# Objective
- In preparation for an initial 2D/3D mesh batching/instancing PR,
enhance `bevymark` to support some different test modes that enable
comparison and optimisation of performance
## Solution
- Use `argh` for command line interface options
- Use seeded `StdRng` for reproducible random number generation
- Add a mode for testing 2D meshes that includes an option to uniquely
vary the data of each material by setting a random flat colour on the
`ColorMaterial`.
- Add a way of specifying the number of different textures to use for
sprites or meshes. These are generated at the same resolution as the
Bevy bird icon, but are just random flat colours for testing.
- Add a benchmark mode that spawns all entities during setup, and
animates the entities using a fixed delta time for reproducible
animation. The initially-spawned entities are still spawned in waves and
animated as they would have been had they spawned at intervals.
---------
Co-authored-by: IceSentry <IceSentry@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
The `viewport_debug` example opens a window that is physically very
large. Probably larger than the screen for the majority of machines.
## Solution
Remove the custom resolution and adjust the pixel coordinates so that
everything lines up.
At the default resolution, everything is still whole numbers even
without adjusting the viewport coordinates.
The WGSL spec says that all scalar or vector integer vertex stage
outputs and fragment stage inputs must be marked as @interpolate(flat).
I think wgpu fixed this up for us, but being explicit is more correct.
# Objective
- Supercedes #8872
- Improve sprite rendering performance after the regression in #9236
## Solution
- Use an instance-rate vertex buffer to store per-instance data.
- Store color, UV offset and scale, and a transform per instance.
- Convert Sprite rect, custom_size, anchor, and flip_x/_y to an affine
3x4 matrix and store the transpose of that in the per-instance data.
This is similar to how MeshUniform uses transpose affine matrices.
- Use a special index buffer that has batches of 6 indices referencing 4
vertices. The lower 2 bits indicate the x and y of a quad such that the
corners are:
```
10 11
00 01
```
UVs are implicit but get modified by UV offset and scale The remaining
upper bits contain the instance index.
## Benchmarks
I will compare versus `main` before #9236 because the results should be
as good as or faster than that. Running `bevymark -- 10000 16` on an M1
Max with `main` at `e8b38925` in yellow, this PR in red:
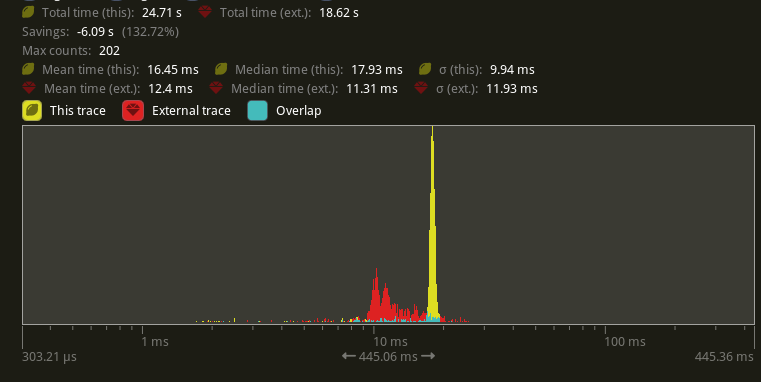
Looking at the median frame times, that's a 37% reduction from before.
---
## Changelog
- Changed: Improved sprite rendering performance by leveraging an
instance-rate vertex buffer.
---------
Co-authored-by: Giacomo Stevanato <giaco.stevanato@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Make `many_cubes` suitable for testing various parts of the upcoming
batching work.
## Solution
- Use `argh` for CLI.
- Default to the sphere layout as it is more useful for benchmarking.
- Add a benchmark mode that advances the camera by a fixed step to
render the same frames across runs.
- Add an option to vary the material data per-instance. The color is
randomized.
- Add an option to generate a number of textures and randomly choose one
per instance.
- Use seeded `StdRng` for deterministic random numbers.
# Objective
Fix#8267.
Fixes half of #7840.
The `ComputedVisibility` component contains two flags: hierarchy
visibility, and view visibility (whether its visible to any cameras).
Due to the modular and open-ended way that view visibility is computed,
it triggers change detection every single frame, even when the value
does not change. Since hierarchy visibility is stored in the same
component as view visibility, this means that change detection for
inherited visibility is completely broken.
At the company I work for, this has become a real issue. We are using
change detection to only re-render scenes when necessary. The broken
state of change detection for computed visibility means that we have to
to rely on the non-inherited `Visibility` component for now. This is
workable in the early stages of our project, but since we will
inevitably want to use the hierarchy, we will have to either:
1. Roll our own solution for computed visibility.
2. Fix the issue for everyone.
## Solution
Split the `ComputedVisibility` component into two: `InheritedVisibilty`
and `ViewVisibility`.
This allows change detection to behave properly for
`InheritedVisibility`.
View visiblity is still erratic, although it is less useful to be able
to detect changes
for this flavor of visibility.
Overall, this actually simplifies the API. Since the visibility system
consists of
self-explaining components, it is much easier to document the behavior
and usage.
This approach is more modular and "ECS-like" -- one could
strip out the `ViewVisibility` component entirely if it's not needed,
and rely only on inherited visibility.
---
## Changelog
- `ComputedVisibility` has been removed in favor of:
`InheritedVisibility` and `ViewVisiblity`.
## Migration Guide
The `ComputedVisibilty` component has been split into
`InheritedVisiblity` and
`ViewVisibility`. Replace any usages of
`ComputedVisibility::is_visible_in_hierarchy`
with `InheritedVisibility::get`, and replace
`ComputedVisibility::is_visible_in_view`
with `ViewVisibility::get`.
```rust
// Before:
commands.spawn(VisibilityBundle {
visibility: Visibility::Inherited,
computed_visibility: ComputedVisibility::default(),
});
// After:
commands.spawn(VisibilityBundle {
visibility: Visibility::Inherited,
inherited_visibility: InheritedVisibility::default(),
view_visibility: ViewVisibility::default(),
});
```
```rust
// Before:
fn my_system(q: Query<&ComputedVisibilty>) {
for vis in &q {
if vis.is_visible_in_hierarchy() {
// After:
fn my_system(q: Query<&InheritedVisibility>) {
for inherited_visibility in &q {
if inherited_visibility.get() {
```
```rust
// Before:
fn my_system(q: Query<&ComputedVisibilty>) {
for vis in &q {
if vis.is_visible_in_view() {
// After:
fn my_system(q: Query<&ViewVisibility>) {
for view_visibility in &q {
if view_visibility.get() {
```
```rust
// Before:
fn my_system(mut q: Query<&mut ComputedVisibilty>) {
for vis in &mut q {
vis.set_visible_in_view();
// After:
fn my_system(mut q: Query<&mut ViewVisibility>) {
for view_visibility in &mut q {
view_visibility.set();
```
---------
Co-authored-by: Robert Swain <robert.swain@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Fixes#9641
- Anonymous sets are named by their system members. When
`ScheduleBuildSettings::report_sets` is on, systems are named by their
sets. So when getting the anonymous set name this would cause an
infinite recursion.
## Solution
- When getting the anonymous system set name, don't get their system's
names with the sets the systems belong to.
## Other Possible solutions
- An alternate solution might be to skip anonymous sets when getting the
system's name for an anonymous set's name.
# Objective
- I broke ambiguity reporting in one of my refactors.
`conflicts_to_string` should have been using the passed in parameter
rather than the one stored on self.
# Objective
I've been collecting some mistakes in the documentation and fixed them
---------
Co-authored-by: Emi <emanuel.boehm@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Nicola Papale <nicopap@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
`Window::physical_cursor_position` checks to see if the cursor's
position is inside the window but it constructs the bounding rect for
the window using its logical size and then checks to see if it contains
the cursor's physical position. When the physical size is smaller than
the logical size, this leaves a dead zone where the cursor is over the
window but its position is unreported.
fixes: #9656
## Solution
Use the physical size of the window.
# Objective
Make it easier to create bounding boxes in user code by providing a
constructor that computes a box surrounding an arbitrary number of
points.
## Solution
Add `Aabb::enclosing`, which accepts iterators, slices, or arrays.
---------
Co-authored-by: Tristan Guichaoua <33934311+tguichaoua@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
- The current `EventReader::iter` has been determined to cause confusion
among new Bevy users. It was suggested by @JoJoJet to rename the method
to better clarify its usage.
- Solves #9624
## Solution
- Rename `EventReader::iter` to `EventReader::read`.
- Rename `EventReader::iter_with_id` to `EventReader::read_with_id`.
- Rename `ManualEventReader::iter` to `ManualEventReader::read`.
- Rename `ManualEventReader::iter_with_id` to
`ManualEventReader::read_with_id`.
---
## Changelog
- `EventReader::iter` has been renamed to `EventReader::read`.
- `EventReader::iter_with_id` has been renamed to
`EventReader::read_with_id`.
- `ManualEventReader::iter` has been renamed to
`ManualEventReader::read`.
- `ManualEventReader::iter_with_id` has been renamed to
`ManualEventReader::read_with_id`.
- Deprecated `EventReader::iter`
- Deprecated `EventReader::iter_with_id`
- Deprecated `ManualEventReader::iter`
- Deprecated `ManualEventReader::iter_with_id`
## Migration Guide
- Existing usages of `EventReader::iter` and `EventReader::iter_with_id`
will have to be changed to `EventReader::read` and
`EventReader::read_with_id` respectively.
- Existing usages of `ManualEventReader::iter` and
`ManualEventReader::iter_with_id` will have to be changed to
`ManualEventReader::read` and `ManualEventReader::read_with_id`
respectively.
# Objective
- Avoid using bevy_internal imports in examples.
## Solution
- Add CI to check for bevy_internal imports like suggested in
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/9547#issuecomment-1689377999
- Fix another import
I don't know much about CI so I don't know if this is the better
approach, but I think is better than doing a pull request every time I
found this lol, any suggestion is welcome.
---------
Co-authored-by: Rob Parrett <robparrett@gmail.com>
# Objective
The latest `clippy` release has a much more aggressive application of
the
[`explicit_iter_loop`](https://rust-lang.github.io/rust-clippy/master/index.html#/explicit_into_iter_loop?groups=pedantic)
pedantic lint.
As a result, clippy now suggests the following:
```diff
-for event in events.iter() {
+for event in &mut events {
```
I'm generally in favor of this lint. Using `for mut item in &mut query`
is also recommended over `for mut item in query.iter_mut()` for good
reasons IMO.
But, it is my personal belief that `&mut events` is much less clear than
`events.iter()`.
Why? The reason is that the events from `EventReader` **are not
mutable**, they are immutable references to each event in the event
reader. `&mut events` suggests we are getting mutable access to events —
similarly to `&mut query` — which is not the case. Using `&mut events`
is therefore misleading.
`IntoIterator` requires a mutable `EventReader` because it updates the
internal `last_event_count`, not because it let you mutate it.
So clippy's suggested improvement is a downgrade.
## Solution
Do not implement `IntoIterator` for `&mut events`.
Without the impl, clippy won't suggest its "fix". This also prevents
generally people from using `&mut events` for iterating `EventReader`s,
which makes the ecosystem every-so-slightly better.
---
## Changelog
- Removed `IntoIterator` impl for `&mut EventReader`
## Migration Guide
- `&mut EventReader` does not implement `IntoIterator` anymore. replace
`for foo in &mut events` by `for foo in events.iter()`
# Objective
- Some of the old ambiguity tests didn't get ported over during schedule
v3.
## Solution
- Port over tests from
15ee98db8d/crates/bevy_ecs/src/schedule/ambiguity_detection.rs (L279-L612)
with minimal changes
- Make a method to convert the ambiguity conflicts to a string for
easier verification of correct results.
# Objective
As far as I can tell, this is no longer needed since the switch to
fancier shader imports via `naga_oil`.
This shouldn't have any affect on compile times because it's in our tree
from `naga_oil`, `tracing-subscriber`, and `rodio`.
# Objective
Rename `Val`'s `evaluate` method to `resolve`.
Implement `resolve` support for `Val`'s viewport variants.
fixes#9535
---
## Changelog
`bevy_ui::ui_node::Val`:
* Renamed the following methods and added a `viewport_size` parameter:
- `evaluate` to `resolve`
- `try_add_with_size` to `try_add_with_context`
- `try_add_assign_with_size` to `try_add_assign_with_context`
- `try_sub_with_size` to `try_sub_with_context`
- `try_sub_assign_with_size` to `try_sub_assign_with_context`
* Implemented `resolve` support for `Val`'s viewport coordinate types
## Migration Guide
* Renamed the following `Val` methods and added a `viewport_size`
parameter:
- `evaluate` to `resolve`
- `try_add_with_size` to `try_add_with_context`
- `try_add_assign_with_size` to `try_add_assign_with_context`
- `try_sub_with_size` to `try_sub_with_context`
- `try_sub_assign_with_size` to `try_sub_assign_with_context`
Legitimately, bevy emits a WARN when encountering entities in UI trees
without NodeBunlde components.
Bevy pretty much always panics when such a thing happens, due to the
update_clipping system.
However, sometimes, it's perfectly legitimate to have a child without UI
nodes in a UI tree. For example, as a "seed" entity that is consumed by
a 3rd party plugin, which will later spawn a valid UI tree. In loading
scenarios, you are pretty much guaranteed to have incomplete children.
The presence of the WARN hints that bevy does not intend to panic on
such occasion (otherwise the warn! would be a panic!) so I assume panic
is an unintended behavior, aka a bug.
## Solution
Early-return instead of panicking.
I did only test that it indeed fixed the panic, not checked for UI
inconsistencies. Though on a logical level, it can only have changed
code that would otherwise panic.
## Alternatives
Instead of early-returning on invalid entity in `update_clipping`, do
not call it with invalid entity in its recursive call.
---
## Changelog
- Do not panic on non-UI child of UI entity
# Objective
Fix#4278Fix#5504Fix#9422
Provide safe ways to borrow an entire entity, while allowing disjoint
mutable access. `EntityRef` and `EntityMut` are not suitable for this,
since they provide access to the entire world -- they are just helper
types for working with `&World`/`&mut World`.
This has potential uses for reflection and serialization
## Solution
Remove `EntityRef::world`, which allows it to soundly be used within
queries.
`EntityMut` no longer supports structural world mutations, which allows
multiple instances of it to exist for different entities at once.
Structural world mutations are performed using the new type
`EntityWorldMut`.
```rust
fn disjoint_system(
q2: Query<&mut A>,
q1: Query<EntityMut, Without<A>>,
) { ... }
let [entity1, entity2] = world.many_entities_mut([id1, id2]);
*entity1.get_mut::<T>().unwrap() = *entity2.get().unwrap();
for entity in world.iter_entities_mut() {
...
}
```
---
## Changelog
- Removed `EntityRef::world`, to fix a soundness issue with queries.
+ Removed the ability to structurally mutate the world using
`EntityMut`, which allows it to be used in queries.
+ Added `EntityWorldMut`, which is used to perform structural mutations
that are no longer allowed using `EntityMut`.
## Migration Guide
**Note for maintainers: ensure that the guide for #9604 is updated
accordingly.**
Removed the method `EntityRef::world`, to fix a soundness issue with
queries. If you need access to `&World` while using an `EntityRef`,
consider passing the world as a separate parameter.
`EntityMut` can no longer perform 'structural' world mutations, such as
adding or removing components, or despawning the entity. Additionally,
`EntityMut::world`, `EntityMut::world_mut` , and
`EntityMut::world_scope` have been removed.
Instead, use the newly-added type `EntityWorldMut`, which is a helper
type for working with `&mut World`.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Move schedule name into `Schedule` to allow the schedule name to be
used for errors and tracing in Schedule methods
- Fixes#9510
## Solution
- Move label onto `Schedule` and adjust api's on `World` and `Schedule`
to not pass explicit label where it makes sense to.
- add name to errors and tracing.
- `Schedule::new` now takes a label so either add the label or use
`Schedule::default` which uses a default label. `default` is mostly used
in doc examples and tests.
---
## Changelog
- move label onto `Schedule` to improve error message and logging for
schedules.
## Migration Guide
`Schedule::new` and `App::add_schedule`
```rust
// old
let schedule = Schedule::new();
app.add_schedule(MyLabel, schedule);
// new
let schedule = Schedule::new(MyLabel);
app.add_schedule(schedule);
```
if you aren't using a label and are using the schedule struct directly
you can use the default constructor.
```rust
// old
let schedule = Schedule::new();
schedule.run(world);
// new
let schedule = Schedule::default();
schedule.run(world);
```
`Schedules:insert`
```rust
// old
let schedule = Schedule::new();
schedules.insert(MyLabel, schedule);
// new
let schedule = Schedule::new(MyLabel);
schedules.insert(schedule);
```
`World::add_schedule`
```rust
// old
let schedule = Schedule::new();
world.add_schedule(MyLabel, schedule);
// new
let schedule = Schedule::new(MyLabel);
world.add_schedule(schedule);
```
# Objective
Every frame, `Events::update` gets called, which clears out any old
events from the buffer. There should be a way of taking ownership of
these old events instead of throwing them away. My use-case is dumping
old events into a debug menu so they can be inspected later.
One potential workaround is to just have a system that clones any
incoming events and stores them in a list -- however, this requires the
events to implement `Clone`.
## Solution
Add `Events::update_drain`, which returns an iterator of the events that
were removed from the buffer.
# Objective
Doc comment for the `global_transform` field in `NodeBundle` says:
```
/// This field is automatically managed by the UI layout system.
```
The `GlobalTransform` component is the thing being managed, not the
`global_transform` field, and the `TransformPropagate` systems do the
managing, not the UI layout system.
# Objective
- Fixes: #9508
- Fixes: #9526
## Solution
- Adds
```rust
fn configure_schedules(&mut self, schedule_build_settings: ScheduleBuildSettings)
```
to `Schedules`, and `App` to simplify applying `ScheduleBuildSettings`
to all schedules.
---
## Migration Guide
- No breaking changes.
- Adds `Schedule::get_build_settings()` getter for the schedule's
`ScheduleBuildSettings`.
- Can replaced manual configuration of all schedules:
```rust
// Old
for (_, schedule) in app.world.resource_mut::<Schedules>().iter_mut() {
schedule.set_build_settings(build_settings);
}
// New
app.configure_schedules(build_settings);
```
# Objective
To enable non exclusive system usage of reflected components and make
reflection more ergonomic to use by making it more in line with standard
entity commands.
## Solution
- Implements a new `EntityCommands` extension trait for reflection
related functions in the reflect module of bevy_ecs.
- Implements 4 new commands, `insert_reflect`,
`insert_reflect_with_registry`, `remove_reflect`, and
`remove_reflect_with_registry`. Both insert commands take a `Box<dyn
Reflect>` component while the remove commands take the component type
name.
- Made `EntityCommands` fields pub(crate) to allow access in the reflect
module. (Might be worth making these just public to enable user end
custom entity commands in a different pr)
- Added basic tests to ensure the commands are actually working.
- Documentation of functions.
---
## Changelog
Added:
- Implements 4 new commands on the new entity commands extension.
- `insert_reflect`
- `remove_reflect`
- `insert_reflect_with_registry`
- `remove_reflect_with_registry`
The commands operate the same except the with_registry commands take a
generic parameter for a resource that implements `AsRef<TypeRegistry>`.
Otherwise the default commands use the `AppTypeRegistry` for reflection
data.
Changed:
- Made `EntityCommands` fields pub(crate) to allow access in the reflect
module.
> Hopefully this time it works. Please don't make me rebase again ☹
# Objective
- Fixes [#8835](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/8835)
## Solution
- Added a note to the `set_volume` docstring which explains how volume
is interpreted.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: GitGhillie <jillisnoordhoek@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Fixes#4917
- Replaces #9602
## Solution
- Replaced `EntityCommand` implementation for `FnOnce` to apply to
`FnOnce(EntityMut)` instead of `FnOnce(Entity, &mut World)`
---
## Changelog
- `FnOnce(Entity, &mut World)` no longer implements `EntityCommand`.
This is a breaking change.
## Migration Guide
### 1. New-Type `FnOnce`
Create an `EntityCommand` type which implements the method you
previously wrote:
```rust
pub struct ClassicEntityCommand<F>(pub F);
impl<F> EntityCommand for ClassicEntityCommand<F>
where
F: FnOnce(Entity, &mut World) + Send + 'static,
{
fn apply(self, id: Entity, world: &mut World) {
(self.0)(id, world);
}
}
commands.add(ClassicEntityCommand(|id: Entity, world: &mut World| {
/* ... */
}));
```
### 2. Extract `(Entity, &mut World)` from `EntityMut`
The method `into_world_mut` can be used to gain access to the `World`
from an `EntityMut`.
```rust
let old = |id: Entity, world: &mut World| {
/* ... */
};
let new = |mut entity: EntityMut| {
let id = entity.id();
let world = entity.into_world_mut();
/* ... */
};
```
# Objective
The name `ManualEventIterator` is long and unnecessary, as this is the
iterator type used for both `EventReader` and `ManualEventReader`.
## Solution
Rename `ManualEventIterator` to `EventIterator`. To ease migration, add
a deprecated type alias with the old name.
---
## Changelog
- The types `ManualEventIterator{WithId}` have been renamed to
`EventIterator{WithId}`.
## Migration Guide
The type `ManualEventIterator` has been renamed to `EventIterator`.
Additonally, `ManualEventIteratorWithId` has been renamed to
`EventIteratorWithId`.
# Objective
#5483 allows for the creation of non-`Sync` locals. However, it's not
actually possible to use these types as there is a `Sync` bound on the
`Deref` impls.
## Solution
Remove the unnecessary bounds.
# Objective
- have errors in configure_set and configure_sets show the line number
of the user calling location rather than pointing to schedule.rs
- use display formatting for the errors
## Example Error Text
```text
// dependency loop
// before
thread 'main' panicked at 'called `Result::unwrap()` on an `Err` value: DependencyLoop("A")', crates\bevy_ecs\src\schedule\schedule.rs:682:39
// after
thread 'main' panicked at 'System set `A` depends on itself.', examples/stress_tests/bevymark.rs:16:9
// hierarchy loop
// before
thread 'main' panicked at 'called `Result::unwrap()` on an `Err` value: HierarchyLoop("A")', crates\bevy_ecs\src\schedule\schedule.rs:682:3
// after
thread 'main' panicked at 'System set `A` contains itself.', examples/stress_tests/bevymark.rs:16:9
// configuring a system type set
// before
thread 'main' panicked at 'configuring system type sets is not allowed', crates\bevy_ecs\src\schedule\config.rs:394:9
//after
thread 'main' panicked at 'configuring system type sets is not allowed', examples/stress_tests/bevymark.rs:16:9
```
Code to produce errors:
```rust
use bevy::prelude::*;
#[derive(SystemSet, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq, Hash)]
enum TestSet {
A,
}
fn main() {
fn foo() {}
let mut app = App::empty();
// Hierarchy Loop
app.configure_set(Main, TestSet::A.in_set(TestSet::A));
// Dependency Loop
app.configure_set(Main, TestSet::A.after(TestSet::A));
// Configure System Type Set
app.configure_set(Main, foo.into_system_set());
}
```
# Objective
A Bezier curve is a curve defined by two or more control points. In the
simplest form, it's just a line. The (arguably) most common type of
Bezier curve is a cubic Bezier, defined by four control points. These
are often used in animation, etc. Bevy has a Bezier curve struct called
`Bezier`. However, this is technically a misnomer as it only represents
cubic Bezier curves.
## Solution
This PR changes the struct name to `CubicBezier` to more accurately
reflect the struct's usage. Since it's exposed in Bevy's prelude, it can
potentially collide with other `Bezier` implementations. While that
might instead be an argument for removing it from the prelude, there's
also something to be said for adding a more general `Bezier` into Bevy,
in which case we'd likely want to use the name `Bezier`. As a final
motivator, not only is the struct located in `cubic_spines.rs`, there
are also several other spline-related structs which follow the
`CubicXxx` naming convention where applicable. For example,
`CubicSegment` represents a cubic Bezier curve (with coefficients
pre-baked).
---
## Migration Guide
- Change all `Bezier` references to `CubicBezier`
# Objective
Fixes#9550
## Solution
Removes a check that asserts that _all_ attribute metas are path-only,
rather than just the `#[deref]` attribute itself.
---
## Changelog
- Fixes an issue where deriving `Deref` with `#[deref]` on a field
causes other attributes to sometimes result in a compile error
---------
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
# Objective
These new defaults match what is used by `Camera2dBundle::default()`,
removing a potential footgun from overriding a field in the projection
component of the bundle.
## Solution
Adjusted the near clipping plane of `OrthographicProjection::default()`
to `-1000.`.
---
## Changelog
Changed: `OrthographicProjection::default()` now matches the value used
in `Camera2dBundle::default()`
## Migration Guide
Workarounds used to keep the projection consistent with the bundle
defaults are no longer required. Meanwhile, uses of
`OrthographicProjection` in 2D scenes may need to be adjusted; the
`near` clipping plane default was changed from `0.0` to `-1000.0`.
# Objective
`sync_simple_transforms` only checks for removed parents and doesn't
filter for `Without<Parent>`, so it overwrites the `GlobalTransform` of
non-orphan entities that were orphaned and then reparented since the
last update.
Introduced by #7264
## Solution
Filter for `Without<Parent>`.
Fixes#9517, #9492
## Changelog
`sync_simple_transforms`:
* Added a `Without<Parent>` filter to the orphaned entities query.
Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/9458.
On case-insensitive filesystems (Windows, Mac, NTFS mounted in Linux,
etc.), a path can be represented in a multiple ways:
- `c:\users\user\rust\assets\hello\world`
- `c:/users/user/rust/assets/hello/world`
- `C:\USERS\USER\rust\assets\hello\world`
If user specifies a path variant that doesn't match asset folder path
bevy calculates, `path.strip_prefix()` will fail, as demonstrated below:
```rs
dbg!(Path::new("c:/foo/bar/baz").strip_prefix("c:/foo"));
// Ok("bar/baz")
dbg!(Path::new("c:/FOO/bar/baz").strip_prefix("c:/foo"));
// StripPrefixError(())
```
This commit rewrites the code in question in a way that prefix stripping
is no longer necessary.
I've tested with the following paths on my computer:
```rs
let res = asset_server.load_folder("C:\\Users\\user\\rust\\assets\\foo\\bar");
dbg!(res);
let res = asset_server.load_folder("c:\\users\\user\\rust\\assets\\foo\\bar");
dbg!(res);
let res = asset_server.load_folder("C:/Users/user/rust/assets/foo/bar");
dbg!(res);
```
# Objective
* There is no way to read the fields of `GridPlacement` once set.
* Values of `0` for `GridPlacement`'s fields are invalid but can be set.
* A non-zero representation would be half the size.
fixes#9474
## Solution
* Add `get_start`, `get_end` and `get_span` accessor methods.
* Change`GridPlacement`'s constructor functions to panic on arguments of
zero.
* Use non-zero types instead of primitives for `GridPlacement`'s fields.
---
## Changelog
`bevy_ui::ui_node::GridPlacement`:
* Field types have been changed to `Option<NonZeroI16>` and
`Option<NonZeroU16>`. This is because zero values are not valid for
`GridPlacement`. Previously, Taffy interpreted these as auto variants.
* Constructor functions for `GridPlacement` panic on arguments of `0`.
* Added accessor functions: `get_start`, `get_end`, and `get_span`.
These return the inner primitive value (if present) of the respective
fields.
## Migration Guide
`GridPlacement`'s constructor functions no longer accept values of `0`.
Given any argument of `0` they will panic with a `GridPlacementError`.
# Objective
- Fixes#9321
## Solution
- `EntityMap` has been replaced by a simple `HashMap<Entity, Entity>`.
---
## Changelog
- `EntityMap::world_scope` has been replaced with `World::world_scope`
to avoid creating a new trait. This is a public facing change to the
call semantics, but has no effect on results or behaviour.
- `EntityMap`, as a `HashMap`, now operates on `&Entity` rather than
`Entity`. This changes many standard access functions (e.g, `.get`) in a
public-facing way.
## Migration Guide
- Calls to `EntityMap::world_scope` can be directly replaced with the
following:
`map.world_scope(&mut world)` -> `world.world_scope(&mut map)`
- Calls to legacy `EntityMap` methods such as `EntityMap::get` must
explicitly include de/reference symbols:
`let entity = map.get(parent);` -> `let &entity = map.get(&parent);`
# Objective
Fixes#9420
## Solution
Remove one of the two `AppExit` event checks in the
`ScheduleRunnerPlugin`'s main loop. Specificially, the check that
happens immediately before calling `App.update()`, to be consistent with
the `WinitPlugin`.
# Objective
fixes#8357
gltf animations can affect multiple "root" nodes (i.e. top level nodes
within a gltf scene).
the current loader adds an AnimationPlayer to each root node which is
affected by any animation. when a clip which affects multiple root nodes
is played on a root node player, the root node name is not checked,
leading to potentially incorrect weights being applied.
also, the `AnimationClip::compatible_with` method will never return true
for those clips, as it checks that all paths start with the root node
name - not all paths start with the same name so it can't return true.
## Solution
- check the first path node name matches the given root
- change compatible_with to return true if `any` match is found
a better alternative would probably be to attach the player to the scene
root instead of the first child, and then walk the full path from there.
this would be breaking (and would stop multiple animations that *don't*
overlap from being played concurrently), but i'm happy to modify to that
if it's preferred.
---------
Co-authored-by: Nicola Papale <nicopap@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
- Meshes with a higher number of joints than `MAX_JOINTS` are crashing
- Fixes partly #9021 (doesn't crash anymore, but the mesh is not
correctly displayed)
## Solution
- Only take up to `MAX_JOINTS` joints when extending the buffer
# Objective
Make code relating to event more readable.
Currently the `impl` block of `Events` is split in two, and the big part
of its implementations are put at the end of the file, far from the
definition of the `struct`.
## Solution
- Move and merge the `impl` blocks of `Events` next to its definition.
- Move the `EventSequence` definition and implementations before the
`Events`, because they're pretty trivial and help understand how
`Events` work, rather than being buried bellow `Events`.
I separated those two steps in two commits to not be too confusing. I
didn't modify any code of documentation. I want to do a second PR with
such modifications after this one is merged.