# Objective
After #10520, I was experiencing seriously degraded performance that
ended up being due to never-drained `AssetEvent` events causing havoc
inside `extract_render_asset::<A>`. The same events being read over and
over again meant the same assets were being prepared every frame for
eternity. For what it's worth, I was noticing this on a static scene
about every 3rd or so time running my project.
* References #10520
* Fixes#11240
Why these events aren't sometimes drained between frames is beyond me
and perhaps worthy of another investigation, but the approach in this PR
effectively restores the original cached `EventReader` behavior (which
fixes it).
## Solution
I followed the [`CachedSystemState`
example](3a666cab23/crates/bevy_ecs/src/system/function_system.rs (L155))
to make sure that the `EventReader` state is cached between frames like
it used to be when it was an argument of `extract_render_asset::<A>`.
# Objective
Keep core dependencies up to date.
## Solution
Update the dependencies.
wgpu 0.19 only supports raw-window-handle (rwh) 0.6, so bumping that was
included in this.
The rwh 0.6 version bump is just the simplest way of doing it. There
might be a way we can take advantage of wgpu's new safe surface creation
api, but I'm not familiar enough with bevy's window management to
untangle it and my attempt ended up being a mess of lifetimes and rustc
complaining about missing trait impls (that were implemented). Thanks to
@MiniaczQ for the (much simpler) rwh 0.6 version bump code.
Unblocks https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/9172 and
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/10812
~~This might be blocked on cpal and oboe updating their ndk versions to
0.8, as they both currently target ndk 0.7 which uses rwh 0.5.2~~ Tested
on android, and everything seems to work correctly (audio properly stops
when minimized, and plays when re-focusing the app).
---
## Changelog
- `wgpu` has been updated to 0.19! The long awaited arcanization has
been merged (for more info, see
https://gfx-rs.github.io/2023/11/24/arcanization.html), and Vulkan
should now be working again on Intel GPUs.
- Targeting WebGPU now requires that you add the new `webgpu` feature
(setting the `RUSTFLAGS` environment variable to
`--cfg=web_sys_unstable_apis` is still required). This feature currently
overrides the `webgl2` feature if you have both enabled (the `webgl2`
feature is enabled by default), so it is not recommended to add it as a
default feature to libraries without putting it behind a flag that
allows library users to opt out of it! In the future we plan on
supporting wasm binaries that can target both webgl2 and webgpu now that
wgpu added support for doing so (see
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/11505).
- `raw-window-handle` has been updated to version 0.6.
## Migration Guide
- `bevy_render::instance_index::get_instance_index()` has been removed
as the webgl2 workaround is no longer required as it was fixed upstream
in wgpu. The `BASE_INSTANCE_WORKAROUND` shaderdef has also been removed.
- WebGPU now requires the new `webgpu` feature to be enabled. The
`webgpu` feature currently overrides the `webgl2` feature so you no
longer need to disable all default features and re-add them all when
targeting `webgpu`, but binaries built with both the `webgpu` and
`webgl2` features will only target the webgpu backend, and will only
work on browsers that support WebGPU.
- Places where you conditionally compiled things for webgl2 need to be
updated because of this change, eg:
- `#[cfg(any(not(feature = "webgl"), not(target_arch = "wasm32")))]`
becomes `#[cfg(any(not(feature = "webgl") ,not(target_arch = "wasm32"),
feature = "webgpu"))]`
- `#[cfg(all(feature = "webgl", target_arch = "wasm32"))]` becomes
`#[cfg(all(feature = "webgl", target_arch = "wasm32", not(feature =
"webgpu")))]`
- `if cfg!(all(feature = "webgl", target_arch = "wasm32"))` becomes `if
cfg!(all(feature = "webgl", target_arch = "wasm32", not(feature =
"webgpu")))`
- `create_texture_with_data` now also takes a `TextureDataOrder`. You
can probably just set this to `TextureDataOrder::default()`
- `TextureFormat`'s `block_size` has been renamed to `block_copy_size`
- See the `wgpu` changelog for anything I might've missed:
https://github.com/gfx-rs/wgpu/blob/trunk/CHANGELOG.md
---------
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
Updates the requirements on
[ruzstd](https://github.com/KillingSpark/zstd-rs) to permit the latest
version.
<details>
<summary>Release notes</summary>
<p><em>Sourced from <a
href="https://github.com/KillingSpark/zstd-rs/releases">ruzstd's
releases</a>.</em></p>
<blockquote>
<h2>Even better no_std</h2>
<p>Switching from thiserror to derive_more allows for no_std builds on
stable rust</p>
</blockquote>
</details>
<details>
<summary>Changelog</summary>
<p><em>Sourced from <a
href="https://github.com/KillingSpark/zstd-rs/blob/master/Changelog.md">ruzstd's
changelog</a>.</em></p>
<blockquote>
<h1>After 0.5.0</h1>
<ul>
<li>Make the hashing checksum optional (thanks to <a
href="https://github.com/tamird"><code>@tamird</code></a>)
<ul>
<li>breaking change as the public API changes based on features</li>
</ul>
</li>
</ul>
</blockquote>
</details>
<details>
<summary>Commits</summary>
<ul>
<li><a
href="e620d2a856"><code>e620d2a</code></a>
Merge pull request <a
href="https://redirect.github.com/KillingSpark/zstd-rs/issues/50">#50</a>
from KillingSpark/remove_thiserror</li>
<li><a
href="9e9d204c63"><code>9e9d204</code></a>
make clippy happy</li>
<li><a
href="f4a6fc0cc1"><code>f4a6fc0</code></a>
bump the version, this is an incompatible change</li>
<li><a
href="64d65b5c4f"><code>64d65b5</code></a>
fix test compile...</li>
<li><a
href="07bbda98c8"><code>07bbda9</code></a>
remove the error_in_core feature and switch the io_nostd to use the
Display t...</li>
<li><a
href="e15eb1e568"><code>e15eb1e</code></a>
Merge pull request <a
href="https://redirect.github.com/KillingSpark/zstd-rs/issues/49">#49</a>
from tamird/clippy</li>
<li><a
href="92a3f2e6b2"><code>92a3f2e</code></a>
Avoid unnecessary cast</li>
<li><a
href="f588d5c362"><code>f588d5c</code></a>
Avoid slow zero-filling initialization</li>
<li><a
href="e79f09876f"><code>e79f098</code></a>
Avoid single-match expression</li>
<li><a
href="c75cc2fbb9"><code>c75cc2f</code></a>
Remove useless assertion</li>
<li>Additional commits viewable in <a
href="https://github.com/KillingSpark/zstd-rs/compare/v0.4.0...v0.5.0">compare
view</a></li>
</ul>
</details>
<br />
Dependabot will resolve any conflicts with this PR as long as you don't
alter it yourself. You can also trigger a rebase manually by commenting
`@dependabot rebase`.
[//]: # (dependabot-automerge-start)
[//]: # (dependabot-automerge-end)
---
<details>
<summary>Dependabot commands and options</summary>
<br />
You can trigger Dependabot actions by commenting on this PR:
- `@dependabot rebase` will rebase this PR
- `@dependabot recreate` will recreate this PR, overwriting any edits
that have been made to it
- `@dependabot merge` will merge this PR after your CI passes on it
- `@dependabot squash and merge` will squash and merge this PR after
your CI passes on it
- `@dependabot cancel merge` will cancel a previously requested merge
and block automerging
- `@dependabot reopen` will reopen this PR if it is closed
- `@dependabot close` will close this PR and stop Dependabot recreating
it. You can achieve the same result by closing it manually
- `@dependabot show <dependency name> ignore conditions` will show all
of the ignore conditions of the specified dependency
- `@dependabot ignore this major version` will close this PR and stop
Dependabot creating any more for this major version (unless you reopen
the PR or upgrade to it yourself)
- `@dependabot ignore this minor version` will close this PR and stop
Dependabot creating any more for this minor version (unless you reopen
the PR or upgrade to it yourself)
- `@dependabot ignore this dependency` will close this PR and stop
Dependabot creating any more for this dependency (unless you reopen the
PR or upgrade to it yourself)
</details>
Signed-off-by: dependabot[bot] <support@github.com>
Co-authored-by: dependabot[bot] <49699333+dependabot[bot]@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
- Prep for https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/10164
- Make deferred_lighting_pass_id a ColorAttachment
- Correctly extract shadow view frusta so that the view uniforms get
populated
- Make some needed things public
- Misc formatting
# Objective
> Can anyone explain to me the reasoning of renaming all the types named
Query to Data. I'm talking about this PR
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/10779 It doesn't make sense to
me that a bunch of types that are used to run queries aren't named Query
anymore. Like ViewQuery on the ViewNode is the type of the Query. I
don't really understand the point of the rename, it just seems like it
hides the fact that a query will run based on those types.
[@IceSentry](https://discord.com/channels/691052431525675048/692572690833473578/1184946251431694387)
## Solution
Revert several renames in #10779.
## Changelog
- `ViewNode::ViewData` is now `ViewNode::ViewQuery` again.
## Migration Guide
- This PR amends the migration guide in
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/10779
---------
Co-authored-by: atlas dostal <rodol@rivalrebels.com>
# Objective
- Add the ability to describe storage texture bindings when deriving
`AsBindGroup`.
- This is especially valuable for the compute story of bevy which
deserves some extra love imo.
## Solution
- This add the ability to annotate struct fields with a
`#[storage_texture(0)]` annotation.
- Instead of adding specific option parsing for all the image formats
and access modes, I simply accept a token stream and defer checking to
see if the option is valid to the compiler. This still results in useful
and friendly errors and is free to maintain and always compatible with
wgpu changes.
---
## Changelog
- The `#[storage_texture(..)]` annotation is now accepted for fields of
`Handle<Image>` in structs that derive `AsBindGroup`.
- The game_of_life compute shader example has been updated to use
`AsBindGroup` together with `[storage_texture(..)]` to obtain the
`BindGroupLayout`.
## Migration Guide
# Objective
- since #9685 ,bevy introduce automatic batching of draw commands,
- `batch_and_prepare_render_phase` take the responsibility for batching
`phaseItem`,
- `GetBatchData` trait is used for indentify each phaseitem how to
batch. it defines a associated type `Data `used for Query to fetch data
from world.
- however,the impl of `GetBatchData ` in bevy always set ` type
Data=Entity` then we acually get following code
`let entity:Entity =query.get(item.entity())` that cause unnecessary
overhead .
## Solution
- remove associated type `Data ` and `Filter` from `GetBatchData `,
- change the type of the `query_item ` parameter in get_batch_data from`
Self::Data` to `Entity`.
- `batch_and_prepare_render_phase ` no longer takes a query using
`F::Data, F::Filter`
- `get_batch_data `now returns `Option<(Self::BufferData,
Option<Self::CompareData>)>`
---
## Performance
based in main merged with #11290
Window 11 ,Intel 13400kf, NV 4070Ti

frame time from 3.34ms to 3 ms, ~ 10%
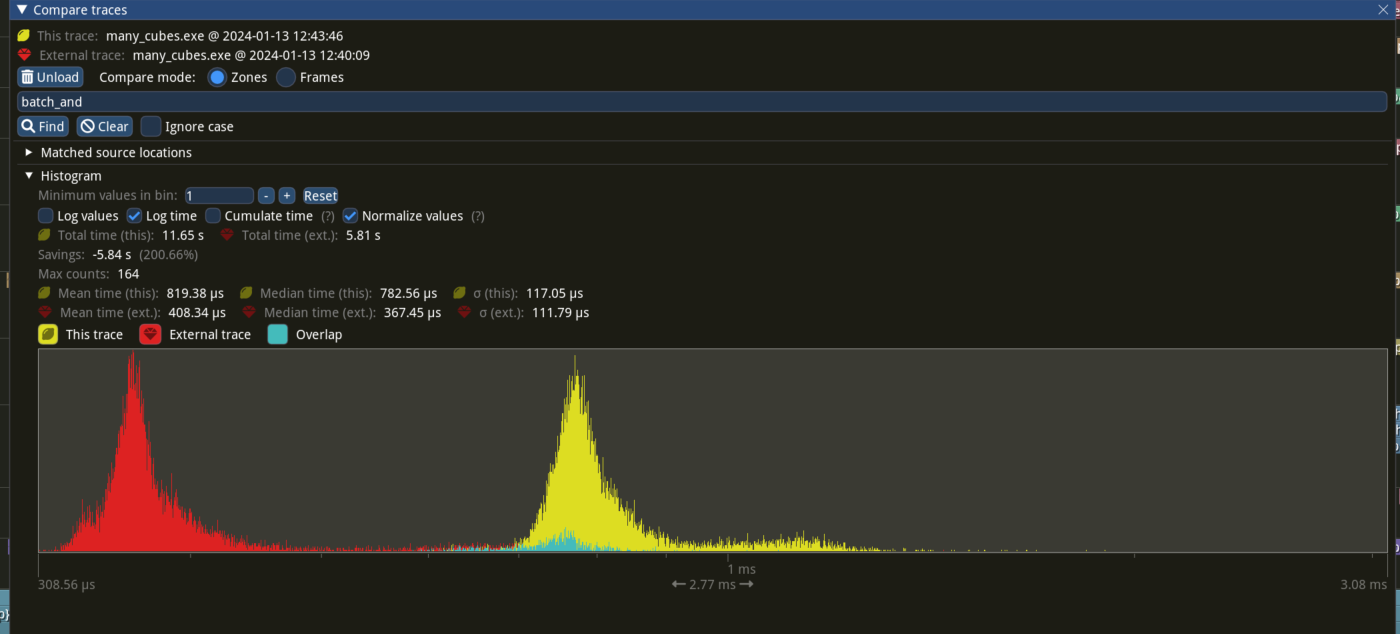
`batch_and_prepare_render_phase` from 800us ~ 400 us
## Migration Guide
trait `GetBatchData` no longer hold associated type `Data `and `Filter`
`get_batch_data` `query_item `type from `Self::Data` to `Entity` and
return `Option<(Self::BufferData, Option<Self::CompareData>)>`
`batch_and_prepare_render_phase` should not have a query
This pull request re-submits #10057, which was backed out for breaking
macOS, iOS, and Android. I've tested this version on macOS and Android
and on the iOS simulator.
# Objective
This pull request implements *reflection probes*, which generalize
environment maps to allow for multiple environment maps in the same
scene, each of which has an axis-aligned bounding box. This is a
standard feature of physically-based renderers and was inspired by [the
corresponding feature in Blender's Eevee renderer].
## Solution
This is a minimal implementation of reflection probes that allows
artists to define cuboid bounding regions associated with environment
maps. For every view, on every frame, a system builds up a list of the
nearest 4 reflection probes that are within the view's frustum and
supplies that list to the shader. The PBR fragment shader searches
through the list, finds the first containing reflection probe, and uses
it for indirect lighting, falling back to the view's environment map if
none is found. Both forward and deferred renderers are fully supported.
A reflection probe is an entity with a pair of components, *LightProbe*
and *EnvironmentMapLight* (as well as the standard *SpatialBundle*, to
position it in the world). The *LightProbe* component (along with the
*Transform*) defines the bounding region, while the
*EnvironmentMapLight* component specifies the associated diffuse and
specular cubemaps.
A frequent question is "why two components instead of just one?" The
advantages of this setup are:
1. It's readily extensible to other types of light probes, in particular
*irradiance volumes* (also known as ambient cubes or voxel global
illumination), which use the same approach of bounding cuboids. With a
single component that applies to both reflection probes and irradiance
volumes, we can share the logic that implements falloff and blending
between multiple light probes between both of those features.
2. It reduces duplication between the existing *EnvironmentMapLight* and
these new reflection probes. Systems can treat environment maps attached
to cameras the same way they treat environment maps applied to
reflection probes if they wish.
Internally, we gather up all environment maps in the scene and place
them in a cubemap array. At present, this means that all environment
maps must have the same size, mipmap count, and texture format. A
warning is emitted if this restriction is violated. We could potentially
relax this in the future as part of the automatic mipmap generation
work, which could easily do texture format conversion as part of its
preprocessing.
An easy way to generate reflection probe cubemaps is to bake them in
Blender and use the `export-blender-gi` tool that's part of the
[`bevy-baked-gi`] project. This tool takes a `.blend` file containing
baked cubemaps as input and exports cubemap images, pre-filtered with an
embedded fork of the [glTF IBL Sampler], alongside a corresponding
`.scn.ron` file that the scene spawner can use to recreate the
reflection probes.
Note that this is intentionally a minimal implementation, to aid
reviewability. Known issues are:
* Reflection probes are basically unsupported on WebGL 2, because WebGL
2 has no cubemap arrays. (Strictly speaking, you can have precisely one
reflection probe in the scene if you have no other cubemaps anywhere,
but this isn't very useful.)
* Reflection probes have no falloff, so reflections will abruptly change
when objects move from one bounding region to another.
* As mentioned before, all cubemaps in the world of a given type
(diffuse or specular) must have the same size, format, and mipmap count.
Future work includes:
* Blending between multiple reflection probes.
* A falloff/fade-out region so that reflected objects disappear
gradually instead of vanishing all at once.
* Irradiance volumes for voxel-based global illumination. This should
reuse much of the reflection probe logic, as they're both GI techniques
based on cuboid bounding regions.
* Support for WebGL 2, by breaking batches when reflection probes are
used.
These issues notwithstanding, I think it's best to land this with
roughly the current set of functionality, because this patch is useful
as is and adding everything above would make the pull request
significantly larger and harder to review.
---
## Changelog
### Added
* A new *LightProbe* component is available that specifies a bounding
region that an *EnvironmentMapLight* applies to. The combination of a
*LightProbe* and an *EnvironmentMapLight* offers *reflection probe*
functionality similar to that available in other engines.
[the corresponding feature in Blender's Eevee renderer]:
https://docs.blender.org/manual/en/latest/render/eevee/light_probes/reflection_cubemaps.html
[`bevy-baked-gi`]: https://github.com/pcwalton/bevy-baked-gi
[glTF IBL Sampler]: https://github.com/KhronosGroup/glTF-IBL-Sampler
# Objective
- Some users want to change the default texture usage of the main camera
but they are currently hardcoded
## Solution
- Add a component that is used to configure the main texture usage field
---
## Changelog
Added `CameraMainTextureUsage`
Added `CameraMainTextureUsage` to `Camera3dBundle` and `Camera2dBundle`
## Migration Guide
Add `main_texture_usages: Default::default()` to your camera bundle.
# Notes
Inspired by: #6815
# Objective
- `DynamicUniformBuffer::push` takes an owned `T` but only uses a shared
reference to it
- This in turn requires users of `DynamicUniformBuffer::push` to
potentially unecessarily clone data
## Solution
- Have `DynamicUniformBuffer::push` take a shared reference to `T`
---
## Changelog
- `DynamicUniformBuffer::push` now takes a `&T` instead of `T`
## Migration Guide
- Users of `DynamicUniformBuffer::push` now need to pass references to
`DynamicUniformBuffer::push` (e.g. existing `uniforms.push(value)` will
now become `uniforms.push(&value)`)
Rebased and finished version of
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/8407. Huge thanks to @GitGhillie
for adjusting all the examples, and the many other people who helped
write this PR (@superdump , @coreh , among others) :)
Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/8369
---
## Changelog
- Added a `brightness` control to `Skybox`.
- Added an `intensity` control to `EnvironmentMapLight`.
- Added `ExposureSettings` and `PhysicalCameraParameters` for
controlling exposure of 3D cameras.
- Removed the baked-in `DirectionalLight` exposure Bevy previously
hardcoded internally.
## Migration Guide
- If using a `Skybox` or `EnvironmentMapLight`, use the new `brightness`
and `intensity` controls to adjust their strength.
- All 3D scene will now have different apparent brightnesses due to Bevy
implementing proper exposure controls. You will have to adjust the
intensity of your lights and/or your camera exposure via the new
`ExposureSettings` component to compensate.
---------
Co-authored-by: Robert Swain <robert.swain@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: GitGhillie <jillisnoordhoek@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Marco Buono <thecoreh@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: vero <email@atlasdostal.com>
Co-authored-by: atlas dostal <rodol@rivalrebels.com>
# Objective
Add support for presenting each UI tree on a specific window and
viewport, while making as few breaking changes as possible.
This PR is meant to resolve the following issues at once, since they're
all related.
- Fixes#5622
- Fixes#5570
- Fixes#5621
Adopted #5892 , but started over since the current codebase diverged
significantly from the original PR branch. Also, I made a decision to
propagate component to children instead of recursively iterating over
nodes in search for the root.
## Solution
Add a new optional component that can be inserted to UI root nodes and
propagate to children to specify which camera it should render onto.
This is then used to get the render target and the viewport for that UI
tree. Since this component is optional, the default behavior should be
to render onto the single camera (if only one exist) and warn of
ambiguity if multiple cameras exist. This reduces the complexity for
users with just one camera, while giving control in contexts where it
matters.
## Changelog
- Adds `TargetCamera(Entity)` component to specify which camera should a
node tree be rendered into. If only one camera exists, this component is
optional.
- Adds an example of rendering UI to a texture and using it as a
material in a 3D world.
- Fixes recalculation of physical viewport size when target scale factor
changes. This can happen when the window is moved between displays with
different DPI.
- Changes examples to demonstrate assigning UI to different viewports
and windows and make interactions in an offset viewport testable.
- Removes `UiCameraConfig`. UI visibility now can be controlled via
combination of explicit `TargetCamera` and `Visibility` on the root
nodes.
---------
Co-authored-by: davier <bricedavier@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecil@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Update async channel to v2.
## Solution
- async channel doesn't support `send_blocking` on wasm anymore. So
don't compile the pipelined rendering plugin on wasm anymore.
- Replaces https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/10405
## Migration Guide
- The `PipelinedRendering` plugin is no longer exported on wasm. If you
are including it in your wasm builds you should remove it.
```rust
#[cfg(all(not(target_arch = "wasm32"))]
app.add_plugins(bevy_render::pipelined_rendering::PipelinedRenderingPlugin);
```
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
Issue #10243: rendering multiple triangles in the same place results in
flickering.
## Solution
Considered these alternatives:
- `depth_bias` may not work, because of high number of entities, so
creating a material per entity is practically not possible
- rendering at slightly different positions does not work, because when
camera is far, float rounding causes the same issues (edit: assuming we
have to use the same `depth_bias`)
- considered implementing deterministic operation like
`query.par_iter().flat_map(...).collect()` to be used in
`check_visibility` system (which would solve the issue since query is
deterministic), and could not figure out how to make it as cheap as
current approach with thread-local collectors (#11249)
So adding an option to sort entities after `check_visibility` system
run.
Should not be too bad, because after visibility check, only a handful
entities remain.
This is probably not the only source of non-determinism in Bevy, but
this is one I could find so far. At least it fixes the repro example.
## Changelog
- `DeterministicRenderingConfig` option to enable deterministic
rendering
## Test
<img width="1392" alt="image"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/28969/c735bce1-3a71-44cd-8677-c19f6c0ee6bd">
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Update to `glam` 0.25, `encase` 0.7 and `hexasphere` to 10.0
## Changelog
Added the `FloatExt` trait to the `bevy_math` prelude which adds `lerp`,
`inverse_lerp` and `remap` methods to the `f32` and `f64` types.
# Objective
This pull request implements *reflection probes*, which generalize
environment maps to allow for multiple environment maps in the same
scene, each of which has an axis-aligned bounding box. This is a
standard feature of physically-based renderers and was inspired by [the
corresponding feature in Blender's Eevee renderer].
## Solution
This is a minimal implementation of reflection probes that allows
artists to define cuboid bounding regions associated with environment
maps. For every view, on every frame, a system builds up a list of the
nearest 4 reflection probes that are within the view's frustum and
supplies that list to the shader. The PBR fragment shader searches
through the list, finds the first containing reflection probe, and uses
it for indirect lighting, falling back to the view's environment map if
none is found. Both forward and deferred renderers are fully supported.
A reflection probe is an entity with a pair of components, *LightProbe*
and *EnvironmentMapLight* (as well as the standard *SpatialBundle*, to
position it in the world). The *LightProbe* component (along with the
*Transform*) defines the bounding region, while the
*EnvironmentMapLight* component specifies the associated diffuse and
specular cubemaps.
A frequent question is "why two components instead of just one?" The
advantages of this setup are:
1. It's readily extensible to other types of light probes, in particular
*irradiance volumes* (also known as ambient cubes or voxel global
illumination), which use the same approach of bounding cuboids. With a
single component that applies to both reflection probes and irradiance
volumes, we can share the logic that implements falloff and blending
between multiple light probes between both of those features.
2. It reduces duplication between the existing *EnvironmentMapLight* and
these new reflection probes. Systems can treat environment maps attached
to cameras the same way they treat environment maps applied to
reflection probes if they wish.
Internally, we gather up all environment maps in the scene and place
them in a cubemap array. At present, this means that all environment
maps must have the same size, mipmap count, and texture format. A
warning is emitted if this restriction is violated. We could potentially
relax this in the future as part of the automatic mipmap generation
work, which could easily do texture format conversion as part of its
preprocessing.
An easy way to generate reflection probe cubemaps is to bake them in
Blender and use the `export-blender-gi` tool that's part of the
[`bevy-baked-gi`] project. This tool takes a `.blend` file containing
baked cubemaps as input and exports cubemap images, pre-filtered with an
embedded fork of the [glTF IBL Sampler], alongside a corresponding
`.scn.ron` file that the scene spawner can use to recreate the
reflection probes.
Note that this is intentionally a minimal implementation, to aid
reviewability. Known issues are:
* Reflection probes are basically unsupported on WebGL 2, because WebGL
2 has no cubemap arrays. (Strictly speaking, you can have precisely one
reflection probe in the scene if you have no other cubemaps anywhere,
but this isn't very useful.)
* Reflection probes have no falloff, so reflections will abruptly change
when objects move from one bounding region to another.
* As mentioned before, all cubemaps in the world of a given type
(diffuse or specular) must have the same size, format, and mipmap count.
Future work includes:
* Blending between multiple reflection probes.
* A falloff/fade-out region so that reflected objects disappear
gradually instead of vanishing all at once.
* Irradiance volumes for voxel-based global illumination. This should
reuse much of the reflection probe logic, as they're both GI techniques
based on cuboid bounding regions.
* Support for WebGL 2, by breaking batches when reflection probes are
used.
These issues notwithstanding, I think it's best to land this with
roughly the current set of functionality, because this patch is useful
as is and adding everything above would make the pull request
significantly larger and harder to review.
---
## Changelog
### Added
* A new *LightProbe* component is available that specifies a bounding
region that an *EnvironmentMapLight* applies to. The combination of a
*LightProbe* and an *EnvironmentMapLight* offers *reflection probe*
functionality similar to that available in other engines.
[the corresponding feature in Blender's Eevee renderer]:
https://docs.blender.org/manual/en/latest/render/eevee/light_probes/reflection_cubemaps.html
[`bevy-baked-gi`]: https://github.com/pcwalton/bevy-baked-gi
[glTF IBL Sampler]: https://github.com/KhronosGroup/glTF-IBL-Sampler
# Objective
- Since #10702, the way bevy updates the window leads to major slowdowns
as seen in
- #11122
- #11220
- Slow is bad, furthermore, _very_ slow is _very_ bad. We should fix
this issue.
## Solution
- Move the app update code into the `Event::WindowEvent { event:
WindowEvent::RedrawRequested }` branch of the event loop.
- Run `window.request_redraw()` When `runner_state.redraw_requested`
- Instead of swapping `ControlFlow` between `Poll` and `Wait`, we always
keep it at `Wait`, and use `window.request_redraw()` to schedule an
immediate call to the event loop.
- `runner_state.redraw_requested` is set to `true` when
`UpdateMode::Continuous` and when a `RequestRedraw` event is received.
- Extract the redraw code into a separate function, because otherwise
I'd go crazy with the indentation level.
- Fix#11122.
## Testing
I tested the WASM builds as follow:
```sh
cargo run -p build-wasm-example -- --api webgl2 bevymark
python -m http.server --directory examples/wasm/ 8080
# Open browser at http://localhost:8080
```
On main, even spawning a couple sprites is super choppy. Even if it says
"300 FPS". While on this branch, it is smooth as butter.
I also found that it fixes all choppiness on window resize (tested on
Linux/X11). This was another issue from #10702 IIRC.
So here is what I tested:
- On `wasm`: `many_foxes` and `bevymark`, with `argh::from_env()`
commented out, otherwise we get a cryptic error.
- Both with `PresentMode::AutoVsync` and `PresentMode::AutoNoVsync`
- On main, it is consistently choppy.
- With this PR, the visible frame rate is consistent with the diagnostic
numbers
- On native (linux/x11) I ran similar tests, making sure that
`AutoVsync` limits to monitor framerate, and `AutoNoVsync` doesn't.
## Future work
Code could be improved, I wanted a quick solution easy to review, but we
really need to make the code more accessible.
- #9768
- ~~**`WinitSettings::desktop_app()` is completely borked.**~~ actually
broken on main as well
### Review guide
Consider enable the non-whitespace diff to see the _real_ change set.
# Objective
- Since #10520, assets are unloaded from RAM by default. This breaks a
number of scenario:
- using `load_folder`
- loading a gltf, then going through its mesh to transform them /
compute a collider / ...
- any assets/subassets scenario should be `Keep` as you can't know what
the user will do with the assets
- android suspension, where GPU memory is unloaded
- Alternative to #11202
## Solution
- Keep assets on CPU memory by default
# Objective
In my code I use a lot of images as render targets.
I'd like some convenience methods for working with this type.
## Solution
- Allow `.into()` to construct a `RenderTarget`
- Add `.as_image()`
---
## Changelog
### Added
- `RenderTarget` can be constructed via `.into()` on a `Handle<Image>`
- `RenderTarget` new method: `as_image`
---------
Signed-off-by: Torstein Grindvik <torstein.grindvik@muybridge.com>
Co-authored-by: Torstein Grindvik <torstein.grindvik@muybridge.com>
# Objective
- No point in keeping Meshes/Images in RAM once they're going to be sent
to the GPU, and kept in VRAM. This saves a _significant_ amount of
memory (several GBs) on scenes like bistro.
- References
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/1782
- https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/8624
## Solution
- Augment RenderAsset with the capability to unload the underlying asset
after extracting to the render world.
- Mesh/Image now have a cpu_persistent_access field. If this field is
RenderAssetPersistencePolicy::Unload, the asset will be unloaded from
Assets<T>.
- A new AssetEvent is sent upon dropping the last strong handle for the
asset, which signals to the RenderAsset to remove the GPU version of the
asset.
---
## Changelog
- Added `AssetEvent::NoLongerUsed` and
`AssetEvent::is_no_longer_used()`. This event is sent when the last
strong handle of an asset is dropped.
- Rewrote the API for `RenderAsset` to allow for unloading the asset
data from the CPU.
- Added `RenderAssetPersistencePolicy`.
- Added `Mesh::cpu_persistent_access` for memory savings when the asset
is not needed except for on the GPU.
- Added `Image::cpu_persistent_access` for memory savings when the asset
is not needed except for on the GPU.
- Added `ImageLoaderSettings::cpu_persistent_access`.
- Added `ExrTextureLoaderSettings`.
- Added `HdrTextureLoaderSettings`.
## Migration Guide
- Asset loaders (GLTF, etc) now load meshes and textures without
`cpu_persistent_access`. These assets will be removed from
`Assets<Mesh>` and `Assets<Image>` once `RenderAssets<Mesh>` and
`RenderAssets<Image>` contain the GPU versions of these assets, in order
to reduce memory usage. If you require access to the asset data from the
CPU in future frames after the GLTF asset has been loaded, modify all
dependent `Mesh` and `Image` assets and set `cpu_persistent_access` to
`RenderAssetPersistencePolicy::Keep`.
- `Mesh` now requires a new `cpu_persistent_access` field. Set it to
`RenderAssetPersistencePolicy::Keep` to mimic the previous behavior.
- `Image` now requires a new `cpu_persistent_access` field. Set it to
`RenderAssetPersistencePolicy::Keep` to mimic the previous behavior.
- `MorphTargetImage::new()` now requires a new `cpu_persistent_access`
parameter. Set it to `RenderAssetPersistencePolicy::Keep` to mimic the
previous behavior.
- `DynamicTextureAtlasBuilder::add_texture()` now requires that the
`TextureAtlas` you pass has an `Image` with `cpu_persistent_access:
RenderAssetPersistencePolicy::Keep`. Ensure you construct the image
properly for the texture atlas.
- The `RenderAsset` trait has significantly changed, and requires
adapting your existing implementations.
- The trait now requires `Clone`.
- The `ExtractedAsset` associated type has been removed (the type itself
is now extracted).
- The signature of `prepare_asset()` is slightly different
- A new `persistence_policy()` method is now required (return
RenderAssetPersistencePolicy::Unload to match the previous behavior).
- Match on the new `NoLongerUsed` variant for exhaustive matches of
`AssetEvent`.
# Objective
There are a lot of doctests that are `ignore`d for no documented reason.
And that should be fixed.
## Solution
I searched the bevy repo with the regex ` ```[a-z,]*ignore ` in order to
find all `ignore`d doctests. For each one of the `ignore`d doctests, I
did the following steps:
1. Attempt to remove the `ignored` attribute while still passing the
test. I did this by adding hidden dummy structs and imports.
2. If step 1 doesn't work, attempt to replace the `ignored` attribute
with the `no_run` attribute while still passing the test.
3. If step 2 doesn't work, keep the `ignored` attribute but add
documentation for why the `ignored` attribute was added.
---------
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Custom render passes, or future passes in the engine (such as
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/10164) need a better way to know
and indicate to the core passes whether the view color/depth/prepass
attachments have been cleared or not yet this frame, to know if they
should clear it themselves or load it.
## Solution
- For all render targets (depth textures, shadow textures, prepass
textures, main textures) use an atomic bool to track whether or not each
texture has been cleared this frame. Abstracted away in the new
ColorAttachment and DepthAttachment wrappers.
---
## Changelog
- Changed `ViewTarget::get_color_attachment()`, removed arguments.
- Changed `ViewTarget::get_unsampled_color_attachment()`, removed
arguments.
- Removed `Camera3d::clear_color`.
- Removed `Camera2d::clear_color`.
- Added `Camera::clear_color`.
- Added `ExtractedCamera::clear_color`.
- Added `ColorAttachment` and `DepthAttachment` wrappers.
- Moved `ClearColor` and `ClearColorConfig` from
`bevy::core_pipeline::clear_color` to `bevy::render::camera`.
- Core render passes now track when a texture is first bound as an
attachment in order to decide whether to clear or load it.
## Migration Guide
- Remove arguments to `ViewTarget::get_color_attachment()` and
`ViewTarget::get_unsampled_color_attachment()`.
- Configure clear color on `Camera` instead of on `Camera3d` and
`Camera2d`.
- Moved `ClearColor` and `ClearColorConfig` from
`bevy::core_pipeline::clear_color` to `bevy::render::camera`.
- `ViewDepthTexture` must now be created via the `new()` method
---------
Co-authored-by: vero <email@atlasdostal.com>
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Make the implementation order consistent between all sources to fit
the order in the trait.
## Solution
- Change the implementation order.
Matches versioning & features from other Cargo.toml files in the
project.
# Objective
Resolves#10932
## Solution
Added smallvec to the bevy_utils cargo.toml and added a line to
re-export the crate. Target version and features set to match what's
used in the other bevy crates.
The error conditions were not documented, this requires the user to
inspect the source code to know when to expect a `None`.
Error conditions should always be documented, so we document them.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Fix an inconsistency in the calculation of aspect ratio's.
- Fixes#10288
## Solution
- Created an intermediate `AspectRatio` struct, as suggested in the
issue. This is currently just used in any places where aspect ratio
calculations happen, to prevent doing it wrong. In my and @mamekoro 's
opinion, it would be better if this was used instead of a normal `f32`
in various places, but I didn't want to make too many changes to begin
with.
## Migration Guide
- Anywhere where you are currently expecting a f32 when getting aspect
ratios, you will now receive a `AspectRatio` struct. this still holds
the same value.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Users are often confused when their command effects are not visible in
the next system. This PR auto inserts sync points if there are deferred
buffers on a system and there are dependents on that system (systems
with after relationships).
- Manual sync points can lead to users adding more than needed and it's
hard for the user to have a global understanding of their system graph
to know which sync points can be merged. However we can easily calculate
which sync points can be merged automatically.
## Solution
1. Add new edge types to allow opting out of new behavior
2. Insert an sync point for each edge whose initial node has deferred
system params.
3. Reuse nodes if they're at the number of sync points away.
* add opt outs for specific edges with `after_ignore_deferred`,
`before_ignore_deferred` and `chain_ignore_deferred`. The
`auto_insert_apply_deferred` boolean on `ScheduleBuildSettings` can be
set to false to opt out for the whole schedule.
## Perf
This has a small negative effect on schedule build times.
```text
group auto-sync main-for-auto-sync
----- ----------- ------------------
build_schedule/1000_schedule 1.06 2.8±0.15s ? ?/sec 1.00 2.7±0.06s ? ?/sec
build_schedule/1000_schedule_noconstraints 1.01 26.2±0.88ms ? ?/sec 1.00 25.8±0.36ms ? ?/sec
build_schedule/100_schedule 1.02 13.1±0.33ms ? ?/sec 1.00 12.9±0.28ms ? ?/sec
build_schedule/100_schedule_noconstraints 1.08 505.3±29.30µs ? ?/sec 1.00 469.4±12.48µs ? ?/sec
build_schedule/500_schedule 1.00 485.5±6.29ms ? ?/sec 1.00 485.5±9.80ms ? ?/sec
build_schedule/500_schedule_noconstraints 1.00 6.8±0.10ms ? ?/sec 1.02 6.9±0.16ms ? ?/sec
```
---
## Changelog
- Auto insert sync points and added `after_ignore_deferred`,
`before_ignore_deferred`, `chain_no_deferred` and
`auto_insert_apply_deferred` APIs to opt out of this behavior
## Migration Guide
- `apply_deferred` points are added automatically when there is ordering
relationship with a system that has deferred parameters like `Commands`.
If you want to opt out of this you can switch from `after`, `before`,
and `chain` to the corresponding `ignore_deferred` API,
`after_ignore_deferred`, `before_ignore_deferred` or
`chain_ignore_deferred` for your system/set ordering.
- You can also set `ScheduleBuildSettings::auto_insert_sync_points` to
`false` if you want to do it for the whole schedule. Note that in this
mode you can still add `apply_deferred` points manually.
- For most manual insertions of `apply_deferred` you should remove them
as they cannot be merged with the automatically inserted points and
might reduce parallelizability of the system graph.
## TODO
- [x] remove any apply_deferred used in the engine
- [x] ~~decide if we should deprecate manually using apply_deferred.~~
We'll still allow inserting manual sync points for now for whatever edge
cases users might have.
- [x] Update migration guide
- [x] rerun schedule build benchmarks
---------
Co-authored-by: Joseph <21144246+JoJoJet@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
- Finish the work done in #8942 .
## Solution
- Rebase the changes made in #8942 and fix the issues stopping it from
being merged earlier
---------
Co-authored-by: Thomas <1234328+thmsgntz@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
Keep up to date with wgpu.
## Solution
Update the wgpu version.
Currently blocked on naga_oil updating to naga 0.14 and releasing a new
version.
3d scenes (or maybe any scene with lighting?) currently don't render
anything due to
```
error: naga_oil bug, please file a report: composer failed to build a valid header: Type [2] '' is invalid
= Capability Capabilities(CUBE_ARRAY_TEXTURES) is required
```
I'm not sure what should be passed in for `wgpu::InstanceFlags`, or if we want to make the gles3minorversion configurable (might be useful for debugging?)
Currently blocked on https://github.com/bevyengine/naga_oil/pull/63, and https://github.com/gfx-rs/wgpu/issues/4569 to be fixed upstream in wgpu first.
## Known issues
Amd+windows+vulkan has issues with texture_binding_arrays (see the image [here](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/10266#issuecomment-1819946278)), but that'll be fixed in the next wgpu/naga version, and you can just use dx12 as a workaround for now (Amd+linux mesa+vulkan texture_binding_arrays are fixed though).
---
## Changelog
Updated wgpu to 0.18, naga to 0.14.2, and naga_oil to 0.11.
- Windows desktop GL should now be less painful as it no longer requires Angle.
- You can now toggle shader validation and debug information for debug and release builds using `WgpuSettings.instance_flags` and [InstanceFlags](https://docs.rs/wgpu/0.18.0/wgpu/struct.InstanceFlags.html)
## Migration Guide
- `RenderPassDescriptor` `color_attachments` (as well as `RenderPassColorAttachment`, and `RenderPassDepthStencilAttachment`) now use `StoreOp::Store` or `StoreOp::Discard` instead of a `boolean` to declare whether or not they should be stored.
- `RenderPassDescriptor` now have `timestamp_writes` and `occlusion_query_set` fields. These can safely be set to `None`.
- `ComputePassDescriptor` now have a `timestamp_writes` field. This can be set to `None` for now.
- See the [wgpu changelog](https://github.com/gfx-rs/wgpu/blob/trunk/CHANGELOG.md#v0180-2023-10-25) for additional details
I didn't notice minus where vertices are generated, so could not
understand the order there.
Adding a comment to help the next person who is going to understand Bevy
by reading its code.
# Objective
add `RenderLayers` awareness to lights. lights default to
`RenderLayers::layer(0)`, and must intersect the camera entity's
`RenderLayers` in order to affect the camera's output.
note that lights already use renderlayers to filter meshes for shadow
casting. this adds filtering lights per view based on intersection of
camera layers and light layers.
fixes#3462
## Solution
PointLights and SpotLights are assigned to individual views in
`assign_lights_to_clusters`, so we simply cull the lights which don't
match the view layers in that function.
DirectionalLights are global, so we
- add the light layers to the `DirectionalLight` struct
- add the view layers to the `ViewUniform` struct
- check for intersection before processing the light in
`apply_pbr_lighting`
potential issue: when mesh/light layers are smaller than the view layers
weird results can occur. e.g:
camera = layers 1+2
light = layers 1
mesh = layers 2
the mesh does not cast shadows wrt the light as (1 & 2) == 0.
the light affects the view as (1+2 & 1) != 0.
the view renders the mesh as (1+2 & 2) != 0.
so the mesh is rendered and lit, but does not cast a shadow.
this could be fixed (so that the light would not affect the mesh in that
view) by adding the light layers to the point and spot light structs,
but i think the setup is pretty unusual, and space is at a premium in
those structs (adding 4 bytes more would reduce the webgl point+spot
light max count to 240 from 256).
I think typical usage is for cameras to have a single layer, and
meshes/lights to maybe have multiple layers to render to e.g. minimaps
as well as primary views.
if there is a good use case for the above setup and we should support
it, please let me know.
---
## Migration Guide
Lights no longer affect all `RenderLayers` by default, now like cameras
and meshes they default to `RenderLayers::layer(0)`. To recover the
previous behaviour and have all lights affect all views, add a
`RenderLayers::all()` component to the light entity.
# Objective
A better alternative version of #10843.
Currently, Bevy has a single `Ray` struct for 3D. To allow better
interoperability with Bevy's primitive shapes (#10572) and some third
party crates (that handle e.g. spatial queries), it would be very useful
to have separate versions for 2D and 3D respectively.
## Solution
Separate `Ray` into `Ray2d` and `Ray3d`. These new structs also take
advantage of the new primitives by using `Direction2d`/`Direction3d` for
the direction:
```rust
pub struct Ray2d {
pub origin: Vec2,
pub direction: Direction2d,
}
pub struct Ray3d {
pub origin: Vec3,
pub direction: Direction3d,
}
```
and by using `Plane2d`/`Plane3d` in `intersect_plane`:
```rust
impl Ray2d {
// ...
pub fn intersect_plane(&self, plane_origin: Vec2, plane: Plane2d) -> Option<f32> {
// ...
}
}
```
---
## Changelog
### Added
- `Ray2d` and `Ray3d`
- `Ray2d::new` and `Ray3d::new` constructors
- `Plane2d::new` and `Plane3d::new` constructors
### Removed
- Removed `Ray` in favor of `Ray3d`
### Changed
- `direction` is now a `Direction2d`/`Direction3d` instead of a vector,
which provides guaranteed normalization
- `intersect_plane` now takes a `Plane2d`/`Plane3d` instead of just a
vector for the plane normal
- `Direction2d` and `Direction3d` now derive `Serialize` and
`Deserialize` to preserve ray (de)serialization
## Migration Guide
`Ray` has been renamed to `Ray3d`.
### Ray creation
Before:
```rust
Ray {
origin: Vec3::ZERO,
direction: Vec3::new(0.5, 0.6, 0.2).normalize(),
}
```
After:
```rust
// Option 1:
Ray3d {
origin: Vec3::ZERO,
direction: Direction3d::new(Vec3::new(0.5, 0.6, 0.2)).unwrap(),
}
// Option 2:
Ray3d::new(Vec3::ZERO, Vec3::new(0.5, 0.6, 0.2))
```
### Plane intersections
Before:
```rust
let result = ray.intersect_plane(Vec2::X, Vec2::Y);
```
After:
```rust
let result = ray.intersect_plane(Vec2::X, Plane2d::new(Vec2::Y));
```
# Objective
avoid panics from `calculate_bounds` systems if entities are despawned
in PostUpdate.
there's a running general discussion (#10166) about command panicking.
in the meantime we may as well fix up some cases where it's clear a
failure to insert is safe.
## Solution
change `.insert(aabb)` to `.try_insert(aabb)`
# Objective
- Shorten paths by removing unnecessary prefixes
## Solution
- Remove the prefixes from many paths which do not need them. Finding
the paths was done automatically using built-in refactoring tools in
Jetbrains RustRover.
# Objective
- Materials should be a more frequent rebind then meshes (due to being
able to use a single vertex buffer, such as in #10164) and therefore
should be in a higher bind group.
---
## Changelog
- For 2d and 3d mesh/material setups (but not UI materials, or other
rendering setups such as gizmos, sprites, or text), mesh data is now in
bind group 1, and material data is now in bind group 2, which is swapped
from how they were before.
## Migration Guide
- Custom 2d and 3d mesh/material shaders should now use bind group 2
`@group(2) @binding(x)` for their bound resources, instead of bind group
1.
- Many internal pieces of rendering code have changed so that mesh data
is now in bind group 1, and material data is now in bind group 2.
Semi-custom rendering setups (that don't use the Material or Material2d
APIs) should adapt to these changes.
# Objective
Related to #10612.
Enable the
[`clippy::manual_let_else`](https://rust-lang.github.io/rust-clippy/master/#manual_let_else)
lint as a warning. The `let else` form seems more idiomatic to me than a
`match`/`if else` that either match a pattern or diverge, and from the
clippy doc, the lint doesn't seem to have any possible false positive.
## Solution
Add the lint as warning in `Cargo.toml`, refactor places where the lint
triggers.
# Objective
- Follow up to #9694
## Solution
- Same api as #9694 but adapted for `BindGroupLayoutEntry`
- Use the same `ShaderStages` visibilty for all entries by default
- Add `BindingType` helper function that mirror the wgsl equivalent and
that make writing layouts much simpler.
Before:
```rust
let layout = render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
label: Some("post_process_bind_group_layout"),
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2,
multisampled: false,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: bevy::render::render_resource::BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(PostProcessSettings::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
],
});
```
After:
```rust
let layout = render_device.create_bind_group_layout(
"post_process_bind_group_layout"),
&BindGroupLayoutEntries::sequential(
ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
(
texture_2d_f32(),
sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
uniform_buffer(false, Some(PostProcessSettings::min_size())),
),
),
);
```
Here's a more extreme example in bevy_solari:
86dab7f5da
---
## Changelog
- Added `BindGroupLayoutEntries` and all `BindingType` helper functions.
## Migration Guide
`RenderDevice::create_bind_group_layout()` doesn't take a
`BindGroupLayoutDescriptor` anymore. You need to provide the parameters
separately
```rust
// 0.12
let layout = render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
label: Some("post_process_bind_group_layout"),
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
// ...
},
],
});
// 0.13
let layout = render_device.create_bind_group_layout(
"post_process_bind_group_layout",
&[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
// ...
},
],
);
```
## TODO
- [x] implement a `Dynamic` variant
- [x] update the `RenderDevice::create_bind_group_layout()` api to match
the one from `RenderDevice::creat_bind_group()`
- [x] docs
# Objective
- Fixes#7680
- This is an updated for https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/8899
which had the same objective but fell a long way behind the latest
changes
## Solution
The traits `WorldQueryData : WorldQuery` and `WorldQueryFilter :
WorldQuery` have been added and some of the types and functions from
`WorldQuery` has been moved into them.
`ReadOnlyWorldQuery` has been replaced with `ReadOnlyWorldQueryData`.
`WorldQueryFilter` is safe (as long as `WorldQuery` is implemented
safely).
`WorldQueryData` is unsafe - safely implementing it requires that
`Self::ReadOnly` is a readonly version of `Self` (this used to be a
safety requirement of `WorldQuery`)
The type parameters `Q` and `F` of `Query` must now implement
`WorldQueryData` and `WorldQueryFilter` respectively.
This makes it impossible to accidentally use a filter in the data
position or vice versa which was something that could lead to bugs.
~~Compile failure tests have been added to check this.~~
It was previously sometimes useful to use `Option<With<T>>` in the data
position. Use `Has<T>` instead in these cases.
The `WorldQuery` derive macro has been split into separate derive macros
for `WorldQueryData` and `WorldQueryFilter`.
Previously it was possible to derive both `WorldQuery` for a struct that
had a mixture of data and filter items. This would not work correctly in
some cases but could be a useful pattern in others. *This is no longer
possible.*
---
## Notes
- The changes outside of `bevy_ecs` are all changing type parameters to
the new types, updating the macro use, or replacing `Option<With<T>>`
with `Has<T>`.
- All `WorldQueryData` types always returned `true` for `IS_ARCHETYPAL`
so I moved it to `WorldQueryFilter` and
replaced all calls to it with `true`. That should be the only logic
change outside of the macro generation code.
- `Changed<T>` and `Added<T>` were being generated by a macro that I
have expanded. Happy to revert that if desired.
- The two derive macros share some functions for implementing
`WorldQuery` but the tidiest way I could find to implement them was to
give them a ton of arguments and ask clippy to ignore that.
## Changelog
### Changed
- Split `WorldQuery` into `WorldQueryData` and `WorldQueryFilter` which
now have separate derive macros. It is not possible to derive both for
the same type.
- `Query` now requires that the first type argument implements
`WorldQueryData` and the second implements `WorldQueryFilter`
## Migration Guide
- Update derives
```rust
// old
#[derive(WorldQuery)]
#[world_query(mutable, derive(Debug))]
struct CustomQuery {
entity: Entity,
a: &'static mut ComponentA
}
#[derive(WorldQuery)]
struct QueryFilter {
_c: With<ComponentC>
}
// new
#[derive(WorldQueryData)]
#[world_query_data(mutable, derive(Debug))]
struct CustomQuery {
entity: Entity,
a: &'static mut ComponentA,
}
#[derive(WorldQueryFilter)]
struct QueryFilter {
_c: With<ComponentC>
}
```
- Replace `Option<With<T>>` with `Has<T>`
```rust
/// old
fn my_system(query: Query<(Entity, Option<With<ComponentA>>)>)
{
for (entity, has_a_option) in query.iter(){
let has_a:bool = has_a_option.is_some();
//todo!()
}
}
/// new
fn my_system(query: Query<(Entity, Has<ComponentA>)>)
{
for (entity, has_a) in query.iter(){
//todo!()
}
}
```
- Fix queries which had filters in the data position or vice versa.
```rust
// old
fn my_system(query: Query<(Entity, With<ComponentA>)>)
{
for (entity, _) in query.iter(){
//todo!()
}
}
// new
fn my_system(query: Query<Entity, With<ComponentA>>)
{
for entity in query.iter(){
//todo!()
}
}
// old
fn my_system(query: Query<AnyOf<(&ComponentA, With<ComponentB>)>>)
{
for (entity, _) in query.iter(){
//todo!()
}
}
// new
fn my_system(query: Query<Option<&ComponentA>, Or<(With<ComponentA>, With<ComponentB>)>>)
{
for entity in query.iter(){
//todo!()
}
}
```
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
Updates [`futures-lite`](https://github.com/smol-rs/futures-lite) in
bevy_tasks to the next major version (1 -> 2).
Also removes the duplication of `futures-lite`, as `async-fs` requires v
2, so there are currently 2 copies of futures-lite in the dependency
tree.
Futures-lite has received [a number of
updates](https://github.com/smol-rs/futures-lite/blob/master/CHANGELOG.md)
since bevy's current version `1.4`.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Mike <mike.hsu@gmail.com>
# Objective
Enables warning on `clippy::undocumented_unsafe_blocks` across the
workspace rather than only in `bevy_ecs`, `bevy_transform` and
`bevy_utils`. This adds a little awkwardness in a few areas of code that
have trivial safety or explain safety for multiple unsafe blocks with
one comment however automatically prevents these comments from being
missed.
## Solution
This adds `undocumented_unsafe_blocks = "warn"` to the workspace
`Cargo.toml` and fixes / adds a few missed safety comments. I also added
`#[allow(clippy::undocumented_unsafe_blocks)]` where the safety is
explained somewhere above.
There are a couple of safety comments I added I'm not 100% sure about in
`bevy_animation` and `bevy_render/src/view` and I'm not sure about the
use of `#[allow(clippy::undocumented_unsafe_blocks)]` compared to adding
comments like `// SAFETY: See above`.
# Objective
- Standardize fmt for toml files
## Solution
- Add [taplo](https://taplo.tamasfe.dev/) to CI (check for fmt and diff
for toml files), for context taplo is used by the most popular extension
in VScode [Even Better
TOML](https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=tamasfe.even-better-toml
- Add contribution section to explain toml fmt with taplo.
Now to pass CI you need to run `taplo fmt --option indent_string=" "` or
if you use vscode have the `Even Better TOML` extension with 4 spaces
for indent
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
The `map_async` method involves a type `BufferAsyncError`:
https://docs.rs/bevy/latest/bevy/render/render_resource/struct.BufferSlice.html#method.map_async
This type is not re-exported in Bevy, so if a user wants to store a
struct involving this type they have to add wgpu manually to their
manifest.
## Solution
- Re-export wgpu::BufferAsyncError
---
## Changelog
### Added
- Re-export wgpu::BufferAsyncError
Signed-off-by: Torstein Grindvik <torstein.grindvik@muybridge.com>
Co-authored-by: Torstein Grindvik <torstein.grindvik@muybridge.com>
# Objective
- Fix adding `#![allow(clippy::type_complexity)]` everywhere. like #9796
## Solution
- Use the new [lints] table that will land in 1.74
(https://doc.rust-lang.org/nightly/cargo/reference/unstable.html#lints)
- inherit lint to the workspace, crates and examples.
```
[lints]
workspace = true
```
## Changelog
- Bump rust version to 1.74
- Enable lints table for the workspace
```toml
[workspace.lints.clippy]
type_complexity = "allow"
```
- Allow type complexity for all crates and examples
```toml
[lints]
workspace = true
```
---------
Co-authored-by: Martín Maita <47983254+mnmaita@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
Closes#10319
## Changelog
* Added a new `Color::rgba_from_array([f32; 4]) -> Color` method.
* Added a new `Color::rgb_from_array([f32; 3]) -> Color` method.
* Added a new `Color::rgba_linear_from_array([f32; 4]) -> Color` method.
* Added a new `Color::rgb_linear_from_array([f32; 3]) -> Color` method.
* Added a new `Color::hsla_from_array([f32; 4]) -> Color` method.
* Added a new `Color::hsl_from_array([f32; 3]) -> Color` method.
* Added a new `Color::lcha_from_array([f32; 4]) -> Color` method.
* Added a new `Color::lch_from_array([f32; 3]) -> Color` method.
* Added a new `Color::rgba_to_vec4(&self) -> Vec4` method.
* Added a new `Color::rgba_to_array(&self) -> [f32; 4]` method.
* Added a new `Color::rgb_to_vec3(&self) -> Vec3` method.
* Added a new `Color::rgb_to_array(&self) -> [f32; 3]` method.
* Added a new `Color::rgba_linear_to_vec4(&self) -> Vec4` method.
* Added a new `Color::rgba_linear_to_array(&self) -> [f32; 4]` method.
* Added a new `Color::rgb_linear_to_vec3(&self) -> Vec3` method.
* Added a new `Color::rgb_linear_to_array(&self) -> [f32; 3]` method.
* Added a new `Color::hsla_to_vec4(&self) -> Vec4` method.
* Added a new `Color::hsla_to_array(&self) -> [f32; 4]` method.
* Added a new `Color::hsl_to_vec3(&self) -> Vec3` method.
* Added a new `Color::hsl_to_array(&self) -> [f32; 3]` method.
* Added a new `Color::lcha_to_vec4(&self) -> Vec4` method.
* Added a new `Color::lcha_to_array(&self) -> [f32; 4]` method.
* Added a new `Color::lch_to_vec3(&self) -> Vec3` method.
* Added a new `Color::lch_to_array(&self) -> [f32; 3]` method.
## Migration Guide
`Color::from(Vec4)` is now `Color::rgba_from_array(impl Into<[f32; 4]>)`
`Vec4::from(Color)` is now `Color::rgba_to_vec4(&self)`
Before:
```rust
let color_vec4 = Vec4::new(0.5, 0.5, 0.5);
let color_from_vec4 = Color::from(color_vec4);
let color_array = [0.5, 0.5, 0.5];
let color_from_array = Color::from(color_array);
```
After:
```rust
let color_vec4 = Vec4::new(0.5, 0.5, 0.5);
let color_from_vec4 = Color::rgba_from_array(color_vec4);
let color_array = [0.5, 0.5, 0.5];
let color_from_array = Color::rgba_from_array(color_array);
```
# Objective
Make sure a camera which has had its render target changed recomputes
its info.
On main, the following is possible:
- System A has an inactive camera with render target set to the default
`Image` (i.e. white 1x1 rgba texture)
Later:
- System B sets the same camera active and sets the `camera.target` to a
newly created `Image`
**Bug**: Since `camera_system` only checks `Modified` and not `Added`
events, the size of the render target is not recomputed, which means the
camera will render with 1x1 size even though the new target is an
entirely different size.
## Solution
- Ensure `camera_system` checks `Added` image assets events
## Changelog
### Fixed
- Cameras which have their render targets changed to a newly created
target with a different size than the previous target will now render
properly
---------
Signed-off-by: Torstein Grindvik <torstein.grindvik@muybridge.com>
Co-authored-by: Torstein Grindvik <torstein.grindvik@muybridge.com>
Co-authored-by: Afonso Lage <lage.afonso@gmail.com>
# Objective
Currently, if a large amount of inactive cameras are spawned, they will
immensely slow down performance.
This can be reproduced by adding
```rust
let default_image = images.add(default());
for _ in 0..10000 {
commands.spawn(Camera3dBundle {
camera: Camera {
is_active: false,
target: RenderTarget::Image(default_image.clone()),
..default()
},
..default()
});
}
```
to for example `3d_shapes`.
Using `tracy`, it's clear that preparing view bind groups for all
cameras is still happening.
Also, visibility checks on the extracted views from inactive cameras
also take place.
## Performance gains
The following `tracy` comparisons show the effect of skipping this
unneeded work.
Yellow is Bevy main, red is with the fix.
### Visibility checks

### Bind group preparation

## Solution
- Check if the cameras are inactive in the appropriate places, and if so
skip them
## Changelog
### Changed
- Do not extract views from inactive cameras or check visiblity from
their extracted views
Signed-off-by: Torstein Grindvik <torstein.grindvik@muybridge.com>
Co-authored-by: Torstein Grindvik <torstein.grindvik@muybridge.com>
# Objective
Hot reloading shader imports on windows is currently broken due to
inconsistent `/` and `\` usage ('/` is used in the user facing APIs and
`\` is produced by notify-rs (and likely other OS apis).
Fixes#10500
## Solution
Standardize import paths when loading a `Shader`. The correct long term
fix is to standardize AssetPath on `/`-only, but this is the right scope
of fix for a patch release.
---------
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
# Objective
Calling `RenderDevice::poll` requires an instance of `wgpu::Maintain`,
but the type was not reexported by bevy. Working around it requires
adding a dependency on `wgpu`, since bevy does not reexport the `wgpu`
crate as a whole anywhere.
## Solution
Reexport `wgpu::Maintain` in `render_resource`, where the other wgpu
types are reexported.
# Objective
Had an issue where I had `VisibilityBundle` inside a bundle that
implements `Clone`, but since `VisibilityBundle` doesn't implement
`Clone` that wasn't possible. This PR fixes that.
## Solution
Implement `Clone` for `VisibilityBundle` by deriving it. And also
`SpatialBundle` too because why not.
---
## Changelog
- Added implementation for `Clone` on `VisibilityBundle` and
`SpatialBundle`.
Preparing next release
This PR has been auto-generated
---------
Co-authored-by: Bevy Auto Releaser <41898282+github-actions[bot]@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
# Objective
Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/9077 (see this issue for
motivations)
## Solution
Implement 1 and 2 of the "How to fix it" section of
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/9077
`update_directional_light_cascades` is split into
`clear_directional_light_cascades` and a generic
`build_directional_light_cascades`, to clear once and potentially insert
many times.
---
## Changelog
`DirectionalLight`'s computation is now generic over `CameraProjection`
and can work with custom camera projections.
## Migration Guide
If you have a component `MyCustomProjection` that implements
`CameraProjection`:
- You need to implement a new required associated method,
`get_frustum_corners`, returning an array of the corners of a subset of
the frustum with given `z_near` and `z_far`, in local camera space.
- You can now add the
`build_directional_light_cascades::<MyCustomProjection>` system in
`SimulationLightSystems::UpdateDirectionalLightCascades` after
`clear_directional_light_cascades` for your projection to work with
directional lights.
---------
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
Alternative to #7310
## Solution
Implemented the suggestion from
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/7310#discussion_r1083356655
I am guessing that these were originally split as an optimization, but I
am not sure since I believe the original author of the code is the one
speculating about combining them up there.
## Benchmarks
I ran three benchmarks to compare main, this PR, and the approach from
#7310
([updated](https://github.com/rparrett/bevy/commits/rebased-parallel-check-visibility)
to the same commit on main).
This seems to perform slightly better than main in scenarios where most
entities have AABBs, and a bit worse when they don't (`many_lights`).
That seems to make sense to me.
Either way, the difference is ~-20 microseconds in the more common
scenarios or ~+100 microseconds in the less common scenario. I would
speculate that this might perform **very slightly** worse in
single-threaded scenarios.
Benches were run in release mode for 2000 frames while capturing a trace
with tracy.
| bench | commit | check_visibility_system mean μs |
| -- | -- | -- |
| many_cubes | main | 929.5 |
| many_cubes | this | 914.0 |
| many_cubes | 7310 | 1003.5 |
| | |
| many_foxes | main | 191.6 |
| many_foxes | this | 173.2 |
| many_foxes | 7310 | 167.9 |
| | |
| many_lights | main | 619.3 |
| many_lights | this | 703.7 |
| many_lights | 7310 | 842.5 |
## Notes
Technically this behaves slightly differently -- prior to this PR, view
visibility was determined even for entities without `GlobalTransform`. I
don't think this has any practical impact though.
IMO, I don't think we need to do this. But I opened a PR because it
seemed like the handiest way to share the code / benchmarks.
## TODO
I have done some rudimentary testing with the examples above, but I can
do some screenshot diffing if it seems like we want to do this.
# Objective
<img width="1920" alt="Screenshot 2023-04-26 at 01 07 34"
src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/418473/234467578-0f34187b-5863-4ea1-88e9-7a6bb8ce8da3.png">
This PR adds both diffuse and specular light transmission capabilities
to the `StandardMaterial`, with support for screen space refractions.
This enables realistically representing a wide range of real-world
materials, such as:
- Glass; (Including frosted glass)
- Transparent and translucent plastics;
- Various liquids and gels;
- Gemstones;
- Marble;
- Wax;
- Paper;
- Leaves;
- Porcelain.
Unlike existing support for transparency, light transmission does not
rely on fixed function alpha blending, and therefore works with both
`AlphaMode::Opaque` and `AlphaMode::Mask` materials.
## Solution
- Introduces a number of transmission related fields in the
`StandardMaterial`;
- For specular transmission:
- Adds logic to take a view main texture snapshot after the opaque
phase; (in order to perform screen space refractions)
- Introduces a new `Transmissive3d` phase to the renderer, to which all
meshes with `transmission > 0.0` materials are sent.
- Calculates a light exit point (of the approximate mesh volume) using
`ior` and `thickness` properties
- Samples the snapshot texture with an adaptive number of taps across a
`roughness`-controlled radius enabling “blurry” refractions
- For diffuse transmission:
- Approximates transmitted diffuse light by using a second, flipped +
displaced, diffuse-only Lambertian lobe for each light source.
## To Do
- [x] Figure out where `fresnel_mix()` is taking place, if at all, and
where `dielectric_specular` is being calculated, if at all, and update
them to use the `ior` value (Not a blocker, just a nice-to-have for more
correct BSDF)
- To the _best of my knowledge, this is now taking place, after
964340cdd. The fresnel mix is actually "split" into two parts in our
implementation, one `(1 - fresnel(...))` in the transmission, and
`fresnel()` in the light implementations. A surface with more
reflectance now will produce slightly dimmer transmission towards the
grazing angle, as more of the light gets reflected.
- [x] Add `transmission_texture`
- [x] Add `diffuse_transmission_texture`
- [x] Add `thickness_texture`
- [x] Add `attenuation_distance` and `attenuation_color`
- [x] Connect values to glTF loader
- [x] `transmission` and `transmission_texture`
- [x] `thickness` and `thickness_texture`
- [x] `ior`
- [ ] `diffuse_transmission` and `diffuse_transmission_texture` (needs
upstream support in `gltf` crate, not a blocker)
- [x] Add support for multiple screen space refraction “steps”
- [x] Conditionally create no transmission snapshot texture at all if
`steps == 0`
- [x] Conditionally enable/disable screen space refraction transmission
snapshots
- [x] Read from depth pre-pass to prevent refracting pixels in front of
the light exit point
- [x] Use `interleaved_gradient_noise()` function for sampling blur in a
way that benefits from TAA
- [x] Drill down a TAA `#define`, tweak some aspects of the effect
conditionally based on it
- [x] Remove const array that's crashing under HLSL (unless a new `naga`
release with https://github.com/gfx-rs/naga/pull/2496 comes out before
we merge this)
- [ ] Look into alternatives to the `switch` hack for dynamically
indexing the const array (might not be needed, compilers seem to be
decent at expanding it)
- [ ] Add pipeline keys for gating transmission (do we really want/need
this?)
- [x] Tweak some material field/function names?
## A Note on Texture Packing
_This was originally added as a comment to the
`specular_transmission_texture`, `thickness_texture` and
`diffuse_transmission_texture` documentation, I removed it since it was
more confusing than helpful, and will likely be made redundant/will need
to be updated once we have a better infrastructure for preprocessing
assets_
Due to how channels are mapped, you can more efficiently use a single
shared texture image
for configuring the following:
- R - `specular_transmission_texture`
- G - `thickness_texture`
- B - _unused_
- A - `diffuse_transmission_texture`
The `KHR_materials_diffuse_transmission` glTF extension also defines a
`diffuseTransmissionColorTexture`,
that _we don't currently support_. One might choose to pack the
intensity and color textures together,
using RGB for the color and A for the intensity, in which case this
packing advice doesn't really apply.
---
## Changelog
- Added a new `Transmissive3d` render phase for rendering specular
transmissive materials with screen space refractions
- Added rendering support for transmitted environment map light on the
`StandardMaterial` as a fallback for screen space refractions
- Added `diffuse_transmission`, `specular_transmission`, `thickness`,
`ior`, `attenuation_distance` and `attenuation_color` to the
`StandardMaterial`
- Added `diffuse_transmission_texture`, `specular_transmission_texture`,
`thickness_texture` to the `StandardMaterial`, gated behind a new
`pbr_transmission_textures` cargo feature (off by default, for maximum
hardware compatibility)
- Added `Camera3d::screen_space_specular_transmission_steps` for
controlling the number of “layers of transparency” rendered for
transmissive objects
- Added a `TransmittedShadowReceiver` component for enabling shadows in
(diffusely) transmitted light. (disabled by default, as it requires
carefully setting up the `thickness` to avoid self-shadow artifacts)
- Added support for the `KHR_materials_transmission`,
`KHR_materials_ior` and `KHR_materials_volume` glTF extensions
- Renamed items related to temporal jitter for greater consistency
## Migration Guide
- `SsaoPipelineKey::temporal_noise` has been renamed to
`SsaoPipelineKey::temporal_jitter`
- The `TAA` shader def (controlled by the presence of the
`TemporalAntiAliasSettings` component in the camera) has been replaced
with the `TEMPORAL_JITTER` shader def (controlled by the presence of the
`TemporalJitter` component in the camera)
- `MeshPipelineKey::TAA` has been replaced by
`MeshPipelineKey::TEMPORAL_JITTER`
- The `TEMPORAL_NOISE` shader def has been consolidated with
`TEMPORAL_JITTER`
# Objective
- We need to check multiple times if a color is fully transparent, e.g.
for performance optimizations.
- Make code more readable.
- Reduce code duplication, to simplify making changes if needed (e.g. if
we need to take floating point weirdness into account later on).
## Solution
- Introduce a new `Color::is_fully_transparent` helper function to
determine if the alpha of a color is 0.
- Use the helper function in our UI rendering code.
---
## Changelog
- Added `Color::is_fully_transparent` helper function.
---------
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Work towards GPU-driven culling
(https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/10164)
## Solution
- Pass the view frustum to the shader view uniform
---
## Changelog
- View Frustums are now extracted to the render world and made available
to shaders
# Objective
Align all error-like types to implement `Error`.
Fixes #10176
## Solution
- Derive `Error` on more types
- Refactor instances of manual implementations that could be derived
This adds thiserror as a dependency to bevy_transform, which might
increase compilation time -- but I don't know of any situation where you
might only use that but not any other crate that pulls in bevy_utils.
The `contributors` example has a `LoadContributorsError` type, but as
it's an example I have not updated it. Doing that would mean either
having a `use bevy_internal::utils::thiserror::Error;` in an example
file, or adding `thiserror` as a dev-dependency to the main `bevy`
crate.
---
## Changelog
- All `…Error` types now implement the `Error` trait
Existing truncation code limits the number of attribute buffers to be
less than or equal to the number of vertices.
Instead the number of elements from each attribute buffer should be
limited to the length of the shortest buffer as mentioned in the earlier
warning.
# Objective
- Fixes#10267
## Solution
- Moves the `.take()` from the outer loop of attribute buffers, to the
inner loop of attribute values.
---
# Objective
- Remove special cases where `clippy::doc_markdown` lint is disabled.
## Solution
- Add default values back into `clippy.toml` by adding `".."` to the
list of `doc-valid-idents`.
- Add `"VSync"` and `"WebGL2"` to the list of `doc-valid-idents`.
- Remove all instances where `clippy::doc_markdown` is allowed.
- Fix `max_mip` formatting so that there isn't a warning.
# Situation
- In case of parent without visibility components, the visibility
inheritance of children creates a panic.
## Solution
- Apply same fallback visibility as parent not found instead of panic.
# Objective
- Build on the changes in https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/9982
- Use `ImageSamplerDescriptor` as the "public image sampler descriptor"
interface in all places (for consistency)
- Make it possible to configure textures to use the "default" sampler
(as configured in the `DefaultImageSampler` resource)
- Fix a bug introduced in #9982 that prevents configured samplers from
being used in Basis, KTX2, and DDS textures
---
## Migration Guide
- When using the `Image` API, use `ImageSamplerDescriptor` instead of
`wgpu::SamplerDescriptor`
- If writing custom wgpu renderer features that work with `Image`, call
`&image_sampler.as_wgpu()` to convert to a wgpu descriptor.
# Objective
First of all, this PR took heavy inspiration from #7760 and #5715. It
intends to also fix#5569, but with a slightly different approach.
This also fixes#9335 by reexporting `DynEq`.
## Solution
The advantage of this API is that we can intern a value without
allocating for zero-sized-types and for enum variants that have no
fields. This PR does this automatically in the `SystemSet` and
`ScheduleLabel` derive macros for unit structs and fieldless enum
variants. So this should cover many internal and external use cases of
`SystemSet` and `ScheduleLabel`. In these optimal use cases, no memory
will be allocated.
- The interning returns a `Interned<dyn SystemSet>`, which is just a
wrapper around a `&'static dyn SystemSet`.
- `Hash` and `Eq` are implemented in terms of the pointer value of the
reference, similar to my first approach of anonymous system sets in
#7676.
- Therefore, `Interned<T>` does not implement `Borrow<T>`, only `Deref`.
- The debug output of `Interned<T>` is the same as the interned value.
Edit:
- `AppLabel` is now also interned and the old
`derive_label`/`define_label` macros were replaced with the new
interning implementation.
- Anonymous set ids are reused for different `Schedule`s, reducing the
amount of leaked memory.
### Pros
- `InternedSystemSet` and `InternedScheduleLabel` behave very similar to
the current `BoxedSystemSet` and `BoxedScheduleLabel`, but can be copied
without an allocation.
- Many use cases don't allocate at all.
- Very fast lookups and comparisons when using `InternedSystemSet` and
`InternedScheduleLabel`.
- The `intern` module might be usable in other areas.
- `Interned{ScheduleLabel, SystemSet, AppLabel}` does implement
`{ScheduleLabel, SystemSet, AppLabel}`, increasing ergonomics.
### Cons
- Implementors of `SystemSet` and `ScheduleLabel` still need to
implement `Hash` and `Eq` (and `Clone`) for it to work.
## Changelog
### Added
- Added `intern` module to `bevy_utils`.
- Added reexports of `DynEq` to `bevy_ecs` and `bevy_app`.
### Changed
- Replaced `BoxedSystemSet` and `BoxedScheduleLabel` with
`InternedSystemSet` and `InternedScheduleLabel`.
- Replaced `impl AsRef<dyn ScheduleLabel>` with `impl ScheduleLabel`.
- Replaced `AppLabelId` with `InternedAppLabel`.
- Changed `AppLabel` to use `Debug` for error messages.
- Changed `AppLabel` to use interning.
- Changed `define_label`/`derive_label` to use interning.
- Replaced `define_boxed_label`/`derive_boxed_label` with
`define_label`/`derive_label`.
- Changed anonymous set ids to be only unique inside a schedule, not
globally.
- Made interned label types implement their label trait.
### Removed
- Removed `define_boxed_label` and `derive_boxed_label`.
## Migration guide
- Replace `BoxedScheduleLabel` and `Box<dyn ScheduleLabel>` with
`InternedScheduleLabel` or `Interned<dyn ScheduleLabel>`.
- Replace `BoxedSystemSet` and `Box<dyn SystemSet>` with
`InternedSystemSet` or `Interned<dyn SystemSet>`.
- Replace `AppLabelId` with `InternedAppLabel` or `Interned<dyn
AppLabel>`.
- Types manually implementing `ScheduleLabel`, `AppLabel` or `SystemSet`
need to implement:
- `dyn_hash` directly instead of implementing `DynHash`
- `as_dyn_eq`
- Pass labels to `World::try_schedule_scope`, `World::schedule_scope`,
`World::try_run_schedule`. `World::run_schedule`, `Schedules::remove`,
`Schedules::remove_entry`, `Schedules::contains`, `Schedules::get` and
`Schedules::get_mut` by value instead of by reference.
---------
Co-authored-by: Joseph <21144246+JoJoJet@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
When a mesh vertex attribute has a vertex count mismatch, a warning
message is printed with the index of the attribute which did not match.
Change to name the attribute, or fall back to the old behaviour if it
was not a known attribute.
Before:
```
MeshVertexAttributeId(2) has a different vertex count (32) than other attributes (64) in this mesh, all attributes will be truncated to match the smallest.
```
After:
```
Vertex_Uv has a different vertex count (32) than other attributes (64) in this mesh, all attributes will be truncated to match the smallest.
```
## Solution
Name the mesh attribute which had a count mismatch.
## Changelog
- If a mesh vertex attribute has a different count than other vertex
attributes, name the offending attribute using a human readable name
Signed-off-by: Torstein Grindvik <torstein.grindvik@muybridge.com>
Co-authored-by: Torstein Grindvik <torstein.grindvik@muybridge.com>
Closes#9946
# Objective
Add a new type mirroring `wgpu::SamplerDescriptor` for
`ImageLoaderSettings` to control how a loaded image should be sampled.
Fix issues with texture sampler descriptors not being set when loading
gltf texture from URI.
## Solution
Add a new `ImageSamplerDescriptor` and its affiliated types that mirrors
`wgpu::SamplerDescriptor`, use it in the image loader settings.
---
## Changelog
### Added
- Added new types `ImageSamplerDescriptor`, `ImageAddressMode`,
`ImageFilterMode`, `ImageCompareFunction` and `ImageSamplerBorderColor`
that mirrors the corresponding wgpu types.
- `ImageLoaderSettings` now carries an `ImageSamplerDescriptor` field
that will be used to determine how the loaded image is sampled, and will
be serialized as part of the image assets `.meta` files.
### Changed
- `Image::from_buffer` now takes the sampler descriptor to use as an
additional parameter.
### Fixed
- Sampler descriptors are set for gltf textures loaded from URI.
# Objective
A follow-up PR for https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/10221
## Changelog
Replaced usages of texture_descriptor.size with the helper methods of
`Image` through the entire engine codebase
# Objective
To get the width or height of an image you do:
```rust
self.texture_descriptor.size.{width, height}
```
that is quite verbose.
This PR adds some convenient methods for Image to reduce verbosity.
## Changelog
* Add a `width()` method for getting the width of an image.
* Add a `height()` method for getting the height of an image.
* Rename the `size()` method to `size_f32()`.
* Add a `size()` method for getting the size of an image as u32.
* Renamed the `aspect_2d()` method to `aspect_ratio()`.
## Migration Guide
Replace calls to the `Image::size()` method with `size_f32()`.
Replace calls to the `Image::aspect_2d()` method with `aspect_ratio()`.
# Objective
- Fix#10165
- On iOS simulator on apple silicon Macs, shader validation is going
through the host, but device limits are reported for the device. They
sometimes differ, and cause the validation to crash on something that
should work
```
-[MTLDebugRenderCommandEncoder validateCommonDrawErrors:]:5775: failed assertion `Draw Errors Validation
Fragment Function(fragment_): the offset into the buffer _naga_oil_mod_MJSXM6K7OBRHEOR2NVSXG2C7OZUWK527MJUW4ZDJNZTXG_memberfog that is bound at buffer index 6 must be a multiple of 256 but was set to 448.
```
## Solution
- Add a custom flag when building for the simulator and override the
buffer alignment
# Objective
- Closes#10049.
- Detect DDS texture containing a cubemap or a cubemap array.
## Solution
- When loading a dds texture, the header capabilities are checked for
the cubemap flag. An error is returned if not all faces are provided.
---
## Changelog
### Added
- Added a new texture error `TextureError::IncompleteCubemap`, used for
dds cubemap textures containing less than 6 faces, as that is not
supported on modern graphics APIs.
### Fixed
- DDS cubemaps are now loaded as cubemaps instead of 2D textures.
## Migration Guide
If you are matching on a `TextureError`, you will need to add a new
branch to handle `TextureError::IncompleteCubemap`.
# Objective
Simplify bind group creation code. alternative to (and based on) #9476
## Solution
- Add a `BindGroupEntries` struct that can transparently be used where
`&[BindGroupEntry<'b>]` is required in BindGroupDescriptors.
Allows constructing the descriptor's entries as:
```rust
render_device.create_bind_group(
"my_bind_group",
&my_layout,
&BindGroupEntries::with_indexes((
(2, &my_sampler),
(3, my_uniform),
)),
);
```
instead of
```rust
render_device.create_bind_group(
"my_bind_group",
&my_layout,
&[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 2,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(&my_sampler),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 3,
resource: my_uniform,
},
],
);
```
or
```rust
render_device.create_bind_group(
"my_bind_group",
&my_layout,
&BindGroupEntries::sequential((&my_sampler, my_uniform)),
);
```
instead of
```rust
render_device.create_bind_group(
"my_bind_group",
&my_layout,
&[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(&my_sampler),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: my_uniform,
},
],
);
```
the structs has no user facing macros, is tuple-type-based so stack
allocated, and has no noticeable impact on compile time.
- Also adds a `DynamicBindGroupEntries` struct with a similar api that
uses a `Vec` under the hood and allows extending the entries.
- Modifies `RenderDevice::create_bind_group` to take separate arguments
`label`, `layout` and `entries` instead of a `BindGroupDescriptor`
struct. The struct can't be stored due to the internal references, and
with only 3 members arguably does not add enough context to justify
itself.
- Modify the codebase to use the new api and the `BindGroupEntries` /
`DynamicBindGroupEntries` structs where appropriate (whenever the
entries slice contains more than 1 member).
## Migration Guide
- Calls to `RenderDevice::create_bind_group({BindGroupDescriptor {
label, layout, entries })` must be amended to
`RenderDevice::create_bind_group(label, layout, entries)`.
- If `label`s have been specified as `"bind_group_name".into()`, they
need to change to just `"bind_group_name"`. `Some("bind_group_name")`
and `None` will still work, but `Some("bind_group_name")` can optionally
be simplified to just `"bind_group_name"`.
---------
Co-authored-by: IceSentry <IceSentry@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
- bump naga_oil to 0.10
- update shader imports to use rusty syntax
## Migration Guide
naga_oil 0.10 reworks the import mechanism to support more syntax to
make it more rusty, and test for item use before importing to determine
which imports are modules and which are items, which allows:
- use rust-style imports
```
#import bevy_pbr::{
pbr_functions::{alpha_discard as discard, apply_pbr_lighting},
mesh_bindings,
}
```
- import partial paths:
```
#import part::of::path
...
path::remainder::function();
```
which will call to `part::of::path::remainder::function`
- use fully qualified paths without importing:
```
// #import bevy_pbr::pbr_functions
bevy_pbr::pbr_functions::pbr()
```
- use imported items without qualifying
```
#import bevy_pbr::pbr_functions::pbr
// for backwards compatibility the old style is still supported:
// #import bevy_pbr::pbr_functions pbr
...
pbr()
```
- allows most imported items to end with `_` and numbers (naga_oil#30).
still doesn't allow struct members to end with `_` or numbers but it's
progress.
- the vast majority of existing shader code will work without changes,
but will emit "deprecated" warnings for old-style imports. these can be
suppressed with the `allow-deprecated` feature.
- partly breaks overrides (as far as i'm aware nobody uses these yet) -
now overrides will only be applied if the overriding module is added as
an additional import in the arguments to `Composer::make_naga_module` or
`Composer::add_composable_module`. this is necessary to support
determining whether imports are modules or items.
# Objective
allow extending `Material`s (including the built in `StandardMaterial`)
with custom vertex/fragment shaders and additional data, to easily get
pbr lighting with custom modifications, or otherwise extend a base
material.
# Solution
- added `ExtendedMaterial<B: Material, E: MaterialExtension>` which
contains a base material and a user-defined extension.
- added example `extended_material` showing how to use it
- modified AsBindGroup to have "unprepared" functions that return raw
resources / layout entries so that the extended material can combine
them
note: doesn't currently work with array resources, as i can't figure out
how to make the OwnedBindingResource::get_binding() work, as wgpu
requires a `&'a[&'a TextureView]` and i have a `Vec<TextureView>`.
# Migration Guide
manual implementations of `AsBindGroup` will need to be adjusted, the
changes are pretty straightforward and can be seen in the diff for e.g.
the `texture_binding_array` example.
---------
Co-authored-by: Robert Swain <robert.swain@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Added support for newer AMD Radeon cards in the mod.rs file located at
``crates/bevy_render/src/view/window/mod.rs``
## Solution
- All I needed to add was ``name.starts_with("Radeon") ||`` to the
existing code on line 347 of
``crates/bevy_render/src/view/window/mod.rs``
---
## Changelog
- Changed ``crates/bevy_render/src/view/window/mod.rs``
# Objective
Current `FixedTime` and `Time` have several problems. This pull aims to
fix many of them at once.
- If there is a longer pause between app updates, time will jump forward
a lot at once and fixed time will iterate on `FixedUpdate` for a large
number of steps. If the pause is merely seconds, then this will just
mean jerkiness and possible unexpected behaviour in gameplay. If the
pause is hours/days as with OS suspend, the game will appear to freeze
until it has caught up with real time.
- If calculating a fixed step takes longer than specified fixed step
period, the game will enter a death spiral where rendering each frame
takes longer and longer due to more and more fixed step updates being
run per frame and the game appears to freeze.
- There is no way to see current fixed step elapsed time inside fixed
steps. In order to track this, the game designer needs to add a custom
system inside `FixedUpdate` that calculates elapsed or step count in a
resource.
- Access to delta time inside fixed step is `FixedStep::period` rather
than `Time::delta`. This, coupled with the issue that `Time::elapsed`
isn't available at all for fixed steps, makes it that time requiring
systems are either implemented to be run in `FixedUpdate` or `Update`,
but rarely work in both.
- Fixes#8800
- Fixes#8543
- Fixes#7439
- Fixes#5692
## Solution
- Create a generic `Time<T>` clock that has no processing logic but
which can be instantiated for multiple usages. This is also exposed for
users to add custom clocks.
- Create three standard clocks, `Time<Real>`, `Time<Virtual>` and
`Time<Fixed>`, all of which contain their individual logic.
- Create one "default" clock, which is just `Time` (or `Time<()>`),
which will be overwritten from `Time<Virtual>` on each update, and
`Time<Fixed>` inside `FixedUpdate` schedule. This way systems that do
not care specifically which time they track can work both in `Update`
and `FixedUpdate` without changes and the behaviour is intuitive.
- Add `max_delta` to virtual time update, which limits how much can be
added to virtual time by a single update. This fixes both the behaviour
after a long freeze, and also the death spiral by limiting how many
fixed timestep iterations there can be per update. Possible future work
could be adding `max_accumulator` to add a sort of "leaky bucket" time
processing to possibly smooth out jumps in time while keeping frame rate
stable.
- Many minor tweaks and clarifications to the time functions and their
documentation.
## Changelog
- `Time::raw_delta()`, `Time::raw_elapsed()` and related methods are
moved to `Time<Real>::delta()` and `Time<Real>::elapsed()` and now match
`Time` API
- `FixedTime` is now `Time<Fixed>` and matches `Time` API.
- `Time<Fixed>` default timestep is now 64 Hz, or 15625 microseconds.
- `Time` inside `FixedUpdate` now reflects fixed timestep time, making
systems portable between `Update ` and `FixedUpdate`.
- `Time::pause()`, `Time::set_relative_speed()` and related methods must
now be called as `Time<Virtual>::pause()` etc.
- There is a new `max_delta` setting in `Time<Virtual>` that limits how
much the clock can jump by a single update. The default value is 0.25
seconds.
- Removed `on_fixed_timer()` condition as `on_timer()` does the right
thing inside `FixedUpdate` now.
## Migration Guide
- Change all `Res<Time>` instances that access `raw_delta()`,
`raw_elapsed()` and related methods to `Res<Time<Real>>` and `delta()`,
`elapsed()`, etc.
- Change access to `period` from `Res<FixedTime>` to `Res<Time<Fixed>>`
and use `delta()`.
- The default timestep has been changed from 60 Hz to 64 Hz. If you wish
to restore the old behaviour, use
`app.insert_resource(Time::<Fixed>::from_hz(60.0))`.
- Change `app.insert_resource(FixedTime::new(duration))` to
`app.insert_resource(Time::<Fixed>::from_duration(duration))`
- Change `app.insert_resource(FixedTime::new_from_secs(secs))` to
`app.insert_resource(Time::<Fixed>::from_seconds(secs))`
- Change `system.on_fixed_timer(duration)` to
`system.on_timer(duration)`. Timers in systems placed in `FixedUpdate`
schedule automatically use the fixed time clock.
- Change `ResMut<Time>` calls to `pause()`, `is_paused()`,
`set_relative_speed()` and related methods to `ResMut<Time<Virtual>>`
calls. The API is the same, with the exception that `relative_speed()`
will return the actual last ste relative speed, while
`effective_relative_speed()` returns 0.0 if the time is paused and
corresponds to the speed that was set when the update for the current
frame started.
## Todo
- [x] Update pull name and description
- [x] Top level documentation on usage
- [x] Fix examples
- [x] Decide on default `max_delta` value
- [x] Decide naming of the three clocks: is `Real`, `Virtual`, `Fixed`
good?
- [x] Decide if the three clock inner structures should be in prelude
- [x] Decide on best way to configure values at startup: is manually
inserting a new clock instance okay, or should there be config struct
separately?
- [x] Fix links in docs
- [x] Decide what should be public and what not
- [x] Decide how `wrap_period` should be handled when it is changed
- [x] ~~Add toggles to disable setting the clock as default?~~ No,
separate pull if needed.
- [x] Add tests
- [x] Reformat, ensure adheres to conventions etc.
- [x] Build documentation and see that it looks correct
## Contributors
Huge thanks to @alice-i-cecile and @maniwani while building this pull.
It was a shared effort!
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Cameron <51241057+maniwani@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Jerome Humbert <djeedai@gmail.com>
# Objective
From my understanding, although resources are not meant to be created
and removed at every frame, they are still meant to be created
dynamically during the lifetime of the App.
But because the extract_resource API does not allow optional resources
from the main world, it's impossible to use resources in the render
phase that were not created before the render sub-app itself.
## Solution
Because the ECS engine already allows for system parameters to be
`Option<Res>`, it just had to be added.
---
## Changelog
- Changed
- `extract_resource` now takes an optional main world resource
- Fixed
- `ExtractResourcePlugin` doesn't cause panics anymore if the resource
is not already inserted
# Objective
Fixes [#10061]
## Solution
Renamed `RenderInstance` to `ExtractInstance`, `RenderInstances` to
`ExtractedInstances` and `RenderInstancePlugin` to
`ExtractInstancesPlugin`
# Objective
- Add a [Deferred
Renderer](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Deferred_shading) to Bevy.
- This allows subsequent passes to access per pixel material information
before/during shading.
- Accessing this per pixel material information is needed for some
features, like GI. It also makes other features (ex. Decals) simpler to
implement and/or improves their capability. There are multiple
approaches to accomplishing this. The deferred shading approach works
well given the limitations of WebGPU and WebGL2.
Motivation: [I'm working on a GI solution for
Bevy](https://youtu.be/eH1AkL-mwhI)
# Solution
- The deferred renderer is implemented with a prepass and a deferred
lighting pass.
- The prepass renders opaque objects into the Gbuffer attachment
(`Rgba32Uint`). The PBR shader generates a `PbrInput` in mostly the same
way as the forward implementation and then [packs it into the
Gbuffer](ec1465559f/crates/bevy_pbr/src/render/pbr.wgsl (L168)).
- The deferred lighting pass unpacks the `PbrInput` and [feeds it into
the pbr()
function](ec1465559f/crates/bevy_pbr/src/deferred/deferred_lighting.wgsl (L65)),
then outputs the shaded color data.
- There is now a resource
[DefaultOpaqueRendererMethod](ec1465559f/crates/bevy_pbr/src/material.rs (L599))
that can be used to set the default render method for opaque materials.
If materials return `None` from
[opaque_render_method()](ec1465559f/crates/bevy_pbr/src/material.rs (L131))
the `DefaultOpaqueRendererMethod` will be used. Otherwise, custom
materials can also explicitly choose to only support Deferred or Forward
by returning the respective
[OpaqueRendererMethod](ec1465559f/crates/bevy_pbr/src/material.rs (L603))
- Deferred materials can be used seamlessly along with both opaque and
transparent forward rendered materials in the same scene. The [deferred
rendering
example](https://github.com/DGriffin91/bevy/blob/deferred/examples/3d/deferred_rendering.rs)
does this.
- The deferred renderer does not support MSAA. If any deferred materials
are used, MSAA must be disabled. Both TAA and FXAA are supported.
- Deferred rendering supports WebGL2/WebGPU.
## Custom deferred materials
- Custom materials can support both deferred and forward at the same
time. The
[StandardMaterial](ec1465559f/crates/bevy_pbr/src/render/pbr.wgsl (L166))
does this. So does [this
example](https://github.com/DGriffin91/bevy_glowy_orb_tutorial/blob/deferred/assets/shaders/glowy.wgsl#L56).
- Custom deferred materials that require PBR lighting can create a
`PbrInput`, write it to the deferred GBuffer and let it be rendered by
the `PBRDeferredLightingPlugin`.
- Custom deferred materials that require custom lighting have two
options:
1. Use the base_color channel of the `PbrInput` combined with the
`STANDARD_MATERIAL_FLAGS_UNLIT_BIT` flag.
[Example.](https://github.com/DGriffin91/bevy_glowy_orb_tutorial/blob/deferred/assets/shaders/glowy.wgsl#L56)
(If the unlit bit is set, the base_color is stored as RGB9E5 for extra
precision)
2. A Custom Deferred Lighting pass can be created, either overriding the
default, or running in addition. The a depth buffer is used to limit
rendering to only the required fragments for each deferred lighting
pass. Materials can set their respective depth id via the
[deferred_lighting_pass_id](b79182d2a3/crates/bevy_pbr/src/prepass/prepass_io.wgsl (L95))
attachment. The custom deferred lighting pass plugin can then set [its
corresponding
depth](ec1465559f/crates/bevy_pbr/src/deferred/deferred_lighting.wgsl (L37)).
Then with the lighting pass using
[CompareFunction::Equal](ec1465559f/crates/bevy_pbr/src/deferred/mod.rs (L335)),
only the fragments with a depth that equal the corresponding depth
written in the material will be rendered.
Custom deferred lighting plugins can also be created to render the
StandardMaterial. The default deferred lighting plugin can be bypassed
with `DefaultPlugins.set(PBRDeferredLightingPlugin { bypass: true })`
---------
Co-authored-by: nickrart <nickolas.g.russell@gmail.com>
~~Currently blocked on an upstream bug that causes crashes when
minimizing/resizing on dx12 https://github.com/gfx-rs/wgpu/issues/3967~~
wgpu 0.17.1 is out which fixes it
# Objective
Keep wgpu up to date.
## Solution
Update wgpu and naga_oil.
Currently this depends on an unreleased (and unmerged) branch of
naga_oil, and hasn't been properly tested yet.
The wgpu side of this seems to have been an extremely trivial upgrade
(all the upgrade work seems to be in naga_oil). This also lets us remove
the workarounds for pack/unpack4x8unorm in the SSAO shaders.
Lets us close the dx12 part of
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/8888
related: https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/9304
---
## Changelog
Update to wgpu 0.17 and naga_oil 0.9
# Objective
- This PR aims to make creating meshes a little bit more ergonomic,
specifically by removing the need for intermediate mutable variables.
## Solution
- We add methods that consume the `Mesh` and return a mesh with the
specified changes, so that meshes can be entirely constructed via
builder-style calls, without intermediate variables;
- Methods are flagged with `#[must_use]` to ensure proper use;
- Examples are updated to use the new methods where applicable. Some
examples are kept with the mutating methods so that users can still
easily discover them, and also where the new methods wouldn't really be
an improvement.
## Examples
Before:
```rust
let mut mesh = Mesh::new(PrimitiveTopology::TriangleList);
mesh.insert_attribute(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION, vs);
mesh.insert_attribute(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL, vns);
mesh.insert_attribute(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_UV_0, vts);
mesh.set_indices(Some(Indices::U32(tris)));
mesh
```
After:
```rust
Mesh::new(PrimitiveTopology::TriangleList)
.with_inserted_attribute(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION, vs)
.with_inserted_attribute(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL, vns)
.with_inserted_attribute(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_UV_0, vts)
.with_indices(Some(Indices::U32(tris)))
```
Before:
```rust
let mut cube = Mesh::from(shape::Cube { size: 1.0 });
cube.generate_tangents().unwrap();
PbrBundle {
mesh: meshes.add(cube),
..default()
}
```
After:
```rust
PbrBundle {
mesh: meshes.add(
Mesh::from(shape::Cube { size: 1.0 })
.with_generated_tangents()
.unwrap(),
),
..default()
}
```
---
## Changelog
- Added consuming builder methods for more ergonomic `Mesh` creation:
`with_inserted_attribute()`, `with_removed_attribute()`,
`with_indices()`, `with_duplicated_vertices()`,
`with_computed_flat_normals()`, `with_generated_tangents()`,
`with_morph_targets()`, `with_morph_target_names()`.
# Objective
Currently, the only way for custom components that participate in
rendering to opt into the higher-performance extraction method in #9903
is to implement the `RenderInstances` data structure and the extraction
logic manually. This is inconvenient compared to the `ExtractComponent`
API.
## Solution
This commit creates a new `RenderInstance` trait that mirrors the
existing `ExtractComponent` method but uses the higher-performance
approach that #9903 uses. Additionally, `RenderInstance` is more
flexible than `ExtractComponent`, because it can extract multiple
components at once. This makes high-performance rendering components
essentially as easy to write as the existing ones based on component
extraction.
---
## Changelog
### Added
A new `RenderInstance` trait is available mirroring `ExtractComponent`,
but using a higher-performance method to extract one or more components
to the render world. If you have custom components that rendering takes
into account, you may consider migration from `ExtractComponent` to
`RenderInstance` for higher performance.