# Objective
Make the name less verbose without sacrificing clarity.
---
## Migration Guide
*Note for maintainers:* This PR has no breaking changes relative to bevy 0.9. Instead of this PR having its own migration guide, we should just edit the changelog for #6404.
The type `UnsafeWorldCellEntityRef` has been renamed to `UnsafeEntityCell`.
# Objective
Continuation of #7560.
`MutUntyped::last_changed` and `set_last_changed` do not behave as described in their docs.
## Solution
Fix them using the same approach that was used for `Mut<>` in #7560.
fixes#6799
# Objective
We should be able to reuse the `Globals` or `View` shader struct definitions from anywhere (including third party plugins) without needing to worry about defining unrelated shader defs.
Also we'd like to refactor these structs to not be repeatedly defined.
## Solution
Refactor both `Globals` and `View` into separate importable shaders.
Use the imports throughout.
Co-authored-by: Torstein Grindvik <52322338+torsteingrindvik@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
- This makes code a little more readable now.
## Solution
- Use `position` provided by `Iter` instead of `enumerating` indices and `map`ping to the index.
This was missed in #7205.
Should be fixed now. 😄
## Migration Guide
- `SpecializedComputePipelines::specialize` now takes a `&PipelineCache` instead of a `&mut PipelineCache`
# Objective
The current `AlignSelf` doc comments:
```rust
pub enum AlignSelf {
/// Use the value of [`AlignItems`]
Auto,
/// If the parent has [`AlignItems::Center`] only this item will be at the start
FlexStart,
/// If the parent has [`AlignItems::Center`] only this item will be at the end
FlexEnd,
/// If the parent has [`AlignItems::FlexStart`] only this item will be at the center
Center,
/// If the parent has [`AlignItems::Center`] only this item will be at the baseline
Baseline,
/// If the parent has [`AlignItems::Center`] only this item will stretch along the whole cross axis
Stretch,
}
```
Actual behaviour of `AlignSelf` in Bevy main:
<img width="642" alt="align_self" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/27962798/217795178-7a82638f-118d-4474-b7f9-ca27f204731d.PNG">
The white label at the top of each column is the parent node's `AlignItems` setting.
`AlignSelf` is always applied, not (as the documentation states) only when the parent has `AlignItems::Center` or `AlignItems::FlexStart` set.
```rust
use bevy::prelude::*;
fn main() {
App::new()
.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins)
.add_startup_system(setup)
.run();
}
fn setup(mut commands: Commands, asset_server: Res<AssetServer>) {
commands.spawn(Camera2dBundle::default());
commands.spawn(NodeBundle {
style: Style {
justify_content: JustifyContent::SpaceAround,
align_items: AlignItems::Center,
size: Size::new(Val::Percent(100.), Val::Percent(100.)),
..Default::default()
},
background_color: BackgroundColor(Color::NAVY),
..Default::default()
}).with_children(|builder| {
for align_items in [
AlignItems::Baseline,
AlignItems::FlexStart,
AlignItems::Center,
AlignItems::FlexEnd,
AlignItems::Stretch,
] {
builder.spawn(NodeBundle {
style: Style {
align_items,
flex_direction: FlexDirection::Column,
justify_content: JustifyContent::SpaceBetween,
size: Size::new(Val::Px(150.), Val::Px(500.)),
..Default::default()
},
background_color: BackgroundColor(Color::DARK_GRAY),
..Default::default()
}).with_children(|builder| {
builder.spawn((
TextBundle {
text: Text::from_section(
format!("AlignItems::{align_items:?}"),
TextStyle {
font: asset_server.load("fonts/FiraSans-Regular.ttf"),
font_size: 16.0,
color: Color::BLACK,
},
),
style: Style {
align_self: AlignSelf::Stretch,
..Default::default()
},
..Default::default()
},
BackgroundColor(Color::WHITE),
));
for align_self in [
AlignSelf::Auto,
AlignSelf::FlexStart,
AlignSelf::Center,
AlignSelf::FlexEnd,
AlignSelf::Baseline,
AlignSelf::Stretch,
] {
builder.spawn((
TextBundle {
text: Text::from_section(
format!("AlignSelf::{align_self:?}"),
TextStyle {
font: asset_server.load("fonts/FiraSans-Regular.ttf"),
font_size: 16.0,
color: Color::WHITE,
},
),
style: Style {
align_self,
..Default::default()
},
..Default::default()
},
BackgroundColor(Color::BLACK),
));
}
});
}
});
}
```
# Objective
Make `last_changed` behave as described in its docs.
## Solution
- Return `changed` instead of `last_change_tick`. `last_change_tick` is the system's previous tick and is just used for comparison.
- Update the docs of the similarly named `set_last_changed` (which does correctly interact with `last_change_tick`) to clarify that the two functions touch different data. (I advocate for renaming one or the other if anyone has any good suggestions).
It also might make sense to return a cloned `Tick` instead of `u32`.
---
## Changelog
- Fixed `DetectChanges::last_changed` returning the wrong value.
- Fixed `DetectChangesMut::set_last_changed` not actually updating the `changed` tick.
## Migration Guide
- The incorrect value that was being returned by `DetectChanges::last_changed` was the previous run tick of the system checking for changed values. If you depended on this value, you can get it from the `SystemChangeTick` `SystemParam` instead.
(Before)

(After)

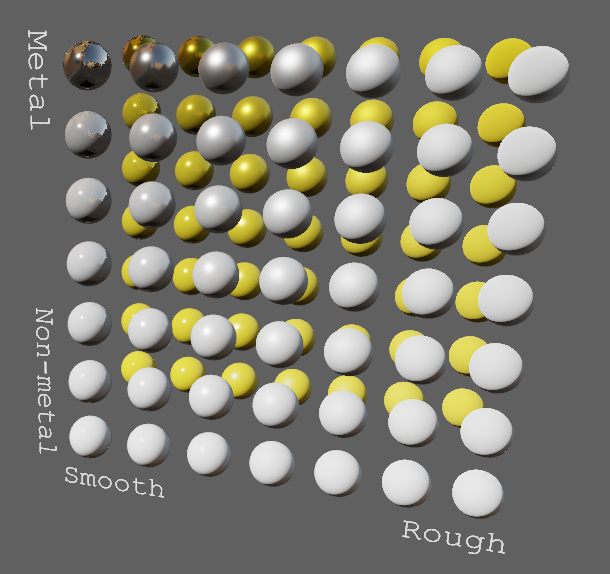
# Objective
- Improve lighting; especially reflections.
- Closes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/4581.
## Solution
- Implement environment maps, providing better ambient light.
- Add microfacet multibounce approximation for specular highlights from Filament.
- Occlusion is no longer incorrectly applied to direct lighting. It now only applies to diffuse indirect light. Unsure if it's also supposed to apply to specular indirect light - the glTF specification just says "indirect light". In the case of ambient occlusion, for instance, that's usually only calculated as diffuse though. For now, I'm choosing to apply this just to indirect diffuse light, and not specular.
- Modified the PBR example to use an environment map, and have labels.
- Added `FallbackImageCubemap`.
## Implementation
- IBL technique references can be found in environment_map.wgsl.
- It's more accurate to use a LUT for the scale/bias. Filament has a good reference on generating this LUT. For now, I just used an analytic approximation.
- For now, environment maps must first be prefiltered outside of bevy using a 3rd party tool. See the `EnvironmentMap` documentation.
- Eventually, we should have our own prefiltering code, so that we can have dynamically changing environment maps, as well as let users drop in an HDR image and use asset preprocessing to create the needed textures using only bevy.
---
## Changelog
- Added an `EnvironmentMapLight` camera component that adds additional ambient light to a scene.
- StandardMaterials will now appear brighter and more saturated at high roughness, due to internal material changes. This is more physically correct.
- Fixed StandardMaterial occlusion being incorrectly applied to direct lighting.
- Added `FallbackImageCubemap`.
Co-authored-by: IceSentry <c.giguere42@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: James Liu <contact@jamessliu.com>
Co-authored-by: Rob Parrett <robparrett@gmail.com>
# Objective
Clarify what the function is actually calculating.
The `Tick::is_older_than` function is actually calculating whether the tick is newer than the system's `last_change_tick`, not older. As far as I can tell, the engine was using it correctly everywhere already.
## Solution
- Rename the function.
---
## Changelog
- `Tick::is_older_than` was renamed to `Tick::is_newer_than`. This is not a functional change, since that was what was always being calculated, despite the wrong name.
## Migration Guide
- Replace usages of `Tick::is_older_than` with `Tick::is_newer_than`.
# Objective
Closes#7202
## Solution
~~Introduce a `not` helper to pipe conditions. Opened mostly for discussion. Maybe create an extension trait with `not` method? Please, advice.~~
Introduce `not(condition)` condition that inverses the result of the passed.
---
## Changelog
### Added
- `not` condition.
# Objective
- Terminology used in field names and docs aren't accurate
- `window_origin` doesn't have any effect when `scaling_mode` is `ScalingMode::None`
- `left`, `right`, `bottom`, and `top` are set automatically unless `scaling_mode` is `None`. Fields that only sometimes give feedback are confusing.
- `ScalingMode::WindowSize` has no arguments, which is inconsistent with other `ScalingMode`s. 1 pixel = 1 world unit is also typically way too wide.
- `OrthographicProjection` feels generally less streamlined than its `PerspectiveProjection` counterpart
- Fixes#5818
- Fixes#6190
## Solution
- Improve consistency in `OrthographicProjection`'s public fields (they should either always give feedback or never give feedback).
- Improve consistency in `ScalingMode`'s arguments
- General usability improvements
- Improve accuracy of terminology:
- "Window" should refer to the physical window on the desktop
- "Viewport" should refer to the component in the window that images are drawn on (typically all of it)
- "View frustum" should refer to the volume captured by the projection
---
## Changelog
### Added
- Added argument to `ScalingMode::WindowSize` that specifies the number of pixels that equals one world unit.
- Added documentation for fields and enums
### Changed
- Renamed `window_origin` to `viewport_origin`, which now:
- Affects all `ScalingMode`s
- Takes a fraction of the viewport's width and height instead of an enum
- Removed `WindowOrigin` enum as it's obsolete
- Renamed `ScalingMode::None` to `ScalingMode::Fixed`, which now:
- Takes arguments to specify the projection size
- Replaced `left`, `right`, `bottom`, and `top` fields with a single `area: Rect`
- `scale` is now applied before updating `area`. Reading from it will take `scale` into account.
- Documentation changes to make terminology more accurate and consistent
## Migration Guide
- Change `window_origin` to `viewport_origin`; replace `WindowOrigin::Center` with `Vec2::new(0.5, 0.5)` and `WindowOrigin::BottomLeft` with `Vec2::new(0.0, 0.0)`
- For shadow projections and such, replace `left`, `right`, `bottom`, and `top` with `area: Rect::new(left, bottom, right, top)`
- For camera projections, remove l/r/b/t values from `OrthographicProjection` instantiations, as they no longer have any effect in any `ScalingMode`
- Change `ScalingMode::None` to `ScalingMode::Fixed`
- Replace manual changes of l/r/b/t with:
- Arguments in `ScalingMode::Fixed` to specify size
- `viewport_origin` to specify offset
- Change `ScalingMode::WindowSize` to `ScalingMode::WindowSize(1.0)`
# Objective
Fix#7571
## Solution
* Removed the offending line.
***
## Changelog
* Removed
* * The line: ``\\ [`apply_system_buffers`]: bevy_ecs::prelude::apply_system_buffers`` from `bevy_app` crate, which overrides the link in that specific comment block.
Co-authored-by: lupan <kallll5@hotmail.com>
Small commit to remove an unused resource scoped within a single bevy_ecs unit test. Also rearranged the initialization to follow initialization conventions of surrounding tests. World/Schedule initialization followed by resource initialization.
This change was tested locally with `cargo test`, and `cargo fmt` was run.
Risk should be tiny as change is scoped to a single unit test and very tiny, and I can't see any way that this resource is being used in the test.
Thank you so much!
# Objective
One of the most important usages of plugin names is currently not mentioned in its documentation: the uniqueness check
## Solution
- Mention that the plugin name is used to check for uniqueness
# Objective
Run conditions are a special type of system that do not modify the world, and which return a bool. Due to the way they are currently implemented, you can *only* use bare function systems as a run condition. Among other things, this prevents the use of system piping with run conditions. This make very basic constructs impossible, such as `my_system.run_if(my_condition.pipe(not))`.
Unblocks a basic solution for #7202.
## Solution
Add the trait `ReadOnlySystem`, which is implemented for any system whose parameters all implement `ReadOnlySystemParam`. Allow any `-> bool` system implementing this trait to be used as a run condition.
---
## Changelog
+ Added the trait `ReadOnlySystem`, which is implemented for any `System` type whose parameters all implement `ReadOnlySystemParam`.
+ Added the function `bevy::ecs::system::assert_is_read_only_system`.
# Objective
Fix#7377Fix#7513
## Solution
Record the changes made to the Bevy `Window` from `winit` as 'canon' to avoid Bevy sending those changes back to `winit` again, causing a feedback loop.
## Changelog
* Removed `ModifiesWindows` system label.
Neither `despawn_window` nor `changed_window` actually modify the `Window` component so all the `.after(ModifiesWindows)` shouldn't be necessary.
* Moved `changed_window` and `despawn_window` systems to `CoreStage::Last` to avoid systems making changes to the `Window` between `changed_window` and the end of the frame as they would be ignored.
## Migration Guide
The `ModifiesWindows` system label was removed.
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
# Objective
Implementing `States` manually is repetitive, so let's not.
One thing I'm unsure of is whether the macro import statement is in the right place.
# Objective
- Prepass opaque and alpha mask are incorrectly sorted back to front. This slipped through review by accident.
## Solution
- Sort prepass opaque and alpha mask front to back
# Objective
add a hook for ambient occlusion to the pbr shader
## Solution
add a hook for ambient occlusion to the pbr shader
Co-authored-by: atlas dostal <rodol@rivalrebels.com>
# Objective
Some render systems that have system set used as a label so that they can be referenced from somewhere else.
The 1:1 translation from `add_system_to_stage(Prepare, prepare_lights.label(PrepareLights))` is `add_system(prepare_lights.in_set(Prepare).in_set(PrepareLights)`, but configuring the `PrepareLights` set to be in `Prepare` would match the intention better (there are no systems in `PrepareLights` outside of `Prepare`) and it is easier for visualization tools to deal with.
# Solution
- replace
```rust
prepare_lights in PrepareLights
prepare_lights in Prepare
```
with
```rs
prepare_lights in PrepareLights
PrepareLights in Prepare
```
**Before**

**After**

# Objective
One pattern to increase parallelism is deferred mutation: instead of directly mutating the world (and preventing other systems from running at the same time), you queue up operations to be applied to the world at the end of the stage. The most common example of this pattern uses the `Commands` SystemParam.
In order to avoid the overhead associated with commands, some power users may want to add their own deferred mutation behavior. To do this, you must implement the unsafe trait `SystemParam`, which interfaces with engine internals in a way that we'd like users to be able to avoid.
## Solution
Add the `Deferred<T>` primitive `SystemParam`, which encapsulates the deferred mutation pattern.
This can be combined with other types of `SystemParam` to safely and ergonomically create powerful custom types.
Essentially, this is just a variant of `Local<T>` which can run code at the end of the stage.
This type is used in the engine to derive `Commands` and `ParallelCommands`, which removes a bunch of unsafe boilerplate.
### Example
```rust
use bevy_ecs::system::{Deferred, SystemBuffer};
/// Sends events with a delay, but may run in parallel with other event writers.
#[derive(SystemParam)]
pub struct BufferedEventWriter<'s, E: Event> {
queue: Deferred<'s, EventQueue<E>>,
}
struct EventQueue<E>(Vec<E>);
impl<'s, E: Event> BufferedEventWriter<'s, E> {
/// Queues up an event to be sent at the end of this stage.
pub fn send(&mut self, event: E) {
self.queue.0.push(event);
}
}
// The `SystemBuffer` trait controls how [`Deferred`] gets applied at the end of the stage.
impl<E: Event> SystemBuffer for EventQueue<E> {
fn apply(&mut self, world: &mut World) {
let mut events = world.resource_mut::<Events<E>>();
for e in self.0.drain(..) {
events.send(e);
}
}
}
```
---
## Changelog
+ Added the `SystemParam` type `Deferred<T>`, which can be used to defer `World` mutations. Powered by the new trait `SystemBuffer`.
# Objective
Buffers in bevy do not allow for setting buffer usage flags which can be useful for setting COPY_SRC, MAP_READ, MAP_WRITE, which allows for buffers to be copied from gpu to cpu for inspection.
## Solution
Add buffer_usage field to buffers and a set_usage function to set them
# Objective
Currently the `GetPath` documentation suggests it can be used with `Tuple` types (reflected tuples). However, this is not currently the case.
## Solution
Add reflection path support for `Tuple` types.
---
## Changelog
- Add reflection path support for `Tuple` types
# Objective
- There is a small perf cost for starting the multithreaded executor.
## Solution
- We can skip that cost when there are zero systems in the schedule. Overall not a big perf boost unless there are a lot of empty schedules that are trying to run, but it is something.
Below is a tracy trace of the run_fixed_update_schedule for many_foxes which has zero systems in it. Yellow is main and red is this pr. The time difference between the peaks of the humps is around 15us.
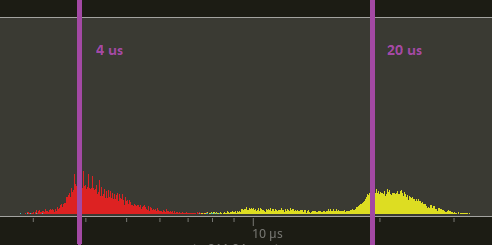
# Objective
- Implementing logic used by system params and `UnsafeWorldCell` on `&World` is sus since `&World` generally denotes shared read only access to world but this is a lie in the above situations. Move most/all logic that uses `&World` to mean `UnsafeWorldCell` onto `UnsafeWorldCell`
- Add a way to take a `&mut World` out of `UnsafeWorldCell` and use this in `WorldCell`'s `Drop` impl instead of a `UnsafeCell` field
---
## Changelog
- changed some `UnsafeWorldCell` methods to take `self` instead of `&self`/`&mut self` since there is literally no point to them doing that
- `UnsafeWorldCell::world` is now used to get immutable access to the whole world instead of just the metadata which can now be done via `UnsafeWorldCell::world_metadata`
- `UnsafeWorldCell::world_mut` now exists and can be used to get a `&mut World` out of `UnsafeWorldCell`
- removed `UnsafeWorldCell::storages` since that is probably unsound since storages contains the actual component/resource data not just metadata
## Migration guide
N/A none of the breaking changes here make any difference for a 0.9->0.10 transition since `UnsafeWorldCell` did not exist in 0.9
# Objective
- Merge the examples on iOS and Android
- Make sure they both work from the same code
## Solution
- don't create window when not in an active state (from #6830)
- exit on suspend on Android (from #6830)
- automatically enable dependency feature of bevy_audio on android so that it works out of the box
- don't inverse y position of touch events
- reuse the same example for both Android and iOS
Fixes#4616Fixes#4103Fixes#3648Fixes#3458Fixes#3249Fixes#86
# Objective
- Fixes#766
## Solution
- Add a new `Lcha` member to `bevy_render::color::Color` enum
---
## Changelog
- Add a new `Lcha` member to `bevy_render::color::Color` enum
- Add `bevy_render::color::LchRepresentation` struct
# Objective
[as noted](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/5950#discussion_r1080762807) by james, transmuting arcs may be UB.
we now store a `*const ()` pointer internally, and only rely on `ptr.cast::<()>().cast::<T>() == ptr`.
as a happy side effect this removes the need for boxing the value, so todo: potentially use this for release mode as well
Implementing GetTypeRegistration in macro impl_reflect_for_veclike! had typos!
It only implement GetTypeRegistration for Vec<T>, but not for VecDeque<T>.
This will cause serialization and deserialization failure.
# Objective
NOTE: This depends on #7267 and should not be merged until #7267 is merged. If you are reviewing this before that is merged, I highly recommend viewing the Base Sets commit instead of trying to find my changes amongst those from #7267.
"Default sets" as described by the [Stageless RFC](https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/pull/45) have some [unfortunate consequences](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/discussions/7365).
## Solution
This adds "base sets" as a variant of `SystemSet`:
A set is a "base set" if `SystemSet::is_base` returns `true`. Typically this will be opted-in to using the `SystemSet` derive:
```rust
#[derive(SystemSet, Clone, Hash, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
#[system_set(base)]
enum MyBaseSet {
A,
B,
}
```
**Base sets are exclusive**: a system can belong to at most one "base set". Adding a system to more than one will result in an error. When possible we fail immediately during system-config-time with a nice file + line number. For the more nested graph-ey cases, this will fail at the final schedule build.
**Base sets cannot belong to other sets**: this is where the word "base" comes from
Systems and Sets can only be added to base sets using `in_base_set`. Calling `in_set` with a base set will fail. As will calling `in_base_set` with a normal set.
```rust
app.add_system(foo.in_base_set(MyBaseSet::A))
// X must be a normal set ... base sets cannot be added to base sets
.configure_set(X.in_base_set(MyBaseSet::A))
```
Base sets can still be configured like normal sets:
```rust
app.add_system(MyBaseSet::B.after(MyBaseSet::Ap))
```
The primary use case for base sets is enabling a "default base set":
```rust
schedule.set_default_base_set(CoreSet::Update)
// this will belong to CoreSet::Update by default
.add_system(foo)
// this will override the default base set with PostUpdate
.add_system(bar.in_base_set(CoreSet::PostUpdate))
```
This allows us to build apis that work by default in the standard Bevy style. This is a rough analog to the "default stage" model, but it use the new "stageless sets" model instead, with all of the ordering flexibility (including exclusive systems) that it provides.
---
## Changelog
- Added "base sets" and ported CoreSet to use them.
## Migration Guide
TODO
Huge thanks to @maniwani, @devil-ira, @hymm, @cart, @superdump and @jakobhellermann for the help with this PR.
# Objective
- Followup #6587.
- Minimal integration for the Stageless Scheduling RFC: https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/pull/45
## Solution
- [x] Remove old scheduling module
- [x] Migrate new methods to no longer use extension methods
- [x] Fix compiler errors
- [x] Fix benchmarks
- [x] Fix examples
- [x] Fix docs
- [x] Fix tests
## Changelog
### Added
- a large number of methods on `App` to work with schedules ergonomically
- the `CoreSchedule` enum
- `App::add_extract_system` via the `RenderingAppExtension` trait extension method
- the private `prepare_view_uniforms` system now has a public system set for scheduling purposes, called `ViewSet::PrepareUniforms`
### Removed
- stages, and all code that mentions stages
- states have been dramatically simplified, and no longer use a stack
- `RunCriteriaLabel`
- `AsSystemLabel` trait
- `on_hierarchy_reports_enabled` run criteria (now just uses an ad hoc resource checking run condition)
- systems in `RenderSet/Stage::Extract` no longer warn when they do not read data from the main world
- `RunCriteriaLabel`
- `transform_propagate_system_set`: this was a nonstandard pattern that didn't actually provide enough control. The systems are already `pub`: the docs have been updated to ensure that the third-party usage is clear.
### Changed
- `System::default_labels` is now `System::default_system_sets`.
- `App::add_default_labels` is now `App::add_default_sets`
- `CoreStage` and `StartupStage` enums are now `CoreSet` and `StartupSet`
- `App::add_system_set` was renamed to `App::add_systems`
- The `StartupSchedule` label is now defined as part of the `CoreSchedules` enum
- `.label(SystemLabel)` is now referred to as `.in_set(SystemSet)`
- `SystemLabel` trait was replaced by `SystemSet`
- `SystemTypeIdLabel<T>` was replaced by `SystemSetType<T>`
- The `ReportHierarchyIssue` resource now has a public constructor (`new`), and implements `PartialEq`
- Fixed time steps now use a schedule (`CoreSchedule::FixedTimeStep`) rather than a run criteria.
- Adding rendering extraction systems now panics rather than silently failing if no subapp with the `RenderApp` label is found.
- the `calculate_bounds` system, with the `CalculateBounds` label, is now in `CoreSet::Update`, rather than in `CoreSet::PostUpdate` before commands are applied.
- `SceneSpawnerSystem` now runs under `CoreSet::Update`, rather than `CoreStage::PreUpdate.at_end()`.
- `bevy_pbr::add_clusters` is no longer an exclusive system
- the top level `bevy_ecs::schedule` module was replaced with `bevy_ecs::scheduling`
- `tick_global_task_pools_on_main_thread` is no longer run as an exclusive system. Instead, it has been replaced by `tick_global_task_pools`, which uses a `NonSend` resource to force running on the main thread.
## Migration Guide
- Calls to `.label(MyLabel)` should be replaced with `.in_set(MySet)`
- Stages have been removed. Replace these with system sets, and then add command flushes using the `apply_system_buffers` exclusive system where needed.
- The `CoreStage`, `StartupStage, `RenderStage` and `AssetStage` enums have been replaced with `CoreSet`, `StartupSet, `RenderSet` and `AssetSet`. The same scheduling guarantees have been preserved.
- Systems are no longer added to `CoreSet::Update` by default. Add systems manually if this behavior is needed, although you should consider adding your game logic systems to `CoreSchedule::FixedTimestep` instead for more reliable framerate-independent behavior.
- Similarly, startup systems are no longer part of `StartupSet::Startup` by default. In most cases, this won't matter to you.
- For example, `add_system_to_stage(CoreStage::PostUpdate, my_system)` should be replaced with
- `add_system(my_system.in_set(CoreSet::PostUpdate)`
- When testing systems or otherwise running them in a headless fashion, simply construct and run a schedule using `Schedule::new()` and `World::run_schedule` rather than constructing stages
- Run criteria have been renamed to run conditions. These can now be combined with each other and with states.
- Looping run criteria and state stacks have been removed. Use an exclusive system that runs a schedule if you need this level of control over system control flow.
- For app-level control flow over which schedules get run when (such as for rollback networking), create your own schedule and insert it under the `CoreSchedule::Outer` label.
- Fixed timesteps are now evaluated in a schedule, rather than controlled via run criteria. The `run_fixed_timestep` system runs this schedule between `CoreSet::First` and `CoreSet::PreUpdate` by default.
- Command flush points introduced by `AssetStage` have been removed. If you were relying on these, add them back manually.
- Adding extract systems is now typically done directly on the main app. Make sure the `RenderingAppExtension` trait is in scope, then call `app.add_extract_system(my_system)`.
- the `calculate_bounds` system, with the `CalculateBounds` label, is now in `CoreSet::Update`, rather than in `CoreSet::PostUpdate` before commands are applied. You may need to order your movement systems to occur before this system in order to avoid system order ambiguities in culling behavior.
- the `RenderLabel` `AppLabel` was renamed to `RenderApp` for clarity
- `App::add_state` now takes 0 arguments: the starting state is set based on the `Default` impl.
- Instead of creating `SystemSet` containers for systems that run in stages, simply use `.on_enter::<State::Variant>()` or its `on_exit` or `on_update` siblings.
- `SystemLabel` derives should be replaced with `SystemSet`. You will also need to add the `Debug`, `PartialEq`, `Eq`, and `Hash` traits to satisfy the new trait bounds.
- `with_run_criteria` has been renamed to `run_if`. Run criteria have been renamed to run conditions for clarity, and should now simply return a bool.
- States have been dramatically simplified: there is no longer a "state stack". To queue a transition to the next state, call `NextState::set`
## TODO
- [x] remove dead methods on App and World
- [x] add `App::add_system_to_schedule` and `App::add_systems_to_schedule`
- [x] avoid adding the default system set at inappropriate times
- [x] remove any accidental cycles in the default plugins schedule
- [x] migrate benchmarks
- [x] expose explicit labels for the built-in command flush points
- [x] migrate engine code
- [x] remove all mentions of stages from the docs
- [x] verify docs for States
- [x] fix uses of exclusive systems that use .end / .at_start / .before_commands
- [x] migrate RenderStage and AssetStage
- [x] migrate examples
- [x] ensure that transform propagation is exported in a sufficiently public way (the systems are already pub)
- [x] ensure that on_enter schedules are run at least once before the main app
- [x] re-enable opt-in to execution order ambiguities
- [x] revert change to `update_bounds` to ensure it runs in `PostUpdate`
- [x] test all examples
- [x] unbreak directional lights
- [x] unbreak shadows (see 3d_scene, 3d_shape, lighting, transparaency_3d examples)
- [x] game menu example shows loading screen and menu simultaneously
- [x] display settings menu is a blank screen
- [x] `without_winit` example panics
- [x] ensure all tests pass
- [x] SubApp doc test fails
- [x] runs_spawn_local tasks fails
- [x] [Fix panic_when_hierachy_cycle test hanging](https://github.com/alice-i-cecile/bevy/pull/120)
## Points of Difficulty and Controversy
**Reviewers, please give feedback on these and look closely**
1. Default sets, from the RFC, have been removed. These added a tremendous amount of implicit complexity and result in hard to debug scheduling errors. They're going to be tackled in the form of "base sets" by @cart in a followup.
2. The outer schedule controls which schedule is run when `App::update` is called.
3. I implemented `Label for `Box<dyn Label>` for our label types. This enables us to store schedule labels in concrete form, and then later run them. I ran into the same set of problems when working with one-shot systems. We've previously investigated this pattern in depth, and it does not appear to lead to extra indirection with nested boxes.
4. `SubApp::update` simply runs the default schedule once. This sucks, but this whole API is incomplete and this was the minimal changeset.
5. `time_system` and `tick_global_task_pools_on_main_thread` no longer use exclusive systems to attempt to force scheduling order
6. Implemetnation strategy for fixed timesteps
7. `AssetStage` was migrated to `AssetSet` without reintroducing command flush points. These did not appear to be used, and it's nice to remove these bottlenecks.
8. Migration of `bevy_render/lib.rs` and pipelined rendering. The logic here is unusually tricky, as we have complex scheduling requirements.
## Future Work (ideally before 0.10)
- Rename schedule_v3 module to schedule or scheduling
- Add a derive macro to states, and likely a `EnumIter` trait of some form
- Figure out what exactly to do with the "systems added should basically work by default" problem
- Improve ergonomics for working with fixed timesteps and states
- Polish FixedTime API to match Time
- Rebase and merge #7415
- Resolve all internal ambiguities (blocked on better tools, especially #7442)
- Add "base sets" to replace the removed default sets.
# Objective
- Currently exclusive systems and applying buffers run outside of the multithreaded executor and just calls the funtions on the thread the schedule is running on. Stageless changes this to run these using tasks in a scope. Specifically It uses `spawn_on_scope` to run these. For the render thread this is incorrect as calling `spawn_on_scope` there runs tasks on the main thread. It should instead run these on the render thread and only run nonsend systems on the main thread.
## Solution
- Add another executor to `Scope` for spawning tasks on the scope. `spawn_on_scope` now always runs the task on the thread the scope is running on. `spawn_on_external` spawns onto the external executor than is optionally passed in. If None is passed `spawn_on_external` will spawn onto the scope executor.
- Eventually this new machinery will be able to be removed. This will happen once a fix for removing NonSend resources from the world lands. So this is a temporary fix to support stageless.
---
## Changelog
- add a spawn_on_external method to allow spawning on the scope's thread or an external thread
## Migration Guide
> No migration guide. The main thread executor was introduced in pipelined rendering which was merged for 0.10. spawn_on_scope now behaves the same way as on 0.9.
# Objective
Fixes#7476. UI scale was being incorrectly ignored when a primary window exists.
## Solution
Always take into account UI scale, regardless of whether a primary window exists.
Tested locally on @forbjok 's minimal repro project https://github.com/forbjok/bevy_ui_repro with this patch, and the issue is fixed on my machine.
# Objective
allow negatively-scaled mesh2ds to render correctly by disabling back-face culling. this brings the mesh2d pipeline into line with the sprite pipeline. i don't see any cases where backface-culling would be useful for 2d meshes.
# Objective
- Make the internals of `RemovedComponents` clearer
## Solution
- Add a wrapper around `Entity`, used in `RemovedComponents` as `Events<RemovedComponentsEntity>`
---
## Changelog
- `RemovedComponents` now internally uses an `Events<RemovedComponentsEntity>` instead of an `Events<Entity>`
The `DoubleEndedIterator` impls produce incorrect results on subsequent calls to `iter()` if the iterator is only partially consumed.
The following code shows what happens
```rust
fn next_back_is_bad() {
let mut events = Events::<TestEvent>::default();
events.send(TestEvent { i: 0 });
events.send(TestEvent { i: 1 });
events.send(TestEvent { i: 2 });
let mut reader = events.get_reader();
let mut iter = reader.iter(&events);
assert_eq!(iter.next_back(), Some(&TestEvent { i: 2 }));
assert_eq!(iter.next(), Some(&TestEvent { i: 0 }));
let mut iter = reader.iter(&events);
// `i: 2` event is returned twice! The `i: 1` event is missed.
assert_eq!(iter.next(), Some(&TestEvent { i: 2 }));
assert_eq!(iter.next(), None);
}
```
I don't think this can be fixed without adding some very convoluted bookkeeping.
## Migration Guide
`ManualEventIterator` and `ManualEventIteratorWithId` are no longer `DoubleEndedIterator`s.
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Improve ergonomics / documentation of cascaded shadow maps
- Allow for the customization of the nearest shadowing distance.
- Fixes#7393
- Fixes#7362
## Solution
- Introduce `CascadeShadowConfigBuilder`
- Tweak various example cascade settings for better quality.
---
## Changelog
- Made examples look nicer under cascaded shadow maps.
- Introduce `CascadeShadowConfigBuilder` to help with creating `CascadeShadowConfig`
## Migration Guide
- Configure settings for cascaded shadow maps for directional lights using the newly introduced `CascadeShadowConfigBuilder`.
Co-authored-by: Robert Swain <robert.swain@gmail.com>
# Objective
Avoid ‘Unable to find a GPU! Make sure you have installed required drivers!’ .
Because many devices only support OpenGL without Vulkan.
Fixes#3191
## Solution
Use all backends supported by wgpu.
# Objective
Removal events are unwieldy and require some knowledge of when to put systems that need to catch events for them, it is very easy to end up missing one and end up with memory leak-ish issues where you don't clean up after yourself.
## Solution
Consolidate removals with the benefits of `Events<...>` (such as double buffering and per system ticks for reading the events) and reduce the special casing of it, ideally I was hoping to move the removals to a `Resource` in the world, but that seems a bit more rough to implement/maintain because of double mutable borrowing issues.
This doesn't go the full length of change detection esque removal detection a la https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/pull/44.
Just tries to make the current workflow a bit more user friendly so detecting removals isn't such a scheduling nightmare.
---
## Changelog
- RemovedComponents<T> is now backed by an `Events<Entity>` for the benefits of double buffering.
## Migration Guide
- Add a `mut` for `removed: RemovedComponents<T>` since we are now modifying an event reader internally.
- Iterating over removed components now requires `&mut removed_components` or `removed_components.iter()` instead of `&removed_components`.
# Objective
Currently, shaders may only have syntax such as
```wgsl
#ifdef FOO
// foo code
#else
#ifdef BAR
// bar code
#else
#ifdef BAZ
// baz code
#else
// fallback code
#endif
#endif
#endif
```
This is hard to read and follow.
Add a way to allow writing `#else ifdef DEFINE` to reduce the number of scopes introduced and to increase readability.
## Solution
Refactor the current preprocessing a bit and add logic to allow `#else ifdef DEFINE`.
This includes per-scope tracking of whether a branch has been accepted.
Add a few tests for this feature.
With these changes we may now write:
```wgsl
#ifdef FOO
// foo code
#else ifdef BAR
// bar code
#else ifdef BAZ
// baz code
#else
// fallback code
#endif
```
instead.
---
## Changelog
- Add `#else ifdef` to shader preprocessing.
# Objective
The trait method `SystemParam::apply` allows a `SystemParam` type to defer world mutations, which is internally used to apply `Commands` at the end of the stage. Any operations that require `&mut World` access must be deferred in this way, since parallel systems do not have exclusive access to the world.
The `ExclusiveSystemParam` trait (added in #6083) has an `apply` method which serves the same purpose. However, deferring mutations in this way does not make sense for exclusive systems since they already have `&mut World` access: there is no need to wait until a hard sync point, as the system *is* a hard sync point. World mutations can and should be performed within the body of the system.
## Solution
Remove the method. There were no implementations of this method in the engine.
---
## Changelog
*Note for maintainers: this changelog makes more sense if it's placed above the one for #6919.*
- Removed the method `ExclusiveSystemParamState::apply`.
## Migration Guide
*Note for maintainers: this migration guide makes more sense if it's placed above the one for #6919.*
The trait method `ExclusiveSystemParamState::apply` has been removed. If you have an exclusive system with buffers that must be applied, you should apply them within the body of the exclusive system.
# Objective
Fixes#7434.
This is my first time contributing to a Rust project, so please let me know if this wasn't the change intended by the linked issue.
## Solution
Adds a test with a system that panics to `bevy_ecs`.
I'm not sure if this is the intended panic message, but this is what the test currently results in:
```
thread 'system::tests::panic_inside_system' panicked at 'called `Option::unwrap()` on a `None` value', /Users/bjorn/workplace/bevy/crates/bevy_tasks/src/task_pool.rs:354:49
```
# Objective
- Update winit to 0.28
## Solution
- Small API change
- A security advisory has been added for a unmaintained crate used by a dependency of winit build script for wayland
I didn't do anything for Android support in this PR though it should be fixable, it should be done in a separate one, maybe https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/6830
---
## Changelog
- `window.always_on_top` has been removed, you can now use `window.window_level`
## Migration Guide
before:
```rust
app.new()
.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins.set(WindowPlugin {
primary_window: Some(Window {
always_on_top: true,
..default()
}),
..default()
}));
```
after:
```rust
app.new()
.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins.set(WindowPlugin {
primary_window: Some(Window {
window_level: bevy:🪟:WindowLevel::AlwaysOnTop,
..default()
}),
..default()
}));
```
# Objective
Fix#7447.
The `SystemParam` derive uses the wrong lifetimes for ignored fields.
## Solution
Use type inference instead of explicitly naming the types of ignored fields. This allows the compiler to automatically use the correct lifetime.
# Objective
- Fix panic_when_hierachy_cycle test hanging
- The problem is that the scope only awaits one task at a time in get_results. In stageless this task is the multithreaded executor. That tasks hangs when a system panics and cannot make anymore progress. This wasn't a problem before because the executor was spawned after all the system tasks had been spawned. But in stageless the executor is spawned before all the system tasks are spawned.
## Solution
- We can catch unwind on each system and close the finish channel if one panics. This then causes the receiver end of the finish channel to panic too.
- this might have a small perf impact, but when running many_foxes it seems to be within the noise. So less than 40us.
## Other possible solutions
- It might be possible to fairly poll all the tasks in get_results in the scope. If we could do that then the scope could panic whenever one of tasks panics. It would require a data structure that we could both poll the futures through a shared ref and also push to it. I tried FuturesUnordered, but it requires an exclusive ref to poll it.
- The catch unwind could be moved onto when we create the tasks for scope instead. We would then need something like a oneshot async channel to inform get_results if a task panics.
# Objective
Ability to use `ReflectComponent` methods in dynamic type contexts with no access to `&World`.
This problem occurred to me when wanting to apply reflected types to an entity where the `&World` reference was already consumed by query iterator leaving only `EntityMut`.
## Solution
- Remove redundant `EntityMut` or `EntityRef` lookup from `World` and `Entity` in favor of taking `EntityMut` directly in `ReflectComponentFns`.
- Added `RefectComponent::contains` to determine without panic whether `apply` can be used.
## Changelog
- Changed function signatures of `ReflectComponent` methods, `apply`, `remove`, `contains`, and `reflect`.
## Migration Guide
- Call `World::entity` before calling into the changed `ReflectComponent` methods, most likely user already has a `EntityRef` or `EntityMut` which was being queried redundantly.
# Objective
- Trying to move some of the fixes from https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/7267 to make that one easier to review
- The MainThreadExecutor is how the render world runs nonsend systems on the main thread for pipelined rendering.
- The multithread executor for stageless wasn't using the MainThreadExecutor.
- MainThreadExecutor was declared in the old executor_parallel module that is getting deleted.
- The way the MainThreadExecutor was getting passed to the scope was actually unsound as the resource could be dropped from the World while the schedule was running
## Solution
- Move MainThreadExecutor to the new multithreaded_executor's file.
- Make the multithreaded executor use the MainThreadExecutor
- Clone the MainThreadExecutor onto the stack and pass that ref in
## Changelog
- Move MainThreadExecutor for stageless migration.
# Objective
- After the multithreaded executor finishes running all the systems, we apply the buffers for any system that hasn't applied it's buffers. This is a courtesy apply for users who forget to order their systems before a apply_system_buffers. When checking stageless, it was found that this apply_system_buffers was running on the executor thread instead of the world's thread. This is a problem because anything with world access should be able to access nonsend resources.
## Solution
- Move the final apply_system_buffers outside of the executor and outside of the scope, so it runs on the same thread that schedule.run is called on.
# Objective
In CSS Flexbox width and height are auto by default, whereas in Bevy their default is `Size::Undefined`.
This means that, unlike in CSS, if you elide a height or width value for a node it will be given zero length (unless it has an explicitly sized child node). This has misled users into falsely assuming that they have to explicitly set a value for both height and width all the time.
relevant issue: #7120
## Solution
Change the `Size` `width` and `height` default values to `Val::Auto`
## Changelog
* Changed the `Size` `width` and `height` default values to `Val::Auto`
## Migration Guide
The default values for `Size` `width` and `height` have been changed from `Val::Undefined` to `Val::Auto`.
It's unlikely to cause any issues with existing code.
# Objective
- The stageless executor keeps track of systems that have run, but have not applied their system buffers. The bitset for that was being cloned into apply_system_buffers and cleared in that function, but we need to clear the original version instead of the cloned version
## Solution
- move the clear out of the apply_system_buffers function.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
Clearing the reader doesn't require iterating the events. Updating the `last_event_count` of the reader is enough.
I rewrote part of the documentation as some of it was incorrect or harder to understand than necessary.
## Changelog
Added `ManualEventReader::clear()`
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
# Objective
During testing, I observed that the `FrameCount` resource (`bevy_core`) was being incremented by `FrameCountPlugin` non-deterministically, during update, subject to the whims of the execution order.
The effect was that the counter could and did change while a frame was still in flight, while user-systems were still executing.
## Solution
I have delayed the incrementing of the `FrameCount` resource to `CoreStage::Last`. The resource was described in the documentation as "*a count of rendered frames*" and, after my change, it actually will match that description.
## Changes
- `CoreStage::Last` was chosen so that the counter will be `0` during all earlier stages of the very first execution of the schedule.
- Documentation added declaring *when* the counter is incremented.
- Hint added, directing users towards `u32::wrapping_sub()` because integer overflow is reasonable to expect.
## Note
Even though this change might have a short time-to-live in light of the upcoming *Stageless* changes, I think this is worthwhile – at least as an in-code reminder that this counter should behave predictably.
# Objective
- Resolve a Fixme to remove the `Default` impl for `HandleType`, once Reflection no longer requires it.
- Presumebly this Comment was made before the `FromReflect` Derive used the `#[reflect(Default)]`, to substitute for the requirment that a ignored field has a `Default`.
## Solution
- Just remove the `Default` derive and comment.
## Objective
A common easy to miss mistake is to write something like:
``` rust
Size::new(Val::Percent(100.), Val::Px(100.));
```
`UiRect` has the `left`, `right`, `all`, `vertical`, etc constructor functions, `Size` is used a lot more frequently but lacks anything similar.
## Solution
Implement `all`, `width` and `height` functions for `Size`.
## Changelog
* Added `all`, `width` and `height` functions to `Size`.
# Problem
The field is called `background_color` but it is also used to hold the colors of text glyphs and images.
It's mildly confusing and longer to type than just `color`.
## Solution
Rename `background_color` to `color`.
## Changelog
* Renamed the `background_color` field of `ExtractedUiNode` to `color`.
## Migration Guide
* The `background_color` field of `ExtractedUiNode` is now named `color`.
# Objective
- Fixes#7430.
## Solution
- Changed fields of `ArrayIter` to be private.
- Add a constructor `new` to `ArrayIter`.
- Replace normal struct creation with `new`.
---
## Changelog
- Add a constructor `new` to `ArrayIter`.
Co-authored-by: Elbert Ronnie <103196773+elbertronnie@users.noreply.github.com>
## Objective
Remove `QueuedText`.
`QueuedText` isn't useful. It's exposed in the `bevy_ui` public interface but can't be used for anything because its `entities` field is private.
## Solution
Remove the `QueuedText` struct and use a `Local<Vec<Entity>` in its place.
## Changelog
* Removed `QueuedText`
# Objective
- Bevy should not have any "internal" execution order ambiguities. These clutter the output of user-facing error reporting, and can result in nasty, nondetermistic, very difficult to solve bugs.
- Verifying this currently involves repeated non-trivial manual work.
## Solution
- [x] add an example to quickly check this
- ~~[ ] ensure that this example panics if there are any unresolved ambiguities~~
- ~~[ ] run the example in CI 😈~~
There's one tricky ambiguity left, between UI and animation. I don't have the tools to fix this without system set configuration, so the remaining work is going to be left to #7267 or another PR after that.
```
2023-01-27T18:38:42.989405Z INFO bevy_ecs::schedule::ambiguity_detection: Execution order ambiguities detected, you might want to add an explicit dependency relation between some of these systems:
* Parallel systems:
-- "bevy_animation::animation_player" and "bevy_ui::flex::flex_node_system"
conflicts: ["bevy_transform::components::transform::Transform"]
```
## Changelog
Resolved internal execution order ambiguities for:
1. Transform propagation (ignored, we need smarter filter checking).
2. Gamepad processing (fixed).
3. bevy_winit's window handling (fixed).
4. Cascaded shadow maps and perspectives (fixed).
Also fixed a desynchronized state bug that could occur when the `Window` component is removed and then added to the same entity in a single frame.
# Objective
- Fix a bug causing performance to drop over time because the GPU fog buffer was endlessly growing
## Solution
- Clear the fog buffer every frame before populating it
# Objective
- Fix `post_processing` and `shader_prepass` examples as they fail when compiling shaders due to missing shader defs
- Fixes#6799
- Fixes#6996
- Fixes#7375
- Supercedes #6997
- Supercedes #7380
## Solution
- The prepass was broken due to a missing `MAX_CASCADES_PER_LIGHT` shader def. Add it.
- The shader used in the `post_processing` example is applied to a 2D mesh, so use the correct mesh2d_view_bindings shader import.
# Objective
- Trying to make it easier to have a more user friendly debugging name for when you want to print out an entity.
## Solution
- Add a new `WorldQuery` struct `DebugName` to format the `Name` if the entity has one, otherwise formats the `Entity` id.
This means we can do this and get more descriptive errors without much more effort:
```rust
fn my_system(moving: Query<(DebugName, &mut Position, &Velocity)>) {
for (name, mut position, velocity) in &mut moving {
position += velocity;
if position.is_nan() {
error!("{:?} has an invalid position state", name);
}
}
}
```
---
## Changelog
- Added `DebugName` world query for more human friendly debug names of entities.
# Objective
In simple cases we might want to derive the `ExtractComponent` trait.
This adds symmetry to the existing `ExtractResource` derive.
## Solution
Add an implementation of `#[derive(ExtractComponent)]`.
The implementation is adapted from the existing `ExtractResource` derive macro.
Additionally, there is an attribute called `extract_component_filter`. This allows specifying a query filter type used when extracting.
If not specified, no filter (equal to `()`) is used.
So:
```rust
#[derive(Component, Clone, ExtractComponent)]
#[extract_component_filter(With<Fuel>)]
pub struct Car {
pub wheels: usize,
}
```
would expand to (a bit cleaned up here):
```rust
impl ExtractComponent for Car
{
type Query = &'static Self;
type Filter = With<Fuel>;
type Out = Self;
fn extract_component(item: QueryItem<'_, Self::Query>) -> Option<Self::Out> {
Some(item.clone())
}
}
```
---
## Changelog
- Added the ability to `#[derive(ExtractComponent)]` with an optional filter.
# Objective
- Fixes#4592
## Solution
- Implement `SrgbColorSpace` for `u8` via `f32`
- Convert KTX2 R8 and R8G8 non-linear sRGB to wgpu `R8Unorm` and `Rg8Unorm` as non-linear sRGB are not supported by wgpu for these formats
- Convert KTX2 R8G8B8 formats to `Rgba8Unorm` and `Rgba8UnormSrgb` by adding an alpha channel as the Rgb variants don't exist in wgpu
---
## Changelog
- Added: Support for KTX2 `R8_SRGB`, `R8_UNORM`, `R8G8_SRGB`, `R8G8_UNORM`, `R8G8B8_SRGB`, `R8G8B8_UNORM` formats by converting to supported wgpu formats as appropriate
# Objective
Add a `FromReflect` derive to the `Aabb` type, like all other math types, so we can reflect `Vec<Aabb>`.
## Solution
Just add it :)
---
## Changelog
### Added
- Implemented `FromReflect` for `Aabb`.
# Objective
Update Bevy to wgpu 0.15.
## Changelog
- Update to wgpu 0.15, wgpu-hal 0.15.1, and naga 0.11
- Users can now use the [DirectX Shader Compiler](https://github.com/microsoft/DirectXShaderCompiler) (DXC) on Windows with DX12 for faster shader compilation and ShaderModel 6.0+ support (requires `dxcompiler.dll` and `dxil.dll`, which are included in DXC downloads from [here](https://github.com/microsoft/DirectXShaderCompiler/releases/latest))
## Migration Guide
### WGSL Top-Level `let` is now `const`
All top level constants are now declared with `const`, catching up with the wgsl spec.
`let` is no longer allowed at the global scope, only within functions.
```diff
-let SOME_CONSTANT = 12.0;
+const SOME_CONSTANT = 12.0;
```
#### `TextureDescriptor` and `SurfaceConfiguration` now requires a `view_formats` field
The new `view_formats` field in the `TextureDescriptor` is used to specify a list of formats the texture can be re-interpreted to in a texture view. Currently only changing srgb-ness is allowed (ex. `Rgba8Unorm` <=> `Rgba8UnormSrgb`). You should set `view_formats` to `&[]` (empty) unless you have a specific reason not to.
#### The DirectX Shader Compiler (DXC) is now supported on DX12
DXC is now the default shader compiler when using the DX12 backend. DXC is Microsoft's replacement for their legacy FXC compiler, and is faster, less buggy, and allows for modern shader features to be used (ShaderModel 6.0+). DXC requires `dxcompiler.dll` and `dxil.dll` to be available, otherwise it will log a warning and fall back to FXC.
You can get `dxcompiler.dll` and `dxil.dll` by downloading the latest release from [Microsoft's DirectXShaderCompiler github repo](https://github.com/microsoft/DirectXShaderCompiler/releases/latest) and copying them into your project's root directory. These must be included when you distribute your Bevy game/app/etc if you plan on supporting the DX12 backend and are using DXC.
`WgpuSettings` now has a `dx12_shader_compiler` field which can be used to choose between either FXC or DXC (if you pass None for the paths for DXC, it will check for the .dlls in the working directory).
# Objective
- Fix#7315
- Add IME support
## Solution
- Add two new fields to `Window`, to control if IME is enabled and the candidate box position
This allows the use of dead keys which are needed in French, or the full IME experience to type using Pinyin
I also added a basic general text input example that can handle IME input.
https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/8672791/213941353-5ed73a73-5dd1-4e66-a7d6-a69b49694c52.mp4
<img width="1392" alt="image" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/418473/203873533-44c029af-13b7-4740-8ea3-af96bd5867c9.png">
<img width="1392" alt="image" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/418473/203873549-36be7a23-b341-42a2-8a9f-ceea8ac7a2b8.png">
# Objective
- Add support for the “classic” distance fog effect, as well as a more advanced atmospheric fog effect.
## Solution
This PR:
- Introduces a new `FogSettings` component that controls distance fog per-camera.
- Adds support for three widely used “traditional” fog falloff modes: `Linear`, `Exponential` and `ExponentialSquared`, as well as a more advanced `Atmospheric` fog;
- Adds support for directional light influence over fog color;
- Extracts fog via `ExtractComponent`, then uses a prepare system that sets up a new dynamic uniform struct (`Fog`), similar to other mesh view types;
- Renders fog in PBR material shader, as a final adjustment to the `output_color`, after PBR is computed (but before tone mapping);
- Adds a new `StandardMaterial` flag to enable fog; (`fog_enabled`)
- Adds convenience methods for easier artistic control when creating non-linear fog types;
- Adds documentation around fog.
---
## Changelog
### Added
- Added support for distance-based fog effects for PBR materials, controllable per-camera via the new `FogSettings` component;
- Added `FogFalloff` enum for selecting between three widely used “traditional” fog falloff modes: `Linear`, `Exponential` and `ExponentialSquared`, as well as a more advanced `Atmospheric` fog;
# Objective
Found while working on #7385.
The struct `EntityMut` has the safety invariant that it's cached `EntityLocation` must always accurately specify where the entity is stored. Thus, any time its location might be invalidated (such as by calling `EntityMut::world_mut` and moving archetypes), the cached location *must* be updated by calling `EntityMut::update_location`.
The method `world_scope` encapsulates this pattern in safe API by requiring world mutations to be done in a closure, after which `update_location` will automatically be called. However, this method has a soundness hole: if a panic occurs within the closure, then `update_location` will never get called. If the panic is caught in an outer scope, then the `EntityMut` will be left with an outdated location, which is undefined behavior.
An example of this can be seen in the unit test `entity_mut_world_scope_panic`, which has been added to this PR as a regression test. Without the other changes in this PR, that test will invoke undefined behavior in safe code.
## Solution
Call `EntityMut::update_location()` from within a `Drop` impl, which ensures that it will get executed even if `EntityMut::world_scope` unwinds.
# Objective
I recently had an issue, where I have a struct:
```
struct Property {
inner: T
}
```
that I use as a wrapper for internal purposes.
I don't want to update my struct definition to
```
struct Property<T: Reflect>{
inner: T
}
```
because I still want to be able to build `Property<T>` for types `T` that are not `Reflect`. (and also because I don't want to update my whole code base with `<T: Reflect>` bounds)
I still wanted to have reflection on it (for `bevy_inspector_egui`), but adding `derive(Reflect)` fails with the error:
`T cannot be sent between threads safely. T needs to implement Sync.`
I believe that `bevy_reflect` should adopt the model of other derives in the case of generics, which is to add the `Reflect` implementation only if the generics also implement `Reflect`. (That is the behaviour of other macros such as `derive(Clone)` or `derive(Debug)`.
It's also the current behavior of `derive(FromReflect)`.
Basically doing something like:
```
impl<T> Reflect for Foo<T>
where T: Reflect
```
## Solution
- I updated the derive macros for `Structs` and `TupleStructs` to add extra `where` bounds.
- Every type that is reflected will need a `T: Reflect` bound
- Ignored types will need a `T: 'static + Send + Sync` bound. Here's the reason. For cases like this:
```
#[derive(Reflect)]
struct Foo<T, U>{
a: T
#[reflect(ignore)]
b: U
}
```
I had to add the bound `'static + Send + Sync` to ignored generics like `U`.
The reason is that we want `Foo<T, U>` to be `Reflect: 'static + Send + Sync`, so `Foo<T, U>` must be able to implement those auto-traits. `Foo<T, U>` will only implement those auto-traits if every generic type implements them, including ignored types.
This means that the previously compile-fail case now compiles:
```
#[derive(Reflect)]
struct Foo<'a> {
#[reflect(ignore)]
value: &'a str,
}
```
But `Foo<'a>` will only be useable in the cases where `'a: 'static` and panic if we don't have `'a: 'static`, which is what we want (nice bonus from this PR ;) )
---
## Changelog
> This section is optional. If this was a trivial fix, or has no externally-visible impact, you can delete this section.
### Added
Possibility to add `derive(Reflect)` to structs and enums that contain generic types, like so:
```
#[derive(Reflect)]
struct Foo<T>{
a: T
}
```
Reflection will only be available if the generic type T also implements `Reflect`.
(previously, this would just return a compiler error)
# Objective
The function `EntityMut::world_scope` is a safe abstraction that allows you to temporarily get mutable access to the underlying `World` of an `EntityMut`. This function is purely stateful, meaning it is not easily possible to return a value from it.
## Solution
Allow returning a computed value from the closure. This is similar to how `World::resource_scope` works.
---
## Changelog
- The function `EntityMut::world_scope` now allows returning a value from the immediately-computed closure.
# Objective
## Use Case
A render node which calls `post_process_write()` on a `ViewTarget` multiple times during a single run of the node means both main textures of this view target is accessed.
If the source texture (which alternate between main textures **a** and **b**) is accessed in a shader during those iterations it means that those textures have to be bound using bind groups.
Preparing bind groups for both main textures ahead of time is desired, which means having access to the _other_ main texture is needed.
## Solution
Add a method on `ViewTarget` for accessing the other main texture.
---
## Changelog
### Added
- `main_texture_other` API on `ViewTarget`
# Objective
There's no period at the end of the first line of the `Name` documentation, and this messes up the grammar of the summary rustdoc creates:
```
↓
Component used to identify an entity. Stores a hash for faster comparisons The hash is eagerly re-computed upon each update to the name.
```
## Solution
I added it.
# Objective
I found several words in code and docs are incorrect. This should be fixed.
## Solution
- Fix several minor typos
Co-authored-by: Chris Ohk <utilforever@gmail.com>
alternative to #5922, implements #5956
builds on top of https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/6402
# Objective
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/5956 goes into more detail, but the TLDR is:
- bevy systems ensure disjoint accesses to resources and components, and for that to work there are methods `World::get_resource_unchecked_mut(&self)`, ..., `EntityRef::get_mut_unchecked(&self)` etc.
- we don't have these unchecked methods for `by_id` variants, so third-party crate authors cannot build their own safe disjoint-access abstractions with these
- having `_unchecked_mut` methods is not great, because in their presence safe code can accidentally violate subtle invariants. Having to go through `world.as_unsafe_world_cell().unsafe_method()` forces you to stop and think about what you want to write in your `// SAFETY` comment.
The alternative is to keep exposing `_unchecked_mut` variants for every operation that we want third-party crates to build upon, but we'd prefer to avoid using these methods alltogether: https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/5922#issuecomment-1241954543
Also, this is something that **cannot be implemented outside of bevy**, so having either this PR or #5922 as an escape hatch with lots of discouraging comments would be great.
## Solution
- add `UnsafeWorldCell` with `unsafe fn get_resource(&self)`, `unsafe fn get_resource_mut(&self)`
- add `fn World::as_unsafe_world_cell(&mut self) -> UnsafeWorldCell<'_>` (and `as_unsafe_world_cell_readonly(&self)`)
- add `UnsafeWorldCellEntityRef` with `unsafe fn get`, `unsafe fn get_mut` and the other utilities on `EntityRef` (no methods for spawning, despawning, insertion)
- use the `UnsafeWorldCell` abstraction in `ReflectComponent`, `ReflectResource` and `ReflectAsset`, so these APIs are easier to reason about
- remove `World::get_resource_mut_unchecked`, `EntityRef::get_mut_unchecked` and use `unsafe { world.as_unsafe_world_cell().get_mut() }` and `unsafe { world.as_unsafe_world_cell().get_entity(entity)?.get_mut() }` instead
This PR does **not** make use of `UnsafeWorldCell` for anywhere else in `bevy_ecs` such as `SystemParam` or `Query`. That is a much larger change, and I am convinced that having `UnsafeWorldCell` is already useful for third-party crates.
Implemented API:
```rust
struct World { .. }
impl World {
fn as_unsafe_world_cell(&self) -> UnsafeWorldCell<'_>;
}
struct UnsafeWorldCell<'w>(&'w World);
impl<'w> UnsafeWorldCell {
unsafe fn world(&self) -> &World;
fn get_entity(&self) -> UnsafeWorldCellEntityRef<'w>; // returns 'w which is `'self` of the `World::as_unsafe_world_cell(&'w self)`
unsafe fn get_resource<T>(&self) -> Option<&'w T>;
unsafe fn get_resource_by_id(&self, ComponentId) -> Option<&'w T>;
unsafe fn get_resource_mut<T>(&self) -> Option<Mut<'w, T>>;
unsafe fn get_resource_mut_by_id(&self) -> Option<MutUntyped<'w>>;
unsafe fn get_non_send_resource<T>(&self) -> Option<&'w T>;
unsafe fn get_non_send_resource_mut<T>(&self) -> Option<Mut<'w, T>>>;
// not included: remove, remove_resource, despawn, anything that might change archetypes
}
struct UnsafeWorldCellEntityRef<'w> { .. }
impl UnsafeWorldCellEntityRef<'w> {
unsafe fn get<T>(&self, Entity) -> Option<&'w T>;
unsafe fn get_by_id(&self, Entity, ComponentId) -> Option<Ptr<'w>>;
unsafe fn get_mut<T>(&self, Entity) -> Option<Mut<'w, T>>;
unsafe fn get_mut_by_id(&self, Entity, ComponentId) -> Option<MutUntyped<'w>>;
unsafe fn get_change_ticks<T>(&self, Entity) -> Option<Mut<'w, T>>;
// fn id, archetype, contains, contains_id, containts_type_id
}
```
<details>
<summary>UnsafeWorldCell docs</summary>
Variant of the [`World`] where resource and component accesses takes a `&World`, and the responsibility to avoid
aliasing violations are given to the caller instead of being checked at compile-time by rust's unique XOR shared rule.
### Rationale
In rust, having a `&mut World` means that there are absolutely no other references to the safe world alive at the same time,
without exceptions. Not even unsafe code can change this.
But there are situations where careful shared mutable access through a type is possible and safe. For this, rust provides the [`UnsafeCell`](std::cell::UnsafeCell)
escape hatch, which allows you to get a `*mut T` from a `&UnsafeCell<T>` and around which safe abstractions can be built.
Access to resources and components can be done uniquely using [`World::resource_mut`] and [`World::entity_mut`], and shared using [`World::resource`] and [`World::entity`].
These methods use lifetimes to check at compile time that no aliasing rules are being broken.
This alone is not enough to implement bevy systems where multiple systems can access *disjoint* parts of the world concurrently. For this, bevy stores all values of
resources and components (and [`ComponentTicks`](crate::component::ComponentTicks)) in [`UnsafeCell`](std::cell::UnsafeCell)s, and carefully validates disjoint access patterns using
APIs like [`System::component_access`](crate::system::System::component_access).
A system then can be executed using [`System::run_unsafe`](crate::system::System::run_unsafe) with a `&World` and use methods with interior mutability to access resource values.
access resource values.
### Example Usage
[`UnsafeWorldCell`] can be used as a building block for writing APIs that safely allow disjoint access into the world.
In the following example, the world is split into a resource access half and a component access half, where each one can
safely hand out mutable references.
```rust
use bevy_ecs::world::World;
use bevy_ecs::change_detection::Mut;
use bevy_ecs::system::Resource;
use bevy_ecs::world::unsafe_world_cell_world::UnsafeWorldCell;
// INVARIANT: existance of this struct means that users of it are the only ones being able to access resources in the world
struct OnlyResourceAccessWorld<'w>(UnsafeWorldCell<'w>);
// INVARIANT: existance of this struct means that users of it are the only ones being able to access components in the world
struct OnlyComponentAccessWorld<'w>(UnsafeWorldCell<'w>);
impl<'w> OnlyResourceAccessWorld<'w> {
fn get_resource_mut<T: Resource>(&mut self) -> Option<Mut<'w, T>> {
// SAFETY: resource access is allowed through this UnsafeWorldCell
unsafe { self.0.get_resource_mut::<T>() }
}
}
// impl<'w> OnlyComponentAccessWorld<'w> {
// ...
// }
// the two interior mutable worlds borrow from the `&mut World`, so it cannot be accessed while they are live
fn split_world_access(world: &mut World) -> (OnlyResourceAccessWorld<'_>, OnlyComponentAccessWorld<'_>) {
let resource_access = OnlyResourceAccessWorld(unsafe { world.as_unsafe_world_cell() });
let component_access = OnlyComponentAccessWorld(unsafe { world.as_unsafe_world_cell() });
(resource_access, component_access)
}
```
</details>
# Objective
Prevent things from breaking tomorrow when rust 1.67 is released.
## Solution
Fix a few `uninlined_format_args` lints in recently introduced code.
# Objective
Fixes#6952
## Solution
- Request WGPU capabilities `SAMPLED_TEXTURE_AND_STORAGE_BUFFER_ARRAY_NON_UNIFORM_INDEXING`, `SAMPLER_NON_UNIFORM_INDEXING` and `UNIFORM_BUFFER_AND_STORAGE_TEXTURE_ARRAY_NON_UNIFORM_INDEXING` when corresponding features are enabled.
- Add an example (`shaders/texture_binding_array`) illustrating (and testing) the use of non-uniform indexed textures and samplers.
## Changelog
- Added new capabilities for shader validation.
- Added example `shaders/texture_binding_array`.
Co-authored-by: Robert Swain <robert.swain@gmail.com>
# Objective
Implements cascaded shadow maps for directional lights, which produces better quality shadows without needing excessively large shadow maps.
Fixes#3629
Before
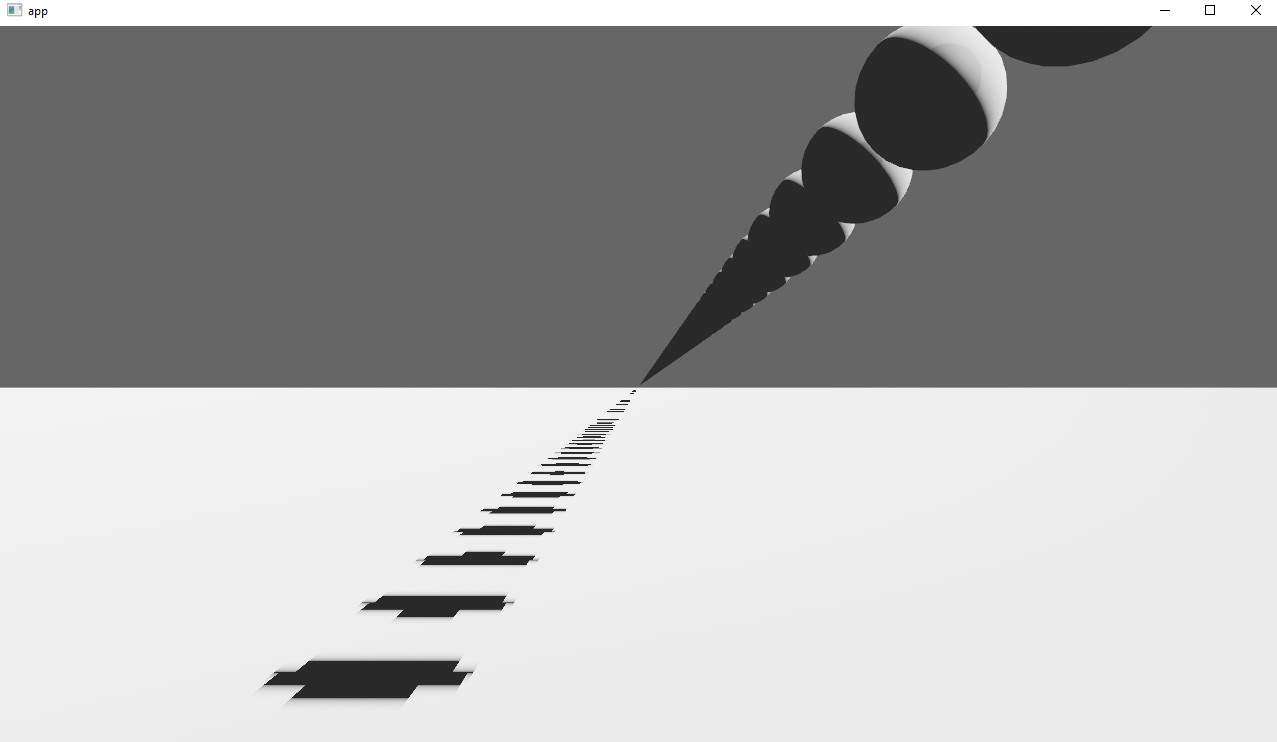
After
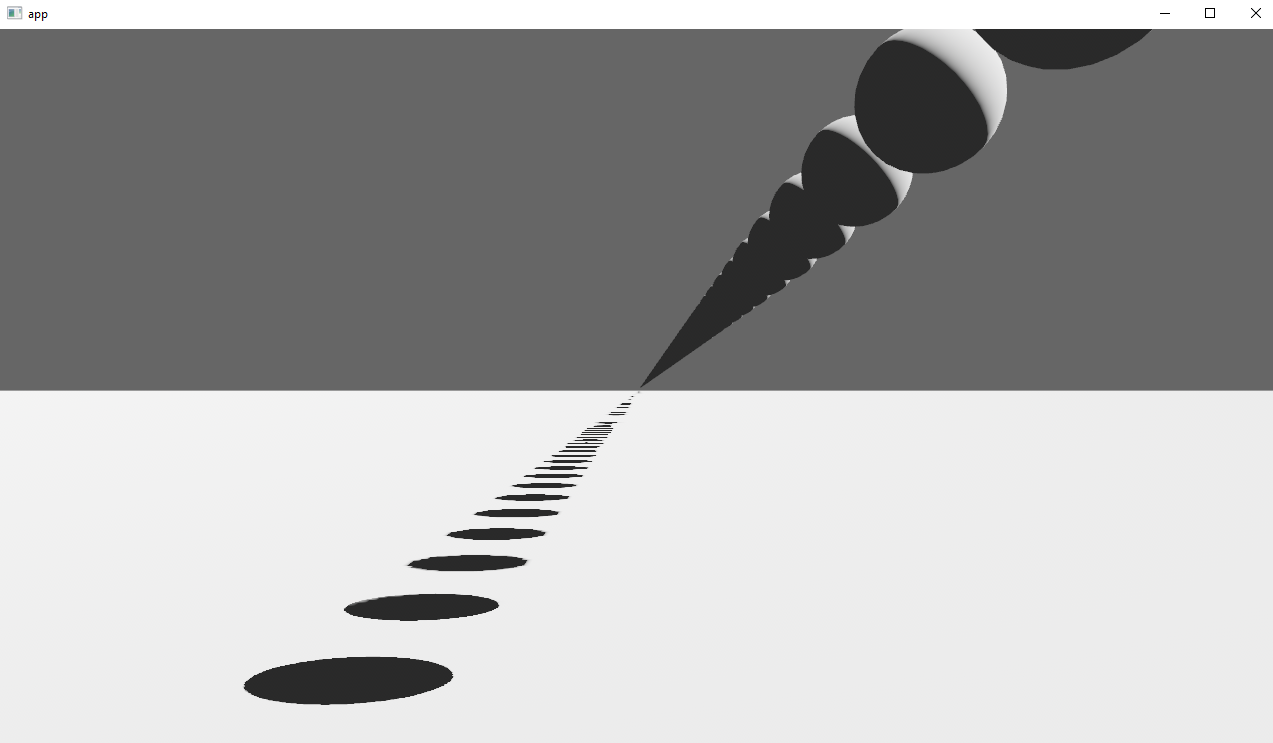
## Solution
Rather than rendering a single shadow map for directional light, the view frustum is divided into a series of cascades, each of which gets its own shadow map. The correct cascade is then sampled for shadow determination.
---
## Changelog
Directional lights now use cascaded shadow maps for improved shadow quality.
## Migration Guide
You no longer have to manually specify a `shadow_projection` for a directional light, and these settings should be removed. If customization of how cascaded shadow maps work is desired, modify the `CascadeShadowConfig` component instead.
# Objective
Fixes#7286. Both `App::add_sub_app` and `App::insert_sub_app` are rather redundant. Before 0.10 is shipped, one of them should be removed.
## Solution
Remove `App::add_sub_app` to prefer `App::insert_sub_app`.
Also hid away `SubApp::extract` since that can be a footgun if someone mutates it for whatever reason. Willing to revert this change if there are objections.
Perhaps we should make `SubApp: Deref<Target=App>`? Might change if we decide to move `!Send` resources into it.
---
## Changelog
Added: `SubApp::new`
Removed: `App::add_sub_app`
## Migration Guide
`App::add_sub_app` has been removed in favor of `App::insert_sub_app`. Use `SubApp::new` and insert it via `App::add_sub_app`
Old:
```rust
let mut sub_app = App::new()
// Build subapp here
app.add_sub_app(MySubAppLabel, sub_app);
```
New:
```rust
let mut sub_app = App::new()
// Build subapp here
app.insert_sub_app(MySubAppLabel, SubApp::new(sub_app, extract_fn));
```
# Objective
- The functions added to utils.wgsl by the prepass assume that mesh_view_bindings are present, which isn't always the case
- Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/7353
## Solution
- Move these functions to their own `prepass_utils.wgsl` file
Co-authored-by: IceSentry <IceSentry@users.noreply.github.com>
# Problem
The `upsert_leaf` method creates a new `MeasureFunc` and, if required, a new leaf node, but then it only adds the new `MeasureFunc` to existing leaf nodes.
## Solution
Add the `MeasureFunc` to new leaf nodes as well.