naga and wgpu should polyfill WGSL instance_index functionality where it
is not available in GLSL. Until that is done, we can work around it in
bevy using a push constant which is converted to a uniform by naga and
wgpu.
# Objective
- Fixes#9375
## Solution
- Use a push constant to pass in the base instance to the shader on
WebGL2 so that base instance + gl_InstanceID is used to correctly
represent the instance index.
## TODO
- [ ] Benchmark vs per-object dynamic offset MeshUniform as this will
now push a uniform value per-draw as well as update the dynamic offset
per-batch.
- [x] Test on DX12 AMD/NVIDIA to check that this PR does not regress any
problems that were observed there. (@Elabajaba @robtfm were testing that
last time - help appreciated. <3 )
---
## Changelog
- Added: `bevy_render::instance_index` shader import which includes a
workaround for the lack of a WGSL `instance_index` polyfill for WebGL2
in naga and wgpu for the time being. It uses a push_constant which gets
converted to a plain uniform by naga and wgpu.
## Migration Guide
Shader code before:
```
struct Vertex {
@builtin(instance_index) instance_index: u32,
...
}
@vertex
fn vertex(vertex_no_morph: Vertex) -> VertexOutput {
...
var model = mesh[vertex_no_morph.instance_index].model;
```
After:
```
#import bevy_render::instance_index
struct Vertex {
@builtin(instance_index) instance_index: u32,
...
}
@vertex
fn vertex(vertex_no_morph: Vertex) -> VertexOutput {
...
var model = mesh[bevy_render::instance_index::get_instance_index(vertex_no_morph.instance_index)].model;
```
# Objective
shader defs associated with a shader via `load_internal_asset!` or
`Shader::from_xxx_with_defs` were being accidentally ignored for
top-level shaders.
## Solution
include the defs for top level shaders.
# Objective
This PR continues https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/8885
It aims to improve the `Mesh` documentation in the following ways:
- Put everything at the "top level" instead of the "impl".
- Explain better what is a Mesh, how it can be created, and that it can
be edited.
- Explain it can be used with a `Material`, and mention
`StandardMaterial`, `PbrBundle`, `ColorMaterial`, and
`ColorMesh2dBundle` since those cover most cases
- Mention the glTF/Bevy vocabulary discrepancy for "Mesh"
- Add an image for the example
- Various nitpicky modifications
## Note
- The image I added is 90.3ko which I think is small enough?
- Since rustdoc doesn't allow cross-reference not in dependencies of a
subcrate [yet](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/74481), I have a
lot of backtick references that are not links :(
- Since rustdoc doesn't allow linking to code in the crate (?) I put
link to github directly.
- Since rustdoc doesn't allow embed images in doc
[yet](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/issues/32104), maybe
[soon](https://github.com/rust-lang/rfcs/pull/3397), I had to put only a
link to the image. I don't think it's worth adding
[embed_doc_image](https://docs.rs/embed-doc-image/latest/embed_doc_image/)
as a dependency for this.
# Objective
This PR updates the name of the enum variant used in the docs for
`OrthographicProjection`.
## Solution
- Change the outdated 'WindowScale` to `WindowSize`.
# Objective
- Reduce the number of rebindings to enable batching of draw commands
## Solution
- Use the new `GpuArrayBuffer` for `MeshUniform` data to store all
`MeshUniform` data in arrays within fewer bindings
- Sort opaque/alpha mask prepass, opaque/alpha mask main, and shadow
phases also by the batch per-object data binding dynamic offset to
improve performance on WebGL2.
---
## Changelog
- Changed: Per-object `MeshUniform` data is now managed by
`GpuArrayBuffer` as arrays in buffers that need to be indexed into.
## Migration Guide
Accessing the `model` member of an individual mesh object's shader
`Mesh` struct the old way where each `MeshUniform` was stored at its own
dynamic offset:
```rust
struct Vertex {
@location(0) position: vec3<f32>,
};
fn vertex(vertex: Vertex) -> VertexOutput {
var out: VertexOutput;
out.clip_position = mesh_position_local_to_clip(
mesh.model,
vec4<f32>(vertex.position, 1.0)
);
return out;
}
```
The new way where one needs to index into the array of `Mesh`es for the
batch:
```rust
struct Vertex {
@builtin(instance_index) instance_index: u32,
@location(0) position: vec3<f32>,
};
fn vertex(vertex: Vertex) -> VertexOutput {
var out: VertexOutput;
out.clip_position = mesh_position_local_to_clip(
mesh[vertex.instance_index].model,
vec4<f32>(vertex.position, 1.0)
);
return out;
}
```
Note that using the instance_index is the default way to pass the
per-object index into the shader, but if you wish to do custom rendering
approaches you can pass it in however you like.
---------
Co-authored-by: robtfm <50659922+robtfm@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Elabajaba <Elabajaba@users.noreply.github.com>
This is not used directly within the rendering code.
# Objective
- Remove extraneous dependency on `wgpu-hal` as it is not used.
## Solution
- The dependency has been removed and should have no externally visible
impact.
# Objective
The `QueryParIter::for_each_mut` function is required when doing
parallel iteration with mutable queries.
This results in an unfortunate stutter:
`query.par_iter_mut().par_for_each_mut()` ('mut' is repeated).
## Solution
- Make `for_each` compatible with mutable queries, and deprecate
`for_each_mut`. In order to prevent `for_each` from being called
multiple times in parallel, we take ownership of the QueryParIter.
---
## Changelog
- `QueryParIter::for_each` is now compatible with mutable queries.
`for_each_mut` has been deprecated as it is now redundant.
## Migration Guide
The method `QueryParIter::for_each_mut` has been deprecated and is no
longer functional. Use `for_each` instead, which now supports mutable
queries.
```rust
// Before:
query.par_iter_mut().for_each_mut(|x| ...);
// After:
query.par_iter_mut().for_each(|x| ...);
```
The method `QueryParIter::for_each` now takes ownership of the
`QueryParIter`, rather than taking a shared reference.
```rust
// Before:
let par_iter = my_query.par_iter().batching_strategy(my_batching_strategy);
par_iter.for_each(|x| {
// ...Do stuff with x...
par_iter.for_each(|y| {
// ...Do nested stuff with y...
});
});
// After:
my_query.par_iter().batching_strategy(my_batching_strategy).for_each(|x| {
// ...Do stuff with x...
my_query.par_iter().batching_strategy(my_batching_strategy).for_each(|y| {
// ...Do nested stuff with y...
});
});
```
# Objective
Fixes#9121
Context:
- `ImageTextureLoader` depends on `RenderDevice` to work out which
compressed image formats it can support
- `RenderDevice` is initialised by `RenderPlugin`
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/8336 made `RenderPlugin`
initialisation async
- This caused `RenderDevice` to be missing at the time of
`ImageTextureLoader` initialisation, which in turn meant UASTC encoded
ktx2 textures were being converted to unsupported formats, and thus
caused panics
## Solution
- Delay `ImageTextureLoader` initialisation
---
## Changelog
- Moved `ImageTextureLoader` initialisation from `ImagePlugin::build()`
to `ImagePlugin::finish()`
- Default to `CompressedImageFormats::NONE` if `RenderDevice` resource
is missing
---------
Co-authored-by: 66OJ66 <hi0obxud@anonaddy.me>
# Objective
Fix#8936.
## Solution
Stop using `unwrap` in the core pipelined rendering logic flow.
Separately also scoped the `sub app` span to just running the render app
instead of including the blocking send.
Current unknowns: should we use `std::panic::catch_unwind` around
running the render app? Other engine threads use it defensively, but
we're letting it bubble up here, and a user-created panic could cause a
deadlock if it kills the thread.
---
## Changelog
Fixed: Pipelined rendering should no longer have spurious panics upon
app exit.
# Objective
- Add a type for uploading a Rust `Vec<T>` to a GPU `array<T>`.
- Makes progress towards https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/89.
## Solution
- Port @superdump's `BatchedUniformBuffer` to bevy main, as a fallback
for WebGL2, which doesn't support storage buffers.
- Rather than getting an `array<T>` in a shader, you get an `array<T,
N>`, and have to rebind every N elements via dynamic offsets.
- Add `GpuArrayBuffer` to abstract over
`StorageBuffer<Vec<T>>`/`BatchedUniformBuffer`.
## Future Work
Add a shader macro kinda thing to abstract over the following
automatically:
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/8204#pullrequestreview-1396911727
---
## Changelog
* Added `GpuArrayBuffer`, `GpuComponentArrayBufferPlugin`,
`GpuArrayBufferable`, and `GpuArrayBufferIndex` types.
* Added `DynamicUniformBuffer::new_with_alignment()`.
---------
Co-authored-by: Robert Swain <robert.swain@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Teodor Tanasoaia <28601907+teoxoy@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: IceSentry <IceSentry@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Vincent <9408210+konsolas@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: robtfm <50659922+robtfm@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
AssetPath shader imports check if the shader is added using the path
without quotes. this causes them to be re-added even if already present,
which can cause previous dependents to get unloaded leading to a
"missing import" error.
## Solution
fix the module name of AssetPath shaders used for checking if it's
already added to correctly use the quoted name.
# Objective
Continue #7867 now that we have URect #7984
- Return `URect` instead of `(UVec2, UVec2)` in
`Camera::physical_viewport_rect`
- Add `URect` and `IRect` to prelude
## Changelog
- Changed `Camera::physical_viewport_rect` return type from `(UVec2,
UVec2)` to `URect`
- `URect` and `IRect` were added to prelude
## Migration Guide
Before:
```rust
fn view_physical_camera_rect(camera_query: Query<&Camera>) {
let camera = camera_query.single();
let Some((min, max)) = camera.physical_viewport_rect() else { return };
dbg!(min, max);
}
```
After:
```rust
fn view_physical_camera_rect(camera_query: Query<&Camera>) {
let camera = camera_query.single();
let Some(URect { min, max }) = camera.physical_viewport_rect() else { return };
dbg!(min, max);
}
```
CI-capable version of #9086
---------
Co-authored-by: Bevy Auto Releaser <41898282+github-actions[bot]@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
# Objective
Fix typos throughout the project.
## Solution
[`typos`](https://github.com/crate-ci/typos) project was used for
scanning, but no automatic corrections were applied. I checked
everything by hand before fixing.
Most of the changes are documentation/comments corrections. Also, there
are few trivial changes to code (variable name, pub(crate) function name
and a few error/panic messages).
## Unsolved
`bevy_reflect_derive` has
[typo](1b51053f19/crates/bevy_reflect/bevy_reflect_derive/src/type_path.rs (L76))
in enum variant name that I didn't fix. Enum is `pub(crate)`, so there
shouldn't be any trouble if fixed. However, code is tightly coupled with
macro usage, so I decided to leave it for more experienced contributor
just in case.
I created this manually as Github didn't want to run CI for the
workflow-generated PR. I'm guessing we didn't hit this in previous
releases because we used bors.
Co-authored-by: Bevy Auto Releaser <41898282+github-actions[bot]@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
bevy_render currently has a dependency on a random older version of
once_cell which is not used anywhere.
## Solution
Remove the dependency
## Changelog
N/A
## Migration Guide
N/A
# Objective
**This implementation is based on
https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/pull/59.**
---
Resolves#4597
Full details and motivation can be found in the RFC, but here's a brief
summary.
`FromReflect` is a very powerful and important trait within the
reflection API. It allows Dynamic types (e.g., `DynamicList`, etc.) to
be formed into Real ones (e.g., `Vec<i32>`, etc.).
This mainly comes into play concerning deserialization, where the
reflection deserializers both return a `Box<dyn Reflect>` that almost
always contain one of these Dynamic representations of a Real type. To
convert this to our Real type, we need to use `FromReflect`.
It also sneaks up in other ways. For example, it's a required bound for
`T` in `Vec<T>` so that `Vec<T>` as a whole can be made `FromReflect`.
It's also required by all fields of an enum as it's used as part of the
`Reflect::apply` implementation.
So in other words, much like `GetTypeRegistration` and `Typed`, it is
very much a core reflection trait.
The problem is that it is not currently treated like a core trait and is
not automatically derived alongside `Reflect`. This makes using it a bit
cumbersome and easy to forget.
## Solution
Automatically derive `FromReflect` when deriving `Reflect`.
Users can then choose to opt-out if needed using the
`#[reflect(from_reflect = false)]` attribute.
```rust
#[derive(Reflect)]
struct Foo;
#[derive(Reflect)]
#[reflect(from_reflect = false)]
struct Bar;
fn test<T: FromReflect>(value: T) {}
test(Foo); // <-- OK
test(Bar); // <-- Panic! Bar does not implement trait `FromReflect`
```
#### `ReflectFromReflect`
This PR also automatically adds the `ReflectFromReflect` (introduced in
#6245) registration to the derived `GetTypeRegistration` impl— if the
type hasn't opted out of `FromReflect` of course.
<details>
<summary><h4>Improved Deserialization</h4></summary>
> **Warning**
> This section includes changes that have since been descoped from this
PR. They will likely be implemented again in a followup PR. I am mainly
leaving these details in for archival purposes, as well as for reference
when implementing this logic again.
And since we can do all the above, we might as well improve
deserialization. We can now choose to deserialize into a Dynamic type or
automatically convert it using `FromReflect` under the hood.
`[Un]TypedReflectDeserializer::new` will now perform the conversion and
return the `Box`'d Real type.
`[Un]TypedReflectDeserializer::new_dynamic` will work like what we have
now and simply return the `Box`'d Dynamic type.
```rust
// Returns the Real type
let reflect_deserializer = UntypedReflectDeserializer::new(®istry);
let mut deserializer = ron:🇩🇪:Deserializer::from_str(input)?;
let output: SomeStruct = reflect_deserializer.deserialize(&mut deserializer)?.take()?;
// Returns the Dynamic type
let reflect_deserializer = UntypedReflectDeserializer::new_dynamic(®istry);
let mut deserializer = ron:🇩🇪:Deserializer::from_str(input)?;
let output: DynamicStruct = reflect_deserializer.deserialize(&mut deserializer)?.take()?;
```
</details>
---
## Changelog
* `FromReflect` is now automatically derived within the `Reflect` derive
macro
* This includes auto-registering `ReflectFromReflect` in the derived
`GetTypeRegistration` impl
* ~~Renamed `TypedReflectDeserializer::new` and
`UntypedReflectDeserializer::new` to
`TypedReflectDeserializer::new_dynamic` and
`UntypedReflectDeserializer::new_dynamic`, respectively~~ **Descoped**
* ~~Changed `TypedReflectDeserializer::new` and
`UntypedReflectDeserializer::new` to automatically convert the
deserialized output using `FromReflect`~~ **Descoped**
## Migration Guide
* `FromReflect` is now automatically derived within the `Reflect` derive
macro. Items with both derives will need to remove the `FromReflect`
one.
```rust
// OLD
#[derive(Reflect, FromReflect)]
struct Foo;
// NEW
#[derive(Reflect)]
struct Foo;
```
If using a manual implementation of `FromReflect` and the `Reflect`
derive, users will need to opt-out of the automatic implementation.
```rust
// OLD
#[derive(Reflect)]
struct Foo;
impl FromReflect for Foo {/* ... */}
// NEW
#[derive(Reflect)]
#[reflect(from_reflect = false)]
struct Foo;
impl FromReflect for Foo {/* ... */}
```
<details>
<summary><h4>Removed Migrations</h4></summary>
> **Warning**
> This section includes changes that have since been descoped from this
PR. They will likely be implemented again in a followup PR. I am mainly
leaving these details in for archival purposes, as well as for reference
when implementing this logic again.
* The reflect deserializers now perform a `FromReflect` conversion
internally. The expected output of `TypedReflectDeserializer::new` and
`UntypedReflectDeserializer::new` is no longer a Dynamic (e.g.,
`DynamicList`), but its Real counterpart (e.g., `Vec<i32>`).
```rust
let reflect_deserializer =
UntypedReflectDeserializer::new_dynamic(®istry);
let mut deserializer = ron:🇩🇪:Deserializer::from_str(input)?;
// OLD
let output: DynamicStruct = reflect_deserializer.deserialize(&mut
deserializer)?.take()?;
// NEW
let output: SomeStruct = reflect_deserializer.deserialize(&mut
deserializer)?.take()?;
```
Alternatively, if this behavior isn't desired, use the
`TypedReflectDeserializer::new_dynamic` and
`UntypedReflectDeserializer::new_dynamic` methods instead:
```rust
// OLD
let reflect_deserializer = UntypedReflectDeserializer::new(®istry);
// NEW
let reflect_deserializer =
UntypedReflectDeserializer::new_dynamic(®istry);
```
</details>
---------
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
Added `GizmoConfig::render_layers`, which will ensure Gizmos are only
rendered on cameras that can see those `RenderLayers`.
---------
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
operate on naga IR directly to improve handling of shader modules.
- give codespan reporting into imported modules
- allow glsl to be used from wgsl and vice-versa
the ultimate objective is to make it possible to
- provide user hooks for core shader functions (to modify light
behaviour within the standard pbr pipeline, for example)
- make automatic binding slot allocation possible
but ... since this is already big, adds some value and (i think) is at
feature parity with the existing code, i wanted to push this now.
## Solution
i made a crate called naga_oil (https://github.com/robtfm/naga_oil -
unpublished for now, could be part of bevy) which manages modules by
- building each module independantly to naga IR
- creating "header" files for each supported language, which are used to
build dependent modules/shaders
- make final shaders by combining the shader IR with the IR for imported
modules
then integrated this into bevy, replacing some of the existing shader
processing stuff. also reworked examples to reflect this.
## Migration Guide
shaders that don't use `#import` directives should work without changes.
the most notable user-facing difference is that imported
functions/variables/etc need to be qualified at point of use, and
there's no "leakage" of visible stuff into your shader scope from the
imports of your imports, so if you used things imported by your imports,
you now need to import them directly and qualify them.
the current strategy of including/'spreading' `mesh_vertex_output`
directly into a struct doesn't work any more, so these need to be
modified as per the examples (e.g. color_material.wgsl, or many others).
mesh data is assumed to be in bindgroup 2 by default, if mesh data is
bound into bindgroup 1 instead then the shader def `MESH_BINDGROUP_1`
needs to be added to the pipeline shader_defs.
# Objective
- Closes#7323
- Reduce texture blurriness for TAA
## Solution
- Add a `MipBias` component and view uniform.
- Switch material `textureSample()` calls to `textureSampleBias()`.
- Add a `-1.0` bias to TAA.
---
## Changelog
- Added `MipBias` camera component, mostly for internal use.
---------
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Add morph targets to `bevy_pbr` (closes#5756) & load them from glTF
- Supersedes #3722
- Fixes#6814
[Morph targets][1] (also known as shape interpolation, shape keys, or
blend shapes) allow animating individual vertices with fine grained
controls. This is typically used for facial expressions. By specifying
multiple poses as vertex offset, and providing a set of weight of each
pose, it is possible to define surprisingly realistic transitions
between poses. Blending between multiple poses also allow composition.
Morph targets are part of the [gltf standard][2] and are a feature of
Unity and Unreal, and babylone.js, it is only natural to implement them
in bevy.
## Solution
This implementation of morph targets uses a 3d texture where each pixel
is a component of an animated attribute. Each layer is a different
target. We use a 2d texture for each target, because the number of
attribute×components×animated vertices is expected to always exceed the
maximum pixel row size limit of webGL2. It copies fairly closely the way
skinning is implemented on the CPU side, while on the GPU side, the
shader morph target implementation is a relatively trivial detail.
We add an optional `morph_texture` to the `Mesh` struct. The
`morph_texture` is built through a method that accepts an iterator over
attribute buffers.
The `MorphWeights` component, user-accessible, controls the blend of
poses used by mesh instances (so that multiple copy of the same mesh may
have different weights), all the weights are uploaded to a uniform
buffer of 256 `f32`. We limit to 16 poses per mesh, and a total of 256
poses.
More literature:
* Old babylone.js implementation (vertex attribute-based):
https://www.eternalcoding.com/dev-log-1-morph-targets/
* Babylone.js implementation (similar to ours):
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LBPRmGgU0PE
* GPU gems 3:
https://developer.nvidia.com/gpugems/gpugems3/part-i-geometry/chapter-3-directx-10-blend-shapes-breaking-limits
* Development discord thread
https://discord.com/channels/691052431525675048/1083325980615114772https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/26321040/231181046-3bca2ab2-d4d9-472e-8098-639f1871ce2e.mp4https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/26321040/d2a0c544-0ef8-45cf-9f99-8c3792f5a258
## Acknowledgements
* Thanks to `storytold` for sponsoring the feature
* Thanks to `superdump` and `james7132` for guidance and help figuring
out stuff
## Future work
- Handling of less and more attributes (eg: animated uv, animated
arbitrary attributes)
- Dynamic pose allocation (so that zero-weighted poses aren't uploaded
to GPU for example, enables much more total poses)
- Better animation API, see #8357
----
## Changelog
- Add morph targets to bevy meshes
- Support up to 64 poses per mesh of individually up to 116508 vertices,
animation currently strictly limited to the position, normal and tangent
attributes.
- Load a morph target using `Mesh::set_morph_targets`
- Add `VisitMorphTargets` and `VisitMorphAttributes` traits to
`bevy_render`, this allows defining morph targets (a fairly complex and
nested data structure) through iterators (ie: single copy instead of
passing around buffers), see documentation of those traits for details
- Add `MorphWeights` component exported by `bevy_render`
- `MorphWeights` control mesh's morph target weights, blending between
various poses defined as morph targets.
- `MorphWeights` are directly inherited by direct children (single level
of hierarchy) of an entity. This allows controlling several mesh
primitives through a unique entity _as per GLTF spec_.
- Add `MorphTargetNames` component, naming each indices of loaded morph
targets.
- Load morph targets weights and buffers in `bevy_gltf`
- handle morph targets animations in `bevy_animation` (previously, it
was a `warn!` log)
- Add the `MorphStressTest.gltf` asset for morph targets testing, taken
from the glTF samples repo, CC0.
- Add morph target manipulation to `scene_viewer`
- Separate the animation code in `scene_viewer` from the rest of the
code, reducing `#[cfg(feature)]` noise
- Add the `morph_targets.rs` example to show off how to manipulate morph
targets, loading `MorpStressTest.gltf`
## Migration Guide
- (very specialized, unlikely to be touched by 3rd parties)
- `MeshPipeline` now has a single `mesh_layouts` field rather than
separate `mesh_layout` and `skinned_mesh_layout` fields. You should
handle all possible mesh bind group layouts in your implementation
- You should also handle properly the new `MORPH_TARGETS` shader def and
mesh pipeline key. A new function is exposed to make this easier:
`setup_moprh_and_skinning_defs`
- The `MeshBindGroup` is now `MeshBindGroups`, cached bind groups are
now accessed through the `get` method.
[1]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Morph_target_animation
[2]:
https://registry.khronos.org/glTF/specs/2.0/glTF-2.0.html#morph-targets
---------
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
Improve the documentation relating to windows, and update the parts that
have not been updated since version 0.8.
Version 0.9 introduced `Window` as a component, before that
`WindowDescriptor` (which would become `Window` later) was used to store
information about how a window will be created. Since version 0.9, from
my understanding, this information will also be synchronised with the
current state of the window, and can be used to modify this state.
However, some of the documentation has not been updated to reflect that,
here is an example:
https://docs.rs/bevy/0.8.0/bevy/window/enum.WindowMode.html /
https://docs.rs/bevy/latest/bevy/window/enum.WindowMode.html (notice
that the verb "Creates" is still there).
This PR aims at improving the documentation relating to windows.
## Solution
- Change "will" for "should" when relevant, "should" implies that the
information should in both direction (from the window state to the
`Window` component and vice-versa) and can be used to get and set, will
implies it is only used to set a state.
- Remove references to "creation" or be more clear about it.
- Reference back the `Window` component for most of its sub-structs.
- Clarify what needs to be clarified
- A lot of other minor changes, including fixing the link to W3schools
in `bevy_winit`
## Warning
Please note that my knowledge about how winit and bevy_winit work is
limited and some of the informations I added in the doc may be
inaccurate. A person who knows better how it works should review some of
my claims, in particular:
- How fullscreen works:
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/8858#discussion_r1232413155
- How WindowResolution / sizes work:
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/8858#discussion_r1233010719
- What happens when `WindowPosition` is set to `Centered` or
`Automatic`. From my understanding of the code, it should always be set
back to `At`, but is it really the case? For example [when creating the
window](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/main/crates/bevy_winit/src/winit_windows.rs#L74),
or when [a `WindowEvent::Moved` is
triggered](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/main/crates/bevy_winit/src/lib.rs#L602)
or when [Centered/Automatic by the code after the window is
created](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/main/crates/bevy_winit/src/system.rs#L243),
am I missing some cases and do the codes I linked do that in all of
them?
- Are there any field in the `Window` component that can't be used to
modify the state of the window, only at creation?
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Jerome Humbert <djeedai@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Fix the AsBindGroup texture attribute visibility flag parsing
- This appears to have been caused by a syn crate update which then the
visibility code got updated
- Also I noticed that by default the vertex and fragment flags were on,
so visibility(compute) would actually make the texture visible to
vertex, fragment and compute shaders, I fixed this too
## Solution
- Update flag parsing to use MetaList.parse_nested_meta function, which
loads the flags into a Vec then loop through those flags
- Change initial visibility flags to use VisibilityFlags::default()
rather than VisibilityFlags::vertex_fragment()
# Objective
- Better consistency with `add_systems`.
- Deprecating `add_plugin` in favor of a more powerful `add_plugins`.
- Allow passing `Plugin` to `add_plugins`.
- Allow passing tuples to `add_plugins`.
## Solution
- `App::add_plugins` now takes an `impl Plugins` parameter.
- `App::add_plugin` is deprecated.
- `Plugins` is a new sealed trait that is only implemented for `Plugin`,
`PluginGroup` and tuples over `Plugins`.
- All examples, benchmarks and tests are changed to use `add_plugins`,
using tuples where appropriate.
---
## Changelog
### Changed
- `App::add_plugins` now accepts all types that implement `Plugins`,
which is implemented for:
- Types that implement `Plugin`.
- Types that implement `PluginGroup`.
- Tuples (up to 16 elements) over types that implement `Plugins`.
- Deprecated `App::add_plugin` in favor of `App::add_plugins`.
## Migration Guide
- Replace `app.add_plugin(plugin)` calls with `app.add_plugins(plugin)`.
---------
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Providing a "noob-friendly" example since not many people are
proficient in 3D modeling / rendering concepts.
## Solution
- Adding more information to the example, with an explanation.
~~~~
_Thanks to Nocta on discord for helping out when I didn't understand the
subject well._
---------
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
# Objective
Fixes#6920
## Solution
From the issue discussion:
> From looking at the `AsBindGroup` derive macro implementation, the
fallback image's `TextureView` is used when the binding's
`Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`. Because this relies on already having
a view that matches the desired binding dimensions, I think the solution
will require creating a separate `GpuImage` for each possible
`TextureViewDimension`.
---
## Changelog
Users can now rely on `FallbackImage` to work with a texture binding of
any dimension.
# Objective
Discovered that PointLight did not implement FromReflect. Adding
FromReflect where Reflect is used. I overreached and applied this rule
everywhere there was a Reflect without a FromReflect, except from where
the compiler wouldn't allow me.
Based from question: https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/discussions/8774
## Solution
- Adding FromReflect where Reflect was already derived
## Notes
First PR I do in this ecosystem, so not sure if this is the usual
approach, that is, to touch many files at once.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
We can currently set `camera.target` to either an `Image` or `Window`.
For OpenXR & WebXR we need to be able to render to a `TextureView`.
This partially addresses #115 as with the addition we can create
internal and external xr crates.
## Solution
A `TextureView` item is added to the `RenderTarget` enum. It holds an id
which is looked up by a `ManualTextureViews` resource, much like how
`Assets<Image>` works.
I believe this approach was first used by @kcking in their [xr
fork](eb39afd51b/crates/bevy_render/src/camera/camera.rs (L322)).
The only change is that a `u32` is used to index the textures as
`FromReflect` does not support `uuid` and I don't know how to implement
that.
---
## Changelog
### Added
Render: Added `RenderTarget::TextureView` as a `camera.target` option,
enabling rendering directly to a `TextureView`.
## Migration Guide
References to the `RenderTarget` enum will need to handle the additional
field, ie in `match` statements.
---
## Comments
- The [wgpu
work](c039a74884)
done by @expenses allows us to create framebuffer texture views from
`wgpu v0.15, bevy 0.10`.
- I got the WebXR techniques from the [xr
fork](https://github.com/dekuraan/xr-bevy) by @dekuraan.
- I have tested this with a wip [external webxr
crate](018e22bb06/crates/bevy_webxr/src/bevy_utils/xr_render.rs (L50))
on an Oculus Quest 2.
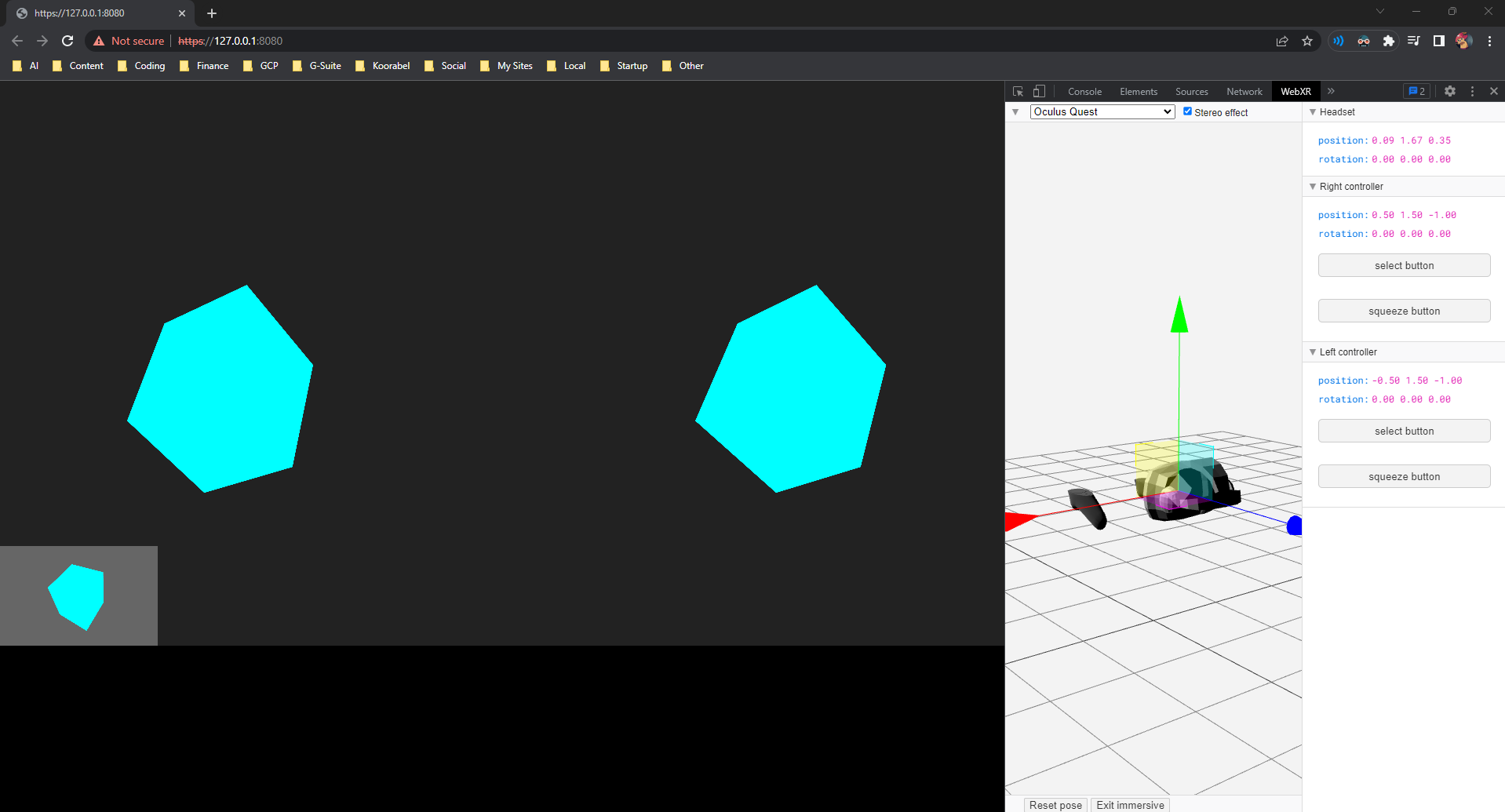
---------
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Paul Hansen <mail@paul.rs>
# Objective
Fix https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/1018 (Textures on the
`Plane` shape appear flipped).
This bug have been around for a very long time apparently, I tested it
was still there (see test code bellow) and sure enough, this image:

... is flipped vertically when used as a texture on a plane (in main,
0.10.1 and 0.9):

I'm pretty confused because this bug is so easy to fix, it has been
around for so long, it is easy to encounter, and PRs touching this code
still didn't fix it: https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/7546 To the
point where I'm wondering if it's actually intended. If it is, please
explain why and this PR can be changed to "mention that in the doc".
## Solution
Fix the UV mapping on the Plane shape
Here is how it looks after the PR

## Test code
```rust
use bevy::{
prelude::*,
};
fn main () {
App::new()
.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins)
.add_startup_system(setup)
.run();
}
fn setup(
mut commands: Commands,
assets: ResMut<AssetServer>,
mut meshes: ResMut<Assets<Mesh>>,
mut materials: ResMut<Assets<StandardMaterial>>,
) {
commands.spawn(Camera3dBundle {
transform: Transform::from_xyz(0., 3., 0.).looking_at(Vec3::ZERO, Vec3::NEG_Z),
..default()
});
let mesh = meshes.add(Mesh::from(shape::Plane::default()));
let texture_image = assets.load("test.png");
let material = materials.add(StandardMaterial {
base_color_texture: Some(texture_image),
..default()
});
commands.spawn(PbrBundle {
mesh,
material,
..default()
});
}
```
## Changelog
Fix textures on `Plane` shapes being flipped vertically.
## Migration Guide
Flip the textures you use on `Plane` shapes.
# Objective
- Rename the `render::primitives::Plane` struct as to not confuse it
with `bevy_render::mesh::shape::Plane`
- Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/8730
## Solution
- Refactor the `render::primitives::Plane` struct to
`render::primitives::HalfSpace`
- Modify documentation to reflect this change
## Changelog
- Renamed `Plane` to `HalfSpace` to more accurately represent it's use
- Renamed `planes` member in `Frustum` to `half_spaces` to reflect
changes
## Migration Guide
- `Plane` has been renamed to `HalfSpace`
- `planes` member in `Frustum` has been renamed to `half_spaces`
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Nicola Papale <nicopap@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
- When a window is closed, the associated camera keeps rendering even if
the RenderTarget isn't valid anymore.
- This is essentially just wasting a lot of performance.
## Solution
- Detect the window close event and disable any camera that used the
window has a RenderTarget.
## Notes
It's possible a similar thing could be done for camera that use an image
handle, but I would fix that in a separate PR.
# Objective
`NoFrustumCulling` doesn't implement `Reflect`, while nothing prevents
it from implementing it.
## Solution
Implement `Reflect` for it.
---
## Changelog
- Add `Reflect` derive to `NoFrustrumCulling`.
- Add `FromReflect` derive to `Visibility`.
Updates the requirements on
[ruzstd](https://github.com/KillingSpark/zstd-rs) to permit the latest
version.
<details>
<summary>Release notes</summary>
<p><em>Sourced from <a
href="https://github.com/KillingSpark/zstd-rs/releases">ruzstd's
releases</a>.</em></p>
<blockquote>
<h2>No-std support and better dict API</h2>
<p>This release features no-std support with big thanks to <a
href="https://github.com/antangelo"><code>@antangelo</code></a>!</p>
<p>Also the API for dictionaries has been revised, which required some
breaking changes in that department</p>
</blockquote>
</details>
<details>
<summary>Commits</summary>
<ul>
<li><a
href="fa7bd9c7b3"><code>fa7bd9c</code></a>
allow streaming decoder to also be used with a &mut FrameDecoder for
easier r...</li>
<li><a
href="3b6403b8e7"><code>3b6403b</code></a>
reenable forcing a different dict</li>
<li><a
href="2be7fbb01b"><code>2be7fbb</code></a>
Merge pull request <a
href="https://redirect.github.com/KillingSpark/zstd-rs/issues/40">#40</a>
from KillingSpark/overhaul_dicts</li>
<li><a
href="343d69b339"><code>343d69b</code></a>
no need to check that the dict still matches at the start of each decode
call</li>
<li><a
href="d73f5e689a"><code>d73f5e6</code></a>
cargo fmt</li>
<li><a
href="f3f09c76f0"><code>f3f09c7</code></a>
improve initing the decoder from a dict</li>
<li><a
href="0b9331dd19"><code>0b9331d</code></a>
make clippy happy</li>
<li><a
href="06433dec34"><code>06433de</code></a>
start overhauling dict API</li>
<li><a
href="1256944604"><code>1256944</code></a>
Update ci.yml</li>
<li><a
href="3449d0a2bf"><code>3449d0a</code></a>
Merge pull request <a
href="https://redirect.github.com/KillingSpark/zstd-rs/issues/39">#39</a>
from antangelo/no_std</li>
<li>Additional commits viewable in <a
href="https://github.com/KillingSpark/zstd-rs/compare/v0.3.1...v0.4.0">compare
view</a></li>
</ul>
</details>
<br />
Dependabot will resolve any conflicts with this PR as long as you don't
alter it yourself. You can also trigger a rebase manually by commenting
`@dependabot rebase`.
[//]: # (dependabot-automerge-start)
[//]: # (dependabot-automerge-end)
---
<details>
<summary>Dependabot commands and options</summary>
<br />
You can trigger Dependabot actions by commenting on this PR:
- `@dependabot rebase` will rebase this PR
- `@dependabot recreate` will recreate this PR, overwriting any edits
that have been made to it
- `@dependabot merge` will merge this PR after your CI passes on it
- `@dependabot squash and merge` will squash and merge this PR after
your CI passes on it
- `@dependabot cancel merge` will cancel a previously requested merge
and block automerging
- `@dependabot reopen` will reopen this PR if it is closed
- `@dependabot close` will close this PR and stop Dependabot recreating
it. You can achieve the same result by closing it manually
- `@dependabot ignore this major version` will close this PR and stop
Dependabot creating any more for this major version (unless you reopen
the PR or upgrade to it yourself)
- `@dependabot ignore this minor version` will close this PR and stop
Dependabot creating any more for this minor version (unless you reopen
the PR or upgrade to it yourself)
- `@dependabot ignore this dependency` will close this PR and stop
Dependabot creating any more for this dependency (unless you reopen the
PR or upgrade to it yourself)
</details>
Signed-off-by: dependabot[bot] <support@github.com>
Co-authored-by: dependabot[bot] <49699333+dependabot[bot]@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
- Introduce a stable alternative to
[`std::any::type_name`](https://doc.rust-lang.org/std/any/fn.type_name.html).
- Rewrite of #5805 with heavy inspiration in design.
- On the path to #5830.
- Part of solving #3327.
## Solution
- Add a `TypePath` trait for static stable type path/name information.
- Add a `TypePath` derive macro.
- Add a `impl_type_path` macro for implementing internal and foreign
types in `bevy_reflect`.
---
## Changelog
- Added `TypePath` trait.
- Added `DynamicTypePath` trait and `get_type_path` method to `Reflect`.
- Added a `TypePath` derive macro.
- Added a `bevy_reflect::impl_type_path` for implementing `TypePath` on
internal and foreign types in `bevy_reflect`.
- Changed `bevy_reflect::utility::(Non)GenericTypeInfoCell` to
`(Non)GenericTypedCell<T>` which allows us to be generic over both
`TypeInfo` and `TypePath`.
- `TypePath` is now a supertrait of `Asset`, `Material` and
`Material2d`.
- `impl_reflect_struct` needs a `#[type_path = "..."]` attribute to be
specified.
- `impl_reflect_value` needs to either specify path starting with a
double colon (`::core::option::Option`) or an `in my_crate::foo`
declaration.
- Added `bevy_reflect_derive::ReflectTypePath`.
- Most uses of `Ident` in `bevy_reflect_derive` changed to use
`ReflectTypePath`.
## Migration Guide
- Implementors of `Asset`, `Material` and `Material2d` now also need to
derive `TypePath`.
- Manual implementors of `Reflect` will need to implement the new
`get_type_path` method.
## Open Questions
- [x] ~This PR currently does not migrate any usages of
`std::any::type_name` to use `bevy_reflect::TypePath` to ease the review
process. Should it?~ Migration will be left to a follow-up PR.
- [ ] This PR adds a lot of `#[derive(TypePath)]` and `T: TypePath` to
satisfy new bounds, mostly when deriving `TypeUuid`. Should we make
`TypePath` a supertrait of `TypeUuid`? [Should we remove `TypeUuid` in
favour of
`TypePath`?](2afbd85532 (r961067892))
# Objective
- `apply_system_buffers` is an unhelpful name: it introduces a new
internal-only concept
- this is particularly rough for beginners as reasoning about how
commands work is a critical stumbling block
## Solution
- rename `apply_system_buffers` to the more descriptive `apply_deferred`
- rename related fields, arguments and methods in the internals fo
bevy_ecs for consistency
- update the docs
## Changelog
`apply_system_buffers` has been renamed to `apply_deferred`, to more
clearly communicate its intent and relation to `Deferred` system
parameters like `Commands`.
## Migration Guide
- `apply_system_buffers` has been renamed to `apply_deferred`
- the `apply_system_buffers` method on the `System` trait has been
renamed to `apply_deferred`
- the `is_apply_system_buffers` function has been replaced by
`is_apply_deferred`
- `Executor::set_apply_final_buffers` is now
`Executor::set_apply_final_deferred`
- `Schedule::apply_system_buffers` is now `Schedule::apply_deferred`
---------
Co-authored-by: JoJoJet <21144246+JoJoJet@users.noreply.github.com>
- Supress false positive `redundant_clone` lints.
- Supress inactionable `result_large_err` lint.
Most of the size(50 out of 68 bytes) is coming from
`naga::WithSpan<naga::valid::ValidationError>`
# Objective
- Make #8015 easier to review;
## Solution
- This commit contains changes not directly related to transmission
required by #8015, in easier-to-review, one-change-per-commit form.
---
## Changelog
### Fixed
- Clear motion vector prepass using `0.0` instead of `1.0`, to avoid TAA
artifacts on transparent objects against the background;
### Added
- The `E` mathematical constant is now available for use in shaders,
exposed under `bevy_pbr::utils`;
- A new `TAA` shader def is now available, for conditionally enabling
shader logic via `#ifdef` when TAA is enabled; (e.g. for jittering
texture samples)
- A new `FallbackImageZero` resource is introduced, for when a fallback
image filled with zeroes is required;
- A new `RenderPhase<I>::render_range()` method is introduced, for
render phases that need to render their items in multiple parceled out
“steps”;
### Changed
- The `MainTargetTextures` struct now holds both `Texture` and
`TextureViews` for the main textures;
- The fog shader functions under `bevy_pbr::fog` now take the a `Fog`
structure as their first argument, instead of relying on the global
`fog` uniform;
- The main textures can now be used as copy sources;
## Migration Guide
- `ViewTarget::main_texture()` and `ViewTarget::main_texture_other()`
now return `&Texture` instead of `&TextureView`. If you were relying on
these methods, replace your usage with
`ViewTarget::main_texture_view()`and
`ViewTarget::main_texture_other_view()`, respectively;
- `ViewTarget::sampled_main_texture()` now returns `Option<&Texture>`
instead of a `Option<&TextureView>`. If you were relying on this method,
replace your usage with `ViewTarget::sampled_main_texture_view()`;
- The `apply_fog()`, `linear_fog()`, `exponential_fog()`,
`exponential_squared_fog()` and `atmospheric_fog()` functions now take a
configurable `Fog` struct. If you were relying on them, update your
usage by adding the global `fog` uniform as their first argument;
# Objective
Fix#8604
## Solution
Use `.add_srgb_suffix()` when creating the screenshot texture.
Allow converting `Bgra8Unorm` images.
Only a two line change for the fix, the `screenshot.rs` changes are just
a bit of cleanup.
# Objective
Fix warnings:
```rs
warning: variable does not need to be mutable
--> /bevy/crates/bevy_app/src/plugin_group.rs:147:13
|
147 | let mut plugin_entry = self
| ----^^^^^^^^^^^^
| |
| help: remove this `mut`
|
= note: `#[warn(unused_mut)]` on by default
warning: variable does not need to be mutable
--> /bevy/crates/bevy_app/src/plugin_group.rs:161:13
|
161 | let mut plugin_entry = self
| ----^^^^^^^^^^^^
| |
| help: remove this `mut`
warning: `bevy_app` (lib) generated 2 warnings (run `cargo fix --lib -p bevy_app` to apply 2 suggestions)
warning: variable does not need to be mutable
--> /bevy/crates/bevy_render/src/view/window.rs:126:13
|
126 | ... let mut extracted_window = extracted_windows.entry(entity).or_insert(Extracte...
| ----^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
= note: `#[warn(unused_mut)]` on by default
warning: `bevy_render` (lib) generated 1 warning (run `cargo fix --lib -p bevy_render` to apply 1 suggestion)
```
## Solution
- Remove the mut keyword in those variables.
# Objective
- Update dependencies `ruzstd` and `basis-universal`
- Alternative to #5278 and #8133
## Solution
- Update the dependencies, fix the code
- Bevy now also depend on `syn@2` so it's not a blocker to update
`ruzstd` anymore
# Objective
Fix an out-of-date doc string.
The old doc string says "returns None if …" and "for a given
descriptor",
but this method neither takes an argument or returns an `Option`.
# Objective
Add support for the [Netpbm](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Netpbm) image
formats, behind a `pnm` feature flag.
My personal use case for this was robotics applications, with `pgm`
being a popular format used in the field to represent world maps in
robots.
I chose the formats and feature name by checking the logic in
[image.rs](a35ed552fa/crates/bevy_render/src/texture/image.rs (L76))
## Solution
Quite straightforward, the `pnm` feature flag already exists in the
`image` crate so it's just creating and exposing a `pnm` feature flag in
the root `Cargo.toml` and forwarding it through `bevy_internal` and
`bevy_render` all the way to the `image` crate.
---
## Changelog
### Added
`pnm` feature to add support for `pam`, `pbm`, `pgm` and `ppm` image
formats.
---------
Signed-off-by: Luca Della Vedova <lucadv@intrinsic.ai>
# Objective
- Fixes#3531
## Solution
- Added an append wrapper to BufferVec based on the function signature
for vec.append()
---
First PR to Bevy. I didn't see any tests for other BufferVec methods
(could have missed them) and currently this method is not used anywhere
in the project. Let me know if there are tests to add or if I should
find somewhere to use append so it is not dead code. The issue mentions
implementing `truncate` and `extend` which were already implemented and
merged
[here](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/6833/files#diff-c8fb332382379e383f1811e30c31991b1e0feb38ca436c357971755368012ced)
# Objective
- When writing render nodes that need a view, you always need to define
a `Query` on the associated view and make sure to update it manually and
query it manually. This is verbose and error prone.
## Solution
- Introduce a new `ViewNode` trait and `ViewNodeRunner` `Node` that will
take care of managing the associated view query automatically.
- The trait is currently a passthrough of the `Node` trait. So it still
has the update/run with all the same data passed in.
- The `ViewNodeRunner` is the actual node that is added to the render
graph and it contains the custom node. This is necessary because it's
the one that takes care of updating the node.
---
## Changelog
- Add `ViewNode`
- Add `ViewNodeRunner`
## Notes
Currently, this only handles the view query, but it could probably have
a ReadOnlySystemState that would also simplify querying all the readonly
resources that most render nodes currently query manually. The issue is
that I don't know how to do that without a `&mut self`.
At first, I tried making this a default feature of all `Node`, but I
kept hitting errors related to traits and generics and stuff I'm not
super comfortable with. This implementations is much simpler and keeps
the default Node behaviour so isn't a breaking change
## Reviewer Notes
The PR looks quite big, but the core of the PR is the changes in
`render_graph/node.rs`. Every other change is simply updating existing
nodes to use this new feature.
## Open questions
~~- Naming is not final, I'm opened to anything. I named it
ViewQueryNode because it's a node with a managed Query on a View.~~
~~- What to do when the query fails? All nodes using this pattern
currently just `return Ok(())` when it fails, so I chose that, but
should it be more flexible?~~
~~- Is the ViewQueryFilter actually necessary? All view queries run on
the entity that is already guaranteed to be a view. Filtering won't do
much, but maybe someone wants to control an effect with the presence of
a component instead of a flag.~~
~~- What to do with Nodes that are empty struct? Implementing
`FromWorld` is pretty verbose but not implementing it means there's 2
ways to create a `ViewNodeRunner` which seems less ideal. This is an
issue now because most node simply existed to hold the query, but now
that they don't hold the query state we are left with a bunch of empty
structs.~~
- Should we have a `RenderGraphApp::add_render_graph_view_node()`, this
isn't necessary, but it could make the code a bit shorter.
---------
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Fixes#8563
## Solution
~~- Implement From<Color> for [u8; 4]~~
~~- also implement From<[u8; 4]> for Color because why not.~~
- implement method `as_rgba_u8` in Color
---------
Co-authored-by: Gino Valente <49806985+MrGVSV@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
- Support WebGPU
- alternative to #5027 that doesn't need any async / await
- fixes#8315
- Surprise fix#7318
## Solution
### For async renderer initialisation
- Update the plugin lifecycle:
- app builds the plugin
- calls `plugin.build`
- registers the plugin
- app starts the event loop
- event loop waits for `ready` of all registered plugins in the same
order
- returns `true` by default
- then call all `finish` then all `cleanup` in the same order as
registered
- then execute the schedule
In the case of the renderer, to avoid anything async:
- building the renderer plugin creates a detached task that will send
back the initialised renderer through a mutex in a resource
- `ready` will wait for the renderer to be present in the resource
- `finish` will take that renderer and place it in the expected
resources by other plugins
- other plugins (that expect the renderer to be available) `finish` are
called and they are able to set up their pipelines
- `cleanup` is called, only custom one is still for pipeline rendering
### For WebGPU support
- update the `build-wasm-example` script to support passing `--api
webgpu` that will build the example with WebGPU support
- feature for webgl2 was always enabled when building for wasm. it's now
in the default feature list and enabled on all platforms, so check for
this feature must also check that the target_arch is `wasm32`
---
## Migration Guide
- `Plugin::setup` has been renamed `Plugin::cleanup`
- `Plugin::finish` has been added, and plugins adding pipelines should
do it in this function instead of `Plugin::build`
```rust
// Before
impl Plugin for MyPlugin {
fn build(&self, app: &mut App) {
app.insert_resource::<MyResource>
.add_systems(Update, my_system);
let render_app = match app.get_sub_app_mut(RenderApp) {
Ok(render_app) => render_app,
Err(_) => return,
};
render_app
.init_resource::<RenderResourceNeedingDevice>()
.init_resource::<OtherRenderResource>();
}
}
// After
impl Plugin for MyPlugin {
fn build(&self, app: &mut App) {
app.insert_resource::<MyResource>
.add_systems(Update, my_system);
let render_app = match app.get_sub_app_mut(RenderApp) {
Ok(render_app) => render_app,
Err(_) => return,
};
render_app
.init_resource::<OtherRenderResource>();
}
fn finish(&self, app: &mut App) {
let render_app = match app.get_sub_app_mut(RenderApp) {
Ok(render_app) => render_app,
Err(_) => return,
};
render_app
.init_resource::<RenderResourceNeedingDevice>();
}
}
```
# Objective
- I want to take screenshots of examples in CI to help with validation
of changes
## Solution
- Can override how much time is updated per frame
- Can specify on which frame to take a screenshots
- Save screenshots in CI
I reused the `TimeUpdateStrategy::ManualDuration` to be able to set the
time update strategy to a fixed duration every frame. Its previous
meaning didn't make much sense to me. This change makes it possible to
have screenshots that are exactly the same across runs.
If this gets merged, I'll add visual comparison of screenshots between
runs to ensure nothing gets broken
## Migration Guide
* `TimeUpdateStrategy::ManualDuration` meaning has changed. Instead of
setting time to `Instant::now()` plus the given duration, it sets time
to last update plus the given duration.
# Objective
- Handle dangling entity references inside scenes
- Handle references to entities with generation > 0 inside scenes
- Fix a latent bug in `Parent`'s `MapEntities` implementation, which
would, if the parent was outside the scene, cause the scene to be loaded
into the new world with a parent reference potentially pointing to some
random entity in that new world.
- Fixes#4793 and addresses #7235
## Solution
- DynamicScenes now identify entities with a `Entity` instead of a u32,
therefore including generation
- `World` exposes a new `reserve_generations` function that despawns an
entity and advances its generation by some extra amount.
- `MapEntities` implementations have a new `get_or_reserve` function
available that will always return an `Entity`, establishing a new
mapping to a dead entity when the entity they are called with is not in
the `EntityMap`. Subsequent calls with that same `Entity` will return
the same newly created dead entity reference, preserving equality
semantics.
- As a result, after loading a scene containing references to dead
entities (or entities otherwise outside the scene), those references
will all point to different generations on a single entity id in the new
world.
---
## Changelog
### Changed
- In serialized scenes, entities are now identified by a u64 instead of
a u32.
- In serialized scenes, components with entity references now have those
references serialize as u64s instead of structs.
### Fixed
- Scenes containing components with entity references will now
deserialize and add to a world reliably.
## Migration Guide
- `MapEntities` implementations must change from a `&EntityMap`
parameter to a `&mut EntityMapper` parameter and can no longer return a
`Result`. Finally, they should switch from calling `EntityMap::get` to
calling `EntityMapper::get_or_reserve`.
---------
Co-authored-by: Nicola Papale <nicopap@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
- Enable taking a screenshot in wasm
- Followup on #7163
## Solution
- Create a blob from the image data, generate a url to that blob, add an
`a` element to the document linking to that url, click on that element,
then revoke the url
- This will automatically trigger a download of the screenshot file in
the browser
# Objective
- Updated to wgpu 0.16.0 and wgpu-hal 0.16.0
---
## Changelog
1. Upgrade wgpu to 0.16.0 and wgpu-hal to 0.16.0
2. Fix the error in native when using a filterable
`TextureSampleType::Float` on a multisample `BindingType::Texture`.
([https://github.com/gfx-rs/wgpu/pull/3686](https://github.com/gfx-rs/wgpu/pull/3686))
---------
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Reduce compilation time
## Solution
- Make `spirv` and `glsl` shader format support optional. They are not
needed for Bevy shaders.
- on my mac (where shaders are compiled to `msl`), this reduces the
total build time by 2 to 5 seconds, improvement should be even better
with less cores
There is a big reduction in compile time for `naga`, and small
improvements on `wgpu` and `bevy_render`
This PR with optional shader formats enabled timings:
<img width="1478" alt="current main"
src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/8672791/234347032-cbd5c276-a9b0-49c3-b793-481677391c18.png">
This PR:
<img width="1479" alt="this pr"
src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/8672791/234347059-a67412a9-da8d-4356-91d8-7b0ae84ca100.png">
---
## Migration Guide
- If you want to use shaders in `spirv`, enable the
`shader_format_spirv` feature
- If you want to use shaders in `glsl`, enable the `shader_format_glsl`
feature
# Objective
`Camera::logical_viewport_rect()` returns `Option<(Vec2, Vec2)>` which
is a tuple of vectors representing the `(min, max)` bounds of the
viewport rect. Since the function says it returns a rect and there is a
`Rect { min, max }` struct in `bevy_math`, using the struct will be
clearer.
## Solution
Replaced `Option<(Vec2, Vec2)>` with `Option<Rect>` for
`Camera::logical_viewport_rect()`.
---
## Changelog
- Changed `Camera::logical_viewport_rect` return type from `(Vec2,
Vec2)` to `Rect`
## Migration Guide
Before:
```
fn view_logical_camera_rect(camera_query: Query<&Camera>) {
let camera = camera_query.single();
let Some((min, max)) = camera.logical_viewport_rect() else { return };
dbg!(min, max);
}
```
After:
```
fn view_logical_camera_rect(camera_query: Query<&Camera>) {
let camera = camera_query.single();
let Some(Rect { min, max }) = camera.logical_viewport_rect() else { return };
dbg!(min, max);
}
```
This line does not appear to be an intended part of the `Panics`
section, but instead looks like it was missed when copy-pasting a
`Panics` section from above.
It confused me when I was reading the docs. At first I read it as if it
was an imperative statement saying not to use `match` statements which
seemed odd and out of place. Once I saw the code it was clearly in err.
# Objective
- Cleanup documentation string to reduce end-user confusion.
Links in the api docs are nice. I noticed that there were several places
where structs / functions and other things were referenced in the docs,
but weren't linked. I added the links where possible / logical.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/1207
# Objective
Right now, it's impossible to capture a screenshot of the entire window
without forking bevy. This is because
- The swapchain texture never has the COPY_SRC usage
- It can't be accessed without taking ownership of it
- Taking ownership of it breaks *a lot* of stuff
## Solution
- Introduce a dedicated api for taking a screenshot of a given bevy
window, and guarantee this screenshot will always match up with what
gets put on the screen.
---
## Changelog
- Added the `ScreenshotManager` resource with two functions,
`take_screenshot` and `save_screenshot_to_disk`
# Objective
fixes#8348
## Solution
- Uses multi-line string with backslashes allowing rustfmt to work
properly in the surrounding area.
---------
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
# Objective
Fix#8321
## Solution
The `old_viewport_size` that is used to detect whether the viewport has
changed was not being updated and thus always `None`.
# Objective
when a mesh uses zero for all bone weights, vertices end up in the
middle of the screen.
## Solution
we can address this by explicitly setting the first bone weight to 1
when the weights are given as zero. this is the approach taken by
[unity](https://forum.unity.com/threads/whats-the-problem-with-this-import-fbx-warning.133736/)
(although that also sets the bone index to zero) and
[three.js](94c1a4b86f/src/objects/SkinnedMesh.js (L98)),
and likely other engines.
## Alternatives
it does add a bit of overhead, and users can always fix this themselves,
though it's a bit awkward particularly with gltfs.
(note - this is for work so my sme status shouldn't apply)
---------
Co-authored-by: ira <JustTheCoolDude@gmail.com>
Fixes issue mentioned in PR #8285.
_Note: By mistake, this is currently dependent on #8285_
# Objective
Ensure consistency in the spelling of the documentation.
Exceptions:
`crates/bevy_mikktspace/src/generated.rs` - Has not been changed from
licence to license as it is part of a licensing agreement.
Maybe for further consistency,
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy-website should also be given a look.
## Solution
### Changed the spelling of the current words (UK/CN/AU -> US) :
cancelled -> canceled (Breaking API changes in #8285)
behaviour -> behavior (Breaking API changes in #8285)
neighbour -> neighbor
grey -> gray
recognise -> recognize
centre -> center
metres -> meters
colour -> color
### ~~Update [`engine_style_guide.md`]~~ Moved to #8324
---
## Changelog
Changed UK spellings in documentation to US
## Migration Guide
Non-breaking changes*
\* If merged after #8285
# Objective
The clippy lint `type_complexity` is known not to play well with bevy.
It frequently triggers when writing complex queries, and taking the
lint's advice of using a type alias almost always just obfuscates the
code with no benefit. Because of this, this lint is currently ignored in
CI, but unfortunately it still shows up when viewing bevy code in an
IDE.
As someone who's made a fair amount of pull requests to this repo, I
will say that this issue has been a consistent thorn in my side. Since
bevy code is filled with spurious, ignorable warnings, it can be very
difficult to spot the *real* warnings that must be fixed -- most of the
time I just ignore all warnings, only to later find out that one of them
was real after I'm done when CI runs.
## Solution
Suppress this lint in all bevy crates. This was previously attempted in
#7050, but the review process ended up making it more complicated than
it needs to be and landed on a subpar solution.
The discussion in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust-clippy/pull/10571
explores some better long-term solutions to this problem. Since there is
no timeline on when these solutions may land, we should resolve this
issue in the meantime by locally suppressing these lints.
### Unresolved issues
Currently, these lints are not suppressed in our examples, since that
would require suppressing the lint in every single source file. They are
still ignored in CI.
# Objective
Make the coordinate systems of screen-space items (cursor position, UI,
viewports, etc.) consistent.
## Solution
Remove the weird double inversion of the cursor position's Y origin.
Once in bevy_winit to the bottom and then again in bevy_ui back to the
top.
This leaves the origin at the top left like it is in every other popular
app framework.
Update the `world_to_viewport`, `viewport_to_world`, and
`viewport_to_world_2d` methods to flip the Y origin (as they should
since the viewport coordinates were always relative to the top left).
## Migration Guide
`Window::cursor_position` now returns the position of the cursor
relative to the top left instead of the bottom left.
This now matches other screen-space coordinates like
`RelativeCursorPosition`, UI, and viewports.
The `world_to_viewport`, `viewport_to_world`, and `viewport_to_world_2d`
methods on `Camera` now return/take the viewport position relative to
the top left instead of the bottom left.
If you were using `world_to_viewport` to position a UI node the returned
`y` value should now be passed into the `top` field on `Style` instead
of the `bottom` field.
Note that this might shift the position of the UI node as it is now
anchored at the top.
If you were passing `Window::cursor_position` to `viewport_to_world` or
`viewport_to_world_2d` no change is necessary.
# Objective
- RenderGraphExt was merged, but only used in limited situations
## Solution
- Fix some remaining issues with the existing api
- Use the new api in the main pass and mass writeback
- Add CORE_2D and CORE_3D constant to make render_graph code shorter
# Objective
While working on #8299, I noticed that we're using a `capacity` field,
even though `wgpu::Buffer` exposes a `size` accessor that does the same
thing.
## Solution
Remove it from all buffer wrappers. Use `wgpu::Buffer::size` instead.
Default to 0 if no buffer has been allocated yet.
# Objective
Fixes#8284. `values` is being pushed to separately from the actual
scratch buffer in `DynamicUniformBuffer::push` and
`DynamicStorageBuffer::push`. In both types, `values` is really only
used to track the number of elements being added to the buffer, yet is
causing extra allocations, size increments and excess copies.
## Solution
Remove it and its remaining uses. Replace it with accesses to `scratch`
instead.
I removed the `len` accessor, as it may be non-trivial to compute just
from `scratch`. If this is still desirable to have, we can keep a `len`
member field to track it instead of relying on `scratch`.
# Objective
- Adding a node to the render_graph can be quite verbose and error prone
because there's a lot of moving parts to it.
## Solution
- Encapsulate this in a simple utility method
- Mostly intended for optional nodes that have specific ordering
- Requires that the `Node` impl `FromWorld`, but every internal node is
built using a new function taking a `&mut World` so it was essentially
already `FromWorld`
- Use it for the bloom, fxaa and taa, nodes.
- The main nodes don't use it because they rely more on the order of
many nodes being added
---
## Changelog
- Impl `FromWorld` for `BloomNode`, `FxaaNode` and `TaaNode`
- Added `RenderGraph::add_node_edges()`
- Added `RenderGraph::sub_graph()`
- Added `RenderGraph::sub_graph_mut()`
- Added `RenderGraphApp`, `RenderGraphApp::add_render_graph_node`,
`RenderGraphApp::add_render_graph_edges`,
`RenderGraphApp::add_render_graph_edge`
## Notes
~~This was taken out of https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/7995
because it works on it's own. Once the linked PR is done, the new
`add_node()` will be simplified a bit since the input/output params
won't be necessary.~~
This feature will be useful in most of the upcoming render nodes so it's
impact will be more relevant at that point.
Partially fixes#7985
## Future work
* Add a way to automatically label nodes or at least make it part of the
trait. This would remove one more field from the functions added in this
PR
* Use it in the main pass 2d/3d
---------
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
The type `&World` is currently in an awkward place, since it has two
meanings:
1. Read-only access to the entire world.
2. Interior mutable access to the world; immutable and/or mutable access
to certain portions of world data.
This makes `&World` difficult to reason about, and surprising to see in
function signatures if one does not know about the interior mutable
property.
The type `UnsafeWorldCell` was added in #6404, which is meant to
alleviate this confusion by adding a dedicated type for interior mutable
world access. However, much of the engine still treats `&World` as an
interior mutable-ish type. One of those places is `SystemParam`.
## Solution
Modify `SystemParam::get_param` to accept `UnsafeWorldCell` instead of
`&World`. Simplify the safety invariants, since the `UnsafeWorldCell`
type encapsulates the concept of constrained world access.
---
## Changelog
`SystemParam::get_param` now accepts an `UnsafeWorldCell` instead of
`&World`. This type provides a high-level API for unsafe interior
mutable world access.
## Migration Guide
For manual implementers of `SystemParam`: the function `get_item` now
takes `UnsafeWorldCell` instead of `&World`. To access world data, use:
* `.get_entity()`, which returns an `UnsafeEntityCell` which can be used
to access component data.
* `get_resource()` and its variants, to access resource data.
# Objective
WebP is a modern image format developed by Google that offers a
significant reduction in file size compared to other image formats such
as PNG and JPEG, while still maintaining good image quality. This makes
it particularly useful for games with large numbers of images, such as
those with high-quality textures or detailed sprites, where file size
and loading times can have a significant impact on performance.
By adding support for WebP images in Bevy, game developers using this
engine can now take advantage of this modern image format and reduce the
memory usage and loading times of their games. This improvement can
ultimately result in a better gaming experience for players.
In summary, the objective of adding WebP image format support in Bevy is
to enable game developers to use a modern image format that provides
better compression rates and smaller file sizes, resulting in faster
loading times and reduced memory usage for their games.
## Solution
To add support for WebP images in Bevy, this pull request leverages the
existing `image` crate support for WebP. This implementation is easily
integrated into the existing Bevy asset-loading system. To maintain
compatibility with existing Bevy projects, WebP image support is
disabled by default, and developers can enable it by adding a feature
flag to their project's `Cargo.toml` file. With this feature, Bevy
becomes even more versatile for game developers and provides a valuable
addition to the game engine.
---
## Changelog
- Added support for WebP image format in Bevy game engine
## Migration Guide
To enable WebP image support in your Bevy project, add the following
line to your project's Cargo.toml file:
```toml
bevy = { version = "*", features = ["webp"]}
```

# Objective
- Implement an alternative antialias technique
- TAA scales based off of view resolution, not geometry complexity
- TAA filters textures, firefly pixels, and other aliasing not covered
by MSAA
- TAA additionally will reduce noise / increase quality in future
stochastic rendering techniques
- Closes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/3663
## Solution
- Add a temporal jitter component
- Add a motion vector prepass
- Add a TemporalAntialias component and plugin
- Combine existing MSAA and FXAA examples and add TAA
## Followup Work
- Prepass motion vector support for skinned meshes
- Move uniforms needed for motion vectors into a separate bind group,
instead of using different bind group layouts
- Reuse previous frame's GPU view buffer for motion vectors, instead of
recomputing
- Mip biasing for sharper textures, and or unjitter texture UVs
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/7323
- Compute shader for better performance
- Investigate FSR techniques
- Historical depth based disocclusion tests, for geometry disocclusion
- Historical luminance/hue based tests, for shading disocclusion
- Pixel "locks" to reduce blending rate / revamp history confidence
mechanism
- Orthographic camera support for TemporalJitter
- Figure out COD's 1-tap bicubic filter
---
## Changelog
- Added MotionVectorPrepass and TemporalJitter
- Added TemporalAntialiasPlugin, TemporalAntialiasBundle, and
TemporalAntialiasSettings
---------
Co-authored-by: IceSentry <c.giguere42@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: IceSentry <IceSentry@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Robert Swain <robert.swain@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Daniel Chia <danstryder@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: robtfm <50659922+robtfm@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Brandon Dyer <brandondyer64@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Edgar Geier <geieredgar@gmail.com>
# Objective
Documentation should no longer be using pre-stageless terminology to
avoid confusion.
## Solution
- update all docs referring to stages to instead refer to sets/schedules
where appropriate
- also mention `apply_system_buffers` for anything system-buffer-related
that previously referred to buffers being applied "at the end of a
stage"
A `RegularPolygon` is described by the circumscribed radius, not the
inscribed radius.
## Objective
- Correct documentation for `RegularPolygon`
## Solution
- Use the correct term
---------
Co-authored-by: Paul Hüber <phueber@kernsp.in>
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Currently, the render graph slots are only used to pass the
view_entity around. This introduces significant boilerplate for very
little value. Instead of using slots for this, make the view_entity part
of the `RenderGraphContext`. This also means we won't need to have
`IN_VIEW` on every node and and we'll be able to use the default impl of
`Node::input()`.
## Solution
- Add `view_entity: Option<Entity>` to the `RenderGraphContext`
- Update all nodes to use this instead of entity slot input
---
## Changelog
- Add optional `view_entity` to `RenderGraphContext`
## Migration Guide
You can now get the view_entity directly from the `RenderGraphContext`.
When implementing the Node:
```rust
// 0.10
struct FooNode;
impl FooNode {
const IN_VIEW: &'static str = "view";
}
impl Node for FooNode {
fn input(&self) -> Vec<SlotInfo> {
vec![SlotInfo::new(Self::IN_VIEW, SlotType::Entity)]
}
fn run(
&self,
graph: &mut RenderGraphContext,
// ...
) -> Result<(), NodeRunError> {
let view_entity = graph.get_input_entity(Self::IN_VIEW)?;
// ...
Ok(())
}
}
// 0.11
struct FooNode;
impl Node for FooNode {
fn run(
&self,
graph: &mut RenderGraphContext,
// ...
) -> Result<(), NodeRunError> {
let view_entity = graph.view_entity();
// ...
Ok(())
}
}
```
When adding the node to the graph, you don't need to specify a slot_edge
for the view_entity.
```rust
// 0.10
let mut graph = RenderGraph::default();
graph.add_node(FooNode::NAME, node);
let input_node_id = draw_2d_graph.set_input(vec![SlotInfo::new(
graph::input::VIEW_ENTITY,
SlotType::Entity,
)]);
graph.add_slot_edge(
input_node_id,
graph::input::VIEW_ENTITY,
FooNode::NAME,
FooNode::IN_VIEW,
);
// add_node_edge ...
// 0.11
let mut graph = RenderGraph::default();
graph.add_node(FooNode::NAME, node);
// add_node_edge ...
```
## Notes
This PR paired with #8007 will help reduce a lot of annoying boilerplate
with the render nodes. Depending on which one gets merged first. It will
require a bit of clean up work to make both compatible.
I tagged this as a breaking change, because using the old system to get
the view_entity will break things because it's not a node input slot
anymore.
## Notes for reviewers
A lot of the diffs are just removing the slots in every nodes and graph
creation. The important part is mostly in the
graph_runner/CameraDriverNode.
# Objective
- @mockersf identified a performance regression of about 25% longer frame times introduced by #7784 in a complex scene with the Amazon Lumberyard bistro scene with both exterior and interior variants and a number of point lights with shadow mapping enabled
- The additional time seemed to be spent in the `ShadowPassNode`
- `ShadowPassNode` encodes the draw commands for the shadow phase. Roughly the same numbers of entities were having draw commands encoded, so something about the way they were being encoded had changed.
- One thing that definitely changed was that the pipeline used will be different depending on the alpha mode, and the scene has lots entities with opaque and blend materials. This suggested that maybe the pipeline was changing a lot so I tried a quick hack to see if it was the problem.
## Solution
- Sort the shadow phase items by their pipeline id
- This groups phase items by their pipeline id, which significantly reduces pipeline rebinding required to the point that the performance regression was gone.
# Objective
Fixes#7757
New function `Color::as_lcha` was added and `Color::as_lch_f32` changed name to `Color::as_lcha_f32`.
----
As a side note I did it as in every other Color function, that is I created very simillar code in `as_lcha` as was in `as_lcha_f32`. However it is totally possible to avoid this code duplication in LCHA and other color variants by doing something like :
```
pub fn as_lcha(self: &Color) -> Color {
let (lightness, chroma, hue, alpha) = self.as_lcha_f32();
return Color::Lcha { lightness, chroma, hue, alpha };
}
```
This is maybe slightly less efficient but it avoids copy-pasting this huge match expression which is error prone. Anyways since it is my first commit here I wanted to be consistent with the rest of code but can refactor all variants in separate PR if somebody thinks it is good idea.
# Objective
- Fixes#7889.
## Solution
- Change the glTF loader to insert a `Camera3dBundle` instead of a manually constructed bundle. This might prevent future issues when new components are required for a 3D Camera to work correctly.
- Register the `ColorGrading` type because `bevy_scene` was complaining about it.
# Objective
- Update `glam` to the latest version.
## Solution
- Update `glam` to version `0.23`.
Since the breaking change in `glam` only affects the `scalar-math` feature, this should cause no issues.
# Objective
Alternative to #7490. I wrote all of the code in this PR, but I have added @robtfm as co-author on commits that build on ideas from #7490. I would not have been able to solve these problems on my own without much more time investment and I'm largely just rephrasing the ideas from that PR.
Fixes#7435Fixes#7361Fixes#5721
## Solution
This implements the solution I [outlined here](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/7490#issuecomment-1426580633).
* Adds "msaa writeback" as an explicit "msaa camera feature" and default to msaa_writeback: true for each camera. If this is true, a camera has MSAA enabled, and it isn't the first camera for the target, add a writeback before the main pass for that camera.
* Adds a CameraOutputMode, which can be used to configure if (and how) the results of a camera's rendering will be written to the final RenderTarget output texture (via the upscaling node). The `blend_state` and `color_attachment_load_op` are now configurable, giving much more control over how a camera will write to the output texture.
* Made cameras with the same target share the same main_texture tracker by using `Arc<AtomicUsize>`, which ensures continuity across cameras. This was previously broken / could produce weird results in some cases. `ViewTarget::main_texture()` is now correct in every context.
* Added a new generic / specializable BlitPipeline, which the new MsaaWritebackNode uses internally. The UpscalingPipelineNode now uses BlitPipeline instead of its own pipeline. We might ultimately need to fork this back out if we choose to add more configurability to the upscaling, but for now this will save on binary size by not embedding the same shader twice.
* Moved the "camera sorting" logic from the camera driver node to its own system. The results are now stored in the `SortedCameras` resource, which can be used anywhere in the renderer. MSAA writeback makes use of this.
---
## Changelog
- Added `Camera::msaa_writeback` which can enable and disable msaa writeback.
- Added specializable `BlitPipeline` and ported the upscaling node to use this.
- Added SortedCameras, exposing information that was previously internal to the camera driver node.
- Made cameras with the same target share the same main_texture tracker, which ensures continuity across cameras.
# Objective
Support the following syntax for adding systems:
```rust
App::new()
.add_system(setup.on_startup())
.add_systems((
show_menu.in_schedule(OnEnter(GameState::Paused)),
menu_ssytem.in_set(OnUpdate(GameState::Paused)),
hide_menu.in_schedule(OnExit(GameState::Paused)),
))
```
## Solution
Add the traits `IntoSystemAppConfig{s}`, which provide the extension methods necessary for configuring which schedule a system belongs to. These extension methods return `IntoSystemAppConfig{s}`, which `App::add_system{s}` uses to choose which schedule to add systems to.
---
## Changelog
+ Added the extension methods `in_schedule(label)` and `on_startup()` for configuring the schedule a system belongs to.
## Future Work
* Replace all uses of `add_startup_system` in the engine.
* Deprecate this method
# Objective
While working on #7784, I noticed that a `#define VAR` in a `.wgsl` file is always effective, even if it its scope is not accepting lines.
Example:
```c
#define A
#ifndef A
#define B
#endif
```
Currently, `B` will be defined although it shouldn't. This PR fixes that.
## Solution
Move the branch responsible for `#define` lines into the last else branch, which is only evaluated if the current scope is accepting lines.
# Objective
There was PR that introduced support for storage buffer is `AsBindGroup` macro [#6129](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/6129), but it does not give more granular control over storage buffer, it will always copy all the data no matter which part of it was updated. There is also currently another open PR #6669 that tries to achieve exactly that, it is just not up to date and seems abandoned (Sorry if that is not right). In this PR I'm proposing a solution for both of these approaches to co-exist using `#[storage(n, buffer)]` and `#[storage(n)]` to distinguish between the cases.
We could also discuss in this PR if there is a need to extend this support to DynamicBuffers as well.
# Objective
- Nothing render
```
ERROR bevy_render::render_resource::pipeline_cache: failed to process shader: Invalid shader def definition for '_import_path': bevy_pbr
```
## Solution
- Fix define regex so that it must have one whitespace after `define`
# Objective
- Fixes#7494
- It is now possible to define a ShaderDef from inside a shader. This can be useful to centralise a value, or making sure an import is only interpreted once
## Solution
- Support `#define <SHADERDEF_NAME> <optional value>`
# Objective
- ambiguities bad
## Solution
- solve ambiguities
- by either ignoring (e.g. on `queue_mesh_view_bind_groups` since `LightMeta` access is different)
- by introducing a dependency (`prepare_windows -> prepare_*` because the latter use the fallback Msaa)
- make `prepare_assets` public so that we can do a proper `.after`
# Objective
- Fix the environment map shader not working under webgl due to textureNumLevels() not being supported
- Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/7722
## Solution
- Instead of using textureNumLevels(), put an extra field in the GpuLights uniform to store the mip count
# Objective
Splits tone mapping from https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/6677 into a separate PR.
Address https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/2264.
Adds tone mapping options:
- None: Bypasses tonemapping for instances where users want colors output to match those set.
- Reinhard
- Reinhard Luminance: Bevy's exiting tonemapping
- [ACES](https://github.com/TheRealMJP/BakingLab/blob/master/BakingLab/ACES.hlsl) (Fitted version, based on the same implementation that Godot 4 uses) see https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/2264
- [AgX](https://github.com/sobotka/AgX)
- SomewhatBoringDisplayTransform
- TonyMcMapface
- Blender Filmic
This PR also adds support for EXR images so they can be used to compare tonemapping options with reference images.
## Migration Guide
- Tonemapping is now an enum with NONE and the various tonemappers.
- The DebandDither is now a separate component.
Co-authored-by: JMS55 <47158642+JMS55@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
Closes#7573
- Make `StartupSet` a base set
## Solution
- Add `#[system_set(base)]` to the enum declaration
- Replace `.in_set(StartupSet::...)` with `.in_base_set(StartupSet::...)`
**Note**: I don't really know what I'm doing and what exactly the difference between base and non-base sets are. I mostly opened this PR based on discussion in Discord. I also don't really know how to test that I didn't break everything. Your reviews are appreciated!
---
## Changelog
- `StartupSet` is now a base set
## Migration Guide
`StartupSet` is now a base set. This means that you have to use `.in_base_set` instead of `.in_set`:
### Before
```rs
app.add_system(foo.in_set(StartupSet::PreStartup))
```
### After
```rs
app.add_system(foo.in_base_set(StartupSet::PreStartup))
```
# Objective
Allow for creating pipelines that use push constants. To be able to use push constants. Fixes#4825
As of right now, trying to call `RenderPass::set_push_constants` will trigger the following error:
```
thread 'main' panicked at 'wgpu error: Validation Error
Caused by:
In a RenderPass
note: encoder = `<CommandBuffer-(0, 59, Vulkan)>`
In a set_push_constant command
provided push constant is for stage(s) VERTEX | FRAGMENT | VERTEX_FRAGMENT, however the pipeline layout has no push constant range for the stage(s) VERTEX | FRAGMENT | VERTEX_FRAGMENT
```
## Solution
Add a field push_constant_ranges to` RenderPipelineDescriptor` and `ComputePipelineDescriptor`.
This PR supersedes #4908 which now contains merge conflicts due to significant changes to `bevy_render`.
Meanwhile, this PR also made the `layout` field of `RenderPipelineDescriptor` and `ComputePipelineDescriptor` non-optional. If the user do not need to specify the bind group layouts, they can simply supply an empty vector here. No need for it to be optional.
---
## Changelog
- Add a field push_constant_ranges to RenderPipelineDescriptor and ComputePipelineDescriptor
- Made the `layout` field of RenderPipelineDescriptor and ComputePipelineDescriptor non-optional.
## Migration Guide
- Add push_constant_ranges: Vec::new() to every `RenderPipelineDescriptor` and `ComputePipelineDescriptor`
- Unwrap the optional values on the `layout` field of `RenderPipelineDescriptor` and `ComputePipelineDescriptor`. If the descriptor has no layout, supply an empty vector.
Co-authored-by: Zhixing Zhang <me@neoto.xin>
# Objective
Fixes#7295
Should we maybe default to 4x if 2x/8x is selected but not supported?
---
## Changelog
- Added 2x and 8x sample counts for MSAA.
# Objective
- Environment maps use these formats, and in the future rendering LUTs will need textures loaded by default in the engine
## Solution
- Make ktx2 and zstd part of the default feature
- Let examples assume these features are enabled
---
## Changelog
- `ktx2` and `zstd` are now party of bevy's default enabled features
## Migration Guide
- If you used the `ktx2` or `zstd` features, you no longer need to explicitly enable them, as they are now part of bevy's default enabled features
# Objective
- Fixes#5432
- Fixes#6680
## Solution
- move code responsible for generating the `impl TypeUuid` from `type_uuid_derive` into a new function, `gen_impl_type_uuid`.
- this allows the new proc macro, `impl_type_uuid`, to call the code for generation.
- added struct `TypeUuidDef` and implemented `syn::Parse` to allow parsing of the input for the new macro.
- finally, used the new macro `impl_type_uuid` to implement `TypeUuid` for the standard library (in `crates/bevy_reflect/src/type_uuid_impl.rs`).
- fixes#6680 by doing a wrapping add of the param's index to its `TYPE_UUID`
Co-authored-by: dis-da-moe <84386186+dis-da-moe@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
We have a few old system labels that are now system sets but are still named or documented as labels. Documentation also generally mentioned system labels in some places.
## Solution
- Clean up naming and documentation regarding system sets
## Migration Guide
`PrepareAssetLabel` is now called `PrepareAssetSet`
# Objective
- Fixes: #7187
Since avoiding the `SRes::into_inner` call does not seem to be possible, this PR tries to at least document its usage.
I am not sure if I explained the lifetime issue correctly, please let me know if something is incorrect.
## Solution
- Add information about the `SRes::into_inner` usage on both `RenderCommand` and `Res`
Profiles show that in extremely hot loops, like the draw loops in the renderer, invoking the trace! macro has noticeable overhead, even if the trace log level is not enabled.
Solve this by introduce a 'wrapper' detailed_trace macro around trace, that wraps the trace! log statement in a trivially false if statement unless a cargo feature is enabled
# Objective
- Eliminate significant overhead observed with trace-level logging in render hot loops, even when trace log level is not enabled.
- This is an alternative solution to the one proposed in #7223
## Solution
- Introduce a wrapper around the `trace!` macro called `detailed_trace!`. This macro wraps the `trace!` macro with an if statement that is conditional on a new cargo feature, `detailed_trace`. When the feature is not enabled (the default), then the if statement is trivially false and should be optimized away at compile time.
- Convert the observed hot occurrences of trace logging in `TrackedRenderPass` with this new macro.
Testing the results of
```
cargo run --profile stress-test --features bevy/trace_tracy --example many_cubes -- spheres
```
shows significant improvement of the `main_opaque_pass_3d` of the renderer, a median time decrease from 6.0ms to 3.5ms.
---
## Changelog
- For performance reasons, some detailed renderer trace logs now require the use of cargo feature `detailed_trace` in addition to setting the log level to `TRACE` in order to be shown.
## Migration Guide
- Some detailed bevy trace events now require the use of the cargo feature `detailed_trace` in addition to enabling `TRACE` level logging to view. Should you wish to see these logs, please compile your code with the bevy feature `detailed_trace`. Currently, the only logs that are affected are the renderer logs pertaining to `TrackedRenderPass` functions
# Objective
There was issue #191 requesting subdivisions on the shape::Plane.
I also could have used this recently. I then write the solution.
Fixes #191
## Solution
I changed the shape::Plane to include subdivisions field and the code to create the subdivisions. I don't know how people are counting subdivisions so as I put in the doc comments 0 subdivisions results in the original geometry of the Plane.
Greater then 0 results in the number of lines dividing the plane.
I didn't know if it would be better to create a new struct that implemented this feature, say SubdivisionPlane or change Plane. I decided on changing Plane as that was what the original issue was.
It would be trivial to alter this to use another struct instead of altering Plane.
The issues of migration, although small, would be eliminated if a new struct was implemented.
## Changelog
### Added
Added subdivisions field to shape::Plane
## Migration Guide
All the examples needed to be updated to initalize the subdivisions field.
Also there were two tests in tests/window that need to be updated.
A user would have to update all their uses of shape::Plane to initalize the subdivisions field.
fixes#6799
# Objective
We should be able to reuse the `Globals` or `View` shader struct definitions from anywhere (including third party plugins) without needing to worry about defining unrelated shader defs.
Also we'd like to refactor these structs to not be repeatedly defined.
## Solution
Refactor both `Globals` and `View` into separate importable shaders.
Use the imports throughout.
Co-authored-by: Torstein Grindvik <52322338+torsteingrindvik@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
- This makes code a little more readable now.
## Solution
- Use `position` provided by `Iter` instead of `enumerating` indices and `map`ping to the index.
This was missed in #7205.
Should be fixed now. 😄
## Migration Guide
- `SpecializedComputePipelines::specialize` now takes a `&PipelineCache` instead of a `&mut PipelineCache`
(Before)

(After)

# Objective
- Improve lighting; especially reflections.
- Closes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/4581.
## Solution
- Implement environment maps, providing better ambient light.
- Add microfacet multibounce approximation for specular highlights from Filament.
- Occlusion is no longer incorrectly applied to direct lighting. It now only applies to diffuse indirect light. Unsure if it's also supposed to apply to specular indirect light - the glTF specification just says "indirect light". In the case of ambient occlusion, for instance, that's usually only calculated as diffuse though. For now, I'm choosing to apply this just to indirect diffuse light, and not specular.
- Modified the PBR example to use an environment map, and have labels.
- Added `FallbackImageCubemap`.
## Implementation
- IBL technique references can be found in environment_map.wgsl.
- It's more accurate to use a LUT for the scale/bias. Filament has a good reference on generating this LUT. For now, I just used an analytic approximation.
- For now, environment maps must first be prefiltered outside of bevy using a 3rd party tool. See the `EnvironmentMap` documentation.
- Eventually, we should have our own prefiltering code, so that we can have dynamically changing environment maps, as well as let users drop in an HDR image and use asset preprocessing to create the needed textures using only bevy.
---
## Changelog
- Added an `EnvironmentMapLight` camera component that adds additional ambient light to a scene.
- StandardMaterials will now appear brighter and more saturated at high roughness, due to internal material changes. This is more physically correct.
- Fixed StandardMaterial occlusion being incorrectly applied to direct lighting.
- Added `FallbackImageCubemap`.
Co-authored-by: IceSentry <c.giguere42@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: James Liu <contact@jamessliu.com>
Co-authored-by: Rob Parrett <robparrett@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Terminology used in field names and docs aren't accurate
- `window_origin` doesn't have any effect when `scaling_mode` is `ScalingMode::None`
- `left`, `right`, `bottom`, and `top` are set automatically unless `scaling_mode` is `None`. Fields that only sometimes give feedback are confusing.
- `ScalingMode::WindowSize` has no arguments, which is inconsistent with other `ScalingMode`s. 1 pixel = 1 world unit is also typically way too wide.
- `OrthographicProjection` feels generally less streamlined than its `PerspectiveProjection` counterpart
- Fixes#5818
- Fixes#6190
## Solution
- Improve consistency in `OrthographicProjection`'s public fields (they should either always give feedback or never give feedback).
- Improve consistency in `ScalingMode`'s arguments
- General usability improvements
- Improve accuracy of terminology:
- "Window" should refer to the physical window on the desktop
- "Viewport" should refer to the component in the window that images are drawn on (typically all of it)
- "View frustum" should refer to the volume captured by the projection
---
## Changelog
### Added
- Added argument to `ScalingMode::WindowSize` that specifies the number of pixels that equals one world unit.
- Added documentation for fields and enums
### Changed
- Renamed `window_origin` to `viewport_origin`, which now:
- Affects all `ScalingMode`s
- Takes a fraction of the viewport's width and height instead of an enum
- Removed `WindowOrigin` enum as it's obsolete
- Renamed `ScalingMode::None` to `ScalingMode::Fixed`, which now:
- Takes arguments to specify the projection size
- Replaced `left`, `right`, `bottom`, and `top` fields with a single `area: Rect`
- `scale` is now applied before updating `area`. Reading from it will take `scale` into account.
- Documentation changes to make terminology more accurate and consistent
## Migration Guide
- Change `window_origin` to `viewport_origin`; replace `WindowOrigin::Center` with `Vec2::new(0.5, 0.5)` and `WindowOrigin::BottomLeft` with `Vec2::new(0.0, 0.0)`
- For shadow projections and such, replace `left`, `right`, `bottom`, and `top` with `area: Rect::new(left, bottom, right, top)`
- For camera projections, remove l/r/b/t values from `OrthographicProjection` instantiations, as they no longer have any effect in any `ScalingMode`
- Change `ScalingMode::None` to `ScalingMode::Fixed`
- Replace manual changes of l/r/b/t with:
- Arguments in `ScalingMode::Fixed` to specify size
- `viewport_origin` to specify offset
- Change `ScalingMode::WindowSize` to `ScalingMode::WindowSize(1.0)`
# Objective
Fix#7377Fix#7513
## Solution
Record the changes made to the Bevy `Window` from `winit` as 'canon' to avoid Bevy sending those changes back to `winit` again, causing a feedback loop.
## Changelog
* Removed `ModifiesWindows` system label.
Neither `despawn_window` nor `changed_window` actually modify the `Window` component so all the `.after(ModifiesWindows)` shouldn't be necessary.
* Moved `changed_window` and `despawn_window` systems to `CoreStage::Last` to avoid systems making changes to the `Window` between `changed_window` and the end of the frame as they would be ignored.
## Migration Guide
The `ModifiesWindows` system label was removed.
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
# Objective
Some render systems that have system set used as a label so that they can be referenced from somewhere else.
The 1:1 translation from `add_system_to_stage(Prepare, prepare_lights.label(PrepareLights))` is `add_system(prepare_lights.in_set(Prepare).in_set(PrepareLights)`, but configuring the `PrepareLights` set to be in `Prepare` would match the intention better (there are no systems in `PrepareLights` outside of `Prepare`) and it is easier for visualization tools to deal with.
# Solution
- replace
```rust
prepare_lights in PrepareLights
prepare_lights in Prepare
```
with
```rs
prepare_lights in PrepareLights
PrepareLights in Prepare
```
**Before**

**After**

# Objective
Buffers in bevy do not allow for setting buffer usage flags which can be useful for setting COPY_SRC, MAP_READ, MAP_WRITE, which allows for buffers to be copied from gpu to cpu for inspection.
## Solution
Add buffer_usage field to buffers and a set_usage function to set them
# Objective
- Fixes#766
## Solution
- Add a new `Lcha` member to `bevy_render::color::Color` enum
---
## Changelog
- Add a new `Lcha` member to `bevy_render::color::Color` enum
- Add `bevy_render::color::LchRepresentation` struct
# Objective
[as noted](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/5950#discussion_r1080762807) by james, transmuting arcs may be UB.
we now store a `*const ()` pointer internally, and only rely on `ptr.cast::<()>().cast::<T>() == ptr`.
as a happy side effect this removes the need for boxing the value, so todo: potentially use this for release mode as well
# Objective
NOTE: This depends on #7267 and should not be merged until #7267 is merged. If you are reviewing this before that is merged, I highly recommend viewing the Base Sets commit instead of trying to find my changes amongst those from #7267.
"Default sets" as described by the [Stageless RFC](https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/pull/45) have some [unfortunate consequences](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/discussions/7365).
## Solution
This adds "base sets" as a variant of `SystemSet`:
A set is a "base set" if `SystemSet::is_base` returns `true`. Typically this will be opted-in to using the `SystemSet` derive:
```rust
#[derive(SystemSet, Clone, Hash, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
#[system_set(base)]
enum MyBaseSet {
A,
B,
}
```
**Base sets are exclusive**: a system can belong to at most one "base set". Adding a system to more than one will result in an error. When possible we fail immediately during system-config-time with a nice file + line number. For the more nested graph-ey cases, this will fail at the final schedule build.
**Base sets cannot belong to other sets**: this is where the word "base" comes from
Systems and Sets can only be added to base sets using `in_base_set`. Calling `in_set` with a base set will fail. As will calling `in_base_set` with a normal set.
```rust
app.add_system(foo.in_base_set(MyBaseSet::A))
// X must be a normal set ... base sets cannot be added to base sets
.configure_set(X.in_base_set(MyBaseSet::A))
```
Base sets can still be configured like normal sets:
```rust
app.add_system(MyBaseSet::B.after(MyBaseSet::Ap))
```
The primary use case for base sets is enabling a "default base set":
```rust
schedule.set_default_base_set(CoreSet::Update)
// this will belong to CoreSet::Update by default
.add_system(foo)
// this will override the default base set with PostUpdate
.add_system(bar.in_base_set(CoreSet::PostUpdate))
```
This allows us to build apis that work by default in the standard Bevy style. This is a rough analog to the "default stage" model, but it use the new "stageless sets" model instead, with all of the ordering flexibility (including exclusive systems) that it provides.
---
## Changelog
- Added "base sets" and ported CoreSet to use them.
## Migration Guide
TODO
Huge thanks to @maniwani, @devil-ira, @hymm, @cart, @superdump and @jakobhellermann for the help with this PR.
# Objective
- Followup #6587.
- Minimal integration for the Stageless Scheduling RFC: https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/pull/45
## Solution
- [x] Remove old scheduling module
- [x] Migrate new methods to no longer use extension methods
- [x] Fix compiler errors
- [x] Fix benchmarks
- [x] Fix examples
- [x] Fix docs
- [x] Fix tests
## Changelog
### Added
- a large number of methods on `App` to work with schedules ergonomically
- the `CoreSchedule` enum
- `App::add_extract_system` via the `RenderingAppExtension` trait extension method
- the private `prepare_view_uniforms` system now has a public system set for scheduling purposes, called `ViewSet::PrepareUniforms`
### Removed
- stages, and all code that mentions stages
- states have been dramatically simplified, and no longer use a stack
- `RunCriteriaLabel`
- `AsSystemLabel` trait
- `on_hierarchy_reports_enabled` run criteria (now just uses an ad hoc resource checking run condition)
- systems in `RenderSet/Stage::Extract` no longer warn when they do not read data from the main world
- `RunCriteriaLabel`
- `transform_propagate_system_set`: this was a nonstandard pattern that didn't actually provide enough control. The systems are already `pub`: the docs have been updated to ensure that the third-party usage is clear.
### Changed
- `System::default_labels` is now `System::default_system_sets`.
- `App::add_default_labels` is now `App::add_default_sets`
- `CoreStage` and `StartupStage` enums are now `CoreSet` and `StartupSet`
- `App::add_system_set` was renamed to `App::add_systems`
- The `StartupSchedule` label is now defined as part of the `CoreSchedules` enum
- `.label(SystemLabel)` is now referred to as `.in_set(SystemSet)`
- `SystemLabel` trait was replaced by `SystemSet`
- `SystemTypeIdLabel<T>` was replaced by `SystemSetType<T>`
- The `ReportHierarchyIssue` resource now has a public constructor (`new`), and implements `PartialEq`
- Fixed time steps now use a schedule (`CoreSchedule::FixedTimeStep`) rather than a run criteria.
- Adding rendering extraction systems now panics rather than silently failing if no subapp with the `RenderApp` label is found.
- the `calculate_bounds` system, with the `CalculateBounds` label, is now in `CoreSet::Update`, rather than in `CoreSet::PostUpdate` before commands are applied.
- `SceneSpawnerSystem` now runs under `CoreSet::Update`, rather than `CoreStage::PreUpdate.at_end()`.
- `bevy_pbr::add_clusters` is no longer an exclusive system
- the top level `bevy_ecs::schedule` module was replaced with `bevy_ecs::scheduling`
- `tick_global_task_pools_on_main_thread` is no longer run as an exclusive system. Instead, it has been replaced by `tick_global_task_pools`, which uses a `NonSend` resource to force running on the main thread.
## Migration Guide
- Calls to `.label(MyLabel)` should be replaced with `.in_set(MySet)`
- Stages have been removed. Replace these with system sets, and then add command flushes using the `apply_system_buffers` exclusive system where needed.
- The `CoreStage`, `StartupStage, `RenderStage` and `AssetStage` enums have been replaced with `CoreSet`, `StartupSet, `RenderSet` and `AssetSet`. The same scheduling guarantees have been preserved.
- Systems are no longer added to `CoreSet::Update` by default. Add systems manually if this behavior is needed, although you should consider adding your game logic systems to `CoreSchedule::FixedTimestep` instead for more reliable framerate-independent behavior.
- Similarly, startup systems are no longer part of `StartupSet::Startup` by default. In most cases, this won't matter to you.
- For example, `add_system_to_stage(CoreStage::PostUpdate, my_system)` should be replaced with
- `add_system(my_system.in_set(CoreSet::PostUpdate)`
- When testing systems or otherwise running them in a headless fashion, simply construct and run a schedule using `Schedule::new()` and `World::run_schedule` rather than constructing stages
- Run criteria have been renamed to run conditions. These can now be combined with each other and with states.
- Looping run criteria and state stacks have been removed. Use an exclusive system that runs a schedule if you need this level of control over system control flow.
- For app-level control flow over which schedules get run when (such as for rollback networking), create your own schedule and insert it under the `CoreSchedule::Outer` label.
- Fixed timesteps are now evaluated in a schedule, rather than controlled via run criteria. The `run_fixed_timestep` system runs this schedule between `CoreSet::First` and `CoreSet::PreUpdate` by default.
- Command flush points introduced by `AssetStage` have been removed. If you were relying on these, add them back manually.
- Adding extract systems is now typically done directly on the main app. Make sure the `RenderingAppExtension` trait is in scope, then call `app.add_extract_system(my_system)`.
- the `calculate_bounds` system, with the `CalculateBounds` label, is now in `CoreSet::Update`, rather than in `CoreSet::PostUpdate` before commands are applied. You may need to order your movement systems to occur before this system in order to avoid system order ambiguities in culling behavior.
- the `RenderLabel` `AppLabel` was renamed to `RenderApp` for clarity
- `App::add_state` now takes 0 arguments: the starting state is set based on the `Default` impl.
- Instead of creating `SystemSet` containers for systems that run in stages, simply use `.on_enter::<State::Variant>()` or its `on_exit` or `on_update` siblings.
- `SystemLabel` derives should be replaced with `SystemSet`. You will also need to add the `Debug`, `PartialEq`, `Eq`, and `Hash` traits to satisfy the new trait bounds.
- `with_run_criteria` has been renamed to `run_if`. Run criteria have been renamed to run conditions for clarity, and should now simply return a bool.
- States have been dramatically simplified: there is no longer a "state stack". To queue a transition to the next state, call `NextState::set`
## TODO
- [x] remove dead methods on App and World
- [x] add `App::add_system_to_schedule` and `App::add_systems_to_schedule`
- [x] avoid adding the default system set at inappropriate times
- [x] remove any accidental cycles in the default plugins schedule
- [x] migrate benchmarks
- [x] expose explicit labels for the built-in command flush points
- [x] migrate engine code
- [x] remove all mentions of stages from the docs
- [x] verify docs for States
- [x] fix uses of exclusive systems that use .end / .at_start / .before_commands
- [x] migrate RenderStage and AssetStage
- [x] migrate examples
- [x] ensure that transform propagation is exported in a sufficiently public way (the systems are already pub)
- [x] ensure that on_enter schedules are run at least once before the main app
- [x] re-enable opt-in to execution order ambiguities
- [x] revert change to `update_bounds` to ensure it runs in `PostUpdate`
- [x] test all examples
- [x] unbreak directional lights
- [x] unbreak shadows (see 3d_scene, 3d_shape, lighting, transparaency_3d examples)
- [x] game menu example shows loading screen and menu simultaneously
- [x] display settings menu is a blank screen
- [x] `without_winit` example panics
- [x] ensure all tests pass
- [x] SubApp doc test fails
- [x] runs_spawn_local tasks fails
- [x] [Fix panic_when_hierachy_cycle test hanging](https://github.com/alice-i-cecile/bevy/pull/120)
## Points of Difficulty and Controversy
**Reviewers, please give feedback on these and look closely**
1. Default sets, from the RFC, have been removed. These added a tremendous amount of implicit complexity and result in hard to debug scheduling errors. They're going to be tackled in the form of "base sets" by @cart in a followup.
2. The outer schedule controls which schedule is run when `App::update` is called.
3. I implemented `Label for `Box<dyn Label>` for our label types. This enables us to store schedule labels in concrete form, and then later run them. I ran into the same set of problems when working with one-shot systems. We've previously investigated this pattern in depth, and it does not appear to lead to extra indirection with nested boxes.
4. `SubApp::update` simply runs the default schedule once. This sucks, but this whole API is incomplete and this was the minimal changeset.
5. `time_system` and `tick_global_task_pools_on_main_thread` no longer use exclusive systems to attempt to force scheduling order
6. Implemetnation strategy for fixed timesteps
7. `AssetStage` was migrated to `AssetSet` without reintroducing command flush points. These did not appear to be used, and it's nice to remove these bottlenecks.
8. Migration of `bevy_render/lib.rs` and pipelined rendering. The logic here is unusually tricky, as we have complex scheduling requirements.
## Future Work (ideally before 0.10)
- Rename schedule_v3 module to schedule or scheduling
- Add a derive macro to states, and likely a `EnumIter` trait of some form
- Figure out what exactly to do with the "systems added should basically work by default" problem
- Improve ergonomics for working with fixed timesteps and states
- Polish FixedTime API to match Time
- Rebase and merge #7415
- Resolve all internal ambiguities (blocked on better tools, especially #7442)
- Add "base sets" to replace the removed default sets.
# Objective
Avoid ‘Unable to find a GPU! Make sure you have installed required drivers!’ .
Because many devices only support OpenGL without Vulkan.
Fixes#3191
## Solution
Use all backends supported by wgpu.
# Objective
Currently, shaders may only have syntax such as
```wgsl
#ifdef FOO
// foo code
#else
#ifdef BAR
// bar code
#else
#ifdef BAZ
// baz code
#else
// fallback code
#endif
#endif
#endif
```
This is hard to read and follow.
Add a way to allow writing `#else ifdef DEFINE` to reduce the number of scopes introduced and to increase readability.
## Solution
Refactor the current preprocessing a bit and add logic to allow `#else ifdef DEFINE`.
This includes per-scope tracking of whether a branch has been accepted.
Add a few tests for this feature.
With these changes we may now write:
```wgsl
#ifdef FOO
// foo code
#else ifdef BAR
// bar code
#else ifdef BAZ
// baz code
#else
// fallback code
#endif
```
instead.
---
## Changelog
- Add `#else ifdef` to shader preprocessing.
# Objective
- Trying to move some of the fixes from https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/7267 to make that one easier to review
- The MainThreadExecutor is how the render world runs nonsend systems on the main thread for pipelined rendering.
- The multithread executor for stageless wasn't using the MainThreadExecutor.
- MainThreadExecutor was declared in the old executor_parallel module that is getting deleted.
- The way the MainThreadExecutor was getting passed to the scope was actually unsound as the resource could be dropped from the World while the schedule was running
## Solution
- Move MainThreadExecutor to the new multithreaded_executor's file.
- Make the multithreaded executor use the MainThreadExecutor
- Clone the MainThreadExecutor onto the stack and pass that ref in
## Changelog
- Move MainThreadExecutor for stageless migration.
# Objective
In simple cases we might want to derive the `ExtractComponent` trait.
This adds symmetry to the existing `ExtractResource` derive.
## Solution
Add an implementation of `#[derive(ExtractComponent)]`.
The implementation is adapted from the existing `ExtractResource` derive macro.
Additionally, there is an attribute called `extract_component_filter`. This allows specifying a query filter type used when extracting.
If not specified, no filter (equal to `()`) is used.
So:
```rust
#[derive(Component, Clone, ExtractComponent)]
#[extract_component_filter(With<Fuel>)]
pub struct Car {
pub wheels: usize,
}
```
would expand to (a bit cleaned up here):
```rust
impl ExtractComponent for Car
{
type Query = &'static Self;
type Filter = With<Fuel>;
type Out = Self;
fn extract_component(item: QueryItem<'_, Self::Query>) -> Option<Self::Out> {
Some(item.clone())
}
}
```
---
## Changelog
- Added the ability to `#[derive(ExtractComponent)]` with an optional filter.
# Objective
- Fixes#4592
## Solution
- Implement `SrgbColorSpace` for `u8` via `f32`
- Convert KTX2 R8 and R8G8 non-linear sRGB to wgpu `R8Unorm` and `Rg8Unorm` as non-linear sRGB are not supported by wgpu for these formats
- Convert KTX2 R8G8B8 formats to `Rgba8Unorm` and `Rgba8UnormSrgb` by adding an alpha channel as the Rgb variants don't exist in wgpu
---
## Changelog
- Added: Support for KTX2 `R8_SRGB`, `R8_UNORM`, `R8G8_SRGB`, `R8G8_UNORM`, `R8G8B8_SRGB`, `R8G8B8_UNORM` formats by converting to supported wgpu formats as appropriate
# Objective
Add a `FromReflect` derive to the `Aabb` type, like all other math types, so we can reflect `Vec<Aabb>`.
## Solution
Just add it :)
---
## Changelog
### Added
- Implemented `FromReflect` for `Aabb`.
# Objective
Update Bevy to wgpu 0.15.
## Changelog
- Update to wgpu 0.15, wgpu-hal 0.15.1, and naga 0.11
- Users can now use the [DirectX Shader Compiler](https://github.com/microsoft/DirectXShaderCompiler) (DXC) on Windows with DX12 for faster shader compilation and ShaderModel 6.0+ support (requires `dxcompiler.dll` and `dxil.dll`, which are included in DXC downloads from [here](https://github.com/microsoft/DirectXShaderCompiler/releases/latest))
## Migration Guide
### WGSL Top-Level `let` is now `const`
All top level constants are now declared with `const`, catching up with the wgsl spec.
`let` is no longer allowed at the global scope, only within functions.
```diff
-let SOME_CONSTANT = 12.0;
+const SOME_CONSTANT = 12.0;
```
#### `TextureDescriptor` and `SurfaceConfiguration` now requires a `view_formats` field
The new `view_formats` field in the `TextureDescriptor` is used to specify a list of formats the texture can be re-interpreted to in a texture view. Currently only changing srgb-ness is allowed (ex. `Rgba8Unorm` <=> `Rgba8UnormSrgb`). You should set `view_formats` to `&[]` (empty) unless you have a specific reason not to.
#### The DirectX Shader Compiler (DXC) is now supported on DX12
DXC is now the default shader compiler when using the DX12 backend. DXC is Microsoft's replacement for their legacy FXC compiler, and is faster, less buggy, and allows for modern shader features to be used (ShaderModel 6.0+). DXC requires `dxcompiler.dll` and `dxil.dll` to be available, otherwise it will log a warning and fall back to FXC.
You can get `dxcompiler.dll` and `dxil.dll` by downloading the latest release from [Microsoft's DirectXShaderCompiler github repo](https://github.com/microsoft/DirectXShaderCompiler/releases/latest) and copying them into your project's root directory. These must be included when you distribute your Bevy game/app/etc if you plan on supporting the DX12 backend and are using DXC.
`WgpuSettings` now has a `dx12_shader_compiler` field which can be used to choose between either FXC or DXC (if you pass None for the paths for DXC, it will check for the .dlls in the working directory).
# Objective
## Use Case
A render node which calls `post_process_write()` on a `ViewTarget` multiple times during a single run of the node means both main textures of this view target is accessed.
If the source texture (which alternate between main textures **a** and **b**) is accessed in a shader during those iterations it means that those textures have to be bound using bind groups.
Preparing bind groups for both main textures ahead of time is desired, which means having access to the _other_ main texture is needed.
## Solution
Add a method on `ViewTarget` for accessing the other main texture.
---
## Changelog
### Added
- `main_texture_other` API on `ViewTarget`
# Objective
I found several words in code and docs are incorrect. This should be fixed.
## Solution
- Fix several minor typos
Co-authored-by: Chris Ohk <utilforever@gmail.com>
# Objective
Fixes#6952
## Solution
- Request WGPU capabilities `SAMPLED_TEXTURE_AND_STORAGE_BUFFER_ARRAY_NON_UNIFORM_INDEXING`, `SAMPLER_NON_UNIFORM_INDEXING` and `UNIFORM_BUFFER_AND_STORAGE_TEXTURE_ARRAY_NON_UNIFORM_INDEXING` when corresponding features are enabled.
- Add an example (`shaders/texture_binding_array`) illustrating (and testing) the use of non-uniform indexed textures and samplers.
## Changelog
- Added new capabilities for shader validation.
- Added example `shaders/texture_binding_array`.
Co-authored-by: Robert Swain <robert.swain@gmail.com>
# Objective
Implements cascaded shadow maps for directional lights, which produces better quality shadows without needing excessively large shadow maps.
Fixes#3629
Before
After
## Solution
Rather than rendering a single shadow map for directional light, the view frustum is divided into a series of cascades, each of which gets its own shadow map. The correct cascade is then sampled for shadow determination.
---
## Changelog
Directional lights now use cascaded shadow maps for improved shadow quality.
## Migration Guide
You no longer have to manually specify a `shadow_projection` for a directional light, and these settings should be removed. If customization of how cascaded shadow maps work is desired, modify the `CascadeShadowConfig` component instead.
# Objective
Fixes#7286. Both `App::add_sub_app` and `App::insert_sub_app` are rather redundant. Before 0.10 is shipped, one of them should be removed.
## Solution
Remove `App::add_sub_app` to prefer `App::insert_sub_app`.
Also hid away `SubApp::extract` since that can be a footgun if someone mutates it for whatever reason. Willing to revert this change if there are objections.
Perhaps we should make `SubApp: Deref<Target=App>`? Might change if we decide to move `!Send` resources into it.
---
## Changelog
Added: `SubApp::new`
Removed: `App::add_sub_app`
## Migration Guide
`App::add_sub_app` has been removed in favor of `App::insert_sub_app`. Use `SubApp::new` and insert it via `App::add_sub_app`
Old:
```rust
let mut sub_app = App::new()
// Build subapp here
app.add_sub_app(MySubAppLabel, sub_app);
```
New:
```rust
let mut sub_app = App::new()
// Build subapp here
app.insert_sub_app(MySubAppLabel, SubApp::new(sub_app, extract_fn));
```
# Objective
`RenderContext`, the core abstraction for running the render graph, currently only supports recording one `CommandBuffer` across the entire render graph. This means the entire buffer must be recorded sequentially, usually via the render graph itself. This prevents parallelization and forces users to only encode their commands in the render graph.
## Solution
Allow `RenderContext` to store a `Vec<CommandBuffer>` that it progressively appends to. By default, the context will not have a command encoder, but will create one as soon as either `begin_tracked_render_pass` or the `command_encoder` accesor is first called. `RenderContext::add_command_buffer` allows users to interrupt the current command encoder, flush it to the vec, append a user-provided `CommandBuffer` and reset the command encoder to start a new buffer. Users or the render graph will call `RenderContext::finish` to retrieve the series of buffers for submitting to the queue.
This allows users to encode their own `CommandBuffer`s outside of the render graph, potentially in different threads, and store them in components or resources.
Ideally, in the future, the core pipeline passes can run in `RenderStage::Render` systems and end up saving the completed command buffers to either `Commands` or a field in `RenderPhase`.
## Alternatives
The alternative is to use to use wgpu's `RenderBundle`s, which can achieve similar results; however it's not universally available (no OpenGL, WebGL, and DX11).
---
## Changelog
Added: `RenderContext::new`
Added: `RenderContext::add_command_buffer`
Added: `RenderContext::finish`
Changed: `RenderContext::render_device` is now private. Use the accessor `RenderContext::render_device()` instead.
Changed: `RenderContext::command_encoder` is now private. Use the accessor `RenderContext::command_encoder()` instead.
Changed: `RenderContext` now supports adding external `CommandBuffer`s for inclusion into the render graphs. These buffers can be encoded outside of the render graph (i.e. in a system).
## Migration Guide
`RenderContext`'s fields are now private. Use the accessors on `RenderContext` instead, and construct it with `RenderContext::new`.
# Objective
Fixes#6931
Continues #6954 by squashing `Msaa` to a flat enum
Helps out #7215
# Solution
```
pub enum Msaa {
Off = 1,
#[default]
Sample4 = 4,
}
```
# Changelog
- Modified
- `Msaa` is now enum
- Defaults to 4 samples
- Uses `.samples()` method to get the sample number as `u32`
# Migration Guide
```
let multi = Msaa { samples: 4 }
// is now
let multi = Msaa::Sample4
multi.samples
// is now
multi.samples()
```
Co-authored-by: Sjael <jakeobrien44@gmail.com>