# Description
@Yethal discovered that `FooterMode::Auto` in the config as
`$env.config.footer_mode = auto` did not work. This PR attempts to fix
that problem by implementing the auto algorithm that was already
supposed to work.
# User-Facing Changes
<!-- List of all changes that impact the user experience here. This
helps us keep track of breaking changes. -->
# Tests + Formatting
<!--
Don't forget to add tests that cover your changes.
Make sure you've run and fixed any issues with these commands:
- `cargo fmt --all -- --check` to check standard code formatting (`cargo
fmt --all` applies these changes)
- `cargo clippy --workspace -- -D warnings -D clippy::unwrap_used` to
check that you're using the standard code style
- `cargo test --workspace` to check that all tests pass (on Windows make
sure to [enable developer
mode](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/apps/get-started/developer-mode-features-and-debugging))
- `cargo run -- -c "use toolkit.nu; toolkit test stdlib"` to run the
tests for the standard library
> **Note**
> from `nushell` you can also use the `toolkit` as follows
> ```bash
> use toolkit.nu # or use an `env_change` hook to activate it
automatically
> toolkit check pr
> ```
-->
# After Submitting
<!-- If your PR had any user-facing changes, update [the
documentation](https://github.com/nushell/nushell.github.io) after the
PR is merged, if necessary. This will help us keep the docs up to date.
-->
# Description
This PR standardizes updates to the config through a new
`UpdateFromValue` trait. For now, this trait is private in case we need
to make changes to it.
Note that this PR adds some additional `ShellError` cases to create
standard error messages for config errors. A follow-up PR will move
usages of the old error cases to these new ones. This PR also uses
`Type::custom` in lots of places (e.g., for string enums). Not sure if
this is something we want to encourage.
# User-Facing Changes
Should be none.
# Description
Currently there is a bit of chaos regarding construction of history file
paths. Various pieces of code across a number of crates reimplement the
same/similar logic:
- There is `get_history_path`, but it requires a directory parameter (it
really just joins it with a file name).
- Some places use a const for the directory parameter, others use a
string literal - in all cases the value seems to be `"nushell"`.
- Some places assume the `"nushell"` value, other plumb it down from
close to the top of the call stack.
- Some places use a constant for history file names while others assume
it.
This PR tries to make it so that the history/config path format is
defined in a single places and so dependencies on it are easier to
follow:
- It removes `get_history_path` and adds a `file_path` method to
`HistoryConfig` instead (an extra motivation being, this is a convenient
place that can be used from all creates that need a history file path)
- Adds a `nu_config_dir` function that returns the nushell configuration
directory.
- Updates existing code to rely on the above, effectively removing
duplicate uses of `"nushell"` and `NUSHELL_FOLDER` and assumptions about
file names associated with different history formats
# User-Facing Changes
None
# Description
Closes#12535
Implements sort-by functionality of #8322
Fixes sort-by part of #8667
This PR does two main things: add a new cell path and closure parameter
to `sort-by`, and attempt to make Nushell's sorting behavior
well-defined.
## `sort-by` features
The `columns` parameter is replaced with a `comparator` parameter, which
can be a cell path or a closure. Examples are from docs PR.
1. Cell paths
The basic interactive usage of `sort-by` is the same. For example, `ls |
sort-by modified` still works the same as before. It is not quite a
drop-in replacement, see [behavior changes](#behavior-changes).
Here's an example of how the cell path comparator might be useful:
```nu
> let cities = [
{name: 'New York', info: { established: 1624, population: 18_819_000 } }
{name: 'Kyoto', info: { established: 794, population: 37_468_000 } }
{name: 'São Paulo', info: { established: 1554, population: 21_650_000 }
}
]
> $cities | sort-by info.established
╭───┬───────────┬────────────────────────────╮
│ # │ name │ info │
├───┼───────────┼────────────────────────────┤
│ 0 │ Kyoto │ ╭─────────────┬──────────╮ │
│ │ │ │ established │ 794 │ │
│ │ │ │ population │ 37468000 │ │
│ │ │ ╰─────────────┴──────────╯ │
│ 1 │ São Paulo │ ╭─────────────┬──────────╮ │
│ │ │ │ established │ 1554 │ │
│ │ │ │ population │ 21650000 │ │
│ │ │ ╰─────────────┴──────────╯ │
│ 2 │ New York │ ╭─────────────┬──────────╮ │
│ │ │ │ established │ 1624 │ │
│ │ │ │ population │ 18819000 │ │
│ │ │ ╰─────────────┴──────────╯ │
╰───┴───────────┴────────────────────────────╯
```
2. Key closures
You can supply a closure which will transform each value into a sorting
key (without changing the underlying data). Here's an example of a key
closure, where we want to sort a list of assignments by their average
grade:
```nu
> let assignments = [
{name: 'Homework 1', grades: [97 89 86 92 89] }
{name: 'Homework 2', grades: [91 100 60 82 91] }
{name: 'Exam 1', grades: [78 88 78 53 90] }
{name: 'Project', grades: [92 81 82 84 83] }
]
> $assignments | sort-by { get grades | math avg }
╭───┬────────────┬───────────────────────╮
│ # │ name │ grades │
├───┼────────────┼───────────────────────┤
│ 0 │ Exam 1 │ [78, 88, 78, 53, 90] │
│ 1 │ Project │ [92, 81, 82, 84, 83] │
│ 2 │ Homework 2 │ [91, 100, 60, 82, 91] │
│ 3 │ Homework 1 │ [97, 89, 86, 92, 89] │
╰───┴────────────┴───────────────────────╯
```
3. Custom sort closure
The `--custom`, or `-c`, flag will tell `sort-by` to interpret closures
as custom sort closures. A custom sort closure has two parameters, and
returns a boolean. The closure should return `true` if the first
parameter comes _before_ the second parameter in the sort order.
For a simple example, we could rewrite a cell path sort as a custom sort
(see
[here](https://github.com/nushell/nushell.github.io/pull/1568/files#diff-a7a233e66a361d8665caf3887eb71d4288000001f401670c72b95cc23a948e86R231)
for a more complex example):
```nu
> ls | sort-by -c {|a, b| $a.size < $b.size }
╭───┬─────────────────────┬──────┬──────────┬────────────────╮
│ # │ name │ type │ size │ modified │
├───┼─────────────────────┼──────┼──────────┼────────────────┤
│ 0 │ my-secret-plans.txt │ file │ 100 B │ 10 minutes ago │
│ 1 │ shopping_list.txt │ file │ 100 B │ 2 months ago │
│ 2 │ myscript.nu │ file │ 1.1 KiB │ 2 weeks ago │
│ 3 │ bigfile.img │ file │ 10.0 MiB │ 3 weeks ago │
╰───┴─────────────────────┴──────┴──────────┴────────────────╯
```
## Making sort more consistent
I think it's important for something as essential as `sort` to have
well-defined semantics. This PR contains some changes to try to make the
behavior of `sort` and `sort-by` consistent. In addition, after working
with the internals of sorting code, I have a much deeper understanding
of all of the edge cases. Here is my attempt to try to better define
some of the semantics of sorting (if you are just interested in changes,
skip to "User-Facing changes")
- `sort`, `sort -v`, and `sort-by` now all work the same. Each
individual sort implementation has been refactored into two functions in
`sort_utils.rs`: `sort`, and `sort_by`. These can also be used in other
parts of Nushell where values need to be sorted.
- `sort` and `sort-by` used to handle `-i` and `-n` differently.
- `sort -n` would consider all values which can't be coerced into a
string to be equal
- `sort-by -i` and `sort-by -n` would only work if all values were
strings
- In this PR, insensitive sort only affects comparison between strings,
and natural sort only applies to numbers and strings (see below).
- (not a change) Before and after this PR, `sort` and `sort-by` support
sorting mixed types. There was a lot of discussion about potentially
making `sort` and `sort-by` only work on lists of homogeneous types, but
the general consensus was that `sort` should not error just because its
input contains incompatible types.
- In order to try to make working with data containing `null` values
easier, I changed the PartialOrd order to sort `Nothing` values to the
end of a list, regardless of what other types the list contains. Before,
`null` would be sorted before `Binary`, `CellPath`, and `Custom` values.
- (not a change) When sorted, lists of mixed types will contain sorted
values of each type in order, for the most part
- (not a change) For example, `[0x[1] (date now) "a" ("yesterday" | into
datetime) "b" 0x[0]]` will be sorted as `["a", "b", a day ago, now, [0],
[1]]`, where sorted strings appear first, then sorted datetimes, etc.
- (not a change) The exception to this is `Int`s and `Float`s, which
will intermix, `Strings` and `Glob`s, which will intermix, and `None` as
described above. Additionally, natural sort will intermix strings with
ints and floats (see below).
- Natural sort no longer coerce all inputs to strings.
- I did originally make natural only apply to strings, but @fdncred
pointed out that the previous behavior also allowed you to sort numeric
strings with numbers. This seems like a useful feature if we are trying
to support sorting with mixed types, so I settled on coercing only
numbers (int, float). This can be reverted if people don't like it.
- Here is an example of this behavior in action, which is the same
before and after this PR:
```nushell
$ [1 "4" 3 "2"] | sort --natural
╭───┬───╮
│ 0 │ 1 │
│ 1 │ 2 │
│ 2 │ 3 │
│ 3 │ 4 │
╰───┴───╯
```
# User-Facing Changes
## New features
- Replaces the `columns` string parameter of `sort-by` with a cell path
or a closure.
- The cell path parameter works exactly as you would expect
- By default, the `closure` parameter acts as a "key sort"; that is,
each element is transformed by the closure into a sorting key
- With the `--custom` (`-c`) parameter, you can define a comparison
function for completely custom sorting order.
## Behavior changes
<details>
<summary><code>sort -v</code> does not coerce record values to
strings</summary>
This was a bit of a surprising behavior, and is now unified with the
behavior of `sort` and `sort-by`. Here's an example where you can
observe the values being implicitly coerced into strings for sorting, as
they are sorted like strings rather than numbers:
Old behavior:
```nushell
$ {foo: 9 bar: 10} | sort -v
╭─────┬────╮
│ bar │ 10 │
│ foo │ 9 │
╰─────┴────╯
```
New behavior:
```nushell
$ {foo: 9 bar: 10} | sort -v
╭─────┬────╮
│ foo │ 9 │
│ bar │ 10 │
╰─────┴────╯
```
</details>
<details>
<summary>Changed <code>sort-by</code> parameters from
<code>string</code> to <code>cell-path</code> or <code>closure</code>.
Typical interactive usage is the same as before, but if passing a
variable to <code>sort-by</code> it must be a cell path (or closure),
not a string</summary>
Old behavior:
```nushell
$ let sort = "modified"
$ ls | sort-by $sort
╭───┬──────┬──────┬──────┬────────────────╮
│ # │ name │ type │ size │ modified │
├───┼──────┼──────┼──────┼────────────────┤
│ 0 │ foo │ file │ 0 B │ 10 hours ago │
│ 1 │ bar │ file │ 0 B │ 35 seconds ago │
╰───┴──────┴──────┴──────┴────────────────╯
```
New behavior:
```nushell
$ let sort = "modified"
$ ls | sort-by $sort
Error: nu:🐚:type_mismatch
× Type mismatch.
╭─[entry #10:1:14]
1 │ ls | sort-by $sort
· ──┬──
· ╰── Cannot sort using a value which is not a cell path or closure
╰────
$ let sort = $."modified"
$ ls | sort-by $sort
╭───┬──────┬──────┬──────┬───────────────╮
│ # │ name │ type │ size │ modified │
├───┼──────┼──────┼──────┼───────────────┤
│ 0 │ foo │ file │ 0 B │ 10 hours ago │
│ 1 │ bar │ file │ 0 B │ 2 minutes ago │
╰───┴──────┴──────┴──────┴───────────────╯
```
</details>
<details>
<summary>Insensitve and natural sorting behavior reworked</summary>
Previously, the `-i` and `-n` worked differently for `sort` and
`sort-by` (see "Making sort more consistent"). Here are examples of how
these options result in different sorts now:
1. `sort -n`
- Old behavior (types other than numbers, strings, dates, and binary
sorted incorrectly)
```nushell
$ [2sec 1sec] | sort -n
╭───┬──────╮
│ 0 │ 2sec │
│ 1 │ 1sec │
╰───┴──────╯
```
- New behavior
```nushell
$ [2sec 1sec] | sort -n
╭───┬──────╮
│ 0 │ 1sec │
│ 1 │ 2sec │
╰───┴──────╯
```
2. `sort-by -i`
- Old behavior (uppercase words appear before lowercase words as they
would in a typical sort, indicating this is not actually an insensitive
sort)
```nushell
$ ["BAR" "bar" "foo" 2 "FOO" 1] | wrap a | sort-by -i a
╭───┬─────╮
│ # │ a │
├───┼─────┤
│ 0 │ 1 │
│ 1 │ 2 │
│ 2 │ BAR │
│ 3 │ FOO │
│ 4 │ bar │
│ 5 │ foo │
╰───┴─────╯
```
- New behavior (strings are sorted stably, indicating this is an
insensitive sort)
```nushell
$ ["BAR" "bar" "foo" 2 "FOO" 1] | wrap a | sort-by -i a
╭───┬─────╮
│ # │ a │
├───┼─────┤
│ 0 │ 1 │
│ 1 │ 2 │
│ 2 │ BAR │
│ 3 │ bar │
│ 4 │ foo │
│ 5 │ FOO │
╰───┴─────╯
```
3. `sort-by -n`
- Old behavior (natural sort does not work when data contains non-string
values)
```nushell
$ ["10" 8 "9"] | wrap a | sort-by -n a
╭───┬────╮
│ # │ a │
├───┼────┤
│ 0 │ 8 │
│ 1 │ 10 │
│ 2 │ 9 │
╰───┴────╯
```
- New behavior
```nushell
$ ["10" 8 "9"] | wrap a | sort-by -n a
╭───┬────╮
│ # │ a │
├───┼────┤
│ 0 │ 8 │
│ 1 │ 9 │
│ 2 │ 10 │
╰───┴────╯
```
</details>
<details>
<summary>
Sorting a list of non-record values with a non-existent column/path now
errors instead of sorting the values directly (<code>sort</code> should
be used for this, not <code>sort-by</code>)
</summary>
Old behavior:
```nushell
$ [2 1] | sort-by foo
╭───┬───╮
│ 0 │ 1 │
│ 1 │ 2 │
╰───┴───╯
```
New behavior:
```nushell
$ [2 1] | sort-by foo
Error: nu:🐚:incompatible_path_access
× Data cannot be accessed with a cell path
╭─[entry #29:1:17]
1 │ [2 1] | sort-by foo
· ─┬─
· ╰── int doesn't support cell paths
╰────
```
</details>
<details>
<summary><code>sort</code> and <code>sort-by</code> output
<code>List</code> instead of <code>ListStream</code> </summary>
This isn't a meaningful change (unless I misunderstand the purpose of
ListStream), since `sort` and `sort-by` both need to collect in order to
do the sorting anyway, but is user observable.
Old behavior:
```nushell
$ ls | sort | describe -d
╭──────────┬───────────────────╮
│ type │ stream │
│ origin │ nushell │
│ subtype │ {record 3 fields} │
│ metadata │ {record 1 field} │
╰──────────┴───────────────────╯
```
```nushell
$ ls | sort-by name | describe -d
╭──────────┬───────────────────╮
│ type │ stream │
│ origin │ nushell │
│ subtype │ {record 3 fields} │
│ metadata │ {record 1 field} │
╰──────────┴───────────────────╯
```
New behavior:
```nushell
ls | sort | describe -d
╭────────┬─────────────────╮
│ type │ list │
│ length │ 22 │
│ values │ [table 22 rows] │
╰────────┴─────────────────╯
```
```nushell
$ ls | sort-by name | describe -d
╭────────┬─────────────────╮
│ type │ list │
│ length │ 22 │
│ values │ [table 22 rows] │
╰────────┴─────────────────╯
```
</details>
- `sort` now errors when nothing is piped in (`sort-by` already did
this)
# Tests + Formatting
I added lots of unit tests on the new sort implementation to enforce new
sort behaviors and prevent regressions.
# After Submitting
See [docs PR](https://github.com/nushell/nushell.github.io/pull/1568),
which is ~2/3 finished.
---------
Co-authored-by: NotTheDr01ds <32344964+NotTheDr01ds@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Ian Manske <ian.manske@pm.me>
# Description
Fixes#14000 by once again calling `set_current_dir()`, but doing so
with the `cwd` from the current state, rather than the (previously
removed) argument to `merge_env()`.
# User-Facing Changes
Bug fix
# Tests + Formatting
If this looks good, I'll look at adding a test case for it.
- 🟢 `toolkit fmt`
- 🟢 `toolkit clippy`
- 🟢 `toolkit test`
- 🟢 `toolkit test stdlib`
# After Submitting
N/A
Updated summary for commit
[612e0e2](612e0e2160)
- While folks are welcome to read through the entire comments, the core
information is summarized here.
# Description
This PR drastically improves startup times of Nushell by only parsing a
single submodule of the Standard Library that provides the `banner` and
`pwd` commands. All other Standard Library commands and submodules are
parsed when imported by the user. This cuts startup times by more than
60%.
At the moment, we have stopped adding to `std-lib` because every
addition adds a small amount to the Nushell startup time.
With this change, we should once again be able to allow new
functionality to be added to the Standard Library without it impacting
`nu` startup times.
# User-Facing Changes
* Nushell now starts about 60% faster
* Breaking change: The `dirs` (Shells) aliases will return a warning
message that it will not be auto-loaded in the following release, along
with instructions on how to restore it (and disable the message)
* The `use std <submodule> *` syntax is available for convenience, but
should be avoided in scripts as it parses the entire `std` module and
all other submodules and places it in scope. The correct syntax to
*just* load a submodule is `use std/<submodule> *` (asterisk optional).
The slash is important. This will be documented.
* `use std *` can be used for convenience to load all of the library but
still incurs the full loading-time.
* `std/dirs`: Semi-breaking change. The `dirs` command replaces the
`show` command. This is more in line with the directory-stack
functionality found in other shells. Existing users will not be impacted
by this as the alias (`shells`) remains the same.
* Breaking-change: Technically a breaking change, but probably only
impacts maintainers of `std`. The virtual path for the standard library
has changed. It could previously be imported using its virtual path (and
technically, this would have been the correct way to do it):
```nu
use NU_STDLIB_VIRTUAL_DIR/std
```
The path is now simply `std/`:
```nu
use std
```
All submodules have moved accordingly.
# Timings
Comparisons below were made:
* In a temporary, clean config directory using `$env.XDG_CONFIG_HOME =
(mktemp -d)`.
* `nu` was run with a release build
* `nu` was run one time to generate the default `config.nu` (etc.) files
- Otherwise timings would include the user-prompt
* The shell was exited and then restarted several times to get timing
samples
(Note: Old timings based on 0.97 rather than 0.98, but in the range of
being accurate)
| Scenario | `$nu.startup-time` |
| --- | --- |
| 0.97.2
([aaaab8e](aaaab8e070))
Without this PR | 23ms - 24ms |
| This PR with deprecated commands | 9ms - <11ms |
| This PR after deprecated commands are removed in following release |
8ms - <10ms |
| Final PR (remove deprecated), using `--no-std-lib` | 6.1ms to 6.4ms |
| Final PR (remove deprecated), using `--no-config-file` | 3.1ms - 3.6ms
|
| Final PR (remove deprecated), using `--no-config-file --no-std-lib` |
1ms - 1.5ms |
*These last two timings point to the opportunity for further
optimization (see comment in thread below (will link once I write it).*
# Implementation details for future maintenance
* `use std banner` is a ridiculously deceptive call. That call parses
and imports *all* of `std` into scope. Simply replacing it with `use
std/core *` is essentially what saves ~14-15ms. This *only* imports the
submodule with the `banner` and `pwd` commands.
* From the code-comments, the reason that `NU_STDLIB_VIRTUAL_DIR` was
used as a prefix was so that there wouldn't be an issue if a user had a
`./std/mod.nu` in the current directory. This does **not** appear to be
an issue. After removing the prefix, I tested with both a relative
module as well as one in the `$env.NU_LIB_DIRS` path, and in all cases
the *internal* `std` still took precedence.
* By removing the prefix, users can now `use std` (and variants) without
requiring that it already be parsed and in scope.
* In the next release, we'll stop autoloading the `dirs` (shells)
functionality. While this only costs an additional 1-1.5ms, I think it's
better moved to the `config.nu` where the user can optionally remove it.
The main reason is its use of aliases (which have also caused issues) -
The `n`, `p`, and `g` short-commands are valuable real-estate, and users
may want to map these to something else.
For this release, there's an `deprecated_dirs` module that is still
autoloaded. As with the top-level commands, use of these will give a
deprecation warning with instructions on how to handle going forward.
To help with this, moved the aliases to their own submodule inside the
`dirs` module.
* Also sneaks in a small change where the top-level `dirs` command is
now the replacement for `dirs show`
* Fixed a double-import of `assert` in `dirs.nu`
* The `show_banner` step is replaced with simply `banner` rather than
re-importing it.
* A `virtual_path` may now be referenced with either a forward-slash or
a backward-slash on Windows. This allows `use std/<submodule>` to work
on all platforms.
# Performance side-notes:
* Future parsing and/or IR improvements should improve performance even
further.
* While the existing load time penalty of `std-lib` was not noticeable
on many systems, Nushell runs on a wide-variety of hardware and OS
platforms. Slower platforms will naturally see a bigger jump in
performance here. For users starting multiple Nushell sessions
frequently (e.g., `tmux`, Zellij, `screen`, et. al.) it is recommended
to keep total startup time (including user configuration) under ~250ms.
# Tests + Formatting
* All tests are green
* Updated tests:
- Removed the test that confirmed that `std` was loaded (since we
don't).
- Removed the `shells` test since it is not autoloaded. Main `dirs.nu`
functionality is tested through `stdlib-test`.
- Many tests assumed that the library was fully loaded, because it was
(even though we didn't intend for it to be). Fixed those tests.
- Tests now import only the necessary submodules (e.g., `use
std/assert`, rather than `use std assert`)
- Some tests *thought* they were loading `std/log`, but were doing so
improperly. This was masked by the now-fixed "load-everything-into-scope
bug". Local CI would pass due the `$env.NU_LOG_<...>` variables being
inherited from the calling process, but would fail in the "clean" GitHub
CI environment. These tests have also been fixed.
* Added additional tests for the changes
# After Submitting
Will update the Standard Library doc page
# Description
Title says it all, changes `EngineState::get_env_var` to return a
`Option<&'a Value>` instead of an owned `Option<Value>`. This avoids
some unnecessary clones.
I also made a similar change to the `PluginExecutionContext` trait.
# Description
Fixes#13949 where `$env.LAST_EXIT_CODE` was not being set for internal
errors.
# Tests + Formatting
Cannot test due to limitations with the `nu_repl` test bin.
# Description
In the PR #13832 I used some newtypes for the old IDs. `SpanId` and
`RegId` already used newtypes, to streamline the code, I made them into
the same style as the other marker-based IDs.
Since `RegId` should be a bit smaller (it uses a `u32` instead of
`usize`) according to @devyn, I made the `Id` type generic with `usize`
as the default inner value.
The question still stands how `Display` should be implemented if even.
# User-Facing Changes
Users of the internal values of `RegId` or `SpanId` have breaking
changes but who outside nushell itself even uses these?
# After Submitting
The IDs will be streamlined and all type-safe.
# Description
In this PR I replaced most of the raw usize IDs with
[newtypes](https://doc.rust-lang.org/rust-by-example/generics/new_types.html).
Some other IDs already started using new types and in this PR I did not
want to touch them. To make the implementation less repetitive, I made
use of a generic `Id<T>` with marker structs. If this lands I would try
to move make other IDs also in this pattern.
Also at some places I needed to use `cast`, I'm not sure if the type was
incorrect and therefore casting not needed or if actually different ID
types intermingle sometimes.
# User-Facing Changes
Probably few, if you got a `DeclId` via a function and placed it later
again it will still work.
# Description
Old code was comparing remaining positional arguments with total number
of arguments, where it should've compared remaining positional with
with remaining arguments of any kind. This means that if a function was
given too few arguments, `calculate_end_span` would believe that it
actually had too many arguments, since after parsing the first few
arguments, the number of remaining arguments needed were fewer than the
*total* number of arguments, of which we had used several.
Fixes#9072
Fixes: https://github.com/nushell/nushell/issues/13930
Fixes: https://github.com/nushell/nushell/issues/12069
Fixes: https://github.com/nushell/nushell/issues/8385
Extracted from #10381
## Bonus
It also improves the error handling on missing positional arguments
before keywords (no longer crashing since #9851). Instead of just giving
the keyword to the parser for the missing positional, we give an
explicit error about a missing positional argument. I would like better
descriptions than "missing var_name" though, but I'm not sure if that's
available without
Old error
```
Error: nu::parser::parse_mismatch
× Parse mismatch during operation.
╭─[entry #1:1:1]
1 │ let = if foo
· ┬
· ╰── expected valid variable name
╰────
```
New error
```
Error: nu::parser::missing_positional
× Missing required positional argument.
╭─[entry #18:1:1]
1 │ let = foo
· ┬
· ╰── missing var_name
╰────
help: Usage: let <var_name> = <initial_value>
```
# User-Facing Changes
The program `alias = = =` is no longer accepted by the parser
This PR sets the current working directory to the location of the
Nushell executable at startup, using `std::env::set_current_dir()`. This
is desirable because after PR
https://github.com/nushell/nushell/pull/12922, we no longer change our
current working directory even after `cd` is executed, and some OS might
lock the directory where Nushell started.
The location of the Nushell executable is chosen because it cannot be
removed while Nushell is running anyways, so we don't have to worry
about OS locking it.
This PR has the side effect that it breaks buggy command even harder.
I'll keep this PR as a draft until these commands are fixed, but it
might be helpful to pull this PR if you're working on fixing one of
those bugs.
---------
Co-authored-by: Devyn Cairns <devyn.cairns@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Darren Schroeder <343840+fdncred@users.noreply.github.com>
# Description
This PR updates the shell_integration defaults so that they work as
described in default_config.nu even when there is no config.nu file.
closes#13924
# User-Facing Changes
<!-- List of all changes that impact the user experience here. This
helps us keep track of breaking changes. -->
# Tests + Formatting
<!--
Don't forget to add tests that cover your changes.
Make sure you've run and fixed any issues with these commands:
- `cargo fmt --all -- --check` to check standard code formatting (`cargo
fmt --all` applies these changes)
- `cargo clippy --workspace -- -D warnings -D clippy::unwrap_used` to
check that you're using the standard code style
- `cargo test --workspace` to check that all tests pass (on Windows make
sure to [enable developer
mode](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/apps/get-started/developer-mode-features-and-debugging))
- `cargo run -- -c "use toolkit.nu; toolkit test stdlib"` to run the
tests for the standard library
> **Note**
> from `nushell` you can also use the `toolkit` as follows
> ```bash
> use toolkit.nu # or use an `env_change` hook to activate it
automatically
> toolkit check pr
> ```
-->
# After Submitting
<!-- If your PR had any user-facing changes, update [the
documentation](https://github.com/nushell/nushell.github.io) after the
PR is merged, if necessary. This will help us keep the docs up to date.
-->
# Description
Instead of handling a foreground process being stopped in any way, we
were simply ignoring SIGTSTP (which the terminal usually sends to the
foreground process group when Ctrl-Z is pressed), and propagating this
to our foreground children. This works for most processes, but it
generally fails for applications which put the terminal in raw mode[1]
and implement their own suspension mechanism (typically TUI apps like
helix[2], neovim[3], top[4] or amp[5]). In these cases, triggering
suspension within the app results in the terminal getting blocked, since
the application is waiting for a SIGCONT, while nushell is waiting for
it to exit.
Fix this by unblocking SIGTSTP for our foreground children (neovim,
helix and probably others send this to themselves while trying to
suspend), and displaying the following message whenever one of them gets
stopped:
nushell currently does not support background jobs
press any key to continue
Pressing any key will then send SIGCONT to the child's process group and
resume waiting.
This fix is probably going to be superseded by a proper background job
implementation (#247) at some point, but for now it's better than
completely blocking the terminal.
[1]
https://docs.rs/crossterm/latest/crossterm/terminal/index.html#raw-mode
[2] https://helix-editor.com/
[3] https://neovim.io/
[4] https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man1/top.1.html
[5] https://amp.rs/
- fixes#1038
- fixes#7335
- fixes#10335
# User-Facing Changes
While any foreground process is running, Ctrl-Z is no longer ignored.
Instead, the message described above is displayed, and nushell waits for
a key to be pressed.
# Tests + Formatting
<!--
Don't forget to add tests that cover your changes.
Make sure you've run and fixed any issues with these commands:
- `cargo fmt --all -- --check` to check standard code formatting (`cargo
fmt --all` applies these changes)
- `cargo clippy --workspace -- -D warnings -D clippy::unwrap_used` to
check that you're using the standard code style
- `cargo test --workspace` to check that all tests pass (on Windows make
sure to [enable developer
mode](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/apps/get-started/developer-mode-features-and-debugging))
- `cargo run -- -c "use toolkit.nu; toolkit test stdlib"` to run the
tests for the standard library
> **Note**
> from `nushell` you can also use the `toolkit` as follows
> ```bash
> use toolkit.nu # or use an `env_change` hook to activate it
automatically
> toolkit check pr
> ```
-->
# After Submitting
<!-- If your PR had any user-facing changes, update [the
documentation](https://github.com/nushell/nushell.github.io) after the
PR is merged, if necessary. This will help us keep the docs up to date.
-->
# Description
Partialy addresses #13868. `try` does not catch non-zero exit code
errors from the last command in a pipeline if the result is assigned to
a variable using `let` (or `mut`).
This was fixed by adding a new `OutDest::Value` case. This is used when
the pipeline is in a "value" position. I.e., it will be collected into a
value. This ended up replacing most of the usages of `OutDest::Capture`.
So, this PR also renames `OutDest::Capture` to `OutDest::PipeSeparate`
to better fit the few remaining use cases for it.
# User-Facing Changes
Bug fix.
# Tests + Formatting
Added two tests.
# Description
Similar to #13870 (thanks @WindSoilder), this PR adds a boolean which
determines whether to ignore any errors from an external command. This
is in order to fix#13876. I.e., `do -p` does not wait for externals to
complete before continuing.
# User-Facing Changes
Bug fix.
# Tests + Formatting
Added a test.
# Description
Makes IR the default evaluator, in preparation to remove the non-IR
evaluator in a future release.
# User-Facing Changes
* Remove `NU_USE_IR` option
* Add `NU_DISABLE_IR` option
* IR is enabled unless `NU_DISABLE_IR` is set
# After Submitting
- [ ] release notes
# Description
Fixes a bug in the IR for `try` to match that of the regular evaluator
(continuing from #13515):
```nushell
# without IR:
try { ^false } catch { 'caught' } # == 'caught'
# with IR:
try { ^false } catch { 'caught' } # error, non-zero exit code
```
In this PR, both now evaluate to `caught`. For the implementation, I had
to add another instruction, and feel free to suggest better
alternatives. In the future, it might be possible to get rid of this
extra instruction.
# User-Facing Changes
Bug fix, `try { ^false } catch { 'caught' }` now works in IR.
# Description
This PR makes it so that non-zero exit codes and termination by signal
are treated as a normal `ShellError`. Currently, these are silent
errors. That is, if an external command fails, then it's code block is
aborted, but the parent block can sometimes continue execution. E.g.,
see #8569 and this example:
```nushell
[1 2] | each { ^false }
```
Before this would give:
```
╭───┬──╮
│ 0 │ │
│ 1 │ │
╰───┴──╯
```
Now, this shows an error:
```
Error: nu:🐚:eval_block_with_input
× Eval block failed with pipeline input
╭─[entry #1:1:2]
1 │ [1 2] | each { ^false }
· ┬
· ╰── source value
╰────
Error: nu:🐚:non_zero_exit_code
× External command had a non-zero exit code
╭─[entry #1:1:17]
1 │ [1 2] | each { ^false }
· ──┬──
· ╰── exited with code 1
╰────
```
This PR fixes#12874, fixes#5960, fixes#10856, and fixes#5347. This
PR also partially addresses #10633 and #10624 (only the last command of
a pipeline is currently checked). It looks like #8569 is already fixed,
but this PR will make sure it is definitely fixed (fixes#8569).
# User-Facing Changes
- Non-zero exit codes and termination by signal now cause an error to be
thrown.
- The error record value passed to a `catch` block may now have an
`exit_code` column containing the integer exit code if the error was due
to an external command.
- Adds new config values, `display_errors.exit_code` and
`display_errors.termination_signal`, which determine whether an error
message should be printed in the respective error cases. For
non-interactive sessions, these are set to `true`, and for interactive
sessions `display_errors.exit_code` is false (via the default config).
# Tests
Added a few tests.
# After Submitting
- Update docs and book.
- Future work:
- Error if other external commands besides the last in a pipeline exit
with a non-zero exit code. Then, deprecate `do -c` since this will be
the default behavior everywhere.
- Add a better mechanism for exit codes and deprecate
`$env.LAST_EXIT_CODE` (it's buggy).
# Description
After merging #13788, I get an error message which says that
`use_grid_icons` is invalid.
I think it's good to report the specific error, and guide user to delete
it.
# Description
After looking at #13751 I noticed that the config setting
`use_grid_icons` seems out of place. So, I removed it from the config
and made it a parameter to the `grid` command.
# Description
This PR fixes#13732. However, I don't think it's a proper fix.
1. It doesn't really show what the problem is.
2. It kind of side-steps the error entirely.
I do think the change in span.rs may be valid because I don't think
span.end should ever be 0. In the example in 13732 the span end was
always 0 and so that made contains_span() return true, which seems like
a false positive.
The `checked_sub()` in ide.rs kind of just stops it from failing
outloud.
I'll leave it to smarter folks than me to land this if they think it's
worthy.
Discovered by @cptpiepmatz that #13749 broke the standalone check for
`nu-protocol`
Explicit use of the feature as workspace root also disables all features
for `serde`. Alternatively we could reconsider this there.
# Description
Cleans up and refactors the config code using the `IntoValue` macro.
Shoutout to @cptpiepmatz for making the macro!
# User-Facing Changes
Should be none.
# After Submitting
Somehow refactor the reverse transformation.
Closes#13687Closes#13686
# Description
Light refactoring of `send_request `in `client.rs`. In the end there are
more lines but now the logic is more concise and facilitates adding new
conditions in the future. Unit tests ran fine and I tested a few cases
manually.
Cool project btw, I'll be using nushell from now on.
# Description
This PR allows the helper attribute `nu_value(rename = "...")` to be
used on struct fields and enum variants. This allows renaming keys and
variants just like [`#[serde(rename =
"name")]`](https://serde.rs/field-attrs.html#rename). This has no
singular variants for `IntoValue` or `FromValue`, both need to use the
same (but I think this shouldn't be an issue for now).
# User-Facing Changes
Users of the derive macros `IntoValue` and `FromValue` may now use
`#[nu_value(rename = "...")]` to rename single fields, but no already
existing code will break.
# Description
This changes the behavior of `tee` to be more transparent when given a
value that isn't a list or range. Previously, anything that wasn't a
byte stream would converted to a list stream using the iterator
implementation, which led to some surprising results. Instead, now, if
the value is a string or binary, it will be treated the same way a byte
stream is, and the output of `tee` is a byte stream instead of the
original value. This is done so that we can synchronize with the other
thread on collect, and potentially capture any error produced by the
closure.
For values that can't be converted to streams, the closure is just run
with a clone of the value instead on another thread. Because we can't
wait for the other thread, there is no way to send an error back to the
original thread, so instead it's just written to stderr using
`report_error_new()`.
There are a couple of follow up edge cases I see where byte streams
aren't necessarily treated exactly the same way strings are, but this
should mostly be a good experience.
Fixes#13489.
# User-Facing Changes
Breaking change.
- `tee` now outputs and sends string/binary stream for string/binary
input.
- `tee` now outputs and sends the original value for any other input
other than lists/ranges.
# Tests + Formatting
Added for new behavior.
# After Submitting
- [ ] release notes: breaking change, command change
removing the `std` feature as well would drop some dependencies tied to
`rust_decimal` from the `Cargo.lock` but unclear to me what the actual
impact on compile times is.
We may want to consider dropping the `byte-unit` dependency altogether
as we have a significant fraction of our own logic to support the byte
units with 1024 and 1000 prefixes. Not sure which fraction is covered by
us or the dependency.
# Description
Implements `IntoValue` for `&str` and `DateTime` as well as other
nushell types like `Record` and `Closure`. Also allows `HashMap`s with
keys besides `String` to implement `IntoValue`.
# Description
`cargo` somewhat recently gained the capability to store `lints`
settings for the crate and workspace, that can override the defaults
from `rustc` and `clippy` lints. This means we can enforce some lints
without having to actively pass them to clippy via `cargo clippy -- -W
...`. So users just forking the repo have an easier time to follow
similar requirements like our CI.
## Limitation
An exception that remains is that those lints apply to both the primary
code base and the tests. Thus we can't include e.g. `unwrap_used`
without generating noise in the tests. Here the setup in the CI remains
the most helpful.
## Included lints
- Add `clippy::unchecked_duration_subtraction` (added by #12549)
# User-Facing Changes
Running `cargo clippy --workspace` should be closer to the CI. This has
benefits for editor configured runs of clippy and saves you from having
to use `toolkit` to be close to CI in more cases.
<!--
if this PR closes one or more issues, you can automatically link the PR
with
them by using one of the [*linking
keywords*](https://docs.github.com/en/issues/tracking-your-work-with-issues/linking-a-pull-request-to-an-issue#linking-a-pull-request-to-an-issue-using-a-keyword),
e.g.
- this PR should close #xxxx
- fixes #xxxx
you can also mention related issues, PRs or discussions!
-->
# Description
<!--
Thank you for improving Nushell. Please, check our [contributing
guide](../CONTRIBUTING.md) and talk to the core team before making major
changes.
Description of your pull request goes here. **Provide examples and/or
screenshots** if your changes affect the user experience.
-->
@sholderbach mentioned that I introduced `convert_case` as a dependency
while we already had `heck` for case conversion. So in this PR replaced
the use `convert_case` with `heck`. Mostly I rebuilt the `convert_case`
API with `heck` to work with it as I like the API of `convert_case` more
than `heck`.
# User-Facing Changes
<!-- List of all changes that impact the user experience here. This
helps us keep track of breaking changes. -->
Nothing changed, the use of `convert_case` wasn't exposed anywhere and
all case conversions are still available.
# Tests + Formatting
<!--
Don't forget to add tests that cover your changes.
Make sure you've run and fixed any issues with these commands:
- `cargo fmt --all -- --check` to check standard code formatting (`cargo
fmt --all` applies these changes)
- `cargo clippy --workspace -- -D warnings -D clippy::unwrap_used` to
check that you're using the standard code style
- `cargo test --workspace` to check that all tests pass (on Windows make
sure to [enable developer
mode](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/apps/get-started/developer-mode-features-and-debugging))
- `cargo run -- -c "use toolkit.nu; toolkit test stdlib"` to run the
tests for the standard library
> **Note**
> from `nushell` you can also use the `toolkit` as follows
> ```bash
> use toolkit.nu # or use an `env_change` hook to activate it
automatically
> toolkit check pr
> ```
-->
No new tests required but my tests in `test_derive` captured some errors
I made while developing this change, (hurray, tests work 🎉)
- 🟢 `toolkit fmt`
- 🟢 `toolkit clippy`
- 🟢 `toolkit test`
- 🟢 `toolkit test stdlib`
# After Submitting
<!-- If your PR had any user-facing changes, update [the
documentation](https://github.com/nushell/nushell.github.io) after the
PR is merged, if necessary. This will help us keep the docs up to date.
-->
# Description
Using derived `IntoValue` and `FromValue` implementations on structs
with named fields currently produce `Value::Record`s where each key is
the key of the Rust struct. For records like the `$nu` constant, that
won't work as this record uses `kebab-case` for it's keys. To accomodate
this, I upgraded the `#[nu_value(rename_all = "...")]` helper attribute
to also work on structs with named fields which will rename the keys via
the same case conversion as the enums already have.
# User-Facing Changes
Users of these macros may choose different key styles for their in
`Value` representation.
# Tests + Formatting
I added the same test suite as enums already have and updated the traits
documentation with more examples that also pass the doc test.
# After Submitting
I played around with the `$nu` constant but got stuck at the point that
these keys are kebab-cased, with this, I can play around more with it.
# Description
<!--
Thank you for improving Nushell. Please, check our [contributing
guide](../CONTRIBUTING.md) and talk to the core team before making major
changes.
Description of your pull request goes here. **Provide examples and/or
screenshots** if your changes affect the user experience.
-->
Currently the parser and the documentation generation use the signature
of the command, which means that it doesn't pick up on the changed name
of the `main` block, and therefore shows the name of the command as
"main" and doesn't find the subcommands. This PR changes the
aforementioned places to use the block signature to fix these issues.
This closes#13397. Incidentally it also causes input/output types to be
shown in the help, which is kinda pointless for scripts since they don't
operate on structured data but maybe not worth the effort to remove.
# User-Facing Changes
<!-- List of all changes that impact the user experience here. This
helps us keep track of breaking changes. -->
```
# example.nu
export def main [] { help main }
export def 'main sub' [] { print 'sub' }
```
Before:
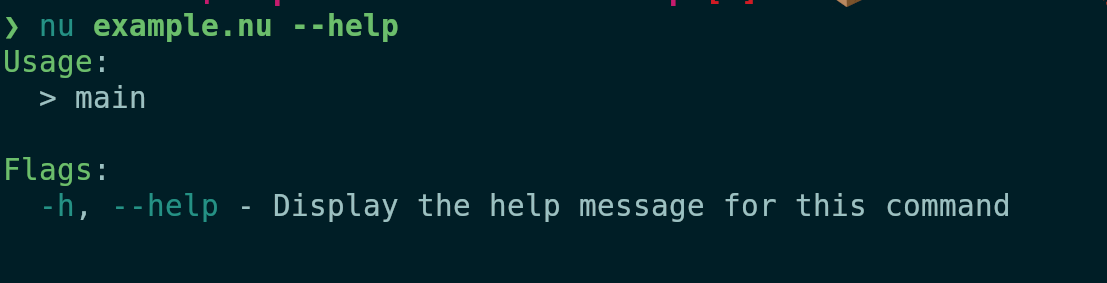

After:
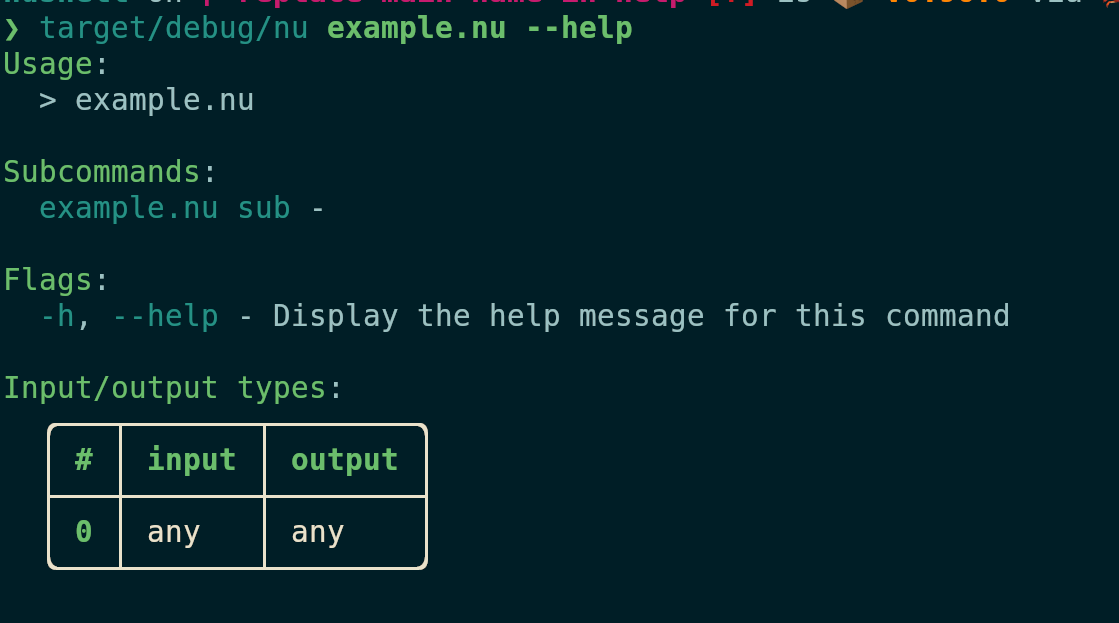
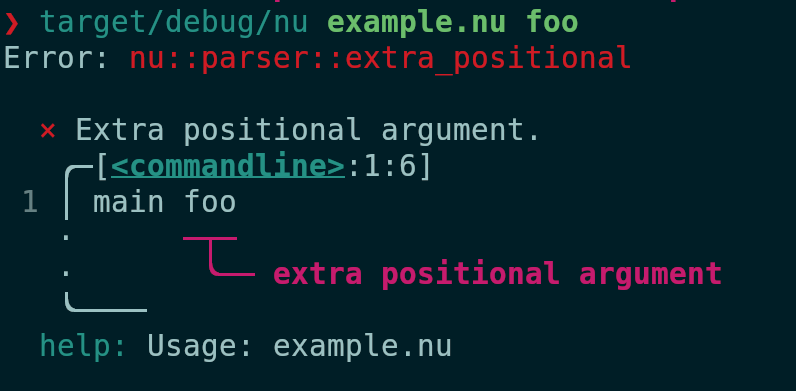
# Tests
<!--
Don't forget to add tests that cover your changes.
Make sure you've run and fixed any issues with these commands:
- `cargo fmt --all -- --check` to check standard code formatting (`cargo
fmt --all` applies these changes)
- `cargo clippy --workspace -- -D warnings -D clippy::unwrap_used` to
check that you're using the standard code style
- `cargo test --workspace` to check that all tests pass (on Windows make
sure to [enable developer
mode](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/apps/get-started/developer-mode-features-and-debugging))
- `cargo run -- -c "use toolkit.nu; toolkit test stdlib"` to run the
tests for the standard library
> **Note**
> from `nushell` you can also use the `toolkit` as follows
> ```bash
> use toolkit.nu # or use an `env_change` hook to activate it
automatically
> toolkit check pr
> ```
-->
Tests are still missing for the subcommands and the input/output types
---------
Co-authored-by: Stefan Holderbach <sholderbach@users.noreply.github.com>
<!--
if this PR closes one or more issues, you can automatically link the PR
with
them by using one of the [*linking
keywords*](https://docs.github.com/en/issues/tracking-your-work-with-issues/linking-a-pull-request-to-an-issue#linking-a-pull-request-to-an-issue-using-a-keyword),
e.g.
- this PR should close #xxxx
- fixes #xxxx
you can also mention related issues, PRs or discussions!
-->
# Description
<!--
Thank you for improving Nushell. Please, check our [contributing
guide](../CONTRIBUTING.md) and talk to the core team before making major
changes.
Description of your pull request goes here. **Provide examples and/or
screenshots** if your changes affect the user experience.
-->
In this PR I expanded the helper attribute `#[nu_value]` on
`#[derive(FromValue)]`. It now allows the usage of `#[nu_value(type_name
= "...")]` to set a type name for the `FromValue::expected_type`
implementation. Currently it only uses the default implementation but
I'd like to change that without having to manually implement the entire
trait on my own.
# User-Facing Changes
<!-- List of all changes that impact the user experience here. This
helps us keep track of breaking changes. -->
Users that derive `FromValue` may now change the name of the expected
type.
# Tests + Formatting
<!--
Don't forget to add tests that cover your changes.
Make sure you've run and fixed any issues with these commands:
- `cargo fmt --all -- --check` to check standard code formatting (`cargo
fmt --all` applies these changes)
- `cargo clippy --workspace -- -D warnings -D clippy::unwrap_used` to
check that you're using the standard code style
- `cargo test --workspace` to check that all tests pass (on Windows make
sure to [enable developer
mode](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/apps/get-started/developer-mode-features-and-debugging))
- `cargo run -- -c "use toolkit.nu; toolkit test stdlib"` to run the
tests for the standard library
> **Note**
> from `nushell` you can also use the `toolkit` as follows
> ```bash
> use toolkit.nu # or use an `env_change` hook to activate it
automatically
> toolkit check pr
> ```
-->
I added some tests that check if this feature work and updated the
documentation about the derive macro.
- 🟢 `toolkit fmt`
- 🟢 `toolkit clippy`
- 🟢 `toolkit test`
- 🟢 `toolkit test stdlib`
# After Submitting
<!-- If your PR had any user-facing changes, update [the
documentation](https://github.com/nushell/nushell.github.io) after the
PR is merged, if necessary. This will help us keep the docs up to date.
-->
<!--
if this PR closes one or more issues, you can automatically link the PR
with
them by using one of the [*linking
keywords*](https://docs.github.com/en/issues/tracking-your-work-with-issues/linking-a-pull-request-to-an-issue#linking-a-pull-request-to-an-issue-using-a-keyword),
e.g.
- this PR should close #xxxx
- fixes #xxxx
you can also mention related issues, PRs or discussions!
-->
# Description
<!--
Thank you for improving Nushell. Please, check our [contributing
guide](../CONTRIBUTING.md) and talk to the core team before making major
changes.
Description of your pull request goes here. **Provide examples and/or
screenshots** if your changes affect the user experience.
-->
I was working with byte collections like `Vec<u8>` and
[`bytes::Bytes`](https://docs.rs/bytes/1.7.1/bytes/struct.Bytes.html),
both are currently not possible to be used directly in a struct that
derives `IntoValue` and `FromValue` at the same time. The `Vec<u8>` will
convert itself into a `Value::List` but expects a `Value::String` or
`Value::Binary` to load from. I now also implemented that it can load
from `Value::List` just like the other `Vec<uX>` versions. For further
working with byte collections the type `bytes::Bytes` is wildly used,
therefore I added a implementation for it. `bytes` is already part of
the dependency graph as many crates (more than 5000 to crates.io) use
it.
# User-Facing Changes
<!-- List of all changes that impact the user experience here. This
helps us keep track of breaking changes. -->
User of `nu-protocol` as library, e.g. plugin developers, can now use
byte collections more easily in their data structures and derive
`IntoValue` and `FromValue` for it.
# Tests + Formatting
<!--
Don't forget to add tests that cover your changes.
Make sure you've run and fixed any issues with these commands:
- `cargo fmt --all -- --check` to check standard code formatting (`cargo
fmt --all` applies these changes)
- `cargo clippy --workspace -- -D warnings -D clippy::unwrap_used` to
check that you're using the standard code style
- `cargo test --workspace` to check that all tests pass (on Windows make
sure to [enable developer
mode](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/apps/get-started/developer-mode-features-and-debugging))
- `cargo run -- -c "use toolkit.nu; toolkit test stdlib"` to run the
tests for the standard library
> **Note**
> from `nushell` you can also use the `toolkit` as follows
> ```bash
> use toolkit.nu # or use an `env_change` hook to activate it
automatically
> toolkit check pr
> ```
-->
I added a few tests that check that these byte collections are correctly
translated in and from `Value`. They live in `test_derive.rs` as part of
the `ByteContainer` and I also explicitely tested that `FromValue` for
`Vec<u8>` works as expected.
- 🟢 `toolkit fmt`
- 🟢 `toolkit clippy`
- 🟢 `toolkit test`
- 🟢 `toolkit test stdlib`
# After Submitting
<!-- If your PR had any user-facing changes, update [the
documentation](https://github.com/nushell/nushell.github.io) after the
PR is merged, if necessary. This will help us keep the docs up to date.
-->
Maybe it should be explored if `Value::Binary` should use `bytes::Bytes`
instead of `Vec<u8>`.
# Description
The meaning of the word usage is specific to describing how a command
function is *used* and not a synonym for general description. Usage can
be used to describe the SYNOPSIS or EXAMPLES sections of a man page
where the permitted argument combinations are shown or example *uses*
are given.
Let's not confuse people and call it what it is a description.
Our `help` command already creates its own *Usage* section based on the
available arguments and doesn't refer to the description with usage.
# User-Facing Changes
`help commands` and `scope commands` will now use `description` or
`extra_description`
`usage`-> `description`
`extra_usage` -> `extra_description`
Breaking change in the plugin protocol:
In the signature record communicated with the engine.
`usage`-> `description`
`extra_usage` -> `extra_description`
The same rename also takes place for the methods on
`SimplePluginCommand` and `PluginCommand`
# Tests + Formatting
- Updated plugin protocol specific changes
# After Submitting
- [ ] update plugin protocol doc
# Description
Fixes#11267
Shifting by a `shift >= num_bits` is undefined in the underlying
operation. Previously we also had an overflow on negative shifts for the
operators `bit-shl` and `bit-shr`
Furthermore I found a severe bug in the implementation of shifting of
`binary` data with the commands `bits shl` and `bits shr`, this
categorically produced incorrect results with shifts that were not
`shift % 4 == 0`. `bits shr` also was able to produce outputs with
different size to the input if the shift was exceeding the length of the
input data by more than a byte.
# User-Facing Changes
It is now an error trying to shift by more than the available bits with:
- `bit-shl` operator
- `bit-shr` operator
- command `bits shl`
- command `bits shr`
# Tests + Formatting
Added testing for all relevant cases
# Description
As part of fixing https://github.com/nushell/nushell/issues/13586, this
PR checks the types of the operands when creating a range. Stuff like
`0..(glob .)` will be rejected at parse time. Additionally, `0..$x` will
be treated as a range and rejected if `x` is not defined, rather than
being treated as a string. A separate PR will need to be made to do
reject streams at runtime, so that stuff like `0..(open /dev/random)`
doesn't hang.
Internally, this PR adds a `ParseError::UnsupportedOperationTernary`
variant, for when you have a range like `1..2..(glob .)`.
# User-Facing Changes
Users will now receive an error if any of the operands in the ranges
they construct have types that aren't compatible with `Type::Number`.
Additionally, if a piece of code looks like a range but some parse error
is encountered while parsing it, that piece of code will still be
treated as a range and the user will be shown the parse error. This
means that a piece of code like `0..$x` will be treated as a range no
matter what. Previously, if `x` weren't the expression would've been
treated as a string `"0..$x"`. I feel like it makes the language less
complicated if we make it less context-sensitive.
Here's an example of the error you get:
```
> 0..(glob .)
Error: nu::parser::unsupported_operation
× range is not supported between int and any.
╭─[entry #1:1:1]
1 │ 0..(glob .)
· ─────┬─────┬┬
· │ │╰── any
· │ ╰── int
· ╰── doesn't support these values
╰────
```
And as an image:
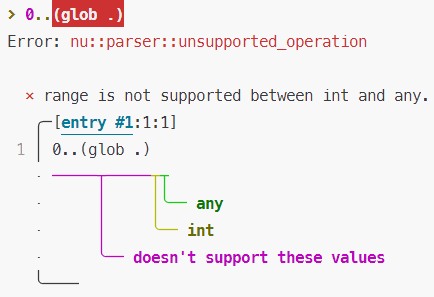
Note: I made the operands themselves (above, `(glob .)`) be garbage,
rather than the `..` operator itself. This doesn't match the behavior of
the math operators (if you do `1 + "foo"`, `+` gets highlighted red).
This is because with ranges, the range operators aren't `Expression`s
themselves, so they can't be turned into garbage. I felt like here, it
makes more sense to highlight the individual operand anyway.
# Description
Something I meant to add a long time ago. We currently don't have a
convenient way to print raw binary data intentionally. You can pipe it
through `cat` to turn it into an unknown stream, or write it to a file
and read it again, but we can't really just e.g. generate msgpack and
write it to stdout without this. For example:
```nushell
[abc def] | to msgpack | print --raw
```
This is useful for nushell scripts that will be piped into something
else. It also means that `nu_plugin_nu_example` probably doesn't need to
do this anymore, but I haven't adjusted it yet:
```nushell
def tell_nushell_encoding [] {
print -n "\u{0004}json"
}
```
This happens to work because 0x04 is a valid UTF-8 character, but it
wouldn't be possible if it were something above 0x80.
`--raw` also formats other things without `table`, I figured the two
things kind of go together. The output is kind of like `to text`.
Debatable whether that should share the same flag, but it was easier
that way and seemed reasonable.
# User-Facing Changes
- `print` new flag: `--raw`
# Tests + Formatting
Added tests.
# After Submitting
- [ ] release notes (command modified)
This PR will close#13501
# Description
This PR expands on [the relay of signals to running plugin
processes](https://github.com/nushell/nushell/pull/13181). The Ctrlc
relay has been generalized to SignalAction::Interrupt and when
reset_signal is called on the main EngineState, a SignalAction::Reset is
now relayed to running plugins.
# User-Facing Changes
The signal handler closure now takes a `signals::SignalAction`, while
previously it took no arguments. The handler will now be called on both
interrupt and reset. The method to register a handler on the plugin side
is now called `register_signal_handler` instead of
`register_ctrlc_handler`
[example](https://github.com/nushell/nushell/pull/13510/files#diff-3e04dff88fd0780a49778a3d1eede092ec729a1264b4ef07ca0d2baa859dad05L38).
This will only affect plugin authors who have started making use of
https://github.com/nushell/nushell/pull/13181, which isn't currently
part of an official release.
The change will also require all of user's plugins to be recompiled in
order that they don't error when a signal is received on the
PluginInterface.
# Testing
```
: example ctrlc
interrupt status: false
waiting for interrupt signal...
^Cinterrupt status: true
peace.
Error: × Operation interrupted
╭─[display_output hook:1:1]
1 │ if (term size).columns >= 100 { table -e } else { table }
· ─┬
· ╰── This operation was interrupted
╰────
: example ctrlc
interrupt status: false <-- NOTE status is false
waiting for interrupt signal...
^Cinterrupt status: true
peace.
Error: × Operation interrupted
╭─[display_output hook:1:1]
1 │ if (term size).columns >= 100 { table -e } else { table }
· ─┬
· ╰── This operation was interrupted
╰────
```
# Description
Part 4 of replacing std::path types with nu_path types added in
https://github.com/nushell/nushell/pull/13115. This PR migrates various
tests throughout the code base.
In some `if let`s we ran the `SharedCow::to_mut` for the test and to get
access to a mutable reference in the happy path. Internally
`Arc::into_mut` has to read atomics and if necessary clone.
For else branches, where we still want to modify the record we
previously called this again (not just in rust, confirmed in the asm).
This would have introduced a `call` instruction and its cost (even if it
would be guaranteed to take the short path in `Arc::into_mut`).
Lifting it get's rid of this.
# Description
Part 3 of replacing `std::path` types with `nu_path` types added in
#13115. This PR targets the paths listed in `$nu`. That is, the home,
config, data, and cache directories.
- **Doccomment style fixes**
- **Forgotten stuff in `nu-pretty-hex`**
- **Don't `for` around an `Option`**
- and more
I think the suggestions here are a net positive, some of the suggestions
moved into #13498 feel somewhat arbitrary, I also raised
https://github.com/rust-lang/rust-clippy/issues/13188 as the nightly
`byte_char_slices` would require either a global allow or otherwise a
ton of granular allows or possibly confusing bytestring literals.
- **Suggested default impl for the new `*Stack`s**
- **Change a hashmap to make clippy happy**
- **Clone from fix**
- **Fix conditional unused in test**
- then **Bump rust toolchain**
# Description
This PR adds a new method to `EngineInterface`: `register_ctrlc_handler`
which takes a closure to run when the plugin's driving engine receives a
ctrlc-signal. It also adds a mirror of the `signals` attribute from the
main shell `EngineState`.
This is an example of how a plugin which makes a long poll http request
can end the request on ctrlc:
https://github.com/cablehead/nu_plugin_http/blob/main/src/commands/request.rs#L68-L77
To facilitate the feature, a new attribute has been added to
`EngineState`: `ctrlc_handlers`. This is a Vec of closures that will be
run when the engine's process receives a ctrlc signal.
When plugins are added to an `engine_state` during a `merge_delta`, the
engine passes the ctrlc_handlers to the plugin's
`.configure_ctrlc_handler` method, which gives the plugin a chance to
register a handler that sends a ctrlc packet through the
`PluginInterface`, if an instance of the plugin is currently running.
On the plugin side: `EngineInterface` also has a ctrlc_handlers Vec of
closures. Plugin calls can use `register_ctrlc_handler` to register a
closure that will be called in the plugin process when the
PluginInput::Ctrlc command is received.
For future reference these are some alternate places that were
investigated for tying the ctrlc trigger to transmitting a Ctrlc packet
through the `PluginInterface`:
- Directly from `src/signals.rs`: the handler there would need a
reference to the Vec<Arc<RegisteredPlugins>>, which would require us to
wrap the plugins in a Mutex, which we don't want to do.
- have `PersistentPlugin.get_plugin` pass down the engine's
CtrlcHandlers to .get and then to .spawn (if the plugin isn't already
running). Once we have CtrlcHandlers in spawn, we can register a handler
to write directly to PluginInterface. We don't want to double down on
passing engine_state to spawn this way though, as it's unpredictable
because it would depend on whether the plugin has already been spawned
or not.
- pass `ctrlc_handlers` to PersistentPlugin::new so it can store it on
itself so it's available to spawn.
- in `PersistentPlugin.spawn`, create a handler that sends to a clone of
the GC event loop's tx. this has the same issues with regards to how to
get CtrlcHandlers to the spawn method, and is more complicated than a
handler that writes directly to PluginInterface
# User-Facing Changes
No breaking changes
---------
Co-authored-by: Ian Manske <ian.manske@pm.me>
# Description
Seems like I developed a bit of a bad habit of trying to link
```rust
/// [`.foo()`]
```
in docstrings, and this just doesn't work automatically; you have to do
```rust
/// [`.foo()`](Self::foo)
```
if you want it to actually link. I think I found and replaced all of
these.
# User-Facing Changes
Just docs.
# Description
Fixes#13441.
I must have forgotten that `Expr::Range` can contain other expressions,
so I wasn't searching for `$in` to replace within it. Easy fix.
# User-Facing Changes
Bug fix, ranges like `6 | 3..$in` work as expected now.
# Tests + Formatting
Added regression test.
# Description
This corrects the parsing of unknown arguments provided to known
externals to behave exactly like external arguments passed to normal
external calls.
I've done this by adding a `SyntaxShape::ExternalArgument` which
triggers the same parsing rules.
Because I didn't like how the highlighting looked, I modified the
flattener to emit `ExternalArg` flat shapes for arguments that have that
syntax shape and are plain strings/globs. This is the same behavior that
external calls have.
Aside from passing the tests, I've also checked manually that the
completer seems to work adequately. I can confirm that specified
positional arguments get completion according to their specified type
(including custom completions), and then anything remaining gets
filepath style completion, as you'd expect from an external command.
Thanks to @OJarrisonn for originally finding this issue.
# User-Facing Changes
- Unknown args are now parsed according to their specified syntax shape,
rather than `Any`. This may be a breaking change, though I think it's
extremely unlikely in practice.
- The unspecified arguments of known externals are now highlighted /
flattened identically to normal external arguments, which makes it more
clear how they're being interpreted, and should help the completer
function properly.
- Known externals now have an implicit rest arg if not specified named
`args`, with a syntax shape of `ExternalArgument`.
# Tests + Formatting
Tests added for the new behaviour. Some old tests had to be corrected to
match.
- 🟢 `toolkit fmt`
- 🟢 `toolkit clippy`
- 🟢 `toolkit test`
- 🟢 `toolkit test stdlib`
# After Submitting
- [ ] release notes (bugfix, and debatable whether it's a breaking
change)
# Description
Trying to help @amtoine out here - the spans calculated by `ast::Call`
by `span()` and `argument_span()` are suspicious and are not properly
guarding against `end` that might be before `start`. Just using
`Span::merge()` / `merge_many()` instead to try to make the behaviour as
simple and consistent as possible. Hopefully then even if the arguments
have some crazy spans, we don't have spans that are just totally
invalid.
# Tests + Formatting
I did check that everything passes with this.
fixes https://github.com/nushell/nushell/issues/13378
# Description
This PR tries to improve usage of system APIs to determine the location
of vendored autoload files.
# User-Facing Changes
The paths listed in #13180 and #13217 are changing. This has not been
part of a release yet, so arguably the user facing changes are only to
unreleased features anyway.
# Tests + Formatting
Haven't done, but if someone wants to help me here, I'm open to doing
it. I just don't know how to properly test this.
# After Submitting
# Description
Adds functionality to the plugin interface to support calling internal
commands from plugins. For example, using `view ir --json`:
```rust
let closure: Value = call.req(0)?;
let Some(decl_id) = engine.find_decl("view ir")? else {
return Err(LabeledError::new("`view ir` not found"));
};
let ir_json = engine.call_decl(
decl_id,
EvaluatedCall::new(call.head)
.with_named("json".into_spanned(call.head), Value::bool(true, call.head))
.with_positional(closure),
PipelineData::Empty,
true,
false,
)?.into_value()?.into_string()?;
let ir = serde_json::from_value(&ir_json);
// ...
```
# User-Facing Changes
Plugin developers can now use `EngineInterface::find_decl()` and
`call_decl()` to call internal commands, which could be handy for
formatters like `to csv` or `to nuon`, or for reflection commands that
help gain insight into the engine.
# Tests + Formatting
- 🟢 `toolkit fmt`
- 🟢 `toolkit clippy`
- 🟢 `toolkit test`
- 🟢 `toolkit test stdlib`
# After Submitting
- [ ] release notes
- [ ] update plugin protocol documentation: `FindDecl`, `CallDecl`
engine calls; `Identifier` engine call response
# Description
This grew quite a bit beyond its original scope, but I've tried to make
`$in` a bit more consistent and easier to work with.
Instead of the parser generating calls to `collect` and creating
closures, this adds `Expr::Collect` which just evaluates in the same
scope and doesn't require any closure.
When `$in` is detected in an expression, it is replaced with a new
variable (also called `$in`) and wrapped in `Expr::Collect`. During
eval, this expression is evaluated directly, with the input and with
that new variable set to the collected value.
Other than being faster and less prone to gotchas, it also makes it
possible to typecheck the output of an expression containing `$in`,
which is nice. This is a breaking change though, because of the lack of
the closure and because now typechecking will actually happen. Also, I
haven't attempted to typecheck the input yet.
The IR generated now just looks like this:
```gas
collect %in
clone %tmp, %in
store-variable $in, %tmp
# %out <- ...expression... <- %in
drop-variable $in
```
(where `$in` is the local variable created for this collection, and not
`IN_VARIABLE_ID`)
which is a lot better than having to create a closure and call `collect
--keep-env`, dealing with all of the capture gathering and allocation
that entails. Ideally we can also detect whether that input is actually
needed, so maybe we don't have to clone, but I haven't tried to do that
yet. Theoretically now that the variable is a unique one every time, it
should be possible to give it a type - I just don't know how to
determine that yet.
On top of that, I've also reworked how `$in` works in pipeline-initial
position. Previously, it was a little bit inconsistent. For example,
this worked:
```nushell
> 3 | do { let x = $in; let y = $in; print $x $y }
3
3
```
However, this causes a runtime variable not found error on the second
`$in`:
```nushell
> def foo [] { let x = $in; let y = $in; print $x $y }; 3 | foo
Error: nu:🐚:variable_not_found
× Variable not found
╭─[entry #115:1:35]
1 │ def foo [] { let x = $in; let y = $in; print $x $y }; 3 | foo
· ─┬─
· ╰── variable not found
╰────
```
I've fixed this by making the first element `$in` detection *always*
happen at the block level, so if you use `$in` in pipeline-initial
position anywhere in a block, it will collect with an implicit
subexpression around the whole thing, and you can then use that `$in`
more than once. In doing this I also rewrote `parse_pipeline()` and
hopefully it's a bit more straightforward and possibly more efficient
too now.
Finally, I've tried to make `let` and `mut` a lot more straightforward
with how they handle the rest of the pipeline, and using a redirection
with `let`/`mut` now does what you'd expect if you assume that they
consume the whole pipeline - the redirection is just processed as
normal. These both work now:
```nushell
let x = ^foo err> err.txt
let y = ^foo out+err>| str length
```
It was previously possible to accomplish this with a subexpression, but
it just seemed like a weird gotcha that you couldn't do it. Intuitively,
`let` and `mut` just seem to take the whole line.
- closes#13137
# User-Facing Changes
- `$in` will behave more consistently with blocks and closures, since
the entire block is now just wrapped to handle it if it appears in the
first pipeline element
- `$in` no longer creates a closure, so what can be done within an
expression containing `$in` is less restrictive
- `$in` containing expressions are now type checked, rather than just
resulting in `any`. However, `$in` itself is still `any`, so this isn't
quite perfect yet
- Redirections are now allowed in `let` and `mut` and behave pretty much
how you'd expect
# Tests + Formatting
Added tests to cover the new behaviour.
# After Submitting
- [ ] release notes (definitely breaking change)
# Description
The name of the `group` command is a little unclear/ambiguous.
Everything I look at it, I think of `group-by`. I think `chunks` more
clearly conveys what the `group` command does. Namely, it divides the
input list into chunks of a certain size. For example,
[`slice::chunks`](https://doc.rust-lang.org/std/primitive.slice.html#method.chunks)
has the same name. So, this PR adds a new `chunks` command to replace
the now deprecated `group` command.
The `chunks` command is a refactored version of `group`. As such, there
is a small performance improvement:
```nushell
# $data is a very large list
> bench { $data | chunks 2 } --rounds 30 | get mean
474ms 921µs 190ns
# deprecation warning was disabled here for fairness
> bench { $data | group 2 } --rounds 30 | get mean
592ms 702µs 440ns
> bench { $data | chunks 200 } --rounds 30 | get mean
374ms 188µs 318ns
> bench { $data | group 200 } --rounds 30 | get mean
481ms 264µs 869ns
> bench { $data | chunks 1 } --rounds 30 | get mean
642ms 574µs 42ns
> bench { $data | group 1 } --rounds 30 | get mean
981ms 602µs 513ns
```
# User-Facing Changes
- `group` command has been deprecated in favor of new `chunks` command.
- `chunks` errors when given a chunk size of `0` whereas `group` returns
chunks with one element.
# Tests + Formatting
Added tests for `chunks`, since `group` did not have any tests.
# After Submitting
Update book if necessary.
# Description
Add `README.md` files to each crate in our workspace (-plugins) and also
include it in the `lib.rs` documentation for <docs.rs> (if there is no
existing `lib.rs` crate documentation)
In all new README I added the defensive comment that the crates are not
considered stable for public consumption. If necessary we can adjust
this if we deem a crate useful for plugin authors.
# Description
This adds tracing for each individual instruction to the `Debugger`
trait. Register contents can be inspected both when entering and leaving
an instruction, and if an instruction produced an error, a reference to
the error is also available. It's not the full `EvalContext` but it's
most of the important parts for getting an idea of what's going on.
Added support for all of this to the `Profiler` / `debug profile` as
well, and the output is quite incredible - super verbose, but you can
see every instruction that's executed and also what the result was if
it's an instruction that has a clearly defined output (many do).
# User-Facing Changes
- Added `--instructions` to `debug profile`, which adds the `pc` and
`instruction` columns to the output.
- `--expr` only works in AST mode, and `--instructions` only works in IR
mode. In the wrong mode, the output for those columns is just blank.
# Tests + Formatting
All passing.
# After Submitting
- [ ] release notes
# Description
This improves the error when the determined output of a custom command
doesn't match the specified output type by adding the actual determined
output type.
# User-Facing Changes
Previous: `command doesn't output {0}`
New: `expected {0}, but command outputs {1}`
# Tests + Formatting
Passing.
# After Submitting
- [ ] release notes? (minor change, but helpful)
# Description
Allows `Stack` to have a modified local `Config`, which is updated
immediately when `$env.config` is assigned to. This means that even
within a script, commands that come after `$env.config` changes will
always see those changes in `Stack::get_config()`.
Also fixed a lot of cases where `engine_state.get_config()` was used
even when `Stack` was available.
Closes#13324.
# User-Facing Changes
- Config changes apply immediately after the assignment is executed,
rather than whenever config is read by a command that needs it.
- Potentially slower performance when executing a lot of lines that
change `$env.config` one after another. Recommended to get `$env.config`
into a `mut` variable first and do modifications, then assign it back.
- Much faster performance when executing a script that made
modifications to `$env.config`, as the changes are only parsed once.
# Tests + Formatting
All passing.
# After Submitting
- [ ] release notes
# Description
`Signature::get_positional()` was returning an owned `PositionalArg`,
which contains a bunch of strings. `ClosureEval` uses this in
`try_add_arg`, making all of that unnecessary cloning a little bit hot.
# User-Facing Changes
Slightly better performance
# Description
Just more efficient allocation during `Stack::gather_captures()` so that
we don't have to grow the `Vec` needlessly.
# User-Facing Changes
Slightly better performance.
# Description
This is another easy performance lift that just changes `env_vars` and
`env_hidden` on `Stack` to use `Arc`. I noticed that these were being
cloned on essentially every closure invocation during captures
gathering, so we're paying the cost for all of that even when we don't
change anything. On top of that, for `env_vars`, there's actually an
entirely fresh `HashMap` created for each child scope, so it's highly
unlikely that we'll modify the parent ones.
Uses `Arc::make_mut` instead to take care of things when we need to
mutate something, and most of the time nothing has to be cloned at all.
# Benchmarks
The benefits are greater the more calls there are to env-cloning
functions like `captures_to_stack()`. Calling custom commands in a loop
is basically best case for a performance improvement. Plain `each` with
a literal block isn't so badly affected because the stack is set up
once.
## random_bytes.nu
```nushell
use std bench
do {
const SCRIPT = ../nu_scripts/benchmarks/random-bytes.nu
let before_change = bench { nu $SCRIPT }
let after_change = bench { target/release/nu $SCRIPT }
{
before: ($before_change | reject times),
after: ($after_change | reject times)
}
}
```
```
╭────────┬──────────────────────────────╮
│ │ ╭──────┬───────────────────╮ │
│ before │ │ mean │ 603ms 759µs 727ns │ │
│ │ │ min │ 593ms 298µs 167ns │ │
│ │ │ max │ 648ms 612µs 291ns │ │
│ │ │ std │ 9ms 335µs 251ns │ │
│ │ ╰──────┴───────────────────╯ │
│ │ ╭──────┬───────────────────╮ │
│ after │ │ mean │ 518ms 400µs 557ns │ │
│ │ │ min │ 507ms 762µs 583ns │ │
│ │ │ max │ 566ms 695µs 166ns │ │
│ │ │ std │ 9ms 554µs 767ns │ │
│ │ ╰──────┴───────────────────╯ │
╰────────┴──────────────────────────────╯
```
## gradient_benchmark_no_check.nu
```nushell
use std bench
do {
const SCRIPT = ../nu_scripts/benchmarks/gradient_benchmark_no_check.nu
let before_change = bench { nu $SCRIPT }
let after_change = bench { target/release/nu $SCRIPT }
{
before: ($before_change | reject times),
after: ($after_change | reject times)
}
}
```
```
╭────────┬──────────────────────────────╮
│ │ ╭──────┬───────────────────╮ │
│ before │ │ mean │ 146ms 543µs 380ns │ │
│ │ │ min │ 142ms 416µs 166ns │ │
│ │ │ max │ 189ms 595µs │ │
│ │ │ std │ 7ms 140µs 342ns │ │
│ │ ╰──────┴───────────────────╯ │
│ │ ╭──────┬───────────────────╮ │
│ after │ │ mean │ 134ms 211µs 678ns │ │
│ │ │ min │ 132ms 433µs 125ns │ │
│ │ │ max │ 135ms 722µs 583ns │ │
│ │ │ std │ 793µs 134ns │ │
│ │ ╰──────┴───────────────────╯ │
╰────────┴──────────────────────────────╯
```
# User-Facing Changes
Better performance, particularly for custom commands, especially if
there are a lot of environment variables. Nothing else.
# Tests + Formatting
All passing.
# Description
This PR adds an internal representation language to Nushell, offering an
alternative evaluator based on simple instructions, stream-containing
registers, and indexed control flow. The number of registers required is
determined statically at compile-time, and the fixed size required is
allocated upon entering the block.
Each instruction is associated with a span, which makes going backwards
from IR instructions to source code very easy.
Motivations for IR:
1. **Performance.** By simplifying the evaluation path and making it
more cache-friendly and branch predictor-friendly, code that does a lot
of computation in Nushell itself can be sped up a decent bit. Because
the IR is fairly easy to reason about, we can also implement
optimization passes in the future to eliminate and simplify code.
2. **Correctness.** The instructions mostly have very simple and
easily-specified behavior, so hopefully engine changes are a little bit
easier to reason about, and they can be specified in a more formal way
at some point. I have made an effort to document each of the
instructions in the docs for the enum itself in a reasonably specific
way. Some of the errors that would have happened during evaluation
before are now moved to the compilation step instead, because they don't
make sense to check during evaluation.
3. **As an intermediate target.** This is a good step for us to bring
the [`new-nu-parser`](https://github.com/nushell/new-nu-parser) in at
some point, as code generated from new AST can be directly compared to
code generated from old AST. If the IR code is functionally equivalent,
it will behave the exact same way.
4. **Debugging.** With a little bit more work, we can probably give
control over advancing the virtual machine that `IrBlock`s run on to
some sort of external driver, making things like breakpoints and single
stepping possible. Tools like `view ir` and [`explore
ir`](https://github.com/devyn/nu_plugin_explore_ir) make it easier than
before to see what exactly is going on with your Nushell code.
The goal is to eventually replace the AST evaluator entirely, once we're
sure it's working just as well. You can help dogfood this by running
Nushell with `$env.NU_USE_IR` set to some value. The environment
variable is checked when Nushell starts, so config runs with IR, or it
can also be set on a line at the REPL to change it dynamically. It is
also checked when running `do` in case within a script you want to just
run a specific piece of code with or without IR.
# Example
```nushell
view ir { |data|
mut sum = 0
for n in $data {
$sum += $n
}
$sum
}
```
```gas
# 3 registers, 19 instructions, 0 bytes of data
0: load-literal %0, int(0)
1: store-variable var 904, %0 # let
2: drain %0
3: drop %0
4: load-variable %1, var 903
5: iterate %0, %1, end 15 # for, label(1), from(14:)
6: store-variable var 905, %0
7: load-variable %0, var 904
8: load-variable %2, var 905
9: binary-op %0, Math(Plus), %2
10: span %0
11: store-variable var 904, %0
12: load-literal %0, nothing
13: drain %0
14: jump 5
15: drop %0 # label(0), from(5:)
16: drain %0
17: load-variable %0, var 904
18: return %0
```
# Benchmarks
All benchmarks run on a base model Mac Mini M1.
## Iterative Fibonacci sequence
This is about as best case as possible, making use of the much faster
control flow. Most code will not experience a speed improvement nearly
this large.
```nushell
def fib [n: int] {
mut a = 0
mut b = 1
for _ in 2..=$n {
let c = $a + $b
$a = $b
$b = $c
}
$b
}
use std bench
bench { 0..50 | each { |n| fib $n } }
```
IR disabled:
```
╭───────┬─────────────────╮
│ mean │ 1ms 924µs 665ns │
│ min │ 1ms 700µs 83ns │
│ max │ 3ms 450µs 125ns │
│ std │ 395µs 759ns │
│ times │ [list 50 items] │
╰───────┴─────────────────╯
```
IR enabled:
```
╭───────┬─────────────────╮
│ mean │ 452µs 820ns │
│ min │ 427µs 417ns │
│ max │ 540µs 167ns │
│ std │ 17µs 158ns │
│ times │ [list 50 items] │
╰───────┴─────────────────╯
```

##
[gradient_benchmark_no_check.nu](https://github.com/nushell/nu_scripts/blob/main/benchmarks/gradient_benchmark_no_check.nu)
IR disabled:
```
╭───┬──────────────────╮
│ 0 │ 27ms 929µs 958ns │
│ 1 │ 21ms 153µs 459ns │
│ 2 │ 18ms 639µs 666ns │
│ 3 │ 19ms 554µs 583ns │
│ 4 │ 13ms 383µs 375ns │
│ 5 │ 11ms 328µs 208ns │
│ 6 │ 5ms 659µs 542ns │
╰───┴──────────────────╯
```
IR enabled:
```
╭───┬──────────────────╮
│ 0 │ 22ms 662µs │
│ 1 │ 17ms 221µs 792ns │
│ 2 │ 14ms 786µs 708ns │
│ 3 │ 13ms 876µs 834ns │
│ 4 │ 13ms 52µs 875ns │
│ 5 │ 11ms 269µs 666ns │
│ 6 │ 6ms 942µs 500ns │
╰───┴──────────────────╯
```
##
[random-bytes.nu](https://github.com/nushell/nu_scripts/blob/main/benchmarks/random-bytes.nu)
I got pretty random results out of this benchmark so I decided not to
include it. Not clear why.
# User-Facing Changes
- IR compilation errors may appear even if the user isn't evaluating
with IR.
- IR evaluation can be enabled by setting the `NU_USE_IR` environment
variable to any value.
- New command `view ir` pretty-prints the IR for a block, and `view ir
--json` can be piped into an external tool like [`explore
ir`](https://github.com/devyn/nu_plugin_explore_ir).
# Tests + Formatting
All tests are passing with `NU_USE_IR=1`, and I've added some more eval
tests to compare the results for some very core operations. I will
probably want to add some more so we don't have to always check
`NU_USE_IR=1 toolkit test --workspace` on a regular basis.
# After Submitting
- [ ] release notes
- [ ] further documentation of instructions?
- [ ] post-release: publish `nu_plugin_explore_ir`
# Description
This PR introduces a new `Signals` struct to replace our adhoc passing
around of `ctrlc: Option<Arc<AtomicBool>>`. Doing so has a few benefits:
- We can better enforce when/where resetting or triggering an interrupt
is allowed.
- Consolidates `nu_utils::ctrl_c::was_pressed` and other ad-hoc
re-implementations into a single place: `Signals::check`.
- This allows us to add other types of signals later if we want. E.g.,
exiting or suspension.
- Similarly, we can more easily change the underlying implementation if
we need to in the future.
- Places that used to have a `ctrlc` of `None` now use
`Signals::empty()`, so we can double check these usages for correctness
in the future.
# Description
Refactors `help operators` so that its output is always up to date with
the parser.
# User-Facing Changes
- The order of output rows for `help operators` was changed.
- `not` is now listed as a boolean operator instead of a comparison
operator.
- Edited some of the descriptions for the operators.
# Description
Bug fix: `PipelineData::check_external_failed()` was not preserving the
original `type_` and `known_size` attributes of the stream passed in for
streams that come from children, so `external-command | into binary` did
not work properly and always ended up still being unknown type.
# User-Facing Changes
The following test case now works as expected:
```nushell
> head -c 2 /dev/urandom | into binary
# Expected: pretty hex dump of binary
# Previous behavior: just raw binary in the terminal
```
# Tests + Formatting
Added a test to cover this to `into binary`
This reverts commit 0cfd5fbece.
The original PR messed up syntax higlighting of aliases and causes
panics of completion in the presence of alias.
<!--
if this PR closes one or more issues, you can automatically link the PR
with
them by using one of the [*linking
keywords*](https://docs.github.com/en/issues/tracking-your-work-with-issues/linking-a-pull-request-to-an-issue#linking-a-pull-request-to-an-issue-using-a-keyword),
e.g.
- this PR should close #xxxx
- fixes #xxxx
you can also mention related issues, PRs or discussions!
-->
# Description
<!--
Thank you for improving Nushell. Please, check our [contributing
guide](../CONTRIBUTING.md) and talk to the core team before making major
changes.
Description of your pull request goes here. **Provide examples and/or
screenshots** if your changes affect the user experience.
-->
# User-Facing Changes
<!-- List of all changes that impact the user experience here. This
helps us keep track of breaking changes. -->
# Tests + Formatting
<!--
Don't forget to add tests that cover your changes.
Make sure you've run and fixed any issues with these commands:
- `cargo fmt --all -- --check` to check standard code formatting (`cargo
fmt --all` applies these changes)
- `cargo clippy --workspace -- -D warnings -D clippy::unwrap_used` to
check that you're using the standard code style
- `cargo test --workspace` to check that all tests pass (on Windows make
sure to [enable developer
mode](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/apps/get-started/developer-mode-features-and-debugging))
- `cargo run -- -c "use toolkit.nu; toolkit test stdlib"` to run the
tests for the standard library
> **Note**
> from `nushell` you can also use the `toolkit` as follows
> ```bash
> use toolkit.nu # or use an `env_change` hook to activate it
automatically
> toolkit check pr
> ```
-->
# After Submitting
<!-- If your PR had any user-facing changes, update [the
documentation](https://github.com/nushell/nushell.github.io) after the
PR is merged, if necessary. This will help us keep the docs up to date.
-->
<!--
if this PR closes one or more issues, you can automatically link the PR
with
them by using one of the [*linking
keywords*](https://docs.github.com/en/issues/tracking-your-work-with-issues/linking-a-pull-request-to-an-issue#linking-a-pull-request-to-an-issue-using-a-keyword),
e.g.
- this PR should close #xxxx
- fixes #xxxx
you can also mention related issues, PRs or discussions!
-->
# Description
<!--
Thank you for improving Nushell. Please, check our [contributing
guide](../CONTRIBUTING.md) and talk to the core team before making major
changes.
Description of your pull request goes here. **Provide examples and/or
screenshots** if your changes affect the user experience.
-->
Part of https://github.com/nushell/nushell/issues/12963, step 2.
This PR refactors Call and related argument structures to remove their
dependency on `Expression::span` which will be removed in the future.
# User-Facing Changes
<!-- List of all changes that impact the user experience here. This
helps us keep track of breaking changes. -->
Should be none. If you see some error messages that look broken, please
report.
# Tests + Formatting
<!--
Don't forget to add tests that cover your changes.
Make sure you've run and fixed any issues with these commands:
- `cargo fmt --all -- --check` to check standard code formatting (`cargo
fmt --all` applies these changes)
- `cargo clippy --workspace -- -D warnings -D clippy::unwrap_used` to
check that you're using the standard code style
- `cargo test --workspace` to check that all tests pass (on Windows make
sure to [enable developer
mode](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/apps/get-started/developer-mode-features-and-debugging))
- `cargo run -- -c "use toolkit.nu; toolkit test stdlib"` to run the
tests for the standard library
> **Note**
> from `nushell` you can also use the `toolkit` as follows
> ```bash
> use toolkit.nu # or use an `env_change` hook to activate it
automatically
> toolkit check pr
> ```
-->
# After Submitting
<!-- If your PR had any user-facing changes, update [the
documentation](https://github.com/nushell/nushell.github.io) after the
PR is merged, if necessary. This will help us keep the docs up to date.
-->
# Description
Provides the ability to use http commands as part of a pipeline.
Additionally, this pull requests extends the pipeline metadata to add a
content_type field. The content_type metadata field allows commands such
as `to json` to set the metadata in the pipeline allowing the http
commands to use it when making requests.
This pull request also introduces the ability to directly stream http
requests from streaming pipelines.
One other small change is that Content-Type will always be set if it is
passed in to the http commands, either indirectly or throw the content
type flag. Previously it was not preserved with requests that were not
of type json or form data.
# User-Facing Changes
* `http post`, `http put`, `http patch`, `http delete` can be used as
part of a pipeline
* `to text`, `to json`, `from json` all set the content_type metadata
field and the http commands will utilize them when making requests.
# Description
Fixes: https://github.com/nushell/nushell/issues/12099
Currently if user run `use voice.nu`, and file is unchanged, then run
`use voice.nu` again. nushell will use the module directly, even if
submodule inside `voice.nu` is changed.
After discussed with @kubouch, I think it's ok to re-parse the module
file when:
1. It exports sub modules which are defined by a file
2. It uses other modules which are defined by a file
## About the change:
To achieve the behavior, we need to add 2 attributes to `Module`:
1. `imported_modules`: it tracks the other modules is imported by the
givem `module`, e.g: `use foo.nu`
2. `file`: the path of a module, if a module is defined by a file, it
will be `Some(path)`, or else it will be `None`.
After the change:
use voice.nu always read the file and parse it.
use voice will still use the module which is saved in EngineState.
# User-Facing Changes
use `xxx.nu` will read the file and parse it if it exports submodules or
uses submodules
# Tests + Formatting
Done
---------
Co-authored-by: Jakub Žádník <kubouch@gmail.com>
# Description
This PR implements script or module autoloading. It does this by finding
the `$nu.vendor-autoload-dir`, lists the contents and sorts them by file
name. These files are evaluated in that order.
To see what's going on, you can use `--log-level warn`
```
❯ cargo r -- --log-level warn
Finished dev [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in 0.58s
Running `target\debug\nu.exe --log-level warn`
2024-06-24 09:23:20.494 PM [WARN ] nu::config_files: set_config_path() cwd: "C:\\Users\\fdncred\\source\\repos\\nushell", default_config: config.nu, key: config-path, config_file_specified: None
2024-06-24 09:23:20.495 PM [WARN ] nu::config_files: set_config_path() cwd: "C:\\Users\\fdncred\\source\\repos\\nushell", default_config: env.nu, key: env-path, config_file_specified: None
2024-06-24 09:23:20.629 PM [WARN ] nu::config_files: setup_config() config_file_specified: None, env_file_specified: None, login: false
2024-06-24 09:23:20.660 PM [WARN ] nu::config_files: read_config_file() config_file_specified: None, is_env_config: true
Hello, from env.nu
2024-06-24 09:23:20.679 PM [WARN ] nu::config_files: read_config_file() config_file_specified: None, is_env_config: false
Hello, from config.nu
Hello, from defs.nu
Activating Microsoft Visual Studio environment.
2024-06-24 09:23:21.398 PM [WARN ] nu::config_files: read_vendor_autoload_files() src\config_files.rs:234:9
2024-06-24 09:23:21.399 PM [WARN ] nu::config_files: read_vendor_autoload_files: C:\ProgramData\nushell\vendor\autoload
2024-06-24 09:23:21.399 PM [WARN ] nu::config_files: AutoLoading: "C:\\ProgramData\\nushell\\vendor\\autoload\\01_get-weather.nu"
2024-06-24 09:23:21.675 PM [WARN ] nu::config_files: AutoLoading: "C:\\ProgramData\\nushell\\vendor\\autoload\\02_temp.nu"
2024-06-24 09:23:21.817 PM [WARN ] nu_cli::repl: Terminal doesn't support use_kitty_protocol config
```
# User-Facing Changes
<!-- List of all changes that impact the user experience here. This
helps us keep track of breaking changes. -->
# Tests + Formatting
<!--
Don't forget to add tests that cover your changes.
Make sure you've run and fixed any issues with these commands:
- `cargo fmt --all -- --check` to check standard code formatting (`cargo
fmt --all` applies these changes)
- `cargo clippy --workspace -- -D warnings -D clippy::unwrap_used` to
check that you're using the standard code style
- `cargo test --workspace` to check that all tests pass (on Windows make
sure to [enable developer
mode](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/apps/get-started/developer-mode-features-and-debugging))
- `cargo run -- -c "use toolkit.nu; toolkit test stdlib"` to run the
tests for the standard library
> **Note**
> from `nushell` you can also use the `toolkit` as follows
> ```bash
> use toolkit.nu # or use an `env_change` hook to activate it
automatically
> toolkit check pr
> ```
-->
# After Submitting
<!-- If your PR had any user-facing changes, update [the
documentation](https://github.com/nushell/nushell.github.io) after the
PR is merged, if necessary. This will help us keep the docs up to date.
-->
<!--
if this PR closes one or more issues, you can automatically link the PR
with
them by using one of the [*linking
keywords*](https://docs.github.com/en/issues/tracking-your-work-with-issues/linking-a-pull-request-to-an-issue#linking-a-pull-request-to-an-issue-using-a-keyword),
e.g.
- this PR should close #xxxx
- fixes #xxxx
you can also mention related issues, PRs or discussions!
-->
# Description
<!--
Thank you for improving Nushell. Please, check our [contributing
guide](../CONTRIBUTING.md) and talk to the core team before making major
changes.
Description of your pull request goes here. **Provide examples and/or
screenshots** if your changes affect the user experience.
-->
# User-Facing Changes
<!-- List of all changes that impact the user experience here. This
helps us keep track of breaking changes. -->
# Tests + Formatting
<!--
Don't forget to add tests that cover your changes.
Make sure you've run and fixed any issues with these commands:
- `cargo fmt --all -- --check` to check standard code formatting (`cargo
fmt --all` applies these changes)
- `cargo clippy --workspace -- -D warnings -D clippy::unwrap_used` to
check that you're using the standard code style
- `cargo test --workspace` to check that all tests pass (on Windows make
sure to [enable developer
mode](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/apps/get-started/developer-mode-features-and-debugging))
- `cargo run -- -c "use toolkit.nu; toolkit test stdlib"` to run the
tests for the standard library
> **Note**
> from `nushell` you can also use the `toolkit` as follows
> ```bash
> use toolkit.nu # or use an `env_change` hook to activate it
automatically
> toolkit check pr
> ```
-->
# After Submitting
<!-- If your PR had any user-facing changes, update [the
documentation](https://github.com/nushell/nushell.github.io) after the
PR is merged, if necessary. This will help us keep the docs up to date.
-->
Fixesnushell/nushell#13207
# Description
This fixes the parsing of command usage when that command comes from a
file with CRLF line endings.
See nushell/nushell#13207 for more details.
# User-Facing Changes
Users on Windows will get correct autocompletion for `std` commands.
# Description
In #13031 I added the derive macros for `FromValue` and `IntoValue`. In
that implementation, in particular for structs with named fields, it was
not possible to omit fields while loading them from a value, when the
field is an `Option`. This PR adds extra handling for this behavior, so
if a field is an `Option` and that field is missing in the `Value`, then
the field becomes `None`. This behavior is also tested in
`nu_protocol::value::test_derive::missing_options`.
# User-Facing Changes
When using structs for options or similar, users can now just emit
fields in the record and the derive `from_value` method will be able to
understand this, if the struct has an `Option` type for that field.
# Tests + Formatting
- 🟢 `toolkit fmt`
- 🟢 `toolkit clippy`
- 🟢 `toolkit test`
- 🟢 `toolkit test stdlib`
# After Submitting
A showcase for this feature would be great, I tried to use the current
derive macro in a plugin of mine for a config but without this addition,
they are annoying to use. So, when this is done, I would add an example
for such plugin configs that may be loaded via `FromValue`.
# Description
This allows plugins to report their version (and potentially other
metadata in the future). The version is shown in `plugin list` and in
`version`.
The metadata is stored in the registry file, and reflects whatever was
retrieved on `plugin add`, not necessarily the running binary. This can
help you to diagnose if there's some kind of mismatch with what you
expect. We could potentially use this functionality to show a warning or
error if a plugin being run does not have the same version as what was
in the cache file, suggesting `plugin add` be run again, but I haven't
done that at this point.
It is optional, and it requires the plugin author to make some code
changes if they want to provide it, since I can't automatically
determine the version of the calling crate or anything tricky like that
to do it.
Example:
```
> plugin list | select name version is_running pid
╭───┬────────────────┬─────────┬────────────┬─────╮
│ # │ name │ version │ is_running │ pid │
├───┼────────────────┼─────────┼────────────┼─────┤
│ 0 │ example │ 0.93.1 │ false │ │
│ 1 │ gstat │ 0.93.1 │ false │ │
│ 2 │ inc │ 0.93.1 │ false │ │
│ 3 │ python_example │ 0.1.0 │ false │ │
╰───┴────────────────┴─────────┴────────────┴─────╯
```
cc @maxim-uvarov (he asked for it)
# User-Facing Changes
- `plugin list` gets a `version` column
- `version` shows plugin versions when available
- plugin authors *should* add `fn metadata()` to their `impl Plugin`,
but don't have to
# Tests + Formatting
Tested the low level stuff and also the `plugin list` column.
# After Submitting
- [ ] update plugin guide docs
- [ ] update plugin protocol docs (`Metadata` call & response)
- [ ] update plugin template (`fn metadata()` should be easy)
- [ ] release notes
# Description
This PR adds a directory to the `$nu` constant that shows where the
system level autoload directory is located at. This folder is modifiable
at compile time with environment variables.
```rust
// Create a system level directory for nushell scripts, modules, completions, etc
// that can be changed by setting the NU_VENDOR_AUTOLOAD_DIR env var on any platform
// before nushell is compiled OR if NU_VENDOR_AUTOLOAD_DIR is not set for non-windows
// systems, the PREFIX env var can be set before compile and used as PREFIX/nushell/vendor/autoload
// pseudo code
// if env var NU_VENDOR_AUTOLOAD_DIR is set, in any platform, use it
// if not, if windows, use ALLUSERPROFILE\nushell\vendor\autoload
// if not, if non-windows, if env var PREFIX is set, use PREFIX/share/nushell/vendor/autoload
// if not, use the default /usr/share/nushell/vendor/autoload
```
### Windows default
```nushell
❯ $nu.vendor-autoload-dir
C:\ProgramData\nushell\vendor\autoload
```
### Non-Windows default
```nushell
❯ $nu.vendor-autoload-dir
/usr/local/share/nushell/vendor/autoload
```
### Non-Windows with PREFIX set
```nushell
❯ PREFIX=/usr/bob cargo r
❯ $nu.vendor-autoload-dir
/usr/bob/share/nushell/vendor/autoload
```
### Non-Windows with NU_VENDOR_AUTOLOAD_DIR set
```nushell
❯ NU_VENDOR_AUTOLOAD_DIR=/some/other/path/nushell/stuff cargo r
❯ $nu.vendor-autoload-dir
/some/other/path/nushell/stuff
```
> [!IMPORTANT]
To be clear, this PR does not do the auto-loading, it just sets up the
folder to support that functionality that can be added in a later PR.
The PR also does not create the folder defined. It's just setting the
$nu constant.
# User-Facing Changes
<!-- List of all changes that impact the user experience here. This
helps us keep track of breaking changes. -->
# Tests + Formatting
<!--
Don't forget to add tests that cover your changes.
Make sure you've run and fixed any issues with these commands:
- `cargo fmt --all -- --check` to check standard code formatting (`cargo
fmt --all` applies these changes)
- `cargo clippy --workspace -- -D warnings -D clippy::unwrap_used` to
check that you're using the standard code style
- `cargo test --workspace` to check that all tests pass (on Windows make
sure to [enable developer
mode](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/apps/get-started/developer-mode-features-and-debugging))
- `cargo run -- -c "use toolkit.nu; toolkit test stdlib"` to run the
tests for the standard library
> **Note**
> from `nushell` you can also use the `toolkit` as follows
> ```bash
> use toolkit.nu # or use an `env_change` hook to activate it
automatically
> toolkit check pr
> ```
-->
# After Submitting
<!-- If your PR had any user-facing changes, update [the
documentation](https://github.com/nushell/nushell.github.io) after the
PR is merged, if necessary. This will help us keep the docs up to date.
-->
# Description
We've had a lot of different issues and PRs related to arg handling with
externals since the rewrite of `run-external` in #12921:
- #12950
- #12955
- #13000
- #13001
- #13021
- #13027
- #13028
- #13073
Many of these are caused by the argument handling of external calls and
`run-external` being very special and involving the parser handing
quoted strings over to `run-external` so that it knows whether to expand
tildes and globs and so on. This is really unusual and also makes it
harder to use `run-external`, and also harder to understand it (and
probably is part of the reason why it was rewritten in the first place).
This PR moves a lot more of that work over to the parser, so that by the
time `run-external` gets it, it's dealing with much more normal Nushell
values. In particular:
- Unquoted strings are handled as globs with no expand
- The unescaped-but-quoted handling of strings was removed, and the
parser constructs normal looking strings instead, removing internal
quotes so that `run-external` doesn't have to do it
- Bare word interpolation is now supported and expansion is done in this
case
- Expressions typed as `Glob` containing `Expr::StringInterpolation` now
produce `Value::Glob` instead, with the quoted status from the expr
passed through so we know if it was a bare word
- Bare word interpolation for values typed as `glob` now possible, but
not implemented
- Because expansion is now triggered by `Value::Glob(_, false)` instead
of looking at the expr, externals now support glob types
# User-Facing Changes
- Bare word interpolation works for external command options, and
otherwise embedded in other strings:
```nushell
^echo --foo=(2 + 2) # prints --foo=4
^echo -foo=$"(2 + 2)" # prints -foo=4
^echo foo="(2 + 2)" # prints (no interpolation!) foo=(2 + 2)
^echo foo,(2 + 2),bar # prints foo,4,bar
```
- Bare word interpolation expands for external command head/args:
```nushell
let name = "exa"
~/.cargo/bin/($name) # this works, and expands the tilde
^$"~/.cargo/bin/($name)" # this doesn't expand the tilde
^echo ~/($name)/* # this glob is expanded
^echo $"~/($name)/*" # this isn't expanded
```
- Ndots are now supported for the head of an external command
(`^.../foo` works)
- Glob values are now supported for head/args of an external command,
and expanded appropriately:
```nushell
^("~/.cargo/bin/exa" | into glob) # the tilde is expanded
^echo ("*.txt" | into glob) # this glob is expanded
```
- `run-external` now works more like any other command, without
expecting a special call convention
for its args:
```nushell
run-external echo "'foo'"
# before PR: 'foo'
# after PR: foo
run-external echo "*.txt"
# before PR: (glob is expanded)
# after PR: *.txt
```
# Tests + Formatting
Lots of tests added and cleaned up. Some tests that weren't active on
Windows changed to use `nu --testbin cococo` so that they can work.
Added a test for Linux only to make sure tilde expansion of commands
works, because changing `HOME` there causes `~` to reliably change.
- 🟢 `toolkit fmt`
- 🟢 `toolkit clippy`
- 🟢 `toolkit test`
- 🟢 `toolkit test stdlib`
# After Submitting
- [ ] release notes: make sure to mention the new syntaxes that are
supported
# Description
After discussing with @sholderbach the cumbersome usage of
`nu_protocol::Value` in Rust, I created a derive macro to simplify it.
I’ve added a new crate called `nu-derive-value`, which includes two
macros, `IntoValue` and `FromValue`. These are re-exported in
`nu-protocol` and should be encouraged to be used via that re-export.
The macros ensure that all types can easily convert from and into
`Value`. For example, as a plugin author, you can define your plugin
configuration using a Rust struct and easily convert it using
`FromValue`. This makes plugin configuration less of a hassle.
I introduced the `IntoValue` trait for a standardized approach to
converting values into `Value` (and a fallible variant `TryIntoValue`).
This trait could potentially replace existing `into_value` methods.
Along with this, I've implemented `FromValue` for several standard types
and refined other implementations to use blanket implementations where
applicable.
I made these design choices with input from @devyn.
There are more improvements possible, but this is a solid start and the
PR is already quite substantial.
# User-Facing Changes
For `nu-protocol` users, these changes simplify the handling of
`Value`s. There are no changes for end-users of nushell itself.
# Tests + Formatting
Documenting the macros itself is not really possible, as they cannot
really reference any other types since they are the root of the
dependency graph. The standard library has the same problem
([std::Debug](https://doc.rust-lang.org/stable/std/fmt/derive.Debug.html)).
However I documented the `FromValue` and `IntoValue` traits completely.
For testing, I made of use `proc-macro2` in the derive macro code. This
would allow testing the generated source code. Instead I just tested
that the derived functionality is correct. This is done in
`nu_protocol::value::test_derive`, as a consumer of `nu-derive-value`
needs to do the testing of the macro usage. I think that these tests
should provide a stable baseline so that users can be sure that the impl
works.
# After Submitting
With these macros available, we can probably use them in some examples
for plugins to showcase the use of them.
# Description
This PR is an attempt to add a standard location for people to put
completions in. I saw this topic come up again recently and IIRC we
decided to create a standard location. I used the dirs-next crate to
dictate where these locations are. I know some people won't like that
but at least this gets the ball rolling in a direction that has a
standard directory.
This is what the default NU_LIB_DIRS looks like now in the
default_env.nu. It should also be like this when starting nushell with
`nu -n`
```nushell
$env.NU_LIB_DIRS = [
($nu.default-config-dir | path join 'scripts') # add <nushell-config-dir>/scripts
($nu.data-dir | path join 'completions') # default home for nushell completions
]
```
I also added these default folders to the `$nu` variable so now there is
`$nu.data-path` and `$nu.cache-path`.
## Data Dir Default

While I was in there, I also decided to add a cache dir
## Cache Dir Default

### This is what the default looks like in Ubuntu.

### This is what it looks like with XDG_CACHE_HOME and XDG_DATA_HOME
overridden
```nushell
XDG_DATA_HOME=/tmp/data_home XDG_CACHE_HOME=/tmp/cache_home cargo r
```

### This is what the defaults look like in Windows (username scrubbed to
protect the innocent)

How my NU_LIB_DIRS is set in the images above
```nushell
$env.NU_LIB_DIRS = [
($nu.default-config-dir | path join 'scripts') # add <nushell-config-dir>/scripts
'/Users/fdncred/src/nu_scripts'
($nu.config-path | path dirname)
($nu.data-dir | path join 'completions') # default home for nushell completions
]
```
Let the debate begin.
# User-Facing Changes
<!-- List of all changes that impact the user experience here. This
helps us keep track of breaking changes. -->
# Tests + Formatting
<!--
Don't forget to add tests that cover your changes.
Make sure you've run and fixed any issues with these commands:
- `cargo fmt --all -- --check` to check standard code formatting (`cargo
fmt --all` applies these changes)
- `cargo clippy --workspace -- -D warnings -D clippy::unwrap_used` to
check that you're using the standard code style
- `cargo test --workspace` to check that all tests pass (on Windows make
sure to [enable developer
mode](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/apps/get-started/developer-mode-features-and-debugging))
- `cargo run -- -c "use toolkit.nu; toolkit test stdlib"` to run the
tests for the standard library
> **Note**
> from `nushell` you can also use the `toolkit` as follows
> ```bash
> use toolkit.nu # or use an `env_change` hook to activate it
automatically
> toolkit check pr
> ```
-->
# After Submitting
<!-- If your PR had any user-facing changes, update [the
documentation](https://github.com/nushell/nushell.github.io) after the
PR is merged, if necessary. This will help us keep the docs up to date.
-->
# Description
#7777 removed the `--numbered` flag from `each`, `par-each`, `reduce`,
and `each while`. It was suggested at the time that it should be removed
from `for` as well, but for several reasons it wasn't.
This PR deprecates `--numbered` in anticipation of removing it in 0.96.
Note: Please review carefully, as this is my first "real" Rust/Nushell
code. I was hoping that some prior commit would be useful as a template,
but since this was an argument on a parser keyword, I didn't find too
much useful. So I had to actually find the relevant helpers in the code
and `nu_protocol` doc and learn how to use them - oh darn ;-) But please
make sure I did it correctly.
# User-Facing Changes
* Use of `--numbered` will result in a deprecation warning.
* Changed help example to demonstrate the new syntax.
* Help shows deprecation notice on the flag