# Objective
Fixes#7295
Should we maybe default to 4x if 2x/8x is selected but not supported?
---
## Changelog
- Added 2x and 8x sample counts for MSAA.
# Objective
- Environment maps use these formats, and in the future rendering LUTs will need textures loaded by default in the engine
## Solution
- Make ktx2 and zstd part of the default feature
- Let examples assume these features are enabled
---
## Changelog
- `ktx2` and `zstd` are now party of bevy's default enabled features
## Migration Guide
- If you used the `ktx2` or `zstd` features, you no longer need to explicitly enable them, as they are now part of bevy's default enabled features
# Objective
- Required features were added to some examples in #7051 even though those features aren't the main focus of the examples
- Don't require features on examples that are useful without them
## Solution
- Remove required features on examples `load_gltf` and `scene_viewer`, but log a warning when they are not enabled
# Objective
There was issue #191 requesting subdivisions on the shape::Plane.
I also could have used this recently. I then write the solution.
Fixes #191
## Solution
I changed the shape::Plane to include subdivisions field and the code to create the subdivisions. I don't know how people are counting subdivisions so as I put in the doc comments 0 subdivisions results in the original geometry of the Plane.
Greater then 0 results in the number of lines dividing the plane.
I didn't know if it would be better to create a new struct that implemented this feature, say SubdivisionPlane or change Plane. I decided on changing Plane as that was what the original issue was.
It would be trivial to alter this to use another struct instead of altering Plane.
The issues of migration, although small, would be eliminated if a new struct was implemented.
## Changelog
### Added
Added subdivisions field to shape::Plane
## Migration Guide
All the examples needed to be updated to initalize the subdivisions field.
Also there were two tests in tests/window that need to be updated.
A user would have to update all their uses of shape::Plane to initalize the subdivisions field.
(Before)

(After)

# Objective
- Improve lighting; especially reflections.
- Closes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/4581.
## Solution
- Implement environment maps, providing better ambient light.
- Add microfacet multibounce approximation for specular highlights from Filament.
- Occlusion is no longer incorrectly applied to direct lighting. It now only applies to diffuse indirect light. Unsure if it's also supposed to apply to specular indirect light - the glTF specification just says "indirect light". In the case of ambient occlusion, for instance, that's usually only calculated as diffuse though. For now, I'm choosing to apply this just to indirect diffuse light, and not specular.
- Modified the PBR example to use an environment map, and have labels.
- Added `FallbackImageCubemap`.
## Implementation
- IBL technique references can be found in environment_map.wgsl.
- It's more accurate to use a LUT for the scale/bias. Filament has a good reference on generating this LUT. For now, I just used an analytic approximation.
- For now, environment maps must first be prefiltered outside of bevy using a 3rd party tool. See the `EnvironmentMap` documentation.
- Eventually, we should have our own prefiltering code, so that we can have dynamically changing environment maps, as well as let users drop in an HDR image and use asset preprocessing to create the needed textures using only bevy.
---
## Changelog
- Added an `EnvironmentMapLight` camera component that adds additional ambient light to a scene.
- StandardMaterials will now appear brighter and more saturated at high roughness, due to internal material changes. This is more physically correct.
- Fixed StandardMaterial occlusion being incorrectly applied to direct lighting.
- Added `FallbackImageCubemap`.
Co-authored-by: IceSentry <c.giguere42@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: James Liu <contact@jamessliu.com>
Co-authored-by: Rob Parrett <robparrett@gmail.com>
# Objective
NOTE: This depends on #7267 and should not be merged until #7267 is merged. If you are reviewing this before that is merged, I highly recommend viewing the Base Sets commit instead of trying to find my changes amongst those from #7267.
"Default sets" as described by the [Stageless RFC](https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/pull/45) have some [unfortunate consequences](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/discussions/7365).
## Solution
This adds "base sets" as a variant of `SystemSet`:
A set is a "base set" if `SystemSet::is_base` returns `true`. Typically this will be opted-in to using the `SystemSet` derive:
```rust
#[derive(SystemSet, Clone, Hash, Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
#[system_set(base)]
enum MyBaseSet {
A,
B,
}
```
**Base sets are exclusive**: a system can belong to at most one "base set". Adding a system to more than one will result in an error. When possible we fail immediately during system-config-time with a nice file + line number. For the more nested graph-ey cases, this will fail at the final schedule build.
**Base sets cannot belong to other sets**: this is where the word "base" comes from
Systems and Sets can only be added to base sets using `in_base_set`. Calling `in_set` with a base set will fail. As will calling `in_base_set` with a normal set.
```rust
app.add_system(foo.in_base_set(MyBaseSet::A))
// X must be a normal set ... base sets cannot be added to base sets
.configure_set(X.in_base_set(MyBaseSet::A))
```
Base sets can still be configured like normal sets:
```rust
app.add_system(MyBaseSet::B.after(MyBaseSet::Ap))
```
The primary use case for base sets is enabling a "default base set":
```rust
schedule.set_default_base_set(CoreSet::Update)
// this will belong to CoreSet::Update by default
.add_system(foo)
// this will override the default base set with PostUpdate
.add_system(bar.in_base_set(CoreSet::PostUpdate))
```
This allows us to build apis that work by default in the standard Bevy style. This is a rough analog to the "default stage" model, but it use the new "stageless sets" model instead, with all of the ordering flexibility (including exclusive systems) that it provides.
---
## Changelog
- Added "base sets" and ported CoreSet to use them.
## Migration Guide
TODO
Huge thanks to @maniwani, @devil-ira, @hymm, @cart, @superdump and @jakobhellermann for the help with this PR.
# Objective
- Followup #6587.
- Minimal integration for the Stageless Scheduling RFC: https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/pull/45
## Solution
- [x] Remove old scheduling module
- [x] Migrate new methods to no longer use extension methods
- [x] Fix compiler errors
- [x] Fix benchmarks
- [x] Fix examples
- [x] Fix docs
- [x] Fix tests
## Changelog
### Added
- a large number of methods on `App` to work with schedules ergonomically
- the `CoreSchedule` enum
- `App::add_extract_system` via the `RenderingAppExtension` trait extension method
- the private `prepare_view_uniforms` system now has a public system set for scheduling purposes, called `ViewSet::PrepareUniforms`
### Removed
- stages, and all code that mentions stages
- states have been dramatically simplified, and no longer use a stack
- `RunCriteriaLabel`
- `AsSystemLabel` trait
- `on_hierarchy_reports_enabled` run criteria (now just uses an ad hoc resource checking run condition)
- systems in `RenderSet/Stage::Extract` no longer warn when they do not read data from the main world
- `RunCriteriaLabel`
- `transform_propagate_system_set`: this was a nonstandard pattern that didn't actually provide enough control. The systems are already `pub`: the docs have been updated to ensure that the third-party usage is clear.
### Changed
- `System::default_labels` is now `System::default_system_sets`.
- `App::add_default_labels` is now `App::add_default_sets`
- `CoreStage` and `StartupStage` enums are now `CoreSet` and `StartupSet`
- `App::add_system_set` was renamed to `App::add_systems`
- The `StartupSchedule` label is now defined as part of the `CoreSchedules` enum
- `.label(SystemLabel)` is now referred to as `.in_set(SystemSet)`
- `SystemLabel` trait was replaced by `SystemSet`
- `SystemTypeIdLabel<T>` was replaced by `SystemSetType<T>`
- The `ReportHierarchyIssue` resource now has a public constructor (`new`), and implements `PartialEq`
- Fixed time steps now use a schedule (`CoreSchedule::FixedTimeStep`) rather than a run criteria.
- Adding rendering extraction systems now panics rather than silently failing if no subapp with the `RenderApp` label is found.
- the `calculate_bounds` system, with the `CalculateBounds` label, is now in `CoreSet::Update`, rather than in `CoreSet::PostUpdate` before commands are applied.
- `SceneSpawnerSystem` now runs under `CoreSet::Update`, rather than `CoreStage::PreUpdate.at_end()`.
- `bevy_pbr::add_clusters` is no longer an exclusive system
- the top level `bevy_ecs::schedule` module was replaced with `bevy_ecs::scheduling`
- `tick_global_task_pools_on_main_thread` is no longer run as an exclusive system. Instead, it has been replaced by `tick_global_task_pools`, which uses a `NonSend` resource to force running on the main thread.
## Migration Guide
- Calls to `.label(MyLabel)` should be replaced with `.in_set(MySet)`
- Stages have been removed. Replace these with system sets, and then add command flushes using the `apply_system_buffers` exclusive system where needed.
- The `CoreStage`, `StartupStage, `RenderStage` and `AssetStage` enums have been replaced with `CoreSet`, `StartupSet, `RenderSet` and `AssetSet`. The same scheduling guarantees have been preserved.
- Systems are no longer added to `CoreSet::Update` by default. Add systems manually if this behavior is needed, although you should consider adding your game logic systems to `CoreSchedule::FixedTimestep` instead for more reliable framerate-independent behavior.
- Similarly, startup systems are no longer part of `StartupSet::Startup` by default. In most cases, this won't matter to you.
- For example, `add_system_to_stage(CoreStage::PostUpdate, my_system)` should be replaced with
- `add_system(my_system.in_set(CoreSet::PostUpdate)`
- When testing systems or otherwise running them in a headless fashion, simply construct and run a schedule using `Schedule::new()` and `World::run_schedule` rather than constructing stages
- Run criteria have been renamed to run conditions. These can now be combined with each other and with states.
- Looping run criteria and state stacks have been removed. Use an exclusive system that runs a schedule if you need this level of control over system control flow.
- For app-level control flow over which schedules get run when (such as for rollback networking), create your own schedule and insert it under the `CoreSchedule::Outer` label.
- Fixed timesteps are now evaluated in a schedule, rather than controlled via run criteria. The `run_fixed_timestep` system runs this schedule between `CoreSet::First` and `CoreSet::PreUpdate` by default.
- Command flush points introduced by `AssetStage` have been removed. If you were relying on these, add them back manually.
- Adding extract systems is now typically done directly on the main app. Make sure the `RenderingAppExtension` trait is in scope, then call `app.add_extract_system(my_system)`.
- the `calculate_bounds` system, with the `CalculateBounds` label, is now in `CoreSet::Update`, rather than in `CoreSet::PostUpdate` before commands are applied. You may need to order your movement systems to occur before this system in order to avoid system order ambiguities in culling behavior.
- the `RenderLabel` `AppLabel` was renamed to `RenderApp` for clarity
- `App::add_state` now takes 0 arguments: the starting state is set based on the `Default` impl.
- Instead of creating `SystemSet` containers for systems that run in stages, simply use `.on_enter::<State::Variant>()` or its `on_exit` or `on_update` siblings.
- `SystemLabel` derives should be replaced with `SystemSet`. You will also need to add the `Debug`, `PartialEq`, `Eq`, and `Hash` traits to satisfy the new trait bounds.
- `with_run_criteria` has been renamed to `run_if`. Run criteria have been renamed to run conditions for clarity, and should now simply return a bool.
- States have been dramatically simplified: there is no longer a "state stack". To queue a transition to the next state, call `NextState::set`
## TODO
- [x] remove dead methods on App and World
- [x] add `App::add_system_to_schedule` and `App::add_systems_to_schedule`
- [x] avoid adding the default system set at inappropriate times
- [x] remove any accidental cycles in the default plugins schedule
- [x] migrate benchmarks
- [x] expose explicit labels for the built-in command flush points
- [x] migrate engine code
- [x] remove all mentions of stages from the docs
- [x] verify docs for States
- [x] fix uses of exclusive systems that use .end / .at_start / .before_commands
- [x] migrate RenderStage and AssetStage
- [x] migrate examples
- [x] ensure that transform propagation is exported in a sufficiently public way (the systems are already pub)
- [x] ensure that on_enter schedules are run at least once before the main app
- [x] re-enable opt-in to execution order ambiguities
- [x] revert change to `update_bounds` to ensure it runs in `PostUpdate`
- [x] test all examples
- [x] unbreak directional lights
- [x] unbreak shadows (see 3d_scene, 3d_shape, lighting, transparaency_3d examples)
- [x] game menu example shows loading screen and menu simultaneously
- [x] display settings menu is a blank screen
- [x] `without_winit` example panics
- [x] ensure all tests pass
- [x] SubApp doc test fails
- [x] runs_spawn_local tasks fails
- [x] [Fix panic_when_hierachy_cycle test hanging](https://github.com/alice-i-cecile/bevy/pull/120)
## Points of Difficulty and Controversy
**Reviewers, please give feedback on these and look closely**
1. Default sets, from the RFC, have been removed. These added a tremendous amount of implicit complexity and result in hard to debug scheduling errors. They're going to be tackled in the form of "base sets" by @cart in a followup.
2. The outer schedule controls which schedule is run when `App::update` is called.
3. I implemented `Label for `Box<dyn Label>` for our label types. This enables us to store schedule labels in concrete form, and then later run them. I ran into the same set of problems when working with one-shot systems. We've previously investigated this pattern in depth, and it does not appear to lead to extra indirection with nested boxes.
4. `SubApp::update` simply runs the default schedule once. This sucks, but this whole API is incomplete and this was the minimal changeset.
5. `time_system` and `tick_global_task_pools_on_main_thread` no longer use exclusive systems to attempt to force scheduling order
6. Implemetnation strategy for fixed timesteps
7. `AssetStage` was migrated to `AssetSet` without reintroducing command flush points. These did not appear to be used, and it's nice to remove these bottlenecks.
8. Migration of `bevy_render/lib.rs` and pipelined rendering. The logic here is unusually tricky, as we have complex scheduling requirements.
## Future Work (ideally before 0.10)
- Rename schedule_v3 module to schedule or scheduling
- Add a derive macro to states, and likely a `EnumIter` trait of some form
- Figure out what exactly to do with the "systems added should basically work by default" problem
- Improve ergonomics for working with fixed timesteps and states
- Polish FixedTime API to match Time
- Rebase and merge #7415
- Resolve all internal ambiguities (blocked on better tools, especially #7442)
- Add "base sets" to replace the removed default sets.
# Objective
- Improve ergonomics / documentation of cascaded shadow maps
- Allow for the customization of the nearest shadowing distance.
- Fixes#7393
- Fixes#7362
## Solution
- Introduce `CascadeShadowConfigBuilder`
- Tweak various example cascade settings for better quality.
---
## Changelog
- Made examples look nicer under cascaded shadow maps.
- Introduce `CascadeShadowConfigBuilder` to help with creating `CascadeShadowConfig`
## Migration Guide
- Configure settings for cascaded shadow maps for directional lights using the newly introduced `CascadeShadowConfigBuilder`.
Co-authored-by: Robert Swain <robert.swain@gmail.com>
# Objective
Update Bevy to wgpu 0.15.
## Changelog
- Update to wgpu 0.15, wgpu-hal 0.15.1, and naga 0.11
- Users can now use the [DirectX Shader Compiler](https://github.com/microsoft/DirectXShaderCompiler) (DXC) on Windows with DX12 for faster shader compilation and ShaderModel 6.0+ support (requires `dxcompiler.dll` and `dxil.dll`, which are included in DXC downloads from [here](https://github.com/microsoft/DirectXShaderCompiler/releases/latest))
## Migration Guide
### WGSL Top-Level `let` is now `const`
All top level constants are now declared with `const`, catching up with the wgsl spec.
`let` is no longer allowed at the global scope, only within functions.
```diff
-let SOME_CONSTANT = 12.0;
+const SOME_CONSTANT = 12.0;
```
#### `TextureDescriptor` and `SurfaceConfiguration` now requires a `view_formats` field
The new `view_formats` field in the `TextureDescriptor` is used to specify a list of formats the texture can be re-interpreted to in a texture view. Currently only changing srgb-ness is allowed (ex. `Rgba8Unorm` <=> `Rgba8UnormSrgb`). You should set `view_formats` to `&[]` (empty) unless you have a specific reason not to.
#### The DirectX Shader Compiler (DXC) is now supported on DX12
DXC is now the default shader compiler when using the DX12 backend. DXC is Microsoft's replacement for their legacy FXC compiler, and is faster, less buggy, and allows for modern shader features to be used (ShaderModel 6.0+). DXC requires `dxcompiler.dll` and `dxil.dll` to be available, otherwise it will log a warning and fall back to FXC.
You can get `dxcompiler.dll` and `dxil.dll` by downloading the latest release from [Microsoft's DirectXShaderCompiler github repo](https://github.com/microsoft/DirectXShaderCompiler/releases/latest) and copying them into your project's root directory. These must be included when you distribute your Bevy game/app/etc if you plan on supporting the DX12 backend and are using DXC.
`WgpuSettings` now has a `dx12_shader_compiler` field which can be used to choose between either FXC or DXC (if you pass None for the paths for DXC, it will check for the .dlls in the working directory).
<img width="1392" alt="image" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/418473/203873533-44c029af-13b7-4740-8ea3-af96bd5867c9.png">
<img width="1392" alt="image" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/418473/203873549-36be7a23-b341-42a2-8a9f-ceea8ac7a2b8.png">
# Objective
- Add support for the “classic” distance fog effect, as well as a more advanced atmospheric fog effect.
## Solution
This PR:
- Introduces a new `FogSettings` component that controls distance fog per-camera.
- Adds support for three widely used “traditional” fog falloff modes: `Linear`, `Exponential` and `ExponentialSquared`, as well as a more advanced `Atmospheric` fog;
- Adds support for directional light influence over fog color;
- Extracts fog via `ExtractComponent`, then uses a prepare system that sets up a new dynamic uniform struct (`Fog`), similar to other mesh view types;
- Renders fog in PBR material shader, as a final adjustment to the `output_color`, after PBR is computed (but before tone mapping);
- Adds a new `StandardMaterial` flag to enable fog; (`fog_enabled`)
- Adds convenience methods for easier artistic control when creating non-linear fog types;
- Adds documentation around fog.
---
## Changelog
### Added
- Added support for distance-based fog effects for PBR materials, controllable per-camera via the new `FogSettings` component;
- Added `FogFalloff` enum for selecting between three widely used “traditional” fog falloff modes: `Linear`, `Exponential` and `ExponentialSquared`, as well as a more advanced `Atmospheric` fog;
Co-authored-by: Robert Swain <robert.swain@gmail.com>
# Objective
Implements cascaded shadow maps for directional lights, which produces better quality shadows without needing excessively large shadow maps.
Fixes#3629
Before
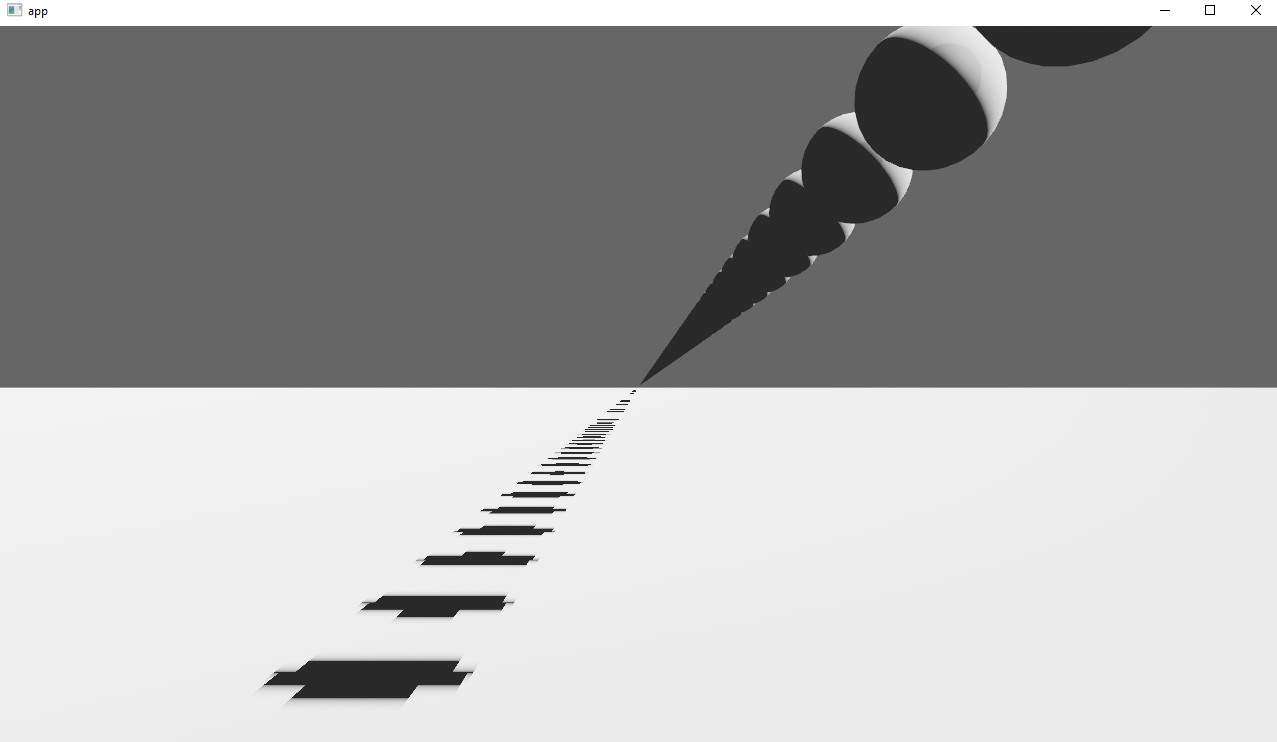
After
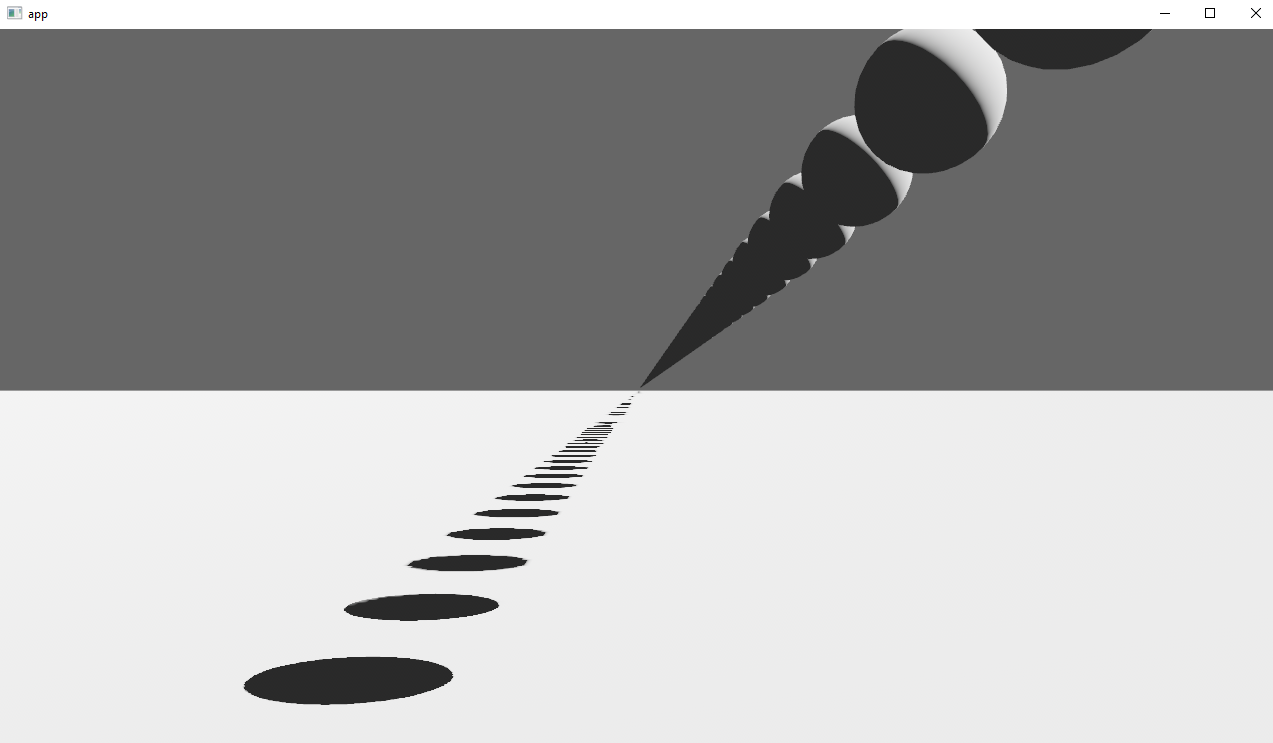
## Solution
Rather than rendering a single shadow map for directional light, the view frustum is divided into a series of cascades, each of which gets its own shadow map. The correct cascade is then sampled for shadow determination.
---
## Changelog
Directional lights now use cascaded shadow maps for improved shadow quality.
## Migration Guide
You no longer have to manually specify a `shadow_projection` for a directional light, and these settings should be removed. If customization of how cascaded shadow maps work is desired, modify the `CascadeShadowConfig` component instead.
# Objective
- This PR adds support for blend modes to the PBR `StandardMaterial`.
<img width="1392" alt="Screenshot 2022-11-18 at 20 00 56" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/418473/202820627-0636219a-a1e5-437a-b08b-b08c6856bf9c.png">
<img width="1392" alt="Screenshot 2022-11-18 at 20 01 01" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/418473/202820615-c8d43301-9a57-49c4-bd21-4ae343c3e9ec.png">
## Solution
- The existing `AlphaMode` enum is extended, adding three more modes: `AlphaMode::Premultiplied`, `AlphaMode::Add` and `AlphaMode::Multiply`;
- All new modes are rendered in the existing `Transparent3d` phase;
- The existing mesh flags for alpha mode are reorganized for a more compact/efficient representation, and new values are added;
- `MeshPipelineKey::TRANSPARENT_MAIN_PASS` is refactored into `MeshPipelineKey::BLEND_BITS`.
- `AlphaMode::Opaque` and `AlphaMode::Mask(f32)` share a single opaque pipeline key: `MeshPipelineKey::BLEND_OPAQUE`;
- `Blend`, `Premultiplied` and `Add` share a single premultiplied alpha pipeline key, `MeshPipelineKey::BLEND_PREMULTIPLIED_ALPHA`. In the shader, color values are premultiplied accordingly (or not) depending on the blend mode to produce the three different results after PBR/tone mapping/dithering;
- `Multiply` uses its own independent pipeline key, `MeshPipelineKey::BLEND_MULTIPLY`;
- Example and documentation are provided.
---
## Changelog
### Added
- Added support for additive and multiplicative blend modes in the PBR `StandardMaterial`, via `AlphaMode::Add` and `AlphaMode::Multiply`;
- Added support for premultiplied alpha in the PBR `StandardMaterial`, via `AlphaMode::Premultiplied`;
# Objective
Fixes#6931
Continues #6954 by squashing `Msaa` to a flat enum
Helps out #7215
# Solution
```
pub enum Msaa {
Off = 1,
#[default]
Sample4 = 4,
}
```
# Changelog
- Modified
- `Msaa` is now enum
- Defaults to 4 samples
- Uses `.samples()` method to get the sample number as `u32`
# Migration Guide
```
let multi = Msaa { samples: 4 }
// is now
let multi = Msaa::Sample4
multi.samples
// is now
multi.samples()
```
Co-authored-by: Sjael <jakeobrien44@gmail.com>
# Objective
Fix https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/4530
- Make it easier to open/close/modify windows by setting them up as `Entity`s with a `Window` component.
- Make multiple windows very simple to set up. (just add a `Window` component to an entity and it should open)
## Solution
- Move all properties of window descriptor to ~components~ a component.
- Replace `WindowId` with `Entity`.
- ~Use change detection for components to update backend rather than events/commands. (The `CursorMoved`/`WindowResized`/... events are kept for user convenience.~
Check each field individually to see what we need to update, events are still kept for user convenience.
---
## Changelog
- `WindowDescriptor` renamed to `Window`.
- Width/height consolidated into a `WindowResolution` component.
- Requesting maximization/minimization is done on the [`Window::state`] field.
- `WindowId` is now `Entity`.
## Migration Guide
- Replace `WindowDescriptor` with `Window`.
- Change `width` and `height` fields in a `WindowResolution`, either by doing
```rust
WindowResolution::new(width, height) // Explicitly
// or using From<_> for tuples for convenience
(1920., 1080.).into()
```
- Replace any `WindowCommand` code to just modify the `Window`'s fields directly and creating/closing windows is now by spawning/despawning an entity with a `Window` component like so:
```rust
let window = commands.spawn(Window { ... }).id(); // open window
commands.entity(window).despawn(); // close window
```
## Unresolved
- ~How do we tell when a window is minimized by a user?~
~Currently using the `Resize(0, 0)` as an indicator of minimization.~
No longer attempting to tell given how finnicky this was across platforms, now the user can only request that a window be maximized/minimized.
## Future work
- Move `exit_on_close` functionality out from windowing and into app(?)
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/5621
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/7099
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/7098
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- When using `Color::hex` for the first time, I was confused by the fact that I can't specify colors using #, which is much more familiar.
- In the code editor (if there is support) there is a preview of the color, which is very convenient.

## Solution
- Allow you to enter colors like `#ff33f2` and use the `.strip_prefix` method to delete the `#` character.
# Objective
The documentation for camera priority is very confusing at the moment, it requires a bit of "double negative" kind of thinking.
# Solution
Flipping the wording on the documentation to reflect more common usecases like having an overlay camera and also renaming it to "order", since priority implies that it will override the other camera rather than have both run.
# Objective
The `WgpuSettings` resource is only used during plugin build. Move it into the `RenderPlugin` struct.
Changing these settings requires re-initializing the render context, which is currently not supported.
If it is supported in the future it should probably be more explicit than changing a field on a resource, maybe something similar to the `CreateWindow` event.
## Migration Guide
```rust
// Before (0.9)
App::new()
.insert_resource(WgpuSettings { .. })
.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins)
// After (0.10)
App::new()
.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins.set(RenderPlugin {
wgpu_settings: WgpuSettings { .. },
}))
```
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
# Objective
`AsBindGroup` can't be used as a trait object because of the constraint `Sized` and because of the associated function.
This is a problem for [`bevy_atmosphere`](https://github.com/JonahPlusPlus/bevy_atmosphere) because it needs to use a trait that depends on `AsBindGroup` as a trait object, for switching out different shaders at runtime. The current solution it employs is reimplementing the trait and derive macro into that trait, instead of constraining to `AsBindGroup`.
## Solution
Remove the `Sized` constraint from `AsBindGroup` and add the constraint `where Self: Sized` to the associated function `bind_group_layout`. Also change `PreparedBindGroup<T: AsBindGroup>` to `PreparedBindGroup<T>` and use it as `PreparedBindGroup<Self::Data>` instead of `PreparedBindGroup<Self>`.
This weakens the constraints, but increases the flexibility of `AsBindGroup`.
I'm not entirely sure why the `Sized` constraint was there, because it worked fine without it (maybe @cart wasn't aware of use cases for `AsBindGroup` as a trait object or this was just leftover from legacy code?).
---
## Changelog
- `AsBindGroup` can be used as a trait object.
# Objective
Adds a cylinder shape. Fixes#2282.
## Solution
- I added a custom cylinder shape, taken from [here](https://github.com/rparrett/typey_birb/blob/main/src/cylinder.rs) with permission from @rparrett.
- I also added the cylinder shape to the `3d_shapes` example scene.
---
## Changelog
- Added cylinder shape
Co-Authored-By: Rob Parrett <robparrett@gmail.com>
Co-Authored-By: davidhof <7483215+davidhof@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
The bloom example has a 2d camera for the UI. This is an artifact of an older version of bevy. All cameras can render the UI now.
## Solution
Remove the 2d camera
Allow passing `Vec`s of glam vector types as vertex attributes.
Alternative to #4548 and #2719
Also used some macros to cut down on all the repetition.
# Migration Guide
Implementations of `From<Vec<[u16; 4]>>` and `From<Vec<[u8; 4]>>` for `VertexAttributeValues` have been removed.
I you're passing either `Vec<[u16; 4]>` or `Vec<[u8; 4]>` into `Mesh::insert_attribute` it will now require wrapping it with right the `VertexAttributeValues` enum variant.
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Adds a bloom pass for HDR-enabled Camera3ds.
- Supersedes (and all credit due to!) https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/3430 and https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/2876
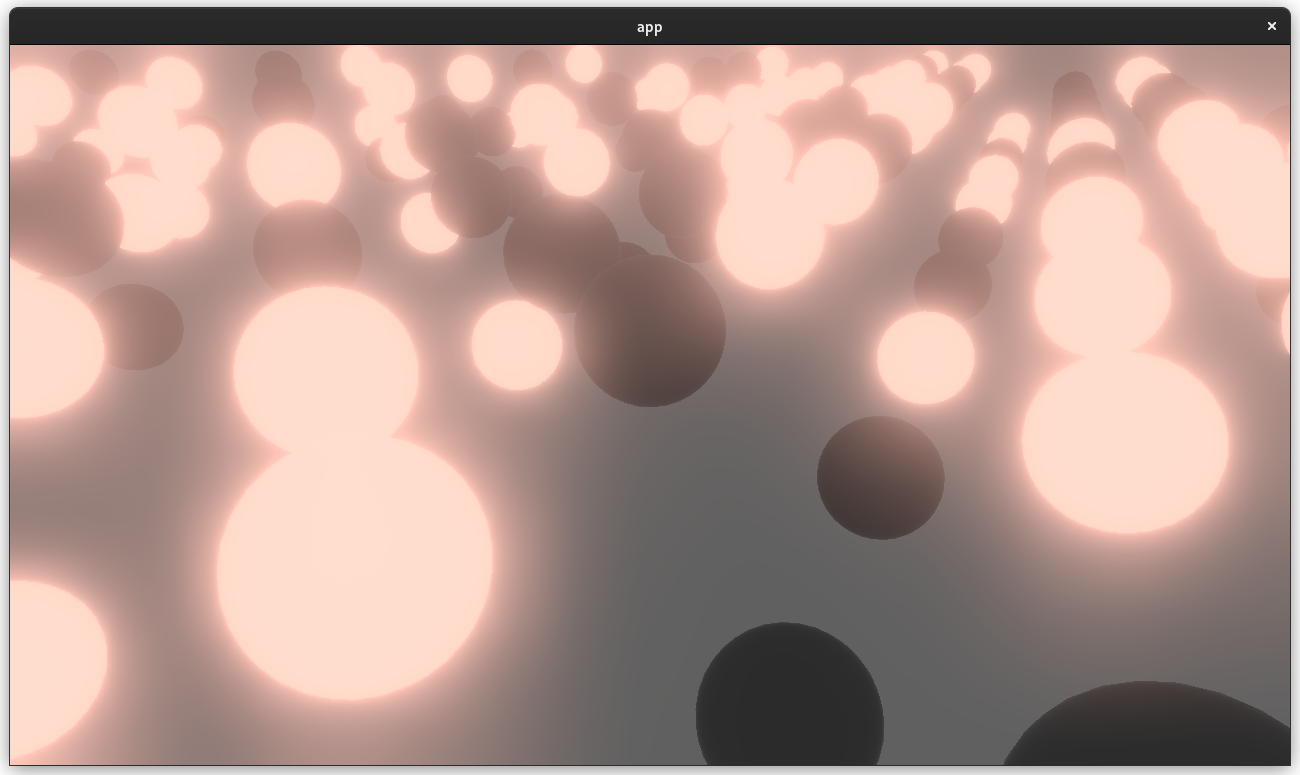
## Solution
- A threshold is applied to isolate emissive samples, and then a series of downscale and upscaling passes are applied and composited together.
- Bloom is applied to 2d or 3d Cameras with hdr: true and a BloomSettings component.
---
## Changelog
- Added a `core_pipeline::bloom::BloomSettings` component.
- Added `BloomNode` that runs between the main pass and tonemapping.
- Added a `BloomPlugin` that is loaded as part of CorePipelinePlugin.
- Added a bloom example project.
Co-authored-by: JMS55 <47158642+JMS55@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: DGriffin91 <github@dgdigital.net>
# Objective
- Add post processing passes for FXAA (Fast Approximate Anti-Aliasing)
- Add example comparing MSAA and FXAA
## Solution
When the FXAA plugin is added, passes for FXAA are inserted between the main pass and the tonemapping pass. Supports using either HDR or LDR output from the main pass.
---
## Changelog
- Add a new FXAANode that runs after the main pass when the FXAA plugin is added.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
Add methods to `Query<&Children>` and `Query<&Parent>` to iterate over descendants and ancestors, respectively.
## Changelog
* Added extension trait for `Query` in `bevy_hierarchy`, `HierarchyQueryExt`
* Added method `iter_descendants` to `Query<&Children>` via `HierarchyQueryExt` for iterating over the descendants of an entity.
* Added method `iter_ancestors` to `Query<&Parent>` via `HierarchyQueryExt` for iterating over the ancestors of an entity.
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Build on #6336 for more plugin configurations
## Solution
- `LogSettings`, `ImageSettings` and `DefaultTaskPoolOptions` are now plugins settings rather than resources
---
## Changelog
- `LogSettings` plugin settings have been move to `LogPlugin`, `ImageSettings` to `ImagePlugin` and `DefaultTaskPoolOptions` to `CorePlugin`
## Migration Guide
The `LogSettings` settings have been moved from a resource to `LogPlugin` configuration:
```rust
// Old (Bevy 0.8)
app
.insert_resource(LogSettings {
level: Level::DEBUG,
filter: "wgpu=error,bevy_render=info,bevy_ecs=trace".to_string(),
})
.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins)
// New (Bevy 0.9)
app.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins.set(LogPlugin {
level: Level::DEBUG,
filter: "wgpu=error,bevy_render=info,bevy_ecs=trace".to_string(),
}))
```
The `ImageSettings` settings have been moved from a resource to `ImagePlugin` configuration:
```rust
// Old (Bevy 0.8)
app
.insert_resource(ImageSettings::default_nearest())
.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins)
// New (Bevy 0.9)
app.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins.set(ImagePlugin::default_nearest()))
```
The `DefaultTaskPoolOptions` settings have been moved from a resource to `CorePlugin::task_pool_options`:
```rust
// Old (Bevy 0.8)
app
.insert_resource(DefaultTaskPoolOptions::with_num_threads(4))
.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins)
// New (Bevy 0.9)
app.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins.set(CorePlugin {
task_pool_options: TaskPoolOptions::with_num_threads(4),
}))
```
# Objective
- Make `Time` API more consistent.
- Support time accel/decel/pause.
## Solution
This is just the `Time` half of #3002. I was told that part isn't controversial.
- Give the "delta time" and "total elapsed time" methods `f32`, `f64`, and `Duration` variants with consistent naming.
- Implement accelerating / decelerating the passage of time.
- Implement stopping time.
---
## Changelog
- Changed `time_since_startup` to `elapsed` because `time.time_*` is just silly.
- Added `relative_speed` and `set_relative_speed` methods.
- Added `is_paused`, `pause`, `unpause` , and methods. (I'd prefer `resume`, but `unpause` matches `Timer` API.)
- Added `raw_*` variants of the "delta time" and "total elapsed time" methods.
- Added `first_update` method because there's a non-zero duration between startup and the first update.
## Migration Guide
- `time.time_since_startup()` -> `time.elapsed()`
- `time.seconds_since_startup()` -> `time.elapsed_seconds_f64()`
- `time.seconds_since_startup_wrapped_f32()` -> `time.elapsed_seconds_wrapped()`
If you aren't sure which to use, most systems should continue to use "scaled" time (e.g. `time.delta_seconds()`). The realtime "unscaled" time measurements (e.g. `time.raw_delta_seconds()`) are mostly for debugging and profiling.
# Objective
- Alpha mask was previously ignored when using an unlit material.
- Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/4479
## Solution
- Extract the alpha discard to a separate function and use it when unlit is true
## Notes
I tried calling `alpha_discard()` before the `if` in pbr.wgsl, but I had errors related to having a `discard` at the beginning before doing the texture sampling. I'm not sure if there's a way to fix that instead of having the function being called in 2 places.
# Objective
I was about to submit a PR to add these two examples to `bevy-website` and re-discovered the inconsistency.
Although it's not a major issue on the website where only the filenames are shown, this would help to visually distinguish the two examples in the list because the names are very prominent.
This also helps out when fuzzy-searching the codebase for these files.
## Solution
Rename `shapes` to `2d_shapes`. Now the filename matches the example name, and the naming structure matches the 3d example.
## Notes
@Nilirad proposed this in https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/4613#discussion_r862455631 but it had slipped away from my brain at that time.
# Objective
Now that we can consolidate Bundles and Components under a single insert (thanks to #2975 and #6039), almost 100% of world spawns now look like `world.spawn().insert((Some, Tuple, Here))`. Spawning an entity without any components is an extremely uncommon pattern, so it makes sense to give spawn the "first class" ergonomic api. This consolidated api should be made consistent across all spawn apis (such as World and Commands).
## Solution
All `spawn` apis (`World::spawn`, `Commands:;spawn`, `ChildBuilder::spawn`, and `WorldChildBuilder::spawn`) now accept a bundle as input:
```rust
// before:
commands
.spawn()
.insert((A, B, C));
world
.spawn()
.insert((A, B, C);
// after
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
world.spawn((A, B, C));
```
All existing instances of `spawn_bundle` have been deprecated in favor of the new `spawn` api. A new `spawn_empty` has been added, replacing the old `spawn` api.
By allowing `world.spawn(some_bundle)` to replace `world.spawn().insert(some_bundle)`, this opened the door to removing the initial entity allocation in the "empty" archetype / table done in `spawn()` (and subsequent move to the actual archetype in `.insert(some_bundle)`).
This improves spawn performance by over 10%:

To take this measurement, I added a new `world_spawn` benchmark.
Unfortunately, optimizing `Commands::spawn` is slightly less trivial, as Commands expose the Entity id of spawned entities prior to actually spawning. Doing the optimization would (naively) require assurances that the `spawn(some_bundle)` command is applied before all other commands involving the entity (which would not necessarily be true, if memory serves). Optimizing `Commands::spawn` this way does feel possible, but it will require careful thought (and maybe some additional checks), which deserves its own PR. For now, it has the same performance characteristics of the current `Commands::spawn_bundle` on main.
**Note that 99% of this PR is simple renames and refactors. The only code that needs careful scrutiny is the new `World::spawn()` impl, which is relatively straightforward, but it has some new unsafe code (which re-uses battle tested BundlerSpawner code path).**
---
## Changelog
- All `spawn` apis (`World::spawn`, `Commands:;spawn`, `ChildBuilder::spawn`, and `WorldChildBuilder::spawn`) now accept a bundle as input
- All instances of `spawn_bundle` have been deprecated in favor of the new `spawn` api
- World and Commands now have `spawn_empty()`, which is equivalent to the old `spawn()` behavior.
## Migration Guide
```rust
// Old (0.8):
commands
.spawn()
.insert_bundle((A, B, C));
// New (0.9)
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
// Old (0.8):
commands.spawn_bundle((A, B, C));
// New (0.9)
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
// Old (0.8):
let entity = commands.spawn().id();
// New (0.9)
let entity = commands.spawn_empty().id();
// Old (0.8)
let entity = world.spawn().id();
// New (0.9)
let entity = world.spawn_empty();
```
# Objective
Take advantage of the "impl Bundle for Component" changes in #2975 / add the follow up changes discussed there.
## Solution
- Change `insert` and `remove` to accept a Bundle instead of a Component (for both Commands and World)
- Deprecate `insert_bundle`, `remove_bundle`, and `remove_bundle_intersection`
- Add `remove_intersection`
---
## Changelog
- Change `insert` and `remove` now accept a Bundle instead of a Component (for both Commands and World)
- `insert_bundle` and `remove_bundle` are deprecated
## Migration Guide
Replace `insert_bundle` with `insert`:
```rust
// Old (0.8)
commands.spawn().insert_bundle(SomeBundle::default());
// New (0.9)
commands.spawn().insert(SomeBundle::default());
```
Replace `remove_bundle` with `remove`:
```rust
// Old (0.8)
commands.entity(some_entity).remove_bundle::<SomeBundle>();
// New (0.9)
commands.entity(some_entity).remove::<SomeBundle>();
```
Replace `remove_bundle_intersection` with `remove_intersection`:
```rust
// Old (0.8)
world.entity_mut(some_entity).remove_bundle_intersection::<SomeBundle>();
// New (0.9)
world.entity_mut(some_entity).remove_intersection::<SomeBundle>();
```
Consider consolidating as many operations as possible to improve ergonomics and cut down on archetype moves:
```rust
// Old (0.8)
commands.spawn()
.insert_bundle(SomeBundle::default())
.insert(SomeComponent);
// New (0.9) - Option 1
commands.spawn().insert((
SomeBundle::default(),
SomeComponent,
))
// New (0.9) - Option 2
commands.spawn_bundle((
SomeBundle::default(),
SomeComponent,
))
```
## Next Steps
Consider changing `spawn` to accept a bundle and deprecate `spawn_bundle`.
Examples inconsistently use either `TAU`, `PI`, `FRAC_PI_2` or `FRAC_PI_4`.
Often in odd ways and without `use`ing the constants, making it difficult to parse.
* Use `PI` to specify angles.
* General code-quality improvements.
* Fix borked `hierarchy` example.
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
*This PR description is an edited copy of #5007, written by @alice-i-cecile.*
# Objective
Follow-up to https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/2254. The `Resource` trait currently has a blanket implementation for all types that meet its bounds.
While ergonomic, this results in several drawbacks:
* it is possible to make confusing, silent mistakes such as inserting a function pointer (Foo) rather than a value (Foo::Bar) as a resource
* it is challenging to discover if a type is intended to be used as a resource
* we cannot later add customization options (see the [RFC](https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/blob/main/rfcs/27-derive-component.md) for the equivalent choice for Component).
* dependencies can use the same Rust type as a resource in invisibly conflicting ways
* raw Rust types used as resources cannot preserve privacy appropriately, as anyone able to access that type can read and write to internal values
* we cannot capture a definitive list of possible resources to display to users in an editor
## Notes to reviewers
* Review this commit-by-commit; there's effectively no back-tracking and there's a lot of churn in some of these commits.
*ira: My commits are not as well organized :')*
* I've relaxed the bound on Local to Send + Sync + 'static: I don't think these concerns apply there, so this can keep things simple. Storing e.g. a u32 in a Local is fine, because there's a variable name attached explaining what it does.
* I think this is a bad place for the Resource trait to live, but I've left it in place to make reviewing easier. IMO that's best tackled with https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/4981.
## Changelog
`Resource` is no longer automatically implemented for all matching types. Instead, use the new `#[derive(Resource)]` macro.
## Migration Guide
Add `#[derive(Resource)]` to all types you are using as a resource.
If you are using a third party type as a resource, wrap it in a tuple struct to bypass orphan rules. Consider deriving `Deref` and `DerefMut` to improve ergonomics.
`ClearColor` no longer implements `Component`. Using `ClearColor` as a component in 0.8 did nothing.
Use the `ClearColorConfig` in the `Camera3d` and `Camera2d` components instead.
Co-authored-by: Alice <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
`bevy::render::texture::ImageSettings` was added to prelude in #5566, so these `use` statements are unnecessary and the examples can be made a bit more concise.
## Solution
Remove `use bevy::render::texture::ImageSettings`
# Objective
- Fix / support KTX2 array / cubemap / cubemap array textures
- Fixes#4495 . Supersedes #4514 .
## Solution
- Add `Option<TextureViewDescriptor>` to `Image` to enable configuration of the `TextureViewDimension` of a texture.
- This allows users to set `D2Array`, `D3`, `Cube`, `CubeArray` or whatever they need
- Automatically configure this when loading KTX2
- Transcode all layers and faces instead of just one
- Use the UASTC block size of 128 bits, and the number of blocks in x/y for a given mip level in order to determine the offset of the layer and face within the KTX2 mip level data
- `wgpu` wants data ordered as layer 0 mip 0..n, layer 1 mip 0..n, etc. See https://docs.rs/wgpu/latest/wgpu/util/trait.DeviceExt.html#tymethod.create_texture_with_data
- Reorder the data KTX2 mip X layer Y face Z to `wgpu` layer Y face Z mip X order
- Add a `skybox` example to demonstrate / test loading cubemaps from PNG and KTX2, including ASTC 4x4, BC7, and ETC2 compression for support everywhere. Note that you need to enable the `ktx2,zstd` features to be able to load the compressed textures.
---
## Changelog
- Fixed: KTX2 array / cubemap / cubemap array textures
- Fixes: Validation failure for compressed textures stored in KTX2 where the width/height are not a multiple of the block dimensions.
- Added: `Image` now has an `Option<TextureViewDescriptor>` field to enable configuration of the texture view. This is useful for configuring the `TextureViewDimension` when it is not just a plain 2D texture and the loader could/did not identify what it should be.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Showcase how to use a `Material` and `Mesh` to spawn 3d lines
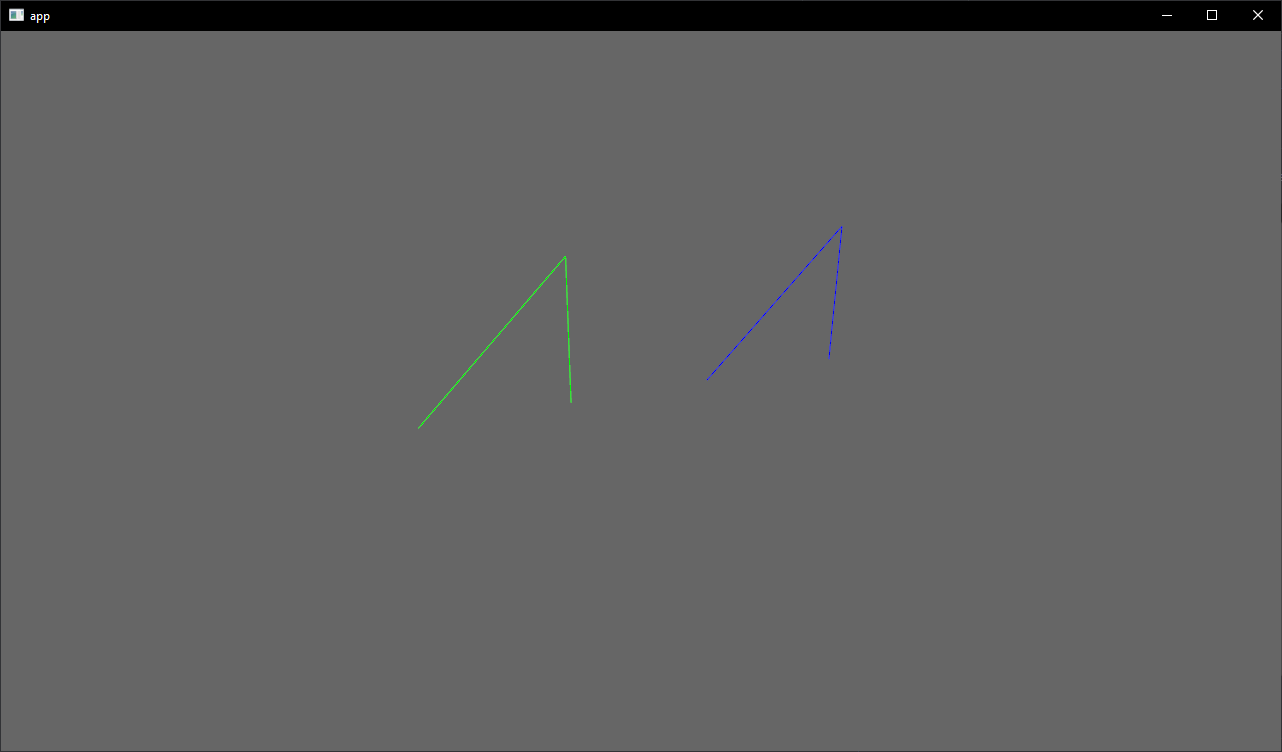
## Solution
- Add an example using a simple `Material` and `Mesh` definition to draw a 3d line
- Shows how to use `LineList` and `LineStrip` in combination with a specialized `Material`
## Notes
This isn't just a primitive shape because it needs a special Material, but I think it's a good showcase of the power of the `Material` and `AsBindGroup` abstractions. All of this is easy to figure out when you know these options are a thing, but I think they are hard to discover which is why I think this should be an example and not shipped with bevy.
Co-authored-by: Charles <IceSentry@users.noreply.github.com>
Remove unnecessary calls to `iter()`/`iter_mut()`.
Mainly updates the use of queries in our code, docs, and examples.
```rust
// From
for _ in list.iter() {
for _ in list.iter_mut() {
// To
for _ in &list {
for _ in &mut list {
```
We already enable the pedantic lint [clippy::explicit_iter_loop](https://rust-lang.github.io/rust-clippy/stable/) inside of Bevy. However, this only warns for a few known types from the standard library.
## Note for reviewers
As you can see the additions and deletions are exactly equal.
Maybe give it a quick skim to check I didn't sneak in a crypto miner, but you don't have to torture yourself by reading every line.
I already experienced enough pain making this PR :)
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
# Objective
add spotlight support
## Solution / Changelog
- add spotlight angles (inner, outer) to ``PointLight`` struct. emitted light is linearly attenuated from 100% to 0% as angle tends from inner to outer. Direction is taken from the existing transform rotation.
- add spotlight direction (vec3) and angles (f32,f32) to ``GpuPointLight`` struct (60 bytes -> 80 bytes) in ``pbr/render/lights.rs`` and ``mesh_view_bind_group.wgsl``
- reduce no-buffer-support max point light count to 204 due to above
- use spotlight data to attenuate light in ``pbr.wgsl``
- do additional cluster culling on spotlights to minimise cost in ``assign_lights_to_clusters``
- changed one of the lights in the lighting demo to a spotlight
- also added a ``spotlight`` demo - probably not justified but so reviewers can see it more easily
## notes
increasing the size of the GpuPointLight struct on my machine reduces the FPS of ``many_lights -- sphere`` from ~150fps to 140fps.
i thought this was a reasonable tradeoff, and felt better than handling spotlights separately which is possible but would mean introducing a new bind group, refactoring light-assignment code and adding new spotlight-specific code in pbr.wgsl. the FPS impact for smaller numbers of lights should be very small.
the cluster culling strategy reintroduces the cluster aabb code which was recently removed... sorry. the aabb is used to get a cluster bounding sphere, which can then be tested fairly efficiently using the strategy described at the end of https://bartwronski.com/2017/04/13/cull-that-cone/. this works well with roughly cubic clusters (where the cluster z size is close to the same as x/y size), less well for other cases like single Z slice / tiled forward rendering. In the worst case we will end up just keeping the culling of the equivalent point light.
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
# Objective
Users often ask for help with rotations as they struggle with `Quat`s.
`Quat` is rather complex and has a ton of verbose methods.
## Solution
Add rotation helper methods to `Transform`.
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Spawning a scene is handled as a special case with a command `spawn_scene` that takes an handle but doesn't let you specify anything else. This is the only handle that works that way.
- Workaround for this have been to add the `spawn_scene` on `ChildBuilder` to be able to specify transform of parent, or to make the `SceneSpawner` available to be able to select entities from a scene by their instance id
## Solution
Add a bundle
```rust
pub struct SceneBundle {
pub scene: Handle<Scene>,
pub transform: Transform,
pub global_transform: GlobalTransform,
pub instance_id: Option<InstanceId>,
}
```
and instead of
```rust
commands.spawn_scene(asset_server.load("models/FlightHelmet/FlightHelmet.gltf#Scene0"));
```
you can do
```rust
commands.spawn_bundle(SceneBundle {
scene: asset_server.load("models/FlightHelmet/FlightHelmet.gltf#Scene0"),
..Default::default()
});
```
The scene will be spawned as a child of the entity with the `SceneBundle`
~I would like to remove the command `spawn_scene` in favor of this bundle but didn't do it yet to get feedback first~
Co-authored-by: François <8672791+mockersf@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
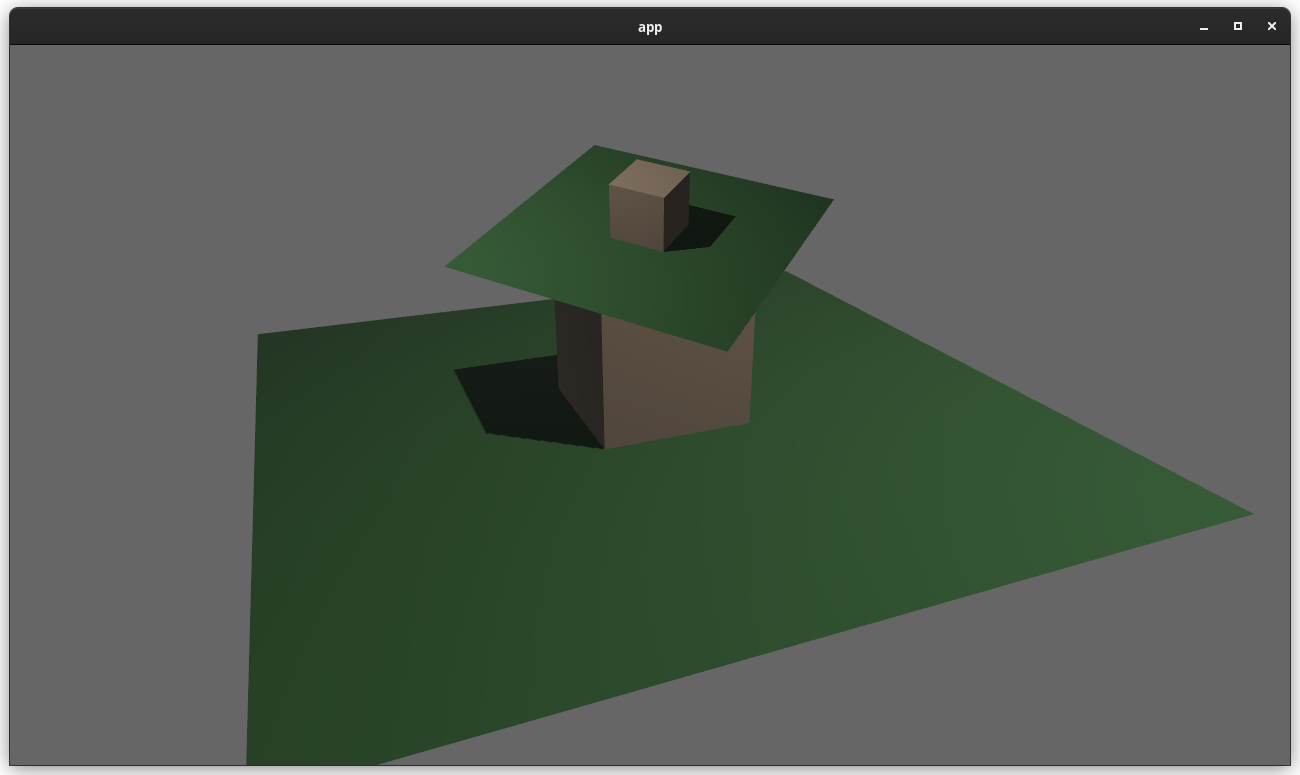
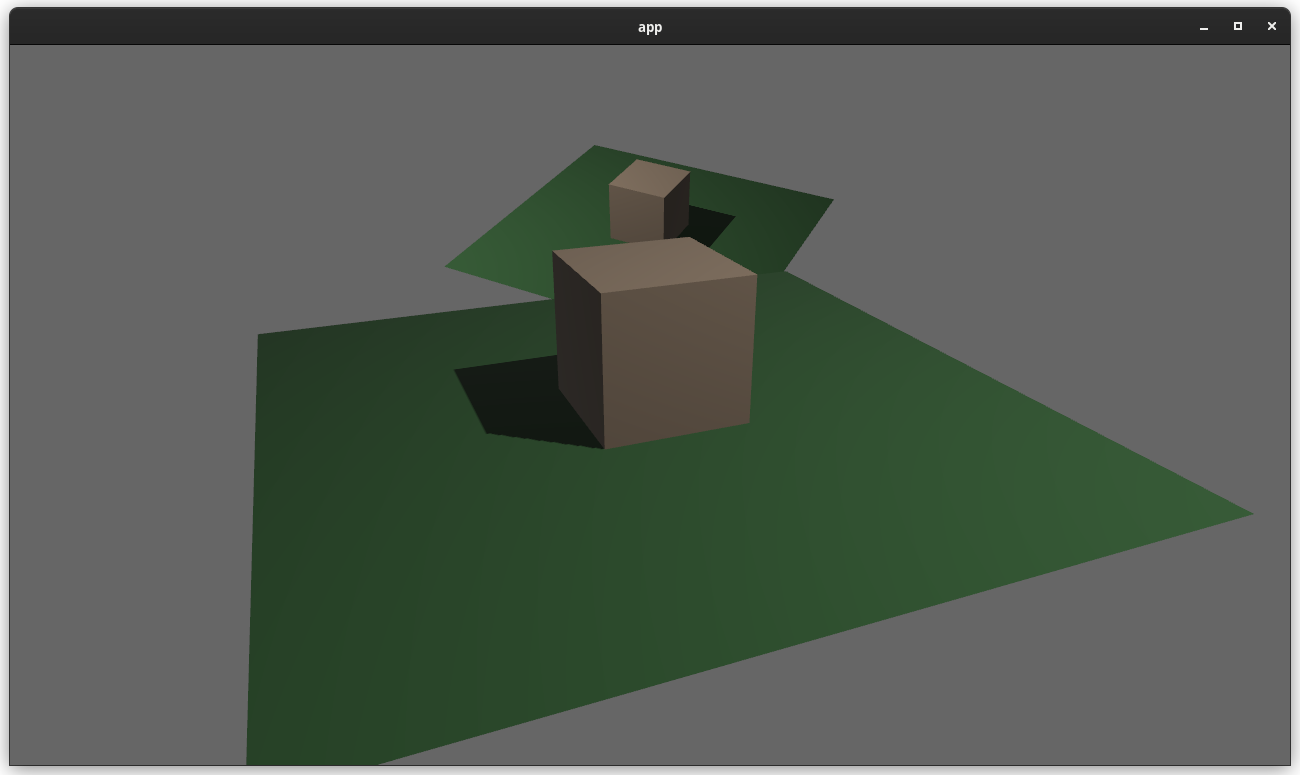
# Objective
Users should be able to configure depth load operations on cameras. Currently every camera clears depth when it is rendered. But sometimes later passes need to rely on depth from previous passes.
## Solution
This adds the `Camera3d::depth_load_op` field with a new `Camera3dDepthLoadOp` value. This is a custom type because Camera3d uses "reverse-z depth" and this helps us record and document that in a discoverable way. It also gives us more control over reflection + other trait impls, whereas `LoadOp` is owned by the `wgpu` crate.
```rust
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle {
camera_3d: Camera3d {
depth_load_op: Camera3dDepthLoadOp::Load,
..default()
},
..default()
});
```
### two_passes example with the "second pass" camera configured to the default (clear depth to 0.0)
### two_passes example with the "second pass" camera configured to "load" the depth
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `Camera3d` now has a `depth_load_op` field, which can configure the Camera's main 3d pass depth loading behavior.
# Objective
Users should be able to render cameras to specific areas of a render target, which enables scenarios like split screen, minimaps, etc.
Builds on the new Camera Driven Rendering added here: #4745Fixes: #202
Alternative to #1389 and #3626 (which are incompatible with the new Camera Driven Rendering)
## Solution
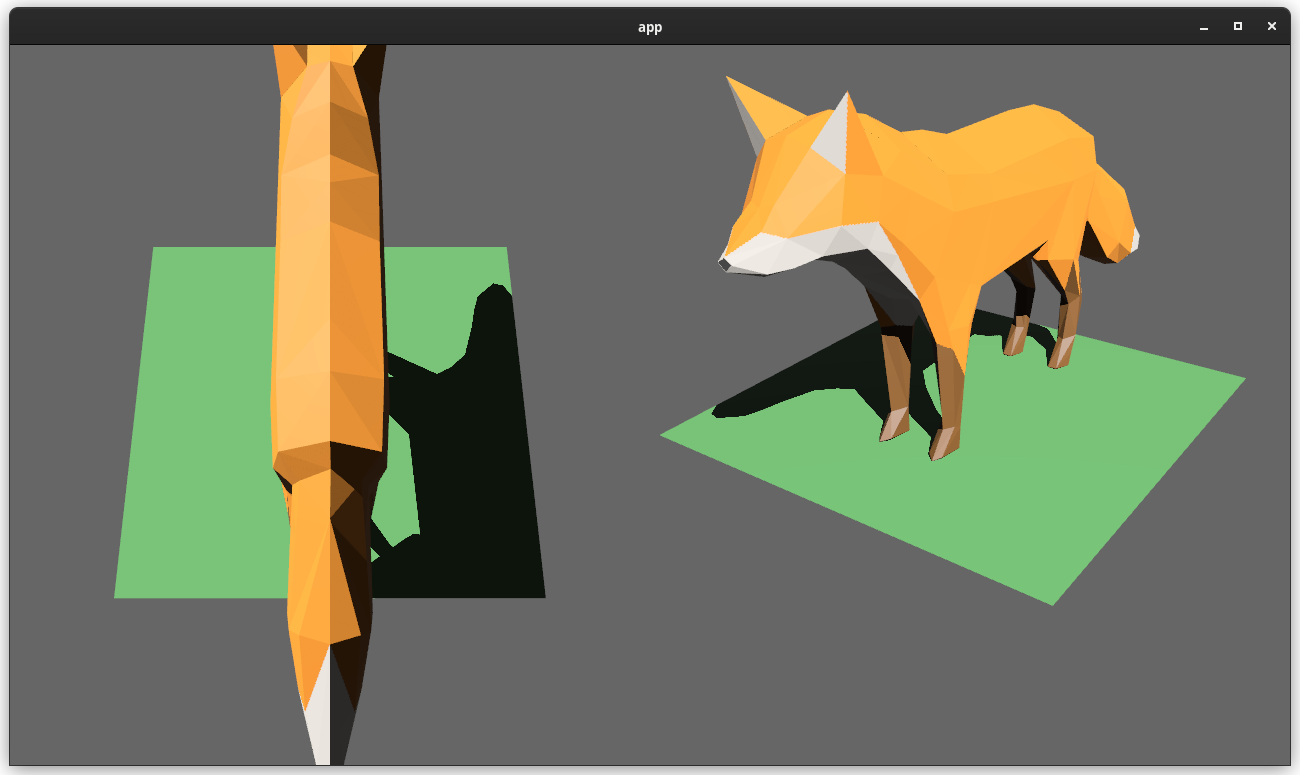
Cameras can now configure an optional "viewport", which defines a rectangle within their render target to draw to. If a `Viewport` is defined, the camera's `CameraProjection`, `View`, and visibility calculations will use the viewport configuration instead of the full render target.
```rust
// This camera will render to the first half of the primary window (on the left side).
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle {
camera: Camera {
viewport: Some(Viewport {
physical_position: UVec2::new(0, 0),
physical_size: UVec2::new(window.physical_width() / 2, window.physical_height()),
depth: 0.0..1.0,
}),
..default()
},
..default()
});
```
To account for this, the `Camera` component has received a few adjustments:
* `Camera` now has some new getter functions:
* `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, `projection_matrix`
* All computed camera values are now private and live on the `ComputedCameraValues` field (logical/physical width/height, the projection matrix). They are now exposed on `Camera` via getters/setters This wasn't _needed_ for viewports, but it was long overdue.
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `Camera` components now have a `viewport` field, which can be set to draw to a portion of a render target instead of the full target.
* `Camera` component has some new functions: `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, and `projection_matrix`
* Added a new split_screen example illustrating how to render two cameras to the same scene
## Migration Guide
`Camera::projection_matrix` is no longer a public field. Use the new `Camera::projection_matrix()` method instead:
```rust
// Bevy 0.7
let projection = camera.projection_matrix;
// Bevy 0.8
let projection = camera.projection_matrix();
```
This adds "high level camera driven rendering" to Bevy. The goal is to give users more control over what gets rendered (and where) without needing to deal with render logic. This will make scenarios like "render to texture", "multiple windows", "split screen", "2d on 3d", "3d on 2d", "pass layering", and more significantly easier.
Here is an [example of a 2d render sandwiched between two 3d renders (each from a different perspective)](https://gist.github.com/cart/4fe56874b2e53bc5594a182fc76f4915):
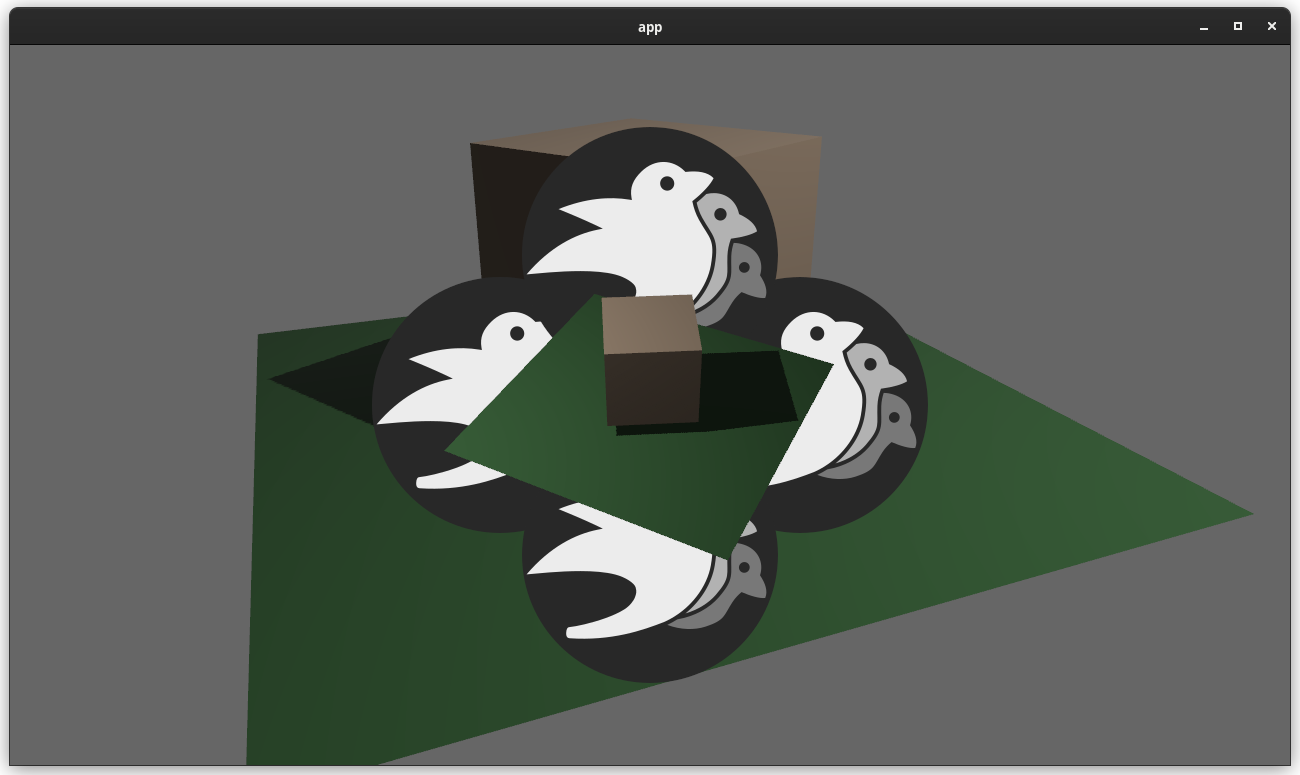

Users can now spawn a camera, point it at a RenderTarget (a texture or a window), and it will "just work".
Rendering to a second window is as simple as spawning a second camera and assigning it to a specific window id:
```rust
// main camera (main window)
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle::default());
// second camera (other window)
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle {
camera: Camera {
target: RenderTarget::Window(window_id),
..default()
},
..default()
});
```
Rendering to a texture is as simple as pointing the camera at a texture:
```rust
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle {
camera: Camera {
target: RenderTarget::Texture(image_handle),
..default()
},
..default()
});
```
Cameras now have a "render priority", which controls the order they are drawn in. If you want to use a camera's output texture as a texture in the main pass, just set the priority to a number lower than the main pass camera (which defaults to `0`).
```rust
// main pass camera with a default priority of 0
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle::default());
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle {
camera: Camera {
target: RenderTarget::Texture(image_handle.clone()),
priority: -1,
..default()
},
..default()
});
commands.spawn_bundle(SpriteBundle {
texture: image_handle,
..default()
})
```
Priority can also be used to layer to cameras on top of each other for the same RenderTarget. This is what "2d on top of 3d" looks like in the new system:
```rust
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle::default());
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle {
camera: Camera {
// this will render 2d entities "on top" of the default 3d camera's render
priority: 1,
..default()
},
..default()
});
```
There is no longer the concept of a global "active camera". Resources like `ActiveCamera<Camera2d>` and `ActiveCamera<Camera3d>` have been replaced with the camera-specific `Camera::is_active` field. This does put the onus on users to manage which cameras should be active.
Cameras are now assigned a single render graph as an "entry point", which is configured on each camera entity using the new `CameraRenderGraph` component. The old `PerspectiveCameraBundle` and `OrthographicCameraBundle` (generic on camera marker components like Camera2d and Camera3d) have been replaced by `Camera3dBundle` and `Camera2dBundle`, which set 3d and 2d default values for the `CameraRenderGraph` and projections.
```rust
// old 3d perspective camera
commands.spawn_bundle(PerspectiveCameraBundle::default())
// new 3d perspective camera
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle::default())
```
```rust
// old 2d orthographic camera
commands.spawn_bundle(OrthographicCameraBundle::new_2d())
// new 2d orthographic camera
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle::default())
```
```rust
// old 3d orthographic camera
commands.spawn_bundle(OrthographicCameraBundle::new_3d())
// new 3d orthographic camera
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle {
projection: OrthographicProjection {
scale: 3.0,
scaling_mode: ScalingMode::FixedVertical,
..default()
}.into(),
..default()
})
```
Note that `Camera3dBundle` now uses a new `Projection` enum instead of hard coding the projection into the type. There are a number of motivators for this change: the render graph is now a part of the bundle, the way "generic bundles" work in the rust type system prevents nice `..default()` syntax, and changing projections at runtime is much easier with an enum (ex for editor scenarios). I'm open to discussing this choice, but I'm relatively certain we will all come to the same conclusion here. Camera2dBundle and Camera3dBundle are much clearer than being generic on marker components / using non-default constructors.
If you want to run a custom render graph on a camera, just set the `CameraRenderGraph` component:
```rust
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle {
camera_render_graph: CameraRenderGraph::new(some_render_graph_name),
..default()
})
```
Just note that if the graph requires data from specific components to work (such as `Camera3d` config, which is provided in the `Camera3dBundle`), make sure the relevant components have been added.
Speaking of using components to configure graphs / passes, there are a number of new configuration options:
```rust
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle {
camera_3d: Camera3d {
// overrides the default global clear color
clear_color: ClearColorConfig::Custom(Color::RED),
..default()
},
..default()
})
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle {
camera_3d: Camera3d {
// disables clearing
clear_color: ClearColorConfig::None,
..default()
},
..default()
})
```
Expect to see more of the "graph configuration Components on Cameras" pattern in the future.
By popular demand, UI no longer requires a dedicated camera. `UiCameraBundle` has been removed. `Camera2dBundle` and `Camera3dBundle` now both default to rendering UI as part of their own render graphs. To disable UI rendering for a camera, disable it using the CameraUi component:
```rust
commands
.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle::default())
.insert(CameraUi {
is_enabled: false,
..default()
})
```
## Other Changes
* The separate clear pass has been removed. We should revisit this for things like sky rendering, but I think this PR should "keep it simple" until we're ready to properly support that (for code complexity and performance reasons). We can come up with the right design for a modular clear pass in a followup pr.
* I reorganized bevy_core_pipeline into Core2dPlugin and Core3dPlugin (and core_2d / core_3d modules). Everything is pretty much the same as before, just logically separate. I've moved relevant types (like Camera2d, Camera3d, Camera3dBundle, Camera2dBundle) into their relevant modules, which is what motivated this reorganization.
* I adapted the `scene_viewer` example (which relied on the ActiveCameras behavior) to the new system. I also refactored bits and pieces to be a bit simpler.
* All of the examples have been ported to the new camera approach. `render_to_texture` and `multiple_windows` are now _much_ simpler. I removed `two_passes` because it is less relevant with the new approach. If someone wants to add a new "layered custom pass with CameraRenderGraph" example, that might fill a similar niche. But I don't feel much pressure to add that in this pr.
* Cameras now have `target_logical_size` and `target_physical_size` fields, which makes finding the size of a camera's render target _much_ simpler. As a result, the `Assets<Image>` and `Windows` parameters were removed from `Camera::world_to_screen`, making that operation much more ergonomic.
* Render order ambiguities between cameras with the same target and the same priority now produce a warning. This accomplishes two goals:
1. Now that there is no "global" active camera, by default spawning two cameras will result in two renders (one covering the other). This would be a silent performance killer that would be hard to detect after the fact. By detecting ambiguities, we can provide a helpful warning when this occurs.
2. Render order ambiguities could result in unexpected / unpredictable render results. Resolving them makes sense.
## Follow Up Work
* Per-Camera viewports, which will make it possible to render to a smaller area inside of a RenderTarget (great for something like splitscreen)
* Camera-specific MSAA config (should use the same "overriding" pattern used for ClearColor)
* Graph Based Camera Ordering: priorities are simple, but they make complicated ordering constraints harder to express. We should consider adopting a "graph based" camera ordering model with "before" and "after" relationships to other cameras (or build it "on top" of the priority system).
* Consider allowing graphs to run subgraphs from any nest level (aka a global namespace for graphs). Right now the 2d and 3d graphs each need their own UI subgraph, which feels "fine" in the short term. But being able to share subgraphs between other subgraphs seems valuable.
* Consider splitting `bevy_core_pipeline` into `bevy_core_2d` and `bevy_core_3d` packages. Theres a shared "clear color" dependency here, which would need a new home.