# Objective
In `bevy_sprite`, the `Anchor` type is not `Copy`. It makes interacting
with it more difficult than necessary.
## Solution
Derive `Copy` on it. The rust API guidelines are that you should derive
`Copy` when possible.
<https://rust-lang.github.io/api-guidelines/interoperability.html#types-eagerly-implement-common-traits-c-common-traits>
Regardless, `Anchor` is a very small `enum` which warrants `Copy`.
---
## Changelog
- In `bevy_sprite` `Anchor` is now `Copy`.
---------
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
**This implementation is based on
https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/pull/59.**
---
Resolves#4597
Full details and motivation can be found in the RFC, but here's a brief
summary.
`FromReflect` is a very powerful and important trait within the
reflection API. It allows Dynamic types (e.g., `DynamicList`, etc.) to
be formed into Real ones (e.g., `Vec<i32>`, etc.).
This mainly comes into play concerning deserialization, where the
reflection deserializers both return a `Box<dyn Reflect>` that almost
always contain one of these Dynamic representations of a Real type. To
convert this to our Real type, we need to use `FromReflect`.
It also sneaks up in other ways. For example, it's a required bound for
`T` in `Vec<T>` so that `Vec<T>` as a whole can be made `FromReflect`.
It's also required by all fields of an enum as it's used as part of the
`Reflect::apply` implementation.
So in other words, much like `GetTypeRegistration` and `Typed`, it is
very much a core reflection trait.
The problem is that it is not currently treated like a core trait and is
not automatically derived alongside `Reflect`. This makes using it a bit
cumbersome and easy to forget.
## Solution
Automatically derive `FromReflect` when deriving `Reflect`.
Users can then choose to opt-out if needed using the
`#[reflect(from_reflect = false)]` attribute.
```rust
#[derive(Reflect)]
struct Foo;
#[derive(Reflect)]
#[reflect(from_reflect = false)]
struct Bar;
fn test<T: FromReflect>(value: T) {}
test(Foo); // <-- OK
test(Bar); // <-- Panic! Bar does not implement trait `FromReflect`
```
#### `ReflectFromReflect`
This PR also automatically adds the `ReflectFromReflect` (introduced in
#6245) registration to the derived `GetTypeRegistration` impl— if the
type hasn't opted out of `FromReflect` of course.
<details>
<summary><h4>Improved Deserialization</h4></summary>
> **Warning**
> This section includes changes that have since been descoped from this
PR. They will likely be implemented again in a followup PR. I am mainly
leaving these details in for archival purposes, as well as for reference
when implementing this logic again.
And since we can do all the above, we might as well improve
deserialization. We can now choose to deserialize into a Dynamic type or
automatically convert it using `FromReflect` under the hood.
`[Un]TypedReflectDeserializer::new` will now perform the conversion and
return the `Box`'d Real type.
`[Un]TypedReflectDeserializer::new_dynamic` will work like what we have
now and simply return the `Box`'d Dynamic type.
```rust
// Returns the Real type
let reflect_deserializer = UntypedReflectDeserializer::new(®istry);
let mut deserializer = ron:🇩🇪:Deserializer::from_str(input)?;
let output: SomeStruct = reflect_deserializer.deserialize(&mut deserializer)?.take()?;
// Returns the Dynamic type
let reflect_deserializer = UntypedReflectDeserializer::new_dynamic(®istry);
let mut deserializer = ron:🇩🇪:Deserializer::from_str(input)?;
let output: DynamicStruct = reflect_deserializer.deserialize(&mut deserializer)?.take()?;
```
</details>
---
## Changelog
* `FromReflect` is now automatically derived within the `Reflect` derive
macro
* This includes auto-registering `ReflectFromReflect` in the derived
`GetTypeRegistration` impl
* ~~Renamed `TypedReflectDeserializer::new` and
`UntypedReflectDeserializer::new` to
`TypedReflectDeserializer::new_dynamic` and
`UntypedReflectDeserializer::new_dynamic`, respectively~~ **Descoped**
* ~~Changed `TypedReflectDeserializer::new` and
`UntypedReflectDeserializer::new` to automatically convert the
deserialized output using `FromReflect`~~ **Descoped**
## Migration Guide
* `FromReflect` is now automatically derived within the `Reflect` derive
macro. Items with both derives will need to remove the `FromReflect`
one.
```rust
// OLD
#[derive(Reflect, FromReflect)]
struct Foo;
// NEW
#[derive(Reflect)]
struct Foo;
```
If using a manual implementation of `FromReflect` and the `Reflect`
derive, users will need to opt-out of the automatic implementation.
```rust
// OLD
#[derive(Reflect)]
struct Foo;
impl FromReflect for Foo {/* ... */}
// NEW
#[derive(Reflect)]
#[reflect(from_reflect = false)]
struct Foo;
impl FromReflect for Foo {/* ... */}
```
<details>
<summary><h4>Removed Migrations</h4></summary>
> **Warning**
> This section includes changes that have since been descoped from this
PR. They will likely be implemented again in a followup PR. I am mainly
leaving these details in for archival purposes, as well as for reference
when implementing this logic again.
* The reflect deserializers now perform a `FromReflect` conversion
internally. The expected output of `TypedReflectDeserializer::new` and
`UntypedReflectDeserializer::new` is no longer a Dynamic (e.g.,
`DynamicList`), but its Real counterpart (e.g., `Vec<i32>`).
```rust
let reflect_deserializer =
UntypedReflectDeserializer::new_dynamic(®istry);
let mut deserializer = ron:🇩🇪:Deserializer::from_str(input)?;
// OLD
let output: DynamicStruct = reflect_deserializer.deserialize(&mut
deserializer)?.take()?;
// NEW
let output: SomeStruct = reflect_deserializer.deserialize(&mut
deserializer)?.take()?;
```
Alternatively, if this behavior isn't desired, use the
`TypedReflectDeserializer::new_dynamic` and
`UntypedReflectDeserializer::new_dynamic` methods instead:
```rust
// OLD
let reflect_deserializer = UntypedReflectDeserializer::new(®istry);
// NEW
let reflect_deserializer =
UntypedReflectDeserializer::new_dynamic(®istry);
```
</details>
---------
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
operate on naga IR directly to improve handling of shader modules.
- give codespan reporting into imported modules
- allow glsl to be used from wgsl and vice-versa
the ultimate objective is to make it possible to
- provide user hooks for core shader functions (to modify light
behaviour within the standard pbr pipeline, for example)
- make automatic binding slot allocation possible
but ... since this is already big, adds some value and (i think) is at
feature parity with the existing code, i wanted to push this now.
## Solution
i made a crate called naga_oil (https://github.com/robtfm/naga_oil -
unpublished for now, could be part of bevy) which manages modules by
- building each module independantly to naga IR
- creating "header" files for each supported language, which are used to
build dependent modules/shaders
- make final shaders by combining the shader IR with the IR for imported
modules
then integrated this into bevy, replacing some of the existing shader
processing stuff. also reworked examples to reflect this.
## Migration Guide
shaders that don't use `#import` directives should work without changes.
the most notable user-facing difference is that imported
functions/variables/etc need to be qualified at point of use, and
there's no "leakage" of visible stuff into your shader scope from the
imports of your imports, so if you used things imported by your imports,
you now need to import them directly and qualify them.
the current strategy of including/'spreading' `mesh_vertex_output`
directly into a struct doesn't work any more, so these need to be
modified as per the examples (e.g. color_material.wgsl, or many others).
mesh data is assumed to be in bindgroup 2 by default, if mesh data is
bound into bindgroup 1 instead then the shader def `MESH_BINDGROUP_1`
needs to be added to the pipeline shader_defs.
# Objective
- Better consistency with `add_systems`.
- Deprecating `add_plugin` in favor of a more powerful `add_plugins`.
- Allow passing `Plugin` to `add_plugins`.
- Allow passing tuples to `add_plugins`.
## Solution
- `App::add_plugins` now takes an `impl Plugins` parameter.
- `App::add_plugin` is deprecated.
- `Plugins` is a new sealed trait that is only implemented for `Plugin`,
`PluginGroup` and tuples over `Plugins`.
- All examples, benchmarks and tests are changed to use `add_plugins`,
using tuples where appropriate.
---
## Changelog
### Changed
- `App::add_plugins` now accepts all types that implement `Plugins`,
which is implemented for:
- Types that implement `Plugin`.
- Types that implement `PluginGroup`.
- Tuples (up to 16 elements) over types that implement `Plugins`.
- Deprecated `App::add_plugin` in favor of `App::add_plugins`.
## Migration Guide
- Replace `app.add_plugin(plugin)` calls with `app.add_plugins(plugin)`.
---------
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
Discovered that PointLight did not implement FromReflect. Adding
FromReflect where Reflect is used. I overreached and applied this rule
everywhere there was a Reflect without a FromReflect, except from where
the compiler wouldn't allow me.
Based from question: https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/discussions/8774
## Solution
- Adding FromReflect where Reflect was already derived
## Notes
First PR I do in this ecosystem, so not sure if this is the usual
approach, that is, to touch many files at once.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Introduce a stable alternative to
[`std::any::type_name`](https://doc.rust-lang.org/std/any/fn.type_name.html).
- Rewrite of #5805 with heavy inspiration in design.
- On the path to #5830.
- Part of solving #3327.
## Solution
- Add a `TypePath` trait for static stable type path/name information.
- Add a `TypePath` derive macro.
- Add a `impl_type_path` macro for implementing internal and foreign
types in `bevy_reflect`.
---
## Changelog
- Added `TypePath` trait.
- Added `DynamicTypePath` trait and `get_type_path` method to `Reflect`.
- Added a `TypePath` derive macro.
- Added a `bevy_reflect::impl_type_path` for implementing `TypePath` on
internal and foreign types in `bevy_reflect`.
- Changed `bevy_reflect::utility::(Non)GenericTypeInfoCell` to
`(Non)GenericTypedCell<T>` which allows us to be generic over both
`TypeInfo` and `TypePath`.
- `TypePath` is now a supertrait of `Asset`, `Material` and
`Material2d`.
- `impl_reflect_struct` needs a `#[type_path = "..."]` attribute to be
specified.
- `impl_reflect_value` needs to either specify path starting with a
double colon (`::core::option::Option`) or an `in my_crate::foo`
declaration.
- Added `bevy_reflect_derive::ReflectTypePath`.
- Most uses of `Ident` in `bevy_reflect_derive` changed to use
`ReflectTypePath`.
## Migration Guide
- Implementors of `Asset`, `Material` and `Material2d` now also need to
derive `TypePath`.
- Manual implementors of `Reflect` will need to implement the new
`get_type_path` method.
## Open Questions
- [x] ~This PR currently does not migrate any usages of
`std::any::type_name` to use `bevy_reflect::TypePath` to ease the review
process. Should it?~ Migration will be left to a follow-up PR.
- [ ] This PR adds a lot of `#[derive(TypePath)]` and `T: TypePath` to
satisfy new bounds, mostly when deriving `TypeUuid`. Should we make
`TypePath` a supertrait of `TypeUuid`? [Should we remove `TypeUuid` in
favour of
`TypePath`?](2afbd85532 (r961067892))
# Objective
Make `Material2dPipeline` reusable. This was already done for PBR
materials in #7548.
## Solution
Expose `extract_materials_2d`, `prepare_materials_2d` and
`ExtractedMaterials2d`.
---
## Changelog
- bevy_sprite: Make `prepare_materials_2d`, `extract_materials_2d` and
`ExtractedMaterials2d` public.
# Objective
- Support WebGPU
- alternative to #5027 that doesn't need any async / await
- fixes#8315
- Surprise fix#7318
## Solution
### For async renderer initialisation
- Update the plugin lifecycle:
- app builds the plugin
- calls `plugin.build`
- registers the plugin
- app starts the event loop
- event loop waits for `ready` of all registered plugins in the same
order
- returns `true` by default
- then call all `finish` then all `cleanup` in the same order as
registered
- then execute the schedule
In the case of the renderer, to avoid anything async:
- building the renderer plugin creates a detached task that will send
back the initialised renderer through a mutex in a resource
- `ready` will wait for the renderer to be present in the resource
- `finish` will take that renderer and place it in the expected
resources by other plugins
- other plugins (that expect the renderer to be available) `finish` are
called and they are able to set up their pipelines
- `cleanup` is called, only custom one is still for pipeline rendering
### For WebGPU support
- update the `build-wasm-example` script to support passing `--api
webgpu` that will build the example with WebGPU support
- feature for webgl2 was always enabled when building for wasm. it's now
in the default feature list and enabled on all platforms, so check for
this feature must also check that the target_arch is `wasm32`
---
## Migration Guide
- `Plugin::setup` has been renamed `Plugin::cleanup`
- `Plugin::finish` has been added, and plugins adding pipelines should
do it in this function instead of `Plugin::build`
```rust
// Before
impl Plugin for MyPlugin {
fn build(&self, app: &mut App) {
app.insert_resource::<MyResource>
.add_systems(Update, my_system);
let render_app = match app.get_sub_app_mut(RenderApp) {
Ok(render_app) => render_app,
Err(_) => return,
};
render_app
.init_resource::<RenderResourceNeedingDevice>()
.init_resource::<OtherRenderResource>();
}
}
// After
impl Plugin for MyPlugin {
fn build(&self, app: &mut App) {
app.insert_resource::<MyResource>
.add_systems(Update, my_system);
let render_app = match app.get_sub_app_mut(RenderApp) {
Ok(render_app) => render_app,
Err(_) => return,
};
render_app
.init_resource::<OtherRenderResource>();
}
fn finish(&self, app: &mut App) {
let render_app = match app.get_sub_app_mut(RenderApp) {
Ok(render_app) => render_app,
Err(_) => return,
};
render_app
.init_resource::<RenderResourceNeedingDevice>();
}
}
```
# Objective
- Updated to wgpu 0.16.0 and wgpu-hal 0.16.0
---
## Changelog
1. Upgrade wgpu to 0.16.0 and wgpu-hal to 0.16.0
2. Fix the error in native when using a filterable
`TextureSampleType::Float` on a multisample `BindingType::Texture`.
([https://github.com/gfx-rs/wgpu/pull/3686](https://github.com/gfx-rs/wgpu/pull/3686))
---------
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Add `Aabb` calculation for `Sprite`, `TextureAtlasSprite` and
`Mesh2d`.
- Enable frustum culling for 2D entities since frustum culling requires
a `Aabb` component in the entity to function.
- Improve 2D performance massively when there are many sprites out of
view. (ex: `many_sprites`)
## Solution
- Derived from @Weasy666's #3944 pull request, which had no activity
since multiple months.
- Adapted the code to the latest version of Bevy.
- Added support for sprites with non-center `Anchor`s to avoid culling
prematurely when part of the sprite is still in view or not culling when
sprite is already out of view.
### Note
- Gives 15.8x performance boosts in some scenarios. (5 fps vs 79 fps
with 409600 sprites in `many_sprites`)
---------
Co-authored-by: ira <JustTheCoolDude@gmail.com>
Links in the api docs are nice. I noticed that there were several places
where structs / functions and other things were referenced in the docs,
but weren't linked. I added the links where possible / logical.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
# Objective
Add Reflection to `TextureAtlasSprite` to bring it inline with `Sprite`
## Solution
Addition of appropriate macros to the type
---
## Changelog
`#[reflect(Component)]` and derive `FromReflect` for
`TextureAtlasSprite`
Added `TextureAtlasSprite` to the TypeRegistry
# Objective
The clippy lint `type_complexity` is known not to play well with bevy.
It frequently triggers when writing complex queries, and taking the
lint's advice of using a type alias almost always just obfuscates the
code with no benefit. Because of this, this lint is currently ignored in
CI, but unfortunately it still shows up when viewing bevy code in an
IDE.
As someone who's made a fair amount of pull requests to this repo, I
will say that this issue has been a consistent thorn in my side. Since
bevy code is filled with spurious, ignorable warnings, it can be very
difficult to spot the *real* warnings that must be fixed -- most of the
time I just ignore all warnings, only to later find out that one of them
was real after I'm done when CI runs.
## Solution
Suppress this lint in all bevy crates. This was previously attempted in
#7050, but the review process ended up making it more complicated than
it needs to be and landed on a subpar solution.
The discussion in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust-clippy/pull/10571
explores some better long-term solutions to this problem. Since there is
no timeline on when these solutions may land, we should resolve this
issue in the meantime by locally suppressing these lints.
### Unresolved issues
Currently, these lints are not suppressed in our examples, since that
would require suppressing the lint in every single source file. They are
still ignored in CI.
# Objective
- `Sprite` components are not included in scene (de)serialization.
- Fixes#8206
## Solution
- Add `#[reflect(Component, Default)]` to `Sprite`
- Add `#[derive(FromReflect)]` to `Sprite` and `Anchor`
---------
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
Support the following syntax for adding systems:
```rust
App::new()
.add_system(setup.on_startup())
.add_systems((
show_menu.in_schedule(OnEnter(GameState::Paused)),
menu_ssytem.in_set(OnUpdate(GameState::Paused)),
hide_menu.in_schedule(OnExit(GameState::Paused)),
))
```
## Solution
Add the traits `IntoSystemAppConfig{s}`, which provide the extension methods necessary for configuring which schedule a system belongs to. These extension methods return `IntoSystemAppConfig{s}`, which `App::add_system{s}` uses to choose which schedule to add systems to.
---
## Changelog
+ Added the extension methods `in_schedule(label)` and `on_startup()` for configuring the schedule a system belongs to.
## Future Work
* Replace all uses of `add_startup_system` in the engine.
* Deprecate this method
# Objective
- ambiguities bad
## Solution
- solve ambiguities
- by either ignoring (e.g. on `queue_mesh_view_bind_groups` since `LightMeta` access is different)
- by introducing a dependency (`prepare_windows -> prepare_*` because the latter use the fallback Msaa)
- make `prepare_assets` public so that we can do a proper `.after`
# Objective
- Fix the environment map shader not working under webgl due to textureNumLevels() not being supported
- Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/7722
## Solution
- Instead of using textureNumLevels(), put an extra field in the GpuLights uniform to store the mip count
# Objective
Splits tone mapping from https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/6677 into a separate PR.
Address https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/2264.
Adds tone mapping options:
- None: Bypasses tonemapping for instances where users want colors output to match those set.
- Reinhard
- Reinhard Luminance: Bevy's exiting tonemapping
- [ACES](https://github.com/TheRealMJP/BakingLab/blob/master/BakingLab/ACES.hlsl) (Fitted version, based on the same implementation that Godot 4 uses) see https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/2264
- [AgX](https://github.com/sobotka/AgX)
- SomewhatBoringDisplayTransform
- TonyMcMapface
- Blender Filmic
This PR also adds support for EXR images so they can be used to compare tonemapping options with reference images.
## Migration Guide
- Tonemapping is now an enum with NONE and the various tonemappers.
- The DebandDither is now a separate component.
Co-authored-by: JMS55 <47158642+JMS55@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
Allow for creating pipelines that use push constants. To be able to use push constants. Fixes#4825
As of right now, trying to call `RenderPass::set_push_constants` will trigger the following error:
```
thread 'main' panicked at 'wgpu error: Validation Error
Caused by:
In a RenderPass
note: encoder = `<CommandBuffer-(0, 59, Vulkan)>`
In a set_push_constant command
provided push constant is for stage(s) VERTEX | FRAGMENT | VERTEX_FRAGMENT, however the pipeline layout has no push constant range for the stage(s) VERTEX | FRAGMENT | VERTEX_FRAGMENT
```
## Solution
Add a field push_constant_ranges to` RenderPipelineDescriptor` and `ComputePipelineDescriptor`.
This PR supersedes #4908 which now contains merge conflicts due to significant changes to `bevy_render`.
Meanwhile, this PR also made the `layout` field of `RenderPipelineDescriptor` and `ComputePipelineDescriptor` non-optional. If the user do not need to specify the bind group layouts, they can simply supply an empty vector here. No need for it to be optional.
---
## Changelog
- Add a field push_constant_ranges to RenderPipelineDescriptor and ComputePipelineDescriptor
- Made the `layout` field of RenderPipelineDescriptor and ComputePipelineDescriptor non-optional.
## Migration Guide
- Add push_constant_ranges: Vec::new() to every `RenderPipelineDescriptor` and `ComputePipelineDescriptor`
- Unwrap the optional values on the `layout` field of `RenderPipelineDescriptor` and `ComputePipelineDescriptor`. If the descriptor has no layout, supply an empty vector.
Co-authored-by: Zhixing Zhang <me@neoto.xin>
# Objective
We have a few old system labels that are now system sets but are still named or documented as labels. Documentation also generally mentioned system labels in some places.
## Solution
- Clean up naming and documentation regarding system sets
## Migration Guide
`PrepareAssetLabel` is now called `PrepareAssetSet`
fixes#6799
# Objective
We should be able to reuse the `Globals` or `View` shader struct definitions from anywhere (including third party plugins) without needing to worry about defining unrelated shader defs.
Also we'd like to refactor these structs to not be repeatedly defined.
## Solution
Refactor both `Globals` and `View` into separate importable shaders.
Use the imports throughout.
Co-authored-by: Torstein Grindvik <52322338+torsteingrindvik@users.noreply.github.com>
Huge thanks to @maniwani, @devil-ira, @hymm, @cart, @superdump and @jakobhellermann for the help with this PR.
# Objective
- Followup #6587.
- Minimal integration for the Stageless Scheduling RFC: https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/pull/45
## Solution
- [x] Remove old scheduling module
- [x] Migrate new methods to no longer use extension methods
- [x] Fix compiler errors
- [x] Fix benchmarks
- [x] Fix examples
- [x] Fix docs
- [x] Fix tests
## Changelog
### Added
- a large number of methods on `App` to work with schedules ergonomically
- the `CoreSchedule` enum
- `App::add_extract_system` via the `RenderingAppExtension` trait extension method
- the private `prepare_view_uniforms` system now has a public system set for scheduling purposes, called `ViewSet::PrepareUniforms`
### Removed
- stages, and all code that mentions stages
- states have been dramatically simplified, and no longer use a stack
- `RunCriteriaLabel`
- `AsSystemLabel` trait
- `on_hierarchy_reports_enabled` run criteria (now just uses an ad hoc resource checking run condition)
- systems in `RenderSet/Stage::Extract` no longer warn when they do not read data from the main world
- `RunCriteriaLabel`
- `transform_propagate_system_set`: this was a nonstandard pattern that didn't actually provide enough control. The systems are already `pub`: the docs have been updated to ensure that the third-party usage is clear.
### Changed
- `System::default_labels` is now `System::default_system_sets`.
- `App::add_default_labels` is now `App::add_default_sets`
- `CoreStage` and `StartupStage` enums are now `CoreSet` and `StartupSet`
- `App::add_system_set` was renamed to `App::add_systems`
- The `StartupSchedule` label is now defined as part of the `CoreSchedules` enum
- `.label(SystemLabel)` is now referred to as `.in_set(SystemSet)`
- `SystemLabel` trait was replaced by `SystemSet`
- `SystemTypeIdLabel<T>` was replaced by `SystemSetType<T>`
- The `ReportHierarchyIssue` resource now has a public constructor (`new`), and implements `PartialEq`
- Fixed time steps now use a schedule (`CoreSchedule::FixedTimeStep`) rather than a run criteria.
- Adding rendering extraction systems now panics rather than silently failing if no subapp with the `RenderApp` label is found.
- the `calculate_bounds` system, with the `CalculateBounds` label, is now in `CoreSet::Update`, rather than in `CoreSet::PostUpdate` before commands are applied.
- `SceneSpawnerSystem` now runs under `CoreSet::Update`, rather than `CoreStage::PreUpdate.at_end()`.
- `bevy_pbr::add_clusters` is no longer an exclusive system
- the top level `bevy_ecs::schedule` module was replaced with `bevy_ecs::scheduling`
- `tick_global_task_pools_on_main_thread` is no longer run as an exclusive system. Instead, it has been replaced by `tick_global_task_pools`, which uses a `NonSend` resource to force running on the main thread.
## Migration Guide
- Calls to `.label(MyLabel)` should be replaced with `.in_set(MySet)`
- Stages have been removed. Replace these with system sets, and then add command flushes using the `apply_system_buffers` exclusive system where needed.
- The `CoreStage`, `StartupStage, `RenderStage` and `AssetStage` enums have been replaced with `CoreSet`, `StartupSet, `RenderSet` and `AssetSet`. The same scheduling guarantees have been preserved.
- Systems are no longer added to `CoreSet::Update` by default. Add systems manually if this behavior is needed, although you should consider adding your game logic systems to `CoreSchedule::FixedTimestep` instead for more reliable framerate-independent behavior.
- Similarly, startup systems are no longer part of `StartupSet::Startup` by default. In most cases, this won't matter to you.
- For example, `add_system_to_stage(CoreStage::PostUpdate, my_system)` should be replaced with
- `add_system(my_system.in_set(CoreSet::PostUpdate)`
- When testing systems or otherwise running them in a headless fashion, simply construct and run a schedule using `Schedule::new()` and `World::run_schedule` rather than constructing stages
- Run criteria have been renamed to run conditions. These can now be combined with each other and with states.
- Looping run criteria and state stacks have been removed. Use an exclusive system that runs a schedule if you need this level of control over system control flow.
- For app-level control flow over which schedules get run when (such as for rollback networking), create your own schedule and insert it under the `CoreSchedule::Outer` label.
- Fixed timesteps are now evaluated in a schedule, rather than controlled via run criteria. The `run_fixed_timestep` system runs this schedule between `CoreSet::First` and `CoreSet::PreUpdate` by default.
- Command flush points introduced by `AssetStage` have been removed. If you were relying on these, add them back manually.
- Adding extract systems is now typically done directly on the main app. Make sure the `RenderingAppExtension` trait is in scope, then call `app.add_extract_system(my_system)`.
- the `calculate_bounds` system, with the `CalculateBounds` label, is now in `CoreSet::Update`, rather than in `CoreSet::PostUpdate` before commands are applied. You may need to order your movement systems to occur before this system in order to avoid system order ambiguities in culling behavior.
- the `RenderLabel` `AppLabel` was renamed to `RenderApp` for clarity
- `App::add_state` now takes 0 arguments: the starting state is set based on the `Default` impl.
- Instead of creating `SystemSet` containers for systems that run in stages, simply use `.on_enter::<State::Variant>()` or its `on_exit` or `on_update` siblings.
- `SystemLabel` derives should be replaced with `SystemSet`. You will also need to add the `Debug`, `PartialEq`, `Eq`, and `Hash` traits to satisfy the new trait bounds.
- `with_run_criteria` has been renamed to `run_if`. Run criteria have been renamed to run conditions for clarity, and should now simply return a bool.
- States have been dramatically simplified: there is no longer a "state stack". To queue a transition to the next state, call `NextState::set`
## TODO
- [x] remove dead methods on App and World
- [x] add `App::add_system_to_schedule` and `App::add_systems_to_schedule`
- [x] avoid adding the default system set at inappropriate times
- [x] remove any accidental cycles in the default plugins schedule
- [x] migrate benchmarks
- [x] expose explicit labels for the built-in command flush points
- [x] migrate engine code
- [x] remove all mentions of stages from the docs
- [x] verify docs for States
- [x] fix uses of exclusive systems that use .end / .at_start / .before_commands
- [x] migrate RenderStage and AssetStage
- [x] migrate examples
- [x] ensure that transform propagation is exported in a sufficiently public way (the systems are already pub)
- [x] ensure that on_enter schedules are run at least once before the main app
- [x] re-enable opt-in to execution order ambiguities
- [x] revert change to `update_bounds` to ensure it runs in `PostUpdate`
- [x] test all examples
- [x] unbreak directional lights
- [x] unbreak shadows (see 3d_scene, 3d_shape, lighting, transparaency_3d examples)
- [x] game menu example shows loading screen and menu simultaneously
- [x] display settings menu is a blank screen
- [x] `without_winit` example panics
- [x] ensure all tests pass
- [x] SubApp doc test fails
- [x] runs_spawn_local tasks fails
- [x] [Fix panic_when_hierachy_cycle test hanging](https://github.com/alice-i-cecile/bevy/pull/120)
## Points of Difficulty and Controversy
**Reviewers, please give feedback on these and look closely**
1. Default sets, from the RFC, have been removed. These added a tremendous amount of implicit complexity and result in hard to debug scheduling errors. They're going to be tackled in the form of "base sets" by @cart in a followup.
2. The outer schedule controls which schedule is run when `App::update` is called.
3. I implemented `Label for `Box<dyn Label>` for our label types. This enables us to store schedule labels in concrete form, and then later run them. I ran into the same set of problems when working with one-shot systems. We've previously investigated this pattern in depth, and it does not appear to lead to extra indirection with nested boxes.
4. `SubApp::update` simply runs the default schedule once. This sucks, but this whole API is incomplete and this was the minimal changeset.
5. `time_system` and `tick_global_task_pools_on_main_thread` no longer use exclusive systems to attempt to force scheduling order
6. Implemetnation strategy for fixed timesteps
7. `AssetStage` was migrated to `AssetSet` without reintroducing command flush points. These did not appear to be used, and it's nice to remove these bottlenecks.
8. Migration of `bevy_render/lib.rs` and pipelined rendering. The logic here is unusually tricky, as we have complex scheduling requirements.
## Future Work (ideally before 0.10)
- Rename schedule_v3 module to schedule or scheduling
- Add a derive macro to states, and likely a `EnumIter` trait of some form
- Figure out what exactly to do with the "systems added should basically work by default" problem
- Improve ergonomics for working with fixed timesteps and states
- Polish FixedTime API to match Time
- Rebase and merge #7415
- Resolve all internal ambiguities (blocked on better tools, especially #7442)
- Add "base sets" to replace the removed default sets.
# Objective
allow negatively-scaled mesh2ds to render correctly by disabling back-face culling. this brings the mesh2d pipeline into line with the sprite pipeline. i don't see any cases where backface-culling would be useful for 2d meshes.
# Objective
Update Bevy to wgpu 0.15.
## Changelog
- Update to wgpu 0.15, wgpu-hal 0.15.1, and naga 0.11
- Users can now use the [DirectX Shader Compiler](https://github.com/microsoft/DirectXShaderCompiler) (DXC) on Windows with DX12 for faster shader compilation and ShaderModel 6.0+ support (requires `dxcompiler.dll` and `dxil.dll`, which are included in DXC downloads from [here](https://github.com/microsoft/DirectXShaderCompiler/releases/latest))
## Migration Guide
### WGSL Top-Level `let` is now `const`
All top level constants are now declared with `const`, catching up with the wgsl spec.
`let` is no longer allowed at the global scope, only within functions.
```diff
-let SOME_CONSTANT = 12.0;
+const SOME_CONSTANT = 12.0;
```
#### `TextureDescriptor` and `SurfaceConfiguration` now requires a `view_formats` field
The new `view_formats` field in the `TextureDescriptor` is used to specify a list of formats the texture can be re-interpreted to in a texture view. Currently only changing srgb-ness is allowed (ex. `Rgba8Unorm` <=> `Rgba8UnormSrgb`). You should set `view_formats` to `&[]` (empty) unless you have a specific reason not to.
#### The DirectX Shader Compiler (DXC) is now supported on DX12
DXC is now the default shader compiler when using the DX12 backend. DXC is Microsoft's replacement for their legacy FXC compiler, and is faster, less buggy, and allows for modern shader features to be used (ShaderModel 6.0+). DXC requires `dxcompiler.dll` and `dxil.dll` to be available, otherwise it will log a warning and fall back to FXC.
You can get `dxcompiler.dll` and `dxil.dll` by downloading the latest release from [Microsoft's DirectXShaderCompiler github repo](https://github.com/microsoft/DirectXShaderCompiler/releases/latest) and copying them into your project's root directory. These must be included when you distribute your Bevy game/app/etc if you plan on supporting the DX12 backend and are using DXC.
`WgpuSettings` now has a `dx12_shader_compiler` field which can be used to choose between either FXC or DXC (if you pass None for the paths for DXC, it will check for the .dlls in the working directory).
# Objective
Fixes#6931
Continues #6954 by squashing `Msaa` to a flat enum
Helps out #7215
# Solution
```
pub enum Msaa {
Off = 1,
#[default]
Sample4 = 4,
}
```
# Changelog
- Modified
- `Msaa` is now enum
- Defaults to 4 samples
- Uses `.samples()` method to get the sample number as `u32`
# Migration Guide
```
let multi = Msaa { samples: 4 }
// is now
let multi = Msaa::Sample4
multi.samples
// is now
multi.samples()
```
Co-authored-by: Sjael <jakeobrien44@gmail.com>
# Objective
Remove the `VerticalAlign` enum.
Text's alignment field should only affect the text's internal text alignment, not its position. The only way to control a `TextBundle`'s position and bounds should be through the manipulation of the constraints in the `Style` components of the nodes in the Bevy UI's layout tree.
`Text2dBundle` should have a separate `Anchor` component that sets its position relative to its transform.
Related issues: #676, #1490, #5502, #5513, #5834, #6717, #6724, #6741, #6748
## Changelog
* Changed `TextAlignment` into an enum with `Left`, `Center`, and `Right` variants.
* Removed the `HorizontalAlign` and `VerticalAlign` types.
* Added an `Anchor` component to `Text2dBundle`
* Added `Component` derive to `Anchor`
* Use `f32::INFINITY` instead of `f32::MAX` to represent unbounded text in Text2dBounds
## Migration Guide
The `alignment` field of `Text` now only affects the text's internal alignment.
### Change `TextAlignment` to TextAlignment` which is now an enum. Replace:
* `TextAlignment::TOP_LEFT`, `TextAlignment::CENTER_LEFT`, `TextAlignment::BOTTOM_LEFT` with `TextAlignment::Left`
* `TextAlignment::TOP_CENTER`, `TextAlignment::CENTER_LEFT`, `TextAlignment::BOTTOM_CENTER` with `TextAlignment::Center`
* `TextAlignment::TOP_RIGHT`, `TextAlignment::CENTER_RIGHT`, `TextAlignment::BOTTOM_RIGHT` with `TextAlignment::Right`
### Changes for `Text2dBundle`
`Text2dBundle` has a new field 'text_anchor' that takes an `Anchor` component that controls its position relative to its transform.
# Objective
- Allow rendering queue systems to use a `Res<PipelineCache>` even for queueing up new rendering pipelines. This is part of unblocking parallel execution queue systems.
## Solution
- Make `PipelineCache` internally mutable w.r.t to queueing new pipelines. Pipelines are no longer immediately updated into the cache state, but rather queued into a Vec. The Vec of pending new pipelines is then later processed at the same time we actually create the queued pipelines on the GPU device.
---
## Changelog
`PipelineCache` no longer requires mutable access in order to queue render / compute pipelines.
## Migration Guide
* Most usages of `resource_mut::<PipelineCache>` and `ResMut<PipelineCache>` can be changed to `resource::<PipelineCache>` and `Res<PipelineCache>` as long as they don't use any methods requiring mutability - the only public method requiring it is `process_queue`.
# Objective
Pipelines can be customized by wrapping an existing pipeline in a newtype and adding custom logic to its implementation of `SpecializedMeshPipeline::specialize`. To make that easier, the wrapped pipeline type needs to implement `Clone`.
For example, the current non-cloneable pipelines require wrapper pipelines to pull apart the wrapped pipeline like this:
```rust
impl FromWorld for Wireframe2dPipeline {
fn from_world(world: &mut World) -> Self {
let p = &world.resource::<Material2dPipeline<ColorMaterial>>();
Self {
mesh2d_pipeline: p.mesh2d_pipeline.clone(),
material2d_layout: p.material2d_layout.clone(),
vertex_shader: p.vertex_shader.clone(),
fragment_shader: p.fragment_shader.clone(),
}
}
}
```
## Solution
Derive or implement `Clone` on all built-in pipeline types. This is easy to do since they mostly just contain cheaply clonable reference-counted types.
---
## Changelog
Implement `Clone` for all pipeline types.
# Objective
Speed up the render phase of rendering. Simplify the trait structure for render commands.
## Solution
- Merge `EntityPhaseItem` into `PhaseItem` (`EntityPhaseItem::entity` -> `PhaseItem::entity`)
- Merge `EntityRenderCommand` into `RenderCommand`.
- Add two associated types to `RenderCommand`: `RenderCommand::ViewWorldQuery` and `RenderCommand::WorldQuery`.
- Use the new associated types to construct two `QueryStates`s for `RenderCommandState`.
- Hoist any `SQuery<T>` fetches in `EntityRenderCommand`s into the aformentioned two queries. Batch fetch them all at once.
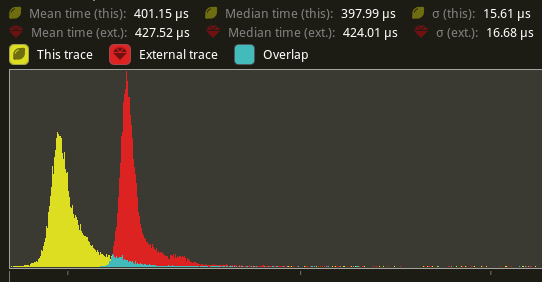
## Performance
`main_opaque_pass_3d` is slightly faster on `many_foxes` (427.52us -> 401.15us)
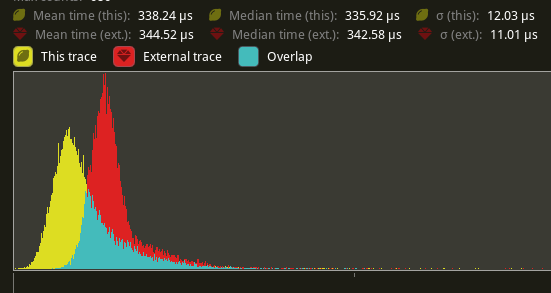
The shadow pass node is also slightly faster (344.52 -> 338.24us)
## Future Work
- Can we hoist the view level queries out of the core loop?
---
## Changelog
Added: `PhaseItem::entity`
Added: `RenderCommand::ViewWorldQuery` associated type.
Added: `RenderCommand::ItemorldQuery` associated type.
Added: `Draw<T>::prepare` optional trait function.
Removed: `EntityPhaseItem` trait
## Migration Guide
TODO
# Objective
- Describe the objective or issue this PR addresses.
SpritePipelineKey could use more constification.
## Solution
Constify SpritePipelineKey implementation.
## Changelog
Co-authored-by: AxiomaticSemantics <117950168+AxiomaticSemantics@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
- Every usage of `DrawFunctionsInternals::get_id()` was followed by a `.unwrap()`. which just adds boilerplate.
## Solution
- Introduce a fallible version of `DrawFunctionsInternals::get_id()` and use it where possible.
- I also took the opportunity to improve the error message a little in the case where it fails.
---
## Changelog
- Added `DrawFunctionsInternals::id()`
# Objective
One of the use-cases for the function `Entity::from_raw` is creating placeholder entity ids, which are meant to be overwritten later. If we use a constant for this instead of `from_raw`, it is more ergonomic and self-documenting.
## Solution
Add a constant that returns an entity ID with an index of `u32::MAX` and a generation of zero. Users are instructed to overwrite this value before using it.
# Objective
- shaders defs can now have a `bool` or `int` value
- `#if SHADER_DEF <operator> 3`
- ok if `SHADER_DEF` is defined, has the correct type and pass the comparison
- `==`, `!=`, `>=`, `>`, `<`, `<=` supported
- `#SHADER_DEF` or `#{SHADER_DEF}`
- will be replaced by the value in the shader code
---
## Migration Guide
- replace `shader_defs.push(String::from("NAME"));` by `shader_defs.push("NAME".into());`
- if you used shader def `NO_STORAGE_BUFFERS_SUPPORT`, check how `AVAILABLE_STORAGE_BUFFER_BINDINGS` is now used in Bevy default shaders
# Objective
- Closes#5262
- Fix color banding caused by quantization.
## Solution
- Adds dithering to the tonemapping node from #3425.
- This is inspired by Godot's default "debanding" shader: https://gist.github.com/belzecue/
- Unlike Godot:
- debanding happens after tonemapping. My understanding is that this is preferred, because we are running the debanding at the last moment before quantization (`[f32, f32, f32, f32]` -> `f32`). This ensures we aren't biasing the dithering strength by applying it in a different (linear) color space.
- This code instead uses and reference the origin source, Valve at GDC 2015
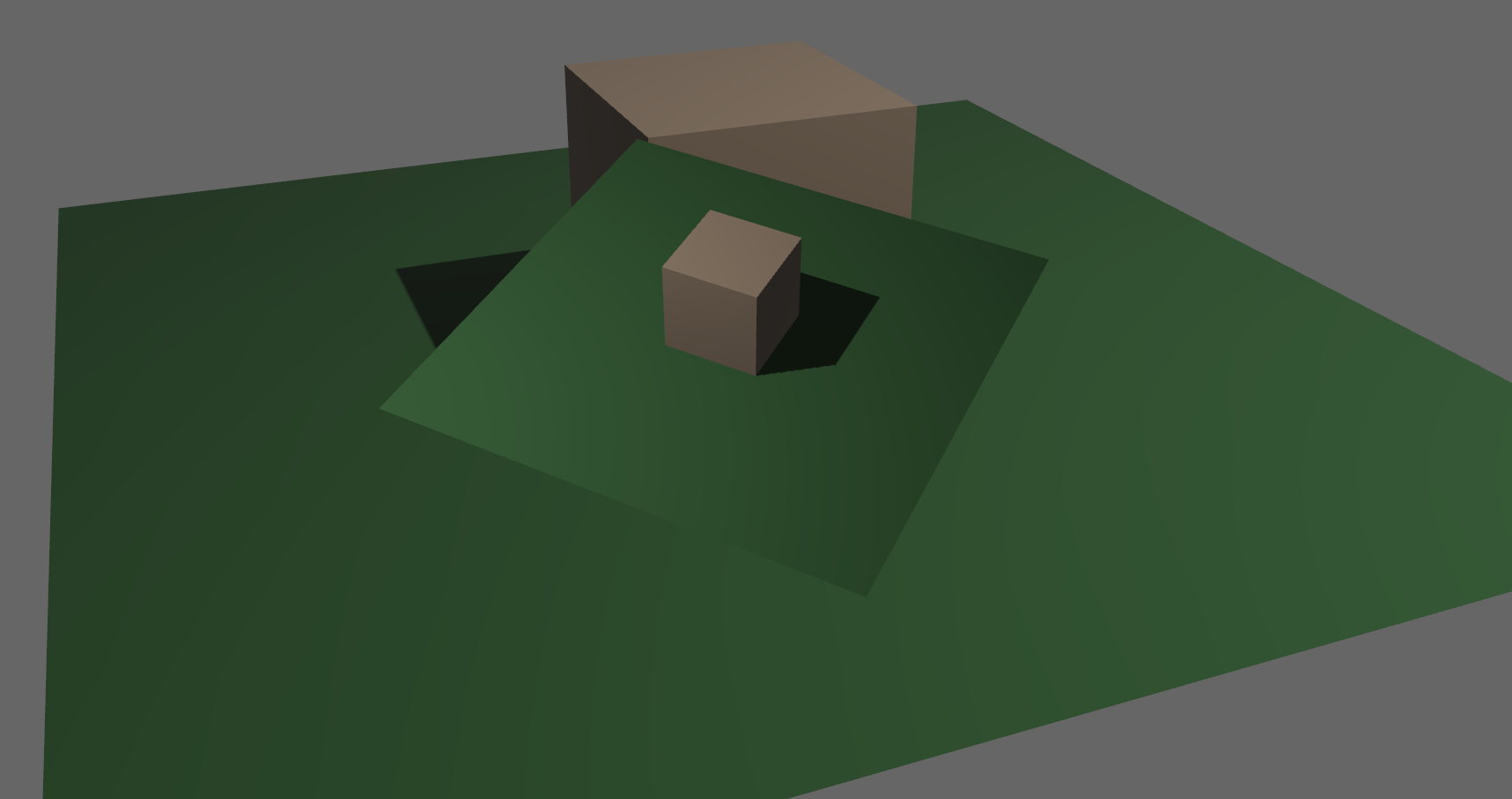
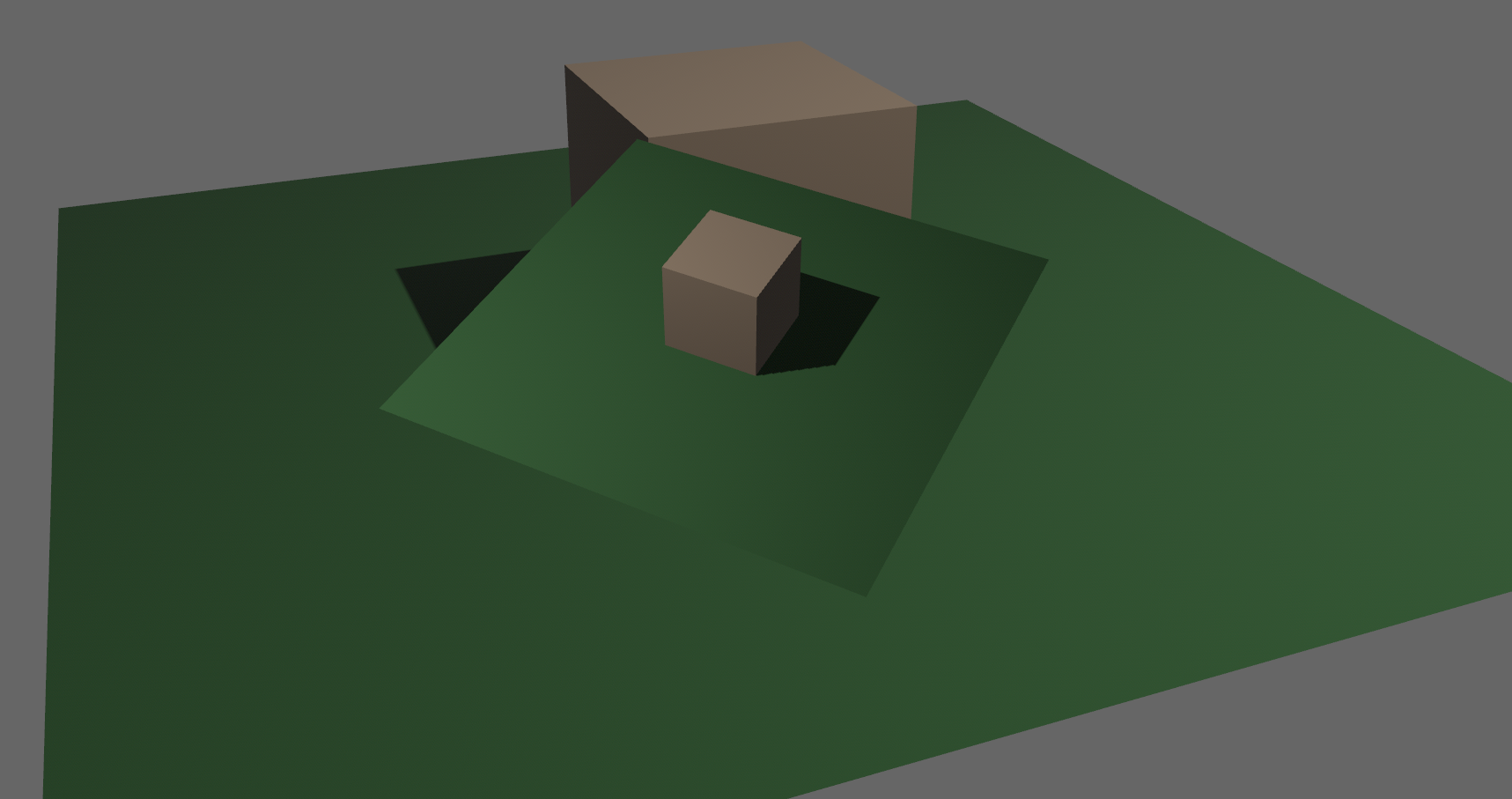
## Additional Notes
Real time rendering to standard dynamic range outputs is limited to 8 bits of depth per color channel. Internally we keep everything in full 32-bit precision (`vec4<f32>`) inside passes and 16-bit between passes until the image is ready to be displayed, at which point the GPU implicitly converts our `vec4<f32>` into a single 32bit value per pixel, with each channel (rgba) getting 8 of those 32 bits.
### The Problem
8 bits of color depth is simply not enough precision to make each step invisible - we only have 256 values per channel! Human vision can perceive steps in luma to about 14 bits of precision. When drawing a very slight gradient, the transition between steps become visible because with a gradient, neighboring pixels will all jump to the next "step" of precision at the same time.
### The Solution
One solution is to simply output in HDR - more bits of color data means the transition between bands will become smaller. However, not everyone has hardware that supports 10+ bit color depth. Additionally, 10 bit color doesn't even fully solve the issue, banding will result in coherent bands on shallow gradients, but the steps will be harder to perceive.
The solution in this PR adds noise to the signal before it is "quantized" or resampled from 32 to 8 bits. Done naively, it's easy to add unneeded noise to the image. To ensure dithering is correct and absolutely minimal, noise is adding *within* one step of the output color depth. When converting from the 32bit to 8bit signal, the value is rounded to the nearest 8 bit value (0 - 255). Banding occurs around the transition from one value to the next, let's say from 50-51. Dithering will never add more than +/-0.5 bits of noise, so the pixels near this transition might round to 50 instead of 51 but will never round more than one step. This means that the output image won't have excess variance:
- in a gradient from 49 to 51, there will be a step between each band at 49, 50, and 51.
- Done correctly, the modified image of this gradient will never have a adjacent pixels more than one step (0-255) from each other.
- I.e. when scanning across the gradient you should expect to see:
```
|-band-| |-band-| |-band-|
Baseline: 49 49 49 50 50 50 51 51 51
Dithered: 49 50 49 50 50 51 50 51 51
Dithered (wrong): 49 50 51 49 50 51 49 51 50
```


You can see from above how correct dithering "fuzzes" the transition between bands to reduce distinct steps in color, without adding excess noise.
### HDR
The previous section (and this PR) assumes the final output is to an 8-bit texture, however this is not always the case. When Bevy adds HDR support, the dithering code will need to take the per-channel depth into account instead of assuming it to be 0-255. Edit: I talked with Rob about this and it seems like the current solution is okay. We may need to revisit once we have actual HDR final image output.
---
## Changelog
### Added
- All pipelines now support deband dithering. This is enabled by default in 3D, and can be toggled in the `Tonemapping` component in camera bundles. Banding is a graphical artifact created when the rendered image is crunched from high precision (f32 per color channel) down to the final output (u8 per channel in SDR). This results in subtle gradients becoming blocky due to the reduced color precision. Deband dithering applies a small amount of noise to the signal before it is "crunched", which breaks up the hard edges of blocks (bands) of color. Note that this does not add excess noise to the image, as the amount of noise is less than a single step of a color channel - just enough to break up the transition between color blocks in a gradient.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>