# Objective
- Several examples are useful for qualitative tests of Bevy's performance
- By contrast, these are less useful for learning material: they are often relatively complex and have large amounts of setup and are performance optimized.
## Solution
- Move bevymark, many_sprites and many_cubes into the new stress_tests example folder
- Move contributors into the games folder: unlike the remaining examples in the 2d folder, it is not focused on demonstrating a clear feature.
Remove the 'chaining' api, as it's peculiar
~~Implement the label traits for `Box<dyn ThatTrait>` (n.b. I'm not confident about this change, but it was the quickest path to not regressing)~~
Remove the need for '`.system`' when using run criteria piping
# Objective
- Make use of storage buffers, where they are available, for clustered forward bindings to support far more point lights in a scene
- Fixes#3605
- Based on top of #4079
This branch on an M1 Max can keep 60fps with about 2150 point lights of radius 1m in the Sponza scene where I've been testing. The bottleneck is mostly assigning lights to clusters which grows faster than linearly (I think 1000 lights was about 1.5ms and 5000 was 7.5ms). I have seen papers and presentations leveraging compute shaders that can get this up to over 1 million. That said, I think any further optimisations should probably be done in a separate PR.
## Solution
- Add `RenderDevice` to the `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` trait `::key()` functions to allow setting flags on the keys depending on feature/limit availability
- Make `GpuPointLights` and `ViewClusterBuffers` into enums containing `UniformVec` and `StorageBuffer` variants. Implement the necessary API on them to make usage the same for both cases, and the only difference is at initialisation time.
- Appropriate shader defs in the shader code to handle the two cases
## Context on some decisions / open questions
- I'm using `max_storage_buffers_per_shader_stage >= 3` as a check to see if storage buffers are supported. I was thinking about diving into 'binding resource management' but it feels like we don't have enough use cases to understand the problem yet, and it is mostly a separate concern to this PR, so I think it should be handled separately.
- Should `ViewClusterBuffers` and `ViewClusterBindings` be merged, duplicating the count variables into the enum variants?
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Changing animation mid animation can leave the model not in its original position
- ~~The movement speed is fixed, no matter the size of the model~~
## Solution
- when changing animation, set it to its initial state and wait for one frame before changing the animation
- ~~when settings the camera controller, use the camera transform to know how far it is from the origin and use the distance for the speed~~
The scene viewer example doesn't run on wasm because it sets the asset folder to `std::env::var("CARGO_MANIFEST_DIR").unwrap()`, which isn't supported on the web.
Solution: set the asset folder to `"."` instead.
# Objective
- `Local`s can no longer be accessed outside of their creating system, but these docs say they can be.
- There's also little reason to have a pure wrapper type for `Local`s; they can just use the real type. The parameter name should be sufficiently documenting.
# Objective
- Only move the camera when explicitly wanted, otherwise the camera goes crazy if the cursor isn't already in the middle of the window when it opens.
## Solution
- Check if the Left mouse button is pressed before updating the mouse delta
- Input is configurable
The example was broken in #3635 when the `ActiveCamera` logic was introduced, after which there could only be one active `Camera3d` globally.
Ideally there could be one `Camera3d` per render target, not globally, but that isn't the case yet.
To fix the example, we need to
- don't use `Camera3d` twice, add a new `SecondWindowCamera3d` marker
- add the `CameraTypePlugin::<SecondWindowCamera3d>`
- extract the correct `RenderPhase`s
- add a 3d pass driver node for the secondary camera
Fixes#4378
Co-authored-by: Jakob Hellermann <hellermann@sipgate.de>
# Objective
- Since #4224, using labels which only refer to one system doesn't make sense.
## Solution
- Remove some of those.
## Future work
- We should remove the ability to use strings as system labels entirely. I haven't in this PR because there are tests which use this, and that's a lot of code to change.
- The only use cases for labels are either intra-crate, which use #4224, or inter-crate, which should either use #4224 or explicit types. Neither of those should use strings.
# Objective
Add a system parameter `ParamSet` to be used as container for conflicting parameters.
## Solution
Added two methods to the SystemParamState trait, which gives the access used by the parameter. Did the implementation. Added some convenience methods to FilteredAccessSet. Changed `get_conflicts` to return every conflicting component instead of breaking on the first conflicting `FilteredAccess`.
Co-authored-by: bilsen <40690317+bilsen@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
Fixes#4344.
## Solution
Add a new component `Text2dBounds` to `Text2dBundle` that specifies the maximum width and height of text. Text will wrap according to this size.
# Objective
Load skeletal weights and indices from GLTF files. Animate meshes.
## Solution
- Load skeletal weights and indices from GLTF files.
- Added `SkinnedMesh` component and ` SkinnedMeshInverseBindPose` asset
- Added `extract_skinned_meshes` to extract joint matrices.
- Added queue phase systems for enqueuing the buffer writes.
Some notes:
- This ports part of # #2359 to the current main.
- This generates new `BufferVec`s and bind groups every frame. The expectation here is that the number of `Query::get` calls during extract is probably going to be the stronger bottleneck, with up to 256 calls per skinned mesh. Until that is optimized, caching buffers and bind groups is probably a non-concern.
- Unfortunately, due to the uniform size requirements, this means a 16KB buffer is allocated for every skinned mesh every frame. There's probably a few ways to get around this, but most of them require either compute shaders or storage buffers, which are both incompatible with WebGL2.
Co-authored-by: james7132 <contact@jamessliu.com>
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: James Liu <contact@jamessliu.com>
# Objective
A common pattern in Rust is the [newtype](https://doc.rust-lang.org/rust-by-example/generics/new_types.html). This is an especially useful pattern in Bevy as it allows us to give common/foreign types different semantics (such as allowing it to implement `Component` or `FromWorld`) or to simply treat them as a "new type" (clever). For example, it allows us to wrap a common `Vec<String>` and do things like:
```rust
#[derive(Component)]
struct Items(Vec<String>);
fn give_sword(query: Query<&mut Items>) {
query.single_mut().0.push(String::from("Flaming Poisoning Raging Sword of Doom"));
}
```
> We could then define another struct that wraps `Vec<String>` without anything clashing in the query.
However, one of the worst parts of this pattern is the ugly `.0` we have to write in order to access the type we actually care about. This is why people often implement `Deref` and `DerefMut` in order to get around this.
Since it's such a common pattern, especially for Bevy, it makes sense to add a derive macro to automatically add those implementations.
## Solution
Added a derive macro for `Deref` and another for `DerefMut` (both exported into the prelude). This works on all structs (including tuple structs) as long as they only contain a single field:
```rust
#[derive(Deref)]
struct Foo(String);
#[derive(Deref, DerefMut)]
struct Bar {
name: String,
}
```
This allows us to then remove that pesky `.0`:
```rust
#[derive(Component, Deref, DerefMut)]
struct Items(Vec<String>);
fn give_sword(query: Query<&mut Items>) {
query.single_mut().push(String::from("Flaming Poisoning Raging Sword of Doom"));
}
```
### Alternatives
There are other alternatives to this such as by using the [`derive_more`](https://crates.io/crates/derive_more) crate. However, it doesn't seem like we need an entire crate just yet since we only need `Deref` and `DerefMut` (for now).
### Considerations
One thing to consider is that the Rust std library recommends _not_ using `Deref` and `DerefMut` for things like this: "`Deref` should only be implemented for smart pointers to avoid confusion" ([reference](https://doc.rust-lang.org/std/ops/trait.Deref.html)). Personally, I believe it makes sense to use it in the way described above, but others may disagree.
### Additional Context
Discord: https://discord.com/channels/691052431525675048/692572690833473578/956648422163746827 (controversiality discussed [here](https://discord.com/channels/691052431525675048/692572690833473578/956711911481835630))
---
## Changelog
- Add `Deref` derive macro (exported to prelude)
- Add `DerefMut` derive macro (exported to prelude)
- Updated most newtypes in examples to use one or both derives
Co-authored-by: MrGVSV <49806985+MrGVSV@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
1. Spawning walls in the Breakout example was hard to follow and error-prone.
2. The strategy used in `paddle_movement_system` was somewhat convoluted.
3. Correctly modifying the size of the arena was hard, due to implicit coupling between the bounds and the bounds that the paddle can move in.
## Solution
1. Refactor this to use a WallBundle struct with a builder; neatly demonstrating some essential patterns along the way.
2. Use clamp and avoid using weird &mut strategies.
3. Refactor logic to allow users to tweak the brick size, and automatically adjust the number of rows and columns to match.
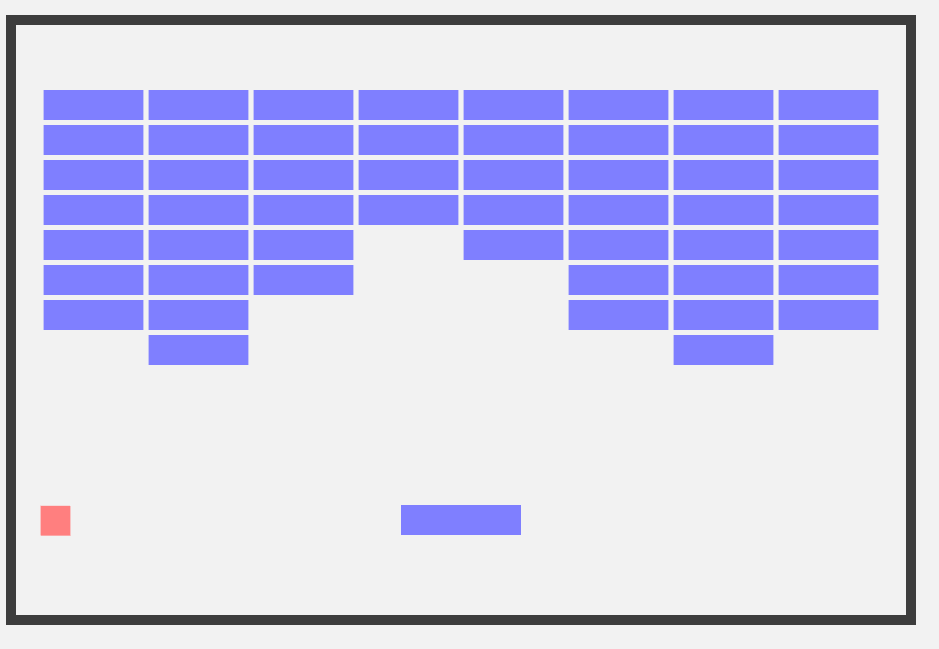
4. Make the brick layout more like classic breakout!
# Objective
- The Breakout example uses system names like `paddle_movement_system`
- _system syntax is redundant
- the [community has spoken](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/discussions/2804), and prefers to avoid `_system` system names by a more than 2:1 ratio
- existing system names were not terribly descriptive
## Solution
- rename the systems to take the form of `verb`, rather than `noun_system` to better capture the behavior they are implenting
- yeet `_system`
This adds the concept of "default labels" for systems (currently scoped to "parallel systems", but this could just as easily be implemented for "exclusive systems"). Function systems now include their function's `SystemTypeIdLabel` by default.
This enables the following patterns:
```rust
// ordering two systems without manually defining labels
app
.add_system(update_velocity)
.add_system(movement.after(update_velocity))
// ordering sets of systems without manually defining labels
app
.add_system(foo)
.add_system_set(
SystemSet::new()
.after(foo)
.with_system(bar)
.with_system(baz)
)
```
Fixes: #4219
Related to: #4220
Credit to @aevyrie @alice-i-cecile @DJMcNab (and probably others) for proposing (and supporting) this idea about a year ago. I was a big dummy that both shut down this (very good) idea and then forgot I did that. Sorry. You all were right!
# Objective
- The components in the Breakout game are defined in a strange fashion.
- Components should decouple behavior wherever possible.
- Systems should be as general as possible, to make extending behavior easier.
- Marker components are idiomatic and useful, but marker components and query filters were not used.
- The existing design makes it challenging for beginners to extend the example into a high-quality game.
## Solution
- Refactor component definitions in the Breakout example to reflect principles above.
## Context
A small portion of the changes made in #2094. Interacts with changes in #4255; merge conflicts will have to be resolved.
# Objective
- Fixes#3970
- To support Bevy's shader abstraction(shader defs, shader imports and hot shader reloading) for compute shaders, I have followed carts advice and change the `PipelinenCache` to accommodate both compute and render pipelines.
## Solution
- renamed `RenderPipelineCache` to `PipelineCache`
- Cached Pipelines are now represented by an enum (render, compute)
- split the `SpecializedPipelines` into `SpecializedRenderPipelines` and `SpecializedComputePipelines`
- updated the game of life example
## Open Questions
- should `SpecializedRenderPipelines` and `SpecializedComputePipelines` be merged and how would we do that?
- should the `get_render_pipeline` and `get_compute_pipeline` methods be merged?
- is pipeline specialization for different entry points a good pattern
Co-authored-by: Kurt Kühnert <51823519+Ku95@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
## Objective
There recently was a discussion on Discord about a possible test case for stress-testing transform hierarchies.
## Solution
Create a test case for stress testing transform propagation.
*Edit:* I have scrapped my previous example and built something more functional and less focused on visuals.
There are three test setups:
- `TestCase::Tree` recursively creates a tree with a specified depth and branch width
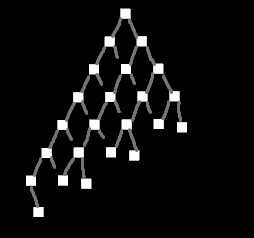
- `TestCase::NonUniformTree` is the same as `Tree` but omits nodes in a way that makes the tree "lean" towards one side, like this:
<details>
<summary></summary>
</details>
- `TestCase::Humanoids` creates one or more separate hierarchies based on the structure of common humanoid rigs
- this can both insert `active` and `inactive` instances of the human rig
It's possible to parameterize which parts of the hierarchy get updated (transform change) and which remain unchanged. This is based on @james7132 suggestion:
There's a probability to decide which entities should remain static. On top of that these changes can be limited to a certain range in the hierarchy (min_depth..max_depth).
# Objective
- The Breakout example has a lot of configurable constant values for setup, but these are buried in the source code.
- Magic numbers scattered in the source code are hard to follow.
- Providing constants up front makes tweaking examples very approachable.
## Solution
- Move magic numbers into constants
## Context
Part of the changes made in #2094; split out for easier review.
# Objective
- Allow quick and easy testing of scenes
## Solution
- Add a `scene-viewer` tool based on `load_gltf`.
- Run it with e.g. `cargo run --release --example scene_viewer --features jpeg -- ../some/path/assets/models/Sponza/glTF/Sponza.gltf#Scene0`
- Configure the asset path as pointing to the repo root for convenience (paths specified relative to current working directory)
- Copy over the camera controller from the `shadow_biases` example
- Support toggling the light animation
- Support toggling shadows
- Support adjusting the directional light shadow projection (cascaded shadow maps will remove the need for this later)
I don't want to do too much on it up-front. Rather we can add features over time as we need them.
# Objective
- Make the example a little easier to follow by removing unnecessary steps.
## Solution
- `Assets<Image>` will give us a handle for our render texture if we call `add()` instead of `set()`. No need to set it manually; one less thing to think about while reading the example.
# Add Transform Examples
- Adding examples for moving/rotating entities (with its own section) to resolve#2400
I've stumbled upon this project and been fiddling around a little. Saw the issue and thought I might just add some examples for the proposed transformations.
Mind to check if I got the gist correctly and suggest anything I can improve?
**Problem**
- whenever you want more than one of the builtin cameras (for example multiple windows, split screen, portals), you need to add a render graph node that executes the correct sub graph, extract the camera into the render world and add the correct `RenderPhase<T>` components
- querying for the 3d camera is annoying because you need to compare the camera's name to e.g. `CameraPlugin::CAMERA_3d`
**Solution**
- Introduce the marker types `Camera3d`, `Camera2d` and `CameraUi`
-> `Query<&mut Transform, With<Camera3d>>` works
- `PerspectiveCameraBundle::new_3d()` and `PerspectiveCameraBundle::<Camera3d>::default()` contain the `Camera3d` marker
- `OrthographicCameraBundle::new_3d()` has `Camera3d`, `OrthographicCameraBundle::new_2d()` has `Camera2d`
- remove `ActiveCameras`, `ExtractedCameraNames`
- run 2d, 3d and ui passes for every camera of their respective marker
-> no custom setup for multiple windows example needed
**Open questions**
- do we need a replacement for `ActiveCameras`? What about a component `ActiveCamera { is_active: bool }` similar to `Visibility`?
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Use the low power, reactive rendering settings for UI examples.
- Make the feature more discoverable by using it in an applicable context.
# Objective
Fixes#4036
## Solution
- Use `VertexBufferLayout::from_vertex_formats`
- Actually put a u32 into `ATTRIBUTE_COLOR` and convert it in the shader
I'm not 100% sure about the color stuff. It seems like `ATTRIBUTE_COLOR` has been `Uint32` this whole time, but this example previously worked with `[f32; 4]` somehow, perhaps because the vertex layout was manually specified.
Let me know if that can be improved, or feel free to close for an alternative fix.
# Objective
- Improve documentation.
- Provide helper functions for common uses of `Windows` relating to getting the primary `Window`.
- Reduce repeated `Window` code.
# Solution
- Adds infallible `primary()` and `primary_mut()` functions with standard error text. This replaces the commonly used `get_primary().unwrap()` seen throughout bevy which has inconsistent or nonexistent error messages.
- Adds `scale_factor(WindowId)` to replace repeated code blocks throughout.
# Considerations
- The added functions can panic if the primary window does not exist.
- It is very uncommon for the primary window to not exist, as seen by the regular use of `get_primary().unwrap()`. Most users will have a single window and will need to reference the primary window in their code multiple times.
- The panic provides a consistent error message to make this class of error easy to spot from the panic text.
- This follows the established standard of short names for infallible-but-unlikely-to-panic functions in bevy.
- Removes line noise for common usage of `Windows`.
# Objective
- Reduce power usage for games when not focused.
- Reduce power usage to ~0 when a desktop application is minimized (opt-in).
- Reduce power usage when focused, only updating on a `winit` event, or the user sends a redraw request. (opt-in)
https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/2632925/156904387-ec47d7de-7f06-4c6f-8aaf-1e952c1153a2.mp4
Note resource usage in the Task Manager in the above video.
## Solution
- Added a type `UpdateMode` that allows users to specify how the winit event loop is updated, without exposing winit types.
- Added two fields to `WinitConfig`, both with the `UpdateMode` type. One configures how the application updates when focused, and the other configures how the application behaves when it is not focused. Users can modify this resource manually to set the type of event loop control flow they want.
- For convenience, two functions were added to `WinitConfig`, that provide reasonable presets: `game()` (default) and `desktop_app()`.
- The `game()` preset, which is used by default, is unchanged from current behavior with one exception: when the app is out of focus the app updates at a minimum of 10fps, or every time a winit event is received. This has a huge positive impact on power use and responsiveness on my machine, which will otherwise continue running the app at many hundreds of fps when out of focus or minimized.
- The `desktop_app()` preset is fully reactive, only updating when user input (winit event) is supplied or a `RedrawRequest` event is sent. When the app is out of focus, it only updates on `Window` events - i.e. any winit event that directly interacts with the window. What this means in practice is that the app uses *zero* resources when minimized or not interacted with, but still updates fluidly when the app is out of focus and the user mouses over the application.
- Added a `RedrawRequest` event so users can force an update even if there are no events. This is useful in an application when you want to, say, run an animation even when the user isn't providing input.
- Added an example `low_power` to demonstrate these changes
## Usage
Configuring the event loop:
```rs
use bevy::winit::{WinitConfig};
// ...
.insert_resource(WinitConfig::desktop_app()) // preset
// or
.insert_resource(WinitConfig::game()) // preset
// or
.insert_resource(WinitConfig{ .. }) // manual
```
Requesting a redraw:
```rs
use bevy:🪟:RequestRedraw;
// ...
fn request_redraw(mut event: EventWriter<RequestRedraw>) {
event.send(RequestRedraw);
}
```
## Other details
- Because we have a single event loop for multiple windows, every time I've mentioned "focused" above, I more precisely mean, "if at least one bevy window is focused".
- Due to a platform bug in winit (https://github.com/rust-windowing/winit/issues/1619), we can't simply use `Window::request_redraw()`. As a workaround, this PR will temporarily set the window mode to `Poll` when a redraw is requested. This is then reset to the user's `WinitConfig` setting on the next frame.
# Objective
- Make the many_cubes example more interesting (and look more like many_sprites)
## Solution
- Actually display many cubes
- Move the camera around
Adds a `default()` shorthand for `Default::default()` ... because life is too short to constantly type `Default::default()`.
```rust
use bevy::prelude::*;
#[derive(Default)]
struct Foo {
bar: usize,
baz: usize,
}
// Normally you would do this:
let foo = Foo {
bar: 10,
..Default::default()
};
// But now you can do this:
let foo = Foo {
bar: 10,
..default()
};
```
The examples have been adapted to use `..default()`. I've left internal crates as-is for now because they don't pull in the bevy prelude, and the ergonomics of each case should be considered individually.
# Objective
- Add ways to control how audio is played
## Solution
- playing a sound will return a (weak) handle to an asset that can be used to control playback
- if the asset is dropped, it will detach the sink (same behaviour as now)
# Objective
- In the large majority of cases, users were calling `.unwrap()` immediately after `.get_resource`.
- Attempting to add more helpful error messages here resulted in endless manual boilerplate (see #3899 and the linked PRs).
## Solution
- Add an infallible variant named `.resource` and so on.
- Use these infallible variants over `.get_resource().unwrap()` across the code base.
## Notes
I did not provide equivalent methods on `WorldCell`, in favor of removing it entirely in #3939.
## Migration Guide
Infallible variants of `.get_resource` have been added that implicitly panic, rather than needing to be unwrapped.
Replace `world.get_resource::<Foo>().unwrap()` with `world.resource::<Foo>()`.
## Impact
- `.unwrap` search results before: 1084
- `.unwrap` search results after: 942
- internal `unwrap_or_else` calls added: 4
- trivial unwrap calls removed from tests and code: 146
- uses of the new `try_get_resource` API: 11
- percentage of the time the unwrapping API was used internally: 93%
# Objective
Will fix#3377 and #3254
## Solution
Use an enum to represent either a `WindowId` or `Handle<Image>` in place of `Camera::window`.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Closes#786
- Closes#2252
- Closes#2588
This PR implements a derive macro that allows users to define their queries as structs with named fields.
## Example
```rust
#[derive(WorldQuery)]
#[world_query(derive(Debug))]
struct NumQuery<'w, T: Component, P: Component> {
entity: Entity,
u: UNumQuery<'w>,
generic: GenericQuery<'w, T, P>,
}
#[derive(WorldQuery)]
#[world_query(derive(Debug))]
struct UNumQuery<'w> {
u_16: &'w u16,
u_32_opt: Option<&'w u32>,
}
#[derive(WorldQuery)]
#[world_query(derive(Debug))]
struct GenericQuery<'w, T: Component, P: Component> {
generic: (&'w T, &'w P),
}
#[derive(WorldQuery)]
#[world_query(filter)]
struct NumQueryFilter<T: Component, P: Component> {
_u_16: With<u16>,
_u_32: With<u32>,
_or: Or<(With<i16>, Changed<u16>, Added<u32>)>,
_generic_tuple: (With<T>, With<P>),
_without: Without<Option<u16>>,
_tp: PhantomData<(T, P)>,
}
fn print_nums_readonly(query: Query<NumQuery<u64, i64>, NumQueryFilter<u64, i64>>) {
for num in query.iter() {
println!("{:#?}", num);
}
}
#[derive(WorldQuery)]
#[world_query(mutable, derive(Debug))]
struct MutNumQuery<'w, T: Component, P: Component> {
i_16: &'w mut i16,
i_32_opt: Option<&'w mut i32>,
}
fn print_nums(mut query: Query<MutNumQuery, NumQueryFilter<u64, i64>>) {
for num in query.iter_mut() {
println!("{:#?}", num);
}
}
```
## TODOs:
- [x] Add support for `&T` and `&mut T`
- [x] Test
- [x] Add support for optional types
- [x] Test
- [x] Add support for `Entity`
- [x] Test
- [x] Add support for nested `WorldQuery`
- [x] Test
- [x] Add support for tuples
- [x] Test
- [x] Add support for generics
- [x] Test
- [x] Add support for query filters
- [x] Test
- [x] Add support for `PhantomData`
- [x] Test
- [x] Refactor `read_world_query_field_type_info`
- [x] Properly document `readonly` attribute for nested queries and the static assertions that guarantee safety
- [x] Test that we never implement `ReadOnlyFetch` for types that need mutable access
- [x] Test that we insert static assertions for nested `WorldQuery` that a user marked as readonly
This PR makes a number of changes to how meshes and vertex attributes are handled, which the goal of enabling easy and flexible custom vertex attributes:
* Reworks the `Mesh` type to use the newly added `VertexAttribute` internally
* `VertexAttribute` defines the name, a unique `VertexAttributeId`, and a `VertexFormat`
* `VertexAttributeId` is used to produce consistent sort orders for vertex buffer generation, replacing the more expensive and often surprising "name based sorting"
* Meshes can be used to generate a `MeshVertexBufferLayout`, which defines the layout of the gpu buffer produced by the mesh. `MeshVertexBufferLayouts` can then be used to generate actual `VertexBufferLayouts` according to the requirements of a specific pipeline. This decoupling of "mesh layout" vs "pipeline vertex buffer layout" is what enables custom attributes. We don't need to standardize _mesh layouts_ or contort meshes to meet the needs of a specific pipeline. As long as the mesh has what the pipeline needs, it will work transparently.
* Mesh-based pipelines now specialize on `&MeshVertexBufferLayout` via the new `SpecializedMeshPipeline` trait (which behaves like `SpecializedPipeline`, but adds `&MeshVertexBufferLayout`). The integrity of the pipeline cache is maintained because the `MeshVertexBufferLayout` is treated as part of the key (which is fully abstracted from implementers of the trait ... no need to add any additional info to the specialization key).
* Hashing `MeshVertexBufferLayout` is too expensive to do for every entity, every frame. To make this scalable, I added a generalized "pre-hashing" solution to `bevy_utils`: `Hashed<T>` keys and `PreHashMap<K, V>` (which uses `Hashed<T>` internally) . Why didn't I just do the quick and dirty in-place "pre-compute hash and use that u64 as a key in a hashmap" that we've done in the past? Because its wrong! Hashes by themselves aren't enough because two different values can produce the same hash. Re-hashing a hash is even worse! I decided to build a generalized solution because this pattern has come up in the past and we've chosen to do the wrong thing. Now we can do the right thing! This did unfortunately require pulling in `hashbrown` and using that in `bevy_utils`, because avoiding re-hashes requires the `raw_entry_mut` api, which isn't stabilized yet (and may never be ... `entry_ref` has favor now, but also isn't available yet). If std's HashMap ever provides the tools we need, we can move back to that. Note that adding `hashbrown` doesn't increase our dependency count because it was already in our tree. I will probably break these changes out into their own PR.
* Specializing on `MeshVertexBufferLayout` has one non-obvious behavior: it can produce identical pipelines for two different MeshVertexBufferLayouts. To optimize the number of active pipelines / reduce re-binds while drawing, I de-duplicate pipelines post-specialization using the final `VertexBufferLayout` as the key. For example, consider a pipeline that needs the layout `(position, normal)` and is specialized using two meshes: `(position, normal, uv)` and `(position, normal, other_vec2)`. If both of these meshes result in `(position, normal)` specializations, we can use the same pipeline! Now we do. Cool!
To briefly illustrate, this is what the relevant section of `MeshPipeline`'s specialization code looks like now:
```rust
impl SpecializedMeshPipeline for MeshPipeline {
type Key = MeshPipelineKey;
fn specialize(
&self,
key: Self::Key,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
) -> RenderPipelineDescriptor {
let mut vertex_attributes = vec![
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL.at_shader_location(1),
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_UV_0.at_shader_location(2),
];
let mut shader_defs = Vec::new();
if layout.contains(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_TANGENT) {
shader_defs.push(String::from("VERTEX_TANGENTS"));
vertex_attributes.push(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_TANGENT.at_shader_location(3));
}
let vertex_buffer_layout = layout
.get_layout(&vertex_attributes)
.expect("Mesh is missing a vertex attribute");
```
Notice that this is _much_ simpler than it was before. And now any mesh with any layout can be used with this pipeline, provided it has vertex postions, normals, and uvs. We even got to remove `HAS_TANGENTS` from MeshPipelineKey and `has_tangents` from `GpuMesh`, because that information is redundant with `MeshVertexBufferLayout`.
This is still a draft because I still need to:
* Add more docs
* Experiment with adding error handling to mesh pipeline specialization (which would print errors at runtime when a mesh is missing a vertex attribute required by a pipeline). If it doesn't tank perf, we'll keep it.
* Consider breaking out the PreHash / hashbrown changes into a separate PR.
* Add an example illustrating this change
* Verify that the "mesh-specialized pipeline de-duplication code" works properly
Please dont yell at me for not doing these things yet :) Just trying to get this in peoples' hands asap.
Alternative to #3120Fixes#3030
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- `WgpuOptions` is mutated to be updated with the actual device limits and features, but this information is readily available to both the main and render worlds through the `RenderDevice` which has .limits() and .features() methods
- Information about the adapter in terms of its name, the backend in use, etc were not being exposed but have clear use cases for being used to take decisions about what rendering code to use. For example, if something works well on AMD GPUs but poorly on Intel GPUs. Or perhaps something works well in Vulkan but poorly in DX12.
## Solution
- Stop mutating `WgpuOptions `and don't insert the updated values into the main and render worlds
- Return `AdapterInfo` from `initialize_renderer` and insert it into the main and render worlds
- Use `RenderDevice` limits in the lighting code that was using `WgpuOptions.limits`.
- Renamed `WgpuOptions` to `WgpuSettings`
I wanted to try one of the new examples but it felt so clunky that I wanted to improve it.
It did make me feel like maybe some input axes abstraction like Unity has might be useful.
Also, eating cake should probably be a separate system from movement.
What is says on the tin.
This has got more to do with making `clippy` slightly more *quiet* than it does with changing anything that might greatly impact readability or performance.
that said, deriving `Default` for a couple of structs is a nice easy win