Fix associated item visibility in block-local impls
Fixes#14046
When we're resolving visibility of block-local items...
> `self` normally refers to the containing non-block module, and `super` to its parent (etc.). However, visibilities must only refer to a module in the DefMap they're written in, so we restrict them when that happens. ([link])
...unless we're resolving visibility of associated items in block-local impls, because that impl is semantically "hoisted" to the nearest (non-block) module. With this PR, we skip the adjustment for such items.
Since visibility representation of those items is modified, this PR also adjusts visibility rendering in `HirDisplay`.
[link]: a6603fc21d/crates/hir-def/src/nameres/path_resolution.rs (L101-L103)
Fix: Run doctests for structs with lifetime parameters from IDE
Fixes#14142: Doctests can't be triggered for structs with lifetimes
This MR adds lifetime parameters to the structs path for runnables so that they can be triggered from an IDE as well.
This is my first MR for rust-analyzer, please let me know if I should change something, either in code or the description here.
Beginning of MIR
This pull request introduces the initial implementation of MIR lowering and interpreting in Rust Analyzer.
The implementation of MIR has potential to bring several benefits:
- Executing a unit test without compiling it: This is my main goal. It can be useful for quickly testing code changes and print-debugging unit tests without the need for a full compilation (ideally in almost zero time, similar to languages like python and js). There is a probability that it goes nowhere, it might become slower than rustc, or it might need some unreasonable amount of memory, or we may fail to support a common pattern/function that make it unusable for most of the codes.
- Constant evaluation: MIR allows for easier and more correct constant evaluation, on par with rustc. If r-a wants to fully support the type system, it needs full const eval, which means arbitrary code execution, which needs MIR or something similar.
- Supporting more diagnostics: MIR can be used to detect errors, most famously borrow checker and lifetime errors, but also mutability errors and uninitialized variables, which can be difficult/impossible to detect in HIR.
- Lowering closures: With MIR we can find out closure capture modes, which is useful in detecting if a closure implements the `FnMut` or `Fn` traits, and calculating its size and data layout.
But the current PR implements no diagnostics and doesn't support closures. About const eval, I removed the old const eval code and it now uses the mir interpreter. Everything that is supported in stable rustc is either implemented or is super easy to implement. About interpreting unit tests, I added an experimental config, disabled by default, that shows a `pass` or `fail` on hover of unit tests (ideally it should be a button similar to `Run test` button, but I didn't figured out how to add them). Currently, no real world test works, due to missing features including closures, heap allocation, `dyn Trait` and ... so at this point it is only useful for me selecting what to implement next.
The implementation of MIR is based on the design of rustc, the data structures are almost copy paste (so it should be easy to migrate it to a possible future stable-mir), but the lowering and interpreting code is from me.
add: clean api to get `raw_ptr` type
There doesn't seem to be an API to fetch the type of `raw_ptr`, which is helpful for a project I work on.
Notes:
- I am unsure about the function name, do let me know if I should use something else.
- Also unsure about where to add tests, for hir changes. Will fix it as needed.
fix:add a case in which remainig is None in resolveing types when resolving hir path.
fix#14030 The variable type is being determined incorrectly
This PR fixed a problem in which `go to definition` is jumping to the incorrect position because it was failing to resolve the type in case it defined in the module when resolving hir.
In addition, I added a test for this issue and refactored the related code.
This is my first PR and I am using a translation tool to write this text. Let me know if you have any problems.
add openDocs command to context menu in VS Code extension
This adds the `openDocs` command to the VS Code context menu. I believe there are probably many user who are unaware of this command existing in the rust analyzer extension, and that this should enhance the discoverability of the command. Additionally, even if people are aware of this capability, it's helpful to have this in the context menu anyway; for example, one might forget the name of the command, or the keybinding they have assigned to it. I think that opening docs is a common enough action to warrant the extra line added to the context menu.
This makes a few other small changes as well. There are two minor style changes to increase style consistency. First, it changes the titles of the two commands that the rust analyzer extension will contribute to the context menu to title case. All standard VS Code commands that appear in the context menu are in title case. Second, it shortens the title of the `openDocs` command from `Open docs under cursor` to `Open Docs`. The implicit assumption in the standard VS Code context menu command titles is that the action applies to the symbol under the cursor: `Go to Definition`, `Find All References`, etc. Note that since these are changes to the command titles, rather than the command names themselves, these changes will not break any users' existing keybindings for these commands.
Second, this adds further restrictions to the `where` clauses of the two commands that the rust analyzer extension will contribute to the context menu, so that the two commands will appear in the context menu only when in a Rust project **and** within a Rust file. Say you have a Python or bash script inside your Rust project. Having these commands appear in the context menu when you right click a symbol in such a non-Rust file is extraneous and potentially confusing.
(This is a large commit. The changes to
`compiler/rustc_middle/src/ty/context.rs` are the most important ones.)
The current naming scheme is a mess, with a mix of `_intern_`, `intern_`
and `mk_` prefixes, with little consistency. In particular, in many
cases it's easy to use an iterator interner when a (preferable) slice
interner is available.
The guiding principles of the new naming system:
- No `_intern_` prefixes.
- The `intern_` prefix is for internal operations.
- The `mk_` prefix is for external operations.
- For cases where there is a slice interner and an iterator interner,
the former is `mk_foo` and the latter is `mk_foo_from_iter`.
Also, `slice_interners!` and `direct_interners!` can now be `pub` or
non-`pub`, which helps enforce the internal/external operations
division.
It's not perfect, but I think it's a clear improvement.
The following lists show everything that was renamed.
slice_interners
- const_list
- mk_const_list -> mk_const_list_from_iter
- intern_const_list -> mk_const_list
- substs
- mk_substs -> mk_substs_from_iter
- intern_substs -> mk_substs
- check_substs -> check_and_mk_substs (this is a weird one)
- canonical_var_infos
- intern_canonical_var_infos -> mk_canonical_var_infos
- poly_existential_predicates
- mk_poly_existential_predicates -> mk_poly_existential_predicates_from_iter
- intern_poly_existential_predicates -> mk_poly_existential_predicates
- _intern_poly_existential_predicates -> intern_poly_existential_predicates
- predicates
- mk_predicates -> mk_predicates_from_iter
- intern_predicates -> mk_predicates
- _intern_predicates -> intern_predicates
- projs
- intern_projs -> mk_projs
- place_elems
- mk_place_elems -> mk_place_elems_from_iter
- intern_place_elems -> mk_place_elems
- bound_variable_kinds
- mk_bound_variable_kinds -> mk_bound_variable_kinds_from_iter
- intern_bound_variable_kinds -> mk_bound_variable_kinds
direct_interners
- region
- intern_region (unchanged)
- const
- mk_const_internal -> intern_const
- const_allocation
- intern_const_alloc -> mk_const_alloc
- layout
- intern_layout -> mk_layout
- adt_def
- intern_adt_def -> mk_adt_def_from_data (unusual case, hard to avoid)
- alloc_adt_def(!) -> mk_adt_def
- external_constraints
- intern_external_constraints -> mk_external_constraints
Other
- type_list
- mk_type_list -> mk_type_list_from_iter
- intern_type_list -> mk_type_list
- tup
- mk_tup -> mk_tup_from_iter
- intern_tup -> mk_tup
fix: Search raw identifiers without prefix
When we find references/usages of a raw identifier, we should disregard `r#` prefix because there are keywords one can use without the prefix in earlier editions (see #13034; this bug is actually fallout from the PR). `name`, the text we're searching for, has already been stripped of the prefix, but the text of nodes we compare it to hasn't been.
The second commit is strictly refactoring, I can remove it if it's not much of value.
fix: Don't expand macros in the same expansion tree after overflow
This patch fixes 2 bugs:
- In `Expander::enter_expand_id()` (and in code paths it's called), we never check whether we've reached the recursion limit. Although it hasn't been reported as far as I'm aware, this may cause hangs or stack overflows if some malformed attribute macro is used on associated items.
- We keep expansion even when recursion limit is reached. Take the following for example:
```rust
macro_rules! foo { () => {{ foo!(); foo!(); }} }
fn main() { foo!(); }
```
We keep expanding the first `foo!()` in each expansion and would reach the limit at some point, *after which* we would try expanding the second `foo!()` in each expansion until it hits the limit again. This will (by default) lead to ~2^128 expansions.
This is essentially what's happening in #14074. Unlike rustc, we don't just stop expanding macros when we fail as long as it produces some tokens so that we can provide completions and other services in incomplete macro calls.
This patch provides a method that takes care of recursion depths (`Expander::within_limit()`) and stops macro expansions in the whole macro expansion tree once it detects recursion depth overflow. To be honest, I'm not really satisfied with this fix because it can still be used in unintended ways to bypass overflow checks, and I'm still seeking ways such that misuses are caught by the compiler by leveraging types or something.
Fixes#14074
fix: don't include `r#` prefix in filesystem changes
Fixes#14131
In addition to fix for #14131, this PR adds raw ident validity checks in rename functionality that we've been missing.
Support DidChangeWorkspaceFolders notifications
This PR enables the `WorkspaceFoldersServerCapabilities` capability for rust-analyzer and implemented support for the associated [`DidChangeWorkspaceFolders`](https://microsoft.github.io/language-server-protocol/specifications/lsp/3.17/specification/#workspace_didChangeWorkspaceFolders) notification to allow clients to update the list of `workspaceFolders` sent during initialization.
## Motivation
This allows clients which lazily autodiscover their workspace roots (like the [helix editor](https://github.com/helix-editor/helix) once [my PR](https://github.com/helix-editor/helix/pull/5748) lands) avoid spawning multiple instances of RA. Right now such clients are forced to either:
* greedily discover all LSP roots in the workspace (precludes the ability to respond to new workspace roots)
* spawn multiple instance of rust-analyzer (one for each root)
* restart rust-analyzer whenever a new workspace is added
Some example use-cases are shown [here](https://github.com/helix-editor/helix/pull/5748#issuecomment-1421012523).
This PR will also improve support for VSCode (and Atom) multi workspaces.
## Implementation
The implementation was fairly straightforward as `rust-analyzer` already supports dynamically reloading workspaces, for example on configuration changes. Furthermore, rust-analyzer also already supports auto-discovering internal workspace from the `workspaceFolders` key in the initialization request. Therefore, the necessary logic just needed to be moved to a central place and reused.
Handle case when BlockExpr is child of IfExpr, WhileExpr, LoopExpr,
ForExpr.
An additional { } will be added when:
- It is not a BlockExpr
- It is a BlockExpr and a child of IfExpr, WhileExpr, LoopExpr, ForExpr.
Support sysroot library source being defined inside the workspace
With this you can now specify `cargo.sysrootSrc`. This is required for the rust workspace such that the `library` folder inside the workspace can be used as the sysroot library sources. We now also recognize if these sources are inside the workspace, tagging the as workspace members.
This does duplicate the sysroot crates still, but I don't think that causes too many problems.
Implement proc-macro-api versioning
So as it stands, we can't really change the proc-macro-api protocol at all without breaking all proc-macro servers again. To somewhat alleviate this we can move the supported ABI mess over to the proc-macro-api now by supporting multiple versions there (versions defined by us at least, not by rustc). Since the proc-macro-api protocol has no versioning scheme at the moment though, the best we can do here is add a new request to query the version from a server. Due to how the server currently works though, if it encounters an unknown request it will exit, meaning we can check if it is a server without support by checking if it exited after our version check request, that way we can support the current circulating server as well.
We need this since our span type will change from `TokenId` to something else at some point, but for that to work we need to comply with that the server expects. So knowing the version the server is using we can decide whether to send our new span data, or the tokenid (assuming we keep that information with our span data as well, alternatively we send irrelevant tokenids). That way we can keep old servers working while the user installations slowly migrate to newer servers that support the new spandata.
Support generic function in `generate_function` assist
Part of #3639
This PR adds support for generic function generation in `generate_function` assist. Now the assist looks for generic parameters and trait bounds in scope, filters out irrelevant ones, and generates new function with them.
See `fn_generic_params()` for the outline of the procedure, and see comments on `filter_unnecessary_bounds()` for criteria for filtering. I think it's good criteria for most cases, but I'm open to opinions and suggestions.
The diff is pretty big, but it should run in linear time w.r.t. the number of nodes we operate on and should be fast enough.
Some notes:
- When we generate function in an existing impl, generic parameters may cause name conflict. While we can detect the conflict and rename conflicting params, I didn't find it worthwhile mainly because it's really easy to resolve on IDE: use Rename functionality.
- I've implemented graph structure myself, because we don't have graph library as a dependency and we only need the simplest one.
- Although `petgraph` is in our dependency graph and I was initially looking to use it, we don't actually depend on it AFAICT since it's only used in chalk's specialization graph handling, which we don't use. I'd be happy to replace my implementation with `petgraph` if it's okay to use it though.
- There are some caveats that I consider out of scope of this PR. See FIXME notes on added tests.
feat: Remove support for 1.58 proc-macro abi
This seems old enough that we can drop the support for it now, the less ABIs we have the less work it is adjusting our span implementation.
Extracted from https://github.com/rust-lang/rust-analyzer/pull/14061, will rebase that over this once merged.
Don't escape non-snippets in assist
I was misunderstanding that we're always sending snippets as response to assist request. For assists that never return snippets like `move_const_to_impl` we don't need to escape, and I don't think `utils::escape_non_snippet()` is useful at the moment since we guarantee that only a single edit will have `InsertTextFormat.Snippet` and we have `utils::render_snippet()` for that.
internal: Remove hover fallback in favor of ranged hover
The fallback is usually more annoying than useful at this point (it messes with the range of diagnostic popups a lot), we now have a ranged hover to check the type of something which works a lot better.
Closes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust-analyzer/issues/11602
Don't respond with a ContentModified while loading the workspace
Initially this was done to prevent frequent inlay hint flickering, but this causes a lot of problems for a bunch of clients. We can (and already kind of have) move this into the semantic token request handlers instead.
Fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust-analyzer/issues/10910
Assist: desugar doc-comment
My need for this arose due to wanting to do feature dependent documentation and therefor convert parts of my doc-comments to attributes.
Not sure about the pub-making of the other handlers functions, but I didn't think it made much sense to reimplement them.
With #13552 the depencency of on the command-group crate was introduced, which also
introduced a dependency on nix. That version of nix does not build on Haiku. This
change introduces a newer version of command-group, which also updates nix from
0.22.3 to 0.26.1, which is compatible on Haiku.
Remove hover inlay tooltips, replace them with location links
Turns out we re-implemented what clients can already figure out through the use of location-links. We might want lazy resolves tooltips later on still, but for now this simplifies things again.
remove recursive 'Display' implementations
closes#13920
`@lnicola` is this the solution you were looking for?
having explicitly unimplemented methods seems preferable to apparently implemented methods that can't be called
Rename `checkOnSave` settings to `check`
Now that flychecks can be triggered without saving the setting name doesn't make that much sense anymore. This PR renames it to just `check`, but keeps `checkOnSave` as the enabling setting.
Add action to expand a declarative macro once, inline. Fixes#13598
This commit adds a new r-a method, `expandMacroInline`, which expands the macro that's currently selected. See #13598 for the most applicable issue; though I suspect it'll resolve part of #5949 and make #11888 significantly easier).
The macro works like this:
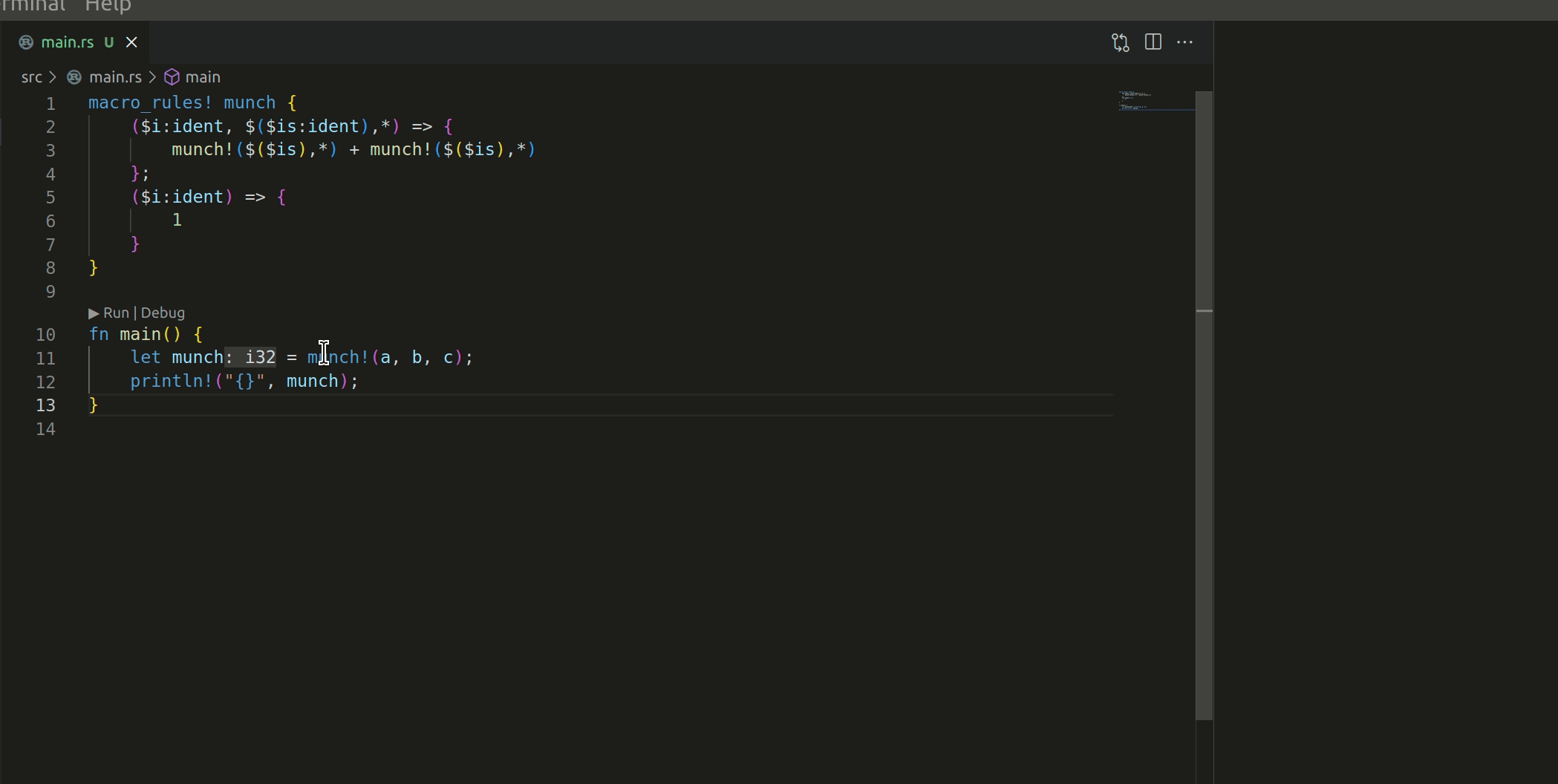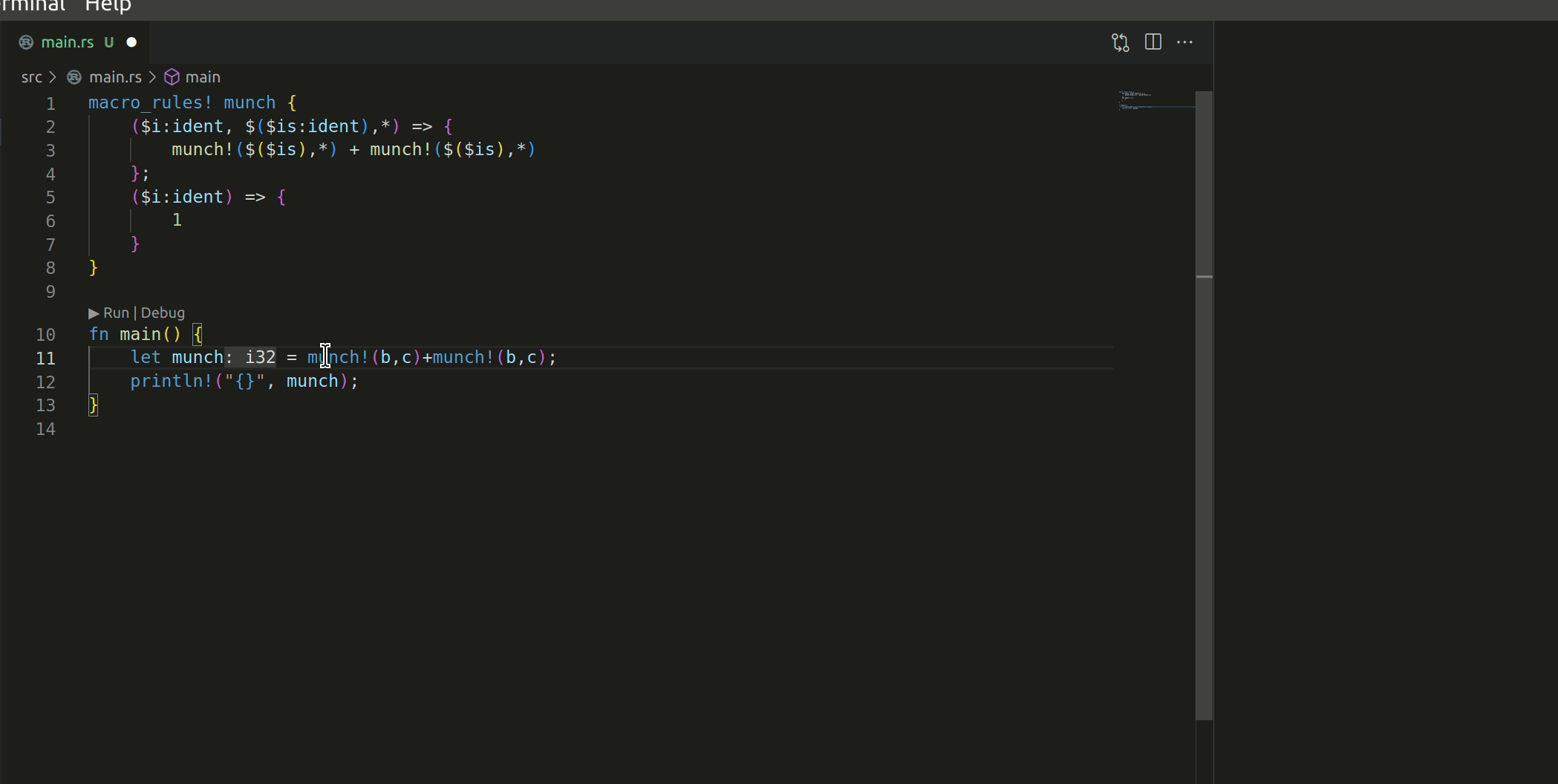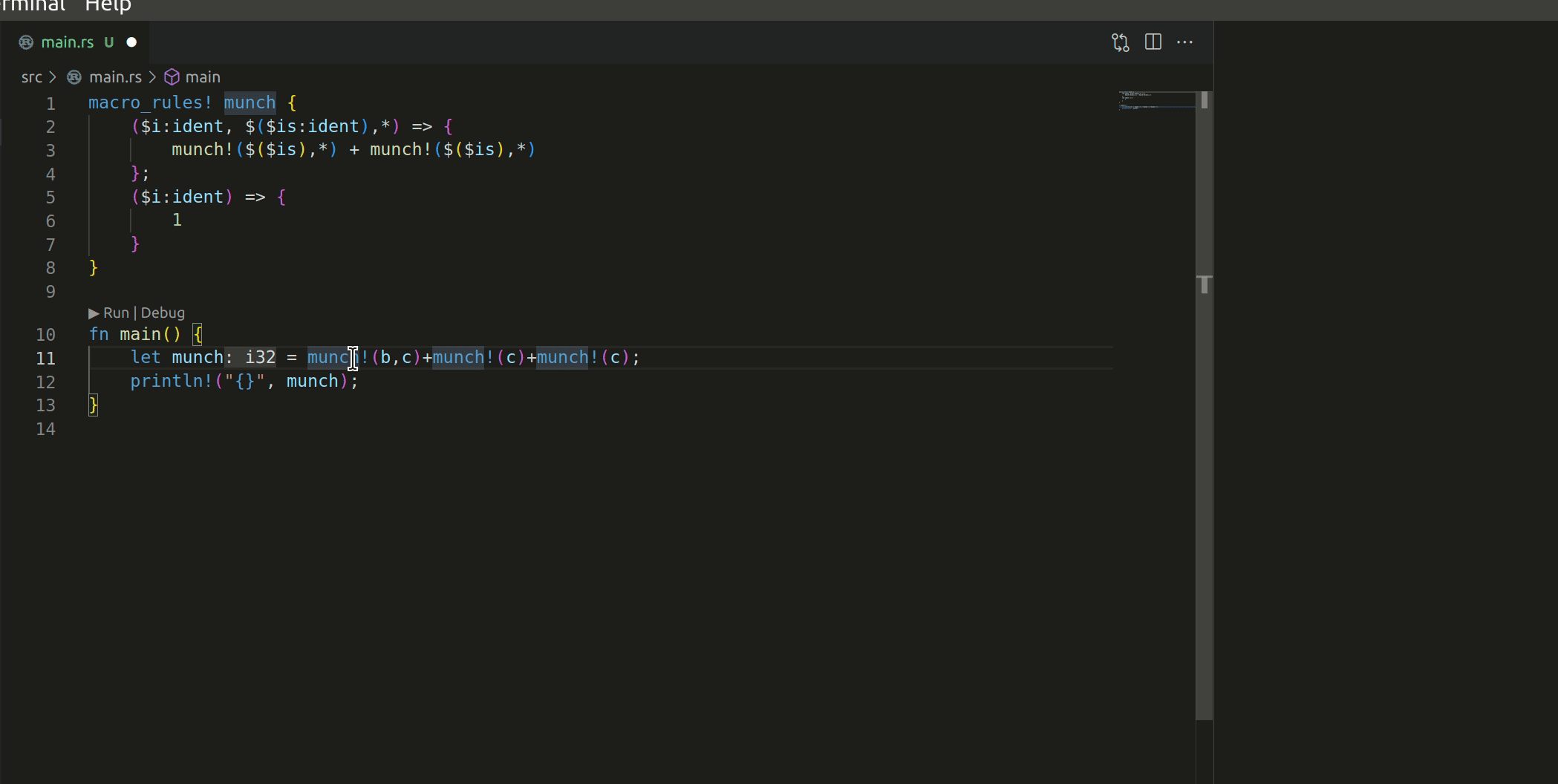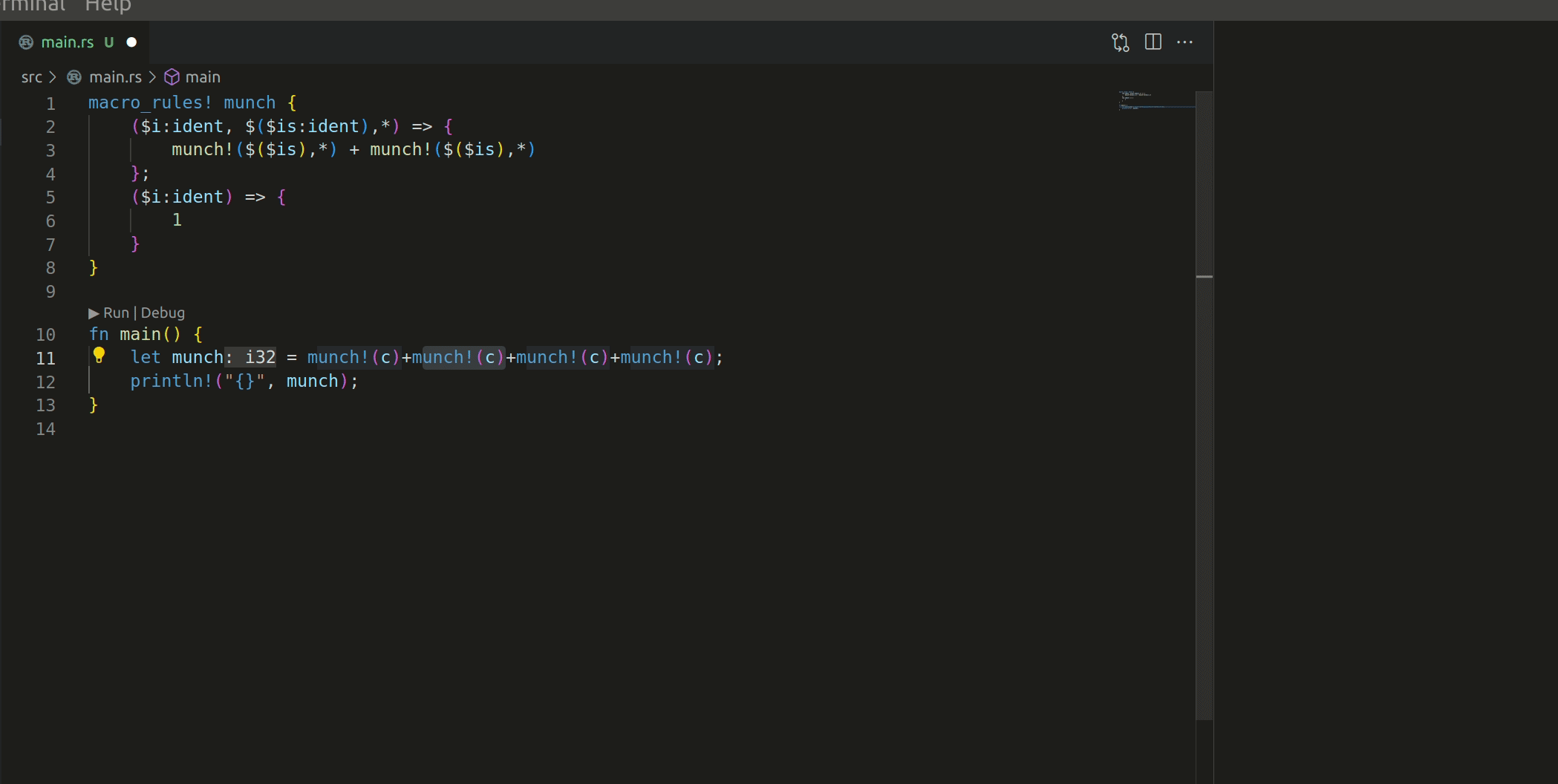
I have 2 questions before this PR can be merged:
1. **Should we rustfmt the output?** The advantage of doing this is neater code. The disadvantages are we'd have to format the whole expr/stmt/block (since there's no point just formatting one part, especially over multiple lines), and maybe it moves the code around more in weird ways. My suggestion here is to start off by not doing any formatting; and if it appears useful we can decide to do formatting in a later release.
2. **Is it worth solving the `$crate` hygiene issue now?** -- I think this PR is usable as of right now for some use-cases; but it is annoying that many common macros (i.e. `println!()`, `format!()`) can't be expanded further unless the user guesses the correct `$crate` value. The trouble with solving that issue is that I think it's complicated and imperfect. If we do solve it; we'd also need to either change the existing `expandMacro`/`expandMacroInline` commands; provide some option to allow/disallow `$crate` expanding; or come to some other compromise.
fix: generate async delegate methods
Fixes a bug where the generated async method doesn't await the result before returning it.
This is an example of what the output looked like:
```rust
struct Age<T>(T);
impl<T> Age<T> {
pub(crate) async fn age<J, 'a>(&'a mut self, ty: T, arg: J) -> T {
self.0
}
}
struct Person<T> {
age: Age<T>,
}
impl<T> Person<T> {
pub(crate) async fn age<J, 'a>(&'a mut self, ty: T, arg: J) -> T {
self.age.age(ty, arg) // .await is missing
}
}
```
The `.await` is missing, so the return type is `impl Future<Output = T>` instead of `T`
feat: add the ability to limit the number of threads launched by `main_loop`
## Motivation
`main_loop` defaults to launch as many threads as cpus in one machine. When developing on multi-core remote servers on multiple projects, this will lead to thousands of idle threads being created. This is very annoying when one wants check whether his program under developing is running correctly via `htop`.
<img width="756" alt="image" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/41831480/206656419-fa3f0dd2-e554-4f36-be1b-29d54739930c.png">
## Contribution
This patch introduce the configuration option `rust-analyzer.numThreads` to set the desired thread number used by the main thread pool.
This should have no effects on the performance as not all threads are actually used.
<img width="1325" alt="image" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/41831480/206656834-fe625c4c-b993-4771-8a82-7427c297fd41.png">
## Demonstration
The following is a snippet of `lunarvim` configuration using my own build.
```lua
vim.list_extend(lvim.lsp.automatic_configuration.skipped_servers, { "rust_analyzer" })
require("lvim.lsp.manager").setup("rust_analyzer", {
cmd = { "env", "RA_LOG=debug", "RA_LOG_FILE=/tmp/ra-test.log",
"/home/jlhu/Projects/rust-analyzer/target/debug/rust-analyzer",
},
init_options = {
numThreads = 4,
},
settings = {
cachePriming = {
numThreads = 8,
},
},
})
```
## Limitations
The `numThreads` can only be modified via `initializationOptions` in early initialisation because everything has to wait until the thread pool starts including the dynamic settings modification support.
The `numThreads` also does not reflect the end results of how many threads is actually created, because I have not yet tracked down everything that spawns threads.
add wrapping/checked/saturating assist
This addresses #13452
I'm not sure about the structure of the code. I'm not sure if it needs to be 3 separate assists, and if that means it needs to be in 3 separate files as well.
Most of the logic is in `util.rs`, which feels funny to me, but there seems to be a pattern of 1 assist per file, and this seems better than duplicating the logic.
Let me know if anything needs changes 😁
fix a bunch of clippy lints
fixes a bunch of clippy lints for fun and profit
i'm aware of this repo's position on clippy. The changes are split into separate commits so they can be reviewed separately
feat: Package Windows release artifacts as ZIP and add symbols file
Closes#13872Closes#7747
CC #10371
This allows us to ship a format that's easier to handle on Windows. As a bonus, we can also include the PDB, to get useful stack traces. Unfortunately, it adds a couple of dependencies to `xtask`, increasing the debug build times from 1.28 to 1.58 s (release from 1.60s to 2.20s) on my system.
Apply fallback before final obligation resolution
Fixes#13249Fixes#13518
We've been applying fallback to type variables independently even when there are some unresolved obligations that associate them. This PR applies fallback to unresolved scalar type variables before the final attempt of resolving obligations, which enables us to infer more.
Unlike rustc, which has separate storages for each kind of type variables, we currently don't have a way to retrieve only integer/float type variables without folding/visiting every single type we've inferred. I've repurposed `TypeVariableData` as bitflags that also hold the kind of the type variable it's referring to so that we can "reconstruct" scalar type variables from their indices.
This PR increases the number of ??ty for rust-analyzer repo not because we regress and fail to infer the existing code but because we fail to infer the new code. It seems we have problems inferring some functions bitflags produces.
Support multi-character punct tokens in MBE
Fixes#11497
In the context of MBE, consecutive puncts are parsed as multi-character punct tokens whenever possible. For example, `:::` is parsed as ``[Punct(`::`), Punct(`:`)]`` and shouldn't get matched to patterns like `: : :` or `: ::`.
We have implemented this behavior only for when we match puncts against `tt` fragments, but not when we match puncts literally. This PR extracts the multi-character punct handling procedure into a separate method and extends its support for literal matching.
For good measure, this PR adds support for `<-` token, which is still [considered as one token in rustc](e396186407/compiler/rustc_ast/src/token.rs (L249)) despite the placement syntax having been removed.
fix: merge multiple intersecting ranges
Fixes#13791
In `check_intersection_and_push()`, there may exist two ranges we should merge with the new one. We've been assuming there should be only one range that intersects, which lead to [this assertion](da15d92a32/crates/text-edit/src/lib.rs (L192)) to fail under specific circumstances.
Use `rustc_safe_intrinsic` attribute to check for intrinsic safety
Instead of maintaining a list that is poorly kept in sync we can just use the attribute.
This will make new RA versions unusable with old toolchains that don't have the attribute yet. Should we keep maintaining the list as a fallback or just don't care?
derive 'Hash'
clippy doesn't like that `PartialEq` is derived, and `Hash` is manually implemented. This PR resolves that by deriving the `Hash` implementation.
Moar linting: needless_borrow, let_unit_value, ...
* There are a few needless borrows that don't seem to be needed. I even did a quick assembly comparison and posted a q to stackoveflow on it. See [here](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/74910196/advantages-of-pass-by-ref-val-with-impl-intoiteratoritem-impl-asrefstr)
* removed several `let _ = ...` when they don't look necessary (even a few ones that were not suggested by clippy (?))
* some unneeded assignment+return - keep the code a bit leaner
* a few `writeln!` instead of `write!`, or even consolidate write!
* a nice optimization to use `ch.is_ascii_digit` instead of `ch.is_digit(10)`
fix: handle lifetime variables in `CallableSig` query
Fixes#13838
The problem is similar to #13223: we've been skipping non-empty binders, letting lifetime bound variables escape.
I ended up refactoring `hir_ty::callable_sig_from_fnonce()`. Like #13223, I chose to make use of `InferenceTable` which is capable of handling variables (I feel we should always use it when we solve trait-related stuff instead of manually building obligations/queries).
I couldn't make up a test that crashes without this patch (since the function I'm fixing is only used *outside* `hir-ty`, simple `hir-ty` test wouldn't cause crash), but at least I tested with my local build and made sure it doesn't crash with the code in the original issue. I'd appreciate any help to find a regression test.
* There are a few needless borrows that don't seem to be needed. I even did a quick assembly comparison and posted a q to stackoveflow on it. See [here](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/74910196/advantages-of-pass-by-ref-val-with-impl-intoiteratoritem-impl-asrefstr)
* removed several `let _ = ...` when they don't look necessary (even a few ones that were not suggested by clippy (?))
* there were a few `then(|| ctor{})` that clippy suggested to replace with `then_some(ctor{})` -- seems reasonable?
* some unneeded assignment+return - keep the code a bit leaner
* a few `writeln!` instead of `write!`, or even consolidate write!
* a nice optimization to use `ch.is_ascii_digit` instead of `ch.is_digit(10)`
This makes code more readale and concise,
moving all format arguments like `format!("{}", foo)`
into the more compact `format!("{foo}")` form.
The change was automatically created with, so there are far less change
of an accidental typo.
```
cargo clippy --fix -- -A clippy::all -W clippy::uninlined_format_args
```
Seems like these can be safely fixed. With one, I was particularly
surprised -- `Some(pats) => &**pats,` in body.rs?
```
cargo clippy --fix -- -A clippy::all -D clippy::explicit_auto_deref
```
I am not certain if this will improve performance,
but it seems having a .clone() without any need should be removed.
This was done with clippy, and manually reviewed:
```
cargo clippy --fix -- -A clippy::all -D clippy::redundant_clone
```
feat: Add an option to hide adjustment hints outside of `unsafe` blocks and functions
As the title suggests: this PR adds an option (namely `rust-analyzer.inlayHints.expressionAdjustmentHints.hideOutsideUnsafe`) that allows to hide adjustment hints outside of `unsafe` blocks and functions:
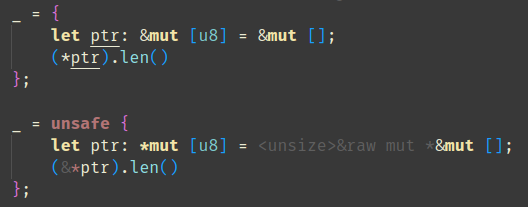
Requested by `@BoxyUwU` <3
fix: Correctly check for parentheses redundancy in `remove_parentheses` assist
This is quite a bunch of code and some hacks, but I _think_ this time it's correct.
I've added a lot of tests, most of which fail with the assist impl from #13733 :')
Complete enum variants without parens when snippets are disabled
This handles the portion of #13767 that bothered me, but I can try to work on the other parts we discussed if needed.
fix: resolve all inference vars in `InferenceResult::assoc_resolutions`
I think this fixes '#13773, ~but still haven't found repro. I'll try finding one so we can have a regression test~.
We should resolve every inference variable in `InferenceResult` after inference is done. We started recording `Substitution`s for each resolved associated items in #13725, but failed to do so which causes crash when analyzing source in IDE layer.
fix: make make_body respect comments in extract_function
Possible fix for #13621
### Points to help in review:
- Earlier we were only considering statements in a block expr and hence comments were being ignored, now we handle tokens hence making it aware of comments and then preserving them using `hacky_block_expr_with_comments`
Seems like I am not able to attach output video, github is glitching for it :(
fix: breaking snippets on typed incomplete suggestions
Possible fix for #7929
Fix the case where if a user types `&&42.o`, snippet completion was still applying &&Ok(42). Note this was fixed previously on `&&42.` but this still remained a problem for this case
Previous relevant PR: #13517
### Points to help in review:
- The main problem why everything broke on adding an extra `o` was, earlier `dot_receiver` was `42.` which was a `LITERAL` but now `42.o` becomes a `FIELD_EXPR`
- Till now `include_references` was just checking for parent of `LITERAL` and if it was a `REF_EXPR`, but now we consider `FIELD_EXPR` and traverse all of them, finally to reach `REF_EXPR`. If `REF_EXPR` is not found we just return the original `initial_element`
- We are constructing a new node during `include_references` because if we rely on `dot_receiver` solely we would get `&&42.o` to be replaced with, but we want `&&42` to be replaced with
### Output Video:
https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/49019259/205420166-efbdef78-5b3a-4aef-ab4b-d892dac056a0.mov
Hope everything I wrote makes sense 😅
Also interestingly previous PR's number was `13517` and this PR's number is `13715`, nicee
feat: allow unwrap block in let initializers
Possible fix for #13679
### Points to help in review:
- I just added a parent case for let statements and it seems everything else was in place already, so turned out to be a small fix
fix: add fallback case in generated `PartialEq` impl
Partially fixes#13727.
When generating `PartialEq` implementations for enums, the original code can already generate the following fallback case:
```rs
_ => std::mem::discriminant(self) == std::mem::discriminant(other),
```
However, it has been suppressed in the following example for no good reason:
```rs
enum Either<T, U> {
Left(T),
Right(U),
}
impl<T, U> PartialEq for Either<T, U> {
fn eq(&self, other: &Self) -> bool {
match (self, other) {
(Self::Left(l0), Self::Left(r0)) => l0 == r0,
(Self::Right(l0), Self::Right(r0)) => l0 == r0,
// _ => std::mem::discriminant(self) == std::mem::discriminant(other),
// ^ this completes the match arms!
}
}
}
```
This PR has removed that suppression logic.
~~Of course, the PR could have suppressed the fallback case generation for single-variant enums instead, but I believe that this case is quite rare and should be caught by `#[warn(unreachable_patterns)]` anyway.~~
After this fix, when the enum has >1 variants, the following fallback arm will be generated :
* `_ => false,` if we've already gone through every case where the variants of `self` and `other` match;
* The original one (as stated above) in other cases.
---
Note: The code example is still wrong after the fix due to incorrect trait bounds.
fix: normalize projection after discarding free `BoundVar`s in RPIT
Fixes#13307
When we lower the return type of a function, it may contain free `BoundVar`s in `OpaqueType`'s substitution, which would cause panic during canonicalization as part of projection normalization. Those `BoundVar`s are irrelevant in this context and will be discarded, and we should defer projection normalization until then.
fix: only shift `BoundVar`s that come from outside lowering context
Fixes#13734
There are some free functions `TyLoweringContext` methods call, which do not know anything about current binders in scope. We need to shift in the `BoundVar`s in substitutions that we get from them (#4952), but not those we get from `TyLoweringContext` methods.
Compute data layout of types
cc #4091
Things that aren't working:
* Closures
* Generators (so no support for `Future` I think)
* Opaque types
* Type alias and associated types which may need normalization
Things that show wrong result:
* ~Enums with explicit discriminant~
* SIMD types
* ~`NonZero*` and similar standard library items which control layout with special attributes~
At the user level, I didn't put much work, since I wasn't confident about what is the best way to present this information. Currently it shows size and align for ADTs, and size, align, offset for struct fields, in the hover, similar to clangd. I used it some days and I feel I liked it, but we may consider it too noisy and move it to an assist or command.
The old value was for the old chalk-engine solver, nowadays the newer chalk-recursive solver is used.
The new solver currently uses fuel a bit more quickly, so a higher value is needed.
Running analysis-stats showed that a value of 100 increases the amount of unknown types,
while for a value of 1000 it's staying mostly the same.
Add `move_const_to_impl` assist
Closes#13277
For the initial implementation, this assist:
- only applies to inherent impl. Much as we can *technically* provide this assist for default impl in trait definitions, it'd be complicated to get it right.
- may break code when the const's name collides with an item of a trait the self type implements.
Comments in the code explain those caveats in a bit more detail.
Fix the case where if a user types `&&42.o`, snippet completion
was still applying &&Ok(42). Note this was fixed previously
on `&&42.` but this still remained a problem for this case
Don't show runnable code lenses in libraries outside of the workspace
Addresses #13664. For now I'm just disabling runnable code lenses since the ones that display the number of references and implementations do work correctly with external code.
Also made a tiny TypeScript change to use the typed `sendNotification` overload.
fix: check tail expressions more precisely in `extract_function`
Fixes#13620
When extracting expressions with control flows into a function, we can avoid wrapping tail expressions in `Option` or `Result` when they are also tail expressions of the container we're extracting from (see #7840, #9773). This is controlled by `ContainerInfo::is_in_tail`, but we've been computing it by checking if the tail expression of the range to extract is contained in the container's syntactically last expression, which may be a block that contains both tail and non-tail expressions (e.g. in #13620, the range to be extracted is not a tail expression but we set the flag to true).
This PR tries to compute the flag as precise as possible by utilizing `for_each_tail_expr()` (and also moves the flag to `Function` struct as it's more of a property of the function to be extracted than of the container).
Mega-sync from `rust-lang/rust`
This essentially implements `@oli-obk's` suggestion here https://github.com/rust-lang/rust-analyzer/pull/13459#issuecomment-1297285607, with `@eddyb's` help.
This PR is equivalent to 14 syncs (back and forth) between `rust-lang/rust` and `rust-lang/rust-analyzer`.
Working from this list (from bottom to top):
```
(x) a2a1d9954⬆️ rust-analyzer
(x) 79923c382⬆️ rust-analyzer
(x) c60b1f641⬆️ rust-analyzer
(x) 8807fc4cc⬆️ rust-analyzer
(x) a99a48e78⬆️ rust-analyzer
(x) 4f55ebbd4⬆️ rust-analyzer
(x) f5fde4df4⬆️ rust-analyzer
(x) 459bbb422⬆️ rust-analyzer
(x) 65e1dc4d9⬆️ rust-analyzer
(x) 3e358a682⬆️ rust-analyzer
(x) 31519bb39⬆️ rust-analyzer
(x) 8231fee46⬆️ rust-analyzer
(x) 22c8c9c40⬆️ rust-analyzer
(x) 9d2cb42a4⬆️ rust-analyzer
```
(This listed was assembled by doing a `git subtree push`, which made a branch, and looking at the new commits in that branch, picking only those that were `⬆️ rust-analyzer` commits)
We used the following commands to simulate merges in both directions:
```shell
TO_MERGE=22c8c9c40 # taken from the list above, bottom to top
git merge --no-edit --no-ff $TO_MERGE
git merge --no-edit --no-ff $(git -C ../rust log --pretty=format:'%cN | %s | %ad => %P' | rg -m1 -F "$(git show --no-patch --pretty=format:%ad $TO_MERGE)" | tee /dev/stderr | rg '.* => \S+ (\S+)$' --replace '$1')
```
We encountered no merge conflicts that Git wasn't able to solve by doing it this way.
Here's what the commit graph looks like (as shown in the Git Lens VSCode extension):
<img width="1345" alt="image" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/7998310/203984523-7c1a690a-8224-416c-8015-ed6e49667066.png">
This PR closes#13459
## Does this unbreak `rust->ra` syncs?
Yes, here's how we tried:
In `rust-analyzer`:
* check out `subtree-fix` (this PR's branch)
* make a new branch off of it: `git checkout -b subtree-fix-merge-test`
* simulate this PR getting merged with `git merge master`
In `rust`:
* pull latest master
* make a new branch: `git checkout -b test-change`
* mess with rust-analyzer (I added a comment to `src/tools/rust-analyzer/Cargo.toml`)
* commit
* run `git subtree push -P src/tools/rust-analyzer ra-local final-sync` (this follows the [Clippy sync guide](https://doc.rust-lang.org/nightly/clippy/development/infrastructure/sync.html))
This created a `final-sync` branch in `rust-analyzer`.
In `rust-analyzer`:
* `git merge --no-ff final-sync` (this follows the [Clippy sync guide](https://doc.rust-lang.org/nightly/clippy/development/infrastructure/sync.html))
Now `git log` in `rust-analyzer` shows this:
```
commit 460128387e46ddfc2b95921b2d7f6e913a3d2b9f (HEAD -> subtree-fix-merge-test)
Merge: 0513fc02a 9ce6a734f
Author: Amos Wenger <amoswenger@gmail.com>
Date: Fri Nov 25 13:28:24 2022 +0100
Merge branch 'final-sync' into subtree-fix-merge-test
commit 0513fc02a08ea9de952983624bd0a00e98044b36
Merge: 38c98d1ff6918009fe
Author: Amos Wenger <amoswenger@gmail.com>
Date: Fri Nov 25 13:28:02 2022 +0100
Merge branch 'master' into subtree-fix-merge-test
commit 9ce6a734f37ef8e53689f1c6f427a9efafe846bd (final-sync)
Author: Amos Wenger <amoswenger@gmail.com>
Date: Fri Nov 25 13:26:26 2022 +0100
Mess with rust-analyzer just for fun
```
And `git diff 0513fc02a08ea9de952983624bd0a00e98044b36` shows this:
```patch
diff --git a/Cargo.toml b/Cargo.toml
index 286ef1e7d..c9e24cd19 100644
--- a/Cargo.toml
+++ b/Cargo.toml
`@@` -32,3 +32,5 `@@` debug = 0
# ungrammar = { path = "../ungrammar" }
# salsa = { path = "../salsa" }
+
+# lol, hi
```
## Does this unbreak `ra->rust` syncs?
Yes, here's how we tried.
From `rust`:
* `git checkout -b sync-from-ra`
* `git subtree pull -P src/tools/rust-analyzer ra-local subtree-fix-merge-test` (this is adapted from the [Clippy sync guide](https://doc.rust-lang.org/nightly/clippy/development/infrastructure/sync.html#performing-the-sync-from-clippy-to-rust-langrust), you would normally use `ra-upstream master` but we're simulating things here)
A commit editor pops up, there was no merge conflicts.
## How do we prevent this from happening again?
Like `@bjorn3` said in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust-analyzer/pull/13459#issuecomment-1293587848
> Whenever syncing from rust-analyzer -> rust you have to immediately sync the merge commit from rust -> rust-analyzer to prevent merge conflicts in the future.
But if we get it wrong again, at least now we have a not-so-painful way to fix it.
Improve goto declaration
Closes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust-analyzer/issues/13599
- goto decl now goes to assoc items of trait declarations over the items of trait implementations
- goto decl now goes to the field declaration (opposed to goto def which shows both the field decl and binding created/local being used)
- also adds back the goto definition fallback that seems to have been dropped at some point.
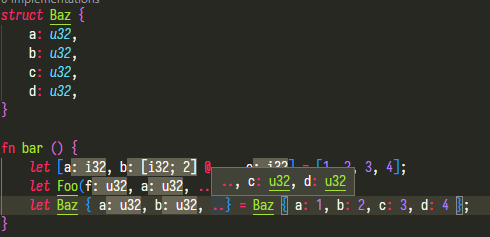
feat: adds hover hint to ".." in record pattern
Hovering on the "rest" pattern in struct destructuring,
```rust
struct Baz {
a: u32,
b: u32,
c: u32,
d: u32
}
let Baz { a, b, ..$0} = Baz { a: 1, b: 2, c: 3, d: 4 };
```
shows:
```
.., c: u32, d: u32
```
Currently only works with struct patterns.