2019-11-13 03:36:02 +00:00
[ package ]
name = "bevy"
2023-07-10 21:19:27 +00:00
version = "0.12.0-dev"
2021-10-27 00:12:14 +00:00
edition = "2021"
2020-11-10 03:26:08 +00:00
categories = [ "game-engines" , "graphics" , "gui" , "rendering" ]
2020-08-10 00:24:27 +00:00
description = "A refreshingly simple data-driven game engine and app framework"
2022-06-01 23:05:30 +00:00
exclude = [ "assets/" , "tools/" , ".github/" , "crates/" , "examples/wasm/assets/" ]
2020-08-10 00:24:27 +00:00
homepage = "https://bevyengine.org"
keywords = [ "game" , "engine" , "gamedev" , "graphics" , "bevy" ]
2021-07-23 21:11:51 +00:00
license = "MIT OR Apache-2.0"
2020-11-10 18:58:51 +00:00
readme = "README.md"
2020-11-10 03:26:08 +00:00
repository = "https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy"
2023-06-01 21:55:18 +00:00
rust-version = "1.70.0"
2020-11-10 03:26:08 +00:00
[ workspace ]
2023-02-17 01:00:07 +00:00
exclude = [
"benches" ,
"crates/bevy_ecs_compile_fail_tests" ,
bevy_derive: Add `#[deref]` attribute (#8552)
# Objective
Bevy code tends to make heavy use of the [newtype](
https://doc.rust-lang.org/rust-by-example/generics/new_types.html)
pattern, which is why we have a dedicated derive for
[`Deref`](https://doc.rust-lang.org/std/ops/trait.Deref.html) and
[`DerefMut`](https://doc.rust-lang.org/std/ops/trait.DerefMut.html).
This derive works for any struct with a single field:
```rust
#[derive(Component, Deref, DerefMut)]
struct MyNewtype(usize);
```
One reason for the single-field limitation is to prevent confusion and
footguns related that would arise from allowing multi-field structs:
<table align="center">
<tr>
<th colspan="2">
Similar structs, different derefs
</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
```rust
#[derive(Deref, DerefMut)]
struct MyStruct {
foo: usize, // <- Derefs usize
bar: String,
}
```
</td>
<td>
```rust
#[derive(Deref, DerefMut)]
struct MyStruct {
bar: String, // <- Derefs String
foo: usize,
}
```
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th colspan="2">
Why `.1`?
</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="2">
```rust
#[derive(Deref, DerefMut)]
struct MyStruct(Vec<usize>, Vec<f32>);
let mut foo = MyStruct(vec![123], vec![1.23]);
// Why can we skip the `.0` here?
foo.push(456);
// But not here?
foo.1.push(4.56);
```
</td>
</tr>
</table>
However, there are certainly cases where it's useful to allow for
structs with multiple fields. Such as for structs with one "real" field
and one `PhantomData` to allow for generics:
```rust
#[derive(Deref, DerefMut)]
struct MyStruct<T>(
// We want use this field for the `Deref`/`DerefMut` impls
String,
// But we need this field so that we can make this struct generic
PhantomData<T>
);
// ERROR: Deref can only be derived for structs with a single field
// ERROR: DerefMut can only be derived for structs with a single field
```
Additionally, the possible confusion and footguns are mainly an issue
for newer Rust/Bevy users. Those familiar with `Deref` and `DerefMut`
understand what adding the derive really means and can anticipate its
behavior.
## Solution
Allow users to opt into multi-field `Deref`/`DerefMut` derives using a
`#[deref]` attribute:
```rust
#[derive(Deref, DerefMut)]
struct MyStruct<T>(
// Use this field for the `Deref`/`DerefMut` impls
#[deref] String,
// We can freely include any other field without a compile error
PhantomData<T>
);
```
This prevents the footgun pointed out in the first issue described in
the previous section, but it still leaves the possible confusion
surrounding `.0`-vs-`.#`. However, the idea is that by making this
behavior explicit with an attribute, users will be more aware of it and
can adapt appropriately.
---
## Changelog
- Added `#[deref]` attribute to `Deref` and `DerefMut` derives
2023-05-16 18:29:09 +00:00
"crates/bevy_macros_compile_fail_tests" ,
2023-02-17 01:00:07 +00:00
"crates/bevy_reflect_compile_fail_tests" ,
]
2022-07-15 22:37:05 +00:00
members = [
"crates/*" ,
2023-02-06 18:08:49 +00:00
"examples/mobile" ,
2022-07-15 22:37:05 +00:00
"tools/ci" ,
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
"tools/build-templated-pages" ,
2022-07-15 22:37:05 +00:00
"tools/build-wasm-example" ,
2023-05-08 19:02:06 +00:00
"tools/example-showcase" ,
2022-07-15 22:37:05 +00:00
"errors" ,
]
2019-11-13 03:36:02 +00:00
2020-03-11 05:20:49 +00:00
[ features ]
2020-09-02 00:02:11 +00:00
default = [
2022-04-02 22:36:02 +00:00
"animation" ,
2022-07-25 15:48:14 +00:00
"bevy_asset" ,
2020-11-10 03:26:08 +00:00
"bevy_audio" ,
"bevy_gilrs" ,
2022-07-25 15:48:14 +00:00
"bevy_scene" ,
2020-11-10 03:26:08 +00:00
"bevy_winit" ,
2022-12-11 18:46:46 +00:00
"bevy_core_pipeline" ,
"bevy_pbr" ,
"bevy_gltf" ,
"bevy_render" ,
"bevy_sprite" ,
"bevy_text" ,
"bevy_ui" ,
2023-07-09 04:22:15 +00:00
"multi-threaded" ,
2020-11-10 03:26:08 +00:00
"png" ,
"hdr" ,
2023-02-17 01:00:07 +00:00
"ktx2" ,
"zstd" ,
2021-12-23 19:19:15 +00:00
"vorbis" ,
2020-11-10 03:26:08 +00:00
"x11" ,
2021-12-18 19:38:05 +00:00
"filesystem_watcher" ,
2023-03-20 20:57:54 +00:00
"bevy_gizmos" ,
2023-02-17 01:00:07 +00:00
"android_shared_stdcxx" ,
2023-03-04 12:05:26 +00:00
"tonemapping_luts" ,
2023-04-21 22:30:18 +00:00
"default_font" ,
Webgpu support (#8336)
# Objective
- Support WebGPU
- alternative to #5027 that doesn't need any async / await
- fixes #8315
- Surprise fix #7318
## Solution
### For async renderer initialisation
- Update the plugin lifecycle:
- app builds the plugin
- calls `plugin.build`
- registers the plugin
- app starts the event loop
- event loop waits for `ready` of all registered plugins in the same
order
- returns `true` by default
- then call all `finish` then all `cleanup` in the same order as
registered
- then execute the schedule
In the case of the renderer, to avoid anything async:
- building the renderer plugin creates a detached task that will send
back the initialised renderer through a mutex in a resource
- `ready` will wait for the renderer to be present in the resource
- `finish` will take that renderer and place it in the expected
resources by other plugins
- other plugins (that expect the renderer to be available) `finish` are
called and they are able to set up their pipelines
- `cleanup` is called, only custom one is still for pipeline rendering
### For WebGPU support
- update the `build-wasm-example` script to support passing `--api
webgpu` that will build the example with WebGPU support
- feature for webgl2 was always enabled when building for wasm. it's now
in the default feature list and enabled on all platforms, so check for
this feature must also check that the target_arch is `wasm32`
---
## Migration Guide
- `Plugin::setup` has been renamed `Plugin::cleanup`
- `Plugin::finish` has been added, and plugins adding pipelines should
do it in this function instead of `Plugin::build`
```rust
// Before
impl Plugin for MyPlugin {
fn build(&self, app: &mut App) {
app.insert_resource::<MyResource>
.add_systems(Update, my_system);
let render_app = match app.get_sub_app_mut(RenderApp) {
Ok(render_app) => render_app,
Err(_) => return,
};
render_app
.init_resource::<RenderResourceNeedingDevice>()
.init_resource::<OtherRenderResource>();
}
}
// After
impl Plugin for MyPlugin {
fn build(&self, app: &mut App) {
app.insert_resource::<MyResource>
.add_systems(Update, my_system);
let render_app = match app.get_sub_app_mut(RenderApp) {
Ok(render_app) => render_app,
Err(_) => return,
};
render_app
.init_resource::<OtherRenderResource>();
}
fn finish(&self, app: &mut App) {
let render_app = match app.get_sub_app_mut(RenderApp) {
Ok(render_app) => render_app,
Err(_) => return,
};
render_app
.init_resource::<RenderResourceNeedingDevice>();
}
}
```
2023-05-04 22:07:57 +00:00
"webgl2" ,
2020-09-02 00:02:11 +00:00
]
2020-11-03 00:30:30 +00:00
2020-11-10 03:26:08 +00:00
# Force dynamic linking, which improves iterative compile times
2023-01-23 14:28:00 +00:00
dynamic_linking = [ "bevy_dylib" , "bevy_internal/dynamic_linking" ]
2020-10-01 20:04:06 +00:00
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# Provides animation functionality
2022-04-02 22:36:02 +00:00
bevy_animation = [ "bevy_internal/bevy_animation" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# Provides asset functionality
2022-07-25 15:48:14 +00:00
bevy_asset = [ "bevy_internal/bevy_asset" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# Provides audio functionality
2020-11-10 03:26:08 +00:00
bevy_audio = [ "bevy_internal/bevy_audio" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# Provides cameras and other basic render pipeline features
2023-03-14 14:10:50 +00:00
bevy_core_pipeline = [ "bevy_internal/bevy_core_pipeline" , "bevy_asset" , "bevy_render" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# Plugin for dynamic loading (using [libloading](https://crates.io/crates/libloading))
2020-11-10 03:26:08 +00:00
bevy_dynamic_plugin = [ "bevy_internal/bevy_dynamic_plugin" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# Adds gamepad support
2020-11-10 03:26:08 +00:00
bevy_gilrs = [ "bevy_internal/bevy_gilrs" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# [glTF](https://www.khronos.org/gltf/) support
2023-03-14 14:10:50 +00:00
bevy_gltf = [ "bevy_internal/bevy_gltf" , "bevy_asset" , "bevy_scene" , "bevy_pbr" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# Adds PBR rendering
2023-03-14 14:10:50 +00:00
bevy_pbr = [ "bevy_internal/bevy_pbr" , "bevy_asset" , "bevy_render" , "bevy_core_pipeline" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# Provides rendering functionality
2022-01-04 19:49:38 +00:00
bevy_render = [ "bevy_internal/bevy_render" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# Provides scene functionality
2023-03-14 14:10:50 +00:00
bevy_scene = [ "bevy_internal/bevy_scene" , "bevy_asset" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# Provides sprite functionality
2023-03-14 14:10:50 +00:00
bevy_sprite = [ "bevy_internal/bevy_sprite" , "bevy_render" , "bevy_core_pipeline" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# Provides text functionality
2023-06-22 02:57:04 +00:00
bevy_text = [ "bevy_internal/bevy_text" , "bevy_asset" , "bevy_sprite" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# A custom ECS-driven UI framework
2023-03-14 14:10:50 +00:00
bevy_ui = [ "bevy_internal/bevy_ui" , "bevy_core_pipeline" , "bevy_text" , "bevy_sprite" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# winit window and input backend
2020-11-10 03:26:08 +00:00
bevy_winit = [ "bevy_internal/bevy_winit" ]
2023-03-20 20:57:54 +00:00
# Adds support for rendering gizmos
bevy_gizmos = [ "bevy_internal/bevy_gizmos" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# Tracing support, saving a file in Chrome Tracing format
2021-12-18 00:09:22 +00:00
trace_chrome = [ "trace" , "bevy_internal/trace_chrome" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# Tracing support, exposing a port for Tracy
2021-12-18 00:09:22 +00:00
trace_tracy = [ "trace" , "bevy_internal/trace_tracy" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
2023-04-17 16:04:46 +00:00
# Tracing support, with memory profiling, exposing a port for Tracy
trace_tracy_memory = [ "trace" , "bevy_internal/trace_tracy" , "bevy_internal/trace_tracy_memory" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# Tracing support
2020-11-11 02:49:49 +00:00
trace = [ "bevy_internal/trace" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# Save a trace of all wgpu calls
2020-11-10 03:26:08 +00:00
wgpu_trace = [ "bevy_internal/wgpu_trace" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# EXR image format support
2023-02-19 20:38:13 +00:00
exr = [ "bevy_internal/exr" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# HDR image format support
2020-11-10 03:26:08 +00:00
hdr = [ "bevy_internal/hdr" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# PNG image format support
2020-11-10 03:26:08 +00:00
png = [ "bevy_internal/png" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# TGA image format support
2020-12-10 02:34:27 +00:00
tga = [ "bevy_internal/tga" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# JPEG image format support
2020-12-10 02:34:27 +00:00
jpeg = [ "bevy_internal/jpeg" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# BMP image format support
2020-12-23 22:53:02 +00:00
bmp = [ "bevy_internal/bmp" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
Added `WebP` image format support (#8220)
# Objective
WebP is a modern image format developed by Google that offers a
significant reduction in file size compared to other image formats such
as PNG and JPEG, while still maintaining good image quality. This makes
it particularly useful for games with large numbers of images, such as
those with high-quality textures or detailed sprites, where file size
and loading times can have a significant impact on performance.
By adding support for WebP images in Bevy, game developers using this
engine can now take advantage of this modern image format and reduce the
memory usage and loading times of their games. This improvement can
ultimately result in a better gaming experience for players.
In summary, the objective of adding WebP image format support in Bevy is
to enable game developers to use a modern image format that provides
better compression rates and smaller file sizes, resulting in faster
loading times and reduced memory usage for their games.
## Solution
To add support for WebP images in Bevy, this pull request leverages the
existing `image` crate support for WebP. This implementation is easily
integrated into the existing Bevy asset-loading system. To maintain
compatibility with existing Bevy projects, WebP image support is
disabled by default, and developers can enable it by adding a feature
flag to their project's `Cargo.toml` file. With this feature, Bevy
becomes even more versatile for game developers and provides a valuable
addition to the game engine.
---
## Changelog
- Added support for WebP image format in Bevy game engine
## Migration Guide
To enable WebP image support in your Bevy project, add the following
line to your project's Cargo.toml file:
```toml
bevy = { version = "*", features = ["webp"]}
```
2023-03-28 19:53:55 +00:00
# WebP image format support
webp = [ "bevy_internal/webp" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# Basis Universal compressed texture support
2022-03-15 22:26:46 +00:00
basis-universal = [ "bevy_internal/basis-universal" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# DDS compressed texture support
2022-03-15 22:26:46 +00:00
dds = [ "bevy_internal/dds" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# KTX2 compressed texture support
2022-03-15 22:26:46 +00:00
ktx2 = [ "bevy_internal/ktx2" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
2023-05-16 23:51:47 +00:00
# PNM image format support, includes pam, pbm, pgm and ppm
pnm = [ "bevy_internal/pnm" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# For KTX2 supercompression
2022-03-15 22:26:46 +00:00
zlib = [ "bevy_internal/zlib" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# For KTX2 supercompression
2022-03-15 22:26:46 +00:00
zstd = [ "bevy_internal/zstd" ]
2020-08-11 06:30:42 +00:00
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# FLAC audio format support
2020-11-10 03:26:08 +00:00
flac = [ "bevy_internal/flac" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# MP3 audio format support
2020-11-10 03:26:08 +00:00
mp3 = [ "bevy_internal/mp3" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# OGG/VORBIS audio format support
2020-11-10 03:26:08 +00:00
vorbis = [ "bevy_internal/vorbis" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# WAV audio format support
2020-11-10 03:26:08 +00:00
wav = [ "bevy_internal/wav" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
2023-03-01 03:22:46 +00:00
# MP3 audio format support (through minimp3)
minimp3 = [ "bevy_internal/minimp3" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# AAC audio format support (through symphonia)
2023-01-09 19:05:30 +00:00
symphonia-aac = [ "bevy_internal/symphonia-aac" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# AAC, FLAC, MP3, MP4, OGG/VORBIS, and WAV audio formats support (through symphonia)
2023-01-09 19:05:30 +00:00
symphonia-all = [ "bevy_internal/symphonia-all" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# FLAC audio format support (through symphonia)
2023-01-09 19:05:30 +00:00
symphonia-flac = [ "bevy_internal/symphonia-flac" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# MP4 audio format support (through symphonia)
2023-01-09 19:05:30 +00:00
symphonia-isomp4 = [ "bevy_internal/symphonia-isomp4" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# OGG/VORBIS audio format support (through symphonia)
2023-01-09 19:05:30 +00:00
symphonia-vorbis = [ "bevy_internal/symphonia-vorbis" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# WAV audio format support (through symphonia)
2023-01-09 19:05:30 +00:00
symphonia-wav = [ "bevy_internal/symphonia-wav" ]
2020-08-11 06:30:42 +00:00
2021-11-13 21:15:22 +00:00
# Enable watching file system for asset hot reload
filesystem_watcher = [ "bevy_internal/filesystem_watcher" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# Enable serialization support through serde
2020-11-10 03:26:08 +00:00
serialize = [ "bevy_internal/serialize" ]
2020-08-22 01:13:50 +00:00
2023-07-09 04:22:15 +00:00
# Enables multithreaded parallelism in the engine. Disabling it forces all engine tasks to run on a single thread.
multi-threaded = [ "bevy_internal/multi-threaded" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# Wayland display server support
2020-11-10 03:26:08 +00:00
wayland = [ "bevy_internal/wayland" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# X11 display server support
2020-11-10 03:26:08 +00:00
x11 = [ "bevy_internal/x11" ]
2020-05-06 01:44:32 +00:00
2022-01-04 19:49:38 +00:00
# Enable rendering of font glyphs using subpixel accuracy
2021-01-03 20:39:11 +00:00
subpixel_glyph_atlas = [ "bevy_internal/subpixel_glyph_atlas" ]
2022-01-04 19:49:38 +00:00
# Enable systems that allow for automated testing on CI
2021-04-14 21:40:36 +00:00
bevy_ci_testing = [ "bevy_internal/bevy_ci_testing" ]
2022-02-18 22:56:57 +00:00
# Enable the "debug asset server" for hot reloading internal assets
debug_asset_server = [ "bevy_internal/debug_asset_server" ]
2022-04-02 22:36:02 +00:00
# Enable animation support, and glTF animation loading
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
animation = [ "bevy_internal/animation" , "bevy_animation" ]
2022-04-02 22:36:02 +00:00
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# Enable using a shared stdlib for cxx on Android
2023-02-06 18:08:49 +00:00
android_shared_stdcxx = [ "bevy_internal/android_shared_stdcxx" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# Enable detailed trace event logging. These trace events are expensive even when off, thus they require compile time opt-in
Introduce detailed_trace macro, use in TrackedRenderPass (#7639)
Profiles show that in extremely hot loops, like the draw loops in the renderer, invoking the trace! macro has noticeable overhead, even if the trace log level is not enabled.
Solve this by introduce a 'wrapper' detailed_trace macro around trace, that wraps the trace! log statement in a trivially false if statement unless a cargo feature is enabled
# Objective
- Eliminate significant overhead observed with trace-level logging in render hot loops, even when trace log level is not enabled.
- This is an alternative solution to the one proposed in #7223
## Solution
- Introduce a wrapper around the `trace!` macro called `detailed_trace!`. This macro wraps the `trace!` macro with an if statement that is conditional on a new cargo feature, `detailed_trace`. When the feature is not enabled (the default), then the if statement is trivially false and should be optimized away at compile time.
- Convert the observed hot occurrences of trace logging in `TrackedRenderPass` with this new macro.
Testing the results of
```
cargo run --profile stress-test --features bevy/trace_tracy --example many_cubes -- spheres
```
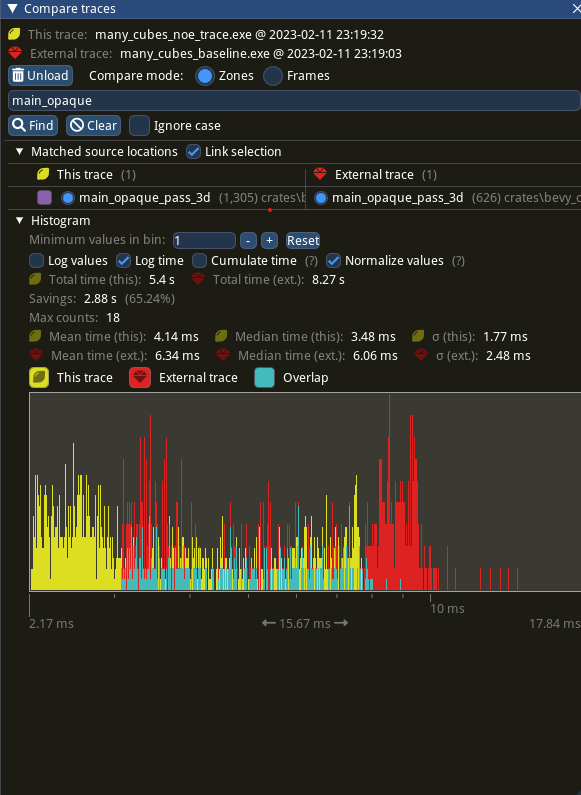
shows significant improvement of the `main_opaque_pass_3d` of the renderer, a median time decrease from 6.0ms to 3.5ms.
---
## Changelog
- For performance reasons, some detailed renderer trace logs now require the use of cargo feature `detailed_trace` in addition to setting the log level to `TRACE` in order to be shown.
## Migration Guide
- Some detailed bevy trace events now require the use of the cargo feature `detailed_trace` in addition to enabling `TRACE` level logging to view. Should you wish to see these logs, please compile your code with the bevy feature `detailed_trace`. Currently, the only logs that are affected are the renderer logs pertaining to `TrackedRenderPass` functions
2023-02-13 18:20:27 +00:00
detailed_trace = [ "bevy_internal/detailed_trace" ]
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
# Include tonemapping Look Up Tables KTX2 files
2023-02-19 20:38:13 +00:00
tonemapping_luts = [ "bevy_internal/tonemapping_luts" ]
2023-03-01 22:45:04 +00:00
# Enable AccessKit on Unix backends (currently only works with experimental screen readers and forks.)
accesskit_unix = [ "bevy_internal/accesskit_unix" ]
2023-03-28 20:18:50 +00:00
# Enable assertions to check the validity of parameters passed to glam
glam_assert = [ "bevy_internal/glam_assert" ]
2023-04-21 22:30:18 +00:00
# Include a default font, containing only ASCII characters, at the cost of a 20kB binary size increase
default_font = [ "bevy_internal/default_font" ]
2023-04-25 19:30:48 +00:00
# Enable support for shaders in GLSL
shader_format_glsl = [ "bevy_internal/shader_format_glsl" ]
# Enable support for shaders in SPIR-V
shader_format_spirv = [ "bevy_internal/shader_format_spirv" ]
2023-06-20 00:55:13 +00:00
# Enable support for transmission-related textures in the `StandardMaterial`, at the risk of blowing past the texture limit in lower-end adapters
pbr_transmission_textures = [ "bevy_internal/pbr_transmission_textures" ]
Webgpu support (#8336)
# Objective
- Support WebGPU
- alternative to #5027 that doesn't need any async / await
- fixes #8315
- Surprise fix #7318
## Solution
### For async renderer initialisation
- Update the plugin lifecycle:
- app builds the plugin
- calls `plugin.build`
- registers the plugin
- app starts the event loop
- event loop waits for `ready` of all registered plugins in the same
order
- returns `true` by default
- then call all `finish` then all `cleanup` in the same order as
registered
- then execute the schedule
In the case of the renderer, to avoid anything async:
- building the renderer plugin creates a detached task that will send
back the initialised renderer through a mutex in a resource
- `ready` will wait for the renderer to be present in the resource
- `finish` will take that renderer and place it in the expected
resources by other plugins
- other plugins (that expect the renderer to be available) `finish` are
called and they are able to set up their pipelines
- `cleanup` is called, only custom one is still for pipeline rendering
### For WebGPU support
- update the `build-wasm-example` script to support passing `--api
webgpu` that will build the example with WebGPU support
- feature for webgl2 was always enabled when building for wasm. it's now
in the default feature list and enabled on all platforms, so check for
this feature must also check that the target_arch is `wasm32`
---
## Migration Guide
- `Plugin::setup` has been renamed `Plugin::cleanup`
- `Plugin::finish` has been added, and plugins adding pipelines should
do it in this function instead of `Plugin::build`
```rust
// Before
impl Plugin for MyPlugin {
fn build(&self, app: &mut App) {
app.insert_resource::<MyResource>
.add_systems(Update, my_system);
let render_app = match app.get_sub_app_mut(RenderApp) {
Ok(render_app) => render_app,
Err(_) => return,
};
render_app
.init_resource::<RenderResourceNeedingDevice>()
.init_resource::<OtherRenderResource>();
}
}
// After
impl Plugin for MyPlugin {
fn build(&self, app: &mut App) {
app.insert_resource::<MyResource>
.add_systems(Update, my_system);
let render_app = match app.get_sub_app_mut(RenderApp) {
Ok(render_app) => render_app,
Err(_) => return,
};
render_app
.init_resource::<OtherRenderResource>();
}
fn finish(&self, app: &mut App) {
let render_app = match app.get_sub_app_mut(RenderApp) {
Ok(render_app) => render_app,
Err(_) => return,
};
render_app
.init_resource::<RenderResourceNeedingDevice>();
}
}
```
2023-05-04 22:07:57 +00:00
# Enable some limitations to be able to use WebGL2. If not enabled, it will default to WebGPU in Wasm
webgl2 = [ "bevy_internal/webgl" ]
2019-11-13 03:36:02 +00:00
[ dependencies ]
2023-07-10 21:19:27 +00:00
bevy_dylib = { path = "crates/bevy_dylib" , version = "0.12.0-dev" , default-features = false , optional = true }
bevy_internal = { path = "crates/bevy_internal" , version = "0.12.0-dev" , default-features = false }
2020-04-06 03:19:02 +00:00
[ dev-dependencies ]
2021-07-15 21:25:49 +00:00
anyhow = "1.0.4"
2021-01-17 21:43:03 +00:00
rand = "0.8.0"
2022-09-02 14:20:49 +00:00
ron = "0.8.0"
2021-08-01 19:14:47 +00:00
serde = { version = "1" , features = [ "derive" ] }
2022-01-05 19:43:11 +00:00
bytemuck = "1.7"
2021-05-23 20:13:55 +00:00
# Needed to poll Task examples
futures-lite = "1.11.3"
2022-02-05 01:52:47 +00:00
crossbeam-channel = "0.5.0"
2019-12-24 00:13:05 +00:00
2020-05-01 20:12:47 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "hello_world"
path = "examples/hello_world.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . hello_world ]
hidden = true
2021-02-22 04:50:05 +00:00
# 2D Rendering
2023-03-04 12:05:26 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "bloom_2d"
path = "examples/2d/bloom_2d.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . bloom_2d ]
name = "2D Bloom"
description = "Illustrates bloom post-processing in 2d"
category = "2D Rendering"
2023-05-19 20:11:41 +00:00
wasm = true
2023-03-04 12:05:26 +00:00
2022-02-02 02:44:51 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "move_sprite"
path = "examples/2d/move_sprite.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . move_sprite ]
name = "Move Sprite"
description = "Changes the transform of a sprite"
category = "2D Rendering"
wasm = true
2022-01-25 22:10:11 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
2022-02-25 15:54:03 +00:00
name = "rotation"
2022-01-25 22:10:11 +00:00
path = "examples/2d/rotation.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . rotation ]
name = "2D Rotation"
description = "Demonstrates rotating entities in 2D with quaternions"
category = "2D Rendering"
wasm = true
Add 2d meshes and materials (#3460)
# Objective
The current 2d rendering is specialized to render sprites, we need a generic way to render 2d items, using meshes and materials like we have for 3d.
## Solution
I cloned a good part of `bevy_pbr` into `bevy_sprite/src/mesh2d`, removed lighting and pbr itself, adapted it to 2d rendering, added a `ColorMaterial`, and modified the sprite rendering to break batches around 2d meshes.
~~The PR is a bit crude; I tried to change as little as I could in both the parts copied from 3d and the current sprite rendering to make reviewing easier. In the future, I expect we could make the sprite rendering a normal 2d material, cleanly integrated with the rest.~~ _edit: see <https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/3460#issuecomment-1003605194>_
## Remaining work
- ~~don't require mesh normals~~ _out of scope_
- ~~add an example~~ _done_
- support 2d meshes & materials in the UI?
- bikeshed names (I didn't think hard about naming, please check if it's fine)
## Remaining questions
- ~~should we add a depth buffer to 2d now that there are 2d meshes?~~ _let's revisit that when we have an opaque render phase_
- ~~should we add MSAA support to the sprites, or remove it from the 2d meshes?~~ _I added MSAA to sprites since it's really needed for 2d meshes_
- ~~how to customize vertex attributes?~~ _#3120_
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
2022-01-08 01:29:08 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "mesh2d"
path = "examples/2d/mesh2d.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . mesh2d ]
name = "Mesh 2D"
description = "Renders a 2d mesh"
category = "2D Rendering"
wasm = true
Add 2d meshes and materials (#3460)
# Objective
The current 2d rendering is specialized to render sprites, we need a generic way to render 2d items, using meshes and materials like we have for 3d.
## Solution
I cloned a good part of `bevy_pbr` into `bevy_sprite/src/mesh2d`, removed lighting and pbr itself, adapted it to 2d rendering, added a `ColorMaterial`, and modified the sprite rendering to break batches around 2d meshes.
~~The PR is a bit crude; I tried to change as little as I could in both the parts copied from 3d and the current sprite rendering to make reviewing easier. In the future, I expect we could make the sprite rendering a normal 2d material, cleanly integrated with the rest.~~ _edit: see <https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/3460#issuecomment-1003605194>_
## Remaining work
- ~~don't require mesh normals~~ _out of scope_
- ~~add an example~~ _done_
- support 2d meshes & materials in the UI?
- bikeshed names (I didn't think hard about naming, please check if it's fine)
## Remaining questions
- ~~should we add a depth buffer to 2d now that there are 2d meshes?~~ _let's revisit that when we have an opaque render phase_
- ~~should we add MSAA support to the sprites, or remove it from the 2d meshes?~~ _I added MSAA to sprites since it's really needed for 2d meshes_
- ~~how to customize vertex attributes?~~ _#3120_
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
2022-01-08 01:29:08 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "mesh2d_manual"
path = "examples/2d/mesh2d_manual.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . mesh2d_manual ]
name = "Manual Mesh 2D"
description = "Renders a custom mesh \"manually\" with \"mid-level\" renderer apis"
category = "2D Rendering"
wasm = true
2022-05-30 16:59:45 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "mesh2d_vertex_color_texture"
path = "examples/2d/mesh2d_vertex_color_texture.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . mesh2d_vertex_color_texture ]
name = "Mesh 2D With Vertex Colors"
description = "Renders a 2d mesh with vertex color attributes"
category = "2D Rendering"
wasm = true
Add an example to draw a rectangle (#2957)
# Objective
Every time I come back to Bevy I face the same issue: how do I draw a rectangle again? How did that work? So I go to https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/tree/main/examples in the hope of finding literally the simplest possible example that draws something on the screen without any dependency such as an image. I don't want to have to add some image first, I just quickly want to get something on the screen with `main.rs` alone so that I can continue building on from that point on. Such an example is particularly helpful for a quick start for smaller projects that don't even need any assets such as images (this is my case currently).
Currently every single example of https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/tree/main/examples#2d-rendering (which is the first section after hello world that beginners will look for for very minimalistic and quick examples) depends on at least an asset or is too complex. This PR solves this.
It also serves as a great comparison for a beginner to realize what Bevy is really like and how different it is from what they may expect Bevy to be. For example for someone coming from [LÖVE](https://love2d.org/), they will have something like this in their head when they think of drawing a rectangle:
```lua
function love.draw()
love.graphics.setColor(0.25, 0.25, 0.75);
love.graphics.rectangle("fill", 0, 0, 50, 50);
end
```
This, of course, differs quite a lot from what you do in Bevy. I imagine there will be people that just want to see something as simple as this in comparison to have a better understanding for the amount of differences.
## Solution
Add a dead simple example drawing a blue 50x50 rectangle in the center with no more and no less than needed.
2021-12-18 00:52:37 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
2022-09-25 00:57:07 +00:00
name = "2d_shapes"
path = "examples/2d/2d_shapes.rs"
Add an example to draw a rectangle (#2957)
# Objective
Every time I come back to Bevy I face the same issue: how do I draw a rectangle again? How did that work? So I go to https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/tree/main/examples in the hope of finding literally the simplest possible example that draws something on the screen without any dependency such as an image. I don't want to have to add some image first, I just quickly want to get something on the screen with `main.rs` alone so that I can continue building on from that point on. Such an example is particularly helpful for a quick start for smaller projects that don't even need any assets such as images (this is my case currently).
Currently every single example of https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/tree/main/examples#2d-rendering (which is the first section after hello world that beginners will look for for very minimalistic and quick examples) depends on at least an asset or is too complex. This PR solves this.
It also serves as a great comparison for a beginner to realize what Bevy is really like and how different it is from what they may expect Bevy to be. For example for someone coming from [LÖVE](https://love2d.org/), they will have something like this in their head when they think of drawing a rectangle:
```lua
function love.draw()
love.graphics.setColor(0.25, 0.25, 0.75);
love.graphics.rectangle("fill", 0, 0, 50, 50);
end
```
This, of course, differs quite a lot from what you do in Bevy. I imagine there will be people that just want to see something as simple as this in comparison to have a better understanding for the amount of differences.
## Solution
Add a dead simple example drawing a blue 50x50 rectangle in the center with no more and no less than needed.
2021-12-18 00:52:37 +00:00
2022-09-25 00:57:07 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . 2 d_shapes ]
name = "2D Shapes"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
description = "Renders a rectangle, circle, and hexagon"
category = "2D Rendering"
wasm = true
2023-04-24 14:20:13 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "custom_gltf_vertex_attribute"
path = "examples/2d/custom_gltf_vertex_attribute.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . custom_gltf_vertex_attribute ]
name = "Custom glTF vertex attribute 2D"
description = "Renders a glTF mesh in 2D with a custom vertex attribute"
category = "2D Rendering"
wasm = true
2023-03-20 20:57:54 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "2d_gizmos"
path = "examples/2d/2d_gizmos.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . 2 d_gizmos ]
name = "2D Gizmos"
description = "A scene showcasing 2D gizmos"
category = "2D Rendering"
wasm = true
2020-05-04 08:22:25 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "sprite"
path = "examples/2d/sprite.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . sprite ]
name = "Sprite"
description = "Renders a sprite"
category = "2D Rendering"
wasm = true
Add Sprite Flipping (#1407)
OK, here's my attempt at sprite flipping. There are a couple of points that I need review/help on, but I think the UX is about ideal:
```rust
.spawn(SpriteBundle {
material: materials.add(texture_handle.into()),
sprite: Sprite {
// Flip the sprite along the x axis
flip: SpriteFlip { x: true, y: false },
..Default::default()
},
..Default::default()
});
```
Now for the issues. The big issue is that for some reason, when flipping the UVs on the sprite, there is a light "bleeding" or whatever you call it where the UV tries to sample past the texture boundry and ends up clipping. This is only noticed when resizing the window, though. You can see a screenshot below.

I am quite baffled why the texture sampling is overrunning like it is and could use some guidance if anybody knows what might be wrong.
The other issue, which I just worked around, is that I had to remove the `#[render_resources(from_self)]` annotation from the Spritesheet because the `SpriteFlip` render resource wasn't being picked up properly in the shader when using it. I'm not sure what the cause of that was, but by removing the annotation and re-organizing the shader inputs accordingly the problem was fixed.
I'm not sure if this is the most efficient way to do this or if there is a better way, but I wanted to try it out if only for the learning experience. Let me know what you think!
2021-03-03 19:26:45 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "sprite_flipping"
path = "examples/2d/sprite_flipping.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . sprite_flipping ]
name = "Sprite Flipping"
description = "Renders a sprite flipped along an axis"
category = "2D Rendering"
wasm = true
2020-06-02 02:23:11 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "sprite_sheet"
path = "examples/2d/sprite_sheet.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . sprite_sheet ]
name = "Sprite Sheet"
description = "Renders an animated sprite"
category = "2D Rendering"
wasm = true
2020-12-27 19:19:03 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "text2d"
path = "examples/2d/text2d.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . text2d ]
name = "Text 2D"
description = "Generates text in 2D"
category = "2D Rendering"
wasm = true
2021-02-22 04:50:05 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "texture_atlas"
path = "examples/2d/texture_atlas.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . texture_atlas ]
name = "Texture Atlas"
description = "Generates a texture atlas (sprite sheet) from individual sprites"
category = "2D Rendering"
2023-05-25 21:57:04 +00:00
wasm = false
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
2022-06-06 17:52:09 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "transparency_2d"
path = "examples/2d/transparency_2d.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . transparency_2d ]
name = "Transparency in 2D"
description = "Demonstrates transparency in 2d"
category = "2D Rendering"
wasm = true
2022-11-14 22:15:46 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "pixel_perfect"
path = "examples/2d/pixel_perfect.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . pixel_perfect ]
name = "Pixel Perfect"
description = "Demonstrates pixel perfect in 2d"
category = "2D Rendering"
wasm = true
2021-02-22 04:50:05 +00:00
# 3D Rendering
2021-01-01 20:58:49 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "3d_scene"
path = "examples/3d/3d_scene.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . 3 d_scene ]
name = "3D Scene"
description = "Simple 3D scene with basic shapes and lighting"
category = "3D Rendering"
wasm = true
Camera Driven Viewports (#4898)
# Objective
Users should be able to render cameras to specific areas of a render target, which enables scenarios like split screen, minimaps, etc.
Builds on the new Camera Driven Rendering added here: #4745
Fixes: #202
Alternative to #1389 and #3626 (which are incompatible with the new Camera Driven Rendering)
## Solution
Cameras can now configure an optional "viewport", which defines a rectangle within their render target to draw to. If a `Viewport` is defined, the camera's `CameraProjection`, `View`, and visibility calculations will use the viewport configuration instead of the full render target.
```rust
// This camera will render to the first half of the primary window (on the left side).
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle {
camera: Camera {
viewport: Some(Viewport {
physical_position: UVec2::new(0, 0),
physical_size: UVec2::new(window.physical_width() / 2, window.physical_height()),
depth: 0.0..1.0,
}),
..default()
},
..default()
});
```
To account for this, the `Camera` component has received a few adjustments:
* `Camera` now has some new getter functions:
* `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, `projection_matrix`
* All computed camera values are now private and live on the `ComputedCameraValues` field (logical/physical width/height, the projection matrix). They are now exposed on `Camera` via getters/setters This wasn't _needed_ for viewports, but it was long overdue.
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `Camera` components now have a `viewport` field, which can be set to draw to a portion of a render target instead of the full target.
* `Camera` component has some new functions: `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, and `projection_matrix`
* Added a new split_screen example illustrating how to render two cameras to the same scene
## Migration Guide
`Camera::projection_matrix` is no longer a public field. Use the new `Camera::projection_matrix()` method instead:
```rust
// Bevy 0.7
let projection = camera.projection_matrix;
// Bevy 0.8
let projection = camera.projection_matrix();
```
2022-06-05 00:27:49 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "3d_shapes"
2022-09-25 00:57:07 +00:00
path = "examples/3d/3d_shapes.rs"
Camera Driven Viewports (#4898)
# Objective
Users should be able to render cameras to specific areas of a render target, which enables scenarios like split screen, minimaps, etc.
Builds on the new Camera Driven Rendering added here: #4745
Fixes: #202
Alternative to #1389 and #3626 (which are incompatible with the new Camera Driven Rendering)
## Solution

Cameras can now configure an optional "viewport", which defines a rectangle within their render target to draw to. If a `Viewport` is defined, the camera's `CameraProjection`, `View`, and visibility calculations will use the viewport configuration instead of the full render target.
```rust
// This camera will render to the first half of the primary window (on the left side).
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle {
camera: Camera {
viewport: Some(Viewport {
physical_position: UVec2::new(0, 0),
physical_size: UVec2::new(window.physical_width() / 2, window.physical_height()),
depth: 0.0..1.0,
}),
..default()
},
..default()
});
```
To account for this, the `Camera` component has received a few adjustments:
* `Camera` now has some new getter functions:
* `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, `projection_matrix`
* All computed camera values are now private and live on the `ComputedCameraValues` field (logical/physical width/height, the projection matrix). They are now exposed on `Camera` via getters/setters This wasn't _needed_ for viewports, but it was long overdue.
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `Camera` components now have a `viewport` field, which can be set to draw to a portion of a render target instead of the full target.
* `Camera` component has some new functions: `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, and `projection_matrix`
* Added a new split_screen example illustrating how to render two cameras to the same scene
## Migration Guide
`Camera::projection_matrix` is no longer a public field. Use the new `Camera::projection_matrix()` method instead:
```rust
// Bevy 0.7
let projection = camera.projection_matrix;
// Bevy 0.8
let projection = camera.projection_matrix();
```
2022-06-05 00:27:49 +00:00
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . 3 d_shapes ]
name = "3D Shapes"
description = "A scene showcasing the built-in 3D shapes"
category = "3D Rendering"
wasm = true
2023-06-23 19:26:37 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "generate_custom_mesh"
path = "examples/3d/generate_custom_mesh.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . generate_custom_mesh ]
name = "Generate Custom Mesh"
description = "Simple showcase of how to generate a custom mesh with a custom texture"
category = "3D Rendering"
wasm = true
Temporal Antialiasing (TAA) (#7291)

# Objective
- Implement an alternative antialias technique
- TAA scales based off of view resolution, not geometry complexity
- TAA filters textures, firefly pixels, and other aliasing not covered
by MSAA
- TAA additionally will reduce noise / increase quality in future
stochastic rendering techniques
- Closes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/3663
## Solution
- Add a temporal jitter component
- Add a motion vector prepass
- Add a TemporalAntialias component and plugin
- Combine existing MSAA and FXAA examples and add TAA
## Followup Work
- Prepass motion vector support for skinned meshes
- Move uniforms needed for motion vectors into a separate bind group,
instead of using different bind group layouts
- Reuse previous frame's GPU view buffer for motion vectors, instead of
recomputing
- Mip biasing for sharper textures, and or unjitter texture UVs
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/7323
- Compute shader for better performance
- Investigate FSR techniques
- Historical depth based disocclusion tests, for geometry disocclusion
- Historical luminance/hue based tests, for shading disocclusion
- Pixel "locks" to reduce blending rate / revamp history confidence
mechanism
- Orthographic camera support for TemporalJitter
- Figure out COD's 1-tap bicubic filter
---
## Changelog
- Added MotionVectorPrepass and TemporalJitter
- Added TemporalAntialiasPlugin, TemporalAntialiasBundle, and
TemporalAntialiasSettings
---------
Co-authored-by: IceSentry <c.giguere42@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: IceSentry <IceSentry@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Robert Swain <robert.swain@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Daniel Chia <danstryder@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: robtfm <50659922+robtfm@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Brandon Dyer <brandondyer64@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Edgar Geier <geieredgar@gmail.com>
2023-03-27 22:22:40 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "anti_aliasing"
path = "examples/3d/anti_aliasing.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . anti_aliasing ]
name = "Anti-aliasing"
description = "Compares different anti-aliasing methods"
category = "3D Rendering"
wasm = false
2023-03-20 20:57:54 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "3d_gizmos"
path = "examples/3d/3d_gizmos.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . 3 d_gizmos ]
name = "3D Gizmos"
description = "A scene showcasing 3D gizmos"
category = "3D Rendering"
wasm = true
Add Distance and Atmospheric Fog support (#6412)
<img width="1392" alt="image" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/418473/203873533-44c029af-13b7-4740-8ea3-af96bd5867c9.png">
<img width="1392" alt="image" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/418473/203873549-36be7a23-b341-42a2-8a9f-ceea8ac7a2b8.png">
# Objective
- Add support for the “classic” distance fog effect, as well as a more advanced atmospheric fog effect.
## Solution
This PR:
- Introduces a new `FogSettings` component that controls distance fog per-camera.
- Adds support for three widely used “traditional” fog falloff modes: `Linear`, `Exponential` and `ExponentialSquared`, as well as a more advanced `Atmospheric` fog;
- Adds support for directional light influence over fog color;
- Extracts fog via `ExtractComponent`, then uses a prepare system that sets up a new dynamic uniform struct (`Fog`), similar to other mesh view types;
- Renders fog in PBR material shader, as a final adjustment to the `output_color`, after PBR is computed (but before tone mapping);
- Adds a new `StandardMaterial` flag to enable fog; (`fog_enabled`)
- Adds convenience methods for easier artistic control when creating non-linear fog types;
- Adds documentation around fog.
---
## Changelog
### Added
- Added support for distance-based fog effects for PBR materials, controllable per-camera via the new `FogSettings` component;
- Added `FogFalloff` enum for selecting between three widely used “traditional” fog falloff modes: `Linear`, `Exponential` and `ExponentialSquared`, as well as a more advanced `Atmospheric` fog;
2023-01-29 15:28:56 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "atmospheric_fog"
path = "examples/3d/atmospheric_fog.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . atmospheric_fog ]
name = "Atmospheric Fog"
description = "A scene showcasing the atmospheric fog effect"
category = "3D Rendering"
wasm = true
[ [ example ] ]
name = "fog"
path = "examples/3d/fog.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . fog ]
name = "Fog"
description = "A scene showcasing the distance fog effect"
category = "3D Rendering"
wasm = true
2023-01-21 21:46:53 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "blend_modes"
path = "examples/3d/blend_modes.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . blend_modes ]
name = "Blend Modes"
description = "Showcases different blend modes"
category = "3D Rendering"
wasm = true
2021-06-02 02:59:17 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
2021-12-14 03:58:23 +00:00
name = "lighting"
path = "examples/3d/lighting.rs"
2021-07-08 02:49:33 +00:00
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . lighting ]
name = "Lighting"
description = "Illustrates various lighting options in a simple scene"
category = "3D Rendering"
wasm = true
2022-07-15 22:37:05 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "lines"
path = "examples/3d/lines.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . lines ]
name = "Lines"
description = "Create a custom material to draw 3d lines"
category = "3D Rendering"
wasm = true
Screen Space Ambient Occlusion (SSAO) MVP (#7402)

# Objective
- Add Screen space ambient occlusion (SSAO). SSAO approximates
small-scale, local occlusion of _indirect_ diffuse light between
objects. SSAO does not apply to direct lighting, such as point or
directional lights.
- This darkens creases, e.g. on staircases, and gives nice contact
shadows where objects meet, giving entities a more "grounded" feel.
- Closes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/3632.
## Solution
- Implement the GTAO algorithm.
-
https://www.activision.com/cdn/research/Practical_Real_Time_Strategies_for_Accurate_Indirect_Occlusion_NEW%20VERSION_COLOR.pdf
-
https://blog.selfshadow.com/publications/s2016-shading-course/activision/s2016_pbs_activision_occlusion.pdf
- Source code heavily based on [Intel's
XeGTAO](https://github.com/GameTechDev/XeGTAO/blob/0d177ce06bfa642f64d8af4de1197ad1bcb862d4/Source/Rendering/Shaders/XeGTAO.hlsli).
- Add an SSAO bevy example.
## Algorithm Overview
* Run a depth and normal prepass
* Create downscaled mips of the depth texture (preprocess_depths pass)
* GTAO pass - for each pixel, take several random samples from the
depth+normal buffers, reconstruct world position, raytrace in screen
space to estimate occlusion. Rather then doing completely random samples
on a hemisphere, you choose random _slices_ of the hemisphere, and then
can analytically compute the full occlusion of that slice. Also compute
edges based on depth differences here.
* Spatial denoise pass - bilateral blur, using edge detection to not
blur over edges. This is the final SSAO result.
* Main pass - if SSAO exists, sample the SSAO texture, and set occlusion
to be the minimum of ssao/material occlusion. This then feeds into the
rest of the PBR shader as normal.
---
## Future Improvements
- Maybe remove the low quality preset for now (too noisy)
- WebGPU fallback (see below)
- Faster depth->world position (see reverted code)
- Bent normals
- Try interleaved gradient noise or spatiotemporal blue noise
- Replace the spatial denoiser with a combined spatial+temporal denoiser
- Render at half resolution and use a bilateral upsample
- Better multibounce approximation
(https://drive.google.com/file/d/1SyagcEVplIm2KkRD3WQYSO9O0Iyi1hfy/view)
## Far-Future Performance Improvements
- F16 math (missing naga-wgsl support
https://github.com/gfx-rs/naga/issues/1884)
- Faster coordinate space conversion for normals
- Faster depth mipchain creation
(https://github.com/GPUOpen-Effects/FidelityFX-SPD) (wgpu/naga does not
currently support subgroup ops)
- Deinterleaved SSAO for better cache efficiency
(https://developer.nvidia.com/sites/default/files/akamai/gameworks/samples/DeinterleavedTexturing.pdf)
## Other Interesting Papers
- Visibility bitmask
(https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00371-022-02703-y,
https://cdrinmatane.github.io/posts/cgspotlight-slides/)
- Screen space diffuse lighting
(https://github.com/Patapom/GodComplex/blob/master/Tests/TestHBIL/2018%20Mayaux%20-%20Horizon-Based%20Indirect%20Lighting%20(HBIL).pdf)
## Platform Support
* SSAO currently does not work on DirectX12 due to issues with wgpu and
naga:
* https://github.com/gfx-rs/wgpu/pull/3798
* https://github.com/gfx-rs/naga/pull/2353
* SSAO currently does not work on WebGPU because r16float is not a valid
storage texture format
https://gpuweb.github.io/gpuweb/wgsl/#storage-texel-formats. We can fix
this with a fallback to r32float.
---
## Changelog
- Added ScreenSpaceAmbientOcclusionSettings,
ScreenSpaceAmbientOcclusionQualityLevel, and
ScreenSpaceAmbientOcclusionBundle
---------
Co-authored-by: IceSentry <c.giguere42@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: IceSentry <IceSentry@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Daniel Chia <danstryder@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Elabajaba <Elabajaba@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Robert Swain <robert.swain@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: robtfm <50659922+robtfm@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Brandon Dyer <brandondyer64@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Edgar Geier <geieredgar@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Nicola Papale <nicopap@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
2023-06-18 21:05:55 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "ssao"
path = "examples/3d/ssao.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . ssao ]
name = "Screen Space Ambient Occlusion"
description = "A scene showcasing screen space ambient occlusion"
category = "3D Rendering"
wasm = false
2022-07-08 19:57:43 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "spotlight"
path = "examples/3d/spotlight.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . spotlight ]
name = "Spotlight"
description = "Illustrates spot lights"
category = "3D Rendering"
wasm = true
2022-11-04 01:34:12 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
2023-03-04 12:05:26 +00:00
name = "bloom_3d"
path = "examples/3d/bloom_3d.rs"
2022-11-04 01:34:12 +00:00
2023-03-04 12:05:26 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . bloom_3d ]
name = "3D Bloom"
2022-11-04 01:34:12 +00:00
description = "Illustrates bloom configuration using HDR and emissive materials"
category = "3D Rendering"
2023-05-19 20:11:41 +00:00
wasm = true
2022-11-04 01:34:12 +00:00
2020-05-01 20:12:47 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
2020-10-18 20:48:15 +00:00
name = "load_gltf"
path = "examples/3d/load_gltf.rs"
2020-05-01 20:12:47 +00:00
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . load_gltf ]
name = "Load glTF"
description = "Loads and renders a glTF file as a scene"
category = "3D Rendering"
wasm = true
2023-02-19 20:38:13 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "tonemapping"
path = "examples/3d/tonemapping.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . tonemapping ]
name = "Tonemapping"
description = "Compares tonemapping options"
category = "3D Rendering"
wasm = true
2021-02-01 00:22:06 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "orthographic"
path = "examples/3d/orthographic.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . orthographic ]
name = "Orthographic View"
description = "Shows how to create a 3D orthographic view (for isometric-look in games or CAD applications)"
category = "3D Rendering"
wasm = true
2020-05-01 20:12:47 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "parenting"
path = "examples/3d/parenting.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . parenting ]
name = "Parenting"
description = "Demonstrates parent->child relationships and relative transformations"
category = "3D Rendering"
wasm = true
2021-03-20 03:22:33 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "pbr"
path = "examples/3d/pbr.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . pbr ]
name = "Physically Based Rendering"
description = "Demonstrates use of Physically Based Rendering (PBR) properties"
category = "3D Rendering"
wasm = true
Add parallax mapping to bevy PBR (#5928)
# Objective
Add a [parallax mapping] shader to bevy. Please note that
this is a 3d technique, NOT a 2d sidescroller feature.
## Solution
- Add related fields to `StandardMaterial`
- update the pbr shader
- Add an example taking advantage of parallax mapping
A pre-existing implementation exists at:
https://github.com/nicopap/bevy_mod_paramap/
The implementation is derived from:
https://web.archive.org/web/20150419215321/http://sunandblackcat.com/tipFullView.php?l=eng&topicid=28
Further discussion on literature is found in the `bevy_mod_paramap`
README.
### Limitations
- The mesh silhouette isn't affected by the depth map.
- The depth of the pixel does not reflect its visual position, resulting
in artifacts for depth-dependent features such as fog or SSAO
- GLTF does not define a height map texture, so somehow the user will
always need to work around this limitation, though [an extension is in
the works][gltf]
### Future work
- It's possible to update the depth in the depth buffer to follow the
parallaxed texture. This would enable interop with depth-based
visual effects, it also allows `discard`ing pixels of materials when
computed depth is higher than the one in depth buffer
- Cheap lower quality single-sample method using [offset limiting]
- Add distance fading, to disable parallaxing (relatively expensive)
on distant objects
- GLTF extension to allow defining height maps. Or a workaround
implemented through a blender plugin to the GLTF exporter that
uses the `extras` field to add height map.
- [Quadratic surface vertex attributes][oliveira_3] to enable parallax
mapping on bending surfaces and allow clean silhouetting.
- noise based sampling, to limit the pancake artifacts.
- Cone mapping ([GPU gems], [Simcity (2013)][simcity]). Requires
preprocessing, increase depth map size, reduces sample count greatly.
- [Quadtree parallax mapping][qpm] (also requires preprocessing)
- Self-shadowing of parallax-mapped surfaces by modifying the shadow map
- Generate depth map from normal map [link to slides], [blender
question]
https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/26321040/223563792-dffcc6ab-70e8-4ff9-90d1-b36c338695ad.mp4
[blender question]:
https://blender.stackexchange.com/questions/89278/how-to-get-a-smooth-curvature-map-from-a-normal-map
[link to slides]:
https://developer.download.nvidia.com/assets/gamedev/docs/nmap2displacement.pdf
[oliveira_3]:
https://www.inf.ufrgs.br/~oliveira/pubs_files/Oliveira_Policarpo_RP-351_Jan_2005.pdf
[GPU gems]:
https://developer.nvidia.com/gpugems/gpugems3/part-iii-rendering/chapter-18-relaxed-cone-stepping-relief-mapping
[simcity]:
https://community.simtropolis.com/omnibus/other-games/building-and-rendering-simcity-2013-r247/
[offset limiting]:
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/marcusstenbeck/tncg14-parallax-mapping/master/documents/Parallax%20Mapping%20with%20Offset%20Limiting%20-%20A%20Per-Pixel%20Approximation%20of%20Uneven%20Surfaces.pdf
[gltf]: https://github.com/KhronosGroup/glTF/pull/2196
[qpm]:
https://www.gamedevs.org/uploads/quadtree-displacement-mapping-with-height-blending.pdf
---
## Changelog
- Add a `depth_map` field to the `StandardMaterial`, it is a grayscale
image where white represents bottom and black the top. If `depth_map`
is set, bevy's pbr shader will use it to do [parallax mapping] to
give an increased feel of depth to the material. This is similar to a
displacement map, but with infinite precision at fairly low cost.
- The fields `parallax_mapping_method`, `parallax_depth_scale` and
`max_parallax_layer_count` allow finer grained control over the
behavior of the parallax shader.
- Add the `parallax_mapping` example to show off the effect.
[parallax mapping]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parallax_mapping
---------
Co-authored-by: Robert Swain <robert.swain@gmail.com>
2023-04-15 10:25:14 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "parallax_mapping"
path = "examples/3d/parallax_mapping.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . parallax_mapping ]
name = "Parallax Mapping"
description = "Demonstrates use of a normal map and depth map for parallax mapping"
category = "3D Rendering"
wasm = true
2022-05-05 00:46:32 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "render_to_texture"
path = "examples/3d/render_to_texture.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . render_to_texture ]
name = "Render to Texture"
description = "Shows how to render to a texture, useful for mirrors, UI, or exporting images"
category = "3D Rendering"
wasm = true
2021-06-27 23:10:23 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
2021-12-14 03:58:23 +00:00
name = "shadow_biases"
path = "examples/3d/shadow_biases.rs"
2021-07-19 19:20:59 +00:00
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . shadow_biases ]
name = "Shadow Biases"
description = "Demonstrates how shadow biases affect shadows in a 3d scene"
category = "3D Rendering"
wasm = true
2021-08-25 19:44:20 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
2021-12-14 03:58:23 +00:00
name = "shadow_caster_receiver"
path = "examples/3d/shadow_caster_receiver.rs"
2020-05-01 20:12:47 +00:00
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . shadow_caster_receiver ]
name = "Shadow Caster and Receiver"
description = "Demonstrates how to prevent meshes from casting/receiving shadows in a 3d scene"
category = "3D Rendering"
wasm = true
Support array / cubemap / cubemap array textures in KTX2 (#5325)
# Objective
- Fix / support KTX2 array / cubemap / cubemap array textures
- Fixes #4495 . Supersedes #4514 .
## Solution
- Add `Option<TextureViewDescriptor>` to `Image` to enable configuration of the `TextureViewDimension` of a texture.
- This allows users to set `D2Array`, `D3`, `Cube`, `CubeArray` or whatever they need
- Automatically configure this when loading KTX2
- Transcode all layers and faces instead of just one
- Use the UASTC block size of 128 bits, and the number of blocks in x/y for a given mip level in order to determine the offset of the layer and face within the KTX2 mip level data
- `wgpu` wants data ordered as layer 0 mip 0..n, layer 1 mip 0..n, etc. See https://docs.rs/wgpu/latest/wgpu/util/trait.DeviceExt.html#tymethod.create_texture_with_data
- Reorder the data KTX2 mip X layer Y face Z to `wgpu` layer Y face Z mip X order
- Add a `skybox` example to demonstrate / test loading cubemaps from PNG and KTX2, including ASTC 4x4, BC7, and ETC2 compression for support everywhere. Note that you need to enable the `ktx2,zstd` features to be able to load the compressed textures.
---
## Changelog
- Fixed: KTX2 array / cubemap / cubemap array textures
- Fixes: Validation failure for compressed textures stored in KTX2 where the width/height are not a multiple of the block dimensions.
- Added: `Image` now has an `Option<TextureViewDescriptor>` field to enable configuration of the texture view. This is useful for configuring the `TextureViewDimension` when it is not just a plain 2D texture and the loader could/did not identify what it should be.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
2022-07-30 07:02:58 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "skybox"
path = "examples/3d/skybox.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . skybox ]
name = "Skybox"
description = "Load a cubemap texture onto a cube like a skybox and cycle through different compressed texture formats."
category = "3D Rendering"
wasm = false
2021-12-30 21:07:26 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "spherical_area_lights"
path = "examples/3d/spherical_area_lights.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . spherical_area_lights ]
name = "Spherical Area Lights"
description = "Demonstrates how point light radius values affect light behavior"
category = "3D Rendering"
wasm = true
Camera Driven Viewports (#4898)
# Objective
Users should be able to render cameras to specific areas of a render target, which enables scenarios like split screen, minimaps, etc.
Builds on the new Camera Driven Rendering added here: #4745
Fixes: #202
Alternative to #1389 and #3626 (which are incompatible with the new Camera Driven Rendering)
## Solution

Cameras can now configure an optional "viewport", which defines a rectangle within their render target to draw to. If a `Viewport` is defined, the camera's `CameraProjection`, `View`, and visibility calculations will use the viewport configuration instead of the full render target.
```rust
// This camera will render to the first half of the primary window (on the left side).
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle {
camera: Camera {
viewport: Some(Viewport {
physical_position: UVec2::new(0, 0),
physical_size: UVec2::new(window.physical_width() / 2, window.physical_height()),
depth: 0.0..1.0,
}),
..default()
},
..default()
});
```
To account for this, the `Camera` component has received a few adjustments:
* `Camera` now has some new getter functions:
* `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, `projection_matrix`
* All computed camera values are now private and live on the `ComputedCameraValues` field (logical/physical width/height, the projection matrix). They are now exposed on `Camera` via getters/setters This wasn't _needed_ for viewports, but it was long overdue.
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `Camera` components now have a `viewport` field, which can be set to draw to a portion of a render target instead of the full target.
* `Camera` component has some new functions: `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, and `projection_matrix`
* Added a new split_screen example illustrating how to render two cameras to the same scene
## Migration Guide
`Camera::projection_matrix` is no longer a public field. Use the new `Camera::projection_matrix()` method instead:
```rust
// Bevy 0.7
let projection = camera.projection_matrix;
// Bevy 0.8
let projection = camera.projection_matrix();
```
2022-06-05 00:27:49 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "split_screen"
path = "examples/3d/split_screen.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . split_screen ]
name = "Split Screen"
description = "Demonstrates how to render two cameras to the same window to accomplish \"split screen\""
category = "3D Rendering"
wasm = true
2020-05-01 20:12:47 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "texture"
path = "examples/3d/texture.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . texture ]
name = "Texture"
description = "Shows configuration of texture materials"
category = "3D Rendering"
wasm = true
2022-06-06 17:52:09 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "transparency_3d"
path = "examples/3d/transparency_3d.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . transparency_3d ]
name = "Transparency in 3D"
description = "Demonstrates transparency in 3d"
category = "3D Rendering"
wasm = true
2023-03-10 06:12:20 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "transmission"
path = "examples/3d/transmission.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . transmission ]
name = "Transmission"
description = "Showcases light transmission in the PBR material"
category = "3D Rendering"
wasm = true
2022-04-12 19:27:30 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "two_passes"
path = "examples/3d/two_passes.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . two_passes ]
name = "Two Passes"
description = "Renders two 3d passes to the same window from different perspectives"
category = "3D Rendering"
wasm = true
2021-01-01 20:58:49 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "update_gltf_scene"
path = "examples/3d/update_gltf_scene.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . update_gltf_scene ]
name = "Update glTF Scene"
description = "Update a scene from a glTF file, either by spawning the scene as a child of another entity, or by accessing the entities of the scene"
category = "3D Rendering"
wasm = true
2022-05-05 00:46:32 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "vertex_colors"
path = "examples/3d/vertex_colors.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . vertex_colors ]
name = "Vertex Colors"
description = "Shows the use of vertex colors"
category = "3D Rendering"
wasm = true
2021-03-04 01:23:24 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "wireframe"
path = "examples/3d/wireframe.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . wireframe ]
name = "Wireframe"
description = "Showcases wireframe rendering"
category = "3D Rendering"
2023-05-29 15:32:11 +00:00
wasm = false
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
2023-03-03 15:08:54 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "no_prepass"
path = "tests/3d/no_prepass.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . no_prepass ]
hidden = true
2022-03-29 18:31:13 +00:00
# Animation
2022-04-02 22:36:02 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "animated_fox"
path = "examples/animation/animated_fox.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . animated_fox ]
name = "Animated Fox"
description = "Plays an animation from a skinned glTF"
category = "Animation"
wasm = true
Add morph targets (#8158)
# Objective
- Add morph targets to `bevy_pbr` (closes #5756) & load them from glTF
- Supersedes #3722
- Fixes #6814
[Morph targets][1] (also known as shape interpolation, shape keys, or
blend shapes) allow animating individual vertices with fine grained
controls. This is typically used for facial expressions. By specifying
multiple poses as vertex offset, and providing a set of weight of each
pose, it is possible to define surprisingly realistic transitions
between poses. Blending between multiple poses also allow composition.
Morph targets are part of the [gltf standard][2] and are a feature of
Unity and Unreal, and babylone.js, it is only natural to implement them
in bevy.
## Solution
This implementation of morph targets uses a 3d texture where each pixel
is a component of an animated attribute. Each layer is a different
target. We use a 2d texture for each target, because the number of
attribute×components×animated vertices is expected to always exceed the
maximum pixel row size limit of webGL2. It copies fairly closely the way
skinning is implemented on the CPU side, while on the GPU side, the
shader morph target implementation is a relatively trivial detail.
We add an optional `morph_texture` to the `Mesh` struct. The
`morph_texture` is built through a method that accepts an iterator over
attribute buffers.
The `MorphWeights` component, user-accessible, controls the blend of
poses used by mesh instances (so that multiple copy of the same mesh may
have different weights), all the weights are uploaded to a uniform
buffer of 256 `f32`. We limit to 16 poses per mesh, and a total of 256
poses.
More literature:
* Old babylone.js implementation (vertex attribute-based):
https://www.eternalcoding.com/dev-log-1-morph-targets/
* Babylone.js implementation (similar to ours):
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LBPRmGgU0PE
* GPU gems 3:
https://developer.nvidia.com/gpugems/gpugems3/part-i-geometry/chapter-3-directx-10-blend-shapes-breaking-limits
* Development discord thread
https://discord.com/channels/691052431525675048/1083325980615114772
https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/26321040/231181046-3bca2ab2-d4d9-472e-8098-639f1871ce2e.mp4
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/26321040/d2a0c544-0ef8-45cf-9f99-8c3792f5a258
## Acknowledgements
* Thanks to `storytold` for sponsoring the feature
* Thanks to `superdump` and `james7132` for guidance and help figuring
out stuff
## Future work
- Handling of less and more attributes (eg: animated uv, animated
arbitrary attributes)
- Dynamic pose allocation (so that zero-weighted poses aren't uploaded
to GPU for example, enables much more total poses)
- Better animation API, see #8357
----
## Changelog
- Add morph targets to bevy meshes
- Support up to 64 poses per mesh of individually up to 116508 vertices,
animation currently strictly limited to the position, normal and tangent
attributes.
- Load a morph target using `Mesh::set_morph_targets`
- Add `VisitMorphTargets` and `VisitMorphAttributes` traits to
`bevy_render`, this allows defining morph targets (a fairly complex and
nested data structure) through iterators (ie: single copy instead of
passing around buffers), see documentation of those traits for details
- Add `MorphWeights` component exported by `bevy_render`
- `MorphWeights` control mesh's morph target weights, blending between
various poses defined as morph targets.
- `MorphWeights` are directly inherited by direct children (single level
of hierarchy) of an entity. This allows controlling several mesh
primitives through a unique entity _as per GLTF spec_.
- Add `MorphTargetNames` component, naming each indices of loaded morph
targets.
- Load morph targets weights and buffers in `bevy_gltf`
- handle morph targets animations in `bevy_animation` (previously, it
was a `warn!` log)
- Add the `MorphStressTest.gltf` asset for morph targets testing, taken
from the glTF samples repo, CC0.
- Add morph target manipulation to `scene_viewer`
- Separate the animation code in `scene_viewer` from the rest of the
code, reducing `#[cfg(feature)]` noise
- Add the `morph_targets.rs` example to show off how to manipulate morph
targets, loading `MorpStressTest.gltf`
## Migration Guide
- (very specialized, unlikely to be touched by 3rd parties)
- `MeshPipeline` now has a single `mesh_layouts` field rather than
separate `mesh_layout` and `skinned_mesh_layout` fields. You should
handle all possible mesh bind group layouts in your implementation
- You should also handle properly the new `MORPH_TARGETS` shader def and
mesh pipeline key. A new function is exposed to make this easier:
`setup_moprh_and_skinning_defs`
- The `MeshBindGroup` is now `MeshBindGroups`, cached bind groups are
now accessed through the `get` method.
[1]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Morph_target_animation
[2]:
https://registry.khronos.org/glTF/specs/2.0/glTF-2.0.html#morph-targets
---------
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
2023-06-22 20:00:01 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "morph_targets"
path = "examples/animation/morph_targets.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . morph_targets ]
name = "Morph Targets"
description = "Plays an animation from a glTF file with meshes with morph targets"
category = "Animation"
wasm = true
2022-04-07 23:53:43 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "animated_transform"
path = "examples/animation/animated_transform.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . animated_transform ]
name = "Animated Transform"
description = "Create and play an animation defined by code that operates on the `Transform` component"
category = "Animation"
wasm = true
2023-04-17 16:16:56 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "cubic_curve"
path = "examples/animation/cubic_curve.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . cubic_curve ]
name = "Cubic Curve"
description = "Bezier curve example showing a cube following a cubic curve"
category = "Animation"
wasm = true
2022-03-29 18:31:13 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "custom_skinned_mesh"
path = "examples/animation/custom_skinned_mesh.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . custom_skinned_mesh ]
name = "Custom Skinned Mesh"
description = "Skinned mesh example with mesh and joints data defined in code"
category = "Animation"
wasm = true
2022-03-29 18:31:13 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "gltf_skinned_mesh"
path = "examples/animation/gltf_skinned_mesh.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . gltf_skinned_mesh ]
name = "glTF Skinned Mesh"
description = "Skinned mesh example with mesh and joints data loaded from a glTF file"
category = "Animation"
wasm = true
2021-02-22 04:50:05 +00:00
# Application
2020-11-09 21:04:27 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "custom_loop"
path = "examples/app/custom_loop.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . custom_loop ]
name = "Custom Loop"
description = "Demonstrates how to create a custom runner (to update an app manually)"
category = "Application"
wasm = false
2021-01-01 21:31:22 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "drag_and_drop"
path = "examples/app/drag_and_drop.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . drag_and_drop ]
name = "Drag and Drop"
description = "An example that shows how to handle drag and drop in an app"
category = "Application"
wasm = false
2020-05-01 20:12:47 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "empty"
path = "examples/app/empty.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . empty ]
name = "Empty"
description = "An empty application (does nothing)"
category = "Application"
wasm = false
2020-11-13 01:23:57 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
2021-02-22 04:50:05 +00:00
name = "empty_defaults"
path = "examples/app/empty_defaults.rs"
2020-11-13 01:23:57 +00:00
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . empty_defaults ]
name = "Empty with Defaults"
description = "An empty application with default plugins"
category = "Application"
wasm = true
2020-05-01 20:12:47 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "headless"
path = "examples/app/headless.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . headless ]
name = "Headless"
description = "An application that runs without default plugins"
category = "Application"
wasm = false
2021-02-22 04:50:05 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "logs"
path = "examples/app/logs.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . logs ]
name = "Logs"
description = "Illustrate how to use generate log output"
category = "Application"
wasm = true
2020-05-03 08:30:10 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "plugin"
path = "examples/app/plugin.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . plugin ]
name = "Plugin"
description = "Demonstrates the creation and registration of a custom plugin"
category = "Application"
wasm = true
2020-10-29 20:04:28 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "plugin_group"
path = "examples/app/plugin_group.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . plugin_group ]
name = "Plugin Group"
description = "Demonstrates the creation and registration of a custom plugin group"
category = "Application"
wasm = true
2020-08-21 05:37:19 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "return_after_run"
path = "examples/app/return_after_run.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . return_after_run ]
name = "Return after Run"
description = "Show how to return to main after the Bevy app has exited"
category = "Application"
wasm = false
2020-08-14 17:15:29 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "thread_pool_resources"
path = "examples/app/thread_pool_resources.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . thread_pool_resources ]
name = "Thread Pool Resources"
description = "Creates and customizes the internal thread pool"
category = "Application"
wasm = false
2022-01-08 10:39:43 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
2022-07-11 14:11:32 +00:00
name = "no_renderer"
path = "examples/app/no_renderer.rs"
2022-01-08 10:39:43 +00:00
2022-07-11 14:11:32 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . no_renderer ]
name = "No Renderer"
description = "An application that runs with default plugins and displays an empty window, but without an actual renderer"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
category = "Application"
wasm = false
2021-12-15 00:15:47 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "without_winit"
path = "examples/app/without_winit.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . without_winit ]
name = "Without Winit"
description = "Create an application without winit (runs single time, no event loop)"
category = "Application"
wasm = false
2021-02-22 04:50:05 +00:00
# Assets
2020-05-17 03:18:30 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "asset_loading"
path = "examples/asset/asset_loading.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . asset_loading ]
name = "Asset Loading"
description = "Demonstrates various methods to load assets"
category = "Assets"
2023-05-25 21:57:04 +00:00
wasm = false
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
2020-10-01 18:31:06 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
2020-10-18 20:48:15 +00:00
name = "custom_asset"
path = "examples/asset/custom_asset.rs"
2020-10-01 18:31:06 +00:00
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . custom_asset ]
name = "Custom Asset"
description = "Implements a custom asset loader"
category = "Assets"
wasm = true
2020-12-18 19:34:44 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "custom_asset_io"
path = "examples/asset/custom_asset_io.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . custom_asset_io ]
name = "Custom Asset IO"
description = "Implements a custom asset io loader"
category = "Assets"
wasm = true
2021-02-22 04:50:05 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "hot_asset_reloading"
path = "examples/asset/hot_asset_reloading.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . hot_asset_reloading ]
name = "Hot Reloading of Assets"
description = "Demonstrates automatic reloading of assets when modified on disk"
category = "Assets"
wasm = true
2021-05-23 20:13:55 +00:00
# Async Tasks
[ [ example ] ]
name = "async_compute"
path = "examples/async_tasks/async_compute.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . async_compute ]
name = "Async Compute"
description = "How to use `AsyncComputeTaskPool` to complete longer running tasks"
category = "Async Tasks"
wasm = false
2022-02-05 01:52:47 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "external_source_external_thread"
path = "examples/async_tasks/external_source_external_thread.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . external_source_external_thread ]
name = "External Source of Data on an External Thread"
description = "How to use an external thread to run an infinite task and communicate with a channel"
category = "Async Tasks"
wasm = false
2021-02-22 04:50:05 +00:00
# Audio
2020-07-16 20:46:51 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "audio"
path = "examples/audio/audio.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . audio ]
name = "Audio"
description = "Shows how to load and play an audio file"
category = "Audio"
wasm = true
2022-03-01 01:12:11 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "audio_control"
path = "examples/audio/audio_control.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . audio_control ]
name = "Audio Control"
description = "Shows how to load and play an audio file, and control how it's played"
category = "Audio"
wasm = true
2023-01-17 22:42:00 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "decodable"
path = "examples/audio/decodable.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . decodable ]
name = "Decodable"
description = "Shows how to create and register a custom audio source by implementing the `Decodable` type."
category = "Audio"
wasm = true
2023-02-20 15:31:07 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "spatial_audio_2d"
path = "examples/audio/spatial_audio_2d.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . spatial_audio_2d ]
name = "Spatial Audio 2D"
description = "Shows how to play spatial audio, and moving the emitter in 2D"
category = "Audio"
wasm = true
[ [ example ] ]
name = "spatial_audio_3d"
path = "examples/audio/spatial_audio_3d.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . spatial_audio_3d ]
name = "Spatial Audio 3D"
description = "Shows how to play spatial audio, and moving the emitter in 3D"
category = "Audio"
wasm = true
2021-02-22 04:50:05 +00:00
# Diagnostics
[ [ example ] ]
name = "log_diagnostics"
path = "examples/diagnostics/log_diagnostics.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . log_diagnostics ]
name = "Log Diagnostics"
description = "Add a plugin that logs diagnostics, like frames per second (FPS), to the console"
category = "Diagnostics"
wasm = true
2020-05-04 21:14:49 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "custom_diagnostic"
path = "examples/diagnostics/custom_diagnostic.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . custom_diagnostic ]
name = "Custom Diagnostic"
description = "Shows how to create a custom diagnostic"
category = "Diagnostics"
wasm = true
2021-02-22 04:50:05 +00:00
# ECS (Entity Component System)
2020-05-04 21:14:49 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
2021-02-22 04:50:05 +00:00
name = "ecs_guide"
path = "examples/ecs/ecs_guide.rs"
2020-05-04 21:14:49 +00:00
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . ecs_guide ]
name = "ECS Guide"
description = "Full guide to Bevy's ECS"
category = "ECS (Entity Component System)"
wasm = false
2023-02-28 00:19:44 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
2023-06-02 14:04:13 +00:00
name = "apply_deferred"
path = "examples/ecs/apply_deferred.rs"
2023-02-28 00:19:44 +00:00
2023-06-02 14:04:13 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . apply_deferred ]
2023-02-28 00:19:44 +00:00
name = "Apply System Buffers"
2023-06-02 14:04:13 +00:00
description = "Show how to use `apply_deferred` system"
2023-02-28 00:19:44 +00:00
category = "ECS (Entity Component System)"
wasm = false
2020-12-31 22:29:08 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
2021-07-12 20:09:43 +00:00
name = "component_change_detection"
path = "examples/ecs/component_change_detection.rs"
2020-12-31 22:29:08 +00:00
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . component_change_detection ]
name = "Component Change Detection"
description = "Change detection on components"
category = "ECS (Entity Component System)"
wasm = false
Implement `WorldQuery` derive macro (#2713)
# Objective
- Closes #786
- Closes #2252
- Closes #2588
This PR implements a derive macro that allows users to define their queries as structs with named fields.
## Example
```rust
#[derive(WorldQuery)]
#[world_query(derive(Debug))]
struct NumQuery<'w, T: Component, P: Component> {
entity: Entity,
u: UNumQuery<'w>,
generic: GenericQuery<'w, T, P>,
}
#[derive(WorldQuery)]
#[world_query(derive(Debug))]
struct UNumQuery<'w> {
u_16: &'w u16,
u_32_opt: Option<&'w u32>,
}
#[derive(WorldQuery)]
#[world_query(derive(Debug))]
struct GenericQuery<'w, T: Component, P: Component> {
generic: (&'w T, &'w P),
}
#[derive(WorldQuery)]
#[world_query(filter)]
struct NumQueryFilter<T: Component, P: Component> {
_u_16: With<u16>,
_u_32: With<u32>,
_or: Or<(With<i16>, Changed<u16>, Added<u32>)>,
_generic_tuple: (With<T>, With<P>),
_without: Without<Option<u16>>,
_tp: PhantomData<(T, P)>,
}
fn print_nums_readonly(query: Query<NumQuery<u64, i64>, NumQueryFilter<u64, i64>>) {
for num in query.iter() {
println!("{:#?}", num);
}
}
#[derive(WorldQuery)]
#[world_query(mutable, derive(Debug))]
struct MutNumQuery<'w, T: Component, P: Component> {
i_16: &'w mut i16,
i_32_opt: Option<&'w mut i32>,
}
fn print_nums(mut query: Query<MutNumQuery, NumQueryFilter<u64, i64>>) {
for num in query.iter_mut() {
println!("{:#?}", num);
}
}
```
## TODOs:
- [x] Add support for `&T` and `&mut T`
- [x] Test
- [x] Add support for optional types
- [x] Test
- [x] Add support for `Entity`
- [x] Test
- [x] Add support for nested `WorldQuery`
- [x] Test
- [x] Add support for tuples
- [x] Test
- [x] Add support for generics
- [x] Test
- [x] Add support for query filters
- [x] Test
- [x] Add support for `PhantomData`
- [x] Test
- [x] Refactor `read_world_query_field_type_info`
- [x] Properly document `readonly` attribute for nested queries and the static assertions that guarantee safety
- [x] Test that we never implement `ReadOnlyFetch` for types that need mutable access
- [x] Test that we insert static assertions for nested `WorldQuery` that a user marked as readonly
2022-02-24 00:19:49 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "custom_query_param"
path = "examples/ecs/custom_query_param.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . custom_query_param ]
name = "Custom Query Parameters"
description = "Groups commonly used compound queries and query filters into a single type"
category = "ECS (Entity Component System)"
wasm = false
2020-05-01 20:12:47 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "event"
path = "examples/ecs/event.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . event ]
name = "Event"
description = "Illustrates event creation, activation, and reception"
category = "ECS (Entity Component System)"
wasm = false
2020-12-13 02:04:42 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "fixed_timestep"
path = "examples/ecs/fixed_timestep.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . fixed_timestep ]
name = "Fixed Timestep"
description = "Shows how to create systems that run every fixed timestep, rather than every tick"
category = "ECS (Entity Component System)"
wasm = false
2022-02-08 16:24:46 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "generic_system"
path = "examples/ecs/generic_system.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . generic_system ]
name = "Generic System"
description = "Shows how to create systems that can be reused with different types"
category = "ECS (Entity Component System)"
wasm = false
2021-02-22 04:50:05 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "hierarchy"
path = "examples/ecs/hierarchy.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . hierarchy ]
name = "Hierarchy"
description = "Creates a hierarchy of parents and children entities"
category = "ECS (Entity Component System)"
wasm = false
Add a method `iter_combinations` on query to iterate over combinations of query results (#1763)
Related to [discussion on discord](https://discord.com/channels/691052431525675048/742569353878437978/824731187724681289)
With const generics, it is now possible to write generic iterator over multiple entities at once.
This enables patterns of query iterations like
```rust
for [e1, e2, e3] in query.iter_combinations() {
// do something with relation of all three entities
}
```
The compiler is able to infer the correct iterator for given size of array, so either of those work
```rust
for [e1, e2] in query.iter_combinations() { ... }
for [e1, e2, e3] in query.iter_combinations() { ... }
```
This feature can be very useful for systems like collision detection.
When you ask for permutations of size K of N entities:
- if K == N, you get one result of all entities
- if K < N, you get all possible subsets of N with size K, without repetition
- if K > N, the result set is empty (no permutation of size K exist)
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
2021-05-17 23:33:47 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "iter_combinations"
path = "examples/ecs/iter_combinations.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . iter_combinations ]
name = "Iter Combinations"
description = "Shows how to iterate over combinations of query results"
category = "ECS (Entity Component System)"
wasm = true
2021-02-22 04:50:05 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "parallel_query"
path = "examples/ecs/parallel_query.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . parallel_query ]
name = "Parallel Query"
description = "Illustrates parallel queries with `ParallelIterator`"
category = "ECS (Entity Component System)"
wasm = false
2021-02-22 04:50:05 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "removal_detection"
path = "examples/ecs/removal_detection.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . removal_detection ]
name = "Removal Detection"
Migrate engine to Schedule v3 (#7267)
Huge thanks to @maniwani, @devil-ira, @hymm, @cart, @superdump and @jakobhellermann for the help with this PR.
# Objective
- Followup #6587.
- Minimal integration for the Stageless Scheduling RFC: https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/pull/45
## Solution
- [x] Remove old scheduling module
- [x] Migrate new methods to no longer use extension methods
- [x] Fix compiler errors
- [x] Fix benchmarks
- [x] Fix examples
- [x] Fix docs
- [x] Fix tests
## Changelog
### Added
- a large number of methods on `App` to work with schedules ergonomically
- the `CoreSchedule` enum
- `App::add_extract_system` via the `RenderingAppExtension` trait extension method
- the private `prepare_view_uniforms` system now has a public system set for scheduling purposes, called `ViewSet::PrepareUniforms`
### Removed
- stages, and all code that mentions stages
- states have been dramatically simplified, and no longer use a stack
- `RunCriteriaLabel`
- `AsSystemLabel` trait
- `on_hierarchy_reports_enabled` run criteria (now just uses an ad hoc resource checking run condition)
- systems in `RenderSet/Stage::Extract` no longer warn when they do not read data from the main world
- `RunCriteriaLabel`
- `transform_propagate_system_set`: this was a nonstandard pattern that didn't actually provide enough control. The systems are already `pub`: the docs have been updated to ensure that the third-party usage is clear.
### Changed
- `System::default_labels` is now `System::default_system_sets`.
- `App::add_default_labels` is now `App::add_default_sets`
- `CoreStage` and `StartupStage` enums are now `CoreSet` and `StartupSet`
- `App::add_system_set` was renamed to `App::add_systems`
- The `StartupSchedule` label is now defined as part of the `CoreSchedules` enum
- `.label(SystemLabel)` is now referred to as `.in_set(SystemSet)`
- `SystemLabel` trait was replaced by `SystemSet`
- `SystemTypeIdLabel<T>` was replaced by `SystemSetType<T>`
- The `ReportHierarchyIssue` resource now has a public constructor (`new`), and implements `PartialEq`
- Fixed time steps now use a schedule (`CoreSchedule::FixedTimeStep`) rather than a run criteria.
- Adding rendering extraction systems now panics rather than silently failing if no subapp with the `RenderApp` label is found.
- the `calculate_bounds` system, with the `CalculateBounds` label, is now in `CoreSet::Update`, rather than in `CoreSet::PostUpdate` before commands are applied.
- `SceneSpawnerSystem` now runs under `CoreSet::Update`, rather than `CoreStage::PreUpdate.at_end()`.
- `bevy_pbr::add_clusters` is no longer an exclusive system
- the top level `bevy_ecs::schedule` module was replaced with `bevy_ecs::scheduling`
- `tick_global_task_pools_on_main_thread` is no longer run as an exclusive system. Instead, it has been replaced by `tick_global_task_pools`, which uses a `NonSend` resource to force running on the main thread.
## Migration Guide
- Calls to `.label(MyLabel)` should be replaced with `.in_set(MySet)`
- Stages have been removed. Replace these with system sets, and then add command flushes using the `apply_system_buffers` exclusive system where needed.
- The `CoreStage`, `StartupStage, `RenderStage` and `AssetStage` enums have been replaced with `CoreSet`, `StartupSet, `RenderSet` and `AssetSet`. The same scheduling guarantees have been preserved.
- Systems are no longer added to `CoreSet::Update` by default. Add systems manually if this behavior is needed, although you should consider adding your game logic systems to `CoreSchedule::FixedTimestep` instead for more reliable framerate-independent behavior.
- Similarly, startup systems are no longer part of `StartupSet::Startup` by default. In most cases, this won't matter to you.
- For example, `add_system_to_stage(CoreStage::PostUpdate, my_system)` should be replaced with
- `add_system(my_system.in_set(CoreSet::PostUpdate)`
- When testing systems or otherwise running them in a headless fashion, simply construct and run a schedule using `Schedule::new()` and `World::run_schedule` rather than constructing stages
- Run criteria have been renamed to run conditions. These can now be combined with each other and with states.
- Looping run criteria and state stacks have been removed. Use an exclusive system that runs a schedule if you need this level of control over system control flow.
- For app-level control flow over which schedules get run when (such as for rollback networking), create your own schedule and insert it under the `CoreSchedule::Outer` label.
- Fixed timesteps are now evaluated in a schedule, rather than controlled via run criteria. The `run_fixed_timestep` system runs this schedule between `CoreSet::First` and `CoreSet::PreUpdate` by default.
- Command flush points introduced by `AssetStage` have been removed. If you were relying on these, add them back manually.
- Adding extract systems is now typically done directly on the main app. Make sure the `RenderingAppExtension` trait is in scope, then call `app.add_extract_system(my_system)`.
- the `calculate_bounds` system, with the `CalculateBounds` label, is now in `CoreSet::Update`, rather than in `CoreSet::PostUpdate` before commands are applied. You may need to order your movement systems to occur before this system in order to avoid system order ambiguities in culling behavior.
- the `RenderLabel` `AppLabel` was renamed to `RenderApp` for clarity
- `App::add_state` now takes 0 arguments: the starting state is set based on the `Default` impl.
- Instead of creating `SystemSet` containers for systems that run in stages, simply use `.on_enter::<State::Variant>()` or its `on_exit` or `on_update` siblings.
- `SystemLabel` derives should be replaced with `SystemSet`. You will also need to add the `Debug`, `PartialEq`, `Eq`, and `Hash` traits to satisfy the new trait bounds.
- `with_run_criteria` has been renamed to `run_if`. Run criteria have been renamed to run conditions for clarity, and should now simply return a bool.
- States have been dramatically simplified: there is no longer a "state stack". To queue a transition to the next state, call `NextState::set`
## TODO
- [x] remove dead methods on App and World
- [x] add `App::add_system_to_schedule` and `App::add_systems_to_schedule`
- [x] avoid adding the default system set at inappropriate times
- [x] remove any accidental cycles in the default plugins schedule
- [x] migrate benchmarks
- [x] expose explicit labels for the built-in command flush points
- [x] migrate engine code
- [x] remove all mentions of stages from the docs
- [x] verify docs for States
- [x] fix uses of exclusive systems that use .end / .at_start / .before_commands
- [x] migrate RenderStage and AssetStage
- [x] migrate examples
- [x] ensure that transform propagation is exported in a sufficiently public way (the systems are already pub)
- [x] ensure that on_enter schedules are run at least once before the main app
- [x] re-enable opt-in to execution order ambiguities
- [x] revert change to `update_bounds` to ensure it runs in `PostUpdate`
- [x] test all examples
- [x] unbreak directional lights
- [x] unbreak shadows (see 3d_scene, 3d_shape, lighting, transparaency_3d examples)
- [x] game menu example shows loading screen and menu simultaneously
- [x] display settings menu is a blank screen
- [x] `without_winit` example panics
- [x] ensure all tests pass
- [x] SubApp doc test fails
- [x] runs_spawn_local tasks fails
- [x] [Fix panic_when_hierachy_cycle test hanging](https://github.com/alice-i-cecile/bevy/pull/120)
## Points of Difficulty and Controversy
**Reviewers, please give feedback on these and look closely**
1. Default sets, from the RFC, have been removed. These added a tremendous amount of implicit complexity and result in hard to debug scheduling errors. They're going to be tackled in the form of "base sets" by @cart in a followup.
2. The outer schedule controls which schedule is run when `App::update` is called.
3. I implemented `Label for `Box<dyn Label>` for our label types. This enables us to store schedule labels in concrete form, and then later run them. I ran into the same set of problems when working with one-shot systems. We've previously investigated this pattern in depth, and it does not appear to lead to extra indirection with nested boxes.
4. `SubApp::update` simply runs the default schedule once. This sucks, but this whole API is incomplete and this was the minimal changeset.
5. `time_system` and `tick_global_task_pools_on_main_thread` no longer use exclusive systems to attempt to force scheduling order
6. Implemetnation strategy for fixed timesteps
7. `AssetStage` was migrated to `AssetSet` without reintroducing command flush points. These did not appear to be used, and it's nice to remove these bottlenecks.
8. Migration of `bevy_render/lib.rs` and pipelined rendering. The logic here is unusually tricky, as we have complex scheduling requirements.
## Future Work (ideally before 0.10)
- Rename schedule_v3 module to schedule or scheduling
- Add a derive macro to states, and likely a `EnumIter` trait of some form
- Figure out what exactly to do with the "systems added should basically work by default" problem
- Improve ergonomics for working with fixed timesteps and states
- Polish FixedTime API to match Time
- Rebase and merge #7415
- Resolve all internal ambiguities (blocked on better tools, especially #7442)
- Add "base sets" to replace the removed default sets.
2023-02-06 02:04:50 +00:00
description = "Query for entities that had a specific component removed earlier in the current frame"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
category = "ECS (Entity Component System)"
wasm = false
2023-02-18 05:32:59 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "run_conditions"
path = "examples/ecs/run_conditions.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . run_conditions ]
name = "Run Conditions"
description = "Run systems only when one or multiple conditions are met"
category = "ECS (Entity Component System)"
wasm = false
2020-05-01 20:12:47 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "startup_system"
path = "examples/ecs/startup_system.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . startup_system ]
name = "Startup System"
description = "Demonstrates a startup system (one that runs once when the app starts up)"
category = "ECS (Entity Component System)"
wasm = false
2020-12-13 02:04:42 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "state"
path = "examples/ecs/state.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . state ]
name = "State"
description = "Illustrates how to use States to control transitioning from a Menu state to an InGame state"
category = "ECS (Entity Component System)"
wasm = false
2020-11-17 02:18:00 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
2022-10-11 15:21:12 +00:00
name = "system_piping"
path = "examples/ecs/system_piping.rs"
2020-11-17 02:18:00 +00:00
2022-10-11 15:21:12 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . system_piping ]
name = "System Piping"
description = "Pipe the output of one system into a second, allowing you to handle any errors gracefully"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
category = "ECS (Entity Component System)"
wasm = false
2022-04-27 18:02:07 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "system_closure"
path = "examples/ecs/system_closure.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . system_closure ]
name = "System Closure"
description = "Show how to use closures as systems, and how to configure `Local` variables by capturing external state"
category = "ECS (Entity Component System)"
wasm = false
2021-03-03 03:11:11 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "system_param"
path = "examples/ecs/system_param.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . system_param ]
name = "System Parameter"
description = "Illustrates creating custom system parameters with `SystemParam`"
category = "ECS (Entity Component System)"
wasm = false
2020-11-27 19:39:33 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "timers"
path = "examples/ecs/timers.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . timers ]
name = "Timers"
description = "Illustrates ticking `Timer` resources inside systems and handling their state"
category = "ECS (Entity Component System)"
wasm = false
2021-02-22 04:50:05 +00:00
# Games
2021-01-21 22:10:02 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "alien_cake_addict"
2022-04-10 02:05:21 +00:00
path = "examples/games/alien_cake_addict.rs"
2021-01-21 22:10:02 +00:00
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . alien_cake_addict ]
name = "Alien Cake Addict"
description = "Eat the cakes. Eat them all. An example 3D game"
category = "Games"
wasm = true
2020-06-27 04:40:09 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "breakout"
2022-04-10 02:05:21 +00:00
path = "examples/games/breakout.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . breakout ]
name = "Breakout"
description = "An implementation of the classic game \"Breakout\""
category = "Games"
wasm = true
2022-04-10 02:05:21 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "contributors"
path = "examples/games/contributors.rs"
2020-06-27 04:40:09 +00:00
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . contributors ]
name = "Contributors"
description = "Displays each contributor as a bouncy bevy-ball!"
category = "Games"
wasm = true
2022-01-14 19:09:42 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "game_menu"
2022-04-10 02:05:21 +00:00
path = "examples/games/game_menu.rs"
2022-01-14 19:09:42 +00:00
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . game_menu ]
name = "Game Menu"
description = "A simple game menu"
category = "Games"
wasm = true
2021-02-22 04:50:05 +00:00
# Input
2020-05-01 20:12:47 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
2021-02-22 04:50:05 +00:00
name = "char_input_events"
path = "examples/input/char_input_events.rs"
2020-05-01 20:12:47 +00:00
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . char_input_events ]
name = "Char Input Events"
description = "Prints out all chars as they are inputted"
category = "Input"
wasm = false
2020-05-01 20:12:47 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
2021-02-22 04:50:05 +00:00
name = "gamepad_input"
path = "examples/input/gamepad_input.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . gamepad_input ]
name = "Gamepad Input"
description = "Shows handling of gamepad input, connections, and disconnections"
category = "Input"
wasm = false
2021-02-22 04:50:05 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "gamepad_input_events"
path = "examples/input/gamepad_input_events.rs"
2020-06-05 06:49:36 +00:00
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . gamepad_input_events ]
name = "Gamepad Input Events"
description = "Iterates and prints gamepad input and connection events"
category = "Input"
wasm = false
2023-04-24 15:28:53 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "gamepad_rumble"
path = "examples/input/gamepad_rumble.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . gamepad_rumble ]
name = "Gamepad Rumble"
description = "Shows how to rumble a gamepad using force feedback"
category = "Input"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
wasm = false
2020-06-05 06:49:36 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "keyboard_input"
path = "examples/input/keyboard_input.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . keyboard_input ]
name = "Keyboard Input"
description = "Demonstrates handling a key press/release"
category = "Input"
wasm = false
2021-03-14 21:00:36 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "keyboard_modifiers"
path = "examples/input/keyboard_modifiers.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . keyboard_modifiers ]
name = "Keyboard Modifiers"
description = "Demonstrates using key modifiers (ctrl, shift)"
category = "Input"
wasm = false
2020-06-05 06:49:36 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "keyboard_input_events"
path = "examples/input/keyboard_input_events.rs"
2020-05-01 20:12:47 +00:00
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . keyboard_input_events ]
name = "Keyboard Input Events"
description = "Prints out all keyboard events"
category = "Input"
wasm = false
2020-11-07 01:15:56 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
2021-02-22 04:50:05 +00:00
name = "mouse_input"
path = "examples/input/mouse_input.rs"
2020-09-18 21:43:47 +00:00
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . mouse_input ]
name = "Mouse Input"
description = "Demonstrates handling a mouse button press/release"
category = "Input"
wasm = false
2020-10-21 17:27:00 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
2021-02-22 04:50:05 +00:00
name = "mouse_input_events"
path = "examples/input/mouse_input_events.rs"
2020-10-21 17:27:00 +00:00
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . mouse_input_events ]
name = "Mouse Input Events"
description = "Prints out all mouse events (buttons, movement, etc.)"
category = "Input"
wasm = false
2022-03-08 17:14:08 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "mouse_grab"
path = "examples/input/mouse_grab.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . mouse_grab ]
name = "Mouse Grab"
description = "Demonstrates how to grab the mouse, locking the cursor to the app's screen"
category = "Input"
wasm = false
2020-10-18 19:24:01 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "touch_input"
path = "examples/input/touch_input.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . touch_input ]
name = "Touch Input"
description = "Displays touch presses, releases, and cancels"
category = "Input"
wasm = false
2020-10-18 19:24:01 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
2020-10-18 20:20:42 +00:00
name = "touch_input_events"
path = "examples/input/touch_input_events.rs"
2020-10-18 19:24:01 +00:00
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . touch_input_events ]
name = "Touch Input Events"
description = "Prints out all touch inputs"
category = "Input"
wasm = false
2023-01-29 20:27:29 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "text_input"
path = "examples/input/text_input.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . text_input ]
name = "Text Input"
description = "Simple text input with IME support"
category = "Input"
wasm = false
2021-02-22 04:50:05 +00:00
# Reflection
2020-05-01 20:12:47 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
2020-11-28 00:39:59 +00:00
name = "reflection"
path = "examples/reflection/reflection.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . reflection ]
name = "Reflection"
description = "Demonstrates how reflection in Bevy provides a way to dynamically interact with Rust types"
category = "Reflection"
wasm = false
2020-11-28 00:39:59 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "generic_reflection"
path = "examples/reflection/generic_reflection.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . generic_reflection ]
name = "Generic Reflection"
description = "Registers concrete instances of generic types that may be used with reflection"
category = "Reflection"
wasm = false
2021-02-22 04:50:05 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "reflection_types"
path = "examples/reflection/reflection_types.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . reflection_types ]
name = "Reflection Types"
description = "Illustrates the various reflection types available"
category = "Reflection"
wasm = false
2020-11-28 00:39:59 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "trait_reflection"
path = "examples/reflection/trait_reflection.rs"
2020-05-01 20:12:47 +00:00
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . trait_reflection ]
name = "Trait Reflection"
description = "Allows reflection with trait objects"
category = "Reflection"
wasm = false
2021-02-22 04:50:05 +00:00
# Scene
2020-05-22 06:58:11 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
2020-11-28 00:39:59 +00:00
name = "scene"
path = "examples/scene/scene.rs"
2020-05-22 06:58:11 +00:00
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . scene ]
name = "Scene"
description = "Demonstrates loading from and saving scenes to files"
category = "Scene"
wasm = false
2021-02-22 04:50:05 +00:00
# Shaders
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
[ [ package . metadata . example_category ] ]
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
name = "Shaders"
description = "" "
These examples demonstrate how to implement different shaders in user code .
A shader in its most common usage is a small program that is run by the GPU per-vertex in a mesh ( a vertex shader ) or per-affected-screen-fragment ( a fragment shader . ) The GPU executes these programs in a highly parallel way .
There are also compute shaders which are used for more general processing leveraging the GPU ' s parallelism .
"" "
Mesh vertex buffer layouts (#3959)
This PR makes a number of changes to how meshes and vertex attributes are handled, which the goal of enabling easy and flexible custom vertex attributes:
* Reworks the `Mesh` type to use the newly added `VertexAttribute` internally
* `VertexAttribute` defines the name, a unique `VertexAttributeId`, and a `VertexFormat`
* `VertexAttributeId` is used to produce consistent sort orders for vertex buffer generation, replacing the more expensive and often surprising "name based sorting"
* Meshes can be used to generate a `MeshVertexBufferLayout`, which defines the layout of the gpu buffer produced by the mesh. `MeshVertexBufferLayouts` can then be used to generate actual `VertexBufferLayouts` according to the requirements of a specific pipeline. This decoupling of "mesh layout" vs "pipeline vertex buffer layout" is what enables custom attributes. We don't need to standardize _mesh layouts_ or contort meshes to meet the needs of a specific pipeline. As long as the mesh has what the pipeline needs, it will work transparently.
* Mesh-based pipelines now specialize on `&MeshVertexBufferLayout` via the new `SpecializedMeshPipeline` trait (which behaves like `SpecializedPipeline`, but adds `&MeshVertexBufferLayout`). The integrity of the pipeline cache is maintained because the `MeshVertexBufferLayout` is treated as part of the key (which is fully abstracted from implementers of the trait ... no need to add any additional info to the specialization key).
* Hashing `MeshVertexBufferLayout` is too expensive to do for every entity, every frame. To make this scalable, I added a generalized "pre-hashing" solution to `bevy_utils`: `Hashed<T>` keys and `PreHashMap<K, V>` (which uses `Hashed<T>` internally) . Why didn't I just do the quick and dirty in-place "pre-compute hash and use that u64 as a key in a hashmap" that we've done in the past? Because its wrong! Hashes by themselves aren't enough because two different values can produce the same hash. Re-hashing a hash is even worse! I decided to build a generalized solution because this pattern has come up in the past and we've chosen to do the wrong thing. Now we can do the right thing! This did unfortunately require pulling in `hashbrown` and using that in `bevy_utils`, because avoiding re-hashes requires the `raw_entry_mut` api, which isn't stabilized yet (and may never be ... `entry_ref` has favor now, but also isn't available yet). If std's HashMap ever provides the tools we need, we can move back to that. Note that adding `hashbrown` doesn't increase our dependency count because it was already in our tree. I will probably break these changes out into their own PR.
* Specializing on `MeshVertexBufferLayout` has one non-obvious behavior: it can produce identical pipelines for two different MeshVertexBufferLayouts. To optimize the number of active pipelines / reduce re-binds while drawing, I de-duplicate pipelines post-specialization using the final `VertexBufferLayout` as the key. For example, consider a pipeline that needs the layout `(position, normal)` and is specialized using two meshes: `(position, normal, uv)` and `(position, normal, other_vec2)`. If both of these meshes result in `(position, normal)` specializations, we can use the same pipeline! Now we do. Cool!
To briefly illustrate, this is what the relevant section of `MeshPipeline`'s specialization code looks like now:
```rust
impl SpecializedMeshPipeline for MeshPipeline {
type Key = MeshPipelineKey;
fn specialize(
&self,
key: Self::Key,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
) -> RenderPipelineDescriptor {
let mut vertex_attributes = vec![
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL.at_shader_location(1),
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_UV_0.at_shader_location(2),
];
let mut shader_defs = Vec::new();
if layout.contains(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_TANGENT) {
shader_defs.push(String::from("VERTEX_TANGENTS"));
vertex_attributes.push(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_TANGENT.at_shader_location(3));
}
let vertex_buffer_layout = layout
.get_layout(&vertex_attributes)
.expect("Mesh is missing a vertex attribute");
```
Notice that this is _much_ simpler than it was before. And now any mesh with any layout can be used with this pipeline, provided it has vertex postions, normals, and uvs. We even got to remove `HAS_TANGENTS` from MeshPipelineKey and `has_tangents` from `GpuMesh`, because that information is redundant with `MeshVertexBufferLayout`.
This is still a draft because I still need to:
* Add more docs
* Experiment with adding error handling to mesh pipeline specialization (which would print errors at runtime when a mesh is missing a vertex attribute required by a pipeline). If it doesn't tank perf, we'll keep it.
* Consider breaking out the PreHash / hashbrown changes into a separate PR.
* Add an example illustrating this change
* Verify that the "mesh-specialized pipeline de-duplication code" works properly
Please dont yell at me for not doing these things yet :) Just trying to get this in peoples' hands asap.
Alternative to #3120
Fixes #3030
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
2022-02-23 23:21:13 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "custom_vertex_attribute"
path = "examples/shader/custom_vertex_attribute.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . custom_vertex_attribute ]
name = "Custom Vertex Attribute"
description = "A shader that reads a mesh's custom vertex attribute"
category = "Shaders"
wasm = true
2022-06-06 00:06:49 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "post_processing"
path = "examples/shader/post_processing.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . post_processing ]
2023-03-16 03:22:17 +00:00
name = "Post Processing - Custom Render Pass"
description = "A custom post processing effect, using a custom render pass that runs after the main pass"
category = "Shaders"
wasm = true
2020-05-01 20:12:47 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "shader_defs"
path = "examples/shader/shader_defs.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . shader_defs ]
name = "Shader Defs"
description = "A shader that uses \"shaders defs\" (a bevy tool to selectively toggle parts of a shader)"
category = "Shaders"
wasm = true
Modular Rendering (#2831)
This changes how render logic is composed to make it much more modular. Previously, all extraction logic was centralized for a given "type" of rendered thing. For example, we extracted meshes into a vector of ExtractedMesh, which contained the mesh and material asset handles, the transform, etc. We looked up bindings for "drawn things" using their index in the `Vec<ExtractedMesh>`. This worked fine for built in rendering, but made it hard to reuse logic for "custom" rendering. It also prevented us from reusing things like "extracted transforms" across contexts.
To make rendering more modular, I made a number of changes:
* Entities now drive rendering:
* We extract "render components" from "app components" and store them _on_ entities. No more centralized uber lists! We now have true "ECS-driven rendering"
* To make this perform well, I implemented #2673 in upstream Bevy for fast batch insertions into specific entities. This was merged into the `pipelined-rendering` branch here: #2815
* Reworked the `Draw` abstraction:
* Generic `PhaseItems`: each draw phase can define its own type of "rendered thing", which can define its own "sort key"
* Ported the 2d, 3d, and shadow phases to the new PhaseItem impl (currently Transparent2d, Transparent3d, and Shadow PhaseItems)
* `Draw` trait and and `DrawFunctions` are now generic on PhaseItem
* Modular / Ergonomic `DrawFunctions` via `RenderCommands`
* RenderCommand is a trait that runs an ECS query and produces one or more RenderPass calls. Types implementing this trait can be composed to create a final DrawFunction. For example the DrawPbr DrawFunction is created from the following DrawCommand tuple. Const generics are used to set specific bind group locations:
```rust
pub type DrawPbr = (
SetPbrPipeline,
SetMeshViewBindGroup<0>,
SetStandardMaterialBindGroup<1>,
SetTransformBindGroup<2>,
DrawMesh,
);
```
* The new `custom_shader_pipelined` example illustrates how the commands above can be reused to create a custom draw function:
```rust
type DrawCustom = (
SetCustomMaterialPipeline,
SetMeshViewBindGroup<0>,
SetTransformBindGroup<2>,
DrawMesh,
);
```
* ExtractComponentPlugin and UniformComponentPlugin:
* Simple, standardized ways to easily extract individual components and write them to GPU buffers
* Ported PBR and Sprite rendering to the new primitives above.
* Removed staging buffer from UniformVec in favor of direct Queue usage
* Makes UniformVec much easier to use and more ergonomic. Completely removes the need for custom render graph nodes in these contexts (see the PbrNode and view Node removals and the much simpler call patterns in the relevant Prepare systems).
* Added a many_cubes_pipelined example to benchmark baseline 3d rendering performance and ensure there were no major regressions during this port. Avoiding regressions was challenging given that the old approach of extracting into centralized vectors is basically the "optimal" approach. However thanks to a various ECS optimizations and render logic rephrasing, we pretty much break even on this benchmark!
* Lifetimeless SystemParams: this will be a bit divisive, but as we continue to embrace "trait driven systems" (ex: ExtractComponentPlugin, UniformComponentPlugin, DrawCommand), the ergonomics of `(Query<'static, 'static, (&'static A, &'static B, &'static)>, Res<'static, C>)` were getting very hard to bear. As a compromise, I added "static type aliases" for the relevant SystemParams. The previous example can now be expressed like this: `(SQuery<(Read<A>, Read<B>)>, SRes<C>)`. If anyone has better ideas / conflicting opinions, please let me know!
* RunSystem trait: a way to define Systems via a trait with a SystemParam associated type. This is used to implement the various plugins mentioned above. I also added SystemParamItem and QueryItem type aliases to make "trait stye" ecs interactions nicer on the eyes (and fingers).
* RenderAsset retrying: ensures that render assets are only created when they are "ready" and allows us to create bind groups directly inside render assets (which significantly simplified the StandardMaterial code). I think ultimately we should swap this out on "asset dependency" events to wait for dependencies to load, but this will require significant asset system changes.
* Updated some built in shaders to account for missing MeshUniform fields
2021-09-23 06:16:11 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
2021-12-14 03:58:23 +00:00
name = "shader_material"
path = "examples/shader/shader_material.rs"
Pipeline Specialization, Shader Assets, and Shader Preprocessing (#3031)
## New Features
This adds the following to the new renderer:
* **Shader Assets**
* Shaders are assets again! Users no longer need to call `include_str!` for their shaders
* Shader hot-reloading
* **Shader Defs / Shader Preprocessing**
* Shaders now support `# ifdef NAME`, `# ifndef NAME`, and `# endif` preprocessor directives
* **Bevy RenderPipelineDescriptor and RenderPipelineCache**
* Bevy now provides its own `RenderPipelineDescriptor` and the wgpu version is now exported as `RawRenderPipelineDescriptor`. This allows users to define pipelines with `Handle<Shader>` instead of needing to manually compile and reference `ShaderModules`, enables passing in shader defs to configure the shader preprocessor, makes hot reloading possible (because the descriptor can be owned and used to create new pipelines when a shader changes), and opens the doors to pipeline specialization.
* The `RenderPipelineCache` now handles compiling and re-compiling Bevy RenderPipelineDescriptors. It has internal PipelineLayout and ShaderModule caches. Users receive a `CachedPipelineId`, which can be used to look up the actual `&RenderPipeline` during rendering.
* **Pipeline Specialization**
* This enables defining per-entity-configurable pipelines that specialize on arbitrary custom keys. In practice this will involve specializing based on things like MSAA values, Shader Defs, Bind Group existence, and Vertex Layouts.
* Adds a `SpecializedPipeline` trait and `SpecializedPipelines<MyPipeline>` resource. This is a simple layer that generates Bevy RenderPipelineDescriptors based on a custom key defined for the pipeline.
* Specialized pipelines are also hot-reloadable.
* This was the result of experimentation with two different approaches:
1. **"generic immediate mode multi-key hash pipeline specialization"**
* breaks up the pipeline into multiple "identities" (the core pipeline definition, shader defs, mesh layout, bind group layout). each of these identities has its own key. looking up / compiling a specific version of a pipeline requires composing all of these keys together
* the benefit of this approach is that it works for all pipelines / the pipeline is fully identified by the keys. the multiple keys allow pre-hashing parts of the pipeline identity where possible (ex: pre compute the mesh identity for all meshes)
* the downside is that any per-entity data that informs the values of these keys could require expensive re-hashes. computing each key for each sprite tanked bevymark performance (sprites don't actually need this level of specialization yet ... but things like pbr and future sprite scenarios might).
* this is the approach rafx used last time i checked
2. **"custom key specialization"**
* Pipelines by default are not specialized
* Pipelines that need specialization implement a SpecializedPipeline trait with a custom key associated type
* This allows specialization keys to encode exactly the amount of information required (instead of needing to be a combined hash of the entire pipeline). Generally this should fit in a small number of bytes. Per-entity specialization barely registers anymore on things like bevymark. It also makes things like "shader defs" way cheaper to hash because we can use context specific bitflags instead of strings.
* Despite the extra trait, it actually generally makes pipeline definitions + lookups simpler: managing multiple keys (and making the appropriate calls to manage these keys) was way more complicated.
* I opted for custom key specialization. It performs better generally and in my opinion is better UX. Fortunately the way this is implemented also allows for custom caches as this all builds on a common abstraction: the RenderPipelineCache. The built in custom key trait is just a simple / pre-defined way to interact with the cache
## Callouts
* The SpecializedPipeline trait makes it easy to inherit pipeline configuration in custom pipelines. The changes to `custom_shader_pipelined` and the new `shader_defs_pipelined` example illustrate how much simpler it is to define custom pipelines based on the PbrPipeline.
* The shader preprocessor is currently pretty naive (it just uses regexes to process each line). Ultimately we might want to build a more custom parser for more performance + better error handling, but for now I'm happy to optimize for "easy to implement and understand".
## Next Steps
* Port compute pipelines to the new system
* Add more preprocessor directives (else, elif, import)
* More flexible vertex attribute specialization / enable cheaply specializing on specific mesh vertex layouts
2021-10-28 19:07:47 +00:00
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . shader_material ]
name = "Material"
description = "A shader and a material that uses it"
category = "Shaders"
wasm = true
2023-01-19 22:11:13 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "shader_prepass"
path = "examples/shader/shader_prepass.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . shader_prepass ]
name = "Material Prepass"
2023-03-02 02:23:06 +00:00
description = "A shader that uses the various textures generated by the prepass"
2023-01-19 22:11:13 +00:00
category = "Shaders"
wasm = false
2022-02-28 22:55:14 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "shader_material_screenspace_texture"
path = "examples/shader/shader_material_screenspace_texture.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . shader_material_screenspace_texture ]
name = "Material - Screenspace Texture"
description = "A shader that samples a texture with view-independent UV coordinates"
category = "Shaders"
wasm = true
2022-01-05 19:43:11 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "shader_material_glsl"
path = "examples/shader/shader_material_glsl.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . shader_material_glsl ]
name = "Material - GLSL"
description = "A shader that uses the GLSL shading language"
category = "Shaders"
wasm = true
2022-01-05 19:43:11 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "shader_instancing"
path = "examples/shader/shader_instancing.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . shader_instancing ]
name = "Instancing"
description = "A shader that renders a mesh multiple times in one draw call"
category = "Shaders"
wasm = true
2022-01-05 19:43:11 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "animate_shader"
path = "examples/shader/animate_shader.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . animate_shader ]
name = "Animated"
description = "A shader that uses dynamic data like the time since startup"
category = "Shaders"
wasm = true
2022-01-05 19:43:11 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "compute_shader_game_of_life"
path = "examples/shader/compute_shader_game_of_life.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . compute_shader_game_of_life ]
name = "Compute - Game of Life"
description = "A compute shader that simulates Conway's Game of Life"
category = "Shaders"
wasm = false
2022-06-28 00:58:50 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "array_texture"
path = "examples/shader/array_texture.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . array_texture ]
name = "Array Texture"
description = "A shader that shows how to reuse the core bevy PBR shading functionality in a custom material that obtains the base color from an array texture."
category = "Shaders"
wasm = true
2023-01-26 13:18:15 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "texture_binding_array"
path = "examples/shader/texture_binding_array.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . texture_binding_array ]
name = "Texture Binding Array (Bindless Textures)"
description = "A shader that shows how to bind and sample multiple textures as a binding array (a.k.a. bindless textures)."
category = "Shaders"
wasm = false
2022-04-10 02:05:21 +00:00
# Stress tests
2023-02-28 14:24:47 +00:00
[ [ package . metadata . example_category ] ]
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
name = "Stress Tests"
description = "" "
These examples are used to test the performance and stability of various parts of the engine in an isolated way .
Due to the focus on performance it ' s recommended to run the stress tests in release mode :
` ` ` sh
cargo run --release --example < example name >
` ` `
"" "
2022-04-10 02:05:21 +00:00
2020-11-13 02:03:57 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "bevymark"
2022-04-10 02:05:21 +00:00
path = "examples/stress_tests/bevymark.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . bevymark ]
name = "Bevymark"
description = "A heavy sprite rendering workload to benchmark your system with Bevy"
category = "Stress Tests"
wasm = true
2022-07-04 13:04:15 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "many_animated_sprites"
path = "examples/stress_tests/many_animated_sprites.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . many_animated_sprites ]
name = "Many Animated Sprites"
2022-07-14 11:03:13 +00:00
description = "Displays many animated sprites in a grid arrangement with slight offsets to their animation timers. Used for performance testing."
2022-07-04 13:04:15 +00:00
category = "Stress Tests"
wasm = true
2022-07-21 14:39:03 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "many_buttons"
path = "examples/stress_tests/many_buttons.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . many_buttons ]
name = "Many Buttons"
description = "Test rendering of many UI elements"
category = "Stress Tests"
wasm = true
2022-04-10 02:05:21 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "many_cubes"
path = "examples/stress_tests/many_cubes.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . many_cubes ]
name = "Many Cubes"
description = "Simple benchmark to test per-entity draw overhead. Run with the `sphere` argument to test frustum culling"
category = "Stress Tests"
wasm = true
2023-03-20 20:57:54 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "many_gizmos"
path = "examples/stress_tests/many_gizmos.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . many_gizmos ]
name = "Many Gizmos"
description = "Test rendering of many gizmos"
category = "Stress Tests"
wasm = true
2022-05-08 02:57:00 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "many_foxes"
path = "examples/stress_tests/many_foxes.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . many_foxes ]
name = "Many Foxes"
description = "Loads an animated fox model and spawns lots of them. Good for testing skinned mesh performance. Takes an unsigned integer argument for the number of foxes to spawn. Defaults to 1000"
category = "Stress Tests"
wasm = true
2023-03-14 00:01:27 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "many_glyphs"
path = "examples/stress_tests/many_glyphs.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . many_glyphs ]
name = "Many Glyphs"
description = "Simple benchmark to test text rendering."
category = "Stress Tests"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
wasm = true
2022-04-10 02:05:21 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "many_lights"
path = "examples/stress_tests/many_lights.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . many_lights ]
name = "Many Lights"
description = "Simple benchmark to test rendering many point lights. Run with `WGPU_SETTINGS_PRIO=webgl2` to restrict to uniform buffers and max 256 lights"
category = "Stress Tests"
wasm = true
2022-04-10 02:05:21 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "many_sprites"
path = "examples/stress_tests/many_sprites.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . many_sprites ]
name = "Many Sprites"
2022-07-14 11:03:13 +00:00
description = "Displays many sprites in a grid arrangement! Used for performance testing. Use `--colored` to enable color tinted sprites."
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
category = "Stress Tests"
wasm = true
2022-04-10 02:05:21 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "transform_hierarchy"
path = "examples/stress_tests/transform_hierarchy.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . transform_hierarchy ]
name = "Transform Hierarchy"
description = "Various test cases for hierarchy and transform propagation performance"
category = "Stress Tests"
2023-05-08 19:02:06 +00:00
wasm = false
2020-11-13 02:03:57 +00:00
2023-03-04 12:29:08 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "text_pipeline"
path = "examples/stress_tests/text_pipeline.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . text_pipeline ]
name = "Text Pipeline"
description = "Text Pipeline benchmark"
category = "Stress Tests"
wasm = false
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
# Tools
2022-03-19 19:14:13 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "scene_viewer"
2022-12-25 00:23:13 +00:00
path = "examples/tools/scene_viewer/main.rs"
2022-03-19 19:14:13 +00:00
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . scene_viewer ]
name = "Scene Viewer"
description = "A simple way to view glTF models with Bevy. Just run `cargo run --release --example scene_viewer /path/to/model.gltf#Scene0`, replacing the path as appropriate. With no arguments it will load the FieldHelmet glTF model from the repository assets subdirectory"
category = "Tools"
wasm = true
2022-09-24 13:21:01 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "gamepad_viewer"
path = "examples/tools/gamepad_viewer.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . gamepad_viewer ]
name = "Gamepad Viewer"
description = "Shows a visualization of gamepad buttons, sticks, and triggers"
category = "Tools"
wasm = false
2023-01-31 01:47:00 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "nondeterministic_system_order"
path = "examples/ecs/nondeterministic_system_order.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . nondeterministic_system_order ]
name = "Nondeterministic System Order"
2023-04-16 16:55:47 +00:00
description = "Systems run in parallel, but their order isn't always deterministic. Here's how to detect and fix this."
2023-01-31 01:47:00 +00:00
category = "ECS (Entity Component System)"
wasm = false
2022-03-15 05:49:49 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "3d_rotation"
path = "examples/transforms/3d_rotation.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . 3 d_rotation ]
name = "3D Rotation"
description = "Illustrates how to (constantly) rotate an object around an axis"
category = "Transforms"
wasm = true
2022-03-15 05:49:49 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "scale"
path = "examples/transforms/scale.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . scale ]
name = "Scale"
description = "Illustrates how to scale an object in each direction"
category = "Transforms"
wasm = true
2022-03-15 05:49:49 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "transform"
path = "examples/transforms/transform.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . transform ]
name = "Transform"
description = "Shows multiple transformations of objects"
category = "Transforms"
wasm = true
2022-03-15 05:49:49 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "translation"
path = "examples/transforms/translation.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . translation ]
name = "Translation"
description = "Illustrates how to move an object along an axis"
category = "Transforms"
wasm = true
2021-02-22 04:50:05 +00:00
# UI (User Interface)
2023-06-14 22:43:38 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "borders"
path = "examples/ui/borders.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . borders ]
name = "Borders"
description = "Demonstrates how to create a node with a border"
category = "UI (User Interface)"
wasm = true
2020-07-18 21:08:46 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "button"
path = "examples/ui/button.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . button ]
name = "Button"
description = "Illustrates creating and updating a button"
category = "UI (User Interface)"
wasm = true
2023-06-19 23:19:34 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "display_and_visibility"
path = "examples/ui/display_and_visibility.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . display_and_visibility ]
name = "Display and Visibility"
description = "Demonstrates how Display and Visibility work in the UI."
category = "UI (User Interface)"
wasm = true
2022-11-21 12:59:10 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "window_fallthrough"
path = "examples/ui/window_fallthrough.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . window_fallthrough ]
name = "Window Fallthrough"
description = "Illustrates how to access `winit::window::Window`'s `hittest` functionality."
category = "UI (User Interface)"
wasm = false
2021-02-22 04:50:05 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "font_atlas_debug"
path = "examples/ui/font_atlas_debug.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . font_atlas_debug ]
name = "Font Atlas Debug"
description = "Illustrates how FontAtlases are populated (used to optimize text rendering internally)"
category = "UI (User Interface)"
wasm = true
2023-04-17 22:23:52 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "overflow"
path = "examples/ui/overflow.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . overflow ]
name = "Overflow"
description = "Simple example demonstrating overflow behavior"
category = "UI (User Interface)"
wasm = true
2023-04-05 23:07:41 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "overflow_debug"
path = "examples/ui/overflow_debug.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . overflow_debug ]
name = "Overflow and Clipping Debug"
description = "An example to debug overflow and clipping behavior"
category = "UI (User Interface)"
wasm = true
2023-01-16 17:17:45 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "relative_cursor_position"
path = "examples/ui/relative_cursor_position.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . relative_cursor_position ]
name = "Relative Cursor Position"
description = "Showcases the RelativeCursorPosition component"
category = "UI (User Interface)"
wasm = true
2023-04-24 14:28:00 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "size_constraints"
path = "examples/ui/size_constraints.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . size_constraints ]
name = "Size Constraints"
description = "Demonstrates how the to use the size constraints to control the size of a UI node."
category = "UI (User Interface)"
wasm = true
2020-05-13 20:09:32 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "text"
path = "examples/ui/text.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . text ]
name = "Text"
description = "Illustrates creating and updating text"
category = "UI (User Interface)"
wasm = true
2020-11-13 00:21:48 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "text_debug"
path = "examples/ui/text_debug.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . text_debug ]
name = "Text Debug"
description = "An example for debugging text layout"
category = "UI (User Interface)"
wasm = true
2023-01-27 19:07:48 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
2023-03-22 08:22:56 +00:00
name = "flex_layout"
path = "examples/ui/flex_layout.rs"
2023-01-27 19:07:48 +00:00
2023-03-22 08:22:56 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . flex_layout ]
name = "Flex Layout"
description = "Demonstrates how the AlignItems and JustifyContent properties can be composed to layout nodes and position text"
2023-01-27 19:07:48 +00:00
category = "UI (User Interface)"
2023-04-17 16:21:38 +00:00
wasm = true
2023-04-24 14:22:31 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "text_wrap_debug"
path = "examples/ui/text_wrap_debug.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . text_wrap_debug ]
name = "Text Wrap Debug"
description = "Demonstrates text wrapping"
category = "UI (User Interface)"
wasm = true
2023-04-17 16:21:38 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "grid"
path = "examples/ui/grid.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . grid ]
name = "CSS Grid"
description = "An example for CSS Grid layout"
2023-04-24 14:22:31 +00:00
2023-04-17 16:21:38 +00:00
category = "UI (User Interface)"
wasm = true
2023-01-27 19:07:48 +00:00
2020-05-01 20:12:47 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
2022-06-06 17:52:09 +00:00
name = "transparency_ui"
path = "examples/ui/transparency_ui.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . transparency_ui ]
name = "Transparency UI"
description = "Demonstrates transparency for UI"
category = "UI (User Interface)"
wasm = true
Add z-index support with a predictable UI stack (#5877)
# Objective
Add consistent UI rendering and interaction where deep nodes inside two different hierarchies will never render on top of one-another by default and offer an escape hatch (z-index) for nodes to change their depth.
## The problem with current implementation
The current implementation of UI rendering is broken in that regard, mainly because [it sets the Z value of the `Transform` component based on a "global Z" space](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/main/crates/bevy_ui/src/update.rs#L43) shared by all nodes in the UI. This doesn't account for the fact that each node's final `GlobalTransform` value will be relative to its parent. This effectively makes the depth unpredictable when two deep trees are rendered on top of one-another.
At the moment, it's also up to each part of the UI code to sort all of the UI nodes. The solution that's offered here does the full sorting of UI node entities once and offers the result through a resource so that all systems can use it.
## Solution
### New ZIndex component
This adds a new optional `ZIndex` enum component for nodes which offers two mechanism:
- `ZIndex::Local(i32)`: Overrides the depth of the node relative to its siblings.
- `ZIndex::Global(i32)`: Overrides the depth of the node relative to the UI root. This basically allows any node in the tree to "escape" the parent and be ordered relative to the entire UI.
Note that in the current implementation, omitting `ZIndex` on a node has the same result as adding `ZIndex::Local(0)`. Additionally, the "global" stacking context is essentially a way to add your node to the root stacking context, so using `ZIndex::Local(n)` on a root node (one without parent) will share that space with all nodes using `Index::Global(n)`.
### New UiStack resource
This adds a new `UiStack` resource which is calculated from both hierarchy and `ZIndex` during UI update and contains a vector of all node entities in the UI, ordered by depth (from farthest from camera to closest). This is exposed publicly by the bevy_ui crate with the hope that it can be used for consistent ordering and to reduce the amount of sorting that needs to be done by UI systems (i.e. instead of sorting everything by `global_transform.z` in every system, this array can be iterated over).
### New z_index example
This also adds a new z_index example that showcases the new `ZIndex` component. It's also a good general demo of the new UI stack system, because making this kind of UI was very broken with the old system (e.g. nodes would render on top of each other, not respecting hierarchy or insert order at all).
---
## Changelog
- Added the `ZIndex` component to bevy_ui.
- Added the `UiStack` resource to bevy_ui, and added implementation in a new `stack.rs` module.
- Removed the previous Z updating system from bevy_ui, because it was replaced with the above.
- Changed bevy_ui rendering to use UiStack instead of z ordering.
- Changed bevy_ui focus/interaction system to use UiStack instead of z ordering.
- Added a new z_index example.
## ZIndex demo
Here's a demo I wrote to test these features
https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/1060971/188329295-d7beebd6-9aee-43ab-821e-d437df5dbe8a.mp4
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
2022-11-02 22:06:04 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "z_index"
path = "examples/ui/z_index.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . z_index ]
name = "UI Z-Index"
description = "Demonstrates how to control the relative depth (z-position) of UI elements"
category = "UI (User Interface)"
wasm = true
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
2022-06-06 17:52:09 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
2020-05-01 20:12:47 +00:00
name = "ui"
path = "examples/ui/ui.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . ui ]
name = "UI"
description = "Illustrates various features of Bevy UI"
category = "UI (User Interface)"
wasm = true
2022-08-29 23:35:53 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "ui_scaling"
2022-10-19 11:36:26 +00:00
path = "examples/ui/ui_scaling.rs"
2022-08-29 23:35:53 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . ui_scaling ]
name = "UI Scaling"
description = "Illustrates how to scale the UI"
category = "UI (User Interface)"
wasm = true
2023-06-19 21:52:02 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "ui_texture_atlas"
path = "examples/ui/ui_texture_atlas.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . ui_texture_atlas ]
name = "UI Texture Atlas"
description = "Illustrates how to use TextureAtlases in UI"
category = "UI (User Interface)"
wasm = true
2023-06-14 22:43:38 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "viewport_debug"
path = "examples/ui/viewport_debug.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . viewport_debug ]
name = "Viewport Debug"
description = "An example for debugging viewport coordinates"
category = "UI (User Interface)"
wasm = true
2021-02-22 04:50:05 +00:00
# Window
2020-06-25 22:24:27 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "clear_color"
path = "examples/window/clear_color.rs"
2021-12-18 19:38:05 +00:00
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . clear_color ]
name = "Clear Color"
description = "Creates a solid color window"
category = "Window"
wasm = true
Reduce power usage with configurable event loop (#3974)
# Objective
- Reduce power usage for games when not focused.
- Reduce power usage to ~0 when a desktop application is minimized (opt-in).
- Reduce power usage when focused, only updating on a `winit` event, or the user sends a redraw request. (opt-in)
https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/2632925/156904387-ec47d7de-7f06-4c6f-8aaf-1e952c1153a2.mp4
Note resource usage in the Task Manager in the above video.
## Solution
- Added a type `UpdateMode` that allows users to specify how the winit event loop is updated, without exposing winit types.
- Added two fields to `WinitConfig`, both with the `UpdateMode` type. One configures how the application updates when focused, and the other configures how the application behaves when it is not focused. Users can modify this resource manually to set the type of event loop control flow they want.
- For convenience, two functions were added to `WinitConfig`, that provide reasonable presets: `game()` (default) and `desktop_app()`.
- The `game()` preset, which is used by default, is unchanged from current behavior with one exception: when the app is out of focus the app updates at a minimum of 10fps, or every time a winit event is received. This has a huge positive impact on power use and responsiveness on my machine, which will otherwise continue running the app at many hundreds of fps when out of focus or minimized.
- The `desktop_app()` preset is fully reactive, only updating when user input (winit event) is supplied or a `RedrawRequest` event is sent. When the app is out of focus, it only updates on `Window` events - i.e. any winit event that directly interacts with the window. What this means in practice is that the app uses *zero* resources when minimized or not interacted with, but still updates fluidly when the app is out of focus and the user mouses over the application.
- Added a `RedrawRequest` event so users can force an update even if there are no events. This is useful in an application when you want to, say, run an animation even when the user isn't providing input.
- Added an example `low_power` to demonstrate these changes
## Usage
Configuring the event loop:
```rs
use bevy::winit::{WinitConfig};
// ...
.insert_resource(WinitConfig::desktop_app()) // preset
// or
.insert_resource(WinitConfig::game()) // preset
// or
.insert_resource(WinitConfig{ .. }) // manual
```
Requesting a redraw:
```rs
use bevy::window::RequestRedraw;
// ...
fn request_redraw(mut event: EventWriter<RequestRedraw>) {
event.send(RequestRedraw);
}
```
## Other details
- Because we have a single event loop for multiple windows, every time I've mentioned "focused" above, I more precisely mean, "if at least one bevy window is focused".
- Due to a platform bug in winit (https://github.com/rust-windowing/winit/issues/1619), we can't simply use `Window::request_redraw()`. As a workaround, this PR will temporarily set the window mode to `Poll` when a redraw is requested. This is then reset to the user's `WinitConfig` setting on the next frame.
2022-03-07 23:32:05 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "low_power"
path = "examples/window/low_power.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . low_power ]
name = "Low Power"
description = "Demonstrates settings to reduce power use for bevy applications"
category = "Window"
wasm = true
2021-12-18 19:38:05 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "multiple_windows"
path = "examples/window/multiple_windows.rs"
2020-06-25 22:24:27 +00:00
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . multiple_windows ]
name = "Multiple Windows"
description = "Demonstrates creating multiple windows, and rendering to them"
category = "Window"
wasm = false
2020-12-28 20:26:50 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "scale_factor_override"
path = "examples/window/scale_factor_override.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . scale_factor_override ]
2022-07-05 16:59:31 +00:00
name = "Scale Factor Override"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
description = "Illustrates how to customize the default window settings"
category = "Window"
wasm = true
2023-04-19 21:28:42 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "screenshot"
path = "examples/window/screenshot.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . screenshot ]
name = "Screenshot"
description = "Shows how to save screenshots to disk"
category = "Window"
2023-04-28 19:37:11 +00:00
wasm = true
2023-04-19 21:28:42 +00:00
2021-12-08 20:53:35 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "transparent_window"
path = "examples/window/transparent_window.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . transparent_window ]
name = "Transparent Window"
description = "Illustrates making the window transparent and hiding the window decoration"
category = "Window"
wasm = false
2020-07-20 09:05:56 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "window_settings"
2020-08-21 05:37:19 +00:00
path = "examples/window/window_settings.rs"
2020-09-16 01:05:31 +00:00
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . window_settings ]
name = "Window Settings"
description = "Demonstrates customizing default window settings"
category = "Window"
wasm = true
Add an example to test small window sizes (#3597)
# Objective
We keep getting issues where things break at small window sizes, e.g #3368 (caused by #3153), #3596 ('caused' by #3545)
## Solution
- Add a test that we can make small windows.
Currently, this fails on my machine with some quite scary vulkan errors:
```
2022-01-08T22:55:13.770261Z ERROR wgpu_hal::vulkan::instance: VALIDATION [VUID-VkSwapchainCreateInfoKHR-imageExtent-01274 (0x7cd0911d)]
Validation Error: [ VUID-VkSwapchainCreateInfoKHR-imageExtent-01274 ] Object 0: handle = 0x1adbd410a60, type = VK_OBJECT_TYPE_DEVICE; | MessageID = 0x7cd0911d | vkCreateSwapchainKHR() called with imageExtent = (225,60), which is outside the bounds returned by vkGetPhysicalDeviceSurfaceCapabilitiesKHR(): currentExtent = (225,56), minImageExtent = (225,56), maxImageExtent = (225,56). The Vulkan spec states: imageExtent must be between minImageExtent and maxImageExtent, inclusive, where minImageExtent and maxImageExtent are members of the VkSurfaceCapabilitiesKHR structure returned by vkGetPhysicalDeviceSurfaceCapabilitiesKHR for the surface (https://vulkan.lunarg.com/doc/view/1.2.198.1/windows/1.2-extensions/vkspec.html#VUID-VkSwapchainCreateInfoKHR-imageExtent-01274)
2022-01-08T22:55:13.770808Z ERROR wgpu_hal::vulkan::instance: objects: (type: DEVICE, hndl: 0x1adbd410a60, name: ?)
2022-01-08T22:55:13.787403Z ERROR wgpu_hal::vulkan::instance: VALIDATION [VUID-VkSwapchainCreateInfoKHR-imageExtent-01274 (0x7cd0911d)]
Validation Error: [ VUID-VkSwapchainCreateInfoKHR-imageExtent-01274 ] Object 0: handle = 0x1adbd410a60, type = VK_OBJECT_TYPE_DEVICE; | MessageID = 0x7cd0911d | vkCreateSwapchainKHR() called with imageExtent = (225,56), which is outside the bounds returned by vkGetPhysicalDeviceSurfaceCapabilitiesKHR(): currentExtent = (225,52), minImageExtent = (225,52), maxImageExtent = (225,52). The Vulkan spec states: imageExtent must be between minImageExtent and maxImageExtent, inclusive, where minImageExtent and maxImageExtent are members of the VkSurfaceCapabilitiesKHR structure returned by vkGetPhysicalDeviceSurfaceCapabilitiesKHR for the surface (https://vulkan.lunarg.com/doc/view/1.2.198.1/windows/1.2-extensions/vkspec.html#VUID-VkSwapchainCreateInfoKHR-imageExtent-01274)
```
etc.
This might be a new issue here, although I'm surprised it's vulkan giving this error; wgpu should stop it if this is illegal.
2022-04-26 22:15:24 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "resizing"
path = "tests/window/resizing.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . resizing ]
hidden = true
Add an example to test small window sizes (#3597)
# Objective
We keep getting issues where things break at small window sizes, e.g #3368 (caused by #3153), #3596 ('caused' by #3545)
## Solution
- Add a test that we can make small windows.
Currently, this fails on my machine with some quite scary vulkan errors:
```
2022-01-08T22:55:13.770261Z ERROR wgpu_hal::vulkan::instance: VALIDATION [VUID-VkSwapchainCreateInfoKHR-imageExtent-01274 (0x7cd0911d)]
Validation Error: [ VUID-VkSwapchainCreateInfoKHR-imageExtent-01274 ] Object 0: handle = 0x1adbd410a60, type = VK_OBJECT_TYPE_DEVICE; | MessageID = 0x7cd0911d | vkCreateSwapchainKHR() called with imageExtent = (225,60), which is outside the bounds returned by vkGetPhysicalDeviceSurfaceCapabilitiesKHR(): currentExtent = (225,56), minImageExtent = (225,56), maxImageExtent = (225,56). The Vulkan spec states: imageExtent must be between minImageExtent and maxImageExtent, inclusive, where minImageExtent and maxImageExtent are members of the VkSurfaceCapabilitiesKHR structure returned by vkGetPhysicalDeviceSurfaceCapabilitiesKHR for the surface (https://vulkan.lunarg.com/doc/view/1.2.198.1/windows/1.2-extensions/vkspec.html#VUID-VkSwapchainCreateInfoKHR-imageExtent-01274)
2022-01-08T22:55:13.770808Z ERROR wgpu_hal::vulkan::instance: objects: (type: DEVICE, hndl: 0x1adbd410a60, name: ?)
2022-01-08T22:55:13.787403Z ERROR wgpu_hal::vulkan::instance: VALIDATION [VUID-VkSwapchainCreateInfoKHR-imageExtent-01274 (0x7cd0911d)]
Validation Error: [ VUID-VkSwapchainCreateInfoKHR-imageExtent-01274 ] Object 0: handle = 0x1adbd410a60, type = VK_OBJECT_TYPE_DEVICE; | MessageID = 0x7cd0911d | vkCreateSwapchainKHR() called with imageExtent = (225,56), which is outside the bounds returned by vkGetPhysicalDeviceSurfaceCapabilitiesKHR(): currentExtent = (225,52), minImageExtent = (225,52), maxImageExtent = (225,52). The Vulkan spec states: imageExtent must be between minImageExtent and maxImageExtent, inclusive, where minImageExtent and maxImageExtent are members of the VkSurfaceCapabilitiesKHR structure returned by vkGetPhysicalDeviceSurfaceCapabilitiesKHR for the surface (https://vulkan.lunarg.com/doc/view/1.2.198.1/windows/1.2-extensions/vkspec.html#VUID-VkSwapchainCreateInfoKHR-imageExtent-01274)
```
etc.
This might be a new issue here, although I'm surprised it's vulkan giving this error; wgpu should stop it if this is illegal.
2022-04-26 22:15:24 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "minimising"
path = "tests/window/minimising.rs"
2022-06-25 20:23:24 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . minimising ]
hidden = true
Add an example to test small window sizes (#3597)
# Objective
We keep getting issues where things break at small window sizes, e.g #3368 (caused by #3153), #3596 ('caused' by #3545)
## Solution
- Add a test that we can make small windows.
Currently, this fails on my machine with some quite scary vulkan errors:
```
2022-01-08T22:55:13.770261Z ERROR wgpu_hal::vulkan::instance: VALIDATION [VUID-VkSwapchainCreateInfoKHR-imageExtent-01274 (0x7cd0911d)]
Validation Error: [ VUID-VkSwapchainCreateInfoKHR-imageExtent-01274 ] Object 0: handle = 0x1adbd410a60, type = VK_OBJECT_TYPE_DEVICE; | MessageID = 0x7cd0911d | vkCreateSwapchainKHR() called with imageExtent = (225,60), which is outside the bounds returned by vkGetPhysicalDeviceSurfaceCapabilitiesKHR(): currentExtent = (225,56), minImageExtent = (225,56), maxImageExtent = (225,56). The Vulkan spec states: imageExtent must be between minImageExtent and maxImageExtent, inclusive, where minImageExtent and maxImageExtent are members of the VkSurfaceCapabilitiesKHR structure returned by vkGetPhysicalDeviceSurfaceCapabilitiesKHR for the surface (https://vulkan.lunarg.com/doc/view/1.2.198.1/windows/1.2-extensions/vkspec.html#VUID-VkSwapchainCreateInfoKHR-imageExtent-01274)
2022-01-08T22:55:13.770808Z ERROR wgpu_hal::vulkan::instance: objects: (type: DEVICE, hndl: 0x1adbd410a60, name: ?)
2022-01-08T22:55:13.787403Z ERROR wgpu_hal::vulkan::instance: VALIDATION [VUID-VkSwapchainCreateInfoKHR-imageExtent-01274 (0x7cd0911d)]
Validation Error: [ VUID-VkSwapchainCreateInfoKHR-imageExtent-01274 ] Object 0: handle = 0x1adbd410a60, type = VK_OBJECT_TYPE_DEVICE; | MessageID = 0x7cd0911d | vkCreateSwapchainKHR() called with imageExtent = (225,56), which is outside the bounds returned by vkGetPhysicalDeviceSurfaceCapabilitiesKHR(): currentExtent = (225,52), minImageExtent = (225,52), maxImageExtent = (225,52). The Vulkan spec states: imageExtent must be between minImageExtent and maxImageExtent, inclusive, where minImageExtent and maxImageExtent are members of the VkSurfaceCapabilitiesKHR structure returned by vkGetPhysicalDeviceSurfaceCapabilitiesKHR for the surface (https://vulkan.lunarg.com/doc/view/1.2.198.1/windows/1.2-extensions/vkspec.html#VUID-VkSwapchainCreateInfoKHR-imageExtent-01274)
```
etc.
This might be a new issue here, although I'm surprised it's vulkan giving this error; wgpu should stop it if this is illegal.
2022-04-26 22:15:24 +00:00
2022-08-29 23:56:43 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "window_resizing"
path = "examples/window/window_resizing.rs"
2023-06-19 22:56:25 +00:00
[ [ example ] ]
name = "fallback_image"
path = "examples/shader/fallback_image.rs"
[ package . metadata . example . fallback_image ]
hidden = true
2022-08-29 23:56:43 +00:00
[ package . metadata . example . window_resizing ]
name = "Window Resizing"
description = "Demonstrates resizing and responding to resizing a window"
category = "Window"
wasm = true
2022-07-25 15:48:13 +00:00
[ profile . wasm-release ]
inherits = "release"
opt-level = "z"
lto = "fat"
codegen-units = 1
2022-12-20 15:59:41 +00:00
[ profile . stress-test ]
inherits = "release"
lto = "fat"
panic = "abort"