Applogies, had to recreate this pr because of branching issue.
Old PR: https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/3033
# Objective
Fixes#3032
Allowing a user to create a transparent window
## Solution
I've allowed the transparent bool to be passed to the winit window builder
# Objective
Fixes#3181
## Solution
Refactored `contributors.rs` example:
- Renamed unclear variables
- Split setup system into two separate systems
Co-authored-by: CrazyRoka <rokarostuk@gmail.com>
# Objective
- iOS CI has linker issues https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/runs/4388921574?check_suite_focus=true
## Solution
- Building for iOS actually requires ~~both iOS SDK for target and~~ macOS SDK for build scripts. ~~I added them both when needed~~ I replaced the iOS SDK with the maOS. This was not an issue on m1 as they are compatible enough to make the build pass.
- This completely confused `shader-sys` which fails to build in this configuration. Luckily as the example now uses the new renderer, I was able to remove the old renderer and depend no more on this lib.
This is confirmed to work:
- on intel mac with simulator
- on m1 mac with simulator
- on m1 mac with real iphone
# Objective
- With #3109 I broke iOS CI: https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/runs/4374891646?check_suite_focus=true
## Solution
- Fix indentation in makefile
- Adds scheme that is now needed
With this, `make install` works on my m1 Mac but still fails on my intel Mac unless I run something like `make install; cargo build --target x86_64-apple-ios; make install; cargo build --target x86_64-apple-ios; make install`. It seems something is off when executing cargo through `xcodebuild` on my setup but not sure what. So this PR will probably not fix iOS CI 😞
# Objective
- Remove `cargo-lipo` as [it's deprecated](https://github.com/TimNN/cargo-lipo#maintenance-status) and doesn't work on new Apple processors
- Fix CI that will fail as soon as GitHub update the worker used by Bevy to macOS 11
## Solution
- Replace `cargo-lipo` with building with the correct target
- Setup the correct path to libraries by using `xcrun --show-sdk-path`
- Also try and fix path to cmake in case it's not found but available through homebrew
## Shader Imports
This adds "whole file" shader imports. These come in two flavors:
### Asset Path Imports
```rust
// /assets/shaders/custom.wgsl
#import "shaders/custom_material.wgsl"
[[stage(fragment)]]
fn fragment() -> [[location(0)]] vec4<f32> {
return get_color();
}
```
```rust
// /assets/shaders/custom_material.wgsl
[[block]]
struct CustomMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CustomMaterial;
```
### Custom Path Imports
Enables defining custom import paths. These are intended to be used by crates to export shader functionality:
```rust
// bevy_pbr2/src/render/pbr.wgsl
#import bevy_pbr::mesh_view_bind_group
#import bevy_pbr::mesh_bind_group
[[block]]
struct StandardMaterial {
base_color: vec4<f32>;
emissive: vec4<f32>;
perceptual_roughness: f32;
metallic: f32;
reflectance: f32;
flags: u32;
};
/* rest of PBR fragment shader here */
```
```rust
impl Plugin for MeshRenderPlugin {
fn build(&self, app: &mut bevy_app::App) {
let mut shaders = app.world.get_resource_mut::<Assets<Shader>>().unwrap();
shaders.set_untracked(
MESH_BIND_GROUP_HANDLE,
Shader::from_wgsl(include_str!("mesh_bind_group.wgsl"))
.with_import_path("bevy_pbr::mesh_bind_group"),
);
shaders.set_untracked(
MESH_VIEW_BIND_GROUP_HANDLE,
Shader::from_wgsl(include_str!("mesh_view_bind_group.wgsl"))
.with_import_path("bevy_pbr::mesh_view_bind_group"),
);
```
By convention these should use rust-style module paths that start with the crate name. Ultimately we might enforce this convention.
Note that this feature implements _run time_ import resolution. Ultimately we should move the import logic into an asset preprocessor once Bevy gets support for that.
## Decouple Mesh Logic from PBR Logic via MeshRenderPlugin
This breaks out mesh rendering code from PBR material code, which improves the legibility of the code, decouples mesh logic from PBR logic, and opens the door for a future `MaterialPlugin<T: Material>` that handles all of the pipeline setup for arbitrary shader materials.
## Removed `RenderAsset<Shader>` in favor of extracting shaders into RenderPipelineCache
This simplifies the shader import implementation and removes the need to pass around `RenderAssets<Shader>`.
## RenderCommands are now fallible
This allows us to cleanly handle pipelines+shaders not being ready yet. We can abort a render command early in these cases, preventing bevy from trying to bind group / do draw calls for pipelines that couldn't be bound. This could also be used in the future for things like "components not existing on entities yet".
# Next Steps
* Investigate using Naga for "partial typed imports" (ex: `#import bevy_pbr::material::StandardMaterial`, which would import only the StandardMaterial struct)
* Implement `MaterialPlugin<T: Material>` for low-boilerplate custom material shaders
* Move shader import logic into the asset preprocessor once bevy gets support for that.
Fixes#3132
# Objective
- Document that the error codes will be rendered on the bevy website (see bevyengine/bevy-website#216)
- Some Cargo.toml files did not include the license or a description field
## Solution
- Readme for the errors crate
- Mark internal/development crates with `publish = false`
- Add missing license/descriptions to some crates
- [x] merge bevyengine/bevy-website#216
Adds new `EntityRenderCommand`, `EntityPhaseItem`, and `CachedPipelinePhaseItem` traits to make it possible to reuse RenderCommands across phases. This should be helpful for features like #3072 . It also makes the trait impls slightly less generic-ey in the common cases.
This also fixes the custom shader examples to account for the recent Frustum Culling and MSAA changes (the UX for these things will be improved later).
This implements the following:
* **Sprite Batching**: Collects sprites in a vertex buffer to draw many sprites with a single draw call. Sprites are batched by their `Handle<Image>` within a specific z-level. When possible, sprites are opportunistically batched _across_ z-levels (when no sprites with a different texture exist between two sprites with the same texture on different z levels). With these changes, I can now get ~130,000 sprites at 60fps on the `bevymark_pipelined` example.
* **Sprite Color Tints**: The `Sprite` type now has a `color` field. Non-white color tints result in a specialized render pipeline that passes the color in as a vertex attribute. I chose to specialize this because passing vertex colors has a measurable price (without colors I get ~130,000 sprites on bevymark, with colors I get ~100,000 sprites). "Colored" sprites cannot be batched with "uncolored" sprites, but I think this is fine because the chance of a "colored" sprite needing to batch with other "colored" sprites is generally probably way higher than an "uncolored" sprite needing to batch with a "colored" sprite.
* **Sprite Flipping**: Sprites can be flipped on their x or y axis using `Sprite::flip_x` and `Sprite::flip_y`. This is also true for `TextureAtlasSprite`.
* **Simpler BufferVec/UniformVec/DynamicUniformVec Clearing**: improved the clearing interface by removing the need to know the size of the final buffer at the initial clear.
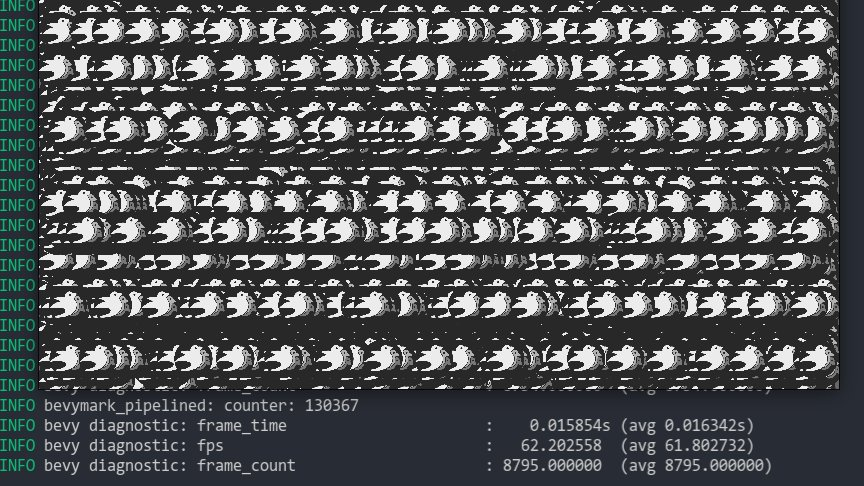
Note that this moves sprites away from entity-driven rendering and back to extracted lists. We _could_ use entities here, but it necessitates that an intermediate list is allocated / populated to collect and sort extracted sprites. This redundant copy, combined with the normal overhead of spawning extracted sprite entities, brings bevymark down to ~80,000 sprites at 60fps. I think making sprites a bit more fixed (by default) is worth it. I view this as acceptable because batching makes normal entity-driven rendering pretty useless anyway (and we would want to batch most custom materials too). We can still support custom shaders with custom bindings, we'll just need to define a specific interface for it.
Add an example that demonstrates the difference between no MSAA and MSAA 4x. This is also useful for testing panics when resizing the window using MSAA. This is on top of #3042 .
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
## New Features
This adds the following to the new renderer:
* **Shader Assets**
* Shaders are assets again! Users no longer need to call `include_str!` for their shaders
* Shader hot-reloading
* **Shader Defs / Shader Preprocessing**
* Shaders now support `# ifdef NAME`, `# ifndef NAME`, and `# endif` preprocessor directives
* **Bevy RenderPipelineDescriptor and RenderPipelineCache**
* Bevy now provides its own `RenderPipelineDescriptor` and the wgpu version is now exported as `RawRenderPipelineDescriptor`. This allows users to define pipelines with `Handle<Shader>` instead of needing to manually compile and reference `ShaderModules`, enables passing in shader defs to configure the shader preprocessor, makes hot reloading possible (because the descriptor can be owned and used to create new pipelines when a shader changes), and opens the doors to pipeline specialization.
* The `RenderPipelineCache` now handles compiling and re-compiling Bevy RenderPipelineDescriptors. It has internal PipelineLayout and ShaderModule caches. Users receive a `CachedPipelineId`, which can be used to look up the actual `&RenderPipeline` during rendering.
* **Pipeline Specialization**
* This enables defining per-entity-configurable pipelines that specialize on arbitrary custom keys. In practice this will involve specializing based on things like MSAA values, Shader Defs, Bind Group existence, and Vertex Layouts.
* Adds a `SpecializedPipeline` trait and `SpecializedPipelines<MyPipeline>` resource. This is a simple layer that generates Bevy RenderPipelineDescriptors based on a custom key defined for the pipeline.
* Specialized pipelines are also hot-reloadable.
* This was the result of experimentation with two different approaches:
1. **"generic immediate mode multi-key hash pipeline specialization"**
* breaks up the pipeline into multiple "identities" (the core pipeline definition, shader defs, mesh layout, bind group layout). each of these identities has its own key. looking up / compiling a specific version of a pipeline requires composing all of these keys together
* the benefit of this approach is that it works for all pipelines / the pipeline is fully identified by the keys. the multiple keys allow pre-hashing parts of the pipeline identity where possible (ex: pre compute the mesh identity for all meshes)
* the downside is that any per-entity data that informs the values of these keys could require expensive re-hashes. computing each key for each sprite tanked bevymark performance (sprites don't actually need this level of specialization yet ... but things like pbr and future sprite scenarios might).
* this is the approach rafx used last time i checked
2. **"custom key specialization"**
* Pipelines by default are not specialized
* Pipelines that need specialization implement a SpecializedPipeline trait with a custom key associated type
* This allows specialization keys to encode exactly the amount of information required (instead of needing to be a combined hash of the entire pipeline). Generally this should fit in a small number of bytes. Per-entity specialization barely registers anymore on things like bevymark. It also makes things like "shader defs" way cheaper to hash because we can use context specific bitflags instead of strings.
* Despite the extra trait, it actually generally makes pipeline definitions + lookups simpler: managing multiple keys (and making the appropriate calls to manage these keys) was way more complicated.
* I opted for custom key specialization. It performs better generally and in my opinion is better UX. Fortunately the way this is implemented also allows for custom caches as this all builds on a common abstraction: the RenderPipelineCache. The built in custom key trait is just a simple / pre-defined way to interact with the cache
## Callouts
* The SpecializedPipeline trait makes it easy to inherit pipeline configuration in custom pipelines. The changes to `custom_shader_pipelined` and the new `shader_defs_pipelined` example illustrate how much simpler it is to define custom pipelines based on the PbrPipeline.
* The shader preprocessor is currently pretty naive (it just uses regexes to process each line). Ultimately we might want to build a more custom parser for more performance + better error handling, but for now I'm happy to optimize for "easy to implement and understand".
## Next Steps
* Port compute pipelines to the new system
* Add more preprocessor directives (else, elif, import)
* More flexible vertex attribute specialization / enable cheaply specializing on specific mesh vertex layouts
Objective
During work on #3009 I've found that not all jobs use actions-rs, and therefore, an previous version of Rust is used for them. So while compilation and other stuff can pass, checking markup and Android build may fail with compilation errors.
Solution
This PR adds `action-rs` for any job running cargo, and updates the edition to 2021.
Upgrades both the old and new renderer to wgpu 0.11 (and naga 0.7). This builds on @zicklag's work here #2556.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
This implements the most minimal variant of #1843 - a derive for marker trait. This is a prerequisite to more complicated features like statically defined storage type or opt-out component reflection.
In order to make component struct's purpose explicit and avoid misuse, it must be annotated with `#[derive(Component)]` (manual impl is discouraged for compatibility). Right now this is just a marker trait, but in the future it might be expanded. Making this change early allows us to make further changes later without breaking backward compatibility for derive macro users.
This already prevents a lot of issues, like using bundles in `insert` calls. Primitive types are no longer valid components as well. This can be easily worked around by adding newtype wrappers and deriving `Component` for them.
One funny example of prevented bad code (from our own tests) is when an newtype struct or enum variant is used. Previously, it was possible to write `insert(Newtype)` instead of `insert(Newtype(value))`. That code compiled, because function pointers (in this case newtype struct constructor) implement `Send + Sync + 'static`, so we allowed them to be used as components. This is no longer the case and such invalid code will trigger a compile error.
Co-authored-by: = <=>
Co-authored-by: TheRawMeatball <therawmeatball@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
This changes how render logic is composed to make it much more modular. Previously, all extraction logic was centralized for a given "type" of rendered thing. For example, we extracted meshes into a vector of ExtractedMesh, which contained the mesh and material asset handles, the transform, etc. We looked up bindings for "drawn things" using their index in the `Vec<ExtractedMesh>`. This worked fine for built in rendering, but made it hard to reuse logic for "custom" rendering. It also prevented us from reusing things like "extracted transforms" across contexts.
To make rendering more modular, I made a number of changes:
* Entities now drive rendering:
* We extract "render components" from "app components" and store them _on_ entities. No more centralized uber lists! We now have true "ECS-driven rendering"
* To make this perform well, I implemented #2673 in upstream Bevy for fast batch insertions into specific entities. This was merged into the `pipelined-rendering` branch here: #2815
* Reworked the `Draw` abstraction:
* Generic `PhaseItems`: each draw phase can define its own type of "rendered thing", which can define its own "sort key"
* Ported the 2d, 3d, and shadow phases to the new PhaseItem impl (currently Transparent2d, Transparent3d, and Shadow PhaseItems)
* `Draw` trait and and `DrawFunctions` are now generic on PhaseItem
* Modular / Ergonomic `DrawFunctions` via `RenderCommands`
* RenderCommand is a trait that runs an ECS query and produces one or more RenderPass calls. Types implementing this trait can be composed to create a final DrawFunction. For example the DrawPbr DrawFunction is created from the following DrawCommand tuple. Const generics are used to set specific bind group locations:
```rust
pub type DrawPbr = (
SetPbrPipeline,
SetMeshViewBindGroup<0>,
SetStandardMaterialBindGroup<1>,
SetTransformBindGroup<2>,
DrawMesh,
);
```
* The new `custom_shader_pipelined` example illustrates how the commands above can be reused to create a custom draw function:
```rust
type DrawCustom = (
SetCustomMaterialPipeline,
SetMeshViewBindGroup<0>,
SetTransformBindGroup<2>,
DrawMesh,
);
```
* ExtractComponentPlugin and UniformComponentPlugin:
* Simple, standardized ways to easily extract individual components and write them to GPU buffers
* Ported PBR and Sprite rendering to the new primitives above.
* Removed staging buffer from UniformVec in favor of direct Queue usage
* Makes UniformVec much easier to use and more ergonomic. Completely removes the need for custom render graph nodes in these contexts (see the PbrNode and view Node removals and the much simpler call patterns in the relevant Prepare systems).
* Added a many_cubes_pipelined example to benchmark baseline 3d rendering performance and ensure there were no major regressions during this port. Avoiding regressions was challenging given that the old approach of extracting into centralized vectors is basically the "optimal" approach. However thanks to a various ECS optimizations and render logic rephrasing, we pretty much break even on this benchmark!
* Lifetimeless SystemParams: this will be a bit divisive, but as we continue to embrace "trait driven systems" (ex: ExtractComponentPlugin, UniformComponentPlugin, DrawCommand), the ergonomics of `(Query<'static, 'static, (&'static A, &'static B, &'static)>, Res<'static, C>)` were getting very hard to bear. As a compromise, I added "static type aliases" for the relevant SystemParams. The previous example can now be expressed like this: `(SQuery<(Read<A>, Read<B>)>, SRes<C>)`. If anyone has better ideas / conflicting opinions, please let me know!
* RunSystem trait: a way to define Systems via a trait with a SystemParam associated type. This is used to implement the various plugins mentioned above. I also added SystemParamItem and QueryItem type aliases to make "trait stye" ecs interactions nicer on the eyes (and fingers).
* RenderAsset retrying: ensures that render assets are only created when they are "ready" and allows us to create bind groups directly inside render assets (which significantly simplified the StandardMaterial code). I think ultimately we should swap this out on "asset dependency" events to wait for dependencies to load, but this will require significant asset system changes.
* Updated some built in shaders to account for missing MeshUniform fields
This updates the `pipelined-rendering` branch to use the latest `bevy_ecs` from `main`. This accomplishes a couple of goals:
1. prepares for upcoming `custom-shaders` branch changes, which were what drove many of the recent bevy_ecs changes on `main`
2. prepares for the soon-to-happen merge of `pipelined-rendering` into `main`. By including bevy_ecs changes now, we make that merge simpler / easier to review.
I split this up into 3 commits:
1. **add upstream bevy_ecs**: please don't bother reviewing this content. it has already received thorough review on `main` and is a literal copy/paste of the relevant folders (the old folders were deleted so the directories are literally exactly the same as `main`).
2. **support manual buffer application in stages**: this is used to enable the Extract step. we've already reviewed this once on the `pipelined-rendering` branch, but its worth looking at one more time in the new context of (1).
3. **support manual archetype updates in QueryState**: same situation as (2).
# Objective
The vast majority of `.single()` usage I've seen is immediately followed by a `.unwrap()`. Since it seems most people use it without handling the error, I think making it easier to just get what you want fast while also having a more verbose alternative when you want to handle the error could help.
## Solution
Instead of having a lot of `.unwrap()` everywhere, this PR introduces a `try_single()` variant that behaves like the current `.single()` and make the new `.single()` panic on error.
# Objective
My attempt at fixing #2075 .
This is my very first contribution to this repo. Also, I'm very new to both Rust and bevy, so any feedback is *deeply* appreciated.
## Solution
- Changed `move_camera_system` so it only targets the camera entity. My approach here differs from the one used in the [cheatbook](https://bevy-cheatbook.github.io/cookbook/cursor2world.html?highlight=maincamera#2d-games) (in which a marker component is used to track the camera), so please, let me know which of them is more idiomatic.
- `move_camera_system` does not require both `Position` and `Transform` anymore (I used `rotate` for rotating the `Transform` in place, but couldn't find an equivalent `translate` method).
- Changed `tick_system` so it only targets the timer entity.
- Sprites are now spawned via a single `spawn_batch` instead of multiple `spawn`s.
# Objective
- The breakout scoreboard was not using the correct text section to display the score integer.
## Solution
- This updates the code to use the correct text section.
# Objective
Make it easier to check if some set of inputs matches a key, such as if you want to allow all of space or up or w for jumping.
Currently, this requires:
```rust
if keyboard.pressed(KeyCode::Space)
|| keyboard.pressed(KeyCode::Up)
|| keyboard.pressed(KeyCode::W) {
// ...
```
## Solution
Add an implementation of the helper methods, which very simply iterate through the items, used as:
```rust
if keyboard.any_pressed([KeyCode::Space, KeyCode::Up, KeyCode::W]) {
```
# Objective
Forward perspective projections have poor floating point precision distribution over the depth range. Reverse projections fair much better, and instead of having to have a far plane, with the reverse projection, using an infinite far plane is not a problem. The infinite reverse perspective projection has become the industry standard. The renderer rework is a great time to migrate to it.
## Solution
All perspective projections, including point lights, have been moved to using `glam::Mat4::perspective_infinite_reverse_rh()` and so have no far plane. As various depth textures are shared between orthographic and perspective projections, a quirk of this PR is that the near and far planes of the orthographic projection are swapped when the Mat4 is computed. This has no impact on 2D/3D orthographic projection usage, and provides consistency in shaders, texture clear values, etc. throughout the codebase.
## Known issues
For some reason, when looking along -Z, all geometry is black. The camera can be translated up/down / strafed left/right and geometry will still be black. Moving forward/backward or rotating the camera away from looking exactly along -Z causes everything to work as expected.
I have tried to debug this issue but both in macOS and Windows I get crashes when doing pixel debugging. If anyone could reproduce this and debug it I would be very grateful. Otherwise I will have to try to debug it further without pixel debugging, though the projections and such all looked fine to me.
# Objective
- Prevent the need to have a system that synchronizes sprite sizes with their images
## Solution
- Read the sprite size from the image asset when rendering the sprite
- Replace the `size` and `resize_mode` fields of `Sprite` with a `custom_size: Option<Vec2>` that will modify the sprite's rendered size to be different than the image size, but only if it is `Some(Vec2)`
# Objective
Allow marking meshes as not casting / receiving shadows.
## Solution
- Added `NotShadowCaster` and `NotShadowReceiver` zero-sized type components.
- Extract these components into `bool`s in `ExtractedMesh`
- Only generate `DrawShadowMesh` `Drawable`s for meshes _without_ `NotShadowCaster`
- Add a `u32` bit `flags` member to `MeshUniform` with one flag indicating whether the mesh is a shadow receiver
- If a mesh does _not_ have the `NotShadowReceiver` component, then it is a shadow receiver, and so the bit in the `MeshUniform` is set, otherwise it is not set.
- Added an example illustrating the functionality.
NOTE: I wanted to have the default state of a mesh as being a shadow caster and shadow receiver, hence the `Not*` components. However, I am on the fence about this. I don't want to have a negative performance impact, nor have people wondering why their custom meshes don't have shadows because they forgot to add `ShadowCaster` and `ShadowReceiver` components, but I also really don't like the double negatives the `Not*` approach incurs. What do you think?
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
A question was raised on Discord about the units of the `PointLight` `intensity` member.
After digging around in the bevy_pbr2 source code and [Google Filament documentation](https://google.github.io/filament/Filament.html#mjx-eqn-pointLightLuminousPower) I discovered that the intention by Filament was that the 'intensity' value for point lights would be in lumens. This makes a lot of sense as these are quite relatable units given basically all light bulbs I've seen sold over the past years are rated in lumens as people move away from thinking about how bright a bulb is relative to a non-halogen incandescent bulb.
However, it seems that the derivation of the conversion between luminous power (lumens, denoted `Φ` in the Filament formulae) and luminous intensity (lumens per steradian, `I` in the Filament formulae) was missed and I can see why as it is tucked right under equation 58 at the link above. As such, while the formula states that for a point light, `I = Φ / 4 π` we have been using `intensity` as if it were luminous intensity `I`.
Before this PR, the intensity field is luminous intensity in lumens per steradian. After this PR, the intensity field is luminous power in lumens, [as suggested by Filament](https://google.github.io/filament/Filament.html#table_lighttypesunits) (unfortunately the link jumps to the table's caption so scroll up to see the actual table).
I appreciate that it may be confusing to call this an intensity, but I think this is intended as more of a non-scientific, human-relatable general term with a bit of hand waving so that most light types can just have an intensity field and for most of them it works in the same way or at least with some relatable value. I'm inclined to think this is reasonable rather than throwing terms like luminous power, luminous intensity, blah at users.
## Solution
- Documented the `PointLight` `intensity` member as 'luminous power' in units of lumens.
- Added a table of examples relating from various types of household lighting to lumen values.
- Added in the mapping from luminous power to luminous intensity when premultiplying the intensity into the colour before it is made into a graphics uniform.
- Updated the documentation in `pbr.wgsl` to clarify the earlier confusion about the missing `/ 4 π`.
- Bumped the intensity of the point lights in `3d_scene_pipelined` to 1600 lumens.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Allow the user to set the clear color when using the pipelined renderer
## Solution
- Add a `ClearColor` resource that can be added to the world to configure the clear color
## Remaining Issues
Currently the `ClearColor` resource is cloned from the app world to the render world every frame. There are two ways I can think of around this:
1. Figure out why `app_world.is_resource_changed::<ClearColor>()` always returns `true` in the `extract` step and fix it so that we are only updating the resource when it changes
2. Require the users to add the `ClearColor` resource to the render sub-app instead of the parent app. This is currently sub-optimal until we have labled sub-apps, and probably a helper funciton on `App` such as `app.with_sub_app(RenderApp, |app| { ... })`. Even if we had that, I think it would be more than we want the user to have to think about. They shouldn't have to know about the render sub-app I don't think.
I think the first option is the best, but I could really use some help figuring out the nuance of why `is_resource_changed` is always returning true in that context.
# Objective
Enable using exact World lifetimes during read-only access . This is motivated by the new renderer's need to allow read-only world-only queries to outlive the query itself (but still be constrained by the world lifetime).
For example:
115b170d1f/pipelined/bevy_pbr2/src/render/mod.rs (L774)
## Solution
Split out SystemParam state and world lifetimes and pipe those lifetimes up to read-only Query ops (and add into_inner for Res). According to every safety test I've run so far (except one), this is safe (see the temporary safety test commit). Note that changing the mutable variants to the new lifetimes would allow aliased mutable pointers (try doing that to see how it affects the temporary safety tests).
The new state lifetime on SystemParam does make `#[derive(SystemParam)]` more cumbersome (the current impl requires PhantomData if you don't use both lifetimes). We can make this better by detecting whether or not a lifetime is used in the derive and adjusting accordingly, but that should probably be done in its own pr.
## Why is this a draft?
The new lifetimes break QuerySet safety in one very specific case (see the query_set system in system_safety_test). We need to solve this before we can use the lifetimes given.
This is due to the fact that QuerySet is just a wrapper over Query, which now relies on world lifetimes instead of `&self` lifetimes to prevent aliasing (but in systems, each Query has its own implied lifetime, not a centralized world lifetime). I believe the fix is to rewrite QuerySet to have its own World lifetime (and own the internal reference). This will complicate the impl a bit, but I think it is doable. I'm curious if anyone else has better ideas.
Personally, I think these new lifetimes need to happen. We've gotta have a way to directly tie read-only World queries to the World lifetime. The new renderer is the first place this has come up, but I doubt it will be the last. Worst case scenario we can come up with a second `WorldLifetimeQuery<Q, F = ()>` parameter to enable these read-only scenarios, but I'd rather not add another type to the type zoo.
## Objective
- Clean up remaining references to the trait `FromResources`, which was replaced in favor of `FromWorld` during the ECS rework.
## Solution
- Remove the derive macro for `FromResources`
- Change doc references of `FromResources` to `FromWorld`
(this is the first item in #2576)
# Objective
- Prevent the need to specify a sprite size when using the pipelined sprite renderer
## Solution
- Re-introduce the sprite auto resize system from the old renderer
# Objective
Restore the functionality of sprite atlases in the new renderer.
### **Note:** This PR relies on #2555
## Solution
Mostly just a copy paste of the existing sprite atlas implementation, however I unified the rendering between sprites and atlases.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
Port bevy_gltf to the pipelined-rendering branch.
## Solution
crates/bevy_gltf has been copied and pasted into pipelined/bevy_gltf2 and modifications were made to work with the pipelined-rendering branch. Notably vertex tangents and vertex colours are not supported.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Remove all the `.system()` possible.
- Check for remaining missing cases.
## Solution
- Remove all `.system()`, fix compile errors
- 32 calls to `.system()` remains, mostly internals, the few others should be removed after #2446
This is extracted out of eb8f973646476b4a4926ba644a77e2b3a5772159 and includes some additional changes to remove all references to AppBuilder and fix examples that still used App::build() instead of App::new(). In addition I didn't extract the sub app feature as it isn't ready yet.
You can use `git diff --diff-filter=M eb8f973646476b4a4926ba644a77e2b3a5772159` to find all differences in this PR. The `--diff-filtered=M` filters all files added in the original commit but not in this commit away.
Co-Authored-By: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
* 3d_scene_pipelined: Use a shallower directional light angle to provoke acne
* cornell_box_pipelined: Remove bias tweaks
* bevy_pbr2: Simplify shadow biases by moving them to linear depth
* bevy_pbr2: Do not use DepthBiasState
* bevy_pbr2: Do not use bilinear filtering for sampling depth textures
* pbr.wgsl: Remove unnecessary comment
* bevy_pbr2: Do manual shadow map depth comparisons for more flexibility
* examples: Add shadow_biases_pipelined example
This is useful for stress testing biases.
* bevy_pbr2: Scale the point light normal bias by the shadow map texel size
This allows the normal bias to be small close to the light source where the
shadow map texel to screen texel ratio is high, but is appropriately large
further away from the light source where the shadow map texel can easily cover
multiple screen texels.
* shadow_biases_pipelined: Add support for toggling directional / point light
* shadow_biases_pipelined: Cleanup
* bevy_pbr2: Scale the directional light normal bias by the shadow map texel size
* shadow_biases_pipelined: Fit the orthographic projection around the scene
* bevy_pbr2: Directional lights should have no shadows outside their projection
Before this change, sampling a fragment position from outside the ndc volume
would result in the return sample being clamped to the edge in x,y or possibly
always casting a shadow for fragment positions past the orthographic
projection's far plane.
* bevy_pbr2: Fix the default directional light normal bias
* Revert "bevy_pbr2: Do manual shadow map depth comparisons for more flexibility"
This reverts commit 7df1bab38a42d8a33bc50ca583d4be37bd9c9f0d.
* shadow_biases_pipelined: Adjust directional light normal bias in 0.1 increments
* pbr.wgsl: Add a couple of clarifying comments
* Revert "bevy_pbr2: Do not use bilinear filtering for sampling depth textures"
This reverts commit f53baab0232ce218866a45cad6902b470f4cf2c4.
* shadow_biases_pipelined: Print usage to terminal
* 3d_scene_pipelined: Use a shallower directional light angle to provoke acne
* cornell_box_pipelined: Remove bias tweaks
* bevy_pbr2: Simplify shadow biases by moving them to linear depth