This changes how render logic is composed to make it much more modular. Previously, all extraction logic was centralized for a given "type" of rendered thing. For example, we extracted meshes into a vector of ExtractedMesh, which contained the mesh and material asset handles, the transform, etc. We looked up bindings for "drawn things" using their index in the `Vec<ExtractedMesh>`. This worked fine for built in rendering, but made it hard to reuse logic for "custom" rendering. It also prevented us from reusing things like "extracted transforms" across contexts.
To make rendering more modular, I made a number of changes:
* Entities now drive rendering:
* We extract "render components" from "app components" and store them _on_ entities. No more centralized uber lists! We now have true "ECS-driven rendering"
* To make this perform well, I implemented #2673 in upstream Bevy for fast batch insertions into specific entities. This was merged into the `pipelined-rendering` branch here: #2815
* Reworked the `Draw` abstraction:
* Generic `PhaseItems`: each draw phase can define its own type of "rendered thing", which can define its own "sort key"
* Ported the 2d, 3d, and shadow phases to the new PhaseItem impl (currently Transparent2d, Transparent3d, and Shadow PhaseItems)
* `Draw` trait and and `DrawFunctions` are now generic on PhaseItem
* Modular / Ergonomic `DrawFunctions` via `RenderCommands`
* RenderCommand is a trait that runs an ECS query and produces one or more RenderPass calls. Types implementing this trait can be composed to create a final DrawFunction. For example the DrawPbr DrawFunction is created from the following DrawCommand tuple. Const generics are used to set specific bind group locations:
```rust
pub type DrawPbr = (
SetPbrPipeline,
SetMeshViewBindGroup<0>,
SetStandardMaterialBindGroup<1>,
SetTransformBindGroup<2>,
DrawMesh,
);
```
* The new `custom_shader_pipelined` example illustrates how the commands above can be reused to create a custom draw function:
```rust
type DrawCustom = (
SetCustomMaterialPipeline,
SetMeshViewBindGroup<0>,
SetTransformBindGroup<2>,
DrawMesh,
);
```
* ExtractComponentPlugin and UniformComponentPlugin:
* Simple, standardized ways to easily extract individual components and write them to GPU buffers
* Ported PBR and Sprite rendering to the new primitives above.
* Removed staging buffer from UniformVec in favor of direct Queue usage
* Makes UniformVec much easier to use and more ergonomic. Completely removes the need for custom render graph nodes in these contexts (see the PbrNode and view Node removals and the much simpler call patterns in the relevant Prepare systems).
* Added a many_cubes_pipelined example to benchmark baseline 3d rendering performance and ensure there were no major regressions during this port. Avoiding regressions was challenging given that the old approach of extracting into centralized vectors is basically the "optimal" approach. However thanks to a various ECS optimizations and render logic rephrasing, we pretty much break even on this benchmark!
* Lifetimeless SystemParams: this will be a bit divisive, but as we continue to embrace "trait driven systems" (ex: ExtractComponentPlugin, UniformComponentPlugin, DrawCommand), the ergonomics of `(Query<'static, 'static, (&'static A, &'static B, &'static)>, Res<'static, C>)` were getting very hard to bear. As a compromise, I added "static type aliases" for the relevant SystemParams. The previous example can now be expressed like this: `(SQuery<(Read<A>, Read<B>)>, SRes<C>)`. If anyone has better ideas / conflicting opinions, please let me know!
* RunSystem trait: a way to define Systems via a trait with a SystemParam associated type. This is used to implement the various plugins mentioned above. I also added SystemParamItem and QueryItem type aliases to make "trait stye" ecs interactions nicer on the eyes (and fingers).
* RenderAsset retrying: ensures that render assets are only created when they are "ready" and allows us to create bind groups directly inside render assets (which significantly simplified the StandardMaterial code). I think ultimately we should swap this out on "asset dependency" events to wait for dependencies to load, but this will require significant asset system changes.
* Updated some built in shaders to account for missing MeshUniform fields
## Objective
The upcoming Bevy Book makes many references to the API documentation of bevy.
Most references belong to the first two chapters of the Bevy Book:
- bevyengine/bevy-website#176
- bevyengine/bevy-website#182
This PR attempts to improve the documentation of `bevy_ecs` and `bevy_app` in order to help readers of the Book who want to delve deeper into technical details.
## Solution
- Add crate and level module documentation
- Document the most important items (basically those included in the preludes), with the following style, where applicable:
- **Summary.** Short description of the item.
- **Second paragraph.** Detailed description of the item, without going too much in the implementation.
- **Code example(s).**
- **Safety or panic notes.**
## Collaboration
Any kind of collaboration is welcome, especially corrections, wording, new ideas and guidelines on where the focus should be put in.
---
### Related issues
- Fixes#2246
# Objective
[Tracy](https://github.com/wolfpld/tracy) is:
> A real time, nanosecond resolution, remote telemetry, hybrid frame and sampling profiler for games and other applications.
With the `trace_tracy` feature enabled, you run your bevy app and either a headless server (`capture`) or a live, interactive profiler UI (`Tracy`), and connect that to your bevy application to then stream the metric data and events, and save it or inspect it live/offline.
Previously when I implemented the spans across systems and stages and I was trying out different profiling tools, Tracy was too unstable on macOS to use. But now, quite some months later, it is working stably with Tracy 0.7.8. You can see timelines, aggregate statistics of mean system/stage execution times, and much more. It's very useful!
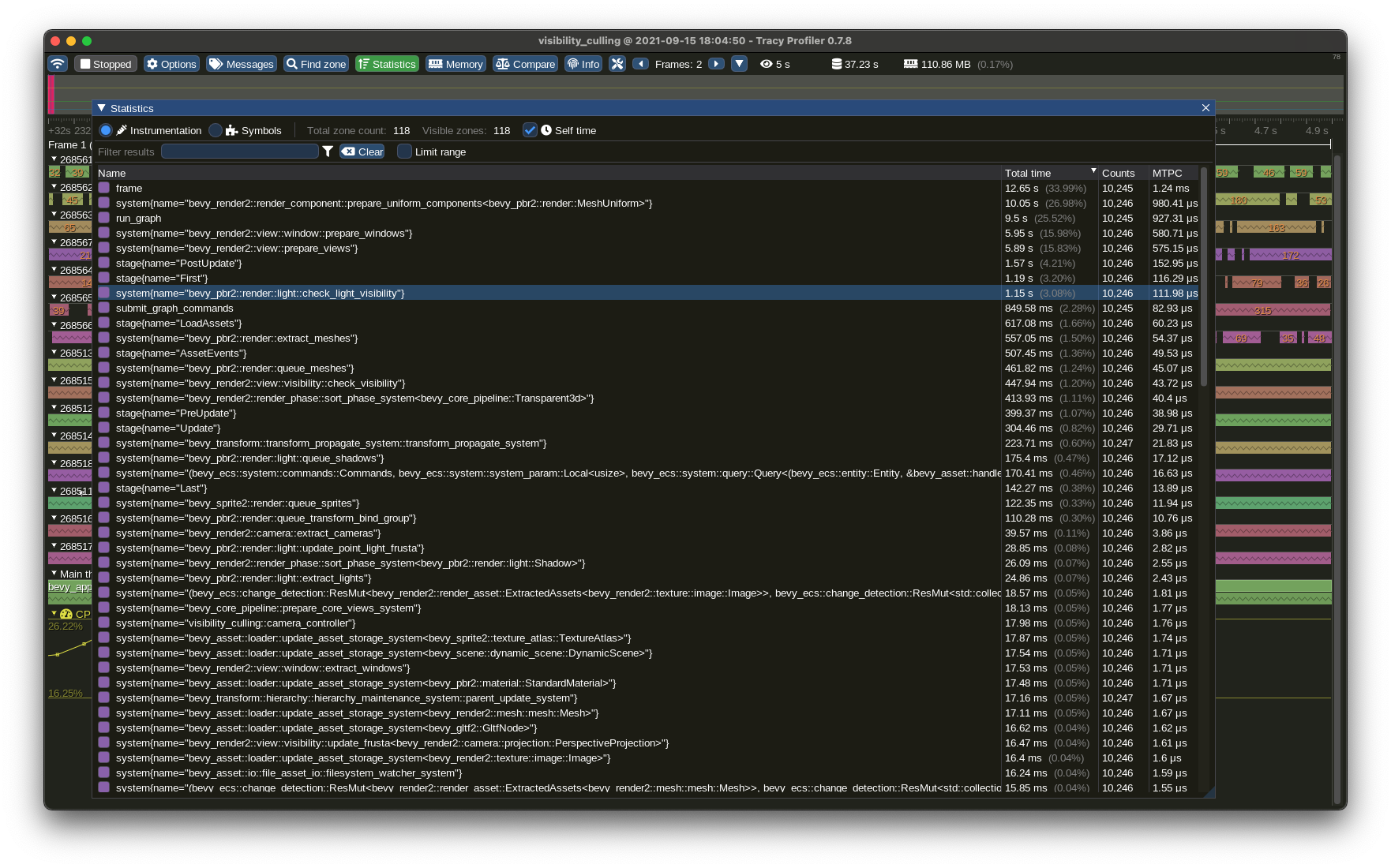
## Solution
- Use the `tracing-tracy` crate which supports our tracing spans
- Expose via the non-default feature `trace_tracy` for consistency with other `trace*` features
Before using this image resulted in an `Error in Queue::write_texture: copy of 0..4 would end up overrunning the bounds of the Source buffer of size 0`
# Objective
Bevy should expose all wgpu types needed for building rendering pipelines.
Closes#2818
## Solution
Add wgpu's StencilOperation to bevy_render2::render_resource's export.
This updates the `pipelined-rendering` branch to use the latest `bevy_ecs` from `main`. This accomplishes a couple of goals:
1. prepares for upcoming `custom-shaders` branch changes, which were what drove many of the recent bevy_ecs changes on `main`
2. prepares for the soon-to-happen merge of `pipelined-rendering` into `main`. By including bevy_ecs changes now, we make that merge simpler / easier to review.
I split this up into 3 commits:
1. **add upstream bevy_ecs**: please don't bother reviewing this content. it has already received thorough review on `main` and is a literal copy/paste of the relevant folders (the old folders were deleted so the directories are literally exactly the same as `main`).
2. **support manual buffer application in stages**: this is used to enable the Extract step. we've already reviewed this once on the `pipelined-rendering` branch, but its worth looking at one more time in the new context of (1).
3. **support manual archetype updates in QueryState**: same situation as (2).
# Objective
- CI is failing again
- These failures result from https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/85200
## Solution
- Fix the errors which result from this by using the given fields
- I also removed the now unused `Debug` impl.
I suspect that we shouldn't use -D warnings for nightly CI - ideally we'd get a discord webhook message into some (non-#github) dedicated channel on warnings.
But this does not implement that.
# Objective
The vast majority of `.single()` usage I've seen is immediately followed by a `.unwrap()`. Since it seems most people use it without handling the error, I think making it easier to just get what you want fast while also having a more verbose alternative when you want to handle the error could help.
## Solution
Instead of having a lot of `.unwrap()` everywhere, this PR introduces a `try_single()` variant that behaves like the current `.single()` and make the new `.single()` panic on error.
# Objective
My attempt at fixing #2075 .
This is my very first contribution to this repo. Also, I'm very new to both Rust and bevy, so any feedback is *deeply* appreciated.
## Solution
- Changed `move_camera_system` so it only targets the camera entity. My approach here differs from the one used in the [cheatbook](https://bevy-cheatbook.github.io/cookbook/cursor2world.html?highlight=maincamera#2d-games) (in which a marker component is used to track the camera), so please, let me know which of them is more idiomatic.
- `move_camera_system` does not require both `Position` and `Transform` anymore (I used `rotate` for rotating the `Transform` in place, but couldn't find an equivalent `translate` method).
- Changed `tick_system` so it only targets the timer entity.
- Sprites are now spawned via a single `spawn_batch` instead of multiple `spawn`s.
# Objective
- Fixes#2751
## Solution
- Avoid changing the window size if there is a scale factor override
- Can be tested with the `scale_factor_override` example - use <kbd>⏎</kbd> to active overriding the scale factor
A few minor changes to fix warnings emitted from clippy on the nightly toolchain, including redundant_allocation, unwrap_or_else_default, and collapsible_match, fixes#2698
# Objective
Make it easier to construct transforms. E.g.
```rs
Transform::from_xyz(0.0, 0.0, 10.0).with_scale(Vec3::splat(2.0))
```
I found myself writing an extension method to do this so I don't have to write:
```rs
Transform {
translation: Vec3::new(0.0, 0.0, 10.0),
scale: Vec3::splat(2.0),
..Default::default()
}
```
## Solution
Add *builder style* methods to `Transform`.
Methods:
- `with_translation`
- `with_rotation`
- `with_scale`
I also added these methods to `GlobalTransform`. But they are probably less useful there.
# Objective
Expand the documentation for NixOS setups (as discussed in Discord)
## Solution
Added more info to `linux_dependencies.md` about NixOS. This is based off my own experience (as documented in [this blog post](https://blog.thomasheartman.com/posts/bevy-getting-started-on-nixos)), so I can't confirm that it'll work for everyone. However, if there are further tweaks necessary, then I think that this should nevertheless work as a good starting point and should give future users an idea of what they may need to change or update.
Feedback and tweaks are very welcome 😄
Updates the requirements on [glam](https://github.com/bitshifter/glam-rs) to permit the latest version.
<details>
<summary>Changelog</summary>
<p><em>Sourced from <a href="https://github.com/bitshifter/glam-rs/blob/main/CHANGELOG.md">glam's changelog</a>.</em></p>
<blockquote>
<h2>[0.18.0] - 2021-08-26</h2>
<h3>Breaking changes</h3>
<ul>
<li>Minimum Supported Version of Rust bumped to 1.51.0 for <code>wasm-bindgen-test</code>
and <code>rustdoc</code> <code>alias</code> support.</li>
</ul>
<h3>Added</h3>
<ul>
<li>Added <code>wasm32</code> SIMD intrinsics support.</li>
<li>Added optional support for the <code>rkyv</code> serialization crate.</li>
<li>Added <code>Rem</code> and <code>RemAssign</code> implementations for all vector types.</li>
<li>Added quaternion <code>xyz()</code> method for returning the vector part of the
quaternion.</li>
<li>Added <code>From((Scalar, Vector3))</code> for 4D vector types.</li>
</ul>
<h3>Changed</h3>
<ul>
<li>Deprecated <code>as_f32()</code>, <code>as_f64()</code>, <code>as_i32()</code> and <code>as_u32()</code> methods in favor
of more specific methods such as <code>as_vec2()</code>, <code>as_dvec2()</code>, <code>as_ivec2()</code> and
<code>as_uvec2()</code> and so on.</li>
</ul>
<h2>[0.17.3] - 2021-07-18</h2>
<h3>Fixed</h3>
<ul>
<li>Fix alignment unit tests on non x86 platforms.</li>
</ul>
<h2>[0.17.2] - 2021-07-15</h2>
<h3>Fixed</h3>
<ul>
<li>Fix alignment unit tests on i686 and S390x.</li>
</ul>
<h2>[0.17.1] - 2021-06-29</h2>
<h3>Added</h3>
<ul>
<li>Added <code>serde</code> support for <code>Affine2</code>, <code>DAffine2</code>, <code>Affine3A</code> and <code>DAffine3</code>.</li>
</ul>
<h2>[0.17.0] - 2021-06-26</h2>
<h3>Breaking changes</h3>
<ul>
<li>The addition of <code>Add</code> and <code>Sub</code> implementations of scalar values for vector
types may create ambiguities with existing calls to <code>add</code> and <code>sub</code>.</li>
<li>Removed <code>From<Mat3></code> implementation for <code>Mat2</code> and <code>From<DMat3></code> for <code>DMat2</code>.
These have been replaced by <code>Mat2::from_mat3()</code> and <code>DMat2::from_mat3()</code>.</li>
<li>Removed <code>From<Mat4></code> implementation for <code>Mat3</code> and <code>From<DMat4></code> for <code>DMat3</code>.
These have been replaced by <code>Mat3::from_mat4()</code> and <code>DMat3::from_mat4()</code>.</li>
</ul>
<!-- raw HTML omitted -->
</blockquote>
<p>... (truncated)</p>
</details>
<details>
<summary>Commits</summary>
<ul>
<li><a href="1b703518e7"><code>1b70351</code></a> Merge pull request <a href="https://github-redirect.dependabot.com/bitshifter/glam-rs/issues/231">#231</a> from bitshifter/prepare-0.18.0</li>
<li><a href="935ad5cf64"><code>935ad5c</code></a> Prepare 0.18.0 release.</li>
<li><a href="8d79d8e907"><code>8d79d8e</code></a> Still managed to mess up the tarpaulin config...</li>
<li><a href="78c30fc72c"><code>78c30fc</code></a> Fix syntax error in tarpaulin config.</li>
<li><a href="0258ce710d"><code>0258ce7</code></a> Can use rustdoc alias after msrv bump to 1.51.0.</li>
<li><a href="f9f7f2407c"><code>f9f7f24</code></a> Tidy up tarpaulin exlcudes.</li>
<li><a href="95dab216e1"><code>95dab21</code></a> Make some dev deps wasm only on not wasm.</li>
<li><a href="342176dde9"><code>342176d</code></a> Merge pull request <a href="https://github-redirect.dependabot.com/bitshifter/glam-rs/issues/230">#230</a> from DJMcNab/bytemuck-spirv</li>
<li><a href="837e5ebf7f"><code>837e5eb</code></a> Bytemuck now compiles on spirv</li>
<li><a href="bb35b1a691"><code>bb35b1a</code></a> Merge pull request <a href="https://github-redirect.dependabot.com/bitshifter/glam-rs/issues/228">#228</a> from bitshifter/wasm32-simd</li>
<li>Additional commits viewable in <a href="https://github.com/bitshifter/glam-rs/compare/0.17.3...0.18.0">compare view</a></li>
</ul>
</details>
<br />
Dependabot will resolve any conflicts with this PR as long as you don't alter it yourself. You can also trigger a rebase manually by commenting `@dependabot rebase`.
[//]: # (dependabot-automerge-start)
[//]: # (dependabot-automerge-end)
---
<details>
<summary>Dependabot commands and options</summary>
<br />
You can trigger Dependabot actions by commenting on this PR:
- `@dependabot rebase` will rebase this PR
- `@dependabot recreate` will recreate this PR, overwriting any edits that have been made to it
- `@dependabot merge` will merge this PR after your CI passes on it
- `@dependabot squash and merge` will squash and merge this PR after your CI passes on it
- `@dependabot cancel merge` will cancel a previously requested merge and block automerging
- `@dependabot reopen` will reopen this PR if it is closed
- `@dependabot close` will close this PR and stop Dependabot recreating it. You can achieve the same result by closing it manually
- `@dependabot ignore this major version` will close this PR and stop Dependabot creating any more for this major version (unless you reopen the PR or upgrade to it yourself)
- `@dependabot ignore this minor version` will close this PR and stop Dependabot creating any more for this minor version (unless you reopen the PR or upgrade to it yourself)
- `@dependabot ignore this dependency` will close this PR and stop Dependabot creating any more for this dependency (unless you reopen the PR or upgrade to it yourself)
</details>
# Objective
- All new PRs should get the "S-Needs-Triage" label. But at the moment we for example are getting quite a few PRs to the new renderer branch that do not get the label.
## Solution
- Remove the required target "main" from the workflow
- Also removed configuration for not needed functionality of the labeler action (see [docs](https://github.com/actions/labeler#inputs))
# Objective
- The breakout scoreboard was not using the correct text section to display the score integer.
## Solution
- This updates the code to use the correct text section.
# Objective
Make it easier to check if some set of inputs matches a key, such as if you want to allow all of space or up or w for jumping.
Currently, this requires:
```rust
if keyboard.pressed(KeyCode::Space)
|| keyboard.pressed(KeyCode::Up)
|| keyboard.pressed(KeyCode::W) {
// ...
```
## Solution
Add an implementation of the helper methods, which very simply iterate through the items, used as:
```rust
if keyboard.any_pressed([KeyCode::Space, KeyCode::Up, KeyCode::W]) {
```
# Objective
Sometimes, the unwraps in `entity_mut` could fail here, if the entity was despawned *before* this command was applied.
The simplest case involves two command buffers:
```rust
use bevy::prelude::*;
fn b(mut commands1: Commands, mut commands2: Commands) {
let id = commands2.spawn().insert_bundle(()).id();
commands1.entity(id).despawn();
}
fn main() {
App::build().add_system(b.system()).run();
}
```
However, a more complicated version arises in the case of ambiguity:
```rust
use std::time::Duration;
use bevy::{app::ScheduleRunnerPlugin, prelude::*};
use rand::Rng;
fn cleanup(mut e: ResMut<Option<Entity>>) {
*e = None;
}
fn sleep_randomly() {
let mut rng = rand::thread_rng();
std:🧵:sleep(Duration::from_millis(rng.gen_range(0..50)));
}
fn spawn(mut commands: Commands, mut e: ResMut<Option<Entity>>) {
*e = Some(commands.spawn().insert_bundle(()).id());
}
fn despawn(mut commands: Commands, e: Res<Option<Entity>>) {
let mut rng = rand::thread_rng();
std:🧵:sleep(Duration::from_millis(rng.gen_range(0..50)));
if let Some(e) = *e {
commands.entity(e).despawn();
}
}
fn main() {
App::build()
.add_system(cleanup.system().label("cleanup"))
.add_system(sleep_randomly.system().label("before_despawn"))
.add_system(despawn.system().after("cleanup").after("before_despawn"))
.add_system(sleep_randomly.system().label("before_spawn"))
.add_system(spawn.system().after("cleanup").after("before_spawn"))
.insert_resource(None::<Entity>)
.add_plugin(ScheduleRunnerPlugin::default())
.run();
}
```
In the cases where this example crashes, it's because `despawn` was ordered before `spawn` in the topological ordering of systems (which determines when buffers are applied). However, `despawn` actually ran *after* `spawn`, because these systems are ambiguous, so the jiggles in the sleeping time triggered a case where this works.
## Solution
- Give a better error message
# Objective
Fix `Option<NonSend<T>>` to work when T isn't `Send`
Fix `Option<NonSendMut<T>>` to work when T isnt in the world.
## Solution
Simple two row fix, properly initialize T in `OptionNonSendState` and remove `T: Component` bound for `Option<NonSendMut<T>>`
also added a rudimentary test
Co-authored-by: Ïvar Källström <ivar.kallstrom@gmail.com>
# Objective
Fixes a usability problem where the user is unable to use their reference to a ComputePipeline in their compute pass.
## Solution
Implements Deref, allowing the user to obtain the reference to the underlying wgpu::ComputePipeline
# Objective
- Make it easy to use HexColorError with `thiserror`, i.e. converting it into other error types.
Makes this possible:
```rust
#[derive(Debug, thiserror::Error)]
pub enum LdtkError {
#[error("An error occured while deserializing")]
Json(#[from] serde_json::Error),
#[error("An error occured while parsing a color")]
HexColor(#[from] bevy::render::color::HexColorError),
}
```
## Solution
- Derive thiserror::Error the same way we do elsewhere (see query.rs for instance)
# Objective
M1 Macs / Apple Silicon / simply aarch64 needs to be specified for it to compile with zld, so users might be surprised to find that they aren't getting the benefits and see the fast compiles they might be seeing on other platforms.
## Solution
- Add it? :)
# Objective
Forward perspective projections have poor floating point precision distribution over the depth range. Reverse projections fair much better, and instead of having to have a far plane, with the reverse projection, using an infinite far plane is not a problem. The infinite reverse perspective projection has become the industry standard. The renderer rework is a great time to migrate to it.
## Solution
All perspective projections, including point lights, have been moved to using `glam::Mat4::perspective_infinite_reverse_rh()` and so have no far plane. As various depth textures are shared between orthographic and perspective projections, a quirk of this PR is that the near and far planes of the orthographic projection are swapped when the Mat4 is computed. This has no impact on 2D/3D orthographic projection usage, and provides consistency in shaders, texture clear values, etc. throughout the codebase.
## Known issues
For some reason, when looking along -Z, all geometry is black. The camera can be translated up/down / strafed left/right and geometry will still be black. Moving forward/backward or rotating the camera away from looking exactly along -Z causes everything to work as expected.
I have tried to debug this issue but both in macOS and Windows I get crashes when doing pixel debugging. If anyone could reproduce this and debug it I would be very grateful. Otherwise I will have to try to debug it further without pixel debugging, though the projections and such all looked fine to me.
# Objective
- Prevent the need to have a system that synchronizes sprite sizes with their images
## Solution
- Read the sprite size from the image asset when rendering the sprite
- Replace the `size` and `resize_mode` fields of `Sprite` with a `custom_size: Option<Vec2>` that will modify the sprite's rendered size to be different than the image size, but only if it is `Some(Vec2)`
# Objective
- Fixes#2674
- Check that benches build
## Solution
- Adds a job that runs `cargo check --benches`
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- QueryState is lacking documentation.
Fixes#2090
## Solution
- Provide documentation that mirrors Query (as suggested in #2090) and modify as needed.
Co-authored-by: James Leflang <59455417+jleflang@users.noreply.github.com>
This upstreams the code changes used by the new renderer to enable cross-app Entity reuse:
* Spawning at specific entities
* get_or_spawn: spawns an entity if it doesn't already exist and returns an EntityMut
* insert_or_spawn_batch: the batched equivalent to `world.get_or_spawn(entity).insert_bundle(bundle)`
* Clearing entities and storages
* Allocating Entities with "invalid" archetypes. These entities cannot be queried / are treated as "non existent". They serve as "reserved" entities that won't show up when calling `spawn()`. They must be "specifically spawned at" using apis like `get_or_spawn(entity)`.
In combination, these changes enable the "render world" to clear entities / storages each frame and reserve all "app world entities". These can then be spawned during the "render extract step".
This refactors "spawn" and "insert" code in a way that I think is a massive improvement to legibility and re-usability. It also yields marginal performance wins by reducing some duplicate lookups (less than a percentage point improvement on insertion benchmarks). There is also some potential for future unsafe reduction (by making BatchSpawner and BatchInserter generic). But for now I want to cut down generic usage to a minimum to encourage smaller binaries and faster compiles.
This is currently a draft because it needs more tests (although this code has already had some real-world testing on my custom-shaders branch).
I also fixed the benchmarks (which currently don't compile!) / added new ones to illustrate batching wins.
After these changes, Bevy ECS is basically ready to accommodate the new renderer. I think the biggest missing piece at this point is "sub apps".
# Objective
- Avoid unnecessary work in the vertex shader of the numerous shadow passes
- Have the natural order of bind groups in the pbr shader: view, material, mesh
## Solution
- Separate out the vertex stage of pbr.wgsl into depth.wgsl
- Remove the unnecessary calculation of uv and normal, as well as removing the unnecessary vertex inputs and outputs
- Use the depth.wgsl for shadow passes
- Reorder the bind groups in pbr.wgsl and PbrShaders to be 0 - view, 1 - material, 2 - mesh in decreasing order of rebind frequency
# Objective
Allow marking meshes as not casting / receiving shadows.
## Solution
- Added `NotShadowCaster` and `NotShadowReceiver` zero-sized type components.
- Extract these components into `bool`s in `ExtractedMesh`
- Only generate `DrawShadowMesh` `Drawable`s for meshes _without_ `NotShadowCaster`
- Add a `u32` bit `flags` member to `MeshUniform` with one flag indicating whether the mesh is a shadow receiver
- If a mesh does _not_ have the `NotShadowReceiver` component, then it is a shadow receiver, and so the bit in the `MeshUniform` is set, otherwise it is not set.
- Added an example illustrating the functionality.
NOTE: I wanted to have the default state of a mesh as being a shadow caster and shadow receiver, hence the `Not*` components. However, I am on the fence about this. I don't want to have a negative performance impact, nor have people wondering why their custom meshes don't have shadows because they forgot to add `ShadowCaster` and `ShadowReceiver` components, but I also really don't like the double negatives the `Not*` approach incurs. What do you think?
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
Add support for configurable shadow map sizes
## Solution
- Add `DirectionalLightShadowMap` and `PointLightShadowMap` resources, which just have size members, to the app world, and add `Extracted*` counterparts to the render world
- Use the configured sizes when rendering shadow maps
- Default sizes remain the same - 4096 for directional light shadow maps, 1024 for point light shadow maps (which are cube maps so 6 faces at 1024x1024 per light)
Makes some tweaks to the SubApp labeling introduced in #2695:
* Ergonomics improvements
* Removes unnecessary allocation when retrieving subapp label
* Removes the newly added "app macros" crate in favor of bevy_derive
* renamed RenderSubApp to RenderApp
@zicklag (for reference)
# Objective
- Clarify vague meaning of "Ltr" and "Rtl". For someone familiar with Flex Box, this is easy to understand, but being more explicit will help beginners or those unfamiliar, without the need to do research.
## Solution
- Change three letter abbreviation to fully descriptive name.
This matches `ahash::RandomState`, which provides both `Debug` and `Clone`.
Notably, implementing `Clone` allows the `StableHashMap`/`Set` to also implement `Clone`.
# Objective
- Allow `bevy_utils::StableHashMap` to be cloned.
## Solution
- Derive `Clone` for `bevy_utils::FixedState`.
- Also derive `Debug`, since we're touching it anyway, and this aligns `FixedState` with `ahash::RandomState`.
This is a rather simple but wide change, and it involves adding a new `bevy_app_macros` crate. Let me know if there is a better way to do any of this!
---
# Objective
- Allow adding and accessing sub-apps by using a label instead of an index
## Solution
- Migrate the bevy label implementation and derive code to the `bevy_utils` and `bevy_macro_utils` crates and then add a new `SubAppLabel` trait to the `bevy_app` crate that is used when adding or getting a sub-app from an app.
# Objective
A question was raised on Discord about the units of the `PointLight` `intensity` member.
After digging around in the bevy_pbr2 source code and [Google Filament documentation](https://google.github.io/filament/Filament.html#mjx-eqn-pointLightLuminousPower) I discovered that the intention by Filament was that the 'intensity' value for point lights would be in lumens. This makes a lot of sense as these are quite relatable units given basically all light bulbs I've seen sold over the past years are rated in lumens as people move away from thinking about how bright a bulb is relative to a non-halogen incandescent bulb.
However, it seems that the derivation of the conversion between luminous power (lumens, denoted `Φ` in the Filament formulae) and luminous intensity (lumens per steradian, `I` in the Filament formulae) was missed and I can see why as it is tucked right under equation 58 at the link above. As such, while the formula states that for a point light, `I = Φ / 4 π` we have been using `intensity` as if it were luminous intensity `I`.
Before this PR, the intensity field is luminous intensity in lumens per steradian. After this PR, the intensity field is luminous power in lumens, [as suggested by Filament](https://google.github.io/filament/Filament.html#table_lighttypesunits) (unfortunately the link jumps to the table's caption so scroll up to see the actual table).
I appreciate that it may be confusing to call this an intensity, but I think this is intended as more of a non-scientific, human-relatable general term with a bit of hand waving so that most light types can just have an intensity field and for most of them it works in the same way or at least with some relatable value. I'm inclined to think this is reasonable rather than throwing terms like luminous power, luminous intensity, blah at users.
## Solution
- Documented the `PointLight` `intensity` member as 'luminous power' in units of lumens.
- Added a table of examples relating from various types of household lighting to lumen values.
- Added in the mapping from luminous power to luminous intensity when premultiplying the intensity into the colour before it is made into a graphics uniform.
- Updated the documentation in `pbr.wgsl` to clarify the earlier confusion about the missing `/ 4 π`.
- Bumped the intensity of the point lights in `3d_scene_pipelined` to 1600 lumens.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
The default perspective projection near plane being at 1 unit feels very far away if one considers units to directly map to real world units such as metres. Not being able to see anything that is closer than 1m is unnecessarily limiting. Using a default of 0.1 makes more sense as it is difficult to even focus on things closer than 10cm in the real world.
## Solution
- Changed the default perspective projection near plane to 0.1.
# Objective
- Allow the user to set the clear color when using the pipelined renderer
## Solution
- Add a `ClearColor` resource that can be added to the world to configure the clear color
## Remaining Issues
Currently the `ClearColor` resource is cloned from the app world to the render world every frame. There are two ways I can think of around this:
1. Figure out why `app_world.is_resource_changed::<ClearColor>()` always returns `true` in the `extract` step and fix it so that we are only updating the resource when it changes
2. Require the users to add the `ClearColor` resource to the render sub-app instead of the parent app. This is currently sub-optimal until we have labled sub-apps, and probably a helper funciton on `App` such as `app.with_sub_app(RenderApp, |app| { ... })`. Even if we had that, I think it would be more than we want the user to have to think about. They shouldn't have to know about the render sub-app I don't think.
I think the first option is the best, but I could really use some help figuring out the nuance of why `is_resource_changed` is always returning true in that context.
# Objective
- the plugin guidelines should be up-to-date and easy to read/understand
## Solution
* point to "Bevy Assets" instead of old "Awesome Bevy"
* restructure sections
* same order for sections and checklist
* Update examples with newest release/rev