* Cleanup redundant code
* Use a type alias to make sure the `caster_query` and
`not_caster_query` really do the same thing and access the same things
**Objective**
Cleanup code that would otherwise be difficult to understand
**Solution**
* `extract_meshes` had two for loops which are functionally identical,
just copy-pasted code. I extracted the common code between the two
and put them into an anonymous function.
* I flattened the tuple literal for the bundle batch, it looks much
less nested and the code is much more readable as a result.
* The parameters of `extract_meshes` were also very daunting, but they
turned out to be the same query repeated twice. I extracted the query
into a type alias.
EDIT: I reworked the PR to **not do anything breaking**, and keep the old allocation behavior. Removing the memorized length was clearly a performance loss, so I kept it.
Removed `const_vec2`/`const_vec3`
and replaced with equivalent `.from_array`.
# Objective
Fixes#5112
## Solution
- `encase` needs to update to `glam` as well. See teoxoy/encase#4 on progress on that.
- `hexasphere` also needs to be updated, see OptimisticPeach/hexasphere#12.
# Objective
Fixes#5153
## Solution
Search for all enums and manually check if they have default impls that can use this new derive.
By my reckoning:
| enum | num |
|-|-|
| total | 159 |
| has default impl | 29 |
| default is unit variant | 23 |
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
# Objective
This fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/5127
## Solution
- Moved texture sample out of branch in `prepare_normal()`.
Co-authored-by: DGriffin91 <github@dgdigital.net>
# Objective
- Make the reusable PBR shading functionality a little more reusable
- Add constructor functions for `StandardMaterial` and `PbrInput` structs to populate them with default values
- Document unclear `PbrInput` members
- Demonstrate how to reuse the bevy PBR shading functionality
- The final important piece from #3969 as the initial shot at making the PBR shader code reusable in custom materials
## Solution
- Add back and rework the 'old' `array_texture` example from pre-0.6.
- Create a custom shader material
- Use a single array texture binding and sampler for the material bind group
- Use a shader that calls `pbr()` from the `bevy_pbr::pbr_functions` import
- Spawn a row of cubes using the custom material
- In the shader, select the array texture layer to sample by using the world position x coordinate modulo the number of array texture layers
<img width="1392" alt="Screenshot 2022-06-23 at 12 28 05" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/302146/175278593-2296f519-f577-4ece-81c0-d842283784a1.png">
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Allow custom shaders to reuse the HDR results of PBR.
## Solution
- Separate `pbr()` and `tone_mapping()` into 2 functions in `pbr_functions.wgsl`.
# Objective
Update pbr mesh shader to use correct normals for skinned meshes.
## Solution
Only use `mesh_normal_local_to_world` for normals if `SKINNED` is not defined.
# Objective
Partially addresses #4291.
Speed up the sort phase for unbatched render phases.
## Solution
Split out one of the optimizations in #4899 and allow implementors of `PhaseItem` to change what kind of sort is used when sorting the items in the phase. This currently includes Stable, Unstable, and Unsorted. Each of these corresponds to `Vec::sort_by_key`, `Vec::sort_unstable_by_key`, and no sorting at all. The default is `Unstable`. The last one can be used as a default if users introduce a preliminary depth prepass.
## Performance
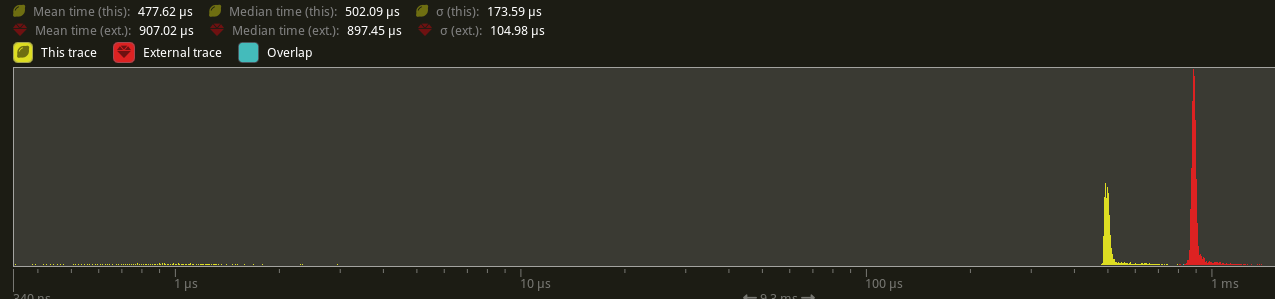
This will not impact the performance of any batched phases, as it is still using a stable sort. 2D's only phase is unchanged. All 3D phases are unbatched currently, and will benefit from this change.
On `many_cubes`, where the primary phase is opaque, this change sees a speed up from 907.02us -> 477.62us, a 47.35% reduction.
## Future Work
There were prior discussions to add support for faster radix sorts in #4291, which in theory should be a `O(n)` instead of a `O(nlog(n))` time. [`voracious`](https://crates.io/crates/voracious_radix_sort) has been proposed, but it seems to be optimize for use cases with more than 30,000 items, which may be atypical for most systems.
Another optimization included in #4899 is to reduce the size of a few of the IDs commonly used in `PhaseItem` implementations to shrink the types to make swapping/sorting faster. Both `CachedPipelineId` and `DrawFunctionId` could be reduced to `u32` instead of `usize`.
Ideally, this should automatically change to use stable sorts when `BatchedPhaseItem` is implemented on the same phase item type, but this requires specialization, which may not land in stable Rust for a short while.
---
## Changelog
Added: `PhaseItem::sort`
## Migration Guide
RenderPhases now default to a unstable sort (via `slice::sort_unstable_by_key`). This can typically improve sort phase performance, but may produce incorrect batching results when implementing `BatchedPhaseItem`. To revert to the older stable sort, manually implement `PhaseItem::sort` to implement a stable sort (i.e. via `slice::sort_by_key`).
Co-authored-by: Federico Rinaldi <gisquerin@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Robert Swain <robert.swain@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: colepoirier <colepoirier@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Builds on top of #4938
- Make clustered-forward PBR lighting/shadows functionality callable
- See #3969 for details
## Solution
- Add `PbrInput` struct type containing a `StandardMaterial`, occlusion, world_position, world_normal, and frag_coord
- Split functionality to calculate the unit view vector, and normal-mapped normal into `bevy_pbr::pbr_functions`
- Split high-level shading flow into `pbr(in: PbrInput, N: vec3<f32>, V: vec3<f32>, is_orthographic: bool)` function in `bevy_pbr::pbr_functions`
- Rework `pbr.wgsl` fragment stage entry point to make use of the new functions
- This has been benchmarked on an M1 Max using `many_cubes -- sphere`. `main` had a median frame time of 15.88ms, this PR 15.99ms, which is a 0.69% frame time increase, which is within noise in my opinion.
---
## Changelog
- Added: PBR shading code is now callable. Import `bevy_pbr::pbr_functions` and its dependencies, create a `PbrInput`, calculate the unit view and normal-mapped normal vectors and whether the projection is orthographic, and call `pbr()`!
# Objective
- `.x` is not the correct syntax to access a column in a matrix in WGSL: https://www.w3.org/TR/WGSL/#matrix-access-expr
- naga accepts it and translates it correctly, but it's not valid when shaders are kept as is and used directly in WGSL
## Solution
- Use the correct syntax
# Objective
- Builds on top of #4901
- Separate out PBR lighting, shadows, clustered forward, and utils from `pbr.wgsl` as part of making the PBR code more reusable and extensible.
- See #3969 for details.
## Solution
- Add `bevy_pbr::utils`, `bevy_pbr::clustered_forward`, `bevy_pbr::lighting`, `bevy_pbr::shadows` shader imports exposing many shader functions for external use
- Split `PI`, `saturate()`, `hsv2rgb()`, and `random1D()` into `bevy_pbr::utils`
- Split clustered-forward-specific functions into `bevy_pbr::clustered_forward`, including moving the debug visualization code into a `cluster_debug_visualization()` function in that import
- Split PBR lighting functions into `bevy_pbr::lighting`
- Split shadow functions into `bevy_pbr::shadows`
---
## Changelog
- Added: `bevy_pbr::utils`, `bevy_pbr::clustered_forward`, `bevy_pbr::lighting`, `bevy_pbr::shadows` shader imports exposing many shader functions for external use
- Split `PI`, `saturate()`, `hsv2rgb()`, and `random1D()` into `bevy_pbr::utils`
- Split clustered-forward-specific functions into `bevy_pbr::clustered_forward`, including moving the debug visualization code into a `cluster_debug_visualization()` function in that import
- Split PBR lighting functions into `bevy_pbr::lighting`
- Split shadow functions into `bevy_pbr::shadows`
# Objective
- Add reusable shader functions for transforming positions / normals / tangents between local and world / clip space for 2D and 3D so that they are done in a simple and correct way
- The next step in #3969 so check there for more details.
## Solution
- Add `bevy_pbr::mesh_functions` and `bevy_sprite::mesh2d_functions` shader imports
- These contain `mesh_` and `mesh2d_` versions of the following functions:
- `mesh_position_local_to_world`
- `mesh_position_world_to_clip`
- `mesh_position_local_to_clip`
- `mesh_normal_local_to_world`
- `mesh_tangent_local_to_world`
- Use them everywhere where it is appropriate
- Notably not in the sprite and UI shaders where `mesh2d_position_world_to_clip` could have been used, but including all the functions depends on the mesh binding so I chose to not use the function there
- NOTE: The `mesh_` and `mesh2d_` functions are currently identical. However, if I had defined only `bevy_pbr::mesh_functions` and used that in bevy_sprite, then bevy_sprite would have a runtime dependency on bevy_pbr, which seems undesirable. I also expect that when we have a proper 2D rendering API, these functions will diverge between 2D and 3D.
---
## Changelog
- Added: `bevy_pbr::mesh_functions` and `bevy_sprite::mesh2d_functions` shader imports containing `mesh_` and `mesh2d_` versions of the following functions:
- `mesh_position_local_to_world`
- `mesh_position_world_to_clip`
- `mesh_position_local_to_clip`
- `mesh_normal_local_to_world`
- `mesh_tangent_local_to_world`
## Migration Guide
- The `skin_tangents` function from the `bevy_pbr::skinning` shader import has been replaced with the `mesh_tangent_local_to_world` function from the `bevy_pbr::mesh_functions` shader import
# Objective
Fix#4958
There was 4 issues:
- this is not true in WASM and on macOS: f28b921209/examples/3d/split_screen.rs (L90)
- ~~I made sure the system was running at least once~~
- I'm sending the event on window creation
- in webgl, setting a viewport has impacts on other render passes
- only in webgl and when there is a custom viewport, I added a render pass without a custom viewport
- shaderdef NO_ARRAY_TEXTURES_SUPPORT was not used by the 2d pipeline
- webgl feature was used but not declared in bevy_sprite, I added it to the Cargo.toml
- shaderdef NO_STORAGE_BUFFERS_SUPPORT was not used by the 2d pipeline
- I added it based on the BufferBindingType
The last commit changes the two last fixes to add the shaderdefs in the shader cache directly instead of needing to do it in each pipeline
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Closes#4464
## Solution
- Specify default mag and min filter types for `Image` instead of using `wgpu`'s defaults.
---
## Changelog
### Changed
- Default `Image` filtering changed from `Nearest` to `Linear`.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- fix#4946
- fix running 3d in wasm
## Solution
- since #4867, the imports are splitter differently, and this shader def was not always set correctly depending on the shader used
- add it when needed
# Objective
Users should be able to render cameras to specific areas of a render target, which enables scenarios like split screen, minimaps, etc.
Builds on the new Camera Driven Rendering added here: #4745Fixes: #202
Alternative to #1389 and #3626 (which are incompatible with the new Camera Driven Rendering)
## Solution
Cameras can now configure an optional "viewport", which defines a rectangle within their render target to draw to. If a `Viewport` is defined, the camera's `CameraProjection`, `View`, and visibility calculations will use the viewport configuration instead of the full render target.
```rust
// This camera will render to the first half of the primary window (on the left side).
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle {
camera: Camera {
viewport: Some(Viewport {
physical_position: UVec2::new(0, 0),
physical_size: UVec2::new(window.physical_width() / 2, window.physical_height()),
depth: 0.0..1.0,
}),
..default()
},
..default()
});
```
To account for this, the `Camera` component has received a few adjustments:
* `Camera` now has some new getter functions:
* `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, `projection_matrix`
* All computed camera values are now private and live on the `ComputedCameraValues` field (logical/physical width/height, the projection matrix). They are now exposed on `Camera` via getters/setters This wasn't _needed_ for viewports, but it was long overdue.
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `Camera` components now have a `viewport` field, which can be set to draw to a portion of a render target instead of the full target.
* `Camera` component has some new functions: `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, and `projection_matrix`
* Added a new split_screen example illustrating how to render two cameras to the same scene
## Migration Guide
`Camera::projection_matrix` is no longer a public field. Use the new `Camera::projection_matrix()` method instead:
```rust
// Bevy 0.7
let projection = camera.projection_matrix;
// Bevy 0.8
let projection = camera.projection_matrix();
```
This adds "high level camera driven rendering" to Bevy. The goal is to give users more control over what gets rendered (and where) without needing to deal with render logic. This will make scenarios like "render to texture", "multiple windows", "split screen", "2d on 3d", "3d on 2d", "pass layering", and more significantly easier.
Here is an [example of a 2d render sandwiched between two 3d renders (each from a different perspective)](https://gist.github.com/cart/4fe56874b2e53bc5594a182fc76f4915):

Users can now spawn a camera, point it at a RenderTarget (a texture or a window), and it will "just work".
Rendering to a second window is as simple as spawning a second camera and assigning it to a specific window id:
```rust
// main camera (main window)
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle::default());
// second camera (other window)
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle {
camera: Camera {
target: RenderTarget::Window(window_id),
..default()
},
..default()
});
```
Rendering to a texture is as simple as pointing the camera at a texture:
```rust
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle {
camera: Camera {
target: RenderTarget::Texture(image_handle),
..default()
},
..default()
});
```
Cameras now have a "render priority", which controls the order they are drawn in. If you want to use a camera's output texture as a texture in the main pass, just set the priority to a number lower than the main pass camera (which defaults to `0`).
```rust
// main pass camera with a default priority of 0
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle::default());
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle {
camera: Camera {
target: RenderTarget::Texture(image_handle.clone()),
priority: -1,
..default()
},
..default()
});
commands.spawn_bundle(SpriteBundle {
texture: image_handle,
..default()
})
```
Priority can also be used to layer to cameras on top of each other for the same RenderTarget. This is what "2d on top of 3d" looks like in the new system:
```rust
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle::default());
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle {
camera: Camera {
// this will render 2d entities "on top" of the default 3d camera's render
priority: 1,
..default()
},
..default()
});
```
There is no longer the concept of a global "active camera". Resources like `ActiveCamera<Camera2d>` and `ActiveCamera<Camera3d>` have been replaced with the camera-specific `Camera::is_active` field. This does put the onus on users to manage which cameras should be active.
Cameras are now assigned a single render graph as an "entry point", which is configured on each camera entity using the new `CameraRenderGraph` component. The old `PerspectiveCameraBundle` and `OrthographicCameraBundle` (generic on camera marker components like Camera2d and Camera3d) have been replaced by `Camera3dBundle` and `Camera2dBundle`, which set 3d and 2d default values for the `CameraRenderGraph` and projections.
```rust
// old 3d perspective camera
commands.spawn_bundle(PerspectiveCameraBundle::default())
// new 3d perspective camera
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle::default())
```
```rust
// old 2d orthographic camera
commands.spawn_bundle(OrthographicCameraBundle::new_2d())
// new 2d orthographic camera
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle::default())
```
```rust
// old 3d orthographic camera
commands.spawn_bundle(OrthographicCameraBundle::new_3d())
// new 3d orthographic camera
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle {
projection: OrthographicProjection {
scale: 3.0,
scaling_mode: ScalingMode::FixedVertical,
..default()
}.into(),
..default()
})
```
Note that `Camera3dBundle` now uses a new `Projection` enum instead of hard coding the projection into the type. There are a number of motivators for this change: the render graph is now a part of the bundle, the way "generic bundles" work in the rust type system prevents nice `..default()` syntax, and changing projections at runtime is much easier with an enum (ex for editor scenarios). I'm open to discussing this choice, but I'm relatively certain we will all come to the same conclusion here. Camera2dBundle and Camera3dBundle are much clearer than being generic on marker components / using non-default constructors.
If you want to run a custom render graph on a camera, just set the `CameraRenderGraph` component:
```rust
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle {
camera_render_graph: CameraRenderGraph::new(some_render_graph_name),
..default()
})
```
Just note that if the graph requires data from specific components to work (such as `Camera3d` config, which is provided in the `Camera3dBundle`), make sure the relevant components have been added.
Speaking of using components to configure graphs / passes, there are a number of new configuration options:
```rust
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle {
camera_3d: Camera3d {
// overrides the default global clear color
clear_color: ClearColorConfig::Custom(Color::RED),
..default()
},
..default()
})
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle {
camera_3d: Camera3d {
// disables clearing
clear_color: ClearColorConfig::None,
..default()
},
..default()
})
```
Expect to see more of the "graph configuration Components on Cameras" pattern in the future.
By popular demand, UI no longer requires a dedicated camera. `UiCameraBundle` has been removed. `Camera2dBundle` and `Camera3dBundle` now both default to rendering UI as part of their own render graphs. To disable UI rendering for a camera, disable it using the CameraUi component:
```rust
commands
.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle::default())
.insert(CameraUi {
is_enabled: false,
..default()
})
```
## Other Changes
* The separate clear pass has been removed. We should revisit this for things like sky rendering, but I think this PR should "keep it simple" until we're ready to properly support that (for code complexity and performance reasons). We can come up with the right design for a modular clear pass in a followup pr.
* I reorganized bevy_core_pipeline into Core2dPlugin and Core3dPlugin (and core_2d / core_3d modules). Everything is pretty much the same as before, just logically separate. I've moved relevant types (like Camera2d, Camera3d, Camera3dBundle, Camera2dBundle) into their relevant modules, which is what motivated this reorganization.
* I adapted the `scene_viewer` example (which relied on the ActiveCameras behavior) to the new system. I also refactored bits and pieces to be a bit simpler.
* All of the examples have been ported to the new camera approach. `render_to_texture` and `multiple_windows` are now _much_ simpler. I removed `two_passes` because it is less relevant with the new approach. If someone wants to add a new "layered custom pass with CameraRenderGraph" example, that might fill a similar niche. But I don't feel much pressure to add that in this pr.
* Cameras now have `target_logical_size` and `target_physical_size` fields, which makes finding the size of a camera's render target _much_ simpler. As a result, the `Assets<Image>` and `Windows` parameters were removed from `Camera::world_to_screen`, making that operation much more ergonomic.
* Render order ambiguities between cameras with the same target and the same priority now produce a warning. This accomplishes two goals:
1. Now that there is no "global" active camera, by default spawning two cameras will result in two renders (one covering the other). This would be a silent performance killer that would be hard to detect after the fact. By detecting ambiguities, we can provide a helpful warning when this occurs.
2. Render order ambiguities could result in unexpected / unpredictable render results. Resolving them makes sense.
## Follow Up Work
* Per-Camera viewports, which will make it possible to render to a smaller area inside of a RenderTarget (great for something like splitscreen)
* Camera-specific MSAA config (should use the same "overriding" pattern used for ClearColor)
* Graph Based Camera Ordering: priorities are simple, but they make complicated ordering constraints harder to express. We should consider adopting a "graph based" camera ordering model with "before" and "after" relationships to other cameras (or build it "on top" of the priority system).
* Consider allowing graphs to run subgraphs from any nest level (aka a global namespace for graphs). Right now the 2d and 3d graphs each need their own UI subgraph, which feels "fine" in the short term. But being able to share subgraphs between other subgraphs seems valuable.
* Consider splitting `bevy_core_pipeline` into `bevy_core_2d` and `bevy_core_3d` packages. Theres a shared "clear color" dependency here, which would need a new home.
# Objective
- Split PBR and 2D mesh shaders into types and bindings to prepare the shaders to be more reusable.
- See #3969 for details. I'm doing this in multiple steps to make review easier.
---
## Changelog
- Changed: 2D and PBR mesh shaders are now split into types and bindings, the following shader imports are available: `bevy_pbr::mesh_view_types`, `bevy_pbr::mesh_view_bindings`, `bevy_pbr::mesh_types`, `bevy_pbr::mesh_bindings`, `bevy_sprite::mesh2d_view_types`, `bevy_sprite::mesh2d_view_bindings`, `bevy_sprite::mesh2d_types`, `bevy_sprite::mesh2d_bindings`
## Migration Guide
- In shaders for 3D meshes:
- `#import bevy_pbr::mesh_view_bind_group` -> `#import bevy_pbr::mesh_view_bindings`
- `#import bevy_pbr::mesh_struct` -> `#import bevy_pbr::mesh_types`
- NOTE: If you are using the mesh bind group at bind group index 2, you can remove those binding statements in your shader and just use `#import bevy_pbr::mesh_bindings` which itself imports the mesh types needed for the bindings.
- In shaders for 2D meshes:
- `#import bevy_sprite::mesh2d_view_bind_group` -> `#import bevy_sprite::mesh2d_view_bindings`
- `#import bevy_sprite::mesh2d_struct` -> `#import bevy_sprite::mesh2d_types`
- NOTE: If you are using the mesh2d bind group at bind group index 2, you can remove those binding statements in your shader and just use `#import bevy_sprite::mesh2d_bindings` which itself imports the mesh2d types needed for the bindings.
# Objective
Models can be produced that do not have vertex tangents but do have normal map textures. The tangents can be generated. There is a way that the vertex tangents can be generated to be exactly invertible to avoid introducing error when recreating the normals in the fragment shader.
## Solution
- After attempts to get https://github.com/gltf-rs/mikktspace to integrate simple glam changes and version bumps, and releases of that crate taking weeks / not being made (no offense intended to the authors/maintainers, bevy just has its own timelines and needs to take care of) it was decided to fork that repository. The following steps were taken:
- mikktspace was forked to https://github.com/bevyengine/mikktspace in order to preserve the repository's history in case the original is ever taken down
- The README in that repo was edited to add a note stating from where the repository was forked and explaining why
- The repo was locked for changes as its only purpose is historical
- The repo was integrated into the bevy repo using `git subtree add --prefix crates/bevy_mikktspace git@github.com:bevyengine/mikktspace.git master`
- In `bevy_mikktspace`:
- The travis configuration was removed
- `cargo fmt` was run
- The `Cargo.toml` was conformed to bevy's (just adding bevy to the keywords, changing the homepage and repository, changing the version to 0.7.0-dev - importantly the license is exactly the same)
- Remove the features, remove `nalgebra` entirely, only use `glam`, suppress clippy.
- This was necessary because our CI runs clippy with `--all-features` and the `nalgebra` and `glam` features are mutually exclusive, plus I don't want to modify this highly numerically-sensitive code just to appease clippy and diverge even more from upstream.
- Rebase https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/1795
- @jakobhellermann said it was fine to copy and paste but it ended up being almost exactly the same with just a couple of adjustments when validating correctness so I decided to actually rebase it and then build on top of it.
- Use the exact same fragment shader code to ensure correct normal mapping.
- Tested with both https://github.com/KhronosGroup/glTF-Sample-Models/tree/master/2.0/NormalTangentMirrorTest which has vertex tangents and https://github.com/KhronosGroup/glTF-Sample-Models/tree/master/2.0/NormalTangentTest which requires vertex tangent generation
Co-authored-by: alteous <alteous@outlook.com>
# Objective
allow meshes with equal z-depth to be rendered in a chosen order / avoid z-fighting
## Solution
add a depth_bias to SpecializedMaterial that is added to the mesh depth used for render-ordering.
# Objective
- Add an `ExtractResourcePlugin` for convenience and consistency
## Solution
- Add an `ExtractResourcePlugin` similar to `ExtractComponentPlugin` but for ECS `Resource`s. The system that is executed simply clones the main world resource into a render world resource, if and only if the main world resource was either added or changed since the last execution of the system.
- Add an `ExtractResource` trait with a `fn extract_resource(res: &Self) -> Self` function. This is used by the `ExtractResourcePlugin` to extract the resource
- Add a derive macro for `ExtractResource` on a `Resource` with the `Clone` trait, that simply returns `res.clone()`
- Use `ExtractResourcePlugin` wherever both possible and appropriate
# Objective
- Fixes#4456
## Solution
- Removed the `near` and `far` fields from the camera and the views.
---
## Changelog
- Removed the `near` and `far` fields from the camera and the views.
- Removed the `ClusterFarZMode::CameraFarPlane` far z mode.
## Migration Guide
- Cameras no longer accept near and far values during initialization
- `ClusterFarZMode::Constant` should be used with the far value instead of `ClusterFarZMode::CameraFarPlane`
# Objective
- noticed a few Vec3 and Vec2 that could be const
## Solution
- Declared them as const
- It seems to make a tiny improvement in example `many_light`, but given that the change is not complex at all it could still be worth it
# Objective
Add support for vertex colors
## Solution
This change is modeled after how vertex tangents are handled, so the shader is conditionally compiled with vertex color support if the mesh has the corresponding attribute set.
Vertex colors are multiplied by the base color. I'm not sure if this is the best for all cases, but may be useful for modifying vertex colors without creating a new mesh.
I chose `VertexFormat::Float32x4`, but I'd prefer 16-bit floats if/when support is added.
## Changelog
### Added
- Vertex colors can be specified using the `Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_COLOR` mesh attribute.
# Objective
- When spawning a sprite the alpha is used for transparency, but when using the `Color::into()` implementation to spawn a `StandardMaterial`, the alpha is ignored.
- Pretty much everytime I want to make something transparent I started with a `Color::rgb().into()` and I'm always surprised that it doesn't work when changing it to `Color::rgba().into()`
- It's possible there's an issue with this approach I am not thinking of, but I'm not sure what's the point of setting an alpha value without the goal of making a color transparent.
## Solution
- Set the alpha_mode to AlphaMode::Blend when the alpha is not the default value.
---
## Migration Guide
This is not a breaking change, but it can easily be migrated to reduce boilerplate
```rust
commands.spawn_bundle(PbrBundle {
mesh: meshes.add(shape::Cube::default().into()),
material: materials.add(StandardMaterial {
base_color: Color::rgba(1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.75),
alpha_mode: AlphaMode::Blend,
..default()
}),
..default()
});
// becomes
commands.spawn_bundle(PbrBundle {
mesh: meshes.add(shape::Cube::default().into()),
material: materials.add(Color::rgba(1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.75).into()),
..default()
});
```
Co-authored-by: Charles <IceSentry@users.noreply.github.com>
### Problem
It currently isn't possible to construct the default value of a reflected type. Because of that, it isn't possible to use `add_component` of `ReflectComponent` to add a new component to an entity because you can't know what the initial value should be.
### Solution
1. add `ReflectDefault` type
```rust
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct ReflectDefault {
default: fn() -> Box<dyn Reflect>,
}
impl ReflectDefault {
pub fn default(&self) -> Box<dyn Reflect> {
(self.default)()
}
}
impl<T: Reflect + Default> FromType<T> for ReflectDefault {
fn from_type() -> Self {
ReflectDefault {
default: || Box::new(T::default()),
}
}
}
```
2. add `#[reflect(Default)]` to all component types that implement `Default` and are user facing (so not `ComputedSize`, `CubemapVisibleEntities` etc.)
This makes it possible to add the default value of a component to an entity without any compile-time information:
```rust
fn main() {
let mut app = App::new();
app.register_type::<Camera>();
let type_registry = app.world.get_resource::<TypeRegistry>().unwrap();
let type_registry = type_registry.read();
let camera_registration = type_registry.get(std::any::TypeId::of::<Camera>()).unwrap();
let reflect_default = camera_registration.data::<ReflectDefault>().unwrap();
let reflect_component = camera_registration
.data::<ReflectComponent>()
.unwrap()
.clone();
let default = reflect_default.default();
drop(type_registry);
let entity = app.world.spawn().id();
reflect_component.add_component(&mut app.world, entity, &*default);
let camera = app.world.entity(entity).get::<Camera>().unwrap();
dbg!(&camera);
}
```
### Open questions
- should we have `ReflectDefault` or `ReflectFromWorld` or both?
# Objective
- While optimising many_cubes, I noticed that all material handles are extracted regardless of whether the entity to which the handle belongs is visible or not. As such >100k handles are extracted when only <20k are visible.
## Solution
- Only extract material handles of visible entities.
- This improves `many_cubes -- sphere` from ~42fps to ~48fps. It reduces not only the extraction time but also system commands time. `Handle<StandardMaterial>` extraction and its system commands went from 0.522ms + 3.710ms respectively, to 0.267ms + 0.227ms an 88% reduction for this system for this case. It's very view dependent but...
# Objective
- Creating and executing render passes has GPU overhead. If there are no phase items in the render phase to draw, then this overhead should not be incurred as it has no benefit.
## Solution
- Check if there are no phase items to draw, and if not, do not construct not execute the render pass
---
## Changelog
- Changed: Do not create nor execute empty render passes
# Objective
- Meshes are queued in opaque phase instead of transparent phase when drawing wireframes.
- There is a name mismatch.
## Solution
- Rename `transparent_phase` to `opaque_phase` in `wireframe.rs`.
# Objective
Reduce the catch-all grab-bag of functionality in bevy_core by moving FloatOrd to bevy_utils.
A step in addressing #2931 and splitting bevy_core into more specific locations.
## Solution
Move FloatOrd into bevy_utils. Fix the compile errors.
As a result, bevy_core_pipeline, bevy_pbr, bevy_sprite, bevy_text, and bevy_ui no longer depend on bevy_core (they were only using it for `FloatOrd` previously).
# Objective
- Related #4276.
- Part of the splitting process of #3503.
## Solution
- Move `Size` to `bevy_ui`.
## Reasons
- `Size` is only needed in `bevy_ui` (because it needs to use `Val` instead of `f32`), but it's also used as a worse `Vec2` replacement in other areas.
- `Vec2` is more powerful than `Size` so it should be used whenever possible.
- Discussion in #3503.
## Changelog
### Changed
- The `Size` type got moved from `bevy_math` to `bevy_ui`.
## Migration Guide
- The `Size` type got moved from `bevy::math` to `bevy::ui`. To migrate you just have to import `bevy::ui::Size` instead of `bevy::math::Math` or use the `bevy::prelude` instead.
Co-authored-by: KDecay <KDecayMusic@protonmail.com>
# Objective
- Fix `ClusterConfig::None`
- This fix is from @robtfm but they didn't have time to submit it, so I am.
## Solution
- Always clear clusters and skip processing when `ClusterConfig::None`
- Conditionally remove `VisiblePointLights` from the view if it is present
# Objective
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/4098 still hasn't fixed minimisation on Windows.
- `Clusters.lights` is assumed to have the number of items given by the product of `Clusters.dimensions`'s axes.
## Solution
- Make that true in `clear`.
# Objective
- Fixes#4234
- Fixes#4473
- Built on top of #3989
- Improve performance of `assign_lights_to_clusters`
## Solution
- Remove the OBB-based cluster light assignment algorithm and calculation of view space AABBs
- Implement the 'iterative sphere refinement' algorithm used in Just Cause 3 by Emil Persson as documented in the Siggraph 2015 Practical Clustered Shading talk by Persson, on pages 42-44 http://newq.net/dl/pub/s2015_practical.pdf
- Adapt to also support orthographic projections
- Add `many_lights -- orthographic` for testing many lights using an orthographic projection
## Results
- `assign_lights_to_clusters` in `many_lights` before this PR on an M1 Max over 1500 frames had a median execution time of 1.71ms. With this PR it is 1.51ms, a reduction of 0.2ms or 11.7% for this system.
---
## Changelog
- Changed: Improved cluster light assignment performance
Co-authored-by: robtfm <50659922+robtfm@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- While animating 501 https://github.com/KhronosGroup/glTF-Sample-Models/tree/master/2.0/BrainStem, I noticed things were getting a little slow
- Looking in tracy, the system `extract_skinned_meshes` is taking a lot of time, with a mean duration of 15.17ms
## Solution
- ~~Use `Vec` instead of a `SmallVec`~~
- ~~Don't use an temporary variable~~
- Compute the affine matrix as an `Affine3A` instead
- Remove the `temp` vec
| |mean|
|---|---|
|base|15.17ms|
|~~vec~~|~~9.31ms~~|
|~~no temp variable~~|~~11.31ms~~|
|removing the temp vector|8.43ms|
|affine|13.21ms|
|all together|7.23ms|
# Objective
- Make use of storage buffers, where they are available, for clustered forward bindings to support far more point lights in a scene
- Fixes#3605
- Based on top of #4079
This branch on an M1 Max can keep 60fps with about 2150 point lights of radius 1m in the Sponza scene where I've been testing. The bottleneck is mostly assigning lights to clusters which grows faster than linearly (I think 1000 lights was about 1.5ms and 5000 was 7.5ms). I have seen papers and presentations leveraging compute shaders that can get this up to over 1 million. That said, I think any further optimisations should probably be done in a separate PR.
## Solution
- Add `RenderDevice` to the `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` trait `::key()` functions to allow setting flags on the keys depending on feature/limit availability
- Make `GpuPointLights` and `ViewClusterBuffers` into enums containing `UniformVec` and `StorageBuffer` variants. Implement the necessary API on them to make usage the same for both cases, and the only difference is at initialisation time.
- Appropriate shader defs in the shader code to handle the two cases
## Context on some decisions / open questions
- I'm using `max_storage_buffers_per_shader_stage >= 3` as a check to see if storage buffers are supported. I was thinking about diving into 'binding resource management' but it feels like we don't have enough use cases to understand the problem yet, and it is mostly a separate concern to this PR, so I think it should be handled separately.
- Should `ViewClusterBuffers` and `ViewClusterBindings` be merged, duplicating the count variables into the enum variants?
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
Animation with shadows crashes with:
```
thread 'main' panicked at 'wgpu error: Validation Error
Caused by:
In Device::create_render_pipeline
note: label = `shadow_pipeline`
error matching VERTEX shader requirements against the pipeline
shader global ResourceBinding { group: 1, binding: 1 } is not available in the layout pipeline layout
visibility flags don't include the shader stage
```
Animation with wireframe crashes with:
```
thread 'main' panicked at 'wgpu error: Validation Error
Caused by:
In Device::create_render_pipeline
note: label = `opaque_mesh_pipeline`
error matching VERTEX shader requirements against the pipeline
shader global ResourceBinding { group: 2, binding: 0 } is not available in the layout pipeline layout
binding is missing from the pipeline layout
```
## Solution
- Fix the bindings
# Objective
Add a system parameter `ParamSet` to be used as container for conflicting parameters.
## Solution
Added two methods to the SystemParamState trait, which gives the access used by the parameter. Did the implementation. Added some convenience methods to FilteredAccessSet. Changed `get_conflicts` to return every conflicting component instead of breaking on the first conflicting `FilteredAccess`.
Co-authored-by: bilsen <40690317+bilsen@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
Load skeletal weights and indices from GLTF files. Animate meshes.
## Solution
- Load skeletal weights and indices from GLTF files.
- Added `SkinnedMesh` component and ` SkinnedMeshInverseBindPose` asset
- Added `extract_skinned_meshes` to extract joint matrices.
- Added queue phase systems for enqueuing the buffer writes.
Some notes:
- This ports part of # #2359 to the current main.
- This generates new `BufferVec`s and bind groups every frame. The expectation here is that the number of `Query::get` calls during extract is probably going to be the stronger bottleneck, with up to 256 calls per skinned mesh. Until that is optimized, caching buffers and bind groups is probably a non-concern.
- Unfortunately, due to the uniform size requirements, this means a 16KB buffer is allocated for every skinned mesh every frame. There's probably a few ways to get around this, but most of them require either compute shaders or storage buffers, which are both incompatible with WebGL2.
Co-authored-by: james7132 <contact@jamessliu.com>
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: James Liu <contact@jamessliu.com>
* Refactor assign_lights_to_clusters to always clear + update clusters, even if the screen size isn't available yet / is zero. This fixes#4167. We still avoid the "expensive" per-light work when the screen size isn't available yet. I also consolidated some logic to eliminate some redundancies.
* Removed _a ton_ of (potentially very large) per-frame reallocations
* Removed `Res<VisiblePointLights>` (a vec) in favor of `Res<GlobalVisiblePointLights>` (a hashmap). We were allocating a new hashmap every frame, the collecting it into a vec every frame, then in another system _re-generating the hashmap_. It is always used like a hashmap, might as well embrace that. We now reuse the same hashmap every frame and dont use any intermediate collections.
* We were re-allocating Clusters aabb and light vectors every frame by re-constructing Clusters every frame. We now re-use the existing collections.
* Reuse per-camera VisiblePointLight vecs when possible instead of allocating them every frame. We now only insert VisiblePointLights if the component doesn't exist yet.
# Objective
- Fixes#3970
- To support Bevy's shader abstraction(shader defs, shader imports and hot shader reloading) for compute shaders, I have followed carts advice and change the `PipelinenCache` to accommodate both compute and render pipelines.
## Solution
- renamed `RenderPipelineCache` to `PipelineCache`
- Cached Pipelines are now represented by an enum (render, compute)
- split the `SpecializedPipelines` into `SpecializedRenderPipelines` and `SpecializedComputePipelines`
- updated the game of life example
## Open Questions
- should `SpecializedRenderPipelines` and `SpecializedComputePipelines` be merged and how would we do that?
- should the `get_render_pipeline` and `get_compute_pipeline` methods be merged?
- is pipeline specialization for different entry points a good pattern
Co-authored-by: Kurt Kühnert <51823519+Ku95@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Reduce time spent in the `check_visibility` system
## Solution
- Use `Vec3A` for all bounding volume types to leverage SIMD optimisations and to avoid repeated runtime conversions from `Vec3` to `Vec3A`
- Inline all bounding volume intersection methods
- Add on-the-fly calculated `Aabb` -> `Sphere` and do `Sphere`-`Frustum` intersection tests before `Aabb`-`Frustum` tests. This is faster for `many_cubes` but could be slower in other cases where the sphere test gives a false-positive that the `Aabb` test discards. Also, I tested precalculating the `Sphere`s and inserting them alongside the `Aabb` but this was slower.
- Do not test meshes against the far plane. Apparently games don't do this anymore with infinite projections, and it's one fewer plane to test against. I made it optional and still do the test for culling lights but that is up for discussion.
- These collectively reduce `check_visibility` execution time in `many_cubes -- sphere` from 2.76ms to 1.48ms and increase frame rate from ~42fps to ~44fps
# Objective
- Support compressed textures including 'universal' formats (ETC1S, UASTC) and transcoding of them to
- Support `.dds`, `.ktx2`, and `.basis` files
## Solution
- Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/3608 Look there for more details.
- Note that the functionality is all enabled through non-default features. If it is desirable to enable some by default, I can do that.
- The `basis-universal` crate, used for `.basis` file support and for transcoding, is built on bindings against a C++ library. It's not feasible to rewrite in Rust in a short amount of time. There are no Rust alternatives of which I am aware and it's specialised code. In its current state it doesn't support the wasm target, but I don't know for sure. However, it is possible to build the upstream C++ library with emscripten, so there is perhaps a way to add support for web too with some shenanigans.
- There's no support for transcoding from BasisLZ/ETC1S in KTX2 files as it was quite non-trivial to implement and didn't feel important given people could use `.basis` files for ETC1S.
# Objective
fix cluster tilesize and tilecount calculations.
Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/4127 & https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/3596
## Solution
- calculate tilesize as smallest integers such that dimensions.xy() tiles will cover the screen
- calculate final dimensions as smallest integers such that final dimensions * tilesize will cover the screen
there is more cleanup that could be done in these functions. a future PR will likely remove the tilesize completely, so this is just a minimal change set to fix the current bug at small screen sizes
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
provide some customisation for default cluster setup
avoid "cluster index lists is full" in all cases (using a strategy outlined by @superdump)
## Solution
Add ClusterConfig enum (which can be inserted into a view at any time) to allow specifying cluster setup with variants:
- None (do not do any light assignment - for views which do not require light info, e.g. minimaps etc)
- Single (one cluster)
- XYZ (explicit cluster counts in each dimension)
- FixedZ (most similar to current - specify Z-slices and total, then x and y counts are dynamically determined to give approximately square clusters based on current aspect ratio)
Defaults to FixedZ { total: 4096, z: 24 } which is similar to the current setup.
Per frame, estimate the number of indices that would be required for the current config and decrease the cluster counts / increase the cluster sizes in the x and y dimensions if the index list would be too small.
notes:
- I didn't put ClusterConfig in the camera bundles to avoid introducing a dependency from bevy_render to bevy_pbr. the ClusterConfig enum comes with a pbr-centric impl block so i didn't want to move that into bevy_render either.
- ~Might want to add None variant to cluster config for views that don't care about lights?~
- Not well tested for orthographic
- ~there's a cluster_muck branch on my repo which includes some diagnostics / a modified lighting example which may be useful for tyre-kicking~ (outdated, i will bring it up to date if required)
anecdotal timings:
FPS on the lighting demo is negligibly better (~5%), maybe due to a small optimisation constraining the light aabb to be in front of the camera
FPS on the lighting demo with 100 extra lights added is ~33% faster, and also renders correctly as the cluster index count is no longer exceeded
## Objective
Currently, all directional and point lights have their viewing frusta recalculated every frame, even if they have not moved or been disabled/enabled.
## Solution
The relevant systems now make use of change detection to only update those lights whose viewing frusta may have changed.
This makes it possible for materials to configure front or
back face culling, or disable culling.
Initially I looked at specializing the Mesh which currently
controls this state but conceptually it seems more appropriate
to control this at the material level, not the mesh level.
_Just for reference this also seems to be consistent with Unity
where materials/shaders can configure the culling mode between
front/back/off - as opposed to configuring any culling state
when importing a mesh._
After some archaeology, trying to understand how this might
relate to the existing 'double_sided' option, it was determined
that double_sided is a more high level lighting option originally
from Filament that will cause the normals for back faces to be
flipped.
For sake of avoiding complexity, but keeping control this
currently keeps the options orthogonal, and adds some clarifying
documentation for `double_sided`. This won't affect any existing
apps since there hasn't been a way to disable backface culling
up until now, so the option was essentially redundant.
double_sided support could potentially be updated to imply
disabling of backface culling.
For reference https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/3734/commits also looks at exposing cull mode control. I think the main difference here is that this patch handles RenderPipelineDescriptor specialization directly within the StandardMaterial implementation instead of communicating info back to the Mesh via the `queue_material_meshes` system.
With the way material.rs builds up the final RenderPipelineDescriptor first by calling specialize for the MeshPipeline followed by specialize for the material then it seems like we have a natural place to override anything in the descriptor that's first configured for the mesh state.
# Objective
Add Visibility for lights
## Solution
- add Visibility to PointLightBundle and DirectionLightBundle
- filter lights used by Visibility.is_visible
note: includes changes from #3916 due to overlap, will be cleaner after that is merged
# Objective
fix#3915
## Solution
the issues are caused by
- lights are assigned to clusters before being filtered down to MAX_POINT_LIGHTS, leading to cluster counts potentially being too high
- after fixing the above, packing the count into 8 bits still causes overflow with exactly 256 lights affecting a cluster
to fix:
```assign_lights_to_clusters```
- limit extracted lights to MAX_POINT_LIGHTS, selecting based on shadow-caster & intensity (if required)
- warn if MAX_POINT_LIGHT count is exceeded
```prepare_lights```
- limit the lights assigned to a cluster to CLUSTER_COUNT_MASK (which is 1 less than MAX_POINT_LIGHTS) to avoid overflowing into the offset bits
notes:
- a better solution to the overflow may be to use more than 8 bits for cluster_count (the comment states only 14 of the remaining 24 bits are used for the offset). this would touch more of the code base but i'm happy to try if it has some benefit.
- intensity is only one way to select lights. it may be worth allowing user configuration of the light filtering, but i can't see a clean way to do that
# Objective
- Optimize assign_lights_to_clusters
## Solution
- Avoid inserting entities into hash sets in inner loops when it is known they will be inserted in at least one iteration of the loop.
- Use a Vec instead of a hash set where the set is not needed
- Avoid explicit calculation of the cluster_index from x,y,z coordinates, instead using row and column offsets and just adding z in the inner loop
- These changes cut the time spent in the system roughly in half
# Objective
- In the large majority of cases, users were calling `.unwrap()` immediately after `.get_resource`.
- Attempting to add more helpful error messages here resulted in endless manual boilerplate (see #3899 and the linked PRs).
## Solution
- Add an infallible variant named `.resource` and so on.
- Use these infallible variants over `.get_resource().unwrap()` across the code base.
## Notes
I did not provide equivalent methods on `WorldCell`, in favor of removing it entirely in #3939.
## Migration Guide
Infallible variants of `.get_resource` have been added that implicitly panic, rather than needing to be unwrapped.
Replace `world.get_resource::<Foo>().unwrap()` with `world.resource::<Foo>()`.
## Impact
- `.unwrap` search results before: 1084
- `.unwrap` search results after: 942
- internal `unwrap_or_else` calls added: 4
- trivial unwrap calls removed from tests and code: 146
- uses of the new `try_get_resource` API: 11
- percentage of the time the unwrapping API was used internally: 93%
# Objective
Will fix#3377 and #3254
## Solution
Use an enum to represent either a `WindowId` or `Handle<Image>` in place of `Camera::window`.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
This PR makes a number of changes to how meshes and vertex attributes are handled, which the goal of enabling easy and flexible custom vertex attributes:
* Reworks the `Mesh` type to use the newly added `VertexAttribute` internally
* `VertexAttribute` defines the name, a unique `VertexAttributeId`, and a `VertexFormat`
* `VertexAttributeId` is used to produce consistent sort orders for vertex buffer generation, replacing the more expensive and often surprising "name based sorting"
* Meshes can be used to generate a `MeshVertexBufferLayout`, which defines the layout of the gpu buffer produced by the mesh. `MeshVertexBufferLayouts` can then be used to generate actual `VertexBufferLayouts` according to the requirements of a specific pipeline. This decoupling of "mesh layout" vs "pipeline vertex buffer layout" is what enables custom attributes. We don't need to standardize _mesh layouts_ or contort meshes to meet the needs of a specific pipeline. As long as the mesh has what the pipeline needs, it will work transparently.
* Mesh-based pipelines now specialize on `&MeshVertexBufferLayout` via the new `SpecializedMeshPipeline` trait (which behaves like `SpecializedPipeline`, but adds `&MeshVertexBufferLayout`). The integrity of the pipeline cache is maintained because the `MeshVertexBufferLayout` is treated as part of the key (which is fully abstracted from implementers of the trait ... no need to add any additional info to the specialization key).
* Hashing `MeshVertexBufferLayout` is too expensive to do for every entity, every frame. To make this scalable, I added a generalized "pre-hashing" solution to `bevy_utils`: `Hashed<T>` keys and `PreHashMap<K, V>` (which uses `Hashed<T>` internally) . Why didn't I just do the quick and dirty in-place "pre-compute hash and use that u64 as a key in a hashmap" that we've done in the past? Because its wrong! Hashes by themselves aren't enough because two different values can produce the same hash. Re-hashing a hash is even worse! I decided to build a generalized solution because this pattern has come up in the past and we've chosen to do the wrong thing. Now we can do the right thing! This did unfortunately require pulling in `hashbrown` and using that in `bevy_utils`, because avoiding re-hashes requires the `raw_entry_mut` api, which isn't stabilized yet (and may never be ... `entry_ref` has favor now, but also isn't available yet). If std's HashMap ever provides the tools we need, we can move back to that. Note that adding `hashbrown` doesn't increase our dependency count because it was already in our tree. I will probably break these changes out into their own PR.
* Specializing on `MeshVertexBufferLayout` has one non-obvious behavior: it can produce identical pipelines for two different MeshVertexBufferLayouts. To optimize the number of active pipelines / reduce re-binds while drawing, I de-duplicate pipelines post-specialization using the final `VertexBufferLayout` as the key. For example, consider a pipeline that needs the layout `(position, normal)` and is specialized using two meshes: `(position, normal, uv)` and `(position, normal, other_vec2)`. If both of these meshes result in `(position, normal)` specializations, we can use the same pipeline! Now we do. Cool!
To briefly illustrate, this is what the relevant section of `MeshPipeline`'s specialization code looks like now:
```rust
impl SpecializedMeshPipeline for MeshPipeline {
type Key = MeshPipelineKey;
fn specialize(
&self,
key: Self::Key,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
) -> RenderPipelineDescriptor {
let mut vertex_attributes = vec![
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL.at_shader_location(1),
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_UV_0.at_shader_location(2),
];
let mut shader_defs = Vec::new();
if layout.contains(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_TANGENT) {
shader_defs.push(String::from("VERTEX_TANGENTS"));
vertex_attributes.push(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_TANGENT.at_shader_location(3));
}
let vertex_buffer_layout = layout
.get_layout(&vertex_attributes)
.expect("Mesh is missing a vertex attribute");
```
Notice that this is _much_ simpler than it was before. And now any mesh with any layout can be used with this pipeline, provided it has vertex postions, normals, and uvs. We even got to remove `HAS_TANGENTS` from MeshPipelineKey and `has_tangents` from `GpuMesh`, because that information is redundant with `MeshVertexBufferLayout`.
This is still a draft because I still need to:
* Add more docs
* Experiment with adding error handling to mesh pipeline specialization (which would print errors at runtime when a mesh is missing a vertex attribute required by a pipeline). If it doesn't tank perf, we'll keep it.
* Consider breaking out the PreHash / hashbrown changes into a separate PR.
* Add an example illustrating this change
* Verify that the "mesh-specialized pipeline de-duplication code" works properly
Please dont yell at me for not doing these things yet :) Just trying to get this in peoples' hands asap.
Alternative to #3120Fixes#3030
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
Adds "hot reloading" of internal assets, which is normally not possible because they are loaded using `include_str` / direct Asset collection access.
This is accomplished via the following:
* Add a new `debug_asset_server` feature flag
* When that feature flag is enabled, create a second App with a second AssetServer that points to a configured location (by default the `crates` folder). Plugins that want to add hot reloading support for their assets can call the new `app.add_debug_asset::<T>()` and `app.init_debug_asset_loader::<T>()` functions.
* Load "internal" assets using the new `load_internal_asset` macro. By default this is identical to the current "include_str + register in asset collection" approach. But if the `debug_asset_server` feature flag is enabled, it will also load the asset dynamically in the debug asset server using the file path. It will then set up a correlation between the "debug asset" and the "actual asset" by listening for asset change events.
This is an alternative to #3673. The goal was to keep the boilerplate and features flags to a minimum for bevy plugin authors, and allow them to home their shaders near relevant code.
This is a draft because I haven't done _any_ quality control on this yet. I'll probably rename things and remove a bunch of unwraps. I just got it working and wanted to use it to start a conversation.
Fixes#3660
This enables shaders to (optionally) define their import path inside their source. This has a number of benefits:
1. enables users to define their own custom paths directly in their assets
2. moves the import path "close" to the asset instead of centralized in the plugin definition, which seems "better" to me.
3. makes "internal hot shader reloading" way more reasonable (see #3966)
4. logically opens the door to importing "parts" of a shader by defining "import_path blocks".
```rust
#define_import_path bevy_pbr::mesh_struct
struct Mesh {
model: mat4x4<f32>;
inverse_transpose_model: mat4x4<f32>;
// 'flags' is a bit field indicating various options. u32 is 32 bits so we have up to 32 options.
flags: u32;
};
let MESH_FLAGS_SHADOW_RECEIVER_BIT: u32 = 1u;
```
# Objective
- `WgpuOptions` is mutated to be updated with the actual device limits and features, but this information is readily available to both the main and render worlds through the `RenderDevice` which has .limits() and .features() methods
- Information about the adapter in terms of its name, the backend in use, etc were not being exposed but have clear use cases for being used to take decisions about what rendering code to use. For example, if something works well on AMD GPUs but poorly on Intel GPUs. Or perhaps something works well in Vulkan but poorly in DX12.
## Solution
- Stop mutating `WgpuOptions `and don't insert the updated values into the main and render worlds
- Return `AdapterInfo` from `initialize_renderer` and insert it into the main and render worlds
- Use `RenderDevice` limits in the lighting code that was using `WgpuOptions.limits`.
- Renamed `WgpuOptions` to `WgpuSettings`
What is says on the tin.
This has got more to do with making `clippy` slightly more *quiet* than it does with changing anything that might greatly impact readability or performance.
that said, deriving `Default` for a couple of structs is a nice easy win
(cherry picked from commit de943381bd2a8b242c94db99e6c7bbd70006d7c3)
# Objective
The view uniform lacks view transform information. The inverse transform is currently provided but this is not sufficient if you do not have access to an `inverse` function (such as in WGSL).
## Solution
Grab the view transform, put it in the view uniform, use the same matrix to compute the inverse as well.
# Objective
The query for `VisiblePointLights` in `check_light_mesh_visibility` has a `Without<DirectionalLight>` filter. However, because `VisiblePointLights` is no longer an alias for `VisibleEntities`, the query won't conflict with the query for `DirectionalLight`s and thus the filter is unnecessary.
## Solution
Remove the filter and the outdated comment explaining its purpose.
# Objective
- Do not panic when mroe than 256 point lights are added the scene
- Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/3682
## Solution
- Only iterate the first `MAX_POINT_LIGHTS` lights instead of as many as there are
## Open questions
- Should we warn that there are more than the maximum allowed number of point lights in the scene?
# Objective
In this PR I added the ability to opt-out graphical backends. Closes#3155.
## Solution
I turned backends into `Option` ~~and removed panicking sub app API to force users handle the error (was suggested by `@cart`)~~.
# Objective
The current 2d rendering is specialized to render sprites, we need a generic way to render 2d items, using meshes and materials like we have for 3d.
## Solution
I cloned a good part of `bevy_pbr` into `bevy_sprite/src/mesh2d`, removed lighting and pbr itself, adapted it to 2d rendering, added a `ColorMaterial`, and modified the sprite rendering to break batches around 2d meshes.
~~The PR is a bit crude; I tried to change as little as I could in both the parts copied from 3d and the current sprite rendering to make reviewing easier. In the future, I expect we could make the sprite rendering a normal 2d material, cleanly integrated with the rest.~~ _edit: see <https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/3460#issuecomment-1003605194>_
## Remaining work
- ~~don't require mesh normals~~ _out of scope_
- ~~add an example~~ _done_
- support 2d meshes & materials in the UI?
- bikeshed names (I didn't think hard about naming, please check if it's fine)
## Remaining questions
- ~~should we add a depth buffer to 2d now that there are 2d meshes?~~ _let's revisit that when we have an opaque render phase_
- ~~should we add MSAA support to the sprites, or remove it from the 2d meshes?~~ _I added MSAA to sprites since it's really needed for 2d meshes_
- ~~how to customize vertex attributes?~~ _#3120_
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Using plain exponential depth slicing for perspective projection cameras results in unnecessarily many slices very close together close to the camera. If the camera is then moved close to a collection of point lights, they will likely exhaust the available uniform buffer space for the lists of which lights affect which clusters.
## Solution
- A simple solution to this is to use a different near plane value for the depth slicing and set it to where the first slice's far plane should be. The default value is 5 and works well. This results in the configured number of depth slices, maintains the exponential slicing beyond the initial slice, and no slices are too small such that they cause problems that are sensitive to the view position.
# Objective
- Allow the user to specify the priority when configuring wgpu features/limits and by default use the maximum capabilities of the chosen adapter.
## Solution
- Add a `WgpuOptionsPriority` enum with `Compatibility`, `Functionality` and `WebGL2` options.
- Add a `priority: WgpuOptionsPriority` member to `WgpuOptions`.
- When initialising the renderer, if `WgpuOptions::priority == WgpuOptionsPriority::Functionality`, query the adapter for the available features and limits, use them when creating a device, and update `WgpuOptions` with those values. If `Compatibility` use the behaviour as before this PR. If `WebGL2` then use the WebGL2 downlevel limits as used when when building for wasm, for convenience of testing WebGL2 limits without having to build for wasm.
- Add an environment variable `WGPU_OPTIONS_PRIO` that takes `compatibility`, `functionality`, `webgl2`.
- Default to `WgpuOptionsPriority::Functionality`.
- Insert updated `WgpuOptions` into render app world as well. This is useful for applying the limits when rendering, such as limiting the directional light shadow map texture to 2048x2048 when using WebGL2 downlevel limits but not on wasm.
- Reduced `draw_state` logs from `debug` to `trace` and added `debug` level logs for the wgpu features and limits. Use `RUST_LOG=bevy_render=debug` to see the output.
# Objective
- Add support for loading lights from glTF 2.0 files
## Solution
- This adds support for the KHR_punctual_lights extension which supports point, directional, and spot lights, though we don't yet support spot lights.
- Inserting light bundles when creating scenes required registering some more light bundle component types.
# Objective
- After updating #2988, all the examples started crashing with
```
thread 'main' panicked at 'Plugin "bevy_render::render_component::ExtractComponentPlugin<bevy_asset::handle::Handle<bevy_pbr::pbr_material::StandardMaterial>>" was already added', crates/bevy_app/src/app.rs:831:33
```
## Solution
Plugin was added twice:
directly:
1d0d8a3397/crates/bevy_pbr/src/lib.rs (L73)
and through `MaterialPlugin`:
1d0d8a3397/crates/bevy_pbr/src/lib.rs (L72)1d0d8a3397/crates/bevy_pbr/src/material.rs (L183)
I removed the extra plugin
Co-authored-by: François <8672791+mockersf@users.noreply.github.com>
#3457 adds the `doc_markdown` clippy lint, which checks doc comments to make sure code identifiers are escaped with backticks. This causes a lot of lint errors, so this is one of a number of PR's that will fix those lint errors one crate at a time.
This PR fixes lints in the `bevy_pbr` crate.
# Objective
- While reading code, found some queries that are `mut` and not used as such
## Solution
- Remove `mut` when possible
Co-authored-by: François <8672791+mockersf@users.noreply.github.com>
This adds "high level" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits, which can be used with a `MaterialPlugin<T: SpecializedMaterial>`. `MaterialPlugin` automatically registers the appropriate resources, draw functions, and queue systems. The `Material` trait is simpler, and should cover most use cases. `SpecializedMaterial` is like `Material`, but it also requires defining a "specialization key" (see #3031). `Material` has a trivial blanket impl of `SpecializedMaterial`, which allows us to use the same types + functions for both.
This makes defining custom 3d materials much simpler (see the `shader_material` example diff) and ensures consistent behavior across all 3d materials (both built in and custom). I ported the built in `StandardMaterial` to `MaterialPlugin`. There is also a new `MaterialMeshBundle<T: SpecializedMaterial>`, which `PbrBundle` aliases to.
# Objective
- Our crevice is still called "crevice", which we can't use for a release
- Users would need to use our "crevice" directly to be able to use the derive macro
## Solution
- Rename crevice to bevy_crevice, and crevice-derive to bevy-crevice-derive
- Re-export it from bevy_render, and use it from bevy_render everywhere
- Fix derive macro to work either from bevy_render, from bevy_crevice, or from bevy
## Remaining
- It is currently re-exported as `bevy::render::bevy_crevice`, is it the path we want?
- After a brief suggestion to Cart, I changed the version to follow Bevy version instead of crevice, do we want that?
- Crevice README.md need to be updated
- in the `Cargo.toml`, there are a few things to change. How do we want to change them? How do we keep attributions to original Crevice?
```
authors = ["Lucien Greathouse <me@lpghatguy.com>"]
documentation = "https://docs.rs/crevice"
homepage = "https://github.com/LPGhatguy/crevice"
repository = "https://github.com/LPGhatguy/crevice"
```
Co-authored-by: François <8672791+mockersf@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
Instead of panicking when the `indices` field of a mesh is `None`, actually manage it.
This is just a question of keeping track of the vertex buffer size.
## Notes
* Relying on this change to improve performance on [bevy_debug_lines using the new renderer](https://github.com/Toqozz/bevy_debug_lines/pull/10)
* I'm still new to rendering, my only expertise with wgpu is the learn-wgpu tutorial, likely I'm overlooking something.
# Objective
- 3d examples fail to run in webgl2 because of unsupported texture formats or texture too large
## Solution
- switch to supported formats if a feature is enabled. I choose a feature instead of a build target to not conflict with a potential webgpu support
Very inspired by 6813b2edc5, and need #3290 to work.
I named the feature `webgl2`, but it's only needed if one want to use PBR in webgl2. Examples using only 2D already work.
Co-authored-by: François <8672791+mockersf@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
Fixes: #3368
Issue was caused by screen size being: `(0, 0)`.
## Solution
Don't update clusters if the screen size is zero. A better solution might be to not render when minimized, but this works in the meantime.
Co-authored-by: John <startoaster23@gmail.com>
# Objective
Fixes#3379
## Solution
The custom mesh pipelines needed to be specialized on each mesh's primitive topology, as done in `queue_meshes()`
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
Fixes#3352Fixes#3208
## Solution
- Update wgpu to 0.12
- Update naga to 0.8
- Resolve compilation errors
- Remove [[block]] from WGSL shaders (because it is depracated and now wgpu cant parse it)
- Replace `elseif` with `else if` in pbr.wgsl
# Objective
This PR fixes a crash when winit is enabled when there is a camera in the world. Part of #3155
## Solution
In this PR, I removed two unwraps and added an example for regression testing.
# Objective
PBR lighting was broken in the new renderer when using orthographic projections due to the way the depth slicing works for the clusters. Fix it.
## Solution
- The default orthographic projection near plane is 0.0. The perspective projection depth slicing does a division by the near plane which gives a floating point NaN and the clustering all breaks down.
- Orthographic projections have a linear depth mapping, so it made intuitive sense to me to do depth slicing with a linear mapping too. The alternative I saw was to try to handle the near plane being at 0.0 and using the exponential depth slicing, but that felt like a hack that didn't make sense.
- As such, I have added code that detects whether the projection is orthographic based on `projection[3][3] == 1.0` and then implemented the orthographic mapping case throughout (when computing cluster AABBs, and when mapping a view space position (or light) to a cluster id in both the rust and shader code).
## Screenshots
Before:

After:
<img width="1392" alt="Screenshot 2021-12-13 at 16 36 53" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/302146/145847314-6f3a2035-5d87-4896-8032-0c3e35e15b7d.png">
Old renderer (slightly lighter due to slight difference in configured intensity):
<img width="1392" alt="Screenshot 2021-12-13 at 16 42 23" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/302146/145847391-6a5e6fe0-22da-4fc1-a6c7-440543689a63.png">
This makes the [New Bevy Renderer](#2535) the default (and only) renderer. The new renderer isn't _quite_ ready for the final release yet, but I want as many people as possible to start testing it so we can identify bugs and address feedback prior to release.
The examples are all ported over and operational with a few exceptions:
* I removed a good portion of the examples in the `shader` folder. We still have some work to do in order to make these examples possible / ergonomic / worthwhile: #3120 and "high level shader material plugins" are the big ones. This is a temporary measure.
* Temporarily removed the multiple_windows example: doing this properly in the new renderer will require the upcoming "render targets" changes. Same goes for the render_to_texture example.
* Removed z_sort_debug: entity visibility sort info is no longer available in app logic. we could do this on the "render app" side, but i dont consider it a priority.
This implements the most minimal variant of #1843 - a derive for marker trait. This is a prerequisite to more complicated features like statically defined storage type or opt-out component reflection.
In order to make component struct's purpose explicit and avoid misuse, it must be annotated with `#[derive(Component)]` (manual impl is discouraged for compatibility). Right now this is just a marker trait, but in the future it might be expanded. Making this change early allows us to make further changes later without breaking backward compatibility for derive macro users.
This already prevents a lot of issues, like using bundles in `insert` calls. Primitive types are no longer valid components as well. This can be easily worked around by adding newtype wrappers and deriving `Component` for them.
One funny example of prevented bad code (from our own tests) is when an newtype struct or enum variant is used. Previously, it was possible to write `insert(Newtype)` instead of `insert(Newtype(value))`. That code compiled, because function pointers (in this case newtype struct constructor) implement `Send + Sync + 'static`, so we allowed them to be used as components. This is no longer the case and such invalid code will trigger a compile error.
Co-authored-by: = <=>
Co-authored-by: TheRawMeatball <therawmeatball@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Remove all the `.system()` possible.
- Check for remaining missing cases.
## Solution
- Remove all `.system()`, fix compile errors
- 32 calls to `.system()` remains, mostly internals, the few others should be removed after #2446
This is extracted out of eb8f973646476b4a4926ba644a77e2b3a5772159 and includes some additional changes to remove all references to AppBuilder and fix examples that still used App::build() instead of App::new(). In addition I didn't extract the sub app feature as it isn't ready yet.
You can use `git diff --diff-filter=M eb8f973646476b4a4926ba644a77e2b3a5772159` to find all differences in this PR. The `--diff-filtered=M` filters all files added in the original commit but not in this commit away.
Co-Authored-By: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
Fixes the frag shader for unlit materials by correcting the scope of the `#ifndef` to include the light functions. Closes#2190, introduced in #2112.
Tested by changing materials in the the `3d_scene` example to be unlit. Unsure how to prevent future regressions without creating a test case scene that will catch these runtime panics.
This gets rid of multiple unsafe blocks that we had to maintain ourselves, and instead depends on library that's commonly used and supported by the ecosystem. We also get support for glam types for free.
There is still some things to clear up with the `Bytes` trait, but that is a bit more substantial change and can be done separately. Also there are already separate efforts to use `crevice` crate, so I've just added that as a TODO.
Changes to get Bevy to compile with wgpu master.
With this, on a Mac:
* 2d examples look fine
* ~~3d examples crash with an error specific to metal about a compilation error~~
* 3d examples work fine after enabling feature `wgpu/cross`
Feature `wgpu/cross` seems to be needed only on some platforms, not sure how to know which. It was introduced in https://github.com/gfx-rs/wgpu-rs/pull/826
Introduced in #1778, not fixed by #1931
The size of `Lights` buffer currently is :
```rust
16 // (color, `[f32; 4]`)
+ 16 // (number of lights, `f32` encoded as a `[f32; 4]`)
+ 10 // (maximum number of lights)
* ( 16 // (light position, `[f32; 4]`
+ 16 // (color, `[16; 4]`)
+ 4 // (inverse_range_squared, `f32`)
)
-> 392
```
This makes the pbr shader crash when running with Xcode debugger or with the WebGL2 backend. They both expect a buffer sized 512. This can also be seen on desktop by adding a second light to a scene with a color, it's position and color will be wrong.
adding a second light to example `load_gltf`:
```rust
commands
.spawn_bundle(PointLightBundle {
transform: Transform::from_xyz(-3.0, 5.0, -3.0),
point_light: PointLight {
color: Color::BLUE,
..Default::default()
},
..Default::default()
})
.insert(Rotates);
```
before fix:
<img width="1392" alt="Screenshot 2021-04-16 at 19 14 59" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/8672791/115060744-866fb080-9ee8-11eb-8915-f87cc872ad48.png">
after fix:
<img width="1392" alt="Screenshot 2021-04-16 at 19 16 44" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/8672791/115060759-8cfe2800-9ee8-11eb-92c2-d79f39c7b36b.png">
This PR changes `inverse_range_squared` to be a `[f32; 4]` instead of a `f32` to have the expected alignement
Fixes#1921
Buffer was growing with the actual number of lights instead of being limited to the max number of lights.
As it's a query that can be exactly sized, I also switched `count()` to `len()`
I've had problems with compiling and running the pbr example:
```
thread 'main' panicked at 'called `Result::unwrap()` on an `Err` value: Compilation("glslang_shader_preprocess:\nInfo log:\nERROR: 0:40: \'#version\' : must occur first in shader \nERROR: 0:40: \'#version\' : bad profile name; use es, core, or compatibility \nERROR: 0:40: \'#version\' : bad tokens following profile -- expected newline \nERROR: 3 compilation errors. No code generated.\n\n\nDebug log:\n\n")', crates/bevy_render/src/pipeline/pipeline_compiler.rs:161:22
```
I've checked each shader, and only one shader hasn't had `#version` in the first line.
This change fixed my issue.
After an inquiry on Reddit about support for Directional Lights and the unused properties on Light, I wanted to clean it up, to hopefully make it ever so slightly more clear for anyone wanting to add additional light types.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
In shaders, `vec3` should be avoided for `std140` layout, as they take the size of a `vec4` and won't support manual padding by adding an additional `float`.
This change is needed for 3D to work in WebGL2. With it, I get PBR to render
<img width="1407" alt="Screenshot 2021-04-02 at 02 57 14" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/8672791/113368551-5a3c2780-935f-11eb-8c8d-e9ba65b5ee98.png">
Without it, nothing renders... @cart Could this be considered for 0.5 release?
Also, I learned shaders 2 days ago, so don't hesitate to correct any issue or misunderstanding I may have
bevy_webgl2 PR in progress for Bevy 0.5 is here if you want to test: https://github.com/rparrett/bevy_webgl2/pull/1
This PR adds normal maps on top of PBR #1554. Once that PR lands, the changes should look simpler.
Edit: Turned out to be so little extra work, I added metallic/roughness texture too. And occlusion and emissive.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
This is a rebase of StarArawns PBR work from #261 with IngmarBitters work from #1160 cherry-picked on top.
I had to make a few minor changes to make some intermediate commits compile and the end result is not yet 100% what I expected, so there's a bit more work to do.
Co-authored-by: John Mitchell <toasterthegamer@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Ingmar Bitter <ingmar.bitter@gmail.com>
Alternative to #1203 and #1611
Camera bindings have historically been "hacked in". They were _required_ in all shaders and only supported a single Mat4. PBR (#1554) requires the CameraView matrix, but adding this using the "hacked" method forced users to either include all possible camera data in a single binding (#1203) or include all possible bindings (#1611).
This approach instead assigns each "active camera" its own RenderResourceBindings, which are populated by CameraNode. The PassNode then retrieves (and initializes) the relevant bind groups for all render pipelines used by visible entities.
* Enables any number of camera bindings , including zero (with any set or binding number ... set 0 should still be used to avoid rebinds).
* Renames Camera binding to CameraViewProj
* Adds CameraView binding
Idea being this would be easier to grasp for end-users. Problem with the logical defaults is this breaks current setups, because light will become 20 times less bright. But most folks won't have customized this resource or will not have used `..Default::default()` due to lack of other fields.
# Bevy ECS V2
This is a rewrite of Bevy ECS (basically everything but the new executor/schedule, which are already awesome). The overall goal was to improve the performance and versatility of Bevy ECS. Here is a quick bulleted list of changes before we dive into the details:
* Complete World rewrite
* Multiple component storage types:
* Tables: fast cache friendly iteration, slower add/removes (previously called Archetypes)
* Sparse Sets: fast add/remove, slower iteration
* Stateful Queries (caches query results for faster iteration. fragmented iteration is _fast_ now)
* Stateful System Params (caches expensive operations. inspired by @DJMcNab's work in #1364)
* Configurable System Params (users can set configuration when they construct their systems. once again inspired by @DJMcNab's work)
* Archetypes are now "just metadata", component storage is separate
* Archetype Graph (for faster archetype changes)
* Component Metadata
* Configure component storage type
* Retrieve information about component size/type/name/layout/send-ness/etc
* Components are uniquely identified by a densely packed ComponentId
* TypeIds are now totally optional (which should make implementing scripting easier)
* Super fast "for_each" query iterators
* Merged Resources into World. Resources are now just a special type of component
* EntityRef/EntityMut builder apis (more efficient and more ergonomic)
* Fast bitset-backed `Access<T>` replaces old hashmap-based approach everywhere
* Query conflicts are determined by component access instead of archetype component access (to avoid random failures at runtime)
* With/Without are still taken into account for conflicts, so this should still be comfy to use
* Much simpler `IntoSystem` impl
* Significantly reduced the amount of hashing throughout the ecs in favor of Sparse Sets (indexed by densely packed ArchetypeId, ComponentId, BundleId, and TableId)
* Safety Improvements
* Entity reservation uses a normal world reference instead of unsafe transmute
* QuerySets no longer transmute lifetimes
* Made traits "unsafe" where relevant
* More thorough safety docs
* WorldCell
* Exposes safe mutable access to multiple resources at a time in a World
* Replaced "catch all" `System::update_archetypes(world: &World)` with `System::new_archetype(archetype: &Archetype)`
* Simpler Bundle implementation
* Replaced slow "remove_bundle_one_by_one" used as fallback for Commands::remove_bundle with fast "remove_bundle_intersection"
* Removed `Mut<T>` query impl. it is better to only support one way: `&mut T`
* Removed with() from `Flags<T>` in favor of `Option<Flags<T>>`, which allows querying for flags to be "filtered" by default
* Components now have is_send property (currently only resources support non-send)
* More granular module organization
* New `RemovedComponents<T>` SystemParam that replaces `query.removed::<T>()`
* `world.resource_scope()` for mutable access to resources and world at the same time
* WorldQuery and QueryFilter traits unified. FilterFetch trait added to enable "short circuit" filtering. Auto impled for cases that don't need it
* Significantly slimmed down SystemState in favor of individual SystemParam state
* System Commands changed from `commands: &mut Commands` back to `mut commands: Commands` (to allow Commands to have a World reference)
Fixes#1320
## `World` Rewrite
This is a from-scratch rewrite of `World` that fills the niche that `hecs` used to. Yes, this means Bevy ECS is no longer a "fork" of hecs. We're going out our own!
(the only shared code between the projects is the entity id allocator, which is already basically ideal)
A huge shout out to @SanderMertens (author of [flecs](https://github.com/SanderMertens/flecs)) for sharing some great ideas with me (specifically hybrid ecs storage and archetype graphs). He also helped advise on a number of implementation details.
## Component Storage (The Problem)
Two ECS storage paradigms have gained a lot of traction over the years:
* **Archetypal ECS**:
* Stores components in "tables" with static schemas. Each "column" stores components of a given type. Each "row" is an entity.
* Each "archetype" has its own table. Adding/removing an entity's component changes the archetype.
* Enables super-fast Query iteration due to its cache-friendly data layout
* Comes at the cost of more expensive add/remove operations for an Entity's components, because all components need to be copied to the new archetype's "table"
* **Sparse Set ECS**:
* Stores components of the same type in densely packed arrays, which are sparsely indexed by densely packed unsigned integers (Entity ids)
* Query iteration is slower than Archetypal ECS because each entity's component could be at any position in the sparse set. This "random access" pattern isn't cache friendly. Additionally, there is an extra layer of indirection because you must first map the entity id to an index in the component array.
* Adding/removing components is a cheap, constant time operation
Bevy ECS V1, hecs, legion, flec, and Unity DOTS are all "archetypal ecs-es". I personally think "archetypal" storage is a good default for game engines. An entity's archetype doesn't need to change frequently in general, and it creates "fast by default" query iteration (which is a much more common operation). It is also "self optimizing". Users don't need to think about optimizing component layouts for iteration performance. It "just works" without any extra boilerplate.
Shipyard and EnTT are "sparse set ecs-es". They employ "packing" as a way to work around the "suboptimal by default" iteration performance for specific sets of components. This helps, but I didn't think this was a good choice for a general purpose engine like Bevy because:
1. "packs" conflict with each other. If bevy decides to internally pack the Transform and GlobalTransform components, users are then blocked if they want to pack some custom component with Transform.
2. users need to take manual action to optimize
Developers selecting an ECS framework are stuck with a hard choice. Select an "archetypal" framework with "fast iteration everywhere" but without the ability to cheaply add/remove components, or select a "sparse set" framework to cheaply add/remove components but with slower iteration performance.
## Hybrid Component Storage (The Solution)
In Bevy ECS V2, we get to have our cake and eat it too. It now has _both_ of the component storage types above (and more can be added later if needed):
* **Tables** (aka "archetypal" storage)
* The default storage. If you don't configure anything, this is what you get
* Fast iteration by default
* Slower add/remove operations
* **Sparse Sets**
* Opt-in
* Slower iteration
* Faster add/remove operations
These storage types complement each other perfectly. By default Query iteration is fast. If developers know that they want to add/remove a component at high frequencies, they can set the storage to "sparse set":
```rust
world.register_component(
ComponentDescriptor:🆕:<MyComponent>(StorageType::SparseSet)
).unwrap();
```
## Archetypes
Archetypes are now "just metadata" ... they no longer store components directly. They do store:
* The `ComponentId`s of each of the Archetype's components (and that component's storage type)
* Archetypes are uniquely defined by their component layouts
* For example: entities with "table" components `[A, B, C]` _and_ "sparse set" components `[D, E]` will always be in the same archetype.
* The `TableId` associated with the archetype
* For now each archetype has exactly one table (which can have no components),
* There is a 1->Many relationship from Tables->Archetypes. A given table could have any number of archetype components stored in it:
* Ex: an entity with "table storage" components `[A, B, C]` and "sparse set" components `[D, E]` will share the same `[A, B, C]` table as an entity with `[A, B, C]` table component and `[F]` sparse set components.
* This 1->Many relationship is how we preserve fast "cache friendly" iteration performance when possible (more on this later)
* A list of entities that are in the archetype and the row id of the table they are in
* ArchetypeComponentIds
* unique densely packed identifiers for (ArchetypeId, ComponentId) pairs
* used by the schedule executor for cheap system access control
* "Archetype Graph Edges" (see the next section)
## The "Archetype Graph"
Archetype changes in Bevy (and a number of other archetypal ecs-es) have historically been expensive to compute. First, you need to allocate a new vector of the entity's current component ids, add or remove components based on the operation performed, sort it (to ensure it is order-independent), then hash it to find the archetype (if it exists). And thats all before we get to the _already_ expensive full copy of all components to the new table storage.
The solution is to build a "graph" of archetypes to cache these results. @SanderMertens first exposed me to the idea (and he got it from @gjroelofs, who came up with it). They propose adding directed edges between archetypes for add/remove component operations. If `ComponentId`s are densely packed, you can use sparse sets to cheaply jump between archetypes.
Bevy takes this one step further by using add/remove `Bundle` edges instead of `Component` edges. Bevy encourages the use of `Bundles` to group add/remove operations. This is largely for "clearer game logic" reasons, but it also helps cut down on the number of archetype changes required. `Bundles` now also have densely-packed `BundleId`s. This allows us to use a _single_ edge for each bundle operation (rather than needing to traverse N edges ... one for each component). Single component operations are also bundles, so this is strictly an improvement over a "component only" graph.
As a result, an operation that used to be _heavy_ (both for allocations and compute) is now two dirt-cheap array lookups and zero allocations.
## Stateful Queries
World queries are now stateful. This allows us to:
1. Cache archetype (and table) matches
* This resolves another issue with (naive) archetypal ECS: query performance getting worse as the number of archetypes goes up (and fragmentation occurs).
2. Cache Fetch and Filter state
* The expensive parts of fetch/filter operations (such as hashing the TypeId to find the ComponentId) now only happen once when the Query is first constructed
3. Incrementally build up state
* When new archetypes are added, we only process the new archetypes (no need to rebuild state for old archetypes)
As a result, the direct `World` query api now looks like this:
```rust
let mut query = world.query::<(&A, &mut B)>();
for (a, mut b) in query.iter_mut(&mut world) {
}
```
Requiring `World` to generate stateful queries (rather than letting the `QueryState` type be constructed separately) allows us to ensure that _all_ queries are properly initialized (and the relevant world state, such as ComponentIds). This enables QueryState to remove branches from its operations that check for initialization status (and also enables query.iter() to take an immutable world reference because it doesn't need to initialize anything in world).
However in systems, this is a non-breaking change. State management is done internally by the relevant SystemParam.
## Stateful SystemParams
Like Queries, `SystemParams` now also cache state. For example, `Query` system params store the "stateful query" state mentioned above. Commands store their internal `CommandQueue`. This means you can now safely use as many separate `Commands` parameters in your system as you want. `Local<T>` system params store their `T` value in their state (instead of in Resources).
SystemParam state also enabled a significant slim-down of SystemState. It is much nicer to look at now.
Per-SystemParam state naturally insulates us from an "aliased mut" class of errors we have hit in the past (ex: using multiple `Commands` system params).
(credit goes to @DJMcNab for the initial idea and draft pr here #1364)
## Configurable SystemParams
@DJMcNab also had the great idea to make SystemParams configurable. This allows users to provide some initial configuration / values for system parameters (when possible). Most SystemParams have no config (the config type is `()`), but the `Local<T>` param now supports user-provided parameters:
```rust
fn foo(value: Local<usize>) {
}
app.add_system(foo.system().config(|c| c.0 = Some(10)));
```
## Uber Fast "for_each" Query Iterators
Developers now have the choice to use a fast "for_each" iterator, which yields ~1.5-3x iteration speed improvements for "fragmented iteration", and minor ~1.2x iteration speed improvements for unfragmented iteration.
```rust
fn system(query: Query<(&A, &mut B)>) {
// you now have the option to do this for a speed boost
query.for_each_mut(|(a, mut b)| {
});
// however normal iterators are still available
for (a, mut b) in query.iter_mut() {
}
}
```
I think in most cases we should continue to encourage "normal" iterators as they are more flexible and more "rust idiomatic". But when that extra "oomf" is needed, it makes sense to use `for_each`.
We should also consider using `for_each` for internal bevy systems to give our users a nice speed boost (but that should be a separate pr).
## Component Metadata
`World` now has a `Components` collection, which is accessible via `world.components()`. This stores mappings from `ComponentId` to `ComponentInfo`, as well as `TypeId` to `ComponentId` mappings (where relevant). `ComponentInfo` stores information about the component, such as ComponentId, TypeId, memory layout, send-ness (currently limited to resources), and storage type.
## Significantly Cheaper `Access<T>`
We used to use `TypeAccess<TypeId>` to manage read/write component/archetype-component access. This was expensive because TypeIds must be hashed and compared individually. The parallel executor got around this by "condensing" type ids into bitset-backed access types. This worked, but it had to be re-generated from the `TypeAccess<TypeId>`sources every time archetypes changed.
This pr removes TypeAccess in favor of faster bitset access everywhere. We can do this thanks to the move to densely packed `ComponentId`s and `ArchetypeComponentId`s.
## Merged Resources into World
Resources had a lot of redundant functionality with Components. They stored typed data, they had access control, they had unique ids, they were queryable via SystemParams, etc. In fact the _only_ major difference between them was that they were unique (and didn't correlate to an entity).
Separate resources also had the downside of requiring a separate set of access controls, which meant the parallel executor needed to compare more bitsets per system and manage more state.
I initially got the "separate resources" idea from `legion`. I think that design was motivated by the fact that it made the direct world query/resource lifetime interactions more manageable. It certainly made our lives easier when using Resources alongside hecs/bevy_ecs. However we already have a construct for safely and ergonomically managing in-world lifetimes: systems (which use `Access<T>` internally).
This pr merges Resources into World:
```rust
world.insert_resource(1);
world.insert_resource(2.0);
let a = world.get_resource::<i32>().unwrap();
let mut b = world.get_resource_mut::<f64>().unwrap();
*b = 3.0;
```
Resources are now just a special kind of component. They have their own ComponentIds (and their own resource TypeId->ComponentId scope, so they don't conflict wit components of the same type). They are stored in a special "resource archetype", which stores components inside the archetype using a new `unique_components` sparse set (note that this sparse set could later be used to implement Tags). This allows us to keep the code size small by reusing existing datastructures (namely Column, Archetype, ComponentFlags, and ComponentInfo). This allows us the executor to use a single `Access<ArchetypeComponentId>` per system. It should also make scripting language integration easier.
_But_ this merge did create problems for people directly interacting with `World`. What if you need mutable access to multiple resources at the same time? `world.get_resource_mut()` borrows World mutably!
## WorldCell
WorldCell applies the `Access<ArchetypeComponentId>` concept to direct world access:
```rust
let world_cell = world.cell();
let a = world_cell.get_resource_mut::<i32>().unwrap();
let b = world_cell.get_resource_mut::<f64>().unwrap();
```
This adds cheap runtime checks (a sparse set lookup of `ArchetypeComponentId` and a counter) to ensure that world accesses do not conflict with each other. Each operation returns a `WorldBorrow<'w, T>` or `WorldBorrowMut<'w, T>` wrapper type, which will release the relevant ArchetypeComponentId resources when dropped.
World caches the access sparse set (and only one cell can exist at a time), so `world.cell()` is a cheap operation.
WorldCell does _not_ use atomic operations. It is non-send, does a mutable borrow of world to prevent other accesses, and uses a simple `Rc<RefCell<ArchetypeComponentAccess>>` wrapper in each WorldBorrow pointer.
The api is currently limited to resource access, but it can and should be extended to queries / entity component access.
## Resource Scopes
WorldCell does not yet support component queries, and even when it does there are sometimes legitimate reasons to want a mutable world ref _and_ a mutable resource ref (ex: bevy_render and bevy_scene both need this). In these cases we could always drop down to the unsafe `world.get_resource_unchecked_mut()`, but that is not ideal!
Instead developers can use a "resource scope"
```rust
world.resource_scope(|world: &mut World, a: &mut A| {
})
```
This temporarily removes the `A` resource from `World`, provides mutable pointers to both, and re-adds A to World when finished. Thanks to the move to ComponentIds/sparse sets, this is a cheap operation.
If multiple resources are required, scopes can be nested. We could also consider adding a "resource tuple" to the api if this pattern becomes common and the boilerplate gets nasty.
## Query Conflicts Use ComponentId Instead of ArchetypeComponentId
For safety reasons, systems cannot contain queries that conflict with each other without wrapping them in a QuerySet. On bevy `main`, we use ArchetypeComponentIds to determine conflicts. This is nice because it can take into account filters:
```rust
// these queries will never conflict due to their filters
fn filter_system(a: Query<&mut A, With<B>>, b: Query<&mut B, Without<B>>) {
}
```
But it also has a significant downside:
```rust
// these queries will not conflict _until_ an entity with A, B, and C is spawned
fn maybe_conflicts_system(a: Query<(&mut A, &C)>, b: Query<(&mut A, &B)>) {
}
```
The system above will panic at runtime if an entity with A, B, and C is spawned. This makes it hard to trust that your game logic will run without crashing.
In this pr, I switched to using `ComponentId` instead. This _is_ more constraining. `maybe_conflicts_system` will now always fail, but it will do it consistently at startup. Naively, it would also _disallow_ `filter_system`, which would be a significant downgrade in usability. Bevy has a number of internal systems that rely on disjoint queries and I expect it to be a common pattern in userspace.
To resolve this, I added a new `FilteredAccess<T>` type, which wraps `Access<T>` and adds with/without filters. If two `FilteredAccess` have with/without values that prove they are disjoint, they will no longer conflict.
## EntityRef / EntityMut
World entity operations on `main` require that the user passes in an `entity` id to each operation:
```rust
let entity = world.spawn((A, )); // create a new entity with A
world.get::<A>(entity);
world.insert(entity, (B, C));
world.insert_one(entity, D);
```
This means that each operation needs to look up the entity location / verify its validity. The initial spawn operation also requires a Bundle as input. This can be awkward when no components are required (or one component is required).
These operations have been replaced by `EntityRef` and `EntityMut`, which are "builder-style" wrappers around world that provide read and read/write operations on a single, pre-validated entity:
```rust
// spawn now takes no inputs and returns an EntityMut
let entity = world.spawn()
.insert(A) // insert a single component into the entity
.insert_bundle((B, C)) // insert a bundle of components into the entity
.id() // id returns the Entity id
// Returns EntityMut (or panics if the entity does not exist)
world.entity_mut(entity)
.insert(D)
.insert_bundle(SomeBundle::default());
{
// returns EntityRef (or panics if the entity does not exist)
let d = world.entity(entity)
.get::<D>() // gets the D component
.unwrap();
// world.get still exists for ergonomics
let d = world.get::<D>(entity).unwrap();
}
// These variants return Options if you want to check existence instead of panicing
world.get_entity_mut(entity)
.unwrap()
.insert(E);
if let Some(entity_ref) = world.get_entity(entity) {
let d = entity_ref.get::<D>().unwrap();
}
```
This _does not_ affect the current Commands api or terminology. I think that should be a separate conversation as that is a much larger breaking change.
## Safety Improvements
* Entity reservation in Commands uses a normal world borrow instead of an unsafe transmute
* QuerySets no longer transmutes lifetimes
* Made traits "unsafe" when implementing a trait incorrectly could cause unsafety
* More thorough safety docs
## RemovedComponents SystemParam
The old approach to querying removed components: `query.removed:<T>()` was confusing because it had no connection to the query itself. I replaced it with the following, which is both clearer and allows us to cache the ComponentId mapping in the SystemParamState:
```rust
fn system(removed: RemovedComponents<T>) {
for entity in removed.iter() {
}
}
```
## Simpler Bundle implementation
Bundles are no longer responsible for sorting (or deduping) TypeInfo. They are just a simple ordered list of component types / data. This makes the implementation smaller and opens the door to an easy "nested bundle" implementation in the future (which i might even add in this pr). Duplicate detection is now done once per bundle type by World the first time a bundle is used.
## Unified WorldQuery and QueryFilter types
(don't worry they are still separate type _parameters_ in Queries .. this is a non-breaking change)
WorldQuery and QueryFilter were already basically identical apis. With the addition of `FetchState` and more storage-specific fetch methods, the overlap was even clearer (and the redundancy more painful).
QueryFilters are now just `F: WorldQuery where F::Fetch: FilterFetch`. FilterFetch requires `Fetch<Item = bool>` and adds new "short circuit" variants of fetch methods. This enables a filter tuple like `(With<A>, Without<B>, Changed<C>)` to stop evaluating the filter after the first mismatch is encountered. FilterFetch is automatically implemented for `Fetch` implementations that return bool.
This forces fetch implementations that return things like `(bool, bool, bool)` (such as the filter above) to manually implement FilterFetch and decide whether or not to short-circuit.
## More Granular Modules
World no longer globs all of the internal modules together. It now exports `core`, `system`, and `schedule` separately. I'm also considering exporting `core` submodules directly as that is still pretty "glob-ey" and unorganized (feedback welcome here).
## Remaining Draft Work (to be done in this pr)
* ~~panic on conflicting WorldQuery fetches (&A, &mut A)~~
* ~~bevy `main` and hecs both currently allow this, but we should protect against it if possible~~
* ~~batch_iter / par_iter (currently stubbed out)~~
* ~~ChangedRes~~
* ~~I skipped this while we sort out #1313. This pr should be adapted to account for whatever we land on there~~.
* ~~The `Archetypes` and `Tables` collections use hashes of sorted lists of component ids to uniquely identify each archetype/table. This hash is then used as the key in a HashMap to look up the relevant ArchetypeId or TableId. (which doesn't handle hash collisions properly)~~
* ~~It is currently unsafe to generate a Query from "World A", then use it on "World B" (despite the api claiming it is safe). We should probably close this gap. This could be done by adding a randomly generated WorldId to each world, then storing that id in each Query. They could then be compared to each other on each `query.do_thing(&world)` operation. This _does_ add an extra branch to each query operation, so I'm open to other suggestions if people have them.~~
* ~~Nested Bundles (if i find time)~~
## Potential Future Work
* Expand WorldCell to support queries.
* Consider not allocating in the empty archetype on `world.spawn()`
* ex: return something like EntityMutUninit, which turns into EntityMut after an `insert` or `insert_bundle` op
* this actually regressed performance last time i tried it, but in theory it should be faster
* Optimize SparseSet::insert (see `PERF` comment on insert)
* Replace SparseArray `Option<T>` with T::MAX to cut down on branching
* would enable cheaper get_unchecked() operations
* upstream fixedbitset optimizations
* fixedbitset could be allocation free for small block counts (store blocks in a SmallVec)
* fixedbitset could have a const constructor
* Consider implementing Tags (archetype-specific by-value data that affects archetype identity)
* ex: ArchetypeA could have `[A, B, C]` table components and `[D(1)]` "tag" component. ArchetypeB could have `[A, B, C]` table components and a `[D(2)]` tag component. The archetypes are different, despite both having D tags because the value inside D is different.
* this could potentially build on top of the `archetype.unique_components` added in this pr for resource storage.
* Consider reverting `all_tuples` proc macro in favor of the old `macro_rules` implementation
* all_tuples is more flexible and produces cleaner documentation (the macro_rules version produces weird type parameter orders due to parser constraints)
* but unfortunately all_tuples also appears to make Rust Analyzer sad/slow when working inside of `bevy_ecs` (does not affect user code)
* Consider "resource queries" and/or "mixed resource and entity component queries" as an alternative to WorldCell
* this is basically just "systems" so maybe it's not worth it
* Add more world ops
* `world.clear()`
* `world.reserve<T: Bundle>(count: usize)`
* Try using the old archetype allocation strategy (allocate new memory on resize and copy everything over). I expect this to improve batch insertion performance at the cost of unbatched performance. But thats just a guess. I'm not an allocation perf pro :)
* Adapt Commands apis for consistency with new World apis
## Benchmarks
key:
* `bevy_old`: bevy `main` branch
* `bevy`: this branch
* `_foreach`: uses an optimized for_each iterator
* ` _sparse`: uses sparse set storage (if unspecified assume table storage)
* `_system`: runs inside a system (if unspecified assume test happens via direct world ops)
### Simple Insert (from ecs_bench_suite)
### Simpler Iter (from ecs_bench_suite)
### Fragment Iter (from ecs_bench_suite)
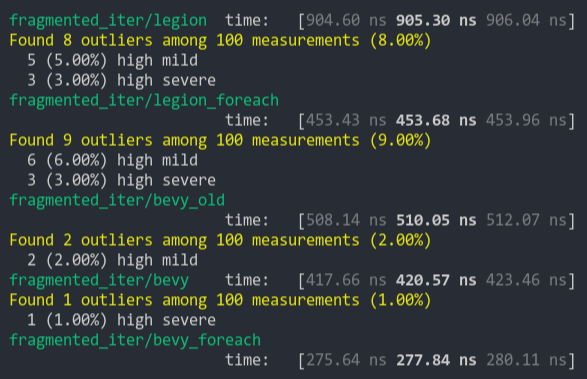
### Sparse Fragmented Iter
Iterate a query that matches 5 entities from a single matching archetype, but there are 100 unmatching archetypes
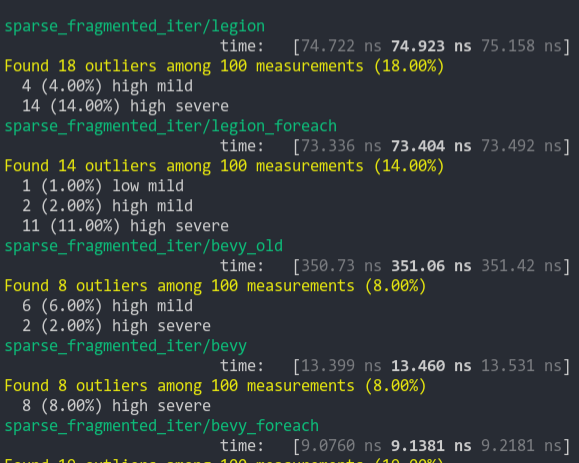
### Schedule (from ecs_bench_suite)
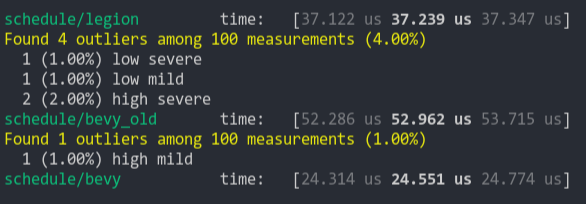
### Add Remove Component (from ecs_bench_suite)
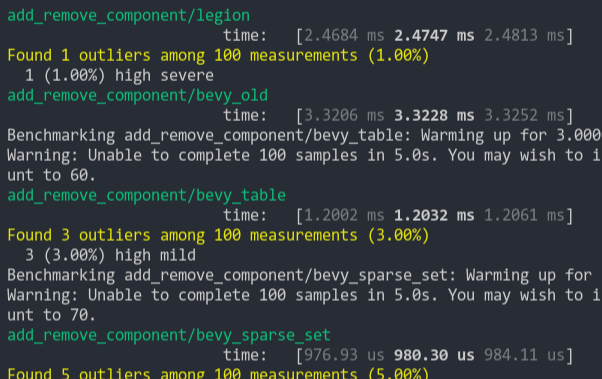
### Add Remove Component Big
Same as the test above, but each entity has 5 "large" matrix components and 1 "large" matrix component is added and removed
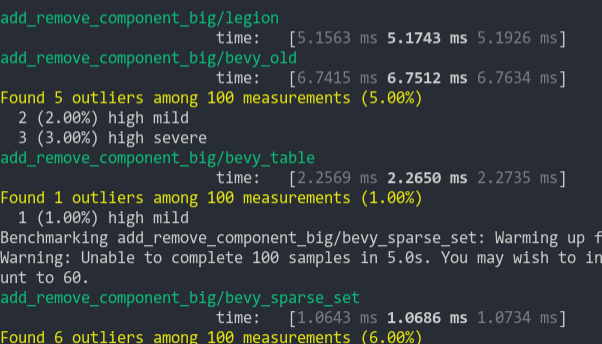
### Get Component
Looks up a single component value a large number of times
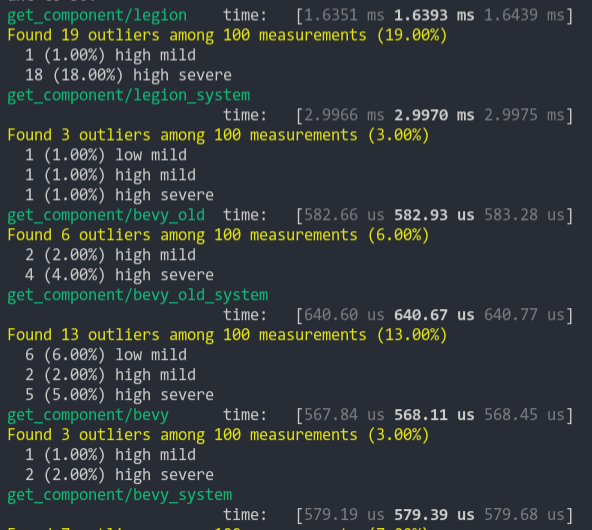
Transform and GlobalTransform are now Similarities.
This resolves precision errors and simplifies the api
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>