mirror of
https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy
synced 2025-01-12 13:18:55 +00:00
90 commits
| Author | SHA1 | Message | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
89e98b208f
|
Initial implementation of the Bevy Remote Protocol (Adopted) (#14880)
# Objective Adopted from #13563. The goal is to implement the Bevy Remote Protocol over HTTP/JSON, allowing the ECS to be interacted with remotely. ## Solution At a high level, there are really two separate things that have been undertaken here: 1. First, `RemotePlugin` has been created, which has the effect of embedding a [JSON-RPC](https://www.jsonrpc.org/specification) endpoint into a Bevy application. 2. Second, the [Bevy Remote Protocol verbs](https://gist.github.com/coreh/1baf6f255d7e86e4be29874d00137d1d#file-bevy-remote-protocol-md) (excluding `POLL`) have been implemented as remote methods for that JSON-RPC endpoint under a Bevy-exclusive namespace (e.g. `bevy/get`, `bevy/list`, etc.). To avoid some repetition, here is the crate-level documentation, which explains the request/response structure, built-in-methods, and custom method configuration: <details> <summary>Click to view crate-level docs</summary> ```rust //! An implementation of the Bevy Remote Protocol over HTTP and JSON, to allow //! for remote control of a Bevy app. //! //! Adding the [`RemotePlugin`] to your [`App`] causes Bevy to accept //! connections over HTTP (by default, on port 15702) while your app is running. //! These *remote clients* can inspect and alter the state of the //! entity-component system. Clients are expected to `POST` JSON requests to the //! root URL; see the `client` example for a trivial example of use. //! //! The Bevy Remote Protocol is based on the JSON-RPC 2.0 protocol. //! //! ## Request objects //! //! A typical client request might look like this: //! //! ```json //! { //! "method": "bevy/get", //! "id": 0, //! "params": { //! "entity": 4294967298, //! "components": [ //! "bevy_transform::components::transform::Transform" //! ] //! } //! } //! ``` //! //! The `id` and `method` fields are required. The `param` field may be omitted //! for certain methods: //! //! * `id` is arbitrary JSON data. The server completely ignores its contents, //! and the client may use it for any purpose. It will be copied via //! serialization and deserialization (so object property order, etc. can't be //! relied upon to be identical) and sent back to the client as part of the //! response. //! //! * `method` is a string that specifies one of the possible [`BrpRequest`] //! variants: `bevy/query`, `bevy/get`, `bevy/insert`, etc. It's case-sensitive. //! //! * `params` is parameter data specific to the request. //! //! For more information, see the documentation for [`BrpRequest`]. //! [`BrpRequest`] is serialized to JSON via `serde`, so [the `serde` //! documentation] may be useful to clarify the correspondence between the Rust //! structure and the JSON format. //! //! ## Response objects //! //! A response from the server to the client might look like this: //! //! ```json //! { //! "jsonrpc": "2.0", //! "id": 0, //! "result": { //! "bevy_transform::components::transform::Transform": { //! "rotation": { "x": 0.0, "y": 0.0, "z": 0.0, "w": 1.0 }, //! "scale": { "x": 1.0, "y": 1.0, "z": 1.0 }, //! "translation": { "x": 0.0, "y": 0.5, "z": 0.0 } //! } //! } //! } //! ``` //! //! The `id` field will always be present. The `result` field will be present if the //! request was successful. Otherwise, an `error` field will replace it. //! //! * `id` is the arbitrary JSON data that was sent as part of the request. It //! will be identical to the `id` data sent during the request, modulo //! serialization and deserialization. If there's an error reading the `id` field, //! it will be `null`. //! //! * `result` will be present if the request succeeded and will contain the response //! specific to the request. //! //! * `error` will be present if the request failed and will contain an error object //! with more information about the cause of failure. //! //! ## Error objects //! //! An error object might look like this: //! //! ```json //! { //! "code": -32602, //! "message": "Missing \"entity\" field" //! } //! ``` //! //! The `code` and `message` fields will always be present. There may also be a `data` field. //! //! * `code` is an integer representing the kind of an error that happened. Error codes documented //! in the [`error_codes`] module. //! //! * `message` is a short, one-sentence human-readable description of the error. //! //! * `data` is an optional field of arbitrary type containing additional information about the error. //! //! ## Built-in methods //! //! The Bevy Remote Protocol includes a number of built-in methods for accessing and modifying data //! in the ECS. Each of these methods uses the `bevy/` prefix, which is a namespace reserved for //! BRP built-in methods. //! //! ### bevy/get //! //! Retrieve the values of one or more components from an entity. //! //! `params`: //! - `entity`: The ID of the entity whose components will be fetched. //! - `components`: An array of fully-qualified type names of components to fetch. //! //! `result`: A map associating each type name to its value on the requested entity. //! //! ### bevy/query //! //! Perform a query over components in the ECS, returning all matching entities and their associated //! component values. //! //! All of the arrays that comprise this request are optional, and when they are not provided, they //! will be treated as if they were empty. //! //! `params`: //! `params`: //! - `data`: //! - `components` (optional): An array of fully-qualified type names of components to fetch. //! - `option` (optional): An array of fully-qualified type names of components to fetch optionally. //! - `has` (optional): An array of fully-qualified type names of components whose presence will be //! reported as boolean values. //! - `filter` (optional): //! - `with` (optional): An array of fully-qualified type names of components that must be present //! on entities in order for them to be included in results. //! - `without` (optional): An array of fully-qualified type names of components that must *not* be //! present on entities in order for them to be included in results. //! //! `result`: An array, each of which is an object containing: //! - `entity`: The ID of a query-matching entity. //! - `components`: A map associating each type name from `components`/`option` to its value on the matching //! entity if the component is present. //! - `has`: A map associating each type name from `has` to a boolean value indicating whether or not the //! entity has that component. If `has` was empty or omitted, this key will be omitted in the response. //! //! ### bevy/spawn //! //! Create a new entity with the provided components and return the resulting entity ID. //! //! `params`: //! - `components`: A map associating each component's fully-qualified type name with its value. //! //! `result`: //! - `entity`: The ID of the newly spawned entity. //! //! ### bevy/destroy //! //! Despawn the entity with the given ID. //! //! `params`: //! - `entity`: The ID of the entity to be despawned. //! //! `result`: null. //! //! ### bevy/remove //! //! Delete one or more components from an entity. //! //! `params`: //! - `entity`: The ID of the entity whose components should be removed. //! - `components`: An array of fully-qualified type names of components to be removed. //! //! `result`: null. //! //! ### bevy/insert //! //! Insert one or more components into an entity. //! //! `params`: //! - `entity`: The ID of the entity to insert components into. //! - `components`: A map associating each component's fully-qualified type name with its value. //! //! `result`: null. //! //! ### bevy/reparent //! //! Assign a new parent to one or more entities. //! //! `params`: //! - `entities`: An array of entity IDs of entities that will be made children of the `parent`. //! - `parent` (optional): The entity ID of the parent to which the child entities will be assigned. //! If excluded, the given entities will be removed from their parents. //! //! `result`: null. //! //! ### bevy/list //! //! List all registered components or all components present on an entity. //! //! When `params` is not provided, this lists all registered components. If `params` is provided, //! this lists only those components present on the provided entity. //! //! `params` (optional): //! - `entity`: The ID of the entity whose components will be listed. //! //! `result`: An array of fully-qualified type names of components. //! //! ## Custom methods //! //! In addition to the provided methods, the Bevy Remote Protocol can be extended to include custom //! methods. This is primarily done during the initialization of [`RemotePlugin`], although the //! methods may also be extended at runtime using the [`RemoteMethods`] resource. //! //! ### Example //! ```ignore //! fn main() { //! App::new() //! .add_plugins(DefaultPlugins) //! .add_plugins( //! // `default` adds all of the built-in methods, while `with_method` extends them //! RemotePlugin::default() //! .with_method("super_user/cool_method".to_owned(), path::to::my:🆒:handler) //! // ... more methods can be added by chaining `with_method` //! ) //! .add_systems( //! // ... standard application setup //! ) //! .run(); //! } //! ``` //! //! The handler is expected to be a system-convertible function which takes optional JSON parameters //! as input and returns a [`BrpResult`]. This means that it should have a type signature which looks //! something like this: //! ``` //! # use serde_json::Value; //! # use bevy_ecs::prelude::{In, World}; //! # use bevy_remote::BrpResult; //! fn handler(In(params): In<Option<Value>>, world: &mut World) -> BrpResult { //! todo!() //! } //! ``` //! //! Arbitrary system parameters can be used in conjunction with the optional `Value` input. The //! handler system will always run with exclusive `World` access. //! //! [the `serde` documentation]: https://serde.rs/ ``` </details> ### Message lifecycle At a high level, the lifecycle of client-server interactions is something like this: 1. The client sends one or more `BrpRequest`s. The deserialized version of that is just the Rust representation of a JSON-RPC request, and it looks like this: ```rust pub struct BrpRequest { /// The action to be performed. Parsing is deferred for the sake of error reporting. pub method: Option<Value>, /// Arbitrary data that will be returned verbatim to the client as part of /// the response. pub id: Option<Value>, /// The parameters, specific to each method. /// /// These are passed as the first argument to the method handler. /// Sometimes params can be omitted. pub params: Option<Value>, } ``` 2. These requests are accumulated in a mailbox resource (small lie but close enough). 3. Each update, the mailbox is drained by a system `process_remote_requests`, where each request is processed according to its `method`, which has an associated handler. Each handler is a Bevy system that runs with exclusive world access and returns a result; e.g.: ```rust pub fn process_remote_get_request(In(params): In<Option<Value>>, world: &World) -> BrpResult { // ... } ``` 4. The result (or an error) is reported back to the client. ## Testing This can be tested by using the `server` and `client` examples. The `client` example is not particularly exhaustive at the moment (it only creates barebones `bevy/query` requests) but is still informative. Other queries can be made using `curl` with the `server` example running. For example, to make a `bevy/list` request and list all registered components: ```bash curl -X POST -d '{ "jsonrpc": "2.0", "id": 1, "method": "bevy/list" }' 127.0.0.1:15702 | jq . ``` --- ## Future direction There were a couple comments on BRP versioning while this was in draft. I agree that BRP versioning is a good idea, but I think that it requires some consensus on a couple fronts: - First of all, what does the version actually mean? Is it a version for the protocol itself or for the `bevy/*` methods implemented using it? Both? - Where does the version actually live? The most natural place is just where we have `"jsonrpc"` right now (at least if it's versioning the protocol itself), but this means we're not actually conforming to JSON-RPC any more (so, for example, any client library used to construct JSON-RPC requests would stop working). I'm not really against that, but it's at least a real decision. - What do we actually do when we encounter mismatched versions? Adding handling for this would be actual scope creep instead of just a little add-on in my opinion. Another thing that would be nice is making the internal structure of the implementation less JSON-specific. Right now, for example, component values that will appear in server responses are quite eagerly converted to JSON `Value`s, which prevents disentangling the handler logic from the communication medium, but it can probably be done in principle and I imagine it would enable more code reuse (e.g. for custom method handlers) in addition to making the internals more readily usable for other formats. --------- Co-authored-by: Patrick Walton <pcwalton@mimiga.net> Co-authored-by: DragonGamesStudios <margos.michal@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: Christopher Biscardi <chris@christopherbiscardi.com> Co-authored-by: Gino Valente <49806985+MrGVSV@users.noreply.github.com> |
||
|
|
55c84cc722
|
Added HeadlessPlugins (#15203) (#15260)
Added a `HeadlessPlugins` plugin group, that adds more default functionality (like logging) than the `MinimumPlugins`. Fixes #15203 Changed the headless example to use the new plugin group. I am not entirely sure if the list of plugins is correct. Are there ones that should be added / removed? ---- The `TerminalCtrlCHandlerPlugin` has interesting effects in the headless example: Installing it a second time it will give a log message about skipping installation, because it is already installed. Ctrl+C will terminate the application in that case. However, _not_ installing it the second time (so only on the app that runs once) has the effect that the app that runs continuously cannot be stopped using Ctrl+C. This implies that, even though the second app did not install the Ctrl+C handler, it did _something_ because it was keeping the one from the first app alive. Not sure if this is a problem or issue, or can be labeled a wierd quirk of having multiple Apps in one executable. |
||
|
|
4ac2a63556
|
Remove all existing system order ambiguities in DefaultPlugins (#15031)
# Objective As discussed in https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/7386, system order ambiguities within `DefaultPlugins` are a source of bugs in the engine and badly pollute diagnostic output for users. We should eliminate them! This PR is an alternative to #15027: with all external ambiguities silenced, this should be much less prone to merge conflicts and the test output should be much easier for authors to understand. Note that system order ambiguities are still permitted in the `RenderApp`: these need a bit of thought in terms of how to test them, and will be fairly involved to fix. While these aren't *good*, they'll generally only cause graphical bugs, not logic ones. ## Solution All remaining system order ambiguities have been resolved. Review this PR commit-by-commit to see how each of these problems were fixed. ## Testing `cargo run --example ambiguity_detection` passes with no panics or logging! |
||
|
|
6adf31babf
|
hooking up observers and clicking for ui node (#14695)
Makes the newly merged picking usable for UI elements. currently it both triggers the events, as well as sends them as throught commands.trigger_targets. We should probably figure out if this is needed for them all. # Objective Hooks up obserers and picking for a very simple example ## Solution upstreamed the UI picking backend from bevy_mod_picking ## Testing tested with the new example picking/simple_picking.rs --- --------- Co-authored-by: Lixou <82600264+DasLixou@users.noreply.github.com> Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: Kristoffer Søholm <k.soeholm@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
d722fef23d
|
Remove deprecated bevy_dynamic_plugin (#14534)
# Objective - Dynamic plugins were deprecated in #13080 due to being unsound. The plan was to deprecate them in 0.14 and remove them in 0.15. ## Solution - Remove all dynamic plugin functionality. - Update documentation to reflect this change. --- ## Migration Guide Dynamic plugins were deprecated in 0.14 for being unsound, and they have now been fully removed. Please consider using the alternatives listed in the `bevy_dynamic_plugin` crate documentation, or worst-case scenario you may copy the code from 0.14. |
||
|
|
c3057d4353
|
plugin_group! macro (adopted) (#14339)
# Objective - Adopted from #11460. - Closes #7332. - The documentation for `DefaultPlugins` and `MinimalPlugins` frequently goes out of date because it is not . ## Solution - Create a macro, `plugin_group!`, to automatically create `PluginGroup`s and document them. ## Testing - Run `cargo-expand` on the generated code for `DefaultPlugins` and `MinimalPlugins`. - Try creating a custom plugin group with the macro. --- ## Showcase - You can now define custom `PluginGroup`s using the `plugin_group!` macro. ```rust plugin_group! { /// My really cool plugic group! pub struct MyPluginGroup { physics:::PhysicsPlugin, rendering:::RenderingPlugin, ui:::UiPlugin, } } ``` <details> <summary>Expanded output</summary> ```rust /// My really cool plugic group! /// /// - [`PhysicsPlugin`](physics::PhysicsPlugin) /// - [`RenderingPlugin`](rendering::RenderingPlugin) /// - [`UiPlugin`](ui::UiPlugin) pub struct MyPluginGroup; impl ::bevy_app::PluginGroup for MyPluginGroup { fn build(self) -> ::bevy_app::PluginGroupBuilder { let mut group = ::bevy_app::PluginGroupBuilder::start::<Self>(); { const _: () = { const fn check_default<T: Default>() {} check_default::<physics::PhysicsPlugin>(); }; group = group.add(<physics::PhysicsPlugin>::default()); } { const _: () = { const fn check_default<T: Default>() {} check_default::<rendering::RenderingPlugin>(); }; group = group.add(<rendering::RenderingPlugin>::default()); } { const _: () = { const fn check_default<T: Default>() {} check_default::<ui::UiPlugin>(); }; group = group.add(<ui::UiPlugin>::default()); } group } } ``` </details> --------- Co-authored-by: Doonv <58695417+doonv@users.noreply.github.com> Co-authored-by: Mateusz Wachowiak <mateusz_wachowiak@outlook.com> |
||
|
|
d7080369a7
|
Fix intra-doc links and make CI test them (#14076)
# Objective - Bevy currently has lot of invalid intra-doc links, let's fix them! - Also make CI test them, to avoid future regressions. - Helps with #1983 (but doesn't fix it, as there could still be explicit links to docs.rs that are broken) ## Solution - Make `cargo r -p ci -- doc-check` check fail on warnings (could also be changed to just some specific lints) - Manually fix all the warnings (note that in some cases it was unclear to me what the fix should have been, I'll try to highlight them in a self-review) |
||
|
|
f607be8777
|
Handle Ctrl+C in the terminal properly (#14001)
# Objective Fixes #13995. ## Solution Override the default `Ctrl+C` handler with one that sends `AppExit` event to every app with `TerminalCtrlCHandlerPlugin`. ## Testing Tested by running the `3d_scene` example and hitting `Ctrl+C` in the terminal. --- ## Changelog Handles `Ctrl+C` in the terminal gracefully. ## Migration Guide If you are overriding the `Ctrl+C` handler then you should call `TerminalCtrlCHandlerPlugin::gracefully_exit` from your handler. It will tell the app to exit. |
||
|
|
aaccbe88aa
|
Upstream CorePlugin from bevy_mod_picking (#13677)
# Objective This is the first of a series of PRs intended to begin the upstreaming process for `bevy_mod_picking`. The purpose of this PR is to: + Create the new `bevy_picking` crate + Upstream `CorePlugin` as `PickingPlugin` + Upstream the core pointer and backend abstractions. This code has been ported verbatim from the corresponding files in [bevy_picking_core](https://github.com/aevyrie/bevy_mod_picking/tree/main/crates/bevy_picking_core/src) with a few tiny naming and docs tweaks. The work here is only an initial foothold to get the up-streaming process started in earnest. We can do refactoring and improvements once this is in-tree. --------- Co-authored-by: Aevyrie <aevyrie@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
ba198151a4
|
Add missing plugins to doc of DefaultPlugins (#13833)
StatesPlugin and GizmoPlugin were missing from the doc comment of DefaultPlugins. I am not sure whether this was for a reason, but i just stumbled over it and it seemed off... ## Testing I'm not sure how to test these changes? |
||
|
|
25f7a29a2f
|
Move state installation methods from bevy_app to bevy_state (#13637)
# Objective After separating `bevy_states`, state installation methods like `init_state` were kept in `bevy_app` under the `bevy_state` feature flag. This is problematic, because `bevy_state` is not a core module, `bevy_app` is, yet it depends on `bevy_state`. This causes practical problems like the inability to use `bevy_hierarchy` inside `bevy_state`, because of circular dependencies. ## Solution - `bevy_state` now has a `bevy_app` feature flag, which gates the new `AppStateExt` trait. All previous state installation methods were moved to this trait. It's implemented for both `SubApp` and `App`. ## Changelog - All state related app methods are now in `AppExtStates` trait in `bevy_state`. - Added `StatesPlugin` which is in `DefaultPlugins` when `bevy_state` is enabled. ## Migration Guide `App::init_state` is now provided by the `bevy_state::app::AppExtStates;` trait: import it if you need this method and are not blob-importing the `bevy` prelude. |
||
|
|
061bee7e3c
|
fix: upgrade to winit v0.30 (#13366)
# Objective - Upgrade winit to v0.30 - Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/13331 ## Solution This is a rewrite/adaptation of the new trait system described and implemented in `winit` v0.30. ## Migration Guide The custom UserEvent is now renamed as WakeUp, used to wake up the loop if anything happens outside the app (a new [custom_user_event](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/13366/files#diff-2de8c0a8d3028d0059a3d80ae31b2bbc1cde2595ce2d317ea378fe3e0cf6ef2d) shows this behavior. The internal `UpdateState` has been removed and replaced internally by the AppLifecycle. When changed, the AppLifecycle is sent as an event. The `UpdateMode` now accepts only two values: `Continuous` and `Reactive`, but the latter exposes 3 new properties to enable reactive to device, user or window events. The previous `UpdateMode::Reactive` is now equivalent to `UpdateMode::reactive()`, while `UpdateMode::ReactiveLowPower` to `UpdateMode::reactive_low_power()`. The `ApplicationLifecycle` has been renamed as `AppLifecycle`, and now contains the possible values of the application state inside the event loop: * `Idle`: the loop has not started yet * `Running` (previously called `Started`): the loop is running * `WillSuspend`: the loop is going to be suspended * `Suspended`: the loop is suspended * `WillResume`: the loop is going to be resumed Note: the `Resumed` state has been removed since the resumed app is just running. Finally, now that `winit` enables this, it extends the `WinitPlugin` to support custom events. ## Test platforms - [x] Windows - [x] MacOs - [x] Linux (x11) - [x] Linux (Wayland) - [x] Android - [x] iOS - [x] WASM/WebGPU - [x] WASM/WebGL2 ## Outstanding issues / regressions - [ ] iOS: build failed in CI - blocking, but may just be flakiness - [x] Cross-platform: when the window is maximised, changes in the scale factor don't apply, to make them apply one has to make the window smaller again. (Re-maximising keeps the updated scale factor) - non-blocking, but good to fix - [ ] Android: it's pretty easy to quickly open and close the app and then the music keeps playing when suspended. - non-blocking but worrying - [ ] Web: the application will hang when switching tabs - Not new, duplicate of https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/13486 - [ ] Cross-platform?: Screenshot failure, `ERROR present_frames: wgpu_core::present: No work has been submitted for this frame before` taking the first screenshot, but after pressing space - non-blocking, but good to fix --------- Co-authored-by: François <francois.mockers@vleue.com> |
||
|
|
5559632977
|
glTF labels: add enum to avoid misspelling and keep up-to-date list documented (#13586)
# Objective - Followup to #13548 - It added a list of all possible labels to documentation. This seems hard to keep up and doesn't stop people from making spelling mistake ## Solution - Add an enum that can create all the labels possible, and encourage its use rather than manually typed labels --------- Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: Rob Parrett <robparrett@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
b0409f63d5
|
Refactor ci_testing and separate it from DevToolsPlugin (#13513)
# Objective - We use [`ci_testing`](https://dev-docs.bevyengine.org/bevy/dev_tools/ci_testing/index.html) to specify per-example configuration on when to take a screenshot, when to exit, etc. - In the future more features may be added, such as #13512. To support this growth, `ci_testing` should be easier to read and maintain. ## Solution - Convert `ci_testing.rs` into the folder `ci_testing`, splitting the configuration and systems into `ci_testing/config.rs` and `ci_testing/systems.rs`. - Convert `setup_app` into the plugin `CiTestingPlugin`. This new plugin is added to both `DefaultPlugins` and `MinimalPlugins`. - Remove `DevToolsPlugin` from `MinimalPlugins`, since it was only used for CI testing. - Clean up some code, add many comments, and add a few unit tests. ## Testing The most important part is that this still passes all of the CI validation checks (merge queue), since that is when it will be used the most. I don't think I changed any behavior, so it should operate the same. You can also test it locally using: ```shell # Run the breakout example, enabling `bevy_ci_testing` and loading the configuration used in CI. CI_TESTING_CONFIG=".github/example-run/breakout.ron" cargo r --example breakout -F bevy_ci_testing ``` --- ## Changelog - Added `CiTestingPlugin`, which is split off from `DevToolsPlugin`. - Removed `DevToolsPlugin` from `MinimalPlugins`. ## Migration Guide Hi maintainers! I believe `DevToolsPlugin` was added within the same release as this PR, so I don't think a migration guide is needed. `DevToolsPlugin` is no longer included in `MinimalPlugins`, so you will need to remove it manually. ```rust // Before App::new() .add_plugins(MinimalPlugins) .run(); // After App::new() .add_plugins(MinimalPlugins) .add_plugins(DevToolsPlugin) .run(); ``` --------- Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: François Mockers <francois.mockers@vleue.com> |
||
|
|
42ba9dfaea
|
Separate state crate (#13216)
# Objective Extracts the state mechanisms into a new crate called "bevy_state". This comes with a few goals: - state wasn't really an inherent machinery of the ecs system, and so keeping it within bevy_ecs felt forced - by mixing it in with bevy_ecs, the maintainability of our more robust state system was significantly compromised moving state into a new crate makes it easier to encapsulate as it's own feature, and easier to read and understand since it's no longer a single, massive file. ## Solution move the state-related elements from bevy_ecs to a new crate ## Testing - Did you test these changes? If so, how? all the automated tests migrated and passed, ran the pre-existing examples without changes to validate. --- ## Migration Guide Since bevy_state is now gated behind the `bevy_state` feature, projects that use state but don't use the `default-features` will need to add that feature flag. Since it is no longer part of bevy_ecs, projects that use bevy_ecs directly will need to manually pull in `bevy_state`, trigger the StateTransition schedule, and handle any of the elements that bevy_app currently sets up. --------- Co-authored-by: Kristoffer Søholm <k.soeholm@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
bb76a2c69c
|
multi_threaded feature rename (#12997)
# Objective Fixes #12966 ## Solution Renaming multi_threaded feature to match snake case ## Migration Guide Bevy feature multi-threaded should be refered to multi_threaded from now on. |
||
|
|
6b95b0137a
|
Switch monolithic lib to module re-exports (#13059)
# Objective Makes crate module docs render correctly in the docs for the monolithic library. Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/13055. ## Solution Swap from ```rust pub mod foo { pub use bevy_foo::*; } ``` to ```rust pub use bevy_foo as foo; ``` |
||
|
|
7b8d502083
|
Fix beta lints (#12980)
# Objective - Fixes #12976 ## Solution This one is a doozy. - Run `cargo +beta clippy --workspace --all-targets --all-features` and fix all issues - This includes: - Moving inner attributes to be outer attributes, when the item in question has both inner and outer attributes - Use `ptr::from_ref` in more scenarios - Extend the valid idents list used by `clippy:doc_markdown` with more names - Use `Clone::clone_from` when possible - Remove redundant `ron` import - Add backticks to **so many** identifiers and items - I'm sorry whoever has to review this --- ## Changelog - Added links to more identifiers in documentation. |
||
|
|
7363268ea8
|
Fix ambiguities causing a crash (#12780)
# Objective - Disabling some plugins causes a crash due to ambiguities relying in feature flags and not checking if both plugins are enabled causing code like this to crash: `app.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins.build().disable::<AnimationPlugin>())` ## Solution - Check if plugins were added before ambiguities. - Move bevy_gizmos ambiguities from bevy_internal to bevy_gizmos since they already depend on them. |
||
|
|
d8383fb535
|
Move PanicHandlerPlugin into bevy_app (#12640)
# Objective - Move `PanicHandlerPlugin` into `bevy_app` - Fixes #12603 . ## Solution - I moved the `bevy_panic_handler` into `bevy_app` - Copy pasted `bevy_panic_handler`'s lib.rs into a separate module in `bevy_app` as a `panic_handler.rs` module file and added the `PanicHandlerPlugin` in lib.rs of `bevy_app` - added the dependency into `cargo.toml` ## Review notes - I probably want some feedback if I imported App and Plugin correctly in `panic_handler.rs` line 10 and 11. - As of yet I have not deleted `bevy_panic_handler` crate, wanted to get a check if I added it correctly. - Once validated that my move was correct, I'll probably have to remove the panic handler find default plugins which I probably need some help to find. - And then remove bevy panic_handler and making sure ci passes. - This is my first issue for contributing to bevy so let me know if I am doing anything wrong. ## tools context - rust is 1.76 version - Windows 11 --------- Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
56bcbb0975
|
Forbid unsafe in most crates in the engine (#12684)
# Objective Resolves #3824. `unsafe` code should be the exception, not the norm in Rust. It's obviously needed for various use cases as it's interfacing with platforms and essentially running the borrow checker at runtime in the ECS, but the touted benefits of Bevy is that we are able to heavily leverage Rust's safety, and we should be holding ourselves accountable to that by minimizing our unsafe footprint. ## Solution Deny `unsafe_code` workspace wide. Add explicit exceptions for the following crates, and forbid it in almost all of the others. * bevy_ecs - Obvious given how much unsafe is needed to achieve performant results * bevy_ptr - Works with raw pointers, even more low level than bevy_ecs. * bevy_render - due to needing to integrate with wgpu * bevy_window - due to needing to integrate with raw_window_handle * bevy_utils - Several unsafe utilities used by bevy_ecs. Ideally moved into bevy_ecs instead of made publicly usable. * bevy_reflect - Required for the unsafe type casting it's doing. * bevy_transform - for the parallel transform propagation * bevy_gizmos - For the SystemParam impls it has. * bevy_assets - To support reflection. Might not be required, not 100% sure yet. * bevy_mikktspace - due to being a conversion from a C library. Pending safe rewrite. * bevy_dynamic_plugin - Inherently unsafe due to the dynamic loading nature. Several uses of unsafe were rewritten, as they did not need to be using them: * bevy_text - a case of `Option::unchecked` could be rewritten as a normal for loop and match instead of an iterator. * bevy_color - the Pod/Zeroable implementations were replaceable with bytemuck's derive macros. |
||
|
|
f096ad4155
|
Set the logo and favicon for all of Bevy's published crates (#12696)
# Objective Currently the built docs only shows the logo and favicon for the top level `bevy` crate. This makes views like https://docs.rs/bevy_ecs/latest/bevy_ecs/ look potentially unrelated to the project at first glance. ## Solution Reproduce the docs attributes for every crate that Bevy publishes. Ideally this would be done with some workspace level Cargo.toml control, but AFAICT, such support does not exist. |
||
|
|
72c51cdab9
|
Make feature(doc_auto_cfg) work (#12642)
# Objective - In #12366 `![cfg_attr(docsrs, feature(doc_auto_cfg))] `was added. But to apply it it needs `--cfg=docsrs` in rustdoc-args. ## Solution - Apply `--cfg=docsrs` to all crates and CI. I also added `[package.metadata.docs.rs]` to all crates to avoid adding code behind a feature and forget adding the metadata. Before:  After:  |
||
|
|
7c7d1e8a64
|
refactor: separate out PanicHandlerPlugin (#12557)
# Objective - Allow configuring of platform-specific panic handlers. - Remove the silent overwrite of the WASM panic handler - Closes #12546 ## Solution - Separates the panic handler to a new plugin, `PanicHandlerPlugin`. - `PanicHandlerPlugin` was added to `DefaultPlugins`. - Can be disabled on `DefaultPlugins`, in the case someone needs to configure custom panic handlers. --- ## Changelog ### Added - A `PanicHandlerPlugin` was added to the `DefaultPlugins`, which now sets sensible target-specific panic handlers. ### Changed - On WASM, the panic stack trace was output to the console through the `BevyLogPlugin`. Since this was separated out into `PanicHandlerPlugin`, you may need to add the new `PanicHandlerPlugin` (included in `DefaultPlugins`). ## Migration Guide - If you used `MinimalPlugins` with `LogPlugin` for a WASM-target build, you will need to add the new `PanicHandlerPlugin` to set the panic behavior to output to the console. Otherwise, you will see the default panic handler (opaque, `unreachable` errors in the console). |
||
|
|
0baedcf55c
|
Fix minimal plugins in ci (#12370)
# Objective - #11341 broke running code using `MinimalPlugins` in CI ## Solution - include `DevToolsPlugin` in `MinimalPlugins` |
||
|
|
6533170e94
|
Add bevy_dev_tools crate (#11341)
# Objective - Resolves #11309 ## Solution - Add `bevy_dev_tools` crate as a default feature. - Add `DevToolsPlugin` and add it to an app if the `bevy_dev_tools` feature is enabled. `bevy_dev_tools` is reserved by @alice-i-cecile, should we wait until it gets transferred to cart before merging? --------- Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: BD103 <59022059+BD103@users.noreply.github.com> |
||
|
|
599e5e4e76
|
Migrate from LegacyColor to bevy_color::Color (#12163)
# Objective - As part of the migration process we need to a) see the end effect of the migration on user ergonomics b) check for serious perf regressions c) actually migrate the code - To accomplish this, I'm going to attempt to migrate all of the remaining user-facing usages of `LegacyColor` in one PR, being careful to keep a clean commit history. - Fixes #12056. ## Solution I've chosen to use the polymorphic `Color` type as our standard user-facing API. - [x] Migrate `bevy_gizmos`. - [x] Take `impl Into<Color>` in all `bevy_gizmos` APIs - [x] Migrate sprites - [x] Migrate UI - [x] Migrate `ColorMaterial` - [x] Migrate `MaterialMesh2D` - [x] Migrate fog - [x] Migrate lights - [x] Migrate StandardMaterial - [x] Migrate wireframes - [x] Migrate clear color - [x] Migrate text - [x] Migrate gltf loader - [x] Register color types for reflection - [x] Remove `LegacyColor` - [x] Make sure CI passes Incidental improvements to ease migration: - added `Color::srgba_u8`, `Color::srgba_from_array` and friends - added `set_alpha`, `is_fully_transparent` and `is_fully_opaque` to the `Alpha` trait - add and immediately deprecate (lol) `Color::rgb` and friends in favor of more explicit and consistent `Color::srgb` - standardized on white and black for most example text colors - added vector field traits to `LinearRgba`: ~~`Add`, `Sub`, `AddAssign`, `SubAssign`,~~ `Mul<f32>` and `Div<f32>`. Multiplications and divisions do not scale alpha. `Add` and `Sub` have been cut from this PR. - added `LinearRgba` and `Srgba` `RED/GREEN/BLUE` - added `LinearRgba_to_f32_array` and `LinearRgba::to_u32` ## Migration Guide Bevy's color types have changed! Wherever you used a `bevy::render::Color`, a `bevy::color::Color` is used instead. These are quite similar! Both are enums storing a color in a specific color space (or to be more precise, using a specific color model). However, each of the different color models now has its own type. TODO... - `Color::rgba`, `Color::rgb`, `Color::rbga_u8`, `Color::rgb_u8`, `Color::rgb_from_array` are now `Color::srgba`, `Color::srgb`, `Color::srgba_u8`, `Color::srgb_u8` and `Color::srgb_from_array`. - `Color::set_a` and `Color::a` is now `Color::set_alpha` and `Color::alpha`. These are part of the `Alpha` trait in `bevy_color`. - `Color::is_fully_transparent` is now part of the `Alpha` trait in `bevy_color` - `Color::r`, `Color::set_r`, `Color::with_r` and the equivalents for `g`, `b` `h`, `s` and `l` have been removed due to causing silent relatively expensive conversions. Convert your `Color` into the desired color space, perform your operations there, and then convert it back into a polymorphic `Color` enum. - `Color::hex` is now `Srgba::hex`. Call `.into` or construct a `Color::Srgba` variant manually to convert it. - `WireframeMaterial`, `ExtractedUiNode`, `ExtractedDirectionalLight`, `ExtractedPointLight`, `ExtractedSpotLight` and `ExtractedSprite` now store a `LinearRgba`, rather than a polymorphic `Color` - `Color::rgb_linear` and `Color::rgba_linear` are now `Color::linear_rgb` and `Color::linear_rgba` - The various CSS color constants are no longer stored directly on `Color`. Instead, they're defined in the `Srgba` color space, and accessed via `bevy::color::palettes::css`. Call `.into()` on them to convert them into a `Color` for quick debugging use, and consider using the much prettier `tailwind` palette for prototyping. - The `LIME_GREEN` color has been renamed to `LIMEGREEN` to comply with the standard naming. - Vector field arithmetic operations on `Color` (add, subtract, multiply and divide by a f32) have been removed. Instead, convert your colors into `LinearRgba` space, and perform your operations explicitly there. This is particularly relevant when working with emissive or HDR colors, whose color channel values are routinely outside of the ordinary 0 to 1 range. - `Color::as_linear_rgba_f32` has been removed. Call `LinearRgba::to_f32_array` instead, converting if needed. - `Color::as_linear_rgba_u32` has been removed. Call `LinearRgba::to_u32` instead, converting if needed. - Several other color conversion methods to transform LCH or HSL colors into float arrays or `Vec` types have been removed. Please reimplement these externally or open a PR to re-add them if you found them particularly useful. - Various methods on `Color` such as `rgb` or `hsl` to convert the color into a specific color space have been removed. Convert into `LinearRgba`, then to the color space of your choice. - Various implicitly-converting color value methods on `Color` such as `r`, `g`, `b` or `h` have been removed. Please convert it into the color space of your choice, then check these properties. - `Color` no longer implements `AsBindGroup`. Store a `LinearRgba` internally instead to avoid conversion costs. --------- Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecil@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: Afonso Lage <lage.afonso@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: Rob Parrett <robparrett@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: Zachary Harrold <zac@harrold.com.au> |
||
|
|
2fbb4c68ae
|
Define a prelude for bevy_color, and add it to bevy_internal (#12158)
# Objective As we start to migrate to `bevy_color` in earnest (#12056), we should make it visible to Bevy users, and usable in examples. ## Solution 1. Add a prelude to `bevy_color`: I've only excluded the rarely used `ColorRange` type and the testing-focused color distance module. I definitely think that some color spaces are less useful than others to end users, but at the same time the types used there are very unlikely to conflict with user-facing types. 2. Add `bevy_color` to `bevy_internal` as an optional crate. 3. Re-export `bevy_color`'s prelude as part of `bevy::prelude`. --------- Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecil@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
de004da8d5
|
Rename bevy_render::Color to LegacyColor (#12069)
# Objective The migration process for `bevy_color` (#12013) will be fairly involved: there will be hundreds of affected files, and a large number of APIs. ## Solution To allow us to proceed granularly, we're going to keep both `bevy_color::Color` (new) and `bevy_render::Color` (old) around until the migration is complete. However, simply doing this directly is confusing! They're both called `Color`, making it very hard to tell when a portion of the code has been ported. As discussed in #12056, by renaming the old `Color` type, we can make it easier to gradually migrate over, one API at a time. ## Migration Guide THIS MIGRATION GUIDE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK. This change should not be shipped to end users: delete this section in the final migration guide! --------- Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecil@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
5f1dd3918b
|
Rework animation to be done in two phases. (#11707)
# Objective Bevy's animation system currently does tree traversals based on `Name` that aren't necessary. Not only do they require in unsafe code because tree traversals are awkward with parallelism, but they are also somewhat slow, brittle, and complex, which manifested itself as way too many queries in #11670. # Solution Divide animation into two phases: animation *advancement* and animation *evaluation*, which run after one another. *Advancement* operates on the `AnimationPlayer` and sets the current animation time to match the game time. *Evaluation* operates on all animation bones in the scene in parallel and sets the transforms and/or morph weights based on the time and the clip. To do this, we introduce a new component, `AnimationTarget`, which the asset loader places on every bone. It contains the ID of the entity containing the `AnimationPlayer`, as well as a UUID that identifies which bone in the animation the target corresponds to. In the case of glTF, the UUID is derived from the full path name to the bone. The rule that `AnimationTarget`s are descendants of the entity containing `AnimationPlayer` is now just a convention, not a requirement; this allows us to eliminate the unsafe code. # Migration guide * `AnimationClip` now uses UUIDs instead of hierarchical paths based on the `Name` component to refer to bones. This has several consequences: - A new component, `AnimationTarget`, should be placed on each bone that you wish to animate, in order to specify its UUID and the associated `AnimationPlayer`. The glTF loader automatically creates these components as necessary, so most uses of glTF rigs shouldn't need to change. - Moving a bone around the tree, or renaming it, no longer prevents an `AnimationPlayer` from affecting it. - Dynamically changing the `AnimationPlayer` component will likely require manual updating of the `AnimationTarget` components. * Entities with `AnimationPlayer` components may now possess descendants that also have `AnimationPlayer` components. They may not, however, animate the same bones. * As they aren't specific to `TypeId`s, `bevy_reflect::utility::NoOpTypeIdHash` and `bevy_reflect::utility::NoOpTypeIdHasher` have been renamed to `bevy_reflect::utility::NoOpHash` and `bevy_reflect::utility::NoOpHasher` respectively. |
||
|
|
694c06f3d0
|
Inverse missing_docs logic (#11676)
# Objective Currently the `missing_docs` lint is allowed-by-default and enabled at crate level when their documentations is complete (see #3492). This PR proposes to inverse this logic by making `missing_docs` warn-by-default and mark crates with imcomplete docs allowed. ## Solution Makes `missing_docs` warn at workspace level and allowed at crate level when the docs is imcomplete. |
||
|
|
59b4921827
|
Add Accessibility plugin to default plugins docs (#11512)
# Objective - Fixes #11453 This is a temporary fix. There is PR fixing it (#11460), but I'm not sure if it's going to be merged before the 0.13 release. |
||
|
|
a657478675
|
resolve all internal ambiguities (#10411)
- ignore all ambiguities that are not a problem - remove `.before(Assets::<Image>::track_assets),` that points into a different schedule (-> should this be caught?) - add some explicit orderings: - run `poll_receivers` and `update_accessibility_nodes` after `window_closed` in `bevy_winit::accessibility` - run `bevy_ui::accessibility::calc_bounds` after `CameraUpdateSystem` - run ` bevy_text::update_text2d_layout` and `bevy_ui::text_system` after `font_atlas_set::remove_dropped_font_atlas_sets` - add `app.ignore_ambiguity(a, b)` function for cases where you want to ignore an ambiguity between two independent plugins `A` and `B` - add `IgnoreAmbiguitiesPlugin` in `DefaultPlugins` that allows cross-crate ambiguities like `bevy_animation`/`bevy_ui` - Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/9511 ## Before **Render**  **PostUpdate**  ## After **Render**  **PostUpdate**  --------- Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecil@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
fd308571c4
|
Remove unnecessary path prefixes (#10749)
# Objective - Shorten paths by removing unnecessary prefixes ## Solution - Remove the prefixes from many paths which do not need them. Finding the paths was done automatically using built-in refactoring tools in Jetbrains RustRover. |
||
|
|
951c9bb1a2
|
Add [lints] table, fix adding #![allow(clippy::type_complexity)] everywhere (#10011)
# Objective - Fix adding `#![allow(clippy::type_complexity)]` everywhere. like #9796 ## Solution - Use the new [lints] table that will land in 1.74 (https://doc.rust-lang.org/nightly/cargo/reference/unstable.html#lints) - inherit lint to the workspace, crates and examples. ``` [lints] workspace = true ``` ## Changelog - Bump rust version to 1.74 - Enable lints table for the workspace ```toml [workspace.lints.clippy] type_complexity = "allow" ``` - Allow type complexity for all crates and examples ```toml [lints] workspace = true ``` --------- Co-authored-by: Martín Maita <47983254+mnmaita@users.noreply.github.com> |
||
|
|
8b21ee45c0
|
Allow Bevy to start from non-main threads on supported platforms (#10020)
# Objective Allow Bevy apps to run without requiring to start from the main thread. This allows other projects and applications to do things like spawning a normal or scoped thread and run Bevy applications there. The current behaviour if you try this is a panic. ## Solution Allow this by default on platforms winit supports this behaviour on (x11, Wayland, Windows). --- ## Changelog ### Added - Added the ability to start Bevy apps outside of the main thread on x11, Wayland, Windows --------- Signed-off-by: Torstein Grindvik <torstein.grindvik@nordicsemi.no> Signed-off-by: Torstein Grindvik <torstein.grindvik@muybridge.com> Co-authored-by: Torstein Grindvik <torstein.grindvik@muybridge.com> Co-authored-by: James Liu <contact@jamessliu.com> |
||
|
|
5e00379431
|
Remove TypeRegistry re-export rename (#9807)
# Objective
The rename is confusing. Each time I import `TypeRegistry` I have to
think at least 10 seconds about how to import it. And I've been working
a lot with bevy reflect, which multiplies the papercut.
In my crates, you can find lots of:
```rust
use bevy::reflect::{TypeRegistryInternal as TypeRegistry};
```
When I "go to definition" on `TypeRegistry` I get to `TypeRegistryArc`.
And when I mean `TypeRegistry` in my function signature, 100% of the
time I mean `TypeRegistry`, not the arc wrapper.
Rust has borrowing, and most use-cases of the TypeRegistry accepts
borrow of the registry, with no need to mutate it.
`TypeRegistryInternal` is also confusing. In bevy crates, it doesn't
exist. The bevy crate documentation often refers to `TypeRegistry` and
link to `TypeRegistryInternal`. It only exists in the bevy re-exports.
It makes it hard to understand which names qualifies which types.
## Solution
Remove the rename, keep the type names as they are in `bevy_reflect`
---
## Changelog
- Remove `TypeRegistry` and `TypeRegistryArc` renames from bevy
`bevy_reflect` re-exports.
## Migration Guide
- `TypeRegistry` as re-exported by the wrapper `bevy` crate is now
`TypeRegistryArc`
- `TypeRegistryInternal` as re-exported by the wrapper `bevy` crate is
now `TypeRegistry`
|
||
|
|
5eb292dc10
|
Bevy Asset V2 (#8624)
# Bevy Asset V2 Proposal ## Why Does Bevy Need A New Asset System? Asset pipelines are a central part of the gamedev process. Bevy's current asset system is missing a number of features that make it non-viable for many classes of gamedev. After plenty of discussions and [a long community feedback period](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/discussions/3972), we've identified a number missing features: * **Asset Preprocessing**: it should be possible to "preprocess" / "compile" / "crunch" assets at "development time" rather than when the game starts up. This enables offloading expensive work from deployed apps, faster asset loading, less runtime memory usage, etc. * **Per-Asset Loader Settings**: Individual assets cannot define their own loaders that override the defaults. Additionally, they cannot provide per-asset settings to their loaders. This is a huge limitation, as many asset types don't provide all information necessary for Bevy _inside_ the asset. For example, a raw PNG image says nothing about how it should be sampled (ex: linear vs nearest). * **Asset `.meta` files**: assets should have configuration files stored adjacent to the asset in question, which allows the user to configure asset-type-specific settings. These settings should be accessible during the pre-processing phase. Modifying a `.meta` file should trigger a re-processing / re-load of the asset. It should be possible to configure asset loaders from the meta file. * **Processed Asset Hot Reloading**: Changes to processed assets (or their dependencies) should result in re-processing them and re-loading the results in live Bevy Apps. * **Asset Dependency Tracking**: The current bevy_asset has no good way to wait for asset dependencies to load. It punts this as an exercise for consumers of the loader apis, which is unreasonable and error prone. There should be easy, ergonomic ways to wait for assets to load and block some logic on an asset's entire dependency tree loading. * **Runtime Asset Loading**: it should be (optionally) possible to load arbitrary assets dynamically at runtime. This necessitates being able to deploy and run the asset server alongside Bevy Apps on _all platforms_. For example, we should be able to invoke the shader compiler at runtime, stream scenes from sources like the internet, etc. To keep deployed binaries (and startup times) small, the runtime asset server configuration should be configurable with different settings compared to the "pre processor asset server". * **Multiple Backends**: It should be possible to load assets from arbitrary sources (filesystems, the internet, remote asset serves, etc). * **Asset Packing**: It should be possible to deploy assets in compressed "packs", which makes it easier and more efficient to distribute assets with Bevy Apps. * **Asset Handoff**: It should be possible to hold a "live" asset handle, which correlates to runtime data, without actually holding the asset in memory. Ex: it must be possible to hold a reference to a GPU mesh generated from a "mesh asset" without keeping the mesh data in CPU memory * **Per-Platform Processed Assets**: Different platforms and app distributions have different capabilities and requirements. Some platforms need lower asset resolutions or different asset formats to operate within the hardware constraints of the platform. It should be possible to define per-platform asset processing profiles. And it should be possible to deploy only the assets required for a given platform. These features have architectural implications that are significant enough to require a full rewrite. The current Bevy Asset implementation got us this far, but it can take us no farther. This PR defines a brand new asset system that implements most of these features, while laying the foundations for the remaining features to be built. ## Bevy Asset V2 Here is a quick overview of the features introduced in this PR. * **Asset Preprocessing**: Preprocess assets at development time into more efficient (and configurable) representations * **Dependency Aware**: Dependencies required to process an asset are tracked. If an asset's processed dependency changes, it will be reprocessed * **Hot Reprocessing/Reloading**: detect changes to asset source files, reprocess them if they have changed, and then hot-reload them in Bevy Apps. * **Only Process Changes**: Assets are only re-processed when their source file (or meta file) has changed. This uses hashing and timestamps to avoid processing assets that haven't changed. * **Transactional and Reliable**: Uses write-ahead logging (a technique commonly used by databases) to recover from crashes / forced-exits. Whenever possible it avoids full-reprocessing / only uncompleted transactions will be reprocessed. When the processor is running in parallel with a Bevy App, processor asset writes block Bevy App asset reads. Reading metadata + asset bytes is guaranteed to be transactional / correctly paired. * **Portable / Run anywhere / Database-free**: The processor does not rely on an in-memory database (although it uses some database techniques for reliability). This is important because pretty much all in-memory databases have unsupported platforms or build complications. * **Configure Processor Defaults Per File Type**: You can say "use this processor for all files of this type". * **Custom Processors**: The `Processor` trait is flexible and unopinionated. It can be implemented by downstream plugins. * **LoadAndSave Processors**: Most asset processing scenarios can be expressed as "run AssetLoader A, save the results using AssetSaver X, and then load the result using AssetLoader B". For example, load this png image using `PngImageLoader`, which produces an `Image` asset and then save it using `CompressedImageSaver` (which also produces an `Image` asset, but in a compressed format), which takes an `Image` asset as input. This means if you have an `AssetLoader` for an asset, you are already half way there! It also means that you can share AssetSavers across multiple loaders. Because `CompressedImageSaver` accepts Bevy's generic Image asset as input, it means you can also use it with some future `JpegImageLoader`. * **Loader and Saver Settings**: Asset Loaders and Savers can now define their own settings types, which are passed in as input when an asset is loaded / saved. Each asset can define its own settings. * **Asset `.meta` files**: configure asset loaders, their settings, enable/disable processing, and configure processor settings * **Runtime Asset Dependency Tracking** Runtime asset dependencies (ex: if an asset contains a `Handle<Image>`) are tracked by the asset server. An event is emitted when an asset and all of its dependencies have been loaded * **Unprocessed Asset Loading**: Assets do not require preprocessing. They can be loaded directly. A processed asset is just a "normal" asset with some extra metadata. Asset Loaders don't need to know or care about whether or not an asset was processed. * **Async Asset IO**: Asset readers/writers use async non-blocking interfaces. Note that because Rust doesn't yet support async traits, there is a bit of manual Boxing / Future boilerplate. This will hopefully be removed in the near future when Rust gets async traits. * **Pluggable Asset Readers and Writers**: Arbitrary asset source readers/writers are supported, both by the processor and the asset server. * **Better Asset Handles** * **Single Arc Tree**: Asset Handles now use a single arc tree that represents the lifetime of the asset. This makes their implementation simpler, more efficient, and allows us to cheaply attach metadata to handles. Ex: the AssetPath of a handle is now directly accessible on the handle itself! * **Const Typed Handles**: typed handles can be constructed in a const context. No more weird "const untyped converted to typed at runtime" patterns! * **Handles and Ids are Smaller / Faster To Hash / Compare**: Typed `Handle<T>` is now much smaller in memory and `AssetId<T>` is even smaller. * **Weak Handle Usage Reduction**: In general Handles are now considered to be "strong". Bevy features that previously used "weak `Handle<T>`" have been ported to `AssetId<T>`, which makes it statically clear that the features do not hold strong handles (while retaining strong type information). Currently Handle::Weak still exists, but it is very possible that we can remove that entirely. * **Efficient / Dense Asset Ids**: Assets now have efficient dense runtime asset ids, which means we can avoid expensive hash lookups. Assets are stored in Vecs instead of HashMaps. There are now typed and untyped ids, which means we no longer need to store dynamic type information in the ID for typed handles. "AssetPathId" (which was a nightmare from a performance and correctness standpoint) has been entirely removed in favor of dense ids (which are retrieved for a path on load) * **Direct Asset Loading, with Dependency Tracking**: Assets that are defined at runtime can still have their dependencies tracked by the Asset Server (ex: if you create a material at runtime, you can still wait for its textures to load). This is accomplished via the (currently optional) "asset dependency visitor" trait. This system can also be used to define a set of assets to load, then wait for those assets to load. * **Async folder loading**: Folder loading also uses this system and immediately returns a handle to the LoadedFolder asset, which means folder loading no longer blocks on directory traversals. * **Improved Loader Interface**: Loaders now have a specific "top level asset type", which makes returning the top-level asset simpler and statically typed. * **Basic Image Settings and Processing**: Image assets can now be processed into the gpu-friendly Basic Universal format. The ImageLoader now has a setting to define what format the image should be loaded as. Note that this is just a minimal MVP ... plenty of additional work to do here. To demo this, enable the `basis-universal` feature and turn on asset processing. * **Simpler Audio Play / AudioSink API**: Asset handle providers are cloneable, which means the Audio resource can mint its own handles. This means you can now do `let sink_handle = audio.play(music)` instead of `let sink_handle = audio_sinks.get_handle(audio.play(music))`. Note that this might still be replaced by https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/8424. **Removed Handle Casting From Engine Features**: Ex: FontAtlases no longer use casting between handle types ## Using The New Asset System ### Normal Unprocessed Asset Loading By default the `AssetPlugin` does not use processing. It behaves pretty much the same way as the old system. If you are defining a custom asset, first derive `Asset`: ```rust #[derive(Asset)] struct Thing { value: String, } ``` Initialize the asset: ```rust app.init_asset:<Thing>() ``` Implement a new `AssetLoader` for it: ```rust #[derive(Default)] struct ThingLoader; #[derive(Serialize, Deserialize, Default)] pub struct ThingSettings { some_setting: bool, } impl AssetLoader for ThingLoader { type Asset = Thing; type Settings = ThingSettings; fn load<'a>( &'a self, reader: &'a mut Reader, settings: &'a ThingSettings, load_context: &'a mut LoadContext, ) -> BoxedFuture<'a, Result<Thing, anyhow::Error>> { Box::pin(async move { let mut bytes = Vec::new(); reader.read_to_end(&mut bytes).await?; // convert bytes to value somehow Ok(Thing { value }) }) } fn extensions(&self) -> &[&str] { &["thing"] } } ``` Note that this interface will get much cleaner once Rust gets support for async traits. `Reader` is an async futures_io::AsyncRead. You can stream bytes as they come in or read them all into a `Vec<u8>`, depending on the context. You can use `let handle = load_context.load(path)` to kick off a dependency load, retrieve a handle, and register the dependency for the asset. Then just register the loader in your Bevy app: ```rust app.init_asset_loader::<ThingLoader>() ``` Now just add your `Thing` asset files into the `assets` folder and load them like this: ```rust fn system(asset_server: Res<AssetServer>) { let handle = Handle<Thing> = asset_server.load("cool.thing"); } ``` You can check load states directly via the asset server: ```rust if asset_server.load_state(&handle) == LoadState::Loaded { } ``` You can also listen for events: ```rust fn system(mut events: EventReader<AssetEvent<Thing>>, handle: Res<SomeThingHandle>) { for event in events.iter() { if event.is_loaded_with_dependencies(&handle) { } } } ``` Note the new `AssetEvent::LoadedWithDependencies`, which only fires when the asset is loaded _and_ all dependencies (and their dependencies) have loaded. Unlike the old asset system, for a given asset path all `Handle<T>` values point to the same underlying Arc. This means Handles can cheaply hold more asset information, such as the AssetPath: ```rust // prints the AssetPath of the handle info!("{:?}", handle.path()) ``` ### Processed Assets Asset processing can be enabled via the `AssetPlugin`. When developing Bevy Apps with processed assets, do this: ```rust app.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins.set(AssetPlugin::processed_dev())) ``` This runs the `AssetProcessor` in the background with hot-reloading. It reads assets from the `assets` folder, processes them, and writes them to the `.imported_assets` folder. Asset loads in the Bevy App will wait for a processed version of the asset to become available. If an asset in the `assets` folder changes, it will be reprocessed and hot-reloaded in the Bevy App. When deploying processed Bevy apps, do this: ```rust app.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins.set(AssetPlugin::processed())) ``` This does not run the `AssetProcessor` in the background. It behaves like `AssetPlugin::unprocessed()`, but reads assets from `.imported_assets`. When the `AssetProcessor` is running, it will populate sibling `.meta` files for assets in the `assets` folder. Meta files for assets that do not have a processor configured look like this: ```rust ( meta_format_version: "1.0", asset: Load( loader: "bevy_render::texture::image_loader::ImageLoader", settings: ( format: FromExtension, ), ), ) ``` This is metadata for an image asset. For example, if you have `assets/my_sprite.png`, this could be the metadata stored at `assets/my_sprite.png.meta`. Meta files are totally optional. If no metadata exists, the default settings will be used. In short, this file says "load this asset with the ImageLoader and use the file extension to determine the image type". This type of meta file is supported in all AssetPlugin modes. If in `Unprocessed` mode, the asset (with the meta settings) will be loaded directly. If in `ProcessedDev` mode, the asset file will be copied directly to the `.imported_assets` folder. The meta will also be copied directly to the `.imported_assets` folder, but with one addition: ```rust ( meta_format_version: "1.0", processed_info: Some(( hash: 12415480888597742505, full_hash: 14344495437905856884, process_dependencies: [], )), asset: Load( loader: "bevy_render::texture::image_loader::ImageLoader", settings: ( format: FromExtension, ), ), ) ``` `processed_info` contains `hash` (a direct hash of the asset and meta bytes), `full_hash` (a hash of `hash` and the hashes of all `process_dependencies`), and `process_dependencies` (the `path` and `full_hash` of every process_dependency). A "process dependency" is an asset dependency that is _directly_ used when processing the asset. Images do not have process dependencies, so this is empty. When the processor is enabled, you can use the `Process` metadata config: ```rust ( meta_format_version: "1.0", asset: Process( processor: "bevy_asset::processor::process::LoadAndSave<bevy_render::texture::image_loader::ImageLoader, bevy_render::texture::compressed_image_saver::CompressedImageSaver>", settings: ( loader_settings: ( format: FromExtension, ), saver_settings: ( generate_mipmaps: true, ), ), ), ) ``` This configures the asset to use the `LoadAndSave` processor, which runs an AssetLoader and feeds the result into an AssetSaver (which saves the given Asset and defines a loader to load it with). (for terseness LoadAndSave will likely get a shorter/friendlier type name when [Stable Type Paths](#7184) lands). `LoadAndSave` is likely to be the most common processor type, but arbitrary processors are supported. `CompressedImageSaver` saves an `Image` in the Basis Universal format and configures the ImageLoader to load it as basis universal. The `AssetProcessor` will read this meta, run it through the LoadAndSave processor, and write the basis-universal version of the image to `.imported_assets`. The final metadata will look like this: ```rust ( meta_format_version: "1.0", processed_info: Some(( hash: 905599590923828066, full_hash: 9948823010183819117, process_dependencies: [], )), asset: Load( loader: "bevy_render::texture::image_loader::ImageLoader", settings: ( format: Format(Basis), ), ), ) ``` To try basis-universal processing out in Bevy examples, (for example `sprite.rs`), change `add_plugins(DefaultPlugins)` to `add_plugins(DefaultPlugins.set(AssetPlugin::processed_dev()))` and run with the `basis-universal` feature enabled: `cargo run --features=basis-universal --example sprite`. To create a custom processor, there are two main paths: 1. Use the `LoadAndSave` processor with an existing `AssetLoader`. Implement the `AssetSaver` trait, register the processor using `asset_processor.register_processor::<LoadAndSave<ImageLoader, CompressedImageSaver>>(image_saver.into())`. 2. Implement the `Process` trait directly and register it using: `asset_processor.register_processor(thing_processor)`. You can configure default processors for file extensions like this: ```rust asset_processor.set_default_processor::<ThingProcessor>("thing") ``` There is one more metadata type to be aware of: ```rust ( meta_format_version: "1.0", asset: Ignore, ) ``` This will ignore the asset during processing / prevent it from being written to `.imported_assets`. The AssetProcessor stores a transaction log at `.imported_assets/log` and uses it to gracefully recover from unexpected stops. This means you can force-quit the processor (and Bevy Apps running the processor in parallel) at arbitrary times! `.imported_assets` is "local state". It should _not_ be checked into source control. It should also be considered "read only". In practice, you _can_ modify processed assets and processed metadata if you really need to test something. But those modifications will not be represented in the hashes of the assets, so the processed state will be "out of sync" with the source assets. The processor _will not_ fix this for you. Either revert the change after you have tested it, or delete the processed files so they can be re-populated. ## Open Questions There are a number of open questions to be discussed. We should decide if they need to be addressed in this PR and if so, how we will address them: ### Implied Dependencies vs Dependency Enumeration There are currently two ways to populate asset dependencies: * **Implied via AssetLoaders**: if an AssetLoader loads an asset (and retrieves a handle), a dependency is added to the list. * **Explicit via the optional Asset::visit_dependencies**: if `server.load_asset(my_asset)` is called, it will call `my_asset.visit_dependencies`, which will grab dependencies that have been manually defined for the asset via the Asset trait impl (which can be derived). This means that defining explicit dependencies is optional for "loaded assets". And the list of dependencies is always accurate because loaders can only produce Handles if they register dependencies. If an asset was loaded with an AssetLoader, it only uses the implied dependencies. If an asset was created at runtime and added with `asset_server.load_asset(MyAsset)`, it will use `Asset::visit_dependencies`. However this can create a behavior mismatch between loaded assets and equivalent "created at runtime" assets if `Assets::visit_dependencies` doesn't exactly match the dependencies produced by the AssetLoader. This behavior mismatch can be resolved by completely removing "implied loader dependencies" and requiring `Asset::visit_dependencies` to supply dependency data. But this creates two problems: * It makes defining loaded assets harder and more error prone: Devs must remember to manually annotate asset dependencies with `#[dependency]` when deriving `Asset`. For more complicated assets (such as scenes), the derive likely wouldn't be sufficient and a manual `visit_dependencies` impl would be required. * Removes the ability to immediately kick off dependency loads: When AssetLoaders retrieve a Handle, they also immediately kick off an asset load for the handle, which means it can start loading in parallel _before_ the asset finishes loading. For large assets, this could be significant. (although this could be mitigated for processed assets if we store dependencies in the processed meta file and load them ahead of time) ### Eager ProcessorDev Asset Loading I made a controversial call in the interest of fast startup times ("time to first pixel") for the "processor dev mode configuration". When initializing the AssetProcessor, current processed versions of unchanged assets are yielded immediately, even if their dependencies haven't been checked yet for reprocessing. This means that non-current-state-of-filesystem-but-previously-valid assets might be returned to the App first, then hot-reloaded if/when their dependencies change and the asset is reprocessed. Is this behavior desirable? There is largely one alternative: do not yield an asset from the processor to the app until all of its dependencies have been checked for changes. In some common cases (load dependency has not changed since last run) this will increase startup time. The main question is "by how much" and is that slower startup time worth it in the interest of only yielding assets that are true to the current state of the filesystem. Should this be configurable? I'm starting to think we should only yield an asset after its (historical) dependencies have been checked for changes + processed as necessary, but I'm curious what you all think. ### Paths Are Currently The Only Canonical ID / Do We Want Asset UUIDs? In this implementation AssetPaths are the only canonical asset identifier (just like the previous Bevy Asset system and Godot). Moving assets will result in re-scans (and currently reprocessing, although reprocessing can easily be avoided with some changes). Asset renames/moves will break code and assets that rely on specific paths, unless those paths are fixed up. Do we want / need "stable asset uuids"? Introducing them is very possible: 1. Generate a UUID and include it in .meta files 2. Support UUID in AssetPath 3. Generate "asset indices" which are loaded on startup and map UUIDs to paths. 4 (maybe). Consider only supporting UUIDs for processed assets so we can generate quick-to-load indices instead of scanning meta files. The main "pro" is that assets referencing UUIDs don't need to be migrated when a path changes. The main "con" is that UUIDs cannot be "lazily resolved" like paths. They need a full view of all assets to answer the question "does this UUID exist". Which means UUIDs require the AssetProcessor to fully finish startup scans before saying an asset doesnt exist. And they essentially require asset pre-processing to use in apps, because scanning all asset metadata files at runtime to resolve a UUID is not viable for medium-to-large apps. It really requires a pre-generated UUID index, which must be loaded before querying for assets. I personally think this should be investigated in a separate PR. Paths aren't going anywhere ... _everyone_ uses filesystems (and filesystem-like apis) to manage their asset source files. I consider them permanent canonical asset information. Additionally, they behave well for both processed and unprocessed asset modes. Given that Bevy is supporting both, this feels like the right canonical ID to start with. UUIDS (and maybe even other indexed-identifier types) can be added later as necessary. ### Folder / File Naming Conventions All asset processing config currently lives in the `.imported_assets` folder. The processor transaction log is in `.imported_assets/log`. Processed assets are added to `.imported_assets/Default`, which will make migrating to processed asset profiles (ex: a `.imported_assets/Mobile` profile) a non-breaking change. It also allows us to create top-level files like `.imported_assets/log` without it being interpreted as an asset. Meta files currently have a `.meta` suffix. Do we like these names and conventions? ### Should the `AssetPlugin::processed_dev` configuration enable `watch_for_changes` automatically? Currently it does (which I think makes sense), but it does make it the only configuration that enables watch_for_changes by default. ### Discuss on_loaded High Level Interface: This PR includes a very rough "proof of concept" `on_loaded` system adapter that uses the `LoadedWithDependencies` event in combination with `asset_server.load_asset` dependency tracking to support this pattern ```rust fn main() { App::new() .init_asset::<MyAssets>() .add_systems(Update, on_loaded(create_array_texture)) .run(); } #[derive(Asset, Clone)] struct MyAssets { #[dependency] picture_of_my_cat: Handle<Image>, #[dependency] picture_of_my_other_cat: Handle<Image>, } impl FromWorld for ArrayTexture { fn from_world(world: &mut World) -> Self { picture_of_my_cat: server.load("meow.png"), picture_of_my_other_cat: server.load("meeeeeeeow.png"), } } fn spawn_cat(In(my_assets): In<MyAssets>, mut commands: Commands) { commands.spawn(SpriteBundle { texture: my_assets.picture_of_my_cat.clone(), ..default() }); commands.spawn(SpriteBundle { texture: my_assets.picture_of_my_other_cat.clone(), ..default() }); } ``` The implementation is _very_ rough. And it is currently unsafe because `bevy_ecs` doesn't expose some internals to do this safely from inside `bevy_asset`. There are plenty of unanswered questions like: * "do we add a Loadable" derive? (effectively automate the FromWorld implementation above) * Should `MyAssets` even be an Asset? (largely implemented this way because it elegantly builds on `server.load_asset(MyAsset { .. })` dependency tracking). We should think hard about what our ideal API looks like (and if this is a pattern we want to support). Not necessarily something we need to solve in this PR. The current `on_loaded` impl should probably be removed from this PR before merging. ## Clarifying Questions ### What about Assets as Entities? This Bevy Asset V2 proposal implementation initially stored Assets as ECS Entities. Instead of `AssetId<T>` + the `Assets<T>` resource it used `Entity` as the asset id and Asset values were just ECS components. There are plenty of compelling reasons to do this: 1. Easier to inline assets in Bevy Scenes (as they are "just" normal entities + components) 2. More flexible queries: use the power of the ECS to filter assets (ex: `Query<Mesh, With<Tree>>`). 3. Extensible. Users can add arbitrary component data to assets. 4. Things like "component visualization tools" work out of the box to visualize asset data. However Assets as Entities has a ton of caveats right now: * We need to be able to allocate entity ids without a direct World reference (aka rework id allocator in Entities ... i worked around this in my prototypes by just pre allocating big chunks of entities) * We want asset change events in addition to ECS change tracking ... how do we populate them when mutations can come from anywhere? Do we use Changed queries? This would require iterating over the change data for all assets every frame. Is this acceptable or should we implement a new "event based" component change detection option? * Reconciling manually created assets with asset-system managed assets has some nuance (ex: are they "loaded" / do they also have that component metadata?) * "how do we handle "static" / default entity handles" (ties in to the Entity Indices discussion: https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/discussions/8319). This is necessary for things like "built in" assets and default handles in things like SpriteBundle. * Storing asset information as a component makes it easy to "invalidate" asset state by removing the component (or forcing modifications). Ideally we have ways to lock this down (some combination of Rust type privacy and ECS validation) In practice, how we store and identify assets is a reasonably superficial change (porting off of Assets as Entities and implementing dedicated storage + ids took less than a day). So once we sort out the remaining challenges the flip should be straightforward. Additionally, I do still have "Assets as Entities" in my commit history, so we can reuse that work. I personally think "assets as entities" is a good endgame, but it also doesn't provide _significant_ value at the moment and it certainly isn't ready yet with the current state of things. ### Why not Distill? [Distill](https://github.com/amethyst/distill) is a high quality fully featured asset system built in Rust. It is very natural to ask "why not just use Distill?". It is also worth calling out that for awhile, [we planned on adopting Distill / I signed off on it](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/708). However I think Bevy has a number of constraints that make Distill adoption suboptimal: * **Architectural Simplicity:** * Distill's processor requires an in-memory database (lmdb) and RPC networked API (using Cap'n Proto). Each of these introduces API complexity that increases maintenance burden and "code grokability". Ignoring tests, documentation, and examples, Distill has 24,237 lines of Rust code (including generated code for RPC + database interactions). If you ignore generated code, it has 11,499 lines. * Bevy builds the AssetProcessor and AssetServer using pluggable AssetReader/AssetWriter Rust traits with simple io interfaces. They do not necessitate databases or RPC interfaces (although Readers/Writers could use them if that is desired). Bevy Asset V2 (at the time of writing this PR) is 5,384 lines of Rust code (ignoring tests, documentation, and examples). Grain of salt: Distill does have more features currently (ex: Asset Packing, GUIDS, remote-out-of-process asset processor). I do plan to implement these features in Bevy Asset V2 and I personally highly doubt they will meaningfully close the 6115 lines-of-code gap. * This complexity gap (which while illustrated by lines of code, is much bigger than just that) is noteworthy to me. Bevy should be hackable and there are pillars of Distill that are very hard to understand and extend. This is a matter of opinion (and Bevy Asset V2 also has complicated areas), but I think Bevy Asset V2 is much more approachable for the average developer. * Necessary disclaimer: counting lines of code is an extremely rough complexity metric. Read the code and form your own opinions. * **Optional Asset Processing:** Not all Bevy Apps (or Bevy App developers) need / want asset preprocessing. Processing increases the complexity of the development environment by introducing things like meta files, imported asset storage, running processors in the background, waiting for processing to finish, etc. Distill _requires_ preprocessing to work. With Bevy Asset V2 processing is fully opt-in. The AssetServer isn't directly aware of asset processors at all. AssetLoaders only care about converting bytes to runtime Assets ... they don't know or care if the bytes were pre-processed or not. Processing is "elegantly" (forgive my self-congratulatory phrasing) layered on top and builds on the existing Asset system primitives. * **Direct Filesystem Access to Processed Asset State:** Distill stores processed assets in a database. This makes debugging / inspecting the processed outputs harder (either requires special tooling to query the database or they need to be "deployed" to be inspected). Bevy Asset V2, on the other hand, stores processed assets in the filesystem (by default ... this is configurable). This makes interacting with the processed state more natural. Note that both Godot and Unity's new asset system store processed assets in the filesystem. * **Portability**: Because Distill's processor uses lmdb and RPC networking, it cannot be run on certain platforms (ex: lmdb is a non-rust dependency that cannot run on the web, some platforms don't support running network servers). Bevy should be able to process assets everywhere (ex: run the Bevy Editor on the web, compile + process shaders on mobile, etc). Distill does partially mitigate this problem by supporting "streaming" assets via the RPC protocol, but this is not a full solve from my perspective. And Bevy Asset V2 can (in theory) also stream assets (without requiring RPC, although this isn't implemented yet) Note that I _do_ still think Distill would be a solid asset system for Bevy. But I think the approach in this PR is a better solve for Bevy's specific "asset system requirements". ### Doesn't async-fs just shim requests to "sync" `std::fs`? What is the point? "True async file io" has limited / spotty platform support. async-fs (and the rust async ecosystem generally ... ex Tokio) currently use async wrappers over std::fs that offload blocking requests to separate threads. This may feel unsatisfying, but it _does_ still provide value because it prevents our task pools from blocking on file system operations (which would prevent progress when there are many tasks to do, but all threads in a pool are currently blocking on file system ops). Additionally, using async APIs for our AssetReaders and AssetWriters also provides value because we can later add support for "true async file io" for platforms that support it. _And_ we can implement other "true async io" asset backends (such as networked asset io). ## Draft TODO - [x] Fill in missing filesystem event APIs: file removed event (which is expressed as dangling RenameFrom events in some cases), file/folder renamed event - [x] Assets without loaders are not moved to the processed folder. This breaks things like referenced `.bin` files for GLTFs. This should be configurable per-non-asset-type. - [x] Initial implementation of Reflect and FromReflect for Handle. The "deserialization" parity bar is low here as this only worked with static UUIDs in the old impl ... this is a non-trivial problem. Either we add a Handle::AssetPath variant that gets "upgraded" to a strong handle on scene load or we use a separate AssetRef type for Bevy scenes (which is converted to a runtime Handle on load). This deserves its own discussion in a different pr. - [x] Populate read_asset_bytes hash when run by the processor (a bit of a special case .. when run by the processor the processed meta will contain the hash so we don't need to compute it on the spot, but we don't want/need to read the meta when run by the main AssetServer) - [x] Delay hot reloading: currently filesystem events are handled immediately, which creates timing issues in some cases. For example hot reloading images can sometimes break because the image isn't finished writing. We should add a delay, likely similar to the [implementation in this PR](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/8503). - [x] Port old platform-specific AssetIo implementations to the new AssetReader interface (currently missing Android and web) - [x] Resolve on_loaded unsafety (either by removing the API entirely or removing the unsafe) - [x] Runtime loader setting overrides - [x] Remove remaining unwraps that should be error-handled. There are number of TODOs here - [x] Pretty AssetPath Display impl - [x] Document more APIs - [x] Resolve spurious "reloading because it has changed" events (to repro run load_gltf with `processed_dev()`) - [x] load_dependency hot reloading currently only works for processed assets. If processing is disabled, load_dependency changes are not hot reloaded. - [x] Replace AssetInfo dependency load/fail counters with `loading_dependencies: HashSet<UntypedAssetId>` to prevent reloads from (potentially) breaking counters. Storing this will also enable "dependency reloaded" events (see [Next Steps](#next-steps)) - [x] Re-add filesystem watcher cargo feature gate (currently it is not optional) - [ ] Migration Guide - [ ] Changelog ## Followup TODO - [ ] Replace "eager unchanged processed asset loading" behavior with "don't returned unchanged processed asset until dependencies have been checked". - [ ] Add true `Ignore` AssetAction that does not copy the asset to the imported_assets folder. - [ ] Finish "live asset unloading" (ex: free up CPU asset memory after uploading an image to the GPU), rethink RenderAssets, and port renderer features. The `Assets` collection uses `Option<T>` for asset storage to support its removal. (1) the Option might not actually be necessary ... might be able to just remove from the collection entirely (2) need to finalize removal apis - [ ] Try replacing the "channel based" asset id recycling with something a bit more efficient (ex: we might be able to use raw atomic ints with some cleverness) - [ ] Consider adding UUIDs to processed assets (scoped just to helping identify moved assets ... not exposed to load queries ... see [Next Steps](#next-steps)) - [ ] Store "last modified" source asset and meta timestamps in processed meta files to enable skipping expensive hashing when the file wasn't changed - [ ] Fix "slow loop" handle drop fix - [ ] Migrate to TypeName - [x] Handle "loader preregistration". See #9429 ## Next Steps * **Configurable per-type defaults for AssetMeta**: It should be possible to add configuration like "all png image meta should default to using nearest sampling" (currently this hard-coded per-loader/processor Settings::default() impls). Also see the "Folder Meta" bullet point. * **Avoid Reprocessing on Asset Renames / Moves**: See the "canonical asset ids" discussion in [Open Questions](#open-questions) and the relevant bullet point in [Draft TODO](#draft-todo). Even without canonical ids, folder renames could avoid reprocessing in some cases. * **Multiple Asset Sources**: Expand AssetPath to support "asset source names" and support multiple AssetReaders in the asset server (ex: `webserver://some_path/image.png` backed by an Http webserver AssetReader). The "default" asset reader would use normal `some_path/image.png` paths. Ideally this works in combination with multiple AssetWatchers for hot-reloading * **Stable Type Names**: this pr removes the TypeUuid requirement from assets in favor of `std::any::type_name`. This makes defining assets easier (no need to generate a new uuid / use weird proc macro syntax). It also makes reading meta files easier (because things have "friendly names"). We also use type names for components in scene files. If they are good enough for components, they are good enough for assets. And consistency across Bevy pillars is desirable. However, `std::any::type_name` is not guaranteed to be stable (although in practice it is). We've developed a [stable type path](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/7184) to resolve this, which should be adopted when it is ready. * **Command Line Interface**: It should be possible to run the asset processor in a separate process from the command line. This will also require building a network-server-backed AssetReader to communicate between the app and the processor. We've been planning to build a "bevy cli" for awhile. This seems like a good excuse to build it. * **Asset Packing**: This is largely an additive feature, so it made sense to me to punt this until we've laid the foundations in this PR. * **Per-Platform Processed Assets**: It should be possible to generate assets for multiple platforms by supporting multiple "processor profiles" per asset (ex: compress with format X on PC and Y on iOS). I think there should probably be arbitrary "profiles" (which can be separate from actual platforms), which are then assigned to a given platform when generating the final asset distribution for that platform. Ex: maybe devs want a "Mobile" profile that is shared between iOS and Android. Or a "LowEnd" profile shared between web and mobile. * **Versioning and Migrations**: Assets, Loaders, Savers, and Processors need to have versions to determine if their schema is valid. If an asset / loader version is incompatible with the current version expected at runtime, the processor should be able to migrate them. I think we should try using Bevy Reflect for this, as it would allow us to load the old version as a dynamic Reflect type without actually having the old Rust type. It would also allow us to define "patches" to migrate between versions (Bevy Reflect devs are currently working on patching). The `.meta` file already has its own format version. Migrating that to new versions should also be possible. * **Real Copy-on-write AssetPaths**: Rust's actual Cow (clone-on-write type) currently used by AssetPath can still result in String clones that aren't actually necessary (cloning an Owned Cow clones the contents). Bevy's asset system requires cloning AssetPaths in a number of places, which result in actual clones of the internal Strings. This is not efficient. AssetPath internals should be reworked to exhibit truer cow-like-behavior that reduces String clones to the absolute minimum. * **Consider processor-less processing**: In theory the AssetServer could run processors "inline" even if the background AssetProcessor is disabled. If we decide this is actually desirable, we could add this. But I don't think its a priority in the short or medium term. * **Pre-emptive dependency loading**: We could encode dependencies in processed meta files, which could then be used by the Asset Server to kick of dependency loads as early as possible (prior to starting the actual asset load). Is this desirable? How much time would this save in practice? * **Optimize Processor With UntypedAssetIds**: The processor exclusively uses AssetPath to identify assets currently. It might be possible to swap these out for UntypedAssetIds in some places, which are smaller / cheaper to hash and compare. * **One to Many Asset Processing**: An asset source file that produces many assets currently must be processed into a single "processed" asset source. If labeled assets can be written separately they can each have their own configured savers _and_ they could be loaded more granularly. Definitely worth exploring! * **Automatically Track "Runtime-only" Asset Dependencies**: Right now, tracking "created at runtime" asset dependencies requires adding them via `asset_server.load_asset(StandardMaterial::default())`. I think with some cleverness we could also do this for `materials.add(StandardMaterial::default())`, making tracking work "everywhere". There are challenges here relating to change detection / ensuring the server is made aware of dependency changes. This could be expensive in some cases. * **"Dependency Changed" events**: Some assets have runtime artifacts that need to be re-generated when one of their dependencies change (ex: regenerate a material's bind group when a Texture needs to change). We are generating the dependency graph so we can definitely produce these events. Buuuuut generating these events will have a cost / they could be high frequency for some assets, so we might want this to be opt-in for specific cases. * **Investigate Storing More Information In Handles**: Handles can now store arbitrary information, which makes it cheaper and easier to access. How much should we move into them? Canonical asset load states (via atomics)? (`handle.is_loaded()` would be very cool). Should we store the entire asset and remove the `Assets<T>` collection? (`Arc<RwLock<Option<Image>>>`?) * **Support processing and loading files without extensions**: This is a pretty arbitrary restriction and could be supported with very minimal changes. * **Folder Meta**: It would be nice if we could define per folder processor configuration defaults (likely in a `.meta` or `.folder_meta` file). Things like "default to linear filtering for all Images in this folder". * **Replace async_broadcast with event-listener?** This might be approximately drop-in for some uses and it feels more light weight * **Support Running the AssetProcessor on the Web**: Most of the hard work is done here, but there are some easy straggling TODOs (make the transaction log an interface instead of a direct file writer so we can write a web storage backend, implement an AssetReader/AssetWriter that reads/writes to something like LocalStorage). * **Consider identifying and preventing circular dependencies**: This is especially important for "processor dependencies", as processing will silently never finish in these cases. * **Built-in/Inlined Asset Hot Reloading**: This PR regresses "built-in/inlined" asset hot reloading (previously provided by the DebugAssetServer). I'm intentionally punting this because I think it can be cleanly implemented with "multiple asset sources" by registering a "debug asset source" (ex: `debug://bevy_pbr/src/render/pbr.wgsl` asset paths) in combination with an AssetWatcher for that asset source and support for "manually loading pats with asset bytes instead of AssetReaders". The old DebugAssetServer was quite nasty and I'd love to avoid that hackery going forward. * **Investigate ways to remove double-parsing meta files**: Parsing meta files currently involves parsing once with "minimal" versions of the meta file to extract the type name of the loader/processor config, then parsing again to parse the "full" meta. This is suboptimal. We should be able to define custom deserializers that (1) assume the loader/processor type name comes first (2) dynamically looks up the loader/processor registrations to deserialize settings in-line (similar to components in the bevy scene format). Another alternative: deserialize as dynamic Reflect objects and then convert. * **More runtime loading configuration**: Support using the Handle type as a hint to select an asset loader (instead of relying on AssetPath extensions) * **More high level Processor trait implementations**: For example, it might be worth adding support for arbitrary chains of "asset transforms" that modify an in-memory asset representation between loading and saving. (ex: load a Mesh, run a `subdivide_mesh` transform, followed by a `flip_normals` transform, then save the mesh to an efficient compressed format). * **Bevy Scene Handle Deserialization**: (see the relevant [Draft TODO item](#draft-todo) for context) * **Explore High Level Load Interfaces**: See [this discussion](#discuss-on_loaded-high-level-interface) for one prototype. * **Asset Streaming**: It would be great if we could stream Assets (ex: stream a long video file piece by piece) * **ID Exchanging**: In this PR Asset Handles/AssetIds are bigger than they need to be because they have a Uuid enum variant. If we implement an "id exchanging" system that trades Uuids for "efficient runtime ids", we can cut down on the size of AssetIds, making them more efficient. This has some open design questions, such as how to spawn entities with "default" handle values (as these wouldn't have access to the exchange api in the current system). * **Asset Path Fixup Tooling**: Assets that inline asset paths inside them will break when an asset moves. The asset system provides the functionality to detect when paths break. We should build a framework that enables formats to define "path migrations". This is especially important for scene files. For editor-generated files, we should also consider using UUIDs (see other bullet point) to avoid the need to migrate in these cases. --------- Co-authored-by: BeastLe9enD <beastle9end@outlook.de> Co-authored-by: Mike <mike.hsu@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: Nicola Papale <nicopap@users.noreply.github.com> |
||
|
|
30d897a8bf
|
fix clippy::default_constructed_unit_structs and trybuild errors (#9144)
# Objective With Rust `1.71.0` ([released a few minutes ago](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/releases/tag/1.71.0)), clippy introduced a new lint ([`default_constructed_unit_structs`](https://rust-lang.github.io/rust-clippy/master/index.html#/default_constructed_unit_structs)) wich prevent calling `default()` on unit structs (e.g. `PhantomData::default()`). ## Solution Apply the lint suggestion. --------- Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
d33f5c759c
|
Add optional single-threaded feature to bevy_ecs/bevy_tasks (#6690)
# Objective Fixes #6689. ## Solution Add `single-threaded` as an optional non-default feature to `bevy_ecs` and `bevy_tasks` that: - disable the `ParallelExecutor` as a default runner - disables the multi-threaded `TaskPool` - internally replace `QueryParIter::for_each` calls with `Query::for_each`. Removed the `Mutex` and `Arc` usage in the single-threaded task pool. 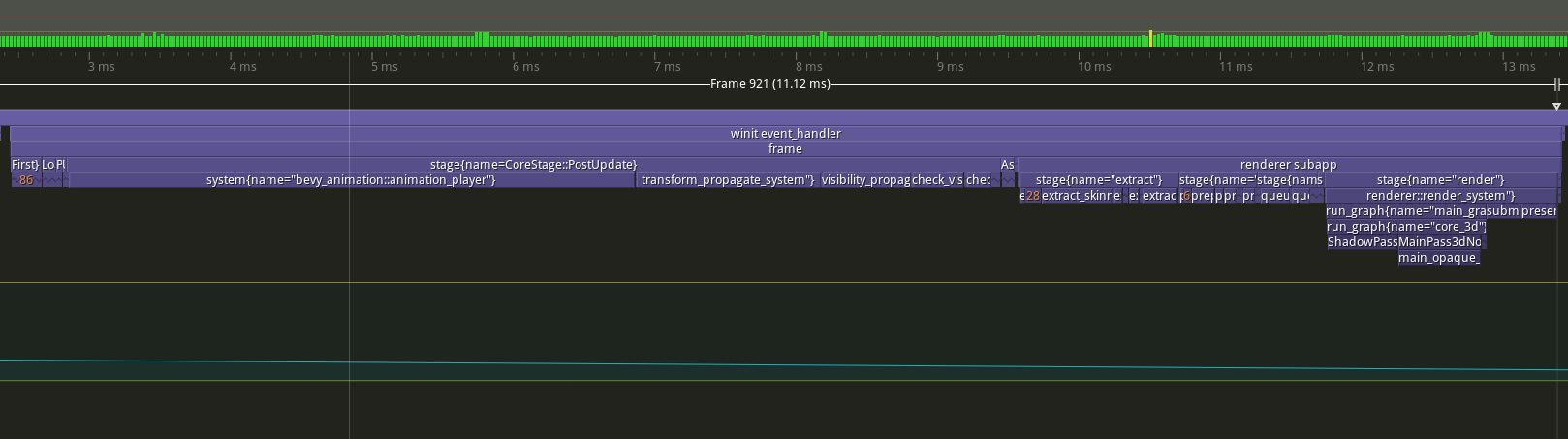 ## Future Work/TODO Create type aliases for `Mutex`, `Arc` that change to single-threaaded equivalents where possible. --- ## Changelog Added: Optional default feature `multi-theaded` to that enables multithreaded parallelism in the engine. Disabling it disables all multithreading in exchange for higher single threaded performance. Does nothing on WASM targets. --------- Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
3ead10a3e0
|
Suppress the clippy::type_complexity lint (#8313)
# Objective The clippy lint `type_complexity` is known not to play well with bevy. It frequently triggers when writing complex queries, and taking the lint's advice of using a type alias almost always just obfuscates the code with no benefit. Because of this, this lint is currently ignored in CI, but unfortunately it still shows up when viewing bevy code in an IDE. As someone who's made a fair amount of pull requests to this repo, I will say that this issue has been a consistent thorn in my side. Since bevy code is filled with spurious, ignorable warnings, it can be very difficult to spot the *real* warnings that must be fixed -- most of the time I just ignore all warnings, only to later find out that one of them was real after I'm done when CI runs. ## Solution Suppress this lint in all bevy crates. This was previously attempted in #7050, but the review process ended up making it more complicated than it needs to be and landed on a subpar solution. The discussion in https://github.com/rust-lang/rust-clippy/pull/10571 explores some better long-term solutions to this problem. Since there is no timeline on when these solutions may land, we should resolve this issue in the meantime by locally suppressing these lints. ### Unresolved issues Currently, these lints are not suppressed in our examples, since that would require suppressing the lint in every single source file. They are still ignored in CI. |
||
|
|
0893852c40
|
Document bevy_gizmos (#8186)
# Objective Fix #8179 ## Solution - Added `#![warn(missing_docs)]` and document all public items. All methods on `Gizmos` have doc examples. - Expanded the docs on the module/crate. Some unfortunate duplication there :/ - Moved the methods from `GizmoBuffer` to be directly on `Gizmos` and made `GizmoBuffer` private. This means the methods on `Gizmos` will show up on its doc page. --------- Co-authored-by: James Liu <contact@jamessliu.com> |
||
|
|
6a85eb3d7e
|
Immediate Mode Line/Gizmo Drawing (#6529)
# Objective Add a convenient immediate mode drawing API for visual debugging. Fixes #5619 Alternative to #1625 Partial alternative to #5734 Based off https://github.com/Toqozz/bevy_debug_lines with some changes: * Simultaneous support for 2D and 3D. * Methods for basic shapes; circles, spheres, rectangles, boxes, etc. * 2D methods. * Removed durations. Seemed niche, and can be handled by users. <details> <summary>Performance</summary> Stress tested using Bevy's recommended optimization settings for the dev profile with the following command. ```bash cargo run --example many_debug_lines \ --config "profile.dev.package.\"*\".opt-level=3" \ --config "profile.dev.opt-level=1" ``` I dipped to 65-70 FPS at 300,000 lines CPU: 3700x RAM Speed: 3200 Mhz GPU: 2070 super - probably not very relevant, mostly cpu/memory bound </details> <details> <summary>Fancy bloom screenshot</summary>  </details> ## Changelog * Added `GizmoPlugin` * Added `Gizmos` system parameter for drawing lines and wireshapes. ### TODO - [ ] Update changelog - [x] Update performance numbers - [x] Add credit to PR description ### Future work - Cache rendering primitives instead of constructing them out of line segments each frame. - Support for drawing solid meshes - Interactions. (See [bevy_mod_gizmos](https://github.com/LiamGallagher737/bevy_mod_gizmos)) - Fancier line drawing. (See [bevy_polyline](https://github.com/ForesightMiningSoftwareCorporation/bevy_polyline)) - Support for `RenderLayers` - Display gizmos for a certain duration. Currently everything displays for one frame (ie. immediate mode) - Changing settings per drawn item like drawing on top or drawing to different `RenderLayers` Co-Authored By: @lassade <felipe.jorge.pereira@gmail.com> Co-Authored By: @The5-1 <agaku@hotmail.de> Co-Authored By: @Toqozz <toqoz@hotmail.com> Co-Authored By: @nicopap <nico@nicopap.ch> --------- Co-authored-by: Robert Swain <robert.swain@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: IceSentry <c.giguere42@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com> |
||
|
|
8d1f6ff7fa |
Integrate AccessKit (#6874)
# Objective UIs created for Bevy cannot currently be made accessible. This PR aims to address that. ## Solution Integrate AccessKit as a dependency, adding accessibility support to existing bevy_ui widgets. ## Changelog ### Added * Integrate with and expose [AccessKit](https://accesskit.dev) for platform accessibility. * Add `Label` for marking text specifically as a label for UI controls. |
||
|
|
0af001edd4 |
Update DefaultPlugins docs (#7742)
# Objective - Updates list of plugins and feature information in `DefaultPlugins` doc comment - Solve the short term issue of https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/7332 ## Solution - Update doc comment to reflect current implementation - Sort plugins by appearance in implementation |
||
|
|
3900b48c88 |
update winit to 0.28 (#7480)
# Objective - Update winit to 0.28 ## Solution - Small API change - A security advisory has been added for a unmaintained crate used by a dependency of winit build script for wayland I didn't do anything for Android support in this PR though it should be fixable, it should be done in a separate one, maybe https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/6830 --- ## Changelog - `window.always_on_top` has been removed, you can now use `window.window_level` ## Migration Guide before: ```rust app.new() .add_plugins(DefaultPlugins.set(WindowPlugin { primary_window: Some(Window { always_on_top: true, ..default() }), ..default() })); ``` after: ```rust app.new() .add_plugins(DefaultPlugins.set(WindowPlugin { primary_window: Some(Window { window_level: bevy:🪟:WindowLevel::AlwaysOnTop, ..default() }), ..default() })); ``` |
||
|
|
6e44d8a251 |
Docs: DefaultPlugins vs. MinimalPlugins and ScheduleRunnerPlugin (#7226)
# Objective The naming of the two plugin groups `DefaultPlugins` and `MinimalPlugins` suggests that one is a super-set of the other but this is not the case. Instead, the two plugin groups are intended for very different purposes. Closes: https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/7173 ## Solution This merge request adds doc. comments that compensate for this and try save the user from confusion. 1. `DefaultPlugins` and `MinimalPlugins` intentions are described. 2. A strong emphasis on embracing `DefaultPlugins` as a whole but controlling what it contains with *Cargo* *features* is added – this is because the ordering in `DefaultPlugins` appears to be important so preventing users with "minimalist" foibles (That's Me!) from recreating the code seems worthwhile. 3. Notes are added explaining the confusing fact that `MinimalPlugins` contains `ScheduleRunnerPlugin` (which is very "important"-sounding) but `DefaultPlugins` does not. |
||
|
|
2027af4c54 |
Pipelined Rendering (#6503)
# Objective - Implement pipelined rendering - Fixes #5082 - Fixes #4718 ## User Facing Description Bevy now implements piplelined rendering! Pipelined rendering allows the app logic and rendering logic to run on different threads leading to large gains in performance.  *tracy capture of many_foxes example* To use pipelined rendering, you just need to add the `PipelinedRenderingPlugin`. If you're using `DefaultPlugins` then it will automatically be added for you on all platforms except wasm. Bevy does not currently support multithreading on wasm which is needed for this feature to work. If you aren't using `DefaultPlugins` you can add the plugin manually. ```rust use bevy::prelude::*; use bevy::render::pipelined_rendering::PipelinedRenderingPlugin; fn main() { App::new() // whatever other plugins you need .add_plugin(RenderPlugin) // needs to be added after RenderPlugin .add_plugin(PipelinedRenderingPlugin) .run(); } ``` If for some reason pipelined rendering needs to be removed. You can also disable the plugin the normal way. ```rust use bevy::prelude::*; use bevy::render::pipelined_rendering::PipelinedRenderingPlugin; fn main() { App::new.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins.build().disable::<PipelinedRenderingPlugin>()); } ``` ### A setup function was added to plugins A optional plugin lifecycle function was added to the `Plugin trait`. This function is called after all plugins have been built, but before the app runner is called. This allows for some final setup to be done. In the case of pipelined rendering, the function removes the sub app from the main app and sends it to the render thread. ```rust struct MyPlugin; impl Plugin for MyPlugin { fn build(&self, app: &mut App) { } // optional function fn setup(&self, app: &mut App) { // do some final setup before runner is called } } ``` ### A Stage for Frame Pacing In the `RenderExtractApp` there is a stage labelled `BeforeIoAfterRenderStart` that systems can be added to. The specific use case for this stage is for a frame pacing system that can delay the start of main app processing in render bound apps to reduce input latency i.e. "frame pacing". This is not currently built into bevy, but exists as `bevy` ```text |-------------------------------------------------------------------| | | BeforeIoAfterRenderStart | winit events | main schedule | | extract |---------------------------------------------------------| | | extract commands | rendering schedule | |-------------------------------------------------------------------| ``` ### Small API additions * `Schedule::remove_stage` * `App::insert_sub_app` * `App::remove_sub_app` * `TaskPool::scope_with_executor` ## Problems and Solutions ### Moving render app to another thread Most of the hard bits for this were done with the render redo. This PR just sends the render app back and forth through channels which seems to work ok. I originally experimented with using a scope to run the render task. It was cuter, but that approach didn't allow render to start before i/o processing. So I switched to using channels. There is much complexity in the coordination that needs to be done, but it's worth it. By moving rendering during i/o processing the frame times should be much more consistent in render bound apps. See https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/4691. ### Unsoundness with Sending World with NonSend resources Dropping !Send things on threads other than the thread they were spawned on is considered unsound. The render world doesn't have any nonsend resources. So if we tell the users to "pretty please don't spawn nonsend resource on the render world", we can avoid this problem. More seriously there is this https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/6534 pr, which patches the unsoundness by aborting the app if a nonsend resource is dropped on the wrong thread. ~~That PR should probably be merged before this one.~~ For a longer term solution we have this discussion going https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/discussions/6552. ### NonSend Systems in render world The render world doesn't have any !Send resources, but it does have a non send system. While Window is Send, winit does have some API's that can only be accessed on the main thread. `prepare_windows` in the render schedule thus needs to be scheduled on the main thread. Currently we run nonsend systems by running them on the thread the TaskPool::scope runs on. When we move render to another thread this no longer works. To fix this, a new `scope_with_executor` method was added that takes a optional `TheadExecutor` that can only be ticked on the thread it was initialized on. The render world then holds a `MainThreadExecutor` resource which can be passed to the scope in the parallel executor that it uses to spawn it's non send systems on. ### Scopes executors between render and main should not share tasks Since the render world and the app world share the `ComputeTaskPool`. Because `scope` has executors for the ComputeTaskPool a system from the main world could run on the render thread or a render system could run on the main thread. This can cause performance problems because it can delay a stage from finishing. See https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/6503#issuecomment-1309791442 for more details. To avoid this problem, `TaskPool::scope` has been changed to not tick the ComputeTaskPool when it's used by the parallel executor. In the future when we move closer to the 1 thread to 1 logical core model we may want to overprovide threads, because the render and main app threads don't do much when executing the schedule. ## Performance My machine is Windows 11, AMD Ryzen 5600x, RX 6600 ### Examples #### This PR with pipelining vs Main > Note that these were run on an older version of main and the performance profile has probably changed due to optimizations Seeing a perf gain from 29% on many lights to 7% on many sprites. <html> <body> <!--StartFragment--><google-sheets-html-origin> | percent | | | Diff | | | Main | | | PR | | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- tracy frame time | mean | median | sigma | mean | median | sigma | mean | median | sigma | mean | median | sigma many foxes | 27.01% | 27.34% | -47.09% | 1.58 | 1.55 | -1.78 | 5.85 | 5.67 | 3.78 | 4.27 | 4.12 | 5.56 many lights | 29.35% | 29.94% | -10.84% | 3.02 | 3.03 | -0.57 | 10.29 | 10.12 | 5.26 | 7.27 | 7.09 | 5.83 many animated sprites | 13.97% | 15.69% | 14.20% | 3.79 | 4.17 | 1.41 | 27.12 | 26.57 | 9.93 | 23.33 | 22.4 | 8.52 3d scene | 25.79% | 26.78% | 7.46% | 0.49 | 0.49 | 0.15 | 1.9 | 1.83 | 2.01 | 1.41 | 1.34 | 1.86 many cubes | 11.97% | 11.28% | 14.51% | 1.93 | 1.78 | 1.31 | 16.13 | 15.78 | 9.03 | 14.2 | 14 | 7.72 many sprites | 7.14% | 9.42% | -85.42% | 1.72 | 2.23 | -6.15 | 24.09 | 23.68 | 7.2 | 22.37 | 21.45 | 13.35 <!--EndFragment--> </body> </html> #### This PR with pipelining disabled vs Main Mostly regressions here. I don't think this should be a problem as users that are disabling pipelined rendering are probably running single threaded and not using the parallel executor. The regression is probably mostly due to the switch to use `async_executor::run` instead of `try_tick` and also having one less thread to run systems on. I'll do a writeup on why switching to `run` causes regressions, so we can try to eventually fix it. Using try_tick causes issues when pipeline rendering is enable as seen [here](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/6503#issuecomment-1380803518) <html> <body> <!--StartFragment--><google-sheets-html-origin> | percent | | | Diff | | | Main | | | PR no pipelining | | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- tracy frame time | mean | median | sigma | mean | median | sigma | mean | median | sigma | mean | median | sigma many foxes | -3.72% | -4.42% | -1.07% | -0.21 | -0.24 | -0.04 | 5.64 | 5.43 | 3.74 | 5.85 | 5.67 | 3.78 many lights | 0.29% | -0.30% | 4.75% | 0.03 | -0.03 | 0.25 | 10.29 | 10.12 | 5.26 | 10.26 | 10.15 | 5.01 many animated sprites | 0.22% | 1.81% | -2.72% | 0.06 | 0.48 | -0.27 | 27.12 | 26.57 | 9.93 | 27.06 | 26.09 | 10.2 3d scene | -15.79% | -14.75% | -31.34% | -0.3 | -0.27 | -0.63 | 1.9 | 1.83 | 2.01 | 2.2 | 2.1 | 2.64 many cubes | -2.85% | -3.30% | 0.00% | -0.46 | -0.52 | 0 | 16.13 | 15.78 | 9.03 | 16.59 | 16.3 | 9.03 many sprites | 2.49% | 2.41% | 0.69% | 0.6 | 0.57 | 0.05 | 24.09 | 23.68 | 7.2 | 23.49 | 23.11 | 7.15 <!--EndFragment--> </body> </html> ### Benchmarks Mostly the same except empty_systems has got a touch slower. The maybe_pipelining+1 column has the compute task pool with an extra thread over default added. This is because pipelining loses one thread over main to execute systems on, since the main thread no longer runs normal systems. <details> <summary>Click Me</summary> ```text group main maybe-pipelining+1 ----- ------------------------- ------------------ busy_systems/01x_entities_03_systems 1.07 30.7±1.32µs ? ?/sec 1.00 28.6±1.35µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/01x_entities_06_systems 1.10 52.1±1.10µs ? ?/sec 1.00 47.2±1.08µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/01x_entities_09_systems 1.00 74.6±1.36µs ? ?/sec 1.00 75.0±1.93µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/01x_entities_12_systems 1.03 100.6±6.68µs ? ?/sec 1.00 98.0±1.46µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/01x_entities_15_systems 1.11 128.5±3.53µs ? ?/sec 1.00 115.5±1.02µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/02x_entities_03_systems 1.16 50.4±2.56µs ? ?/sec 1.00 43.5±3.00µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/02x_entities_06_systems 1.00 87.1±1.27µs ? ?/sec 1.05 91.5±7.15µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/02x_entities_09_systems 1.04 139.9±6.37µs ? ?/sec 1.00 134.0±1.06µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/02x_entities_12_systems 1.05 179.2±3.47µs ? ?/sec 1.00 170.1±3.17µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/02x_entities_15_systems 1.01 219.6±3.75µs ? ?/sec 1.00 218.1±2.55µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/03x_entities_03_systems 1.10 70.6±2.33µs ? ?/sec 1.00 64.3±0.69µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/03x_entities_06_systems 1.02 130.2±3.11µs ? ?/sec 1.00 128.0±1.34µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/03x_entities_09_systems 1.00 195.0±10.11µs ? ?/sec 1.00 194.8±1.41µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/03x_entities_12_systems 1.01 261.7±4.05µs ? ?/sec 1.00 259.8±4.11µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/03x_entities_15_systems 1.00 318.0±3.04µs ? ?/sec 1.06 338.3±20.25µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/04x_entities_03_systems 1.00 82.9±0.63µs ? ?/sec 1.02 84.3±0.63µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/04x_entities_06_systems 1.01 181.7±3.65µs ? ?/sec 1.00 179.8±1.76µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/04x_entities_09_systems 1.04 265.0±4.68µs ? ?/sec 1.00 255.3±1.98µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/04x_entities_12_systems 1.00 335.9±3.00µs ? ?/sec 1.05 352.6±15.84µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/04x_entities_15_systems 1.00 418.6±10.26µs ? ?/sec 1.08 450.2±39.58µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/05x_entities_03_systems 1.07 114.3±0.95µs ? ?/sec 1.00 106.9±1.52µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/05x_entities_06_systems 1.08 229.8±2.90µs ? ?/sec 1.00 212.3±4.18µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/05x_entities_09_systems 1.03 329.3±1.99µs ? ?/sec 1.00 319.2±2.43µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/05x_entities_12_systems 1.06 454.7±6.77µs ? ?/sec 1.00 430.1±3.58µs ? ?/sec busy_systems/05x_entities_15_systems 1.03 554.6±6.15µs ? ?/sec 1.00 538.4±23.87µs ? ?/sec contrived/01x_entities_03_systems 1.00 14.0±0.15µs ? ?/sec 1.08 15.1±0.21µs ? ?/sec contrived/01x_entities_06_systems 1.04 28.5±0.37µs ? ?/sec 1.00 27.4±0.44µs ? ?/sec contrived/01x_entities_09_systems 1.00 41.5±4.38µs ? ?/sec 1.02 42.2±2.24µs ? ?/sec contrived/01x_entities_12_systems 1.06 55.9±1.49µs ? ?/sec 1.00 52.6±1.36µs ? ?/sec contrived/01x_entities_15_systems 1.02 68.0±2.00µs ? ?/sec 1.00 66.5±0.78µs ? ?/sec contrived/02x_entities_03_systems 1.03 25.2±0.38µs ? ?/sec 1.00 24.6±0.52µs ? ?/sec contrived/02x_entities_06_systems 1.00 46.3±0.49µs ? ?/sec 1.04 48.1±4.13µs ? ?/sec contrived/02x_entities_09_systems 1.02 70.4±0.99µs ? ?/sec 1.00 68.8±1.04µs ? ?/sec contrived/02x_entities_12_systems 1.06 96.8±1.49µs ? ?/sec 1.00 91.5±0.93µs ? ?/sec contrived/02x_entities_15_systems 1.02 116.2±0.95µs ? ?/sec 1.00 114.2±1.42µs ? ?/sec contrived/03x_entities_03_systems 1.00 33.2±0.38µs ? ?/sec 1.01 33.6±0.45µs ? ?/sec contrived/03x_entities_06_systems 1.00 62.4±0.73µs ? ?/sec 1.01 63.3±1.05µs ? ?/sec contrived/03x_entities_09_systems 1.02 96.4±0.85µs ? ?/sec 1.00 94.8±3.02µs ? ?/sec contrived/03x_entities_12_systems 1.01 126.3±4.67µs ? ?/sec 1.00 125.6±2.27µs ? ?/sec contrived/03x_entities_15_systems 1.03 160.2±9.37µs ? ?/sec 1.00 156.0±1.53µs ? ?/sec contrived/04x_entities_03_systems 1.02 41.4±3.39µs ? ?/sec 1.00 40.5±0.52µs ? ?/sec contrived/04x_entities_06_systems 1.00 78.9±1.61µs ? ?/sec 1.02 80.3±1.06µs ? ?/sec contrived/04x_entities_09_systems 1.02 121.8±3.97µs ? ?/sec 1.00 119.2±1.46µs ? ?/sec contrived/04x_entities_12_systems 1.00 157.8±1.48µs ? ?/sec 1.01 160.1±1.72µs ? ?/sec contrived/04x_entities_15_systems 1.00 197.9±1.47µs ? ?/sec 1.08 214.2±34.61µs ? ?/sec contrived/05x_entities_03_systems 1.00 49.1±0.33µs ? ?/sec 1.01 49.7±0.75µs ? ?/sec contrived/05x_entities_06_systems 1.00 95.0±0.93µs ? ?/sec 1.00 94.6±0.94µs ? ?/sec contrived/05x_entities_09_systems 1.01 143.2±1.68µs ? ?/sec 1.00 142.2±2.00µs ? ?/sec contrived/05x_entities_12_systems 1.00 191.8±2.03µs ? ?/sec 1.01 192.7±7.88µs ? ?/sec contrived/05x_entities_15_systems 1.02 239.7±3.71µs ? ?/sec 1.00 235.8±4.11µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/000_systems 1.01 47.8±0.67ns ? ?/sec 1.00 47.5±2.02ns ? ?/sec empty_systems/001_systems 1.00 1743.2±126.14ns ? ?/sec 1.01 1761.1±70.10ns ? ?/sec empty_systems/002_systems 1.01 2.2±0.04µs ? ?/sec 1.00 2.2±0.02µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/003_systems 1.02 2.7±0.09µs ? ?/sec 1.00 2.7±0.16µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/004_systems 1.00 3.1±0.11µs ? ?/sec 1.00 3.1±0.24µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/005_systems 1.00 3.5±0.05µs ? ?/sec 1.11 3.9±0.70µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/010_systems 1.00 5.5±0.12µs ? ?/sec 1.03 5.7±0.17µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/015_systems 1.00 7.9±0.19µs ? ?/sec 1.06 8.4±0.16µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/020_systems 1.00 10.4±1.25µs ? ?/sec 1.02 10.6±0.18µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/025_systems 1.00 12.4±0.39µs ? ?/sec 1.14 14.1±1.07µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/030_systems 1.00 15.1±0.39µs ? ?/sec 1.05 15.8±0.62µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/035_systems 1.00 16.9±0.47µs ? ?/sec 1.07 18.0±0.37µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/040_systems 1.00 19.3±0.41µs ? ?/sec 1.05 20.3±0.39µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/045_systems 1.00 22.4±1.67µs ? ?/sec 1.02 22.9±0.51µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/050_systems 1.00 24.4±1.67µs ? ?/sec 1.01 24.7±0.40µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/055_systems 1.05 28.6±5.27µs ? ?/sec 1.00 27.2±0.70µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/060_systems 1.02 29.9±1.64µs ? ?/sec 1.00 29.3±0.66µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/065_systems 1.02 32.7±3.15µs ? ?/sec 1.00 32.1±0.98µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/070_systems 1.00 33.0±1.42µs ? ?/sec 1.03 34.1±1.44µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/075_systems 1.00 34.8±0.89µs ? ?/sec 1.04 36.2±0.70µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/080_systems 1.00 37.0±1.82µs ? ?/sec 1.05 38.7±1.37µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/085_systems 1.00 38.7±0.76µs ? ?/sec 1.05 40.8±0.83µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/090_systems 1.00 41.5±1.09µs ? ?/sec 1.04 43.2±0.82µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/095_systems 1.00 43.6±1.10µs ? ?/sec 1.04 45.2±0.99µs ? ?/sec empty_systems/100_systems 1.00 46.7±2.27µs ? ?/sec 1.03 48.1±1.25µs ? ?/sec ``` </details> ## Migration Guide ### App `runner` and SubApp `extract` functions are now required to be Send This was changed to enable pipelined rendering. If this breaks your use case please report it as these new bounds might be able to be relaxed. ## ToDo * [x] redo benchmarking * [x] reinvestigate the perf of the try_tick -> run change for task pool scope |
||
|
|
329b71fa62 |
Break CorePlugin into TaskPoolPlugin, TypeRegistrationPlugin, FrameCountPlugin. (#7083)
# Objective - Fixes #7081. ## Solution - Moved functionality from kitchen sink plugin `CorePlugin` to separate plugins, `TaskPoolPlugin`, `TypeRegistrationPlugin`, `FrameCountPlugin`. `TaskPoolOptions` resource should now be used with `TaskPoolPlugin`. ## Changelog Minimal changes made (code kept in `bevy_core/lib.rs`). ## Migration Guide - `CorePlugin` broken into separate plugins. If not using `DefaultPlugins` or `MinimalPlugins` `PluginGroup`s, the replacement for `CorePlugin` is now to add `TaskPoolPlugin`, `TypeRegistrationPlugin`, and `FrameCountPlugin` to the app. ## Notes - Consistent with Bevy goal "modularity over deep integration" but the functionality of `TypeRegistrationPlugin` and `FrameCountPlugin` is weak (the code has to go somewhere, though!). - No additional tests written. |
||
|
|
741a91ed46 |
Replace WgpuAdapterInfo with RenderAdapterInfo in the documentation. (#7036)
# Objective Fixes #6598 In addition, macOS can also support GL backends through ANGLE. |