/4989#issuecomment-1208421496
# Objective
Right now, users have to implement basic system adapters such as `Option` <-> `Result` conversions by themselves. This is slightly annoying and discourages the use of system chaining.
## Solution
Add the module `system_adapter` to the prelude, which contains a collection of common adapters. This is very ergonomic in practice.
## Examples
Convenient early returning.
```rust
use bevy::prelude::*;
App::new()
// If the system fails, just try again next frame.
.add_system(pet_dog.chain(system_adapter::ignore))
.run();
#[derive(Component)]
struct Dog;
fn pet_dog(dogs: Query<(&Name, Option<&Parent>), With<Dog>>) -> Option<()> {
let (dog, dad) = dogs.iter().next()?;
println!("You pet {dog}. He/she/they are a good boy/girl/pupper.");
let (dad, _) = dogs.get(dad?.get()).ok()?;
println!("Their dad's name is {dad}");
Some(())
}
```
Converting the output of a system
```rust
use bevy::prelude::*;
App::new()
.add_system(
find_name
.chain(system_adapter::new(String::from))
.chain(spawn_with_name),
)
.run();
fn find_name() -> &'static str { /* ... */ }
fn spawn_with_name(In(name): In<String>, mut commands: Commands) {
commands.spawn().insert(Name::new(name));
}
```
---
## Changelog
* Added the module `bevy_ecs::prelude::system_adapter`, which contains a collection of common system chaining adapters.
* `new` - Converts a regular fn to a system adapter.
* `unwrap` - Similar to `Result::unwrap`
* `ignore` - Discards the output of the previous system.
# Objective
- Fixes#4451
## Solution
- Conditionally compile entity ID cursor as `AtomicI32` when compiling on a platform that does not support 64-bit atomics.
- This effectively raises the MSRV to 1.60 as it uses a `#[cfg]` that was only just stabilized there. (should this be noted in changelog?)
---
## Changelog
- Added `bevy_ecs` support for platforms without 64-bit atomic ints
## Migration Guide
N/A
# Objective
- Fixes#5365
- The `assert!()` when the resource from `World::resource_scope` is inserted into the world is not descriptive.
## Solution
- Add more context to the assert inside of `World::resource_scope` when the `FnOnce` param inserts the resource.
# Objective
- Similar to `SystemChangeTick`, probably somewhat useful for debugging messages.
---
## Changelog
- Added `SystemName` which copies the `SystemMeta::name` field so it can be accessed within a system.
# Objective
Rust 1.63 resolved [an issue](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/83701) that prevents you from combining explicit generic arguments with `impl Trait` arguments.
Now, we no longer need to use dynamic dispatch to work around this.
## Migration Guide
The methods `Schedule::get_stage` and `get_stage_mut` now accept `impl StageLabel` instead of `&dyn StageLabel`.
### Before
```rust
let stage = schedule.get_stage_mut::<SystemStage>(&MyLabel)?;
```
### After
```rust
let stage = schedule.get_stage_mut::<SystemStage>(MyLabel)?;
```
# Objective
Make CI pass on bevy main.
Update to rust-1.63, updated clippy to 1.63 which introduced the following enhancements:
- [undocumented_unsafe_blocks](https://rust-lang.github.io/rust-clippy/master/index.html#undocumented_unsafe_blocks): Now also lints on unsafe trait implementations
This caught two incorrectly written ( but existing) safety comments for unsafe traits.
## Solution
Fix the comment to use `SAFETY:`
# Objective
While trying out the lint `unsafe_op_in_unsafe_fn` I noticed that `insert_resource_by_id` didn't drop the old value if it already existed, and reimplemented `Column::replace` manually for no apparent reason.
## Solution
- use `Column::replace` and add a test expecting the correct drop count
---
## Changelog
- `World::insert_resource_by_id` will now correctly drop the old resource value, if one already existed
# Objective
- `ReflectMut` served no purpose that wasn't met by `Mut<dyn Reflect>` which is easier to understand since you have to deal with fewer types
- there is another `ReflectMut` type that could be confused with this one
## Solution/Changelog
- relax `T: ?Sized` bound in `Mut<T>`
- replace all instances of `ReflectMut` with `Mut<dyn Reflect>`
# Objective
Provide a safe API to access an `EntityMut`'s `World`.
## Solution
* Add `EntityMut::into_world_mut` for safe access to the entity's world.
---
## Changelog
* Add `EntityMut::into_world_mut` for safe access to the entity's world.
*This PR description is an edited copy of #5007, written by @alice-i-cecile.*
# Objective
Follow-up to https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/2254. The `Resource` trait currently has a blanket implementation for all types that meet its bounds.
While ergonomic, this results in several drawbacks:
* it is possible to make confusing, silent mistakes such as inserting a function pointer (Foo) rather than a value (Foo::Bar) as a resource
* it is challenging to discover if a type is intended to be used as a resource
* we cannot later add customization options (see the [RFC](https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/blob/main/rfcs/27-derive-component.md) for the equivalent choice for Component).
* dependencies can use the same Rust type as a resource in invisibly conflicting ways
* raw Rust types used as resources cannot preserve privacy appropriately, as anyone able to access that type can read and write to internal values
* we cannot capture a definitive list of possible resources to display to users in an editor
## Notes to reviewers
* Review this commit-by-commit; there's effectively no back-tracking and there's a lot of churn in some of these commits.
*ira: My commits are not as well organized :')*
* I've relaxed the bound on Local to Send + Sync + 'static: I don't think these concerns apply there, so this can keep things simple. Storing e.g. a u32 in a Local is fine, because there's a variable name attached explaining what it does.
* I think this is a bad place for the Resource trait to live, but I've left it in place to make reviewing easier. IMO that's best tackled with https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/4981.
## Changelog
`Resource` is no longer automatically implemented for all matching types. Instead, use the new `#[derive(Resource)]` macro.
## Migration Guide
Add `#[derive(Resource)]` to all types you are using as a resource.
If you are using a third party type as a resource, wrap it in a tuple struct to bypass orphan rules. Consider deriving `Deref` and `DerefMut` to improve ergonomics.
`ClearColor` no longer implements `Component`. Using `ClearColor` as a component in 0.8 did nothing.
Use the `ClearColorConfig` in the `Camera3d` and `Camera2d` components instead.
Co-authored-by: Alice <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
Simplify the worldquery trait hierarchy as much as possible by putting it all in one trait. If/when gats are stabilised this can be trivially migrated over to use them, although that's not why I made this PR, those reasons are:
- Moves all of the conceptually related unsafe code for a worldquery next to eachother
- Removes now unnecessary traits simplifying the "type system magic" in bevy_ecs
---
## Changelog
All methods/functions/types/consts on `FetchState` and `Fetch` traits have been moved to the `WorldQuery` trait and the other traits removed. `WorldQueryGats` now only contains an `Item` and `Fetch` assoc type.
## Migration Guide
Implementors should move items in impls to the `WorldQuery/Gats` traits and remove any `Fetch`/`FetchState` impls
Any use sites of items in the `Fetch`/`FetchState` traits should be updated to use the `WorldQuery` trait items instead
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
Currently, actually using a `Local` on a system requires that it be `T: FromWorld`, but that requirement is only expressed on the `SystemParam` machinery, which leads to the confusing error message for when the user attempts to add an invalid system. By adding these bounds to `Local` directly, it improves clarity on usage and semantics.
## Solution
- Add `T: FromWorld` bound to `Local`'s definition
## Migration Guide
- It might be possible for references to `Local`s without `T: FromWorld` to exist, but these should be exceedingly rare and probably dead code. In the event that one of these is encountered, the easiest solutions are to delete the code or wrap the inner `T` in an `Option` to allow it to be default constructed to `None`.
# Objective
Replace `many_for_each_mut` with `iter_many_mut` using the same tricks to avoid aliased mutability that `iter_combinations_mut` uses.
<sub>I tried rebasing the draft PR I made for this before and it died. F</sub>
## Why
`many_for_each_mut` is worse for a few reasons:
1. The closure prevents the use of `continue`, `break`, and `return` behaves like a limited `continue`.
2. rustfmt will crumple it and double the indentation when the line gets too long.
```rust
query.many_for_each_mut(
&entity_list,
|(mut transform, velocity, mut component_c)| {
// Double trouble.
},
);
```
3. It is more surprising to have `many_for_each_mut` as a mutable counterpart to `iter_many` than `iter_many_mut`.
4. It required a separate unsafe fn; more unsafe code to maintain.
5. The `iter_many_mut` API matches the existing `iter_combinations_mut` API.
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
# Objective
`ReadOnlyWorldQuery` should have required `Self::ReadOnly = Self` so that calling `.iter()` on a readonly query is equivelent to calling `iter_mut()`.
## Solution
add `ReadOnly = Self` to the definition of `ReadOnlyWorldQuery`
---
## Changelog
ReadOnlyWorldQuery's `ReadOnly` assoc type is now always equal to `Self`
## Migration Guide
Make `Self::ReadOnly = Self` hold
# Objective
Enable treating components and resources equally, which can
simplify the implementation of some systems where only the change
detection feature is relevant and not the kind of object (resource or
component).
## Solution
Implement `From<ResMut<T>>` and `From<NonSendMut<T>>` for
`Mut`. Since the 3 structs are similar, and only differ by their system
param role, the conversion is trivial.
---
## Changelog
Added - `From<ResMut>` and `From<NonSendMut>` for `Mut<T>`.
# Objective
I noticed while working on #5366 that the documentation for label types wasn't working correctly. Having experimented with this for a few weeks, I believe that generating docs in macros is more effort than it's worth.
## Solution
Add more boilerplate, copy-paste and edit the docs across types. This also lets us add custom doctests for specific types. Also, we don't need `concat_idents` as a dependency anymore.
# Objective
- Allows conversion of mutable queries to immutable queries.
- Fixes#4606
## Solution
- Add `to_readonly` method on `Query`, which uses `QueryState::as_readonly`
- `AsRef` is not feasible because creation of new queries is needed.
---
## Changelog
### Added
- Allows conversion of mutable queries to immutable queries using `Query::to_readonly`.
after #5355, three methods were added on world:
* `send_event`
* `send_event_batch`
* `send_default_event`
rename `send_default_event` to `send_event_default` for better discoverability
# Objective
- With access to `World`, it's not obvious how to send an event.
- This is especially useful if you are writing a `Command` that needs to send an `Event`.
- `Events` are a first-class construct in bevy, even though they are just `Resources` under the hood. Their methods should be discoverable.
## Solution
- Provide a simple helpers to send events through `Res<Events<T>>`.
---
## Changelog
> `send_event`, `send_default_event`, and `send_event_batch` methods added to `World`.
# Objective
remove `QF` generics from a bunch of types and methods on query related items. this has a few benefits:
- simplifies type signatures `fn iter(&self) -> QueryIter<'_, 's, Q::ReadOnly, F::ReadOnly>` is (imo) conceptually simpler than `fn iter(&self) -> QueryIter<'_, 's, Q, ROQueryFetch<'_, Q>, F>`
- `Fetch` is mostly an implementation detail but previously we had to expose it on every `iter` `get` etc method
- Allows us to potentially in the future simplify the `WorldQuery` trait hierarchy by removing the `Fetch` trait
## Solution
remove the `QF` generic and add a way to (unsafely) turn `&QueryState<Q1, F1>` into `&QueryState<Q2, F2>`
---
## Changelog/Migration Guide
The `QF` generic was removed from various `Query` iterator types and some methods, you should update your code to use the type of the corresponding worldquery of the fetch type that was being used, or call `as_readonly`/`as_nop` to convert a querystate to the appropriate type. For example:
`.get_single_unchecked_manual::<ROQueryFetch<Q>>(..)` -> `.as_readonly().get_single_unchecked_manual(..)`
`my_field: QueryIter<'w, 's, Q, ROQueryFetch<'w, Q>, F>` -> `my_field: QueryIter<'w, 's, Q::ReadOnly, F::ReadOnly>`
# Objective
- Closes#4954
- Reduce the complexity of the `{System, App, *}Label` APIs.
## Solution
For the sake of brevity I will only refer to `SystemLabel`, but everything applies to all of the other label types as well.
- Add `SystemLabelId`, a lightweight, `copy` struct.
- Convert custom types into `SystemLabelId` using the trait `SystemLabel`.
## Changelog
- String literals implement `SystemLabel` for now, but this should be changed with #4409 .
## Migration Guide
- Any previous use of `Box<dyn SystemLabel>` should be replaced with `SystemLabelId`.
- `AsSystemLabel` trait has been modified.
- No more output generics.
- Method `as_system_label` now returns `SystemLabelId`, removing an unnecessary level of indirection.
- If you *need* a label that is determined at runtime, you can use `Box::leak`. Not recommended.
## Questions for later
* Should we generate a `Debug` impl along with `#[derive(*Label)]`?
* Should we rename `as_str()`?
* Should we remove the extra derives (such as `Hash`) from builtin `*Label` types?
* Should we automatically derive types like `Clone, Copy, PartialEq, Eq`?
* More-ergonomic comparisons between `Label` and `LabelId`.
* Move `Dyn{Eq, Hash,Clone}` somewhere else.
* Some API to make interning dynamic labels easier.
* Optimize string representation
* Empty string for unit structs -- no debug info but faster comparisons
* Don't show enum types -- same tradeoffs as asbove.
Add compile time check for if a system is an exclusive system. Resolves#4788
Co-authored-by: Daniel Liu <mr.picklepinosaur@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Daniel Liu <danieliu3120@gmail.com>
Following https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/5124 I decided to add the `ExactSizeIterator` impl for `QueryCombinationIter`.
Also:
- Clean up the tests for `size_hint` and `len` for both the normal `QueryIter` and `QueryCombinationIter`.
- Add tests to `QueryCombinationIter` when it shouldn't be `ExactSizeIterator`
---
## Changelog
- Added `ExactSizeIterator` implementation for `QueryCombinatonIter`
# Objective
- `.iter_combinations_*()` cannot be used on custom derived `WorldQuery`, so this fixes that
- Fixes#5284
## Solution
- `#[derive(Clone)]` on the `Fetch` of the proc macro derive.
- `#[derive(Clone)]` for `AnyOf` to satisfy tests.
# Objective
Improve documentation, information users of the limitations in bevy's idiomatic patterns, and suggesting alternatives for when those limitations are encountered.
## Solution
* Add documentation to `Commands` informing the user of the option of writing one-shot commands with closures.
* Add documentation to `EventWriter` regarding the limitations of event types, and suggesting alternatives using commands.
# Objective
- Added a bunch of backticks to things that should have them, like equations, abstract variable names,
- Changed all small x, y, and z to capitals X, Y, Z.
This might be more annoying than helpful; Feel free to refuse this PR.
Remove unnecessary calls to `iter()`/`iter_mut()`.
Mainly updates the use of queries in our code, docs, and examples.
```rust
// From
for _ in list.iter() {
for _ in list.iter_mut() {
// To
for _ in &list {
for _ in &mut list {
```
We already enable the pedantic lint [clippy::explicit_iter_loop](https://rust-lang.github.io/rust-clippy/stable/) inside of Bevy. However, this only warns for a few known types from the standard library.
## Note for reviewers
As you can see the additions and deletions are exactly equal.
Maybe give it a quick skim to check I didn't sneak in a crypto miner, but you don't have to torture yourself by reading every line.
I already experienced enough pain making this PR :)
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
# Objective
`ReflectResource` and `ReflectComponent` will panic on `apply` method if there is no such component. It's not very ergonomic. And not very good for performance since I need to check if such component exists first.
## Solution
* Add `ReflectComponent::apply_or_insert` and `ReflectResource::apply_or_insert` functions.
* Rename `ReflectComponent::add` into `ReflectComponent::insert` for consistency.
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `ReflectResource::apply_or_insert` and `ReflectComponent::apply_on_insert`.
### Changed
* Rename `ReflectComponent::add` into `ReflectComponent::insert` for consistency.
* Use `ReflectComponent::apply_on_insert` in `DynamicScene` instead of manual checking.
## Migration Guide
* Rename `ReflectComponent::add` into `ReflectComponent::insert`.
# Objective
- Currently, the `Extract` `RenderStage` is executed on the main world, with the render world available as a resource.
- However, when needing access to resources in the render world (e.g. to mutate them), the only way to do so was to get exclusive access to the whole `RenderWorld` resource.
- This meant that effectively only one extract which wrote to resources could run at a time.
- We didn't previously make `Extract`ing writing to the world a non-happy path, even though we want to discourage that.
## Solution
- Move the extract stage to run on the render world.
- Add the main world as a `MainWorld` resource.
- Add an `Extract` `SystemParam` as a convenience to access a (read only) `SystemParam` in the main world during `Extract`.
## Future work
It should be possible to avoid needing to use `get_or_spawn` for the render commands, since now the `Commands`' `Entities` matches up with the world being executed on.
We need to determine how this interacts with https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/3519
It's theoretically possible to remove the need for the `value` method on `Extract`. However, that requires slightly changing the `SystemParam` interface, which would make it more complicated. That would probably mess up the `SystemState` api too.
## Todo
I still need to add doc comments to `Extract`.
---
## Changelog
### Changed
- The `Extract` `RenderStage` now runs on the render world (instead of the main world as before).
You must use the `Extract` `SystemParam` to access the main world during the extract phase.
Resources on the render world can now be accessed using `ResMut` during extract.
### Removed
- `Commands::spawn_and_forget`. Use `Commands::get_or_spawn(e).insert_bundle(bundle)` instead
## Migration Guide
The `Extract` `RenderStage` now runs on the render world (instead of the main world as before).
You must use the `Extract` `SystemParam` to access the main world during the extract phase. `Extract` takes a single type parameter, which is any system parameter (such as `Res`, `Query` etc.). It will extract this from the main world, and returns the result of this extraction when `value` is called on it.
For example, if previously your extract system looked like:
```rust
fn extract_clouds(mut commands: Commands, clouds: Query<Entity, With<Cloud>>) {
for cloud in clouds.iter() {
commands.get_or_spawn(cloud).insert(Cloud);
}
}
```
the new version would be:
```rust
fn extract_clouds(mut commands: Commands, mut clouds: Extract<Query<Entity, With<Cloud>>>) {
for cloud in clouds.value().iter() {
commands.get_or_spawn(cloud).insert(Cloud);
}
}
```
The diff is:
```diff
--- a/src/clouds.rs
+++ b/src/clouds.rs
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
-fn extract_clouds(mut commands: Commands, clouds: Query<Entity, With<Cloud>>) {
- for cloud in clouds.iter() {
+fn extract_clouds(mut commands: Commands, mut clouds: Extract<Query<Entity, With<Cloud>>>) {
+ for cloud in clouds.value().iter() {
commands.get_or_spawn(cloud).insert(Cloud);
}
}
```
You can now also access resources from the render world using the normal system parameters during `Extract`:
```rust
fn extract_assets(mut render_assets: ResMut<MyAssets>, source_assets: Extract<Res<MyAssets>>) {
*render_assets = source_assets.clone();
}
```
Please note that all existing extract systems need to be updated to match this new style; even if they currently compile they will not run as expected. A warning will be emitted on a best-effort basis if this is not met.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
`EntityMap` lacks documentation, don't have `len()` / `is_empty` and `insert` doesn't work as in the regular HashMap`.
## Solution
* Add `len()` method.
* Return previously mapped entity from `insert()` as in the regular `HashMap`.
* Add documentation.
---
## Changelog
* Add `EntityMap::len()`.
* Return previously mapped entity from `EntityMap::insert()` as in the regular `HashMap`.
* Add documentation for `EntityMap` methods.
# Objective
Remove suffixes from reflect component and resource methods to closer match bevy norms.
## Solution
removed suffixes and also fixed a spelling error
---
# Objective
- Help users fix issue when their app panic when executing a command on a despawned entity
## Solution
- Add an error code and a page describing how to debug the issue
# Objective
`SAFETY` comments are meant to be placed before `unsafe` blocks and should contain the reasoning of why in this case the usage of unsafe is okay. This is useful when reading the code because it makes it clear which assumptions are required for safety, and makes it easier to spot possible unsoundness holes. It also forces the code writer to think of something to write and maybe look at the safety contracts of any called unsafe methods again to double-check their correct usage.
There's a clippy lint called `undocumented_unsafe_blocks` which warns when using a block without such a comment.
## Solution
- since clippy expects `SAFETY` instead of `SAFE`, rename those
- add `SAFETY` comments in more places
- for the last remaining 3 places, add an `#[allow()]` and `// TODO` since I wasn't comfortable enough with the code to justify their safety
- add ` #![warn(clippy::undocumented_unsafe_blocks)]` to `bevy_ecs`
### Note for reviewers
The first commit only renames `SAFETY` to `SAFE` so it doesn't need a thorough review.
cb042a416e..55cef2d6fa is the diff for all other changes.
### Safety comments where I'm not too familiar with the code
774012ece5/crates/bevy_ecs/src/entity/mod.rs (L540-L546)774012ece5/crates/bevy_ecs/src/world/entity_ref.rs (L249-L252)
### Locations left undocumented with a `TODO` comment
5dde944a30/crates/bevy_ecs/src/schedule/executor_parallel.rs (L196-L199)5dde944a30/crates/bevy_ecs/src/world/entity_ref.rs (L287-L289)5dde944a30/crates/bevy_ecs/src/world/entity_ref.rs (L413-L415)
Co-authored-by: Jakob Hellermann <hellermann@sipgate.de>
# Objective
We don't have reflection for resources.
## Solution
Introduce reflection for resources.
Continues #3580 (by @Davier), related to #3576.
---
## Changelog
### Added
* Reflection on a resource type (by adding `ReflectResource`):
```rust
#[derive(Reflect)]
#[reflect(Resource)]
struct MyResourse;
```
### Changed
* Rename `ReflectComponent::add_component` into `ReflectComponent::insert_component` for consistency.
## Migration Guide
* Rename `ReflectComponent::add_component` into `ReflectComponent::insert_component`.
# Objective
This is a common and useful type. I frequently use this when working with `Events` resource directly, typically when caching the data or manipulating the `World` directly.
This is also useful when manually configuring the cleanup strategy for events.
The first leak:
```rust
#[test]
fn blob_vec_drop_empty_capacity() {
let item_layout = Layout:🆕:<Foo>();
let drop = drop_ptr::<Foo>;
let _ = unsafe { BlobVec::new(item_layout, Some(drop), 0) };
}
```
this is because we allocate the swap scratch in blobvec regardless of what the capacity is, but we only deallocate if capacity is > 0
The second leak:
```rust
#[test]
fn panic_while_overwriting_component() {
let helper = DropTestHelper::new();
let res = panic::catch_unwind(|| {
let mut world = World::new();
world
.spawn()
.insert(helper.make_component(true, 0))
.insert(helper.make_component(false, 1));
println!("Done inserting! Dropping world...");
});
let drop_log = helper.finish(res);
assert_eq!(
&*drop_log,
[
DropLogItem::Create(0),
DropLogItem::Create(1),
DropLogItem::Drop(0),
]
);
}
```
this is caused by us not running the drop impl on the to-be-inserted component if the drop impl of the overwritten component panics
---
managed to figure out where the leaks were by using this 10/10 command
```
cargo --quiet test --lib -- --list | sed 's/: test$//' | MIRIFLAGS="-Zmiri-disable-isolation" xargs -n1 cargo miri test --lib -- --exact
```
which runs every test one by one rather than all at once which let miri actually tell me which test had the leak 🙃
# Objective
- Nightly clippy lints should be fixed before they get stable and break CI
## Solution
- fix new clippy lints
- ignore `significant_drop_in_scrutinee` since it isn't relevant in our loop https://github.com/rust-lang/rust-clippy/issues/8987
```rust
for line in io::stdin().lines() {
...
}
```
Co-authored-by: Jakob Hellermann <hellermann@sipgate.de>
# Objective
Fixes#5153
## Solution
Search for all enums and manually check if they have default impls that can use this new derive.
By my reckoning:
| enum | num |
|-|-|
| total | 159 |
| has default impl | 29 |
| default is unit variant | 23 |
# Objective
CI is now failing with some changes that landed in 1.62.
## Solution
* Fix an unused lifetime by using it (we double-used the `w` lifetime).
* Update compile_fail error messages
* temporarily disable check-unused-dependencies
# Objective
- Provide a way to see the components of an entity.
- Fixes#1467
## Solution
- Add `World::inspect_entity`. It accepts an `Entity` and returns a vector of `&ComponentInfo` that the entity has.
- Add `EntityCommands::log_components`. It logs the component names of the entity. (info level)
---
## Changelog
### Added
- Ability to inspect components of an entity through `World::inspect_entity` or `EntityCommands::log_components`
There are some outdated error messages for when a resource is not found. It references `add_resource` and `add_non_send_resource` which were renamed to `insert_resource` and `insert_non_send_resource`.
# Objective
- Fixes#3142
## Solution
- Done according to #3142
- Created new marker trait `ArchetypeFilter`
- Implement said trait to:
- `With<T>`
- `Without<T>`
- tuples containing only types that implement `ArchetypeFilter`, from 0 to 15 elements
- `Or<T>` where T is a tuple as described previously
- Changed `ExactSizeIterator` impl to include a new generic that must implement `WorldQuery` and `ArchetypeFilter`
- Added new tests
---
## Changelog
### Added
- `Query`s with archetypal filters can now use `.iter().len()` to get the exact size of the iterator.
# Objective
Speed up entity moves between tables by reducing the number of copies conducted. Currently three separate copies are conducted: `src[index] -> swap scratch`, `src[last] -> src[index]`, and `swap scratch -> dst[target]`. The first and last copies can be merged by directly using the copy `src[index] -> dst[target]`, which can save quite some time if the component(s) in question are large.
## Solution
This PR does the following:
- Adds `BlobVec::swap_remove_unchecked(usize, PtrMut<'_>)`, which is identical to `swap_remove_and_forget_unchecked`, but skips the `swap_scratch` and directly copies the component into the provided `PtrMut<'_>`.
- Build `Column::initialize_from_unchecked(&mut Column, usize, usize)` on top of it, which uses the above to directly initialize a row from another column.
- Update most of the table move APIs to use `initialize_from_unchecked` instead of a combination of `swap_remove_and_forget_unchecked` and `initialize`.
This is an alternative, though orthogonal, approach to achieve the same performance gains as seen in #4853. This (hopefully) shouldn't run into the same Miri limitations that said PR currently does. After this PR, `swap_remove_and_forget_unchecked` is still in use for Resources and swap_scratch likely still should be removed, so #4853 still has use, even if this PR is merged.
## Performance
TODO: Microbenchmark
This PR shows similar improvements to commands that add or remove table components that result in a table move. When tested on `many_cubes sphere`, some of the more command heavy systems saw notable improvements. In particular, `prepare_uniform_components<T>`, this saw a reduction in time from 1.35ms to 1.13ms (a 16.3% improvement) on my local machine, a similar if not slightly better gain than what #4853 showed [here](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/4853#issuecomment-1159346106).
The command heavy `Extract` stage also saw a smaller overall improvement:
---
## Changelog
Added: `BlobVec::swap_remove_unchecked`.
Added: `Column::initialize_from_unchecked`.
# Objective
- Simplify the process of obtaining a `ComponentId` instance corresponding to a `Component`.
- Resolves#5060.
## Solution
- Add a `component_id::<T: Component>(&self)` function to both `World` and `Components` to retrieve the `ComponentId` associated with `T` from a immutable reference.
---
## Changelog
- Added `World::component_id::<C>()` and `Components::component_id::<C>()` to retrieve a `Component`'s corresponding `ComponentId` if it exists.
# Objective
Closes#1557. Partially addresses #3362.
Cleanup the public facing API for storage types. Most of these APIs are difficult to use safely when directly interfacing with these types, and is also currently impossible to interact with in normal ECS use as there is no `World::storages_mut`. The majority of these types should be easy enough to read, and perhaps mutate the contents, but never structurally altered without the same checks in the rest of bevy_ecs code. This both cleans up the public facing types and helps use unused code detection to remove a few of the APIs we're not using internally.
## Solution
- Mark all APIs that take `&mut T` under `bevy_ecs::storage` as `pub(crate)` or `pub(super)`
- Cleanup after it all.
Entire type visibility changes:
- `BlobVec` is `pub(super)`, only storage code should be directly interacting with it.
- `SparseArray` is now `pub(crate)` for the entire type. It's an implementation detail for `Table` and `(Component)SparseSet`.
- `TableMoveResult` is now `pub(crate)
---
## Changelog
TODO
## Migration Guide
Dear God, I hope not.
# Objective
The descriptions included in the API docs of `entity` module, `Entity` struct, and `Component` trait have some issues:
1. the concept of entity is not clearly defined,
2. descriptions are a little bit out of place,
3. in a case the description leak too many details about the implementation,
4. some descriptions are not exhaustive,
5. there are not enough examples,
6. the content can be formatted in a much better way.
## Solution
1. ~~Stress the fact that entity is an abstract and elementary concept. Abstract because the concept of entity is not hardcoded into the library but emerges from the interaction of `Entity` with every other part of `bevy_ecs`, like components and world methods. Elementary because it is a fundamental concept that cannot be defined with other terms (like point in euclidean geometry, or time in classical physics).~~ We decided to omit the definition of entity in the API docs ([see why]). It is only described in its relationship with components.
2. Information has been moved to relevant places and links are used instead in the other places.
3. Implementation details about `Entity` have been reduced.
4. Descriptions have been made more exhaustive by stating how to obtain and use items. Entity operations are enriched with `World` methods.
5. Examples have been added or enriched.
6. Sections have been added to organize content. Entity operations are now laid out in a table.
### Todo list
- [x] Break lines at sentence-level.
## For reviewers
- ~~I added a TODO over `Component` docs, make sure to check it out and discuss it if necessary.~~ ([Resolved])
- You can easily check the rendered documentation by doing `cargo doc -p bevy_ecs --no-deps --open`.
[see why]: https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/4767#discussion_r875106329
[Resolved]: https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/4767#discussion_r874127825
builds on top of #4780
# Objective
`Reflect` and `Serialize` are currently very tied together because `Reflect` has a `fn serialize(&self) -> Option<Serializable<'_>>` method. Because of that, we can either implement `Reflect` for types like `Option<T>` with `T: Serialize` and have `fn serialize` be implemented, or without the bound but having `fn serialize` return `None`.
By separating `ReflectSerialize` into a separate type (like how it already is for `ReflectDeserialize`, `ReflectDefault`), we could separately `.register::<Option<T>>()` and `.register_data::<Option<T>, ReflectSerialize>()` only if the type `T: Serialize`.
This PR does not change the registration but allows it to be changed in a future PR.
## Solution
- add the type
```rust
struct ReflectSerialize { .. }
impl<T: Reflect + Serialize> FromType<T> for ReflectSerialize { .. }
```
- remove `#[reflect(Serialize)]` special casing.
- when serializing reflect value types, look for `ReflectSerialize` in the `TypeRegistry` instead of calling `value.serialize()`
# Objective
- Fix a type inference regression introduced by #3001
- Make read only bounds on world queries more user friendly
ptrification required you to write `Q::Fetch: ReadOnlyFetch` as `for<'w> QueryFetch<'w, Q>: ReadOnlyFetch` which has the same type inference problem as `for<'w> QueryFetch<'w, Q>: FilterFetch<'w>` had, i.e. the following code would error:
```rust
#[derive(Component)]
struct Foo;
fn bar(a: Query<(&Foo, Without<Foo>)>) {
foo(a);
}
fn foo<Q: WorldQuery>(a: Query<Q, ()>)
where
for<'w> QueryFetch<'w, Q>: ReadOnlyFetch,
{
}
```
`for<..>` bounds are also rather user unfriendly..
## Solution
Remove the `ReadOnlyFetch` trait in favour of a `ReadOnlyWorldQuery` trait, and remove `WorldQueryGats::ReadOnlyFetch` in favor of `WorldQuery::ReadOnly` allowing the previous code snippet to be written as:
```rust
#[derive(Component)]
struct Foo;
fn bar(a: Query<(&Foo, Without<Foo>)>) {
foo(a);
}
fn foo<Q: ReadOnlyWorldQuery>(a: Query<Q, ()>) {}
```
This avoids the `for<...>` bound which makes the code simpler and also fixes the type inference issue.
The reason for moving the two functions out of `FetchState` and into `WorldQuery` is to allow the world query `&mut T` to share a `State` with the `&T` world query so that it can have `type ReadOnly = &T`. Presumably it would be possible to instead have a `ReadOnlyRefMut<T>` world query and then do `type ReadOnly = ReadOnlyRefMut<T>` much like how (before this PR) we had a `ReadOnlyWriteFetch<T>`. A side benefit of the current solution in this PR is that it will likely make it easier in the future to support an API such as `Query<&mut T> -> Query<&T>`. The primary benefit IMO is just that `ReadOnlyRefMut<T>` and its associated fetch would have to reimplement all of the logic that the `&T` world query impl does but this solution avoids that :)
---
## Changelog/Migration Guide
The trait `ReadOnlyFetch` has been replaced with `ReadOnlyWorldQuery` along with the `WorldQueryGats::ReadOnlyFetch` assoc type which has been replaced with `<WorldQuery::ReadOnly as WorldQueryGats>::Fetch`
- Any where clauses such as `QueryFetch<Q>: ReadOnlyFetch` should be replaced with `Q: ReadOnlyWorldQuery`.
- Any custom world query impls should implement `ReadOnlyWorldQuery` insead of `ReadOnlyFetch`
Functions `update_component_access` and `update_archetype_component_access` have been moved from the `FetchState` trait to `WorldQuery`
- Any callers should now call `Q::update_component_access(state` instead of `state.update_component_access` (and `update_archetype_component_access` respectively)
- Any custom world query impls should move the functions from the `FetchState` impl to `WorldQuery` impl
`WorldQuery` has been made an `unsafe trait`, `FetchState` has been made a safe `trait`. (I think this is how it should have always been, but regardless this is _definitely_ necessary now that the two functions have been moved to `WorldQuery`)
- If you have a custom `FetchState` impl make it a normal `impl` instead of `unsafe impl`
- If you have a custom `WorldQuery` impl make it an `unsafe impl`, if your code was sound before it is going to still be sound
# Objective
- Fixes#4271
## Solution
- Check for a pending transition in addition to a scheduled operation.
- I don't see a valid reason for updating the state unless both `scheduled` and `transition` are empty.
# Objective
Following #4855, `Column` is just a parallel `BlobVec`/`Vec<UnsafeCell<ComponentTicks>>` pair, which is identical to the dense and ticks vecs in `ComponentSparseSet`, which has some code duplication with `Column`.
## Solution
Replace dense and ticks in `ComponentSparseSet` with a `Column`.
# Objective
Most of our `Iterator` impls satisfy the requirements of `std::iter::FusedIterator`, which has internal specialization that optimizes `Interator::fuse`. The std lib iterator combinators do have a few that rely on `fuse`, so this could optimize those use cases. I don't think we're using any of them in the engine itself, but beyond a light increase in compile time, it doesn't hurt to implement the trait.
## Solution
Implement the trait for all eligible iterators in first party crates. Also add a missing `ExactSizeIterator` on an iterator that could use it.
Right now, a direct reference to the target TaskPool is required to launch tasks on the pools, despite the three newtyped pools (AsyncComputeTaskPool, ComputeTaskPool, and IoTaskPool) effectively acting as global instances. The need to pass a TaskPool reference adds notable friction to spawning subtasks within existing tasks. Possible use cases for this may include chaining tasks within the same pool like spawning separate send/receive I/O tasks after waiting on a network connection to be established, or allowing cross-pool dependent tasks like starting dependent multi-frame computations following a long I/O load.
Other task execution runtimes provide static access to spawning tasks (i.e. `tokio::spawn`), which is notably easier to use than the reference passing required by `bevy_tasks` right now.
This PR makes does the following:
* Adds `*TaskPool::init` which initializes a `OnceCell`'ed with a provided TaskPool. Failing if the pool has already been initialized.
* Adds `*TaskPool::get` which fetches the initialized global pool of the respective type or panics. This generally should not be an issue in normal Bevy use, as the pools are initialized before they are accessed.
* Updated default task pool initialization to either pull the global handles and save them as resources, or if they are already initialized, pull the a cloned global handle as the resource.
This should make it notably easier to build more complex task hierarchies for dependent tasks. It should also make writing bevy-adjacent, but not strictly bevy-only plugin crates easier, as the global pools ensure it's all running on the same threads.
One alternative considered is keeping a thread-local reference to the pool for all threads in each pool to enable the same `tokio::spawn` interface. This would spawn tasks on the same pool that a task is currently running in. However this potentially leads to potential footgun situations where long running blocking tasks run on `ComputeTaskPool`.
# Objective
Improve querying ergonomics around collections and iterators of entities.
Example how queries over Children might be done currently.
```rust
fn system(foo_query: Query<(&Foo, &Children)>, bar_query: Query<(&Bar, &Children)>) {
for (foo, children) in &foo_query {
for child in children.iter() {
if let Ok((bar, children)) = bar_query.get(*child) {
for child in children.iter() {
if let Ok((foo, children)) = foo_query.get(*child) {
// D:
}
}
}
}
}
}
```
Answers #4868
Partially addresses #4864Fixes#1470
## Solution
Based on the great work by @deontologician in #2563
Added `iter_many` and `many_for_each_mut` to `Query`.
These take a list of entities (Anything that implements `IntoIterator<Item: Borrow<Entity>>`).
`iter_many` returns a `QueryManyIter` iterator over immutable results of a query (mutable data will be cast to an immutable form).
`many_for_each_mut` calls a closure for every result of the query, ensuring not aliased mutability.
This iterator goes over the list of entities in order and returns the result from the query for it. Skipping over any entities that don't match the query.
Also added `unsafe fn iter_many_unsafe`.
### Examples
```rust
#[derive(Component)]
struct Counter {
value: i32
}
#[derive(Component)]
struct Friends {
list: Vec<Entity>,
}
fn system(
friends_query: Query<&Friends>,
mut counter_query: Query<&mut Counter>,
) {
for friends in &friends_query {
for counter in counter_query.iter_many(&friends.list) {
println!("Friend's counter: {:?}", counter.value);
}
counter_query.many_for_each_mut(&friends.list, |mut counter| {
counter.value += 1;
println!("Friend's counter: {:?}", counter.value);
});
}
}
```
Here's how example in the Objective section can be written with this PR.
```rust
fn system(foo_query: Query<(&Foo, &Children)>, bar_query: Query<(&Bar, &Children)>) {
for (foo, children) in &foo_query {
for (bar, children) in bar_query.iter_many(children) {
for (foo, children) in foo_query.iter_many(children) {
// :D
}
}
}
}
```
## Additional changes
Implemented `IntoIterator` for `&Children` because why not.
## Todo
- Bikeshed!
Co-authored-by: deontologician <deontologician@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
(follow-up to #4423)
# Objective
Currently, it isn't possible to easily fire commands from within par_for_each blocks. This PR allows for issuing commands from within parallel scopes.
# Objective
This PR aims to improve the soundness of `CommandQueue`. In particular it aims to:
- make it sound to store commands that contain padding or uninitialized bytes;
- avoid uses of commands after moving them in the queue's buffer (`std::mem::forget` is technically a use of its argument);
- remove useless checks: `self.bytes.as_mut_ptr().is_null()` is always `false` because even `Vec`s that haven't allocated use a dangling pointer. Moreover the same pointer was used to write the command, so it ought to be valid for reads if it was for writes.
## Solution
- To soundly store padding or uninitialized bytes `CommandQueue` was changed to contain a `Vec<MaybeUninit<u8>>` instead of `Vec<u8>`;
- To avoid uses of the command through `std::mem::forget`, `ManuallyDrop` was used.
## Other observations
While writing this PR I noticed that `CommandQueue` doesn't seem to drop the commands that weren't applied. While this is a pretty niche case (you would have to be manually using `CommandQueue`/`std::mem::swap`ping one), I wonder if it should be documented anyway.
# Objective
Don't allocate memory for Component types known at compile-time. Save a bit of memory.
## Solution
Change `ComponentDescriptor::name` from `String` to `Cow<'static, str>` to use the `&'static str` returned by `std::any::type_name`.
# Objective
`debug_assert!` macros must still compile properly in release mode due to how they're implemented. This is causing release builds to fail.
## Solution
Change them to `assert!` macros inside `#[cfg(debug_assertions)]` blocks.
# Objective
- Higher order system could not be created by users.
- However, a simple change to `SystemParamFunction` allows this.
- Higher order systems in this case mean functions which return systems created using other systems, such as `chain` (which is basically equivalent to map)
## Solution
- Change `SystemParamFunction` to be a safe abstraction over `FnMut([In<In>,] ...params)->Out`.
- Note that I believe `SystemParamFunction` should not have been counted as part of our public api before this PR.
- This is because its only use was an unsafe function without an actionable safety comment.
- The safety comment was basically 'call this within bevy code'.
- I also believe that there are no external users in its current form.
- A quick search on Google and in the discord confirmed this.
## See also
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/4666, which uses this and subsumes the example here
---
## Changelog
### Added
- `SystemParamFunction`, which can be used to create higher order systems.
# Objective
Use less memory to store SparseSet components.
## Solution
Change `ComponentSparseSet` to only use `Entity::id` in it's key internally, and change the usize value in it's SparseArray to use u32 instead, as it cannot have more than u32::MAX live entities stored at once.
This should reduce the overhead of storing components in sparse set storage by 50%.
# Objective
Fixes#3183. Requiring a `&TaskPool` parameter is sort of meaningless if the only correct one is to use the one provided by `Res<ComputeTaskPool>` all the time.
## Solution
Have `QueryState` save a clone of the `ComputeTaskPool` which is used for all `par_for_each` functions.
~~Adds a small overhead of the internal `Arc` clone as a part of the startup, but the ergonomics win should be well worth this hardly-noticable overhead.~~
Updated the docs to note that it will panic the task pool is not present as a resource.
# Future Work
If https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/pull/54 is approved, we can replace these resource lookups with a static function call instead to get the `ComputeTaskPool`.
---
## Changelog
Removed: The `task_pool` parameter of `Query(State)::par_for_each(_mut)`. These calls will use the `World`'s `ComputeTaskPool` resource instead.
## Migration Guide
The `task_pool` parameter for `Query(State)::par_for_each(_mut)` has been removed. Remove these parameters from all calls to these functions.
Before:
```rust
fn parallel_system(
task_pool: Res<ComputeTaskPool>,
query: Query<&MyComponent>,
) {
query.par_for_each(&task_pool, 32, |comp| {
...
});
}
```
After:
```rust
fn parallel_system(query: Query<&MyComponent>) {
query.par_for_each(32, |comp| {
...
});
}
```
If using `Query(State)` outside of a system run by the scheduler, you may need to manually configure and initialize a `ComputeTaskPool` as a resource in the `World`.
# Objective
The `ComponentId` in `Column` is redundant as it's stored in parallel in the surrounding `SparseSet` all the time.
## Solution
Remove it. Add `SparseSet::iter(_mut)` to parallel `HashMap::iter(_mut)` to allow iterating pairs of columns and their IDs.
---
## Changelog
Added: `SparseSet::iter` and `SparseSet::iter_mut`.
# Objective
- Rebase of #3159.
- Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/3156
- add #[inline] to single related functions so that they matches with other function defs
## Solution
* added functions to QueryState
* get_single_unchecked_manual
* get_single_unchecked
* get_single
* get_single_mut
* single
* single_mut
* make Query::get_single use QueryState::get_single_unchecked_manual
* added #[inline]
---
## Changelog
### Added
Functions `QueryState::single`, `QueryState::get_single`, `QueryState::single_mut`, `QueryState::get_single_mut`, `QueryState::get_single_unchecked`, `QueryState::get_single_unchecked_manual`.
### Changed
`QuerySingleError` is now in the `state` module.
## Migration Guide
Change `query::QuerySingleError` to `state::QuerySingleError`
Co-authored-by: 2ne1ugly <chattermin@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: 2ne1ugly <47616772+2ne1ugly@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
the code in these fns are always identical so stop having two functions
## Solution
make them the same function
---
## Changelog
change `matches_archetype` and `matches_table` to `fn matches_component_set(&self, &SparseArray<ComponentId, usize>) -> bool` then do extremely boring updating of all `FetchState` impls
## Migration Guide
- move logic of `matches_archetype` and `matches_table` into `matches_component_set` in any manual `FetchState` impls
# Objective
Even if bevy itself does not provide any builtin scripting or modding APIs, it should have the foundations for building them yourself.
For that it should be enough to have APIs that are not tied to the actual rust types with generics, but rather accept `ComponentId`s and `bevy_ptr` ptrs.
## Solution
Add the following APIs to bevy
```rust
fn EntityRef::get_by_id(ComponentId) -> Option<Ptr<'w>>;
fn EntityMut::get_by_id(ComponentId) -> Option<Ptr<'_>>;
fn EntityMut::get_mut_by_id(ComponentId) -> Option<MutUntyped<'_>>;
fn World::get_resource_by_id(ComponentId) -> Option<Ptr<'_>>;
fn World::get_resource_mut_by_id(ComponentId) -> Option<MutUntyped<'_>>;
// Safety: `value` must point to a valid value of the component
unsafe fn World::insert_resource_by_id(ComponentId, value: OwningPtr);
fn ComponentDescriptor::new_with_layout(..) -> Self;
fn World::init_component_with_descriptor(ComponentDescriptor) -> ComponentId;
```
~~This PR would definitely benefit from #3001 (lifetime'd pointers) to make sure that the lifetimes of the pointers are valid and the my-move pointer in `insert_resource_by_id` could be an `OwningPtr`, but that can be adapter later if/when #3001 is merged.~~
### Not in this PR
- inserting components on entities (this is very tied to types with bundles and the `BundleInserter`)
- an untyped version of a query (needs good API design, has a large implementation complexity, can be done in a third-party crate)
Co-authored-by: Jakob Hellermann <hellermann@sipgate.de>
# Objective
Fixes#4657
Example code that wasnt panic'ing before this PR (and so was unsound):
```rust
#[test]
#[should_panic = "error[B0001]"]
fn option_has_no_filter_with() {
fn sys(_1: Query<(Option<&A>, &mut B)>, _2: Query<&mut B, Without<A>>) {}
let mut world = World::default();
run_system(&mut world, sys);
}
#[test]
#[should_panic = "error[B0001]"]
fn any_of_has_no_filter_with() {
fn sys(_1: Query<(AnyOf<(&A, ())>, &mut B)>, _2: Query<&mut B, Without<A>>) {}
let mut world = World::default();
run_system(&mut world, sys);
}
#[test]
#[should_panic = "error[B0001]"]
fn or_has_no_filter_with() {
fn sys(_1: Query<&mut B, Or<(With<A>, With<B>)>>, _2: Query<&mut B, Without<A>>) {}
let mut world = World::default();
run_system(&mut world, sys);
}
```
## Solution
- Only add the intersection of `with`/`without` accesses of all the elements in `Or/AnyOf` to the world query's `FilteredAccess<ComponentId>` instead of the union.
- `Option`'s fix can be thought of the same way since its basically `AnyOf<T, ()>` but its impl is just simpler as `()` has no `with`/`without` accesses
---
## Changelog
- `Or`/`AnyOf`/`Option` will now report more query conflicts in order to fix unsoundness
## Migration Guide
- If you are now getting query conflicts from `Or`/`AnyOf`/`Option` rip to you and ur welcome for it now being caught
# Objective
We have duplicated code between `QueryIter` and `QueryIterationCursor`. Reuse that code.
## Solution
- Reuse `QueryIterationCursor` inside `QueryIter`.
- Slim down `QueryIter` by removing the `&'w World`. It was only being used by the `size_hint` and `ExactSizeIterator` impls, which can use the QueryState and &Archetypes in the type already.
- Benchmark to make sure there is no significant regression.
Relevant benchmark results seem to show that there is no tangible difference between the two. Everything seems to be either identical or within a workable margin of error here.
```
group embed-cursor main
----- ------------ ----
fragmented_iter/base 1.00 387.4±19.70ns ? ?/sec 1.07 413.1±27.95ns ? ?/sec
many_maps_iter 1.00 27.3±0.22ms ? ?/sec 1.00 27.4±0.10ms ? ?/sec
simple_iter/base 1.00 13.8±0.07µs ? ?/sec 1.00 13.7±0.17µs ? ?/sec
simple_iter/sparse 1.00 61.9±0.37µs ? ?/sec 1.00 62.2±0.64µs ? ?/sec
simple_iter/system 1.00 13.7±0.34µs ? ?/sec 1.00 13.7±0.10µs ? ?/sec
sparse_fragmented_iter/base 1.00 11.0±0.54ns ? ?/sec 1.03 11.3±0.48ns ? ?/sec
world_query_iter/50000_entities_sparse 1.08 105.0±2.68µs ? ?/sec 1.00 97.5±2.18µs ? ?/sec
world_query_iter/50000_entities_table 1.00 27.3±0.13µs ? ?/sec 1.00 27.3±0.37µs ? ?/sec
```
# Objective
- We do a lot of function pointer calls in a hot loop (clearing entities in render). This is slow, since calling function pointers cannot be optimised out. We can avoid that in the cases where the function call is a no-op.
- Alternative to https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/2897
- On my machine, in `many_cubes`, this reduces dropping time from ~150μs to ~80μs.
## Solution
- Make `drop` in `BlobVec` an `Option`, recording whether the given drop impl is required or not.
- Note that this does add branching in some cases - we could consider splitting this into two fields, i.e. unconditionally call the `drop` fn pointer.
- My intuition of how often types stored in `World` should have non-trivial drops makes me think that would be slower, however.
N.B. Even once this lands, we should still test having a 'drop_multiple' variant - for types with a real `Drop` impl, the current implementation is definitely optimal.
# Objective
`bevy_ecs` assumes that `u32 as usize` is a lossless operation and in a few cases relies on this for soundness and correctness. The only platforms that Rust compiles to where this invariant is broken are 16-bit systems.
A very clear example of this behavior is in the SparseSetIndex impl for Entity, where it converts a u32 into a usize to act as an index. If usize is 16-bit, the conversion will overflow and provide the caller with the wrong index. This can easily result in previously unforseen aliased mutable borrows (i.e. Query::get_many_mut).
## Solution
Explicitly fail compilation on 16-bit platforms instead of introducing UB.
Properly supporting 16-bit systems will likely need a workable use case first.
---
## Changelog
Removed: Ability to compile `bevy_ecs` on 16-bit platforms.
## Migration Guide
`bevy_ecs` will now explicitly fail to compile on 16-bit platforms. If this is required, there is currently no alternative. Please file an issue (https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues) to help detail your use case.
# Objective
- It's pretty common to want to check if an EventReader has received one or multiple events while also needing to consume the iterator to "clear" the EventReader.
- The current approach is to do something like `events.iter().count() > 0` or `events.iter().last().is_some()`. It's not immediately obvious that the purpose of that is to consume the events and check if there were any events. My solution doesn't really solve that part, but it encapsulates the pattern.
## Solution
- Add a `.clear()` method that consumes the iterator.
- It takes the EventReader by value to make sure it isn't used again after it has been called.
---
## Migration Guide
Not a breaking change, but if you ever found yourself in a situation where you needed to consume the EventReader and check if there was any events you can now use
```rust
fn system(events: EventReader<MyEvent>) {
if !events.is_empty {
events.clear();
// Process the fact that one or more event was received
}
}
```
Co-authored-by: Charles <IceSentry@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
`Query::par_for_each` and it's variants do not show up when profiling using `tracy` or other profilers. Failing to show the impact of changing batch size, the overhead of scheduling tasks, overall thread utilization, etc. other than the effect on the surrounding system.
## Solution
Add a child span that is entered on every spawned task.
Example view of the results in `tracy` using a modified `parallel_query`:
---
## Changelog
Added: `tracing` spans for `Query::par_for_each` and its variants. Spans should now be visible for all
# Objective
- The code in `events.rs` was a bit messy. There was lots of duplication between `EventReader` and `ManualEventReader`, and the state management code is not needed.
## Solution
- Clean it up.
## Future work
Should we remove the type parameter from `ManualEventReader`?
It doesn't have any meaning outside of its source `Events`. But there's no real reason why it needs to have a type parameter - it's just plain data. I didn't remove it yet to keep the type safety in some of the users of it (primarily related to `&mut World` usage)
Required for https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/4402.
# Objective
- derived `SystemParam` implementations were never `ReadOnlySystemParamFetch`
- We want them to be, e.g. for `EventReader`
## Solution
- If possible, 'forward' the impl of `ReadOnlySystemParamFetch`.
# Objective
- (Eventually) reduce noise in reporting access conflicts between unordered systems.
- `SystemStage` only looks at unfiltered `ComponentId` access, any conflicts reported are potentially `false`.
- the systems could still be accessing disjoint archetypes
- Comparing systems' filtered access sets can maybe avoid that (for statically known component types).
- #4204
## Solution
- Modify `SparseSetIndex` trait to require `PartialEq`, `Eq`, and `Hash` (all internal types except `BundleId` already did).
- Add `is_compatible` and `get_conflicts` methods to `FilteredAccessSet<T>`
- (existing method renamed to `get_conflicts_single`)
- Add docs for those and all the other methods while I'm at it.
## Objective
- ~~Make absurdly long-lived changes stay detectable for even longer (without leveling up to `u64`).~~
- Give all changes a consistent maximum lifespan.
- Improve code clarity.
## Solution
- ~~Increase the frequency of `check_tick` scans to increase the oldest reliably-detectable change.~~
(Deferred until we can benchmark the cost of a scan.)
- Ignore changes older than the maximum reliably-detectable age.
- General refactoring—name the constants, use them everywhere, and update the docs.
- Update test cases to check for the specified behavior.
## Related
This PR addresses (at least partially) the concerns raised in:
- #3071
- #3082 (and associated PR #3084)
## Background
- #1471
Given the minimum interval between `check_ticks` scans, `N`, the oldest reliably-detectable change is `u32::MAX - (2 * N - 1)` (or `MAX_CHANGE_AGE`). Reducing `N` from ~530 million (current value) to something like ~2 million would extend the lifetime of changes by a billion.
| minimum `check_ticks` interval | oldest reliably-detectable change | usable % of `u32::MAX` |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `u32::MAX / 8` (536,870,911) | `(u32::MAX / 4) * 3` | 75.0% |
| `2_000_000` | `u32::MAX - 3_999_999` | 99.9% |
Similarly, changes are still allowed to be between `MAX_CHANGE_AGE`-old and `u32::MAX`-old in the interim between `check_tick` scans. While we prevent their age from overflowing, the test to detect changes still compares raw values. This makes failure ultimately unreliable, since when ancient changes stop being detected varies depending on when the next scan occurs.
## Open Question
Currently, systems and system states are incorrectly initialized with their `last_change_tick` set to `0`, which doesn't handle wraparound correctly.
For consistent behavior, they should either be initialized to the world's `last_change_tick` (and detect no changes) or to `MAX_CHANGE_AGE` behind the world's current `change_tick` (and detect everything as a change). I've currently gone with the latter since that was closer to the existing behavior.
## Follow-up Work
(Edited: entire section)
We haven't actually profiled how long a `check_ticks` scan takes on a "large" `World` , so we don't know if it's safe to increase their frequency. However, we are currently relying on play sessions not lasting long enough to trigger a scan and apps not having enough entities/archetypes for it to be "expensive" (our assumption). That isn't a real solution. (Either scanning never costs enough to impact frame times or we provide an option to use `u64` change ticks. Nobody will accept random hiccups.)
To further extend the lifetime of changes, we actually only need to increment the world tick if a system has `Fetch: !ReadOnlySystemParamFetch`. The behavior will be identical because all writes are sequenced, but I'm not sure how to implement that in a way that the compiler can optimize the branch out.
Also, since having no false positives depends on a `check_ticks` scan running at least every `2 * N - 1` ticks, a `last_check_tick` should also be stored in the `World` so that any lull in system execution (like a command flush) could trigger a scan if needed. To be completely robust, all the systems initialized on the world should be scanned, not just those in the current stage.
# Objective
- Remove `Resource` binding on events, introduce a new `Event` trait
- Ensure event iterators are `ExactSizeIterator`
## Solution
- Builds on #2382 and #2969
## Changelog
- Events<T>, EventWriter<T>, EventReader<T> and so on now require that the underlying type is Event, rather than Resource. Both of these are trivial supertraits of Send + Sync + 'static with universal blanket implementations: this change is currently purely cosmetic.
- Event reader iterators now implement ExactSizeIterator
1. change `PtrMut::as_ptr(self)` and `OwnedPtr::as_ptr(self)` to take `&self`, otherwise printing the pointer will prevent doing anything else afterwards
2. make all `as_ptr` methods safe. There's nothing unsafe about obtaining a pointer, these kinds of methods are safe in std as well [str::as_ptr](https://doc.rust-lang.org/stable/std/primitive.str.html#method.as_ptr), [Rc::as_ptr](https://doc.rust-lang.org/stable/std/rc/struct.Rc.html#method.as_ptr)
3. rename `offset`/`add` to `byte_offset`/`byte_add`. The unprefixed methods in std add in increments of `std::mem::size_of::<T>`, not in bytes. There's a PR for rust to add these byte_ methods https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/95643 and at the call site it makes it much more clear that you need to do `.byte_add(i * layout_size)` instead of `.add(i)`
# Objective
The pointer types introduced in #3001 are useful not just in `bevy_ecs`, but also in crates like `bevy_reflect` (#4475) or even outside of bevy.
## Solution
Extract `Ptr<'a>`, `PtrMut<'a>`, `OwnedPtr<'a>`, `ThinSlicePtr<'a, T>` and `UnsafeCellDeref` from `bevy_ecs::ptr` into `bevy_ptr`.
**Note:** `bevy_ecs` still reexports the `bevy_ptr` as `bevy_ecs::ptr` so that crates like `bevy_transform` can use the `Bundle` derive without needing to depend on `bevy_ptr` themselves.
# Objective
- `RunOnce` was a manual `System` implementation.
- Adding run criteria to stages was yet to be systemyoten
## Solution
- Make it a normal function
- yeet
## Changelog
- Replaced `RunOnce` with `ShouldRun::once`
## Migration guide
The run criterion `RunOnce`, which would make the controlled systems run only once, has been replaced with a new run criterion function `ShouldRun::once`. Replace all instances of `RunOnce` with `ShouldRun::once`.
# Objective
The `Ptr` types gives free access to the underlying `NonNull<u8>`, which adds more publicly visible pointer wrangling than there needs to be. There are also a few edge cases where Ptr types could be more readily utilized for properly validating the soundness of ECS operations.
## Solution
- Replace `*Ptr(Mut)::inner` with `cast` which requires a concrete type to give the pointer. This function could also have a `debug_assert` with an alignment check to ensure that the pointer is aligned properly, but is currently not included.
- Use `OwningPtr::read` in ECS macros over casting the inner pointer around.
# Objective
1. Previously, the `change_tick` and `last_change_tick` fields on `SystemChangeTick` [were `pub`](https://docs.rs/bevy/0.6.1/bevy/ecs/system/struct.SystemChangeTick.html).
1. This was actively misleading, as while this can be fetched as a `SystemParam`, a copy is returned instead
2. This information could be useful for debugging, but there was no way to investigate when data was changed.
3. There were no docs!
## Solution
1. Move these to a getter method.
2. Add `last_changed` method to the `DetectChanges` trait to enable inspection of when data was last changed.
3. Add docs.
# Changelog
`SystemChangeTick` now provides getter methods for the current and previous change tick, rather than public fields.
This can be combined with `DetectChanges::last_changed()` to debug the timing of changes.
# Migration guide
The `change_tick` and `last_change_tick` fields on `SystemChangeTick` are now private, use the corresponding getter method instead.
# Objective
- Manually running systems is a somewhat obscure process: systems must be initialized before they are run
- The unwrap is rather hard to debug.
## Solution
- Replace unwraps in `FunctionSystem` methods with expects (progress towards #3892).
- Briefly document this requirement.
The only tests we had for `derive(WorldQuery)` checked that the derive doesnt panic/emit a `compiler_error!`. This PR adds tests that actually assert the returned values of a query using the derived `WorldQuery` impl. Also adds a compile fail test to check that we correctly error on read only world queries containing mutable world queries.
# Objective
`bevy_ecs` has large amounts of unsafe code which is hard to get right and makes it difficult to audit for soundness.
## Solution
Introduce lifetimed, type-erased pointers: `Ptr<'a>` `PtrMut<'a>` `OwningPtr<'a>'` and `ThinSlicePtr<'a, T>` which are newtypes around a raw pointer with a lifetime and conceptually representing strong invariants about the pointee and validity of the pointer.
The process of converting bevy_ecs to use these has already caught multiple cases of unsound behavior.
## Changelog
TL;DR for release notes: `bevy_ecs` now uses lifetimed, type-erased pointers internally, significantly improving safety and legibility without sacrificing performance. This should have approximately no end user impact, unless you were meddling with the (unfortunately public) internals of `bevy_ecs`.
- `Fetch`, `FilterFetch` and `ReadOnlyFetch` trait no longer have a `'state` lifetime
- this was unneeded
- `ReadOnly/Fetch` associated types on `WorldQuery` are now on a new `WorldQueryGats<'world>` trait
- was required to work around lack of Generic Associated Types (we wish to express `type Fetch<'a>: Fetch<'a>`)
- `derive(WorldQuery)` no longer requires `'w` lifetime on struct
- this was unneeded, and improves the end user experience
- `EntityMut::get_unchecked_mut` returns `&'_ mut T` not `&'w mut T`
- allows easier use of unsafe API with less footguns, and can be worked around via lifetime transmutery as a user
- `Bundle::from_components` now takes a `ctx` parameter to pass to the `FnMut` closure
- required because closure return types can't borrow from captures
- `Fetch::init` takes `&'world World`, `Fetch::set_archetype` takes `&'world Archetype` and `&'world Tables`, `Fetch::set_table` takes `&'world Table`
- allows types implementing `Fetch` to store borrows into world
- `WorldQuery` trait now has a `shrink` fn to shorten the lifetime in `Fetch::<'a>::Item`
- this works around lack of subtyping of assoc types, rust doesnt allow you to turn `<T as Fetch<'static>>::Item'` into `<T as Fetch<'a>>::Item'`
- `QueryCombinationsIter` requires this
- Most types implementing `Fetch` now have a lifetime `'w`
- allows the fetches to store borrows of world data instead of using raw pointers
## Migration guide
- `EntityMut::get_unchecked_mut` returns a more restricted lifetime, there is no general way to migrate this as it depends on your code
- `Bundle::from_components` implementations must pass the `ctx` arg to `func`
- `Bundle::from_components` callers have to use a fn arg instead of closure captures for borrowing from world
- Remove lifetime args on `derive(WorldQuery)` structs as it is nonsensical
- `<Q as WorldQuery>::ReadOnly/Fetch` should be changed to either `RO/QueryFetch<'world>` or `<Q as WorldQueryGats<'world>>::ReadOnly/Fetch`
- `<F as Fetch<'w, 's>>` should be changed to `<F as Fetch<'w>>`
- Change the fn sigs of `Fetch::init/set_archetype/set_table` to match respective trait fn sigs
- Implement the required `fn shrink` on any `WorldQuery` implementations
- Move assoc types `Fetch` and `ReadOnlyFetch` on `WorldQuery` impls to `WorldQueryGats` impls
- Pass an appropriate `'world` lifetime to whatever fetch struct you are for some reason using
### Type inference regression
in some cases rustc may give spurrious errors when attempting to infer the `F` parameter on a query/querystate this can be fixed by manually specifying the type, i.e. `QueryState:🆕:<_, ()>(world)`. The error is rather confusing:
```rust=
error[E0271]: type mismatch resolving `<() as Fetch<'_>>::Item == bool`
--> crates/bevy_pbr/src/render/light.rs:1413:30
|
1413 | main_view_query: QueryState::new(world),
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ expected `bool`, found `()`
|
= note: required because of the requirements on the impl of `for<'x> FilterFetch<'x>` for `<() as WorldQueryGats<'x>>::Fetch`
note: required by a bound in `bevy_ecs::query::QueryState::<Q, F>::new`
--> crates/bevy_ecs/src/query/state.rs:49:32
|
49 | for<'x> QueryFetch<'x, F>: FilterFetch<'x>,
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ required by this bound in `bevy_ecs::query::QueryState::<Q, F>::new`
```
---
Made with help from @BoxyUwU and @alice-i-cecile
Co-authored-by: Boxy <supbscripter@gmail.com>
# Objective
Reduce from scratch build time.
## Solution
Reduce the size of the critical path by removing dependencies between crates where not necessary. For `cargo check --no-default-features` this reduced build time from ~51s to ~45s. For some commits I am not completely sure if the tradeoff between build time reduction and convenience caused by the commit is acceptable. If not, I can drop them.
## Objective
This fixes#1686.
`size_hint` can be useful even if a little niche. For example,
`collect::<Vec<_>>()` uses the `size_hint` of Iterator it collects from
to pre-allocate a memory slice large enough to not require re-allocating
when pushing all the elements of the iterator.
## Solution
To this effect I made the following changes:
* Add a `IS_ARCHETYPAL` associated constant to the `Fetch` trait,
this constant tells us when it is safe to assume that the `Fetch`
relies exclusively on archetypes to filter queried entities
* Add `IS_ARCHETYPAL` to all the implementations of `Fetch`
* Use that constant in `QueryIter::size_hint` to provide a more useful
## Migration guide
The new associated constant is an API breaking change. For the user,
if they implemented a custom `Fetch`, it means they have to add this
associated constant to their implementation. Either `true` if it doesn't limit
the number of entities returned in a query beyond that of archetypes, or
`false` for when it does.
# Objective
- `EntityRef` and `EntityMut` are surpisingly important public types when working directly with the `World`.
- They're undocumented.
## Solution
- Just add docs!
# Objective
`AsSystemLabel` has been introduced on system descriptors to make ordering systems more convenient, but `SystemSet::before` and `SystemSet::after` still take `SystemLabels` directly:
use bevy::ecs::system::AsSystemLabel;
/*…*/ SystemSet::new().before(foo.as_system_label()) /*…*/
is currently necessary instead of
/*…*/ SystemSet::new().before(foo) /*…*/
## Solution
Use `AsSystemLabel` for `SystemSet`
The only way to soundly use this API is already encapsulated within `EntityMut::get`, so this api is removed.
# Migration guide
Replace calls to `EntityMut::get_unchecked` with calls to `EntityMut::get`.
# Objective
- The current API docs of `Commands` is very short and is very opaque to newcomers.
## Solution
- Try to explain what it is without requiring knowledge of other parts of `bevy_ecs` like `World` or `SystemParam`.
Co-authored-by: Charles <IceSentry@users.noreply.github.com>
Free at last!
# Objective
- Using `.system()` is no longer needed anywhere, and anyone using it will have already gotten a deprecation warning.
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/3302 was a super special case for `.system()`, since it was so prevelant. However, that's no reason.
- Despite it being deprecated, another couple of uses of it have already landed, including in the deprecating PR.
- These have all been because of doc examples having warnings not breaking CI - 🎟️?
## Solution
- Remove it.
- It's gone
---
## Changelog
- You can no longer use `.system()`
## Migration Guide
- You can no longer use `.system()`. It was deprecated in 0.7.0, and you should have followed the deprecation warning then. You can just remove the method call.

- Thanks to the @TheRawMeatball for producing
# Objective
- Provide more information when despawning an entity
## Solution
- Add a debug log when despawning an entity
- Add spans to the recursive ways of despawning an entity
```sh
RUST_LOG=debug cargo run --example panic --features trace
# RUST_LOG=debug needed to show debug logs from bevy_ecs
# --features trace needed to have the extra spans
...
DEBUG bevy_app:frame:stage{name=Update}:system_commands{name="panic::despawn_parent"}:command{name="DespawnRecursive" entity=0v0}: bevy_ecs::world: Despawning entity 1v0
DEBUG bevy_app:frame:stage{name=Update}:system_commands{name="panic::despawn_parent"}:command{name="DespawnRecursive" entity=0v0}: bevy_ecs::world: Despawning entity 0v0
```
# Objective
- Previously, `iter_combinations()` does not work on queries that have filters.
- Fixes#3651
## Solution
- Derived Copy on all `*Fetch<T>` structs, and manually implemented `Clone` to allow the test to pass (`.count()` does not work on `QueryCombinationIter` when `Clone` is derived)
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Make it possible to use `System`s outside of the scheduler/executor without having to define logic to track new archetypes and call `System::add_archetype()` for each.
## Solution
- Replace `System::add_archetype(&Archetype)` with `System::update_archetypes(&World)`, making systems responsible for tracking their own most recent archetype generation the way that `SystemState` already does.
This has minimal (or simplifying) effect on most of the code with the exception of `FunctionSystem`, which must now track the latest `ArchetypeGeneration` it saw instead of relying on the executor to do it.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
Remove the 'chaining' api, as it's peculiar
~~Implement the label traits for `Box<dyn ThatTrait>` (n.b. I'm not confident about this change, but it was the quickest path to not regressing)~~
Remove the need for '`.system`' when using run criteria piping
# Objective
Make `FromWorld` more useful for abstractions with a form similar to
```rs
trait FancyAbstraction {
type PreInitializedData: FromWorld;
}
```
## Solution
Add a `FromWorld` implementation for `SystemState` as well as a way to group together multiple `FromWorld` implementing types as one.
Note: I plan to follow up this PR with another to add `Local` support to exclusive systems, which should get a fair amount of use from the `FromWorld` implementation on `SystemState`.
Fixes#3408#3001 also solves this but I dont see it getting merged any time soon so...
# Objective
make bevy ecs a lil bit less unsound
## Solution
make `EntityMut::get_component_mut` return borrows from self instead of `'w`
# Objective
- std's new APIs do the same thing as `Query::get_multiple_mut`, but are called `get_many`: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/83608
## Solution
- Find and replace `get_multiple` with `get_many`
# Objective
- Clarify `RemovedComponents` are flushed in `CoreStage::Last` and systems relying on that should run before that stage
## Solution
- Update `RemovedComponents` doc comment
# Objective
make bevy ecs a lil bit less unsound
## Solution
make unsound API unsafe so that there is an unsafe block to blame:
```rust
use bevy_ecs::prelude::*;
#[derive(Debug, Component)]
struct Foo(u8);
fn main() {
let mut world = World::new();
let e1 = world.spawn().id();
let e2 = world.spawn().insert(Foo(2)).id();
world.entities_mut().meta[0] = world.entities_mut().meta[1].clone();
let foo = world.entity(e1).get::<Foo>().unwrap();
// whoo i love having components i dont have
dbg!(foo);
}
```
This is not _strictly_ speaking UB, however:
- `Query::get_multiple` cannot work if this is allowed
- bevy_ecs is a pile of unsafe code whose soundness generally depends on the world being in a "correct" state with "no funny business" so it seems best to disallow this
- it is trivial to get bevy to panic inside of functions with safety invariants that have been violated (the entity location is not valid)
- it seems to violate what the safety invariant on `Entities::flush` is trying to ensure
# Objective
- The inability to have multiple active mutable borrows into a query is a common source of borrow-checker pain for users.
- This is a pointless restriction if and only if we can guarantee that the entities they are accessing are unique.
- This could already by bypassed with get_unchecked, but that is an extremely unsafe API.
- Closes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/2042.
## Solution
- Add `get_multiple`, `get_multiple_mut` and their unchecked equivalents (`multiple` and `multiple_mut`) to `Query` and `QueryState`.
- Improve the `QueryEntityError` type to provide more useful error information.
## Changelog
- Added `get_multiple`, `get_multiple_mut` and their unchecked equivalents (`multiple` and `multiple_mut`) to Query and QueryState.
## Migration Guide
- The `QueryEntityError` enum now has a `AliasedMutability variant, and returns the offending entity.
## Context
This is a fresh attempt at #3333; rebasing was behaving very badly and it was important to rebase on top of the recent query soundness fixes. Many thanks to all the reviewers in that thread, especially @BoxyUwU for the help with lifetimes.
## To-do
- [x] Add compile fail tests
- [x] Successfully deduplicate code
- [x] Decide what to do about failing doc tests
- [x] Get some reviews for lifetime soundness
# Objective
Add a system parameter `ParamSet` to be used as container for conflicting parameters.
## Solution
Added two methods to the SystemParamState trait, which gives the access used by the parameter. Did the implementation. Added some convenience methods to FilteredAccessSet. Changed `get_conflicts` to return every conflicting component instead of breaking on the first conflicting `FilteredAccess`.
Co-authored-by: bilsen <40690317+bilsen@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
Fixes#1529
Run bevy_ecs in miri
## Solution
- Don't set thread names when running in miri rust-lang/miri/issues/1717
- Update `event-listener` to `2.5.2` as previous versions have UB that is detected by miri: [event-listener commit](1fa31c553e)
- Ignore memory leaks when running in miri as they are impossible to track down rust-lang/miri/issues/1481
- Make `table_add_remove_many` test less "many" because miri is really quite slow :)
- Make CI run `RUSTFLAGS="-Zrandomize-layout" MIRIFLAGS="-Zmiri-ignore-leaks -Zmiri-tag-raw-pointers -Zmiri-disable-isolation" cargo +nightly miri test -p bevy_ecs`
This adds the concept of "default labels" for systems (currently scoped to "parallel systems", but this could just as easily be implemented for "exclusive systems"). Function systems now include their function's `SystemTypeIdLabel` by default.
This enables the following patterns:
```rust
// ordering two systems without manually defining labels
app
.add_system(update_velocity)
.add_system(movement.after(update_velocity))
// ordering sets of systems without manually defining labels
app
.add_system(foo)
.add_system_set(
SystemSet::new()
.after(foo)
.with_system(bar)
.with_system(baz)
)
```
Fixes: #4219
Related to: #4220
Credit to @aevyrie @alice-i-cecile @DJMcNab (and probably others) for proposing (and supporting) this idea about a year ago. I was a big dummy that both shut down this (very good) idea and then forgot I did that. Sorry. You all were right!
# Objective
make bevy ecs a lil bit less unsound
## Solution
yeet unsound API `World::components_mut`:
```rust
use bevy_ecs::prelude::*;
#[derive(Component)]
struct Foo(u8);
#[derive(Debug, Component)]
struct Bar([u8; 100]);
fn main() {
let mut world = World::new();
let e = world.spawn().insert(Foo(0)).id();
*world.components_mut() = Default::default();
let bar = world.entity_mut(e).remove::<Bar>().unwrap();
// oopsies reading memory copied from outside allocation
dbg!(bar);
}
```
Tracing added support for "inline span entering", which cuts down on a lot of complexity:
```rust
let span = info_span!("my_span").entered();
```
This adapts our code to use this pattern where possible, and updates our docs to recommend it.
This produces equivalent tracing behavior. Here is a side by side profile of "before" and "after" these changes.
# Objective
- Fixes#3300
- `RunSystem` is messy
## Solution
- Adds the trick theorised in https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/3300#issuecomment-991791234
P.S. I also want this for an experimental refactoring of `Assets`, to remove the duplication of `Events<AssetEvent<T>>`
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- In the large majority of cases, users were calling `.unwrap()` immediately after `.get_resource`.
- Attempting to add more helpful error messages here resulted in endless manual boilerplate (see #3899 and the linked PRs).
## Solution
- Add an infallible variant named `.resource` and so on.
- Use these infallible variants over `.get_resource().unwrap()` across the code base.
## Notes
I did not provide equivalent methods on `WorldCell`, in favor of removing it entirely in #3939.
## Migration Guide
Infallible variants of `.get_resource` have been added that implicitly panic, rather than needing to be unwrapped.
Replace `world.get_resource::<Foo>().unwrap()` with `world.resource::<Foo>()`.
## Impact
- `.unwrap` search results before: 1084
- `.unwrap` search results after: 942
- internal `unwrap_or_else` calls added: 4
- trivial unwrap calls removed from tests and code: 146
- uses of the new `try_get_resource` API: 11
- percentage of the time the unwrapping API was used internally: 93%
# Objective
Continuation of #2663 due to git problems - better documentation for Query::par_for_each and par_for_each_mut
## Solution
Going into more detail about the function parameters
# Objective
- Fix the ugliness of the `config` api.
- Supercedes #2440, #2463, #2491
## Solution
- Since #2398, capturing closure systems have worked.
- Use those instead where we needed config before
- Remove the rest of the config api.
- Related: #2777
# Objective
- Closes#786
- Closes#2252
- Closes#2588
This PR implements a derive macro that allows users to define their queries as structs with named fields.
## Example
```rust
#[derive(WorldQuery)]
#[world_query(derive(Debug))]
struct NumQuery<'w, T: Component, P: Component> {
entity: Entity,
u: UNumQuery<'w>,
generic: GenericQuery<'w, T, P>,
}
#[derive(WorldQuery)]
#[world_query(derive(Debug))]
struct UNumQuery<'w> {
u_16: &'w u16,
u_32_opt: Option<&'w u32>,
}
#[derive(WorldQuery)]
#[world_query(derive(Debug))]
struct GenericQuery<'w, T: Component, P: Component> {
generic: (&'w T, &'w P),
}
#[derive(WorldQuery)]
#[world_query(filter)]
struct NumQueryFilter<T: Component, P: Component> {
_u_16: With<u16>,
_u_32: With<u32>,
_or: Or<(With<i16>, Changed<u16>, Added<u32>)>,
_generic_tuple: (With<T>, With<P>),
_without: Without<Option<u16>>,
_tp: PhantomData<(T, P)>,
}
fn print_nums_readonly(query: Query<NumQuery<u64, i64>, NumQueryFilter<u64, i64>>) {
for num in query.iter() {
println!("{:#?}", num);
}
}
#[derive(WorldQuery)]
#[world_query(mutable, derive(Debug))]
struct MutNumQuery<'w, T: Component, P: Component> {
i_16: &'w mut i16,
i_32_opt: Option<&'w mut i32>,
}
fn print_nums(mut query: Query<MutNumQuery, NumQueryFilter<u64, i64>>) {
for num in query.iter_mut() {
println!("{:#?}", num);
}
}
```
## TODOs:
- [x] Add support for `&T` and `&mut T`
- [x] Test
- [x] Add support for optional types
- [x] Test
- [x] Add support for `Entity`
- [x] Test
- [x] Add support for nested `WorldQuery`
- [x] Test
- [x] Add support for tuples
- [x] Test
- [x] Add support for generics
- [x] Test
- [x] Add support for query filters
- [x] Test
- [x] Add support for `PhantomData`
- [x] Test
- [x] Refactor `read_world_query_field_type_info`
- [x] Properly document `readonly` attribute for nested queries and the static assertions that guarantee safety
- [x] Test that we never implement `ReadOnlyFetch` for types that need mutable access
- [x] Test that we insert static assertions for nested `WorldQuery` that a user marked as readonly
For some keys, it is too expensive to hash them on every lookup. Historically in Bevy, we have regrettably done the "wrong" thing in these cases (pre-computing hashes, then re-hashing them) because Rust's built in hashed collections don't give us the tools we need to do otherwise. Doing this is "wrong" because two different values can result in the same hash. Hashed collections generally get around this by falling back to equality checks on hash collisions. You can't do that if the key _is_ the hash. Additionally, re-hashing a hash increase the odds of collision!
#3959 needs pre-hashing to be viable, so I decided to finally properly solve the problem. The solution involves two different changes:
1. A new generalized "pre-hashing" solution in bevy_utils: `Hashed<T>` types, which store a value alongside a pre-computed hash. And `PreHashMap<K, V>` (which uses `Hashed<T>` internally) . `PreHashMap` is just an alias for a normal HashMap that uses `Hashed<T>` as the key and a new `PassHash` implementation as the Hasher.
2. Replacing the `std::collections` re-exports in `bevy_utils` with equivalent `hashbrown` impls. Avoiding re-hashes requires the `raw_entry_mut` api, which isn't stabilized yet (and may never be ... `entry_ref` has favor now, but also isn't available yet). If std's HashMap ever provides the tools we need, we can move back to that. The latest version of `hashbrown` adds support for the `entity_ref` api, so we can move to that in preparation for an std migration, if thats the direction they seem to be going in. Note that adding hashbrown doesn't increase our dependency count because it was already in our tree.
In addition to providing these core tools, I also ported the "table identity hashing" in `bevy_ecs` to `raw_entry_mut`, which was a particularly egregious case.
The biggest outstanding case is `AssetPathId`, which stores a pre-hash. We need AssetPathId to be cheaply clone-able (and ideally Copy), but `Hashed<AssetPath>` requires ownership of the AssetPath, which makes cloning ids way more expensive. We could consider doing `Hashed<Arc<AssetPath>>`, but cloning an arc is still a non-trivial expensive that needs to be considered. I would like to handle this in a separate PR. And given that we will be re-evaluating the Bevy Assets implementation in the very near future, I'd prefer to hold off until after that conversation is concluded.
# Objective
- `SystemStates` rock for dealing with exclusive world access, but are hard to figure out how to use.
- Fixes#3341.
## Solution
- Clearly document how to use `SystemState`, and why they're useful as an end-user.
What is says on the tin.
This has got more to do with making `clippy` slightly more *quiet* than it does with changing anything that might greatly impact readability or performance.
that said, deriving `Default` for a couple of structs is a nice easy win
# Objective
- Fixes#3078
- Fixes#1397
## Solution
- Implement Commands::init_resource.
- Also implement for World, for consistency and to simplify internal structure.
- While we're here, clean up some of the docs for Command and World resource modification.
# Objective
- `serde_json` assumes that numbers being deserialized are either u64 or i64.
- `Entity` serializes and deserializes as a u32.
- Deserializing an `Entity` with `serde_json` fails with: `Error("invalid type: integer 10947, expected expected Entity"`
## Solution
- Implemented a visitor for u64 that allows an `Entity` to be deserialized in this case.
- While I was here, also fixed the redundant "expected expected Entity" in the error message
- Tested the change in a local project which now correctly deserializes `Entity` structs with `serde_json` when it couldn't before
Implements a new Queryable called AnyOf, which will return an item as long as at least one of it's requested Queryables returns something. For example, a `Query<AnyOf<(&A, &B, &C)>>` will return items with type `(Option<&A>, Option<&B>, Option<&C>)`, and will guarantee that for every element at least one of the option s is Some. This is a shorthand for queries like `Query<(Option<&A>, Option<&B>, Option<&C>), Or<(With<A>, With<B>, With&C>)>>`.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Provide impls for mutable types to relevant immutable types.
- Closes#2005
## Solution
- impl From<ResMut> for Res
- impl From<NonSendMut> for NonSend
- Mut to &/&mut already impl'd in change_detection_impl! macro
# Objective
It would be useful to be able to restart a state (such as if an operation fails and needs to be retried from `on_enter`). Currently, it seems the way to restart a state is to transition to a dummy state and then transition back.
## Solution
The solution is to add a `restart` method on `State<T>` that allows for transitioning to the already-active state.
## Context
Based on [this](https://discord.com/channels/691052431525675048/742884593551802431/920335041756815441) question from the Discord.
Closes#2385
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
When using empty events, it can feel redundant to have to specify the type of the event when sending it.
## Solution
Add a new `fire()` function that sends the default value of the event. This requires that the event derives Default.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
Make it possible to use `&World` as a system parameter
## Solution
It seems like all the pieces were already in place, very simple impl
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
Provide a non-consuming method of checking if there are events in an `EventReader`.
Fixes#2967
## Solution
Implements the `len` and `is_empty` functions for `EventReader` and `ManualEventReader`, giving users the ability to check for the presence of new events without consuming any.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
Calling forget would invalidate the data pointer before it is used.
## Solution
Use `ManuallyDrop` to prevent the value from being dropped without moving it.
This is my first contribution to this exciting project! Thanks so much for your wonderful work. If there is anything that I can improve about this PR, please let me know :)
# Objective
- Fixes#2899
- If a simple one-off command is needed to be added within a System, this simplifies that process so that we can simply do `commands.add(|world: &mut World| { /* code here */ })` instead of defining a custom type implementing `Command`.
## Solution
- This is achieved by `impl Command for F where F: FnOnce(&mut World) + Send + Sync + 'static` as just calling the function.
I am not sure if the bounds can be further relaxed but needed the whole `Send`, `Sync`, and `'static` to get it to compile.
# Objective
A user on Discord couldn't derive SystemParam for this Struct:
```rs
#[derive(SystemParam)]
pub struct SpatialQuery<'w, 's, Q: WorldQuery + Send + Sync + 'static, F: WorldQuery + Send + Sync + 'static = ()>
where
F::Fetch: FilterFetch,
{
query: Query<'w, 's, (C, &'static Transform), F>,
}
```
## Solution
1. The `where`-clause is now also copied to the `SystemParamFetch` impl Block.
2. The `SystemParamState` impl Block no longer gets any defaults for generics
Co-authored-by: MinerSebas <66798382+MinerSebas@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
Fixes#3566
## Solution
- [x] Fix broken links in private docs.
- [x] Add the `--document-private-items` flag to the CI.
## Note
The following was said by @killercup in #3566:
> I don't have time to confirm this but I assume that linking to private items throws an error/warning when just running cargo doc, and --document-private-item might actually hide that warning. So to test this, you'd have to run it twice.
I tested this and this is thankfully not the case. If you are linking to a private item you will get a warning no matter if you run `cargo doc` or `cargo doc --document-private-items`.
### Example
I added `struct Test;` to `bevy_core/src/name.rs` and linked to it inside of a doc comment using ``[`Test`]``. After that I ran `cargo doc -p bevy_core --document-private-items` using `RUSTDOCFLAGS="-D warnings"` and got the following output (note the last sentence):
```rust
error: public documentation for `Name` links to private item `Test`
--> crates/bevy_core/src/name.rs:11:82
|
11 | /// Component used to identify an entity. Stores a hash for faster comparisons [`Test`]
| ^^^^ this item is private
|
= note: `-D rustdoc::private-intra-doc-links` implied by `-D warnings`
= note: this link resolves only because you passed `--document-private-items`, but will break without
```
# Objective
Currently, simply calling `iter` on an event reader will mark all of it's events as read, even if the returned iterator is never used
## Solution
With this, the cursor will simply move to the last unread, but available event when iter is called, and incremented by one per `next` call.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Calling .id() has no purpose unless you use the Entity returned
- This is an easy source of confusion for beginners.
- This is easily missed during refactors.
## Solution
- Mark the appropriate methods as #[must_use]
# Objective
- Fixes#3616
## Solution
- As described in the issue, documentation for `iter_manual` was copied from `iter_combinations` and did not reflect the behavior of the method. I've pulled some information from #2351 to create a more accurate description.
# Objective
- Removes warning about accidently inserting bundles with `EntityCommands::insert`, but since a component now needs to implement `Component` it is unnecessary.
# Objective
This PR extends the `Events` documentation by:
- informing user about the possible race condition
- explicitly explaining the unusual double buffer implementation
Fixes#3305
Co-authored-by: MiniaczQ <jakub.motyka.2000@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: MiniaczQ <MiniaczQ@gmail.com>
#3457 adds the `doc_markdown` clippy lint, which checks doc comments to make sure code identifiers are escaped with backticks. This causes a lot of lint errors, so this is one of a number of PR's that will fix those lint errors one crate at a time.
This PR fixes lints in the `bevy_ecs` crate.
# Objective
- Fixes#1920.
- Users often want to know how to get the values of removed components (#1655).
- Stand-alone `bevy_ecs` behavior is very unintuitive, as `World::clear_trackers()` must be manually called.
- Fixes#2999 by extending the existing test (thanks @hymm for pointing me to it) to be clearer and check for component removal as well.
## Solution
- Better docs!
- Better tests!
# Objective
Remove the `StorageType` parameter from `ComponentDescriptor::new_resource` as discussed in #3361.
- fixes#3361
## Solution
- Parameter removed.
- Basic docs added.
## Note
Left a [comment](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/3361#issuecomment-996433346) about `SparseStorage` being the more reasonable choice.
Co-authored-by: r4gus <david@thesugar.de>
Dynamic types (`DynamicStruct`, `DynamicTupleStruct`, `DynamicTuple`, `DynamicList` and `DynamicMap`) are used when deserializing scenes, but currently they can only be applied to existing concrete types. This leads to issues when trying to spawn non trivial deserialized scene.
For components, the issue is avoided by requiring that reflected components implement ~~`FromResources`~~ `FromWorld` (or `Default`). When spawning, a new concrete type is created that way, and the dynamic type is applied to it. Unfortunately, some components don't have any valid implementation of these traits.
In addition, any `Vec` or `HashMap` inside a component will panic when a dynamic type is pushed into it (for instance, `Text` panics when adding a text section).
To solve this issue, this PR adds the `FromReflect` trait that creates a concrete type from a dynamic type that represent it, derives the trait alongside the `Reflect` trait, drops the ~~`FromResources`~~ `FromWorld` requirement on reflected components, ~~and enables reflection for UI and Text bundles~~. It also adds the requirement that fields ignored with `#[reflect(ignore)]` implement `Default`, since we need to initialize them somehow.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- While reading code, found some queries that are `mut` and not used as such
## Solution
- Remove `mut` when possible
Co-authored-by: François <8672791+mockersf@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
- Storages are used to store the ECS data.
- They're undocumented.
## Solution
- Add some very basic docs.
## Notes
- Some of this was hard to immediately understand when reading the code, so suggestions on improvements / things to add are particularly welcome.
Fixes#2566Fixes#3005
There are only READMEs in the 4 crates here (with the exception of bevy itself).
Those 4 crates are ecs, reflect, tasks, and transform.
These should each now include their respective README files.
Co-authored-by: Hoidigan <57080125+Hoidigan@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Daniel Nelsen <57080125+Hoidigan@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
I thought I'd have a go a trying to fix#2597.
Hopefully fixes#2597.
## Solution
I reused the memory pointed to by the value parameter, that is already required by `insert` to not be dropped, to contain the extracted value while dropping it.
Fills in some gaps we had in our Bevy ECS tracing spans:
* Exclusive systems
* System Commands (for `apply_buffers = true` cases)
* System archetype updates
* Parallel system execution prep
# Objective
- New clippy lints with rust 1.57 are failing
## Solution
- Fixed clippy lints following suggestions
- I ignored clippy in old renderer because there was many and it will be removed soon
A sample implementation of how to have `iter()` work on mutable queries without breaking aliasing rules.
# Objective
- Fixes#753
## Solution
- Added a ReadOnlyFetch to WorldQuery that is the `&T` version of `&mut T` that is used to specify the return type for read only operations like `iter()`.
- ~~As the comment suggests specifying the bound doesn't work due to restrictions on defining recursive implementations (like `Or`). However bounds on the functions are fine~~ Never mind I misread how `Or` was constructed, bounds now exist.
- Note that the only mutable one has a new `Fetch` for readonly as the `State` has to be the same for any of this to work
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
This is a squash-and-rebase of @Ku95's documentation of the new renderer onto the latest `pipelined-rendering` branch.
Original PR is #2884.
Co-authored-by: dataphract <dataphract@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
bevy_ecs has several compile_fail tests that assert lifetime safety. In the past, these tests have been green for the wrong reasons (see e.g. #2984). This PR makes sure, that they will fail if the compiler error changes.
## Solution
Use [trybuild](https://crates.io/crates/trybuild) to assert the compiler errors.
The UI tests are in a separate crate that is not part of the Bevy workspace. This is to ensure that they do not break Bevy's crater builds. The tests get executed by the CI workflow on the stable toolchain.
# Objective
- `bevy_ecs` exposes as an optional feature `bevy_reflect`. Disabling it doesn't compile.
- `bevy_asset` exposes as an optional feature `filesystem_watcher`. Disabling it doesn't compile. It is also not possible to disable this feature from Bevy
## Solution
- Fix compilation errors when disabling the default features. Make it possible to disable the feature `filesystem_watcher` from Bevy
# Objective
- Improve error descriptions and help understand how to fix them
- I noticed one today that could be expanded, it seemed like a good starting point
## Solution
- Start something like https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/tree/master/compiler/rustc_error_codes/src/error_codes
- Remove sentence about Rust mutability rules which is not very helpful in the error message
I decided to start the error code with B for Bevy so that they're not confused with error code from rust (which starts with E)
Longer term, there are a few more evolutions that can continue this:
- the code samples should be compiled check, and even executed for some of them to check they have the correct error code in a panic
- the error could be build on a page in the website like https://doc.rust-lang.org/error-index.html
- most panic should have their own error code
# Objective
- Bevy has several `compile_fail` test
- #2254 added `#[derive(Component)]`
- Those tests now fail for a different reason.
- This was not caught as these test still "successfully" failed to compile.
## Solution
- Add `#[derive(Component)]` to the doctest
- Also changed their cfg attribute from `doc` to `doctest`, so that these tests don't appear when running `cargo doc` with `--document-private-items`
#2605 changed the lifetime annotations on `get_component` introducing unsoundness as you could keep the returned borrow even after using the query.
Example unsoundness:
```rust
use bevy::prelude::*;
fn main() {
App::new()
.add_startup_system(startup)
.add_system(unsound)
.run();
}
#[derive(Debug, Component, PartialEq, Eq)]
struct Foo(Vec<u32>);
fn startup(mut c: Commands) {
let e = c.spawn().insert(Foo(vec![10])).id();
c.insert_resource(e);
}
fn unsound(mut q: Query<&mut Foo>, res: Res<Entity>) {
let foo = q.get_component::<Foo>(*res).unwrap();
let mut foo2 = q.iter_mut().next().unwrap();
let first_elem = &foo.0[0];
for _ in 0..16 {
foo2.0.push(12);
}
dbg!(*first_elem);
}
```
output:
`[src/main.rs:26] *first_elem = 0`
Add the entity ID and generation to the expect() message of two
world accessors, to make it easier to debug use-after-free issues.
Coupled with e.g. bevy-inspector-egui which also displays the entity ID,
this makes it much easier to identify what entity is being misused.
# Objective
Make it easier to identity an entity being accessed after being deleted.
## Solution
Augment the error message of some `expect()` call with the entity ID and
generation. Combined with some external tool like `bevy-inspector-egui`, which
also displays the entity ID, this increases the chances to be able to identify
the entity, and therefore find the error that led to a use-after-despawn.
# Objective
- Fixes#2904 (see for context)
## Solution
- Simply hoist span creation out of the threaded task
- Confirmed to solve the issue locally
Now all events have the full span parent tree up through `bevy_ecs::schedule::stage` all the way to `bevy_app::app::bevy_app` (and its parents in bevy-consumer code, if any).
# Objective
- Avoid usages of `format!` that ~immediately get passed to another `format!`. This avoids a temporary allocation and is just generally cleaner.
## Solution
- `bevy_derive::shader_defs` does a `format!("{}", val.to_string())`, which is better written as just `format!("{}", val)`
- `bevy_diagnostic::log_diagnostics_plugin` does a `format!("{:>}", format!(...))`, which is better written as `format!("{:>}", format_args!(...))`
- `bevy_ecs::schedule` does `tracing::info!(..., name = &*format!("{:?}", val))`, which is better written with the tracing shorthand `tracing::info!(..., name = ?val)`
- `bevy_reflect::reflect` does `f.write_str(&format!(...))`, which is better written as `write!(f, ...)` (this could also be written using `f.debug_tuple`, but I opted to maintain alt debug behavior)
- `bevy_reflect::serde::{ser, de}` do `serde::Error::custom(format!(...))`, which is better written as `Error::custom(format_args!(...))`, as `Error::custom` takes `impl Display` and just immediately calls `format!` again
This implements the most minimal variant of #1843 - a derive for marker trait. This is a prerequisite to more complicated features like statically defined storage type or opt-out component reflection.
In order to make component struct's purpose explicit and avoid misuse, it must be annotated with `#[derive(Component)]` (manual impl is discouraged for compatibility). Right now this is just a marker trait, but in the future it might be expanded. Making this change early allows us to make further changes later without breaking backward compatibility for derive macro users.
This already prevents a lot of issues, like using bundles in `insert` calls. Primitive types are no longer valid components as well. This can be easily worked around by adding newtype wrappers and deriving `Component` for them.
One funny example of prevented bad code (from our own tests) is when an newtype struct or enum variant is used. Previously, it was possible to write `insert(Newtype)` instead of `insert(Newtype(value))`. That code compiled, because function pointers (in this case newtype struct constructor) implement `Send + Sync + 'static`, so we allowed them to be used as components. This is no longer the case and such invalid code will trigger a compile error.
Co-authored-by: = <=>
Co-authored-by: TheRawMeatball <therawmeatball@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
Fixes these issues:
- `WorldId`s currently aren't necessarily unique
- I want to guarantee that they're unique to safeguard my librarified version of https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/discussions/2805
- There probably hasn't been a collision yet, but they could technically collide
- `SystemId` isn't used for anything
- It's no longer used now that `Locals` are stored within the `System`.
- `bevy_ecs` depends on rand
## Solution
- Instead of randomly generating `WorldId`s, just use an incrementing atomic counter, panicing on overflow.
- Remove `SystemId`
- We do need to allow Locals for exclusive systems at some point, but exclusive systems couldn't access their own `SystemId` anyway.
- Now that these don't depend on rand, move it to a dev-dependency
## Todo
Determine if `WorldId` should be `u32` based instead
Changed out unwraps to use if let syntax instead. Returning false when None.
Also modified an existing test to encompass these methods
This PR fixes#2828
This changes how render logic is composed to make it much more modular. Previously, all extraction logic was centralized for a given "type" of rendered thing. For example, we extracted meshes into a vector of ExtractedMesh, which contained the mesh and material asset handles, the transform, etc. We looked up bindings for "drawn things" using their index in the `Vec<ExtractedMesh>`. This worked fine for built in rendering, but made it hard to reuse logic for "custom" rendering. It also prevented us from reusing things like "extracted transforms" across contexts.
To make rendering more modular, I made a number of changes:
* Entities now drive rendering:
* We extract "render components" from "app components" and store them _on_ entities. No more centralized uber lists! We now have true "ECS-driven rendering"
* To make this perform well, I implemented #2673 in upstream Bevy for fast batch insertions into specific entities. This was merged into the `pipelined-rendering` branch here: #2815
* Reworked the `Draw` abstraction:
* Generic `PhaseItems`: each draw phase can define its own type of "rendered thing", which can define its own "sort key"
* Ported the 2d, 3d, and shadow phases to the new PhaseItem impl (currently Transparent2d, Transparent3d, and Shadow PhaseItems)
* `Draw` trait and and `DrawFunctions` are now generic on PhaseItem
* Modular / Ergonomic `DrawFunctions` via `RenderCommands`
* RenderCommand is a trait that runs an ECS query and produces one or more RenderPass calls. Types implementing this trait can be composed to create a final DrawFunction. For example the DrawPbr DrawFunction is created from the following DrawCommand tuple. Const generics are used to set specific bind group locations:
```rust
pub type DrawPbr = (
SetPbrPipeline,
SetMeshViewBindGroup<0>,
SetStandardMaterialBindGroup<1>,
SetTransformBindGroup<2>,
DrawMesh,
);
```
* The new `custom_shader_pipelined` example illustrates how the commands above can be reused to create a custom draw function:
```rust
type DrawCustom = (
SetCustomMaterialPipeline,
SetMeshViewBindGroup<0>,
SetTransformBindGroup<2>,
DrawMesh,
);
```
* ExtractComponentPlugin and UniformComponentPlugin:
* Simple, standardized ways to easily extract individual components and write them to GPU buffers
* Ported PBR and Sprite rendering to the new primitives above.
* Removed staging buffer from UniformVec in favor of direct Queue usage
* Makes UniformVec much easier to use and more ergonomic. Completely removes the need for custom render graph nodes in these contexts (see the PbrNode and view Node removals and the much simpler call patterns in the relevant Prepare systems).
* Added a many_cubes_pipelined example to benchmark baseline 3d rendering performance and ensure there were no major regressions during this port. Avoiding regressions was challenging given that the old approach of extracting into centralized vectors is basically the "optimal" approach. However thanks to a various ECS optimizations and render logic rephrasing, we pretty much break even on this benchmark!
* Lifetimeless SystemParams: this will be a bit divisive, but as we continue to embrace "trait driven systems" (ex: ExtractComponentPlugin, UniformComponentPlugin, DrawCommand), the ergonomics of `(Query<'static, 'static, (&'static A, &'static B, &'static)>, Res<'static, C>)` were getting very hard to bear. As a compromise, I added "static type aliases" for the relevant SystemParams. The previous example can now be expressed like this: `(SQuery<(Read<A>, Read<B>)>, SRes<C>)`. If anyone has better ideas / conflicting opinions, please let me know!
* RunSystem trait: a way to define Systems via a trait with a SystemParam associated type. This is used to implement the various plugins mentioned above. I also added SystemParamItem and QueryItem type aliases to make "trait stye" ecs interactions nicer on the eyes (and fingers).
* RenderAsset retrying: ensures that render assets are only created when they are "ready" and allows us to create bind groups directly inside render assets (which significantly simplified the StandardMaterial code). I think ultimately we should swap this out on "asset dependency" events to wait for dependencies to load, but this will require significant asset system changes.
* Updated some built in shaders to account for missing MeshUniform fields
## Objective
The upcoming Bevy Book makes many references to the API documentation of bevy.
Most references belong to the first two chapters of the Bevy Book:
- bevyengine/bevy-website#176
- bevyengine/bevy-website#182
This PR attempts to improve the documentation of `bevy_ecs` and `bevy_app` in order to help readers of the Book who want to delve deeper into technical details.
## Solution
- Add crate and level module documentation
- Document the most important items (basically those included in the preludes), with the following style, where applicable:
- **Summary.** Short description of the item.
- **Second paragraph.** Detailed description of the item, without going too much in the implementation.
- **Code example(s).**
- **Safety or panic notes.**
## Collaboration
Any kind of collaboration is welcome, especially corrections, wording, new ideas and guidelines on where the focus should be put in.
---
### Related issues
- Fixes#2246
This updates the `pipelined-rendering` branch to use the latest `bevy_ecs` from `main`. This accomplishes a couple of goals:
1. prepares for upcoming `custom-shaders` branch changes, which were what drove many of the recent bevy_ecs changes on `main`
2. prepares for the soon-to-happen merge of `pipelined-rendering` into `main`. By including bevy_ecs changes now, we make that merge simpler / easier to review.
I split this up into 3 commits:
1. **add upstream bevy_ecs**: please don't bother reviewing this content. it has already received thorough review on `main` and is a literal copy/paste of the relevant folders (the old folders were deleted so the directories are literally exactly the same as `main`).
2. **support manual buffer application in stages**: this is used to enable the Extract step. we've already reviewed this once on the `pipelined-rendering` branch, but its worth looking at one more time in the new context of (1).
3. **support manual archetype updates in QueryState**: same situation as (2).
# Objective
The vast majority of `.single()` usage I've seen is immediately followed by a `.unwrap()`. Since it seems most people use it without handling the error, I think making it easier to just get what you want fast while also having a more verbose alternative when you want to handle the error could help.
## Solution
Instead of having a lot of `.unwrap()` everywhere, this PR introduces a `try_single()` variant that behaves like the current `.single()` and make the new `.single()` panic on error.
# Objective
Sometimes, the unwraps in `entity_mut` could fail here, if the entity was despawned *before* this command was applied.
The simplest case involves two command buffers:
```rust
use bevy::prelude::*;
fn b(mut commands1: Commands, mut commands2: Commands) {
let id = commands2.spawn().insert_bundle(()).id();
commands1.entity(id).despawn();
}
fn main() {
App::build().add_system(b.system()).run();
}
```
However, a more complicated version arises in the case of ambiguity:
```rust
use std::time::Duration;
use bevy::{app::ScheduleRunnerPlugin, prelude::*};
use rand::Rng;
fn cleanup(mut e: ResMut<Option<Entity>>) {
*e = None;
}
fn sleep_randomly() {
let mut rng = rand::thread_rng();
std:🧵:sleep(Duration::from_millis(rng.gen_range(0..50)));
}
fn spawn(mut commands: Commands, mut e: ResMut<Option<Entity>>) {
*e = Some(commands.spawn().insert_bundle(()).id());
}
fn despawn(mut commands: Commands, e: Res<Option<Entity>>) {
let mut rng = rand::thread_rng();
std:🧵:sleep(Duration::from_millis(rng.gen_range(0..50)));
if let Some(e) = *e {
commands.entity(e).despawn();
}
}
fn main() {
App::build()
.add_system(cleanup.system().label("cleanup"))
.add_system(sleep_randomly.system().label("before_despawn"))
.add_system(despawn.system().after("cleanup").after("before_despawn"))
.add_system(sleep_randomly.system().label("before_spawn"))
.add_system(spawn.system().after("cleanup").after("before_spawn"))
.insert_resource(None::<Entity>)
.add_plugin(ScheduleRunnerPlugin::default())
.run();
}
```
In the cases where this example crashes, it's because `despawn` was ordered before `spawn` in the topological ordering of systems (which determines when buffers are applied). However, `despawn` actually ran *after* `spawn`, because these systems are ambiguous, so the jiggles in the sleeping time triggered a case where this works.
## Solution
- Give a better error message
# Objective
Fix `Option<NonSend<T>>` to work when T isn't `Send`
Fix `Option<NonSendMut<T>>` to work when T isnt in the world.
## Solution
Simple two row fix, properly initialize T in `OptionNonSendState` and remove `T: Component` bound for `Option<NonSendMut<T>>`
also added a rudimentary test
Co-authored-by: Ïvar Källström <ivar.kallstrom@gmail.com>
# Objective
- QueryState is lacking documentation.
Fixes#2090
## Solution
- Provide documentation that mirrors Query (as suggested in #2090) and modify as needed.
Co-authored-by: James Leflang <59455417+jleflang@users.noreply.github.com>
This upstreams the code changes used by the new renderer to enable cross-app Entity reuse:
* Spawning at specific entities
* get_or_spawn: spawns an entity if it doesn't already exist and returns an EntityMut
* insert_or_spawn_batch: the batched equivalent to `world.get_or_spawn(entity).insert_bundle(bundle)`
* Clearing entities and storages
* Allocating Entities with "invalid" archetypes. These entities cannot be queried / are treated as "non existent". They serve as "reserved" entities that won't show up when calling `spawn()`. They must be "specifically spawned at" using apis like `get_or_spawn(entity)`.
In combination, these changes enable the "render world" to clear entities / storages each frame and reserve all "app world entities". These can then be spawned during the "render extract step".
This refactors "spawn" and "insert" code in a way that I think is a massive improvement to legibility and re-usability. It also yields marginal performance wins by reducing some duplicate lookups (less than a percentage point improvement on insertion benchmarks). There is also some potential for future unsafe reduction (by making BatchSpawner and BatchInserter generic). But for now I want to cut down generic usage to a minimum to encourage smaller binaries and faster compiles.
This is currently a draft because it needs more tests (although this code has already had some real-world testing on my custom-shaders branch).
I also fixed the benchmarks (which currently don't compile!) / added new ones to illustrate batching wins.
After these changes, Bevy ECS is basically ready to accommodate the new renderer. I think the biggest missing piece at this point is "sub apps".
This is a rather simple but wide change, and it involves adding a new `bevy_app_macros` crate. Let me know if there is a better way to do any of this!
---
# Objective
- Allow adding and accessing sub-apps by using a label instead of an index
## Solution
- Migrate the bevy label implementation and derive code to the `bevy_utils` and `bevy_macro_utils` crates and then add a new `SubAppLabel` trait to the `bevy_app` crate that is used when adding or getting a sub-app from an app.
# Objective
While implementing a plugin for my rollback networking library, I needed to load/save parts of the world. For this, I made a WorldSnapshot that works quite like the current DynamicScene. Using a TypeRegistry to register component types I want to save/load and then using ReflectComponents methods to add or apply components of the given types.
However, I noticed there is no method to remove components from entities through the ReflectComponent.
## Solution
I added a `remove_component` field to the `ReflectComponent` struct, as well as a `pub fn remove_component(&self, world: &mut World, entity: Entity)` to call that function in `remove_component`. This follows exactly the same pattern all other methods/fields in this struct look like.
This is an example how it could be used (at least how I would use it):
6c003f86f1/src/world_snapshot.rs (L133)
# Objective
Enable using exact World lifetimes during read-only access . This is motivated by the new renderer's need to allow read-only world-only queries to outlive the query itself (but still be constrained by the world lifetime).
For example:
115b170d1f/pipelined/bevy_pbr2/src/render/mod.rs (L774)
## Solution
Split out SystemParam state and world lifetimes and pipe those lifetimes up to read-only Query ops (and add into_inner for Res). According to every safety test I've run so far (except one), this is safe (see the temporary safety test commit). Note that changing the mutable variants to the new lifetimes would allow aliased mutable pointers (try doing that to see how it affects the temporary safety tests).
The new state lifetime on SystemParam does make `#[derive(SystemParam)]` more cumbersome (the current impl requires PhantomData if you don't use both lifetimes). We can make this better by detecting whether or not a lifetime is used in the derive and adjusting accordingly, but that should probably be done in its own pr.
## Why is this a draft?
The new lifetimes break QuerySet safety in one very specific case (see the query_set system in system_safety_test). We need to solve this before we can use the lifetimes given.
This is due to the fact that QuerySet is just a wrapper over Query, which now relies on world lifetimes instead of `&self` lifetimes to prevent aliasing (but in systems, each Query has its own implied lifetime, not a centralized world lifetime). I believe the fix is to rewrite QuerySet to have its own World lifetime (and own the internal reference). This will complicate the impl a bit, but I think it is doable. I'm curious if anyone else has better ideas.
Personally, I think these new lifetimes need to happen. We've gotta have a way to directly tie read-only World queries to the World lifetime. The new renderer is the first place this has come up, but I doubt it will be the last. Worst case scenario we can come up with a second `WorldLifetimeQuery<Q, F = ()>` parameter to enable these read-only scenarios, but I'd rather not add another type to the type zoo.
# Objective
This:
```rust
use bevy::prelude::*;
fn main() {
App::new()
.add_system(test)
.run();
}
fn test(entities: Query<Entity>) {
let mut combinations = entities.iter_combinations_mut();
while let Some([e1, e2]) = combinations.fetch_next() {
dbg!(e1);
}
}
```
fails with the message "the trait bound `bevy::ecs::query::EntityFetch: std::clone::Clone` is not satisfied".
## Solution
It works after adding the naive clone implementation to EntityFetch. I'm not super familiar with ECS internals, so I'd appreciate input on this.
# Objective
There is currently a 1-to-1 mapping between components and real rust types. This means that it is impossible for multiple components to be represented by the same rust type or for a component to not have a rust type at all. This means that component types can't be defined in languages other than rust like necessary for scripting or sandboxed (wasm?) plugins.
## Solution
Refactor `ComponentDescriptor` and `Bundle` to remove `TypeInfo`. `Bundle` now uses `ComponentId` instead. `ComponentDescriptor` is now always created from a rust type instead of through the `TypeInfo` indirection. A future PR may make it possible to construct a `ComponentDescriptor` from it's fields without a rust type being involved.
# Objective
- Remove all the `.system()` possible.
- Check for remaining missing cases.
## Solution
- Remove all `.system()`, fix compile errors
- 32 calls to `.system()` remains, mostly internals, the few others should be removed after #2446
# Objective
While looking at the code of `World`, I noticed two basic functions (`get` and `get_mut`) that are probably called a lot and with simple code that are not `inline`
## Solution
- Add benchmark to check impact
- Add `#[inline]`
```
group this pr main
----- ---- ----
world_entity/50000_entities 1.00 115.9±11.90µs ? ?/sec 1.71 198.5±29.54µs ? ?/sec
world_get/50000_entities_SparseSet 1.00 409.9±46.96µs ? ?/sec 1.18 483.5±36.41µs ? ?/sec
world_get/50000_entities_Table 1.00 391.3±29.83µs ? ?/sec 1.16 455.6±57.85µs ? ?/sec
world_query_for_each/50000_entities_SparseSet 1.02 121.3±18.36µs ? ?/sec 1.00 119.4±13.88µs ? ?/sec
world_query_for_each/50000_entities_Table 1.03 13.8±0.96µs ? ?/sec 1.00 13.3±0.54µs ? ?/sec
world_query_get/50000_entities_SparseSet 1.00 666.9±54.36µs ? ?/sec 1.03 687.1±57.77µs ? ?/sec
world_query_get/50000_entities_Table 1.01 584.4±55.12µs ? ?/sec 1.00 576.3±36.13µs ? ?/sec
world_query_iter/50000_entities_SparseSet 1.01 169.7±19.50µs ? ?/sec 1.00 168.6±32.56µs ? ?/sec
world_query_iter/50000_entities_Table 1.00 26.2±1.38µs ? ?/sec 1.91 50.0±4.40µs ? ?/sec
```
I didn't add benchmarks for the mutable path but I don't see how it could hurt to make it inline too...
This is extracted out of eb8f973646476b4a4926ba644a77e2b3a5772159 and includes some additional changes to remove all references to AppBuilder and fix examples that still used App::build() instead of App::new(). In addition I didn't extract the sub app feature as it isn't ready yet.
You can use `git diff --diff-filter=M eb8f973646476b4a4926ba644a77e2b3a5772159` to find all differences in this PR. The `--diff-filtered=M` filters all files added in the original commit but not in this commit away.
Co-Authored-By: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
This logic was in both `remove_bundle` and ` remove_bundle_intersection` but only differed by whether we call `.._forget_missing_..` or `.._drop_missing_..`
* bevy_pbr2: Add support for most of the StandardMaterial textures
Normal maps are not included here as they require tangents in a vertex attribute.
* bevy_pbr2: Ensure RenderCommandQueue is ready for PbrShaders init
* texture_pipelined: Add a light to the scene so we can see stuff
* WIP bevy_pbr2: back to front sorting hack
* bevy_pbr2: Uniform control flow for texture sampling in pbr.frag
From 'fintelia' on the Bevy Render Rework Round 2 discussion:
"My understanding is that GPUs these days never use the "execute both branches
and select the result" strategy. Rather, what they do is evaluate the branch
condition on all threads of a warp, and jump over it if all of them evaluate to
false. If even a single thread needs to execute the if statement body, however,
then the remaining threads are paused until that is completed."
* bevy_pbr2: Simplify texture and sampler names
The StandardMaterial_ prefix is no longer needed
* bevy_pbr2: Match default 'AmbientColor' of current bevy_pbr for now
* bevy_pbr2: Convert from non-linear to linear sRGB for the color uniform
* bevy_pbr2: Add pbr_pipelined example
* Fix view vector in pbr frag to work in ortho
* bevy_pbr2: Use a 90 degree y fov and light range projection for lights
* bevy_pbr2: Add AmbientLight resource
* bevy_pbr2: Convert PointLight color to linear sRGB for use in fragment shader
* bevy_pbr2: pbr.frag: Rename PointLight.projection to view_projection
The uniform contains the view_projection matrix so this was incorrect.
* bevy_pbr2: PointLight is an OmniLight as it has a radius
* bevy_pbr2: Factoring out duplicated code
* bevy_pbr2: Implement RenderAsset for StandardMaterial
* Remove unnecessary texture and sampler clones
* fix comment formatting
* remove redundant Buffer:from
* Don't extract meshes when their material textures aren't ready
* make missing textures in the queue step an error
Co-authored-by: Aevyrie <aevyrie@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Continue work of #2398 and friends.
- Make `.system()` optional in chaining.
## Solution
- Slight change to `IntoChainSystem` signature and implementation.
- Remove some usages of `.system()` in the chaining example, to verify the implementation.
---
I swear, I'm not splitting these up on purpose, I just legit forgot about most of the things where `System` appears in public API, and my trait usage explorer mingles that with the gajillion internal uses.
In case you're wondering what happened to part 5, #2446 ate it.
# Objective
- Currently `Commands` are quite slow due to the need to allocate for each command and wrap it in a `Box<dyn Command>`.
- For example:
```rust
fn my_system(mut cmds: Commands) {
cmds.spawn().insert(42).insert(3.14);
}
```
will have 3 separate `Box<dyn Command>` that need to be allocated and ran.
## Solution
- Utilize a specialized data structure keyed `CommandQueueInner`.
- The purpose of `CommandQueueInner` is to hold a collection of commands in contiguous memory.
- This allows us to store each `Command` type contiguously in memory and quickly iterate through them and apply the `Command::write` trait function to each element.
In #2034, the `Remove` Command did not get the same treatment as the rest of the commands. There's no discussion saying it shouldn't have public fields, so I am assuming it was an oversight. This fixes that oversight.
# Objective
- Continue work of #2398 and friends.
- Make `.system()` optional in run criteria APIs.
## Solution
- Slight change to `RunCriteriaDescriptorCoercion` signature and implementors.
- Implement `IntoRunCriteria` for `IntoSystem` rather than `System`.
- Remove some usages of `.system()` with run criteria in tests of `stage.rs`, to verify the implementation.
# Objective
Beginners semi-regularly appear on the Discord asking for help with using `QuerySet` when they have a system with conflicting data access.
This happens because the Resulting Panic message only mentions `QuerySet` as a solution, even if in most cases `Without<T>` was enough to solve the problem.
## Solution
Mention the usage of `Without<T>` to create disjoint queries as an alternative to `QuerySet`
## Open Questions
- Is `disjoint` a too technical/mathematical word?
- Should `Without<T>` be mentioned before or after `QuerySet`?
- Before: Using `Without<T>` should be preferred and mentioning it first reinforces this for a reader.
- After: The Panics can be very long and a Reader could skip to end and only see the `QuerySet`
Co-authored-by: MinerSebas <66798382+MinerSebas@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
- Continue work of #2398 and #2403.
- Make `.system()` syntax optional when using `.config()` API.
## Solution
- Introduce new prelude trait, `ConfigurableSystem`, that shorthands `my_system.system().config(...)` as `my_system.config(...)`.
- Expand `configure_system_local` test to also cover the new syntax.
# Objective
- Add inline documentation for `StorageType`.
- Currently the README in `bevy_ecs` provides docs for `StorageType`, however, adding addition inline docs makes it simpler for users who are actively reading the source code.
## Solution
- Add inline docs.
# Objective
- Extend work done in #2398.
- Make `.system()` syntax optional when using system descriptor API.
## Solution
- Slight change to `ParallelSystemDescriptorCoercion` signature and implementors.
---
I haven't touched exclusive systems, because it looks like the only two other solutions are going back to doubling our system insertion methods, or starting to lean into stageless. The latter will invalidate the former, so I think exclusive systems should remian pariahs until stageless.
I can grep & nuke `.system()` thorughout the codebase now, which might take a while, or we can do that in subsequent PR(s).
This can be your 6 months post-christmas present.
# Objective
- Make `.system` optional
- yeet
- It's ugly
- Alternative title: `.system` is dead; long live `.system`
- **yeet**
## Solution
- Use a higher ranked lifetime, and some trait magic.
N.B. This PR does not actually remove any `.system`s, except in a couple of examples. Once this is merged we can do that piecemeal across crates, and decide on syntax for labels.
# Objective
Currently, you can add `Option<Res<T>` or `Option<ResMut<T>` as a SystemParam, if the Resource could potentially not exist, but this functionality doesn't exist for `NonSend` and `NonSendMut`
## Solution
Adds implementations to use `Option<NonSend<T>>` and Option<NonSendMut<T>> as SystemParams.
# Objective
- CI jobs are starting to fail due to `clippy::bool-assert-comparison` and `clippy::single_component_path_imports` being triggered.
## Solution
- Fix all uses where `asset_eq!(<condition>, <bool>)` could be replace by `assert!`
- Move the `#[allow()]` for `single_component_path_imports` to `#![allow()]` at the start of the files.
# Objective
- The `DetectChanges` trait is used for types that detect change on mutable access (such as `ResMut`, `Mut`, etc...)
- `DetectChanges` was not implemented for `NonSendMut`
## Solution
- implement `NonSendMut` in terms of `DetectChanges`
# Objective
Currently, you can't call `is_added` or `is_changed` on a `NonSend` SystemParam, unless the Resource is a Component (implements `Send` and `Sync`).
This defeats the purpose of providing change detection for NonSend Resources.
While fixing this, I also noticed that `NonSend` does not have a bound at all on its struct.
## Solution
Change the bounds of `T` to always be `'static`.
## Problem
- The `Query` struct does not provide an easy way to check if it is empty.
- Specifically, users have to use `.iter().peekable()` or `.iter().next().is_none()` which is not very ergonomic.
- Fixes: #2270
## Solution
- Implement an `is_empty` function for queries to more easily check if the query is empty.
This enables `SystemParams` to be used outside of function systems. Anything can create and store `SystemState`, which enables efficient "param state cached" access to `SystemParams`.
It adds a `ReadOnlySystemParamFetch` trait, which enables safe `SystemState::get` calls without unique world access.
I renamed the old `SystemState` to `SystemMeta` to enable us to mirror the `QueryState` naming convention (but I'm happy to discuss alternative names if people have other ideas). I initially pitched this as `ParamState`, but given that it needs to include full system metadata, that doesn't feel like a particularly accurate name.
```rust
#[derive(Eq, PartialEq, Debug)]
struct A(usize);
#[derive(Eq, PartialEq, Debug)]
struct B(usize);
let mut world = World::default();
world.insert_resource(A(42));
world.spawn().insert(B(7));
// we get nice lifetime elision when declaring the type on the left hand side
let mut system_state: SystemState<(Res<A>, Query<&B>)> = SystemState::new(&mut world);
let (a, query) = system_state.get(&world);
assert_eq!(*a, A(42), "returned resource matches initial value");
assert_eq!(
*query.single().unwrap(),
B(7),
"returned component matches initial value"
);
// mutable system params require unique world access
let mut system_state: SystemState<(ResMut<A>, Query<&mut B>)> = SystemState::new(&mut world);
let (a, query) = system_state.get_mut(&mut world);
// static lifetimes are required when declaring inside of structs
struct SomeContainer {
state: SystemState<(Res<'static, A>, Res<'static, B>)>
}
// this can be shortened using type aliases, which will be useful for complex param tuples
type MyParams<'a> = (Res<'a, A>, Res<'a, B>);
struct SomeContainer {
state: SystemState<MyParams<'static>>
}
// It is the user's responsibility to call SystemState::apply(world) for parameters that queue up work
let mut system_state: SystemState<(Commands, Query<&B>)> = SystemState::new(&mut world);
{
let (mut commands, query) = system_state.get(&world);
commands.insert_resource(3.14);
}
system_state.apply(&mut world);
```
## Future Work
* Actually use SystemState inside FunctionSystem. This would be trivial, but it requires FunctionSystem to wrap SystemState in Option in its current form (which complicates system metadata lookup). I'd prefer to hold off until we adopt something like the later designs linked in #1364, which enable us to contruct Systems using a World reference (and also remove the need for `.system`).
* Consider a "scoped" approach to automatically call SystemState::apply when systems params are no longer being used (either a container type with a Drop impl, or a function that takes a closure for user logic operating on params).
When dropping the data, we originally only checked the size of an individual item instead of the size of the allocation. However with a capacity of 0, we attempt to deallocate a pointer which was not the result of allocation. That is, an item of `Layout { size_: 8, align_: 8 }` produces an array of `Layout { size_: 0, align_: 8 }` when `capacity = 0`.
Fixes#2294
## Objective
- Fixes: #2275
- `Assets` were being flagged as 'changed' each frame regardless of if the assets were actually being updated.
## Solution
- Only have `Assets` change detection be triggered when the collection is actually modified.
- This includes utilizing `ResMut` further down the stack instead of a `&mut Assets` directly.
Continuing the work on reducing the safety footguns in the code, I've removed one extra `UnsafeCell` in favour of safe `Cell` usage inisde `ComponentTicks`. That change led to discovery of misbehaving component insert logic, where data wasn't properly dropped when overwritten. Apart from that being fixed, some method names were changed to better convey the "initialize new allocation" and "replace existing allocation" semantic.
Depends on #2221, I will rebase this PR after the dependency is merged. For now, review just the last commit.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
`ResMut`, `Mut` and `ReflectMut` all share very similar code for change detection.
This PR is a first pass at refactoring these implementation and removing a lot of the duplicated code.
Note, this introduces a new trait `ChangeDetectable`.
Please feel free to comment away and let me know what you think!
I've noticed that we are overusing interior mutability of the Table data, where in many cases we already own a unique reference to it. That prompted a slight refactor aiming to reduce number of safety constraints that must be manually upheld. Now the majority of those are just about avoiding bound checking, which is relatively easy to prove right.
Another aspect is reducing the complexity of Table struct. Notably, we don't ever use archetypes stored there, so this whole thing goes away. Capacity and grow amount were mostly superficial, as we are already using Vecs inside anyway, so I've got rid of those too. Now the overall table capacity is being driven by the internal entity Vec capacity. This has a side effect of automatically implementing exponential growth pattern for BitVecs reallocations inside Table, which to my measurements slightly improves performance in tests that are heavy on inserts. YMMV, but I hope that those tests were at least remotely correct.
The previous implementation of `Events::extend` iterated through each event and manually `sent` it via `Events:;send`.
However, this could be a minor performance hit since calling `Vec::push` in a loop is not optimal.
This refactors the code to use `Vec::extend`.
This new api stems from this [discord conversation](https://discord.com/channels/691052431525675048/742569353878437978/844057268172357663).
This exposes a public facing `set_changed` method on `ResMut` and `Mut`.
As a side note: `ResMut` and `Mut` have a lot of duplicated code, I have a PR I may put up later that refactors these commonalities into a trait.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
- simplified code around archetype generations a little bit, as the special case value is not actually needed
- removed unnecessary UnsafeCell around pointer value that is never updated through shared references
- fixed and added a test for correct drop behaviour when removing sparse components through remove_bundle command
While trying to figure out how to implement a `SystemParam`, I spent a
long time looking for a feature that would do exactly what `Config`
does. I ignored it at first because all the examples I could find used
`()` and I couldn't see a way to modify it.
This is documented in other places, but `Config` is a logical place to
include some breadcrumbs. I've added some text that gives a brief
overview of what `Config` is for, and links to the existing docs on
`FunctionSystem::config` for more details.
This would have saved me from embarrassing myself by filing https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/2178.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
During PR #2046 @cart suggested that the `(): ()` notation is less legible than `_input: ()`. The first notation still managed to slip in though. This PR applies the second writing.
Related to [discussion on discord](https://discord.com/channels/691052431525675048/742569353878437978/824731187724681289)
With const generics, it is now possible to write generic iterator over multiple entities at once.
This enables patterns of query iterations like
```rust
for [e1, e2, e3] in query.iter_combinations() {
// do something with relation of all three entities
}
```
The compiler is able to infer the correct iterator for given size of array, so either of those work
```rust
for [e1, e2] in query.iter_combinations() { ... }
for [e1, e2, e3] in query.iter_combinations() { ... }
```
This feature can be very useful for systems like collision detection.
When you ask for permutations of size K of N entities:
- if K == N, you get one result of all entities
- if K < N, you get all possible subsets of N with size K, without repetition
- if K > N, the result set is empty (no permutation of size K exist)
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
This can save users from having to type `&*X` all the time at the cost of some complexity in the type signature. For instance, this allows me to accommodate @jakobhellermann's suggestion in #1799 without requiring users to type `&*windows` 99% of the time.
`ParallelSystemContainer`'s `system` pointer was extracted from box, but it was never deallocated. This change adds missing drop implementation that cleans up that memory.
The first commit monomorphizes `add_system_inner` which I think was intended to be monomorphized anyway. The second commit moves the type argument of `GraphNode` to an associated type.
In response to #2023, here is a draft for a PR.
Fixes#2023
I've added an example to show how to use `WithBundle`, and also to test it out.
Right now there is a bug: If a bundle and a query are "the same", then it doesn't filter out
what it needs to filter out.
Example:
```
Print component initated from bundle.
[examples/ecs/query_bundle.rs:57] x = Dummy( <========= This should not get printed
111,
)
[examples/ecs/query_bundle.rs:57] x = Dummy(
222,
)
Show all components
[examples/ecs/query_bundle.rs:50] x = Dummy(
111,
)
[examples/ecs/query_bundle.rs:50] x = Dummy(
222,
)
```
However, it behaves the right way, if I add one more component to the bundle,
so the query and the bundle doesn't look the same:
```
Print component initated from bundle.
[examples/ecs/query_bundle.rs:57] x = Dummy(
222,
)
Show all components
[examples/ecs/query_bundle.rs:50] x = Dummy(
111,
)
[examples/ecs/query_bundle.rs:50] x = Dummy(
222,
)
```
I hope this helps. I'm definitely up for tinkering with this, and adding anything that I'm asked to add
or change.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
I'm using Bevy ECS in a project of mine and I'd like to do world changes asynchronously.
The current public API for creating entities, `Commands` , has a lifetime that restricts it from being sent across threads. `CommandQueue` on the other hand is a Vec of commands that can be later ran on a World.
So far this is all public, but the commands themselves are private API. I know the intented use is with `Commands`, but that's not possible for my use case as I mentioned, and so I simply copied over the code for the commands I need and it works. Obviously, this isn't a nice solution, so I'd like to ask if it's not out of scope to make the commands public?
The documentation for `ShouldRun` doesn't completely explain what each of the variants you can return does. For instance, it isn't very clear that looping systems aren't executed again until after all the systems in a stage have had a chance to run.
This PR adds to the documentation for `ShouldRun`, and hopefully clarifies what is happening during a stage's execution when run criteria are checked and systems are being executed.
Some panic messages for systems include the system name, but there's a few panic messages which do not. This PR adds the system name for the remaining panic messages.
This is a continuation of the work done in #1864.
Related: #1846
This shrinks breakout from 316k to 310k when using `--feature dynamic`.
I haven't run the ecs benchmark to test performance as my laptop is too noisy for reliable benchmarking.
We discussed with @alice-i-cecile privately on iterators and agreed that making a custom ordered iterator over query makes no sense since materialization is required anyway and it's better to reuse existing components or code. Therefore, just adding an example to the documentation as requested.
Fixes#1470.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
This includes a lot of single line comments where either saying more wasn't helpful or due to me not knowing enough about things yet to be able to go more indepth. Proofreading is very much welcome.
Fixes#1846
Got scared of the other "Requested resource does not exist" error at line 395 in `system_param.rs`, under `impl<'a, T: Component> SystemParamFetch<'a> for ResMutState<T> {`. Someone with better knowledge of the code might be able to go in and improve that one.
Fixes#1809. It makes it also possible to use `derive` for `SystemParam` inside ECS and avoid manual implementation. An alternative solution to macro changes is to use `use crate as bevy_ecs;` in `event.rs`.
fixes#1772
1st commit: the limit was at 11 as the macro was not using a range including the upper end. I changed that as it feels the purpose of the macro is clearer that way.
2nd commit: as suggested in the `// TODO`, I added a `Config` trait to go to 16 elements tuples. This means that if someone has a custom system parameter with a config that is not a tuple or an `Option`, they will have to implement `Config` for it instead of the standard `Default`.
I think [collection, thing_removed_from_collection] is a more natural order than [thing_removed_from_collection, collection]. Just a small tweak that I think we should include in 0.5.
Fixes#1753.
The problem was introduced while reworking the logic around stages' own criteria. Before #1675 they used to be stored and processed inline with the systems' criteria, and systems without criteria used that of their stage. After, criteria-less systems think they should run, always. This PR more or less restores previous behavior; a less cludge solution can wait until after 0.5 - ideally, until stageless.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
This is intended to help protect users against #1671. It doesn't resolve the issue, but I think its a good stop-gap solution for 0.5. A "full" fix would be very involved (and maybe not worth the added complexity).
Removing the checks on this line https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/main/crates/bevy_sprite/src/frustum_culling.rs#L64 and running the "many_sprites" example revealed two corner case bugs in bevy_ecs. The first, a simple and honest missed line introduced in #1471. The other, an insidious monster that has been there since the ECS v2 rewrite, just waiting for the time to strike:
1. #1471 accidentally removed the "insert" line for sparse set components with the "mutated" bundle state. Re-adding it fixes the problem. I did a slight refactor here to make the implementation simpler and remove a branch.
2. The other issue is nastier. ECS v2 added an "archetype graph". When determining what components were added/mutated during an archetype change, we read the FromBundle edge (which encodes this state) on the "new" archetype. The problem is that unlike "add edges" which are guaranteed to be unique for a given ("graph node", "bundle id") pair, FromBundle edges are not necessarily unique:
```rust
// OLD_ARCHETYPE -> NEW_ARCHETYPE
// [] -> [usize]
e.insert(2usize);
// [usize] -> [usize, i32]
e.insert(1i32);
// [usize, i32] -> [usize, i32]
e.insert(1i32);
// [usize, i32] -> [usize]
e.remove::<i32>();
// [usize] -> [usize, i32]
e.insert(1i32);
```
Note that the second `e.insert(1i32)` command has a different "archetype graph edge" than the first, but they both lead to the same "new archetype".
The fix here is simple: just remove FromBundle edges because they are broken and store the information in the "add edges", which are guaranteed to be unique.
FromBundle edges were added to cut down on the number of archetype accesses / make the archetype access patterns nicer. But benching this change resulted in no significant perf changes and the addition of get_2_mut() for archetypes resolves the access pattern issue.
In the current impl, next clears out the entire stack and replaces it with a new state. This PR moves this functionality into a replace method, and changes the behavior of next to only change the top state.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
I'm opening this prematurely; consider this an RFC that predates RFCs and therefore not super-RFC-like.
This PR does two "big" things: decouple run criteria from system sets, reimagine system sets as weapons of mass system description.
### What it lets us do:
* Reuse run criteria within a stage.
* Pipe output of one run criteria as input to another.
* Assign labels, dependencies, run criteria, and ambiguity sets to many systems at the same time.
### Things already done:
* Decoupled run criteria from system sets.
* Mass system description superpowers to `SystemSet`.
* Implemented `RunCriteriaDescriptor`.
* Removed `VirtualSystemSet`.
* Centralized all run criteria of `SystemStage`.
* Extended system descriptors with per-system run criteria.
* `.before()` and `.after()` for run criteria.
* Explicit order between state driver and related run criteria. Fixes#1672.
* Opt-in run criteria deduplication; default behavior is to panic.
* Labels (not exposed) for state run criteria; state run criteria are deduplicated.
### API issues that need discussion:
* [`FixedTimestep::step(1.0).label("my label")`](eaccf857cd/crates/bevy_ecs/src/schedule/run_criteria.rs (L120-L122)) and [`FixedTimestep::step(1.0).with_label("my label")`](eaccf857cd/crates/bevy_core/src/time/fixed_timestep.rs (L86-L89)) are both valid but do very different things.
---
I will try to maintain this post up-to-date as things change. Do check the diffs in "edited" thingy from time to time.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
Resolves#1253#1562
This makes the Commands apis consistent with World apis. This moves to a "type state" pattern (like World) where the "current entity" is stored in an `EntityCommands` builder.
In general this tends to cuts down on indentation and line count. It comes at the cost of needing to type `commands` more and adding more semicolons to terminate expressions.
I also added `spawn_bundle` to Commands because this is a common enough operation that I think its worth providing a shorthand.
Fixes#1692
Alternative to #1696
This ensures that the capacity actually grows in increments of grow_amount, and also ensures that Table capacity is always <= column and entity vec capacity.
Debug logs that describe the new logic (running the example in #1692)
[out.txt](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/files/6173808/out.txt)
# Problem Definition
The current change tracking (via flags for both components and resources) fails to detect changes made by systems that are scheduled to run earlier in the frame than they are.
This issue is discussed at length in [#68](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/68) and [#54](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/54).
This is very much a draft PR, and contributions are welcome and needed.
# Criteria
1. Each change is detected at least once, no matter the ordering.
2. Each change is detected at most once, no matter the ordering.
3. Changes should be detected the same frame that they are made.
4. Competitive ergonomics. Ideally does not require opting-in.
5. Low CPU overhead of computation.
6. Memory efficient. This must not increase over time, except where the number of entities / resources does.
7. Changes should not be lost for systems that don't run.
8. A frame needs to act as a pure function. Given the same set of entities / components it needs to produce the same end state without side-effects.
**Exact** change-tracking proposals satisfy criteria 1 and 2.
**Conservative** change-tracking proposals satisfy criteria 1 but not 2.
**Flaky** change tracking proposals satisfy criteria 2 but not 1.
# Code Base Navigation
There are three types of flags:
- `Added`: A piece of data was added to an entity / `Resources`.
- `Mutated`: A piece of data was able to be modified, because its `DerefMut` was accessed
- `Changed`: The bitwise OR of `Added` and `Changed`
The special behavior of `ChangedRes`, with respect to the scheduler is being removed in [#1313](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/1313) and does not need to be reproduced.
`ChangedRes` and friends can be found in "bevy_ecs/core/resources/resource_query.rs".
The `Flags` trait for Components can be found in "bevy_ecs/core/query.rs".
`ComponentFlags` are stored in "bevy_ecs/core/archetypes.rs", defined on line 446.
# Proposals
**Proposal 5 was selected for implementation.**
## Proposal 0: No Change Detection
The baseline, where computations are performed on everything regardless of whether it changed.
**Type:** Conservative
**Pros:**
- already implemented
- will never miss events
- no overhead
**Cons:**
- tons of repeated work
- doesn't allow users to avoid repeating work (or monitoring for other changes)
## Proposal 1: Earlier-This-Tick Change Detection
The current approach as of Bevy 0.4. Flags are set, and then flushed at the end of each frame.
**Type:** Flaky
**Pros:**
- already implemented
- simple to understand
- low memory overhead (2 bits per component)
- low time overhead (clear every flag once per frame)
**Cons:**
- misses systems based on ordering
- systems that don't run every frame miss changes
- duplicates detection when looping
- can lead to unresolvable circular dependencies
## Proposal 2: Two-Tick Change Detection
Flags persist for two frames, using a double-buffer system identical to that used in events.
A change is observed if it is found in either the current frame's list of changes or the previous frame's.
**Type:** Conservative
**Pros:**
- easy to understand
- easy to implement
- low memory overhead (4 bits per component)
- low time overhead (bit mask and shift every flag once per frame)
**Cons:**
- can result in a great deal of duplicated work
- systems that don't run every frame miss changes
- duplicates detection when looping
## Proposal 3: Last-Tick Change Detection
Flags persist for two frames, using a double-buffer system identical to that used in events.
A change is observed if it is found in the previous frame's list of changes.
**Type:** Exact
**Pros:**
- exact
- easy to understand
- easy to implement
- low memory overhead (4 bits per component)
- low time overhead (bit mask and shift every flag once per frame)
**Cons:**
- change detection is always delayed, possibly causing painful chained delays
- systems that don't run every frame miss changes
- duplicates detection when looping
## Proposal 4: Flag-Doubling Change Detection
Combine Proposal 2 and Proposal 3. Differentiate between `JustChanged` (current behavior) and `Changed` (Proposal 3).
Pack this data into the flags according to [this implementation proposal](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/68#issuecomment-769174804).
**Type:** Flaky + Exact
**Pros:**
- allows users to acc
- easy to implement
- low memory overhead (4 bits per component)
- low time overhead (bit mask and shift every flag once per frame)
**Cons:**
- users must specify the type of change detection required
- still quite fragile to system ordering effects when using the flaky `JustChanged` form
- cannot get immediate + exact results
- systems that don't run every frame miss changes
- duplicates detection when looping
## [SELECTED] Proposal 5: Generation-Counter Change Detection
A global counter is increased after each system is run. Each component saves the time of last mutation, and each system saves the time of last execution. Mutation is detected when the component's counter is greater than the system's counter. Discussed [here](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/68#issuecomment-769174804). How to handle addition detection is unsolved; the current proposal is to use the highest bit of the counter as in proposal 1.
**Type:** Exact (for mutations), flaky (for additions)
**Pros:**
- low time overhead (set component counter on access, set system counter after execution)
- robust to systems that don't run every frame
- robust to systems that loop
**Cons:**
- moderately complex implementation
- must be modified as systems are inserted dynamically
- medium memory overhead (4 bytes per component + system)
- unsolved addition detection
## Proposal 6: System-Data Change Detection
For each system, track which system's changes it has seen. This approach is only worth fully designing and implementing if Proposal 5 fails in some way.
**Type:** Exact
**Pros:**
- exact
- conceptually simple
**Cons:**
- requires storing data on each system
- implementation is complex
- must be modified as systems are inserted dynamically
## Proposal 7: Total-Order Change Detection
Discussed [here](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/68#issuecomment-754326523). This proposal is somewhat complicated by the new scheduler, but I believe it should still be conceptually feasible. This approach is only worth fully designing and implementing if Proposal 5 fails in some way.
**Type:** Exact
**Pros:**
- exact
- efficient data storage relative to other exact proposals
**Cons:**
- requires access to the scheduler
- complex implementation and difficulty grokking
- must be modified as systems are inserted dynamically
# Tests
- We will need to verify properties 1, 2, 3, 7 and 8. Priority: 1 > 2 = 3 > 8 > 7
- Ideally we can use identical user-facing syntax for all proposals, allowing us to re-use the same syntax for each.
- When writing tests, we need to carefully specify order using explicit dependencies.
- These tests will need to be duplicated for both components and resources.
- We need to be sure to handle cases where ambiguous system orders exist.
`changing_system` is always the system that makes the changes, and `detecting_system` always detects the changes.
The component / resource changed will be simple boolean wrapper structs.
## Basic Added / Mutated / Changed
2 x 3 design:
- Resources vs. Components
- Added vs. Changed vs. Mutated
- `changing_system` runs before `detecting_system`
- verify at the end of tick 2
## At Least Once
2 x 3 design:
- Resources vs. Components
- Added vs. Changed vs. Mutated
- `changing_system` runs after `detecting_system`
- verify at the end of tick 2
## At Most Once
2 x 3 design:
- Resources vs. Components
- Added vs. Changed vs. Mutated
- `changing_system` runs once before `detecting_system`
- increment a counter based on the number of changes detected
- verify at the end of tick 2
## Fast Detection
2 x 3 design:
- Resources vs. Components
- Added vs. Changed vs. Mutated
- `changing_system` runs before `detecting_system`
- verify at the end of tick 1
## Ambiguous System Ordering Robustness
2 x 3 x 2 design:
- Resources vs. Components
- Added vs. Changed vs. Mutated
- `changing_system` runs [before/after] `detecting_system` in tick 1
- `changing_system` runs [after/before] `detecting_system` in tick 2
## System Pausing
2 x 3 design:
- Resources vs. Components
- Added vs. Changed vs. Mutated
- `changing_system` runs in tick 1, then is disabled by run criteria
- `detecting_system` is disabled by run criteria until it is run once during tick 3
- verify at the end of tick 3
## Addition Causes Mutation
2 design:
- Resources vs. Components
- `adding_system_1` adds a component / resource
- `adding system_2` adds the same component / resource
- verify the `Mutated` flag at the end of the tick
- verify the `Added` flag at the end of the tick
First check tests for: https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/333
Second check tests for: https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/1443
## Changes Made By Commands
- `adding_system` runs in Update in tick 1, and sends a command to add a component
- `detecting_system` runs in Update in tick 1 and 2, after `adding_system`
- We can't detect the changes in tick 1, since they haven't been processed yet
- If we were to track these changes as being emitted by `adding_system`, we can't detect the changes in tick 2 either, since `detecting_system` has already run once after `adding_system` :(
# Benchmarks
See: [general advice](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/master/docs/profiling.md), [Criterion crate](https://github.com/bheisler/criterion.rs)
There are several critical parameters to vary:
1. entity count (1 to 10^9)
2. fraction of entities that are changed (0% to 100%)
3. cost to perform work on changed entities, i.e. workload (1 ns to 1s)
1 and 2 should be varied between benchmark runs. 3 can be added on computationally.
We want to measure:
- memory cost
- run time
We should collect these measurements across several frames (100?) to reduce bootup effects and accurately measure the mean, variance and drift.
Entity-component change detection is much more important to benchmark than resource change detection, due to the orders of magnitude higher number of pieces of data.
No change detection at all should be included in benchmarks as a second control for cases where missing changes is unacceptable.
## Graphs
1. y: performance, x: log_10(entity count), color: proposal, facet: performance metric. Set cost to perform work to 0.
2. y: run time, x: cost to perform work, color: proposal, facet: fraction changed. Set number of entities to 10^6
3. y: memory, x: frames, color: proposal
# Conclusions
1. Is the theoretical categorization of the proposals correct according to our tests?
2. How does the performance of the proposals compare without any load?
3. How does the performance of the proposals compare with realistic loads?
4. At what workload does more exact change tracking become worth the (presumably) higher overhead?
5. When does adding change-detection to save on work become worthwhile?
6. Is there enough divergence in performance between the best solutions in each class to ship more than one change-tracking solution?
# Implementation Plan
1. Write a test suite.
2. Verify that tests fail for existing approach.
3. Write a benchmark suite.
4. Get performance numbers for existing approach.
5. Implement, test and benchmark various solutions using a Git branch per proposal.
6. Create a draft PR with all solutions and present results to team.
7. Select a solution and replace existing change detection.
Co-authored-by: Brice DAVIER <bricedavier@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
An alternative to StateStages that uses SystemSets. Also includes pop and push operations since this was originally developed for my personal project which needed them.
Fixes all warnings from `cargo doc --all`.
Those related to code blocks were introduced in #1612, but re-formatting using the experimental features in `rustfmt.toml` doesn't seem to reintroduce them.
These are largely targeted at beginners, as `Entity`, `Component` and `System` are the most obvious terms to search when first getting introduced to Bevy.
Removes `get_unchecked` and `get_unchecked_mut` from `Tables` and `Archetypes` collections in favor of safe Index implementations. This fixes a safety error in `Archetypes::get_id_or_insert()` (which previously relied on TableId being valid to be safe ... the alternative was to make that method unsafe too). It also cuts down on a lot of unsafe and makes the code easier to look at. I'm not sure what changed since the last benchmark, but these numbers are more favorable than my last tests of similar changes. I didn't include the Components collection as those severely killed perf last time I tried. But this does inspire me to try again (just in a separate pr)!
Note that the `simple_insert/bevy_unbatched` benchmark fluctuates a lot on both branches (this was also true for prior versions of bevy). It seems like the allocator has more variance for many small allocations. And `sparse_frag_iter/bevy` operates on such a small scale that 10% fluctuations are common.
Some benches do take a small hit here, but I personally think its worth it.
This also fixes a safety error in Query::for_each_mut, which needed to mutably borrow Query (aaahh!).
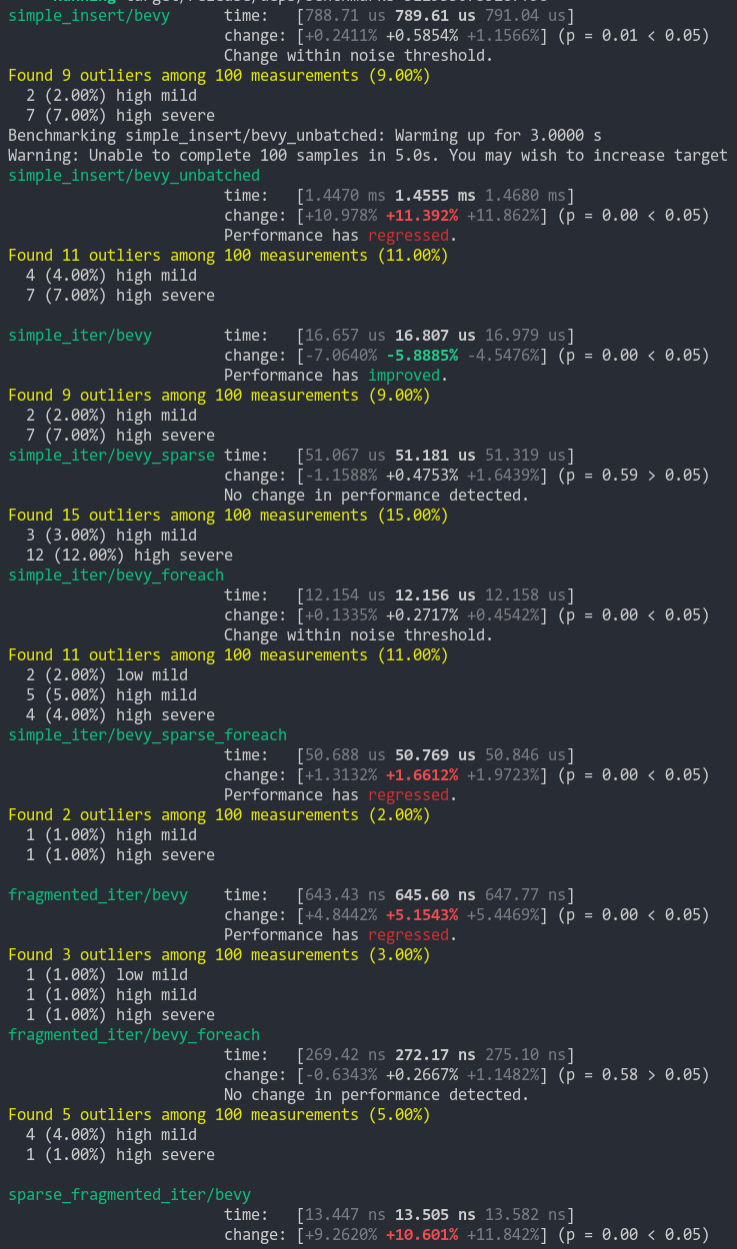
* Adds labels and orderings to systems that need them (uses the new many-to-many labels for InputSystem)
* Removes the Event, PreEvent, Scene, and Ui stages in favor of First, PreUpdate, and PostUpdate (there is more collapsing potential, such as the Asset stages and _maybe_ removing First, but those have more nuance so they should be handled separately)
* Ambiguity detection now prints component conflicts
* Removed broken change filters from flex calculation (which implicitly relied on the z-update system always modifying translation.z). This will require more work to make it behave as expected so i just removed it (and it was already doing this work every frame).
* Systems can now have more than one label attached to them.
* System labels no longer have to be unique in the stage.
Code like this is now possible:
```rust
SystemStage::parallel()
.with_system(system_0.system().label("group one").label("first"))
.with_system(system_1.system().label("group one").after("first"))
.with_system(system_2.system().after("group one"))
```
I've opted to use only the system name in ambiguity reporting, which previously was only a fallback; this, obviously, is because labels aren't one-to-one with systems anymore. We could allow users to name systems to improve this; we'll then have to think about whether or not we want to allow using the name as a label (this would, effectively, introduce implicit labelling, not all implications of which are clear to me yet wrt many-to-many labels).
Dependency cycle errors are reported using the system names and only the labels that form the cycle, with each system-system "edge" in the cycle represented as one or several labels.
Slightly unrelated: `.before()` and `.after()` with a label not attached to any system no longer crashes, and logs a warning instead. This is necessary to, for example, allow plugins to specify execution order with systems of potentially missing other plugins.
Adds `get_unique` and `get_unique_mut` to extend the query api and cover a common use case. Also establishes a second impl block where non-core APIs that don't access the internal fields of queries can live.
This allows users to write systems that do not panic if a resource does not exist at runtime (such as if it has not been inserted yet).
This is a copy-paste of the impls for `Res` and `ResMut`, with an extra check to see if the resource exists.
There might be a cleaner way to do it than this check. I don't know.
I've also added a clearer description of what bundles are used for, and explained that you can't query for bundles (a very common beginner confusion).
Co-authored-by: MinerSebas <scherthan_sebastian@web.de>
Co-authored-by: Renato Caldas <renato@calgera.com>
The bevy ecs v2 rewrite seems to have removed the `Or` query filter from the prelude, which I assume was done on accident, since `With` and `Without` are still there.
# Bevy ECS V2
This is a rewrite of Bevy ECS (basically everything but the new executor/schedule, which are already awesome). The overall goal was to improve the performance and versatility of Bevy ECS. Here is a quick bulleted list of changes before we dive into the details:
* Complete World rewrite
* Multiple component storage types:
* Tables: fast cache friendly iteration, slower add/removes (previously called Archetypes)
* Sparse Sets: fast add/remove, slower iteration
* Stateful Queries (caches query results for faster iteration. fragmented iteration is _fast_ now)
* Stateful System Params (caches expensive operations. inspired by @DJMcNab's work in #1364)
* Configurable System Params (users can set configuration when they construct their systems. once again inspired by @DJMcNab's work)
* Archetypes are now "just metadata", component storage is separate
* Archetype Graph (for faster archetype changes)
* Component Metadata
* Configure component storage type
* Retrieve information about component size/type/name/layout/send-ness/etc
* Components are uniquely identified by a densely packed ComponentId
* TypeIds are now totally optional (which should make implementing scripting easier)
* Super fast "for_each" query iterators
* Merged Resources into World. Resources are now just a special type of component
* EntityRef/EntityMut builder apis (more efficient and more ergonomic)
* Fast bitset-backed `Access<T>` replaces old hashmap-based approach everywhere
* Query conflicts are determined by component access instead of archetype component access (to avoid random failures at runtime)
* With/Without are still taken into account for conflicts, so this should still be comfy to use
* Much simpler `IntoSystem` impl
* Significantly reduced the amount of hashing throughout the ecs in favor of Sparse Sets (indexed by densely packed ArchetypeId, ComponentId, BundleId, and TableId)
* Safety Improvements
* Entity reservation uses a normal world reference instead of unsafe transmute
* QuerySets no longer transmute lifetimes
* Made traits "unsafe" where relevant
* More thorough safety docs
* WorldCell
* Exposes safe mutable access to multiple resources at a time in a World
* Replaced "catch all" `System::update_archetypes(world: &World)` with `System::new_archetype(archetype: &Archetype)`
* Simpler Bundle implementation
* Replaced slow "remove_bundle_one_by_one" used as fallback for Commands::remove_bundle with fast "remove_bundle_intersection"
* Removed `Mut<T>` query impl. it is better to only support one way: `&mut T`
* Removed with() from `Flags<T>` in favor of `Option<Flags<T>>`, which allows querying for flags to be "filtered" by default
* Components now have is_send property (currently only resources support non-send)
* More granular module organization
* New `RemovedComponents<T>` SystemParam that replaces `query.removed::<T>()`
* `world.resource_scope()` for mutable access to resources and world at the same time
* WorldQuery and QueryFilter traits unified. FilterFetch trait added to enable "short circuit" filtering. Auto impled for cases that don't need it
* Significantly slimmed down SystemState in favor of individual SystemParam state
* System Commands changed from `commands: &mut Commands` back to `mut commands: Commands` (to allow Commands to have a World reference)
Fixes#1320
## `World` Rewrite
This is a from-scratch rewrite of `World` that fills the niche that `hecs` used to. Yes, this means Bevy ECS is no longer a "fork" of hecs. We're going out our own!
(the only shared code between the projects is the entity id allocator, which is already basically ideal)
A huge shout out to @SanderMertens (author of [flecs](https://github.com/SanderMertens/flecs)) for sharing some great ideas with me (specifically hybrid ecs storage and archetype graphs). He also helped advise on a number of implementation details.
## Component Storage (The Problem)
Two ECS storage paradigms have gained a lot of traction over the years:
* **Archetypal ECS**:
* Stores components in "tables" with static schemas. Each "column" stores components of a given type. Each "row" is an entity.
* Each "archetype" has its own table. Adding/removing an entity's component changes the archetype.
* Enables super-fast Query iteration due to its cache-friendly data layout
* Comes at the cost of more expensive add/remove operations for an Entity's components, because all components need to be copied to the new archetype's "table"
* **Sparse Set ECS**:
* Stores components of the same type in densely packed arrays, which are sparsely indexed by densely packed unsigned integers (Entity ids)
* Query iteration is slower than Archetypal ECS because each entity's component could be at any position in the sparse set. This "random access" pattern isn't cache friendly. Additionally, there is an extra layer of indirection because you must first map the entity id to an index in the component array.
* Adding/removing components is a cheap, constant time operation
Bevy ECS V1, hecs, legion, flec, and Unity DOTS are all "archetypal ecs-es". I personally think "archetypal" storage is a good default for game engines. An entity's archetype doesn't need to change frequently in general, and it creates "fast by default" query iteration (which is a much more common operation). It is also "self optimizing". Users don't need to think about optimizing component layouts for iteration performance. It "just works" without any extra boilerplate.
Shipyard and EnTT are "sparse set ecs-es". They employ "packing" as a way to work around the "suboptimal by default" iteration performance for specific sets of components. This helps, but I didn't think this was a good choice for a general purpose engine like Bevy because:
1. "packs" conflict with each other. If bevy decides to internally pack the Transform and GlobalTransform components, users are then blocked if they want to pack some custom component with Transform.
2. users need to take manual action to optimize
Developers selecting an ECS framework are stuck with a hard choice. Select an "archetypal" framework with "fast iteration everywhere" but without the ability to cheaply add/remove components, or select a "sparse set" framework to cheaply add/remove components but with slower iteration performance.
## Hybrid Component Storage (The Solution)
In Bevy ECS V2, we get to have our cake and eat it too. It now has _both_ of the component storage types above (and more can be added later if needed):
* **Tables** (aka "archetypal" storage)
* The default storage. If you don't configure anything, this is what you get
* Fast iteration by default
* Slower add/remove operations
* **Sparse Sets**
* Opt-in
* Slower iteration
* Faster add/remove operations
These storage types complement each other perfectly. By default Query iteration is fast. If developers know that they want to add/remove a component at high frequencies, they can set the storage to "sparse set":
```rust
world.register_component(
ComponentDescriptor:🆕:<MyComponent>(StorageType::SparseSet)
).unwrap();
```
## Archetypes
Archetypes are now "just metadata" ... they no longer store components directly. They do store:
* The `ComponentId`s of each of the Archetype's components (and that component's storage type)
* Archetypes are uniquely defined by their component layouts
* For example: entities with "table" components `[A, B, C]` _and_ "sparse set" components `[D, E]` will always be in the same archetype.
* The `TableId` associated with the archetype
* For now each archetype has exactly one table (which can have no components),
* There is a 1->Many relationship from Tables->Archetypes. A given table could have any number of archetype components stored in it:
* Ex: an entity with "table storage" components `[A, B, C]` and "sparse set" components `[D, E]` will share the same `[A, B, C]` table as an entity with `[A, B, C]` table component and `[F]` sparse set components.
* This 1->Many relationship is how we preserve fast "cache friendly" iteration performance when possible (more on this later)
* A list of entities that are in the archetype and the row id of the table they are in
* ArchetypeComponentIds
* unique densely packed identifiers for (ArchetypeId, ComponentId) pairs
* used by the schedule executor for cheap system access control
* "Archetype Graph Edges" (see the next section)
## The "Archetype Graph"
Archetype changes in Bevy (and a number of other archetypal ecs-es) have historically been expensive to compute. First, you need to allocate a new vector of the entity's current component ids, add or remove components based on the operation performed, sort it (to ensure it is order-independent), then hash it to find the archetype (if it exists). And thats all before we get to the _already_ expensive full copy of all components to the new table storage.
The solution is to build a "graph" of archetypes to cache these results. @SanderMertens first exposed me to the idea (and he got it from @gjroelofs, who came up with it). They propose adding directed edges between archetypes for add/remove component operations. If `ComponentId`s are densely packed, you can use sparse sets to cheaply jump between archetypes.
Bevy takes this one step further by using add/remove `Bundle` edges instead of `Component` edges. Bevy encourages the use of `Bundles` to group add/remove operations. This is largely for "clearer game logic" reasons, but it also helps cut down on the number of archetype changes required. `Bundles` now also have densely-packed `BundleId`s. This allows us to use a _single_ edge for each bundle operation (rather than needing to traverse N edges ... one for each component). Single component operations are also bundles, so this is strictly an improvement over a "component only" graph.
As a result, an operation that used to be _heavy_ (both for allocations and compute) is now two dirt-cheap array lookups and zero allocations.
## Stateful Queries
World queries are now stateful. This allows us to:
1. Cache archetype (and table) matches
* This resolves another issue with (naive) archetypal ECS: query performance getting worse as the number of archetypes goes up (and fragmentation occurs).
2. Cache Fetch and Filter state
* The expensive parts of fetch/filter operations (such as hashing the TypeId to find the ComponentId) now only happen once when the Query is first constructed
3. Incrementally build up state
* When new archetypes are added, we only process the new archetypes (no need to rebuild state for old archetypes)
As a result, the direct `World` query api now looks like this:
```rust
let mut query = world.query::<(&A, &mut B)>();
for (a, mut b) in query.iter_mut(&mut world) {
}
```
Requiring `World` to generate stateful queries (rather than letting the `QueryState` type be constructed separately) allows us to ensure that _all_ queries are properly initialized (and the relevant world state, such as ComponentIds). This enables QueryState to remove branches from its operations that check for initialization status (and also enables query.iter() to take an immutable world reference because it doesn't need to initialize anything in world).
However in systems, this is a non-breaking change. State management is done internally by the relevant SystemParam.
## Stateful SystemParams
Like Queries, `SystemParams` now also cache state. For example, `Query` system params store the "stateful query" state mentioned above. Commands store their internal `CommandQueue`. This means you can now safely use as many separate `Commands` parameters in your system as you want. `Local<T>` system params store their `T` value in their state (instead of in Resources).
SystemParam state also enabled a significant slim-down of SystemState. It is much nicer to look at now.
Per-SystemParam state naturally insulates us from an "aliased mut" class of errors we have hit in the past (ex: using multiple `Commands` system params).
(credit goes to @DJMcNab for the initial idea and draft pr here #1364)
## Configurable SystemParams
@DJMcNab also had the great idea to make SystemParams configurable. This allows users to provide some initial configuration / values for system parameters (when possible). Most SystemParams have no config (the config type is `()`), but the `Local<T>` param now supports user-provided parameters:
```rust
fn foo(value: Local<usize>) {
}
app.add_system(foo.system().config(|c| c.0 = Some(10)));
```
## Uber Fast "for_each" Query Iterators
Developers now have the choice to use a fast "for_each" iterator, which yields ~1.5-3x iteration speed improvements for "fragmented iteration", and minor ~1.2x iteration speed improvements for unfragmented iteration.
```rust
fn system(query: Query<(&A, &mut B)>) {
// you now have the option to do this for a speed boost
query.for_each_mut(|(a, mut b)| {
});
// however normal iterators are still available
for (a, mut b) in query.iter_mut() {
}
}
```
I think in most cases we should continue to encourage "normal" iterators as they are more flexible and more "rust idiomatic". But when that extra "oomf" is needed, it makes sense to use `for_each`.
We should also consider using `for_each` for internal bevy systems to give our users a nice speed boost (but that should be a separate pr).
## Component Metadata
`World` now has a `Components` collection, which is accessible via `world.components()`. This stores mappings from `ComponentId` to `ComponentInfo`, as well as `TypeId` to `ComponentId` mappings (where relevant). `ComponentInfo` stores information about the component, such as ComponentId, TypeId, memory layout, send-ness (currently limited to resources), and storage type.
## Significantly Cheaper `Access<T>`
We used to use `TypeAccess<TypeId>` to manage read/write component/archetype-component access. This was expensive because TypeIds must be hashed and compared individually. The parallel executor got around this by "condensing" type ids into bitset-backed access types. This worked, but it had to be re-generated from the `TypeAccess<TypeId>`sources every time archetypes changed.
This pr removes TypeAccess in favor of faster bitset access everywhere. We can do this thanks to the move to densely packed `ComponentId`s and `ArchetypeComponentId`s.
## Merged Resources into World
Resources had a lot of redundant functionality with Components. They stored typed data, they had access control, they had unique ids, they were queryable via SystemParams, etc. In fact the _only_ major difference between them was that they were unique (and didn't correlate to an entity).
Separate resources also had the downside of requiring a separate set of access controls, which meant the parallel executor needed to compare more bitsets per system and manage more state.
I initially got the "separate resources" idea from `legion`. I think that design was motivated by the fact that it made the direct world query/resource lifetime interactions more manageable. It certainly made our lives easier when using Resources alongside hecs/bevy_ecs. However we already have a construct for safely and ergonomically managing in-world lifetimes: systems (which use `Access<T>` internally).
This pr merges Resources into World:
```rust
world.insert_resource(1);
world.insert_resource(2.0);
let a = world.get_resource::<i32>().unwrap();
let mut b = world.get_resource_mut::<f64>().unwrap();
*b = 3.0;
```
Resources are now just a special kind of component. They have their own ComponentIds (and their own resource TypeId->ComponentId scope, so they don't conflict wit components of the same type). They are stored in a special "resource archetype", which stores components inside the archetype using a new `unique_components` sparse set (note that this sparse set could later be used to implement Tags). This allows us to keep the code size small by reusing existing datastructures (namely Column, Archetype, ComponentFlags, and ComponentInfo). This allows us the executor to use a single `Access<ArchetypeComponentId>` per system. It should also make scripting language integration easier.
_But_ this merge did create problems for people directly interacting with `World`. What if you need mutable access to multiple resources at the same time? `world.get_resource_mut()` borrows World mutably!
## WorldCell
WorldCell applies the `Access<ArchetypeComponentId>` concept to direct world access:
```rust
let world_cell = world.cell();
let a = world_cell.get_resource_mut::<i32>().unwrap();
let b = world_cell.get_resource_mut::<f64>().unwrap();
```
This adds cheap runtime checks (a sparse set lookup of `ArchetypeComponentId` and a counter) to ensure that world accesses do not conflict with each other. Each operation returns a `WorldBorrow<'w, T>` or `WorldBorrowMut<'w, T>` wrapper type, which will release the relevant ArchetypeComponentId resources when dropped.
World caches the access sparse set (and only one cell can exist at a time), so `world.cell()` is a cheap operation.
WorldCell does _not_ use atomic operations. It is non-send, does a mutable borrow of world to prevent other accesses, and uses a simple `Rc<RefCell<ArchetypeComponentAccess>>` wrapper in each WorldBorrow pointer.
The api is currently limited to resource access, but it can and should be extended to queries / entity component access.
## Resource Scopes
WorldCell does not yet support component queries, and even when it does there are sometimes legitimate reasons to want a mutable world ref _and_ a mutable resource ref (ex: bevy_render and bevy_scene both need this). In these cases we could always drop down to the unsafe `world.get_resource_unchecked_mut()`, but that is not ideal!
Instead developers can use a "resource scope"
```rust
world.resource_scope(|world: &mut World, a: &mut A| {
})
```
This temporarily removes the `A` resource from `World`, provides mutable pointers to both, and re-adds A to World when finished. Thanks to the move to ComponentIds/sparse sets, this is a cheap operation.
If multiple resources are required, scopes can be nested. We could also consider adding a "resource tuple" to the api if this pattern becomes common and the boilerplate gets nasty.
## Query Conflicts Use ComponentId Instead of ArchetypeComponentId
For safety reasons, systems cannot contain queries that conflict with each other without wrapping them in a QuerySet. On bevy `main`, we use ArchetypeComponentIds to determine conflicts. This is nice because it can take into account filters:
```rust
// these queries will never conflict due to their filters
fn filter_system(a: Query<&mut A, With<B>>, b: Query<&mut B, Without<B>>) {
}
```
But it also has a significant downside:
```rust
// these queries will not conflict _until_ an entity with A, B, and C is spawned
fn maybe_conflicts_system(a: Query<(&mut A, &C)>, b: Query<(&mut A, &B)>) {
}
```
The system above will panic at runtime if an entity with A, B, and C is spawned. This makes it hard to trust that your game logic will run without crashing.
In this pr, I switched to using `ComponentId` instead. This _is_ more constraining. `maybe_conflicts_system` will now always fail, but it will do it consistently at startup. Naively, it would also _disallow_ `filter_system`, which would be a significant downgrade in usability. Bevy has a number of internal systems that rely on disjoint queries and I expect it to be a common pattern in userspace.
To resolve this, I added a new `FilteredAccess<T>` type, which wraps `Access<T>` and adds with/without filters. If two `FilteredAccess` have with/without values that prove they are disjoint, they will no longer conflict.
## EntityRef / EntityMut
World entity operations on `main` require that the user passes in an `entity` id to each operation:
```rust
let entity = world.spawn((A, )); // create a new entity with A
world.get::<A>(entity);
world.insert(entity, (B, C));
world.insert_one(entity, D);
```
This means that each operation needs to look up the entity location / verify its validity. The initial spawn operation also requires a Bundle as input. This can be awkward when no components are required (or one component is required).
These operations have been replaced by `EntityRef` and `EntityMut`, which are "builder-style" wrappers around world that provide read and read/write operations on a single, pre-validated entity:
```rust
// spawn now takes no inputs and returns an EntityMut
let entity = world.spawn()
.insert(A) // insert a single component into the entity
.insert_bundle((B, C)) // insert a bundle of components into the entity
.id() // id returns the Entity id
// Returns EntityMut (or panics if the entity does not exist)
world.entity_mut(entity)
.insert(D)
.insert_bundle(SomeBundle::default());
{
// returns EntityRef (or panics if the entity does not exist)
let d = world.entity(entity)
.get::<D>() // gets the D component
.unwrap();
// world.get still exists for ergonomics
let d = world.get::<D>(entity).unwrap();
}
// These variants return Options if you want to check existence instead of panicing
world.get_entity_mut(entity)
.unwrap()
.insert(E);
if let Some(entity_ref) = world.get_entity(entity) {
let d = entity_ref.get::<D>().unwrap();
}
```
This _does not_ affect the current Commands api or terminology. I think that should be a separate conversation as that is a much larger breaking change.
## Safety Improvements
* Entity reservation in Commands uses a normal world borrow instead of an unsafe transmute
* QuerySets no longer transmutes lifetimes
* Made traits "unsafe" when implementing a trait incorrectly could cause unsafety
* More thorough safety docs
## RemovedComponents SystemParam
The old approach to querying removed components: `query.removed:<T>()` was confusing because it had no connection to the query itself. I replaced it with the following, which is both clearer and allows us to cache the ComponentId mapping in the SystemParamState:
```rust
fn system(removed: RemovedComponents<T>) {
for entity in removed.iter() {
}
}
```
## Simpler Bundle implementation
Bundles are no longer responsible for sorting (or deduping) TypeInfo. They are just a simple ordered list of component types / data. This makes the implementation smaller and opens the door to an easy "nested bundle" implementation in the future (which i might even add in this pr). Duplicate detection is now done once per bundle type by World the first time a bundle is used.
## Unified WorldQuery and QueryFilter types
(don't worry they are still separate type _parameters_ in Queries .. this is a non-breaking change)
WorldQuery and QueryFilter were already basically identical apis. With the addition of `FetchState` and more storage-specific fetch methods, the overlap was even clearer (and the redundancy more painful).
QueryFilters are now just `F: WorldQuery where F::Fetch: FilterFetch`. FilterFetch requires `Fetch<Item = bool>` and adds new "short circuit" variants of fetch methods. This enables a filter tuple like `(With<A>, Without<B>, Changed<C>)` to stop evaluating the filter after the first mismatch is encountered. FilterFetch is automatically implemented for `Fetch` implementations that return bool.
This forces fetch implementations that return things like `(bool, bool, bool)` (such as the filter above) to manually implement FilterFetch and decide whether or not to short-circuit.
## More Granular Modules
World no longer globs all of the internal modules together. It now exports `core`, `system`, and `schedule` separately. I'm also considering exporting `core` submodules directly as that is still pretty "glob-ey" and unorganized (feedback welcome here).
## Remaining Draft Work (to be done in this pr)
* ~~panic on conflicting WorldQuery fetches (&A, &mut A)~~
* ~~bevy `main` and hecs both currently allow this, but we should protect against it if possible~~
* ~~batch_iter / par_iter (currently stubbed out)~~
* ~~ChangedRes~~
* ~~I skipped this while we sort out #1313. This pr should be adapted to account for whatever we land on there~~.
* ~~The `Archetypes` and `Tables` collections use hashes of sorted lists of component ids to uniquely identify each archetype/table. This hash is then used as the key in a HashMap to look up the relevant ArchetypeId or TableId. (which doesn't handle hash collisions properly)~~
* ~~It is currently unsafe to generate a Query from "World A", then use it on "World B" (despite the api claiming it is safe). We should probably close this gap. This could be done by adding a randomly generated WorldId to each world, then storing that id in each Query. They could then be compared to each other on each `query.do_thing(&world)` operation. This _does_ add an extra branch to each query operation, so I'm open to other suggestions if people have them.~~
* ~~Nested Bundles (if i find time)~~
## Potential Future Work
* Expand WorldCell to support queries.
* Consider not allocating in the empty archetype on `world.spawn()`
* ex: return something like EntityMutUninit, which turns into EntityMut after an `insert` or `insert_bundle` op
* this actually regressed performance last time i tried it, but in theory it should be faster
* Optimize SparseSet::insert (see `PERF` comment on insert)
* Replace SparseArray `Option<T>` with T::MAX to cut down on branching
* would enable cheaper get_unchecked() operations
* upstream fixedbitset optimizations
* fixedbitset could be allocation free for small block counts (store blocks in a SmallVec)
* fixedbitset could have a const constructor
* Consider implementing Tags (archetype-specific by-value data that affects archetype identity)
* ex: ArchetypeA could have `[A, B, C]` table components and `[D(1)]` "tag" component. ArchetypeB could have `[A, B, C]` table components and a `[D(2)]` tag component. The archetypes are different, despite both having D tags because the value inside D is different.
* this could potentially build on top of the `archetype.unique_components` added in this pr for resource storage.
* Consider reverting `all_tuples` proc macro in favor of the old `macro_rules` implementation
* all_tuples is more flexible and produces cleaner documentation (the macro_rules version produces weird type parameter orders due to parser constraints)
* but unfortunately all_tuples also appears to make Rust Analyzer sad/slow when working inside of `bevy_ecs` (does not affect user code)
* Consider "resource queries" and/or "mixed resource and entity component queries" as an alternative to WorldCell
* this is basically just "systems" so maybe it's not worth it
* Add more world ops
* `world.clear()`
* `world.reserve<T: Bundle>(count: usize)`
* Try using the old archetype allocation strategy (allocate new memory on resize and copy everything over). I expect this to improve batch insertion performance at the cost of unbatched performance. But thats just a guess. I'm not an allocation perf pro :)
* Adapt Commands apis for consistency with new World apis
## Benchmarks
key:
* `bevy_old`: bevy `main` branch
* `bevy`: this branch
* `_foreach`: uses an optimized for_each iterator
* ` _sparse`: uses sparse set storage (if unspecified assume table storage)
* `_system`: runs inside a system (if unspecified assume test happens via direct world ops)
### Simple Insert (from ecs_bench_suite)
### Simpler Iter (from ecs_bench_suite)
### Fragment Iter (from ecs_bench_suite)
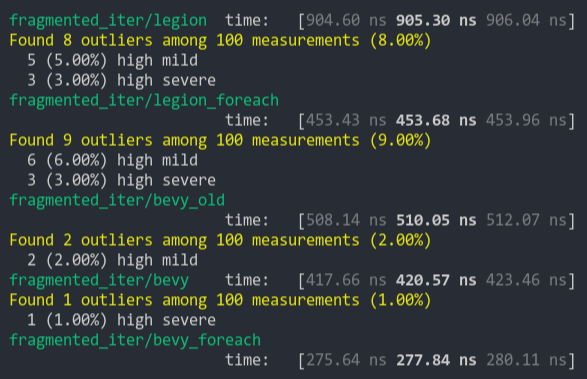
### Sparse Fragmented Iter
Iterate a query that matches 5 entities from a single matching archetype, but there are 100 unmatching archetypes
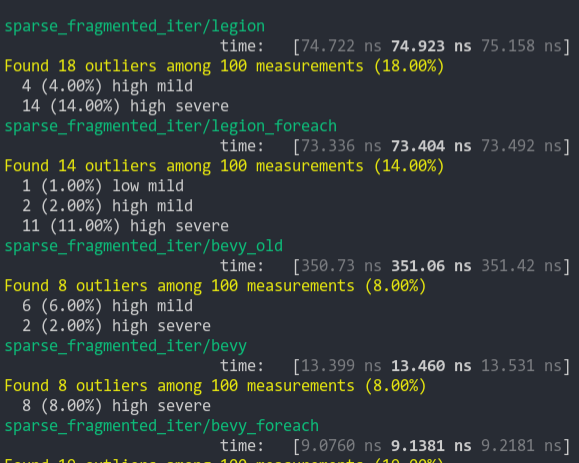
### Schedule (from ecs_bench_suite)
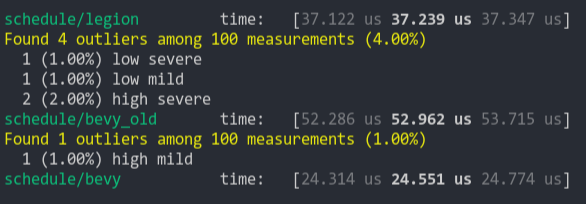
### Add Remove Component (from ecs_bench_suite)
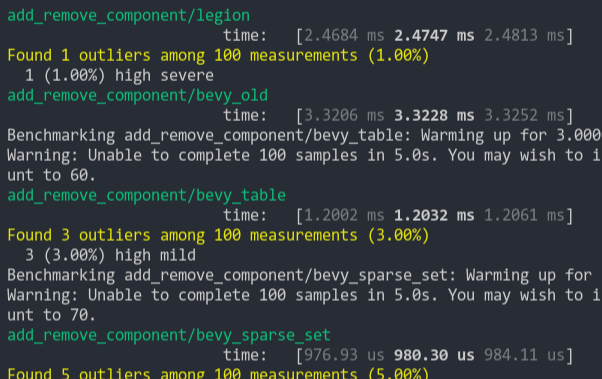
### Add Remove Component Big
Same as the test above, but each entity has 5 "large" matrix components and 1 "large" matrix component is added and removed
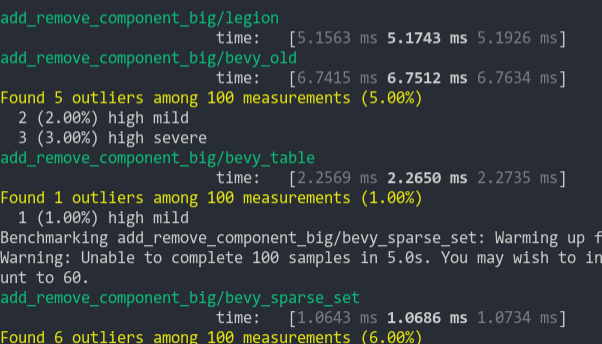
### Get Component
Looks up a single component value a large number of times
It took me a little while to figure out how to use the `SystemParam` derive macro to easily create my own params. So I figured I'd add some docs and an example with what I learned.
- Fixed a bug in the `SystemParam` derive macro where it didn't detect the correct crate name when used in an example (no longer relevant, replaced by #1426 - see further)
- Added some doc comments and a short example code block in the docs for the `SystemParam` trait
- Added a more complete example with explanatory comments in examples
This replaces `ChangedRes` with simple associated methods that return the same info, but don't block execution. Also, since ChangedRes was infectious and was the only reason `FetchSystemParam::get_params` and `System::run_unsafe` returned `Option`s, their implementation could be simplified after this PR is merged, or as part of it with a future commit.
This PR is easiest to review commit by commit.
Followup on https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/1309#issuecomment-767310084
- [x] Switch from a bash script to an xtask rust workspace member.
- Results in ~30s longer CI due to compilation of the xtask itself
- Enables Bevy contributors on any platform to run `cargo ci` to run linting -- if the default available Rust is the same version as on CI, then the command should give an identical result.
- [x] Use the xtask from official CI so there's only one place to update.
- [x] Bonus: Run clippy on the _entire_ workspace (existing CI setup was missing the `--workspace` flag
- [x] Clean up newly-exposed clippy errors
~#1388 builds on this to clean up newly discovered clippy errors -- I thought it might be nicer as a separate PR.~ Nope, merged it into this one so CI would pass.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
The existing snippet fails to compile with:
```
no method named `system` found for fn item `fn(bevy::prelude::Commands) {example_system}` in the current scope
```
Relying on TypeId being some hash internally isn't future-proof because there is no guarantee about internal layout or structure of TypeId. I benchmarked TypeId noop hasher vs fxhash and found that there is very little difference.
Also fxhash is likely to be better supported because it is widely used in rustc itself.
[Benchmarks of hashers](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/1097)
[Engine wide benchmarks](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/1119#issuecomment-751361215)
* move print diagnostics to log
* entity count diagnostic
* asset count diagnostic
* remove useless `pub`s
* use `BTreeMap` instead of `HashMap`
* get entity count from world
* keep ordered list of diagnostics
* only update global transforms when they (or their ancestors) have changed
* only update render resource nodes when they have changed (quality check plz)
* only update entity mesh specialization when mesh (or mesh component) has changed
* only update sprite size when changed
* remove stale bind groups
* fix setting size of loading sprites
* store unmatched render resource binding results
* reduce state changes
* cargo fmt + clippy
* remove cached "NoMatch" results when new bindings are added to RenderResourceBindings
* inline current_entity in world_builder
* try creating bind groups even when they havent changed
* render_resources_node: update all entities when resized
* fmt
`ArchetypeAccess` was tracking `immutable` and `mutable` separately.
This means that checking is_compatible requires three checks:
m+m, m+i, i+m.
Instead, continue tracking `mutable` accesses, but instead of
`immutable` track `immutable | mutable` as another `accessed` bit mask.
This drops the comparisons to two (m+a, a+m) and turns out to be
what the rest of the code base wants too, unifying various duplicated
checks and loops.
* Add mutated tracker on resources and ChangedRes query for added or mutated resources.
* ResMut:::new() now takes a reference to a 'mutated' flag in its archetype.
* Change FetchResource so that get() returns an Option. Systems using Resources will only be called if all fetched Resources are Some(). This is done to implement ChangedRes, which is Some iff the Resource has been changed.
* Add OrRes for a logical or in tuples of Resource queries.
* Separate resource query get() in is_some() and get() methods for clarity
* Remove unneeded unsafe
* Change ResMut::new()