# Objective
Fix#4278Fix#5504Fix#9422
Provide safe ways to borrow an entire entity, while allowing disjoint
mutable access. `EntityRef` and `EntityMut` are not suitable for this,
since they provide access to the entire world -- they are just helper
types for working with `&World`/`&mut World`.
This has potential uses for reflection and serialization
## Solution
Remove `EntityRef::world`, which allows it to soundly be used within
queries.
`EntityMut` no longer supports structural world mutations, which allows
multiple instances of it to exist for different entities at once.
Structural world mutations are performed using the new type
`EntityWorldMut`.
```rust
fn disjoint_system(
q2: Query<&mut A>,
q1: Query<EntityMut, Without<A>>,
) { ... }
let [entity1, entity2] = world.many_entities_mut([id1, id2]);
*entity1.get_mut::<T>().unwrap() = *entity2.get().unwrap();
for entity in world.iter_entities_mut() {
...
}
```
---
## Changelog
- Removed `EntityRef::world`, to fix a soundness issue with queries.
+ Removed the ability to structurally mutate the world using
`EntityMut`, which allows it to be used in queries.
+ Added `EntityWorldMut`, which is used to perform structural mutations
that are no longer allowed using `EntityMut`.
## Migration Guide
**Note for maintainers: ensure that the guide for #9604 is updated
accordingly.**
Removed the method `EntityRef::world`, to fix a soundness issue with
queries. If you need access to `&World` while using an `EntityRef`,
consider passing the world as a separate parameter.
`EntityMut` can no longer perform 'structural' world mutations, such as
adding or removing components, or despawning the entity. Additionally,
`EntityMut::world`, `EntityMut::world_mut` , and
`EntityMut::world_scope` have been removed.
Instead, use the newly-added type `EntityWorldMut`, which is a helper
type for working with `&mut World`.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Move schedule name into `Schedule` to allow the schedule name to be
used for errors and tracing in Schedule methods
- Fixes#9510
## Solution
- Move label onto `Schedule` and adjust api's on `World` and `Schedule`
to not pass explicit label where it makes sense to.
- add name to errors and tracing.
- `Schedule::new` now takes a label so either add the label or use
`Schedule::default` which uses a default label. `default` is mostly used
in doc examples and tests.
---
## Changelog
- move label onto `Schedule` to improve error message and logging for
schedules.
## Migration Guide
`Schedule::new` and `App::add_schedule`
```rust
// old
let schedule = Schedule::new();
app.add_schedule(MyLabel, schedule);
// new
let schedule = Schedule::new(MyLabel);
app.add_schedule(schedule);
```
if you aren't using a label and are using the schedule struct directly
you can use the default constructor.
```rust
// old
let schedule = Schedule::new();
schedule.run(world);
// new
let schedule = Schedule::default();
schedule.run(world);
```
`Schedules:insert`
```rust
// old
let schedule = Schedule::new();
schedules.insert(MyLabel, schedule);
// new
let schedule = Schedule::new(MyLabel);
schedules.insert(schedule);
```
`World::add_schedule`
```rust
// old
let schedule = Schedule::new();
world.add_schedule(MyLabel, schedule);
// new
let schedule = Schedule::new(MyLabel);
world.add_schedule(schedule);
```
# Objective
Every frame, `Events::update` gets called, which clears out any old
events from the buffer. There should be a way of taking ownership of
these old events instead of throwing them away. My use-case is dumping
old events into a debug menu so they can be inspected later.
One potential workaround is to just have a system that clones any
incoming events and stores them in a list -- however, this requires the
events to implement `Clone`.
## Solution
Add `Events::update_drain`, which returns an iterator of the events that
were removed from the buffer.
# Objective
- Fixes: #9508
- Fixes: #9526
## Solution
- Adds
```rust
fn configure_schedules(&mut self, schedule_build_settings: ScheduleBuildSettings)
```
to `Schedules`, and `App` to simplify applying `ScheduleBuildSettings`
to all schedules.
---
## Migration Guide
- No breaking changes.
- Adds `Schedule::get_build_settings()` getter for the schedule's
`ScheduleBuildSettings`.
- Can replaced manual configuration of all schedules:
```rust
// Old
for (_, schedule) in app.world.resource_mut::<Schedules>().iter_mut() {
schedule.set_build_settings(build_settings);
}
// New
app.configure_schedules(build_settings);
```
# Objective
To enable non exclusive system usage of reflected components and make
reflection more ergonomic to use by making it more in line with standard
entity commands.
## Solution
- Implements a new `EntityCommands` extension trait for reflection
related functions in the reflect module of bevy_ecs.
- Implements 4 new commands, `insert_reflect`,
`insert_reflect_with_registry`, `remove_reflect`, and
`remove_reflect_with_registry`. Both insert commands take a `Box<dyn
Reflect>` component while the remove commands take the component type
name.
- Made `EntityCommands` fields pub(crate) to allow access in the reflect
module. (Might be worth making these just public to enable user end
custom entity commands in a different pr)
- Added basic tests to ensure the commands are actually working.
- Documentation of functions.
---
## Changelog
Added:
- Implements 4 new commands on the new entity commands extension.
- `insert_reflect`
- `remove_reflect`
- `insert_reflect_with_registry`
- `remove_reflect_with_registry`
The commands operate the same except the with_registry commands take a
generic parameter for a resource that implements `AsRef<TypeRegistry>`.
Otherwise the default commands use the `AppTypeRegistry` for reflection
data.
Changed:
- Made `EntityCommands` fields pub(crate) to allow access in the reflect
module.
> Hopefully this time it works. Please don't make me rebase again ☹
# Objective
- Fixes#4917
- Replaces #9602
## Solution
- Replaced `EntityCommand` implementation for `FnOnce` to apply to
`FnOnce(EntityMut)` instead of `FnOnce(Entity, &mut World)`
---
## Changelog
- `FnOnce(Entity, &mut World)` no longer implements `EntityCommand`.
This is a breaking change.
## Migration Guide
### 1. New-Type `FnOnce`
Create an `EntityCommand` type which implements the method you
previously wrote:
```rust
pub struct ClassicEntityCommand<F>(pub F);
impl<F> EntityCommand for ClassicEntityCommand<F>
where
F: FnOnce(Entity, &mut World) + Send + 'static,
{
fn apply(self, id: Entity, world: &mut World) {
(self.0)(id, world);
}
}
commands.add(ClassicEntityCommand(|id: Entity, world: &mut World| {
/* ... */
}));
```
### 2. Extract `(Entity, &mut World)` from `EntityMut`
The method `into_world_mut` can be used to gain access to the `World`
from an `EntityMut`.
```rust
let old = |id: Entity, world: &mut World| {
/* ... */
};
let new = |mut entity: EntityMut| {
let id = entity.id();
let world = entity.into_world_mut();
/* ... */
};
```
# Objective
The name `ManualEventIterator` is long and unnecessary, as this is the
iterator type used for both `EventReader` and `ManualEventReader`.
## Solution
Rename `ManualEventIterator` to `EventIterator`. To ease migration, add
a deprecated type alias with the old name.
---
## Changelog
- The types `ManualEventIterator{WithId}` have been renamed to
`EventIterator{WithId}`.
## Migration Guide
The type `ManualEventIterator` has been renamed to `EventIterator`.
Additonally, `ManualEventIteratorWithId` has been renamed to
`EventIteratorWithId`.
# Objective
#5483 allows for the creation of non-`Sync` locals. However, it's not
actually possible to use these types as there is a `Sync` bound on the
`Deref` impls.
## Solution
Remove the unnecessary bounds.
# Objective
- have errors in configure_set and configure_sets show the line number
of the user calling location rather than pointing to schedule.rs
- use display formatting for the errors
## Example Error Text
```text
// dependency loop
// before
thread 'main' panicked at 'called `Result::unwrap()` on an `Err` value: DependencyLoop("A")', crates\bevy_ecs\src\schedule\schedule.rs:682:39
// after
thread 'main' panicked at 'System set `A` depends on itself.', examples/stress_tests/bevymark.rs:16:9
// hierarchy loop
// before
thread 'main' panicked at 'called `Result::unwrap()` on an `Err` value: HierarchyLoop("A")', crates\bevy_ecs\src\schedule\schedule.rs:682:3
// after
thread 'main' panicked at 'System set `A` contains itself.', examples/stress_tests/bevymark.rs:16:9
// configuring a system type set
// before
thread 'main' panicked at 'configuring system type sets is not allowed', crates\bevy_ecs\src\schedule\config.rs:394:9
//after
thread 'main' panicked at 'configuring system type sets is not allowed', examples/stress_tests/bevymark.rs:16:9
```
Code to produce errors:
```rust
use bevy::prelude::*;
#[derive(SystemSet, Clone, Debug, PartialEq, Eq, Hash)]
enum TestSet {
A,
}
fn main() {
fn foo() {}
let mut app = App::empty();
// Hierarchy Loop
app.configure_set(Main, TestSet::A.in_set(TestSet::A));
// Dependency Loop
app.configure_set(Main, TestSet::A.after(TestSet::A));
// Configure System Type Set
app.configure_set(Main, foo.into_system_set());
}
```
# Objective
- Fixes#9321
## Solution
- `EntityMap` has been replaced by a simple `HashMap<Entity, Entity>`.
---
## Changelog
- `EntityMap::world_scope` has been replaced with `World::world_scope`
to avoid creating a new trait. This is a public facing change to the
call semantics, but has no effect on results or behaviour.
- `EntityMap`, as a `HashMap`, now operates on `&Entity` rather than
`Entity`. This changes many standard access functions (e.g, `.get`) in a
public-facing way.
## Migration Guide
- Calls to `EntityMap::world_scope` can be directly replaced with the
following:
`map.world_scope(&mut world)` -> `world.world_scope(&mut map)`
- Calls to legacy `EntityMap` methods such as `EntityMap::get` must
explicitly include de/reference symbols:
`let entity = map.get(parent);` -> `let &entity = map.get(&parent);`
# Objective
Make code relating to event more readable.
Currently the `impl` block of `Events` is split in two, and the big part
of its implementations are put at the end of the file, far from the
definition of the `struct`.
## Solution
- Move and merge the `impl` blocks of `Events` next to its definition.
- Move the `EventSequence` definition and implementations before the
`Events`, because they're pretty trivial and help understand how
`Events` work, rather than being buried bellow `Events`.
I separated those two steps in two commits to not be too confusing. I
didn't modify any code of documentation. I want to do a second PR with
such modifications after this one is merged.
# Objective
Similar to #6344, but contains only `ReflectBundle` changes. Useful for
scripting. The implementation has also been updated to look exactly like
`ReflectComponent`.
---
## Changelog
### Added
- Reflection for bundles.
---------
Co-authored-by: Gino Valente <49806985+MrGVSV@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
Any time we wish to transform the output of a system, we currently use
system piping to do so:
```rust
my_system.pipe(|In(x)| do_something(x))
```
Unfortunately, system piping is not a zero cost abstraction. Each call
to `.pipe` requires allocating two extra access sets: one for the second
system and one for the combined accesses of both systems. This also adds
extra work to each call to `update_archetype_component_access`, which
stacks as one adds multiple layers of system piping.
## Solution
Add the `AdapterSystem` abstraction: similar to `CombinatorSystem`, this
allows you to implement a trait to generically control how a system is
run and how its inputs and outputs are processed. Unlike
`CombinatorSystem`, this does not have any overhead when computing world
accesses which makes it ideal for simple operations such as inverting or
ignoring the output of a system.
Add the extension method `.map(...)`: this is similar to `.pipe(...)`,
only it accepts a closure as an argument instead of an `In<T>` system.
```rust
my_system.map(do_something)
```
This has the added benefit of making system names less messy: a system
that ignores its output will just be called `my_system`, instead of
`Pipe(my_system, ignore)`
---
## Changelog
TODO
## Migration Guide
The `system_adapter` functions have been deprecated: use `.map` instead,
which is a lightweight alternative to `.pipe`.
```rust
// Before:
my_system.pipe(system_adapter::ignore)
my_system.pipe(system_adapter::unwrap)
my_system.pipe(system_adapter::new(T::from))
// After:
my_system.map(std::mem::drop)
my_system.map(Result::unwrap)
my_system.map(T::from)
// Before:
my_system.pipe(system_adapter::info)
my_system.pipe(system_adapter::dbg)
my_system.pipe(system_adapter::warn)
my_system.pipe(system_adapter::error)
// After:
my_system.map(bevy_utils::info)
my_system.map(bevy_utils::dbg)
my_system.map(bevy_utils::warn)
my_system.map(bevy_utils::error)
```
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
- break up large build_schedule system to make it easier to read
- Clean up related error messages.
- I have a follow up PR that adds the schedule name to the error
messages, but wanted to break this up from that.
## Changelog
- refactor `build_schedule` to be easier to read
## Sample Error Messages
Dependency Cycle
```text
thread 'main' panicked at 'System dependencies contain cycle(s).
schedule has 1 before/after cycle(s):
cycle 1: system set 'A' must run before itself
system set 'A'
... which must run before system set 'B'
... which must run before system set 'A'
', crates\bevy_ecs\src\schedule\schedule.rs:228:13
```
```text
thread 'main' panicked at 'System dependencies contain cycle(s).
schedule has 1 before/after cycle(s):
cycle 1: system 'foo' must run before itself
system 'foo'
... which must run before system 'bar'
... which must run before system 'foo'
', crates\bevy_ecs\src\schedule\schedule.rs:228:13
```
Hierarchy Cycle
```text
thread 'main' panicked at 'System set hierarchy contains cycle(s).
schedule has 1 in_set cycle(s):
cycle 1: set 'A' contains itself
set 'A'
... which contains set 'B'
... which contains set 'A'
', crates\bevy_ecs\src\schedule\schedule.rs:230:13
```
System Type Set
```text
thread 'main' panicked at 'Tried to order against `SystemTypeSet(fn foo())` in a schedule that has more than one `SystemTypeSet(fn foo())` instance. `SystemTypeSet(fn foo())` is a `SystemTypeSet` and cannot be used for ordering if ambiguous. Use a different set without this restriction.', crates\bevy_ecs\src\schedule\schedule.rs:230:13
```
Hierarchy Redundancy
```text
thread 'main' panicked at 'System set hierarchy contains redundant edges.
hierarchy contains redundant edge(s) -- system set 'X' cannot be child of set 'A', longer path exists
', crates\bevy_ecs\src\schedule\schedule.rs:230:13
```
Systems have ordering but interset
```text
thread 'main' panicked at '`A` and `C` have a `before`-`after` relationship (which may be transitive) but share systems.', crates\bevy_ecs\src\schedule\schedule.rs:227:51
```
Cross Dependency
```text
thread 'main' panicked at '`A` and `B` have both `in_set` and `before`-`after` relationships (these might be transitive). This combination is unsolvable as a system cannot run before or after a set it belongs to.', crates\bevy_ecs\src\schedule\schedule.rs:230:13
```
Ambiguity
```text
thread 'main' panicked at 'Systems with conflicting access have indeterminate run order.
1 pairs of systems with conflicting data access have indeterminate execution order. Consider adding `before`, `after`, or `ambiguous_with` relationships between these:
-- res_mut and res_ref
conflict on: ["bevymark::ambiguity::X"]
', crates\bevy_ecs\src\schedule\schedule.rs:230:13
```
# Objective
Sometimes you want to create a plugin with a custom run condition. In a
function, you take the `Condition` trait and then make a
`BoxedCondition` from it to store it. And then you want to add that
condition to a system, but you can't, because there is only the `run_if`
function available which takes `impl Condition<M>` instead of
`BoxedCondition`. So you have to create a wrapper type for the
`BoxedCondition` and implement the `System` and `ReadOnlySystem` traits
for the wrapper (Like it's done in the picture below). It's very
inconvenient and boilerplate. But there is an easy solution for that:
make the `run_if_inner` system that takes a `BoxedCondition` public.
Also, it makes sense to make `in_set_inner` function public as well with
the same motivation.

A chunk of the source code of the `bevy-inspector-egui` crate.
## Solution
Make `run_if_inner` function public.
Rename `run_if_inner` to `run_if_dyn`.
Make `in_set_inner` function public.
Rename `in_set_inner` to `in_set_dyn`.
## Changelog
Changed visibility of `run_if_inner` from `pub(crate)` to `pub`.
Renamed `run_if_inner` to `run_if_dyn`.
Changed visibility of `in_set_inner` from `pub(crate)` to `pub`.
Renamed `in_set_inner` to `in_set_dyn`.
## Migration Guide
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Joseph <21144246+JoJoJet@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
* `Local` and `SystemName` implement `Debug` manually, but they could
derive it.
* `QueryState` and `dyn System` have unconventional debug formatting.
# Objective
[Rust 1.72.0](https://blog.rust-lang.org/2023/08/24/Rust-1.72.0.html) is
now stable.
# Notes
- `let-else` formatting has arrived!
- I chose to allow `explicit_iter_loop` due to
https://github.com/rust-lang/rust-clippy/issues/11074.
We didn't hit any of the false positives that prevent compilation, but
fixing this did produce a lot of the "symbol soup" mentioned, e.g. `for
image in &mut *image_events {`.
Happy to undo this if there's consensus the other way.
---------
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
While being nobody other's issue as far I can tell, I want to create a
trait I plan to implement on `App` where more than one schedule is
modified.
My workaround so far was working with a closure that returns an
`ExecutorKind` from a match of the method variable.
It makes it easier for me to being able to clone `ExecutorKind` and I
don't see this being controversial for others working with Bevy.
I did nothing more than adding `Clone` to the derived traits, no
migration guide needed.
(If this worked out then the GitHub editor is not too shabby.)
# Objective
Just like
[`set_if_neq`](https://docs.rs/bevy_ecs/latest/bevy_ecs/change_detection/trait.DetectChangesMut.html#method.set_if_neq),
being able to express the "I don't want to unnecessarily trigger the
change detection" but with the ability to handle the previous value if
change occurs.
## Solution
Add `replace_if_neq` to `DetectChangesMut`.
---
## Changelog
- Added `DetectChangesMut::replace_if_neq`: like `set_if_neq` change the
value only if the new value if different from the current one, but
return the previous value if the change occurs.
Add a `RunSystem` extension trait to allow for immediate execution of
systems on a `World` for debugging and/or testing purposes.
# Objective
Fixes#6184
Initially, I made this CL as `ApplyCommands`. After a discussion with
@cart , we decided a more generic implementation would be better to
support all systems. This is the new revised CL. Sorry for the long
delay! 😅
This CL allows users to do this:
```rust
use bevy::prelude::*;
use bevy::ecs::system::RunSystem;
struct T(usize);
impl Resource for T {}
fn system(In(n): In<usize>, mut commands: Commands) -> usize {
commands.insert_resource(T(n));
n + 1
}
let mut world = World::default();
let n = world.run_system_with(1, system);
assert_eq!(n, 2);
assert_eq!(world.resource::<T>().0, 1);
```
## Solution
This is implemented as a trait extension and not included in any
preludes to ensure it's being used consciously.
Internally, it just initializes and runs a systems, and applies any
deferred parameters all "in place".
The trait has 2 functions (one of which calls the other by default):
- `run_system_with` is the general implementation, which allows user to
pass system input parameters
- `run_system` is the ergonomic wrapper for systems with no input
parameter (to avoid having the user pass `()` as input).
~~Additionally, this trait is also implemented for `&mut App`. I added
this mainly for ergonomics (`app.run_system` vs.
`app.world.run_system`).~~ (Removed based on feedback)
---------
Co-authored-by: Pascal Hertleif <killercup@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Fixes#9114
## Solution
Inside `ScheduleGraph::build_schedule()` the variable `node_count =
self.systems.len() + self.system_sets.len()` is used to calculate the
indices for the `reachable` bitset derived from `self.hierarchy.graph`.
However, the number of nodes inside `self.hierarchy.graph` does not
always correspond to `self.systems.len() + self.system_sets.len()` when
`ambiguous_with` is used, because an ambiguous set is added to
`system_sets` (because we need an `NodeId` for the ambiguity graph)
without adding a node to `self.hierarchy`.
In this PR, we rename `node_count` to the more descriptive name
`hg_node_count` and set it to `self.hierarchy.graph.node_count()`.
---------
Co-authored-by: James Liu <contact@jamessliu.com>
# Objective
Fixes#9113
## Solution
disable `multi-threaded` default feature
## Migration Guide
The `multi-threaded` feature in `bevy_ecs` and `bevy_tasks` is no longer
enabled by default. However, this remains a default feature for the
umbrella `bevy` crate. If you depend on `bevy_ecs` or `bevy_tasks`
directly, you should consider enabling this to allow systems to run in
parallel.
# Objective
The `lifetimeless` module has been a source of confusion for bevy users
for a while now.
## Solution
Add a couple paragraph explaining that, yes, you can use one of the type
alias safely, without ever leaking any memory.
# Objective
Cloning a `WorldQuery` type's "fetch" struct was made unsafe in #5593,
by adding the `unsafe fn clone_fetch` to `WorldQuery`. However, as that
method's documentation explains, it is not the right place to put the
safety invariant:
> While calling this method on its own cannot cause UB it is marked
`unsafe` as the caller must ensure that the returned value is not used
in any way that would cause two `QueryItem<Self>` for the same
`archetype_index` or `table_row` to be alive at the same time.
You can clone a fetch struct all you want and it will never cause
undefined behavior -- in order for something to go wrong, you need to
improperly call `WorldQuery::fetch` with it (which is marked unsafe).
Additionally, making it unsafe to clone a fetch struct does not even
prevent undefined behavior, since there are other ways to incorrectly
use a fetch struct. For example, you could just call fetch more than
once for the same entity, which is not currently forbidden by any
documented invariants.
## Solution
Document a safety invariant on `WorldQuery::fetch` that requires the
caller to not create aliased `WorldQueryItem`s for mutable types. Remove
the `clone_fetch` function, and add the bound `Fetch: Clone` instead.
---
## Changelog
- Removed the associated function `WorldQuery::clone_fetch`, and added a
`Clone` bound to `WorldQuery::Fetch`.
## Migration Guide
### `fetch` invariants
The function `WorldQuery::fetch` has had the following safety invariant
added:
> If this type does not implement `ReadOnlyWorldQuery`, then the caller
must ensure that it is impossible for more than one `Self::Item` to
exist for the same entity at any given time.
This invariant was always required for soundness, but was previously
undocumented. If you called this function manually anywhere, you should
check to make sure that this invariant is not violated.
### Removed `clone_fetch`
The function `WorldQuery::clone_fetch` has been removed. The associated
type `WorldQuery::Fetch` now has the bound `Clone`.
Before:
```rust
struct MyFetch<'w> { ... }
unsafe impl WorldQuery for MyQuery {
...
type Fetch<'w> = MyFetch<'w>
unsafe fn clone_fetch<'w>(fetch: &Self::Fetch<'w>) -> Self::Fetch<'w> {
MyFetch {
field1: fetch.field1,
field2: fetch.field2.clone(),
...
}
}
}
```
After:
```rust
#[derive(Clone)]
struct MyFetch<'w> { ... }
unsafe impl WorldQuery for MyQuery {
...
type Fetch<'w> = MyFetch<'w>;
}
```
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
# Objective
The `QueryParIter::for_each_mut` function is required when doing
parallel iteration with mutable queries.
This results in an unfortunate stutter:
`query.par_iter_mut().par_for_each_mut()` ('mut' is repeated).
## Solution
- Make `for_each` compatible with mutable queries, and deprecate
`for_each_mut`. In order to prevent `for_each` from being called
multiple times in parallel, we take ownership of the QueryParIter.
---
## Changelog
- `QueryParIter::for_each` is now compatible with mutable queries.
`for_each_mut` has been deprecated as it is now redundant.
## Migration Guide
The method `QueryParIter::for_each_mut` has been deprecated and is no
longer functional. Use `for_each` instead, which now supports mutable
queries.
```rust
// Before:
query.par_iter_mut().for_each_mut(|x| ...);
// After:
query.par_iter_mut().for_each(|x| ...);
```
The method `QueryParIter::for_each` now takes ownership of the
`QueryParIter`, rather than taking a shared reference.
```rust
// Before:
let par_iter = my_query.par_iter().batching_strategy(my_batching_strategy);
par_iter.for_each(|x| {
// ...Do stuff with x...
par_iter.for_each(|y| {
// ...Do nested stuff with y...
});
});
// After:
my_query.par_iter().batching_strategy(my_batching_strategy).for_each(|x| {
// ...Do stuff with x...
my_query.par_iter().batching_strategy(my_batching_strategy).for_each(|y| {
// ...Do nested stuff with y...
});
});
```
### **Adopted #6430**
# Objective
`MutUntyped` is the untyped variant of `Mut<T>` that stores a `PtrMut`
instead of a `&mut T`. Working with a `MutUntyped` is a bit annoying,
because as soon you want to use the ptr e.g. as a `&mut dyn Reflect` you
cannot use a type like `Mut<dyn Reflect>` but instead need to carry
around a `&mut dyn Reflect` and a `impl FnMut()` to mark the value as
changed.
## Solution
* Provide a method `map_unchanged` to turn a `MutUntyped` into a
`Mut<T>` by mapping the `PtrMut<'a>` to a `&'a mut T`
This can be used like this:
```rust
// SAFETY: ptr is of type `u8`
let val: Mut<u8> = mut_untyped.map_unchanged(|ptr| unsafe { ptr.deref_mut::<u8>() });
// SAFETY: from the context it is known that `ReflectFromPtr` was made for the type of the `MutUntyped`
let val: Mut<dyn Reflect> = mut_untyped.map_unchanged(|ptr| unsafe { reflect_from_ptr.as_reflect_ptr_mut(ptr) });
```
Note that nothing prevents you from doing
```rust
mut_untyped.map_unchanged(|ptr| &mut ());
```
or using any other mutable reference you can get, but IMO that is fine
since that will only result in a `Mut` that will dereference to that
value and mark the original value as changed. The lifetimes here prevent
anything bad from happening.
## Alternatives
1. Make `Ticks` public and provide a method to get construct a `Mut`
from `Ticks` and `&mut T`. More powerful and more easy to misuse.
2. Do nothing. People can still do everything they want, but they need
to pass (`&mut dyn Reflect, impl FnMut() + '_)` around instead of
`Mut<dyn Reflect>`
## Changelog
- add `MutUntyped::map_unchanged` to turn a `MutUntyped` into its typed
counterpart
---------
Co-authored-by: Jakob Hellermann <jakob.hellermann@protonmail.com>
Co-authored-by: JoJoJet <21144246+JoJoJet@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
Fixes#9200
Switches ()'s to []'s when talking about the optional `_mut` suffix in
the ECS Query Struct page to have more idiomatic docs.
## Solution
Replace `()` with `[]` in appropriate doc pages.
CI-capable version of #9086
---------
Co-authored-by: Bevy Auto Releaser <41898282+github-actions[bot]@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: François <mockersf@gmail.com>
# Objective
Fix typos throughout the project.
## Solution
[`typos`](https://github.com/crate-ci/typos) project was used for
scanning, but no automatic corrections were applied. I checked
everything by hand before fixing.
Most of the changes are documentation/comments corrections. Also, there
are few trivial changes to code (variable name, pub(crate) function name
and a few error/panic messages).
## Unsolved
`bevy_reflect_derive` has
[typo](1b51053f19/crates/bevy_reflect/bevy_reflect_derive/src/type_path.rs (L76))
in enum variant name that I didn't fix. Enum is `pub(crate)`, so there
shouldn't be any trouble if fixed. However, code is tightly coupled with
macro usage, so I decided to leave it for more experienced contributor
just in case.
I created this manually as Github didn't want to run CI for the
workflow-generated PR. I'm guessing we didn't hit this in previous
releases because we used bors.
Co-authored-by: Bevy Auto Releaser <41898282+github-actions[bot]@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
Fixes#6689.
## Solution
Add `single-threaded` as an optional non-default feature to `bevy_ecs`
and `bevy_tasks` that:
- disable the `ParallelExecutor` as a default runner
- disables the multi-threaded `TaskPool`
- internally replace `QueryParIter::for_each` calls with
`Query::for_each`.
Removed the `Mutex` and `Arc` usage in the single-threaded task pool.
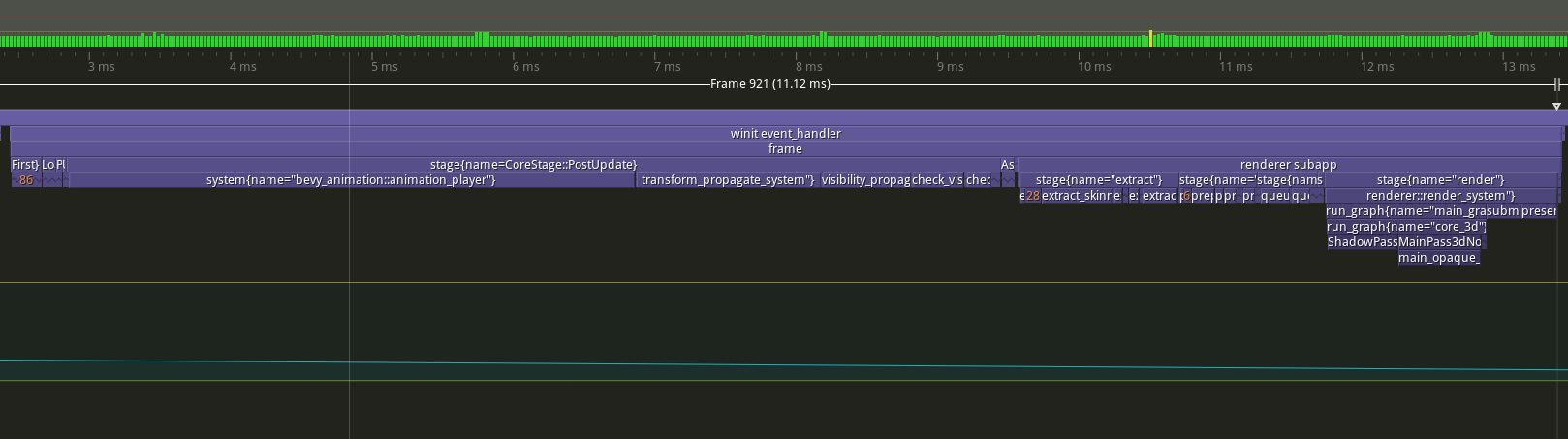
## Future Work/TODO
Create type aliases for `Mutex`, `Arc` that change to single-threaaded
equivalents where possible.
---
## Changelog
Added: Optional default feature `multi-theaded` to that enables
multithreaded parallelism in the engine. Disabling it disables all
multithreading in exchange for higher single threaded performance. Does
nothing on WASM targets.
---------
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Remove need to call `.get()` on two ticks to compare them for
equality.
## Solution
- Derive `Eq` and `PartialEq`.
---
## Changelog
> `Tick` now implements `Eq` and `PartialEq`
# Objective
**This implementation is based on
https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/pull/59.**
---
Resolves#4597
Full details and motivation can be found in the RFC, but here's a brief
summary.
`FromReflect` is a very powerful and important trait within the
reflection API. It allows Dynamic types (e.g., `DynamicList`, etc.) to
be formed into Real ones (e.g., `Vec<i32>`, etc.).
This mainly comes into play concerning deserialization, where the
reflection deserializers both return a `Box<dyn Reflect>` that almost
always contain one of these Dynamic representations of a Real type. To
convert this to our Real type, we need to use `FromReflect`.
It also sneaks up in other ways. For example, it's a required bound for
`T` in `Vec<T>` so that `Vec<T>` as a whole can be made `FromReflect`.
It's also required by all fields of an enum as it's used as part of the
`Reflect::apply` implementation.
So in other words, much like `GetTypeRegistration` and `Typed`, it is
very much a core reflection trait.
The problem is that it is not currently treated like a core trait and is
not automatically derived alongside `Reflect`. This makes using it a bit
cumbersome and easy to forget.
## Solution
Automatically derive `FromReflect` when deriving `Reflect`.
Users can then choose to opt-out if needed using the
`#[reflect(from_reflect = false)]` attribute.
```rust
#[derive(Reflect)]
struct Foo;
#[derive(Reflect)]
#[reflect(from_reflect = false)]
struct Bar;
fn test<T: FromReflect>(value: T) {}
test(Foo); // <-- OK
test(Bar); // <-- Panic! Bar does not implement trait `FromReflect`
```
#### `ReflectFromReflect`
This PR also automatically adds the `ReflectFromReflect` (introduced in
#6245) registration to the derived `GetTypeRegistration` impl— if the
type hasn't opted out of `FromReflect` of course.
<details>
<summary><h4>Improved Deserialization</h4></summary>
> **Warning**
> This section includes changes that have since been descoped from this
PR. They will likely be implemented again in a followup PR. I am mainly
leaving these details in for archival purposes, as well as for reference
when implementing this logic again.
And since we can do all the above, we might as well improve
deserialization. We can now choose to deserialize into a Dynamic type or
automatically convert it using `FromReflect` under the hood.
`[Un]TypedReflectDeserializer::new` will now perform the conversion and
return the `Box`'d Real type.
`[Un]TypedReflectDeserializer::new_dynamic` will work like what we have
now and simply return the `Box`'d Dynamic type.
```rust
// Returns the Real type
let reflect_deserializer = UntypedReflectDeserializer::new(®istry);
let mut deserializer = ron:🇩🇪:Deserializer::from_str(input)?;
let output: SomeStruct = reflect_deserializer.deserialize(&mut deserializer)?.take()?;
// Returns the Dynamic type
let reflect_deserializer = UntypedReflectDeserializer::new_dynamic(®istry);
let mut deserializer = ron:🇩🇪:Deserializer::from_str(input)?;
let output: DynamicStruct = reflect_deserializer.deserialize(&mut deserializer)?.take()?;
```
</details>
---
## Changelog
* `FromReflect` is now automatically derived within the `Reflect` derive
macro
* This includes auto-registering `ReflectFromReflect` in the derived
`GetTypeRegistration` impl
* ~~Renamed `TypedReflectDeserializer::new` and
`UntypedReflectDeserializer::new` to
`TypedReflectDeserializer::new_dynamic` and
`UntypedReflectDeserializer::new_dynamic`, respectively~~ **Descoped**
* ~~Changed `TypedReflectDeserializer::new` and
`UntypedReflectDeserializer::new` to automatically convert the
deserialized output using `FromReflect`~~ **Descoped**
## Migration Guide
* `FromReflect` is now automatically derived within the `Reflect` derive
macro. Items with both derives will need to remove the `FromReflect`
one.
```rust
// OLD
#[derive(Reflect, FromReflect)]
struct Foo;
// NEW
#[derive(Reflect)]
struct Foo;
```
If using a manual implementation of `FromReflect` and the `Reflect`
derive, users will need to opt-out of the automatic implementation.
```rust
// OLD
#[derive(Reflect)]
struct Foo;
impl FromReflect for Foo {/* ... */}
// NEW
#[derive(Reflect)]
#[reflect(from_reflect = false)]
struct Foo;
impl FromReflect for Foo {/* ... */}
```
<details>
<summary><h4>Removed Migrations</h4></summary>
> **Warning**
> This section includes changes that have since been descoped from this
PR. They will likely be implemented again in a followup PR. I am mainly
leaving these details in for archival purposes, as well as for reference
when implementing this logic again.
* The reflect deserializers now perform a `FromReflect` conversion
internally. The expected output of `TypedReflectDeserializer::new` and
`UntypedReflectDeserializer::new` is no longer a Dynamic (e.g.,
`DynamicList`), but its Real counterpart (e.g., `Vec<i32>`).
```rust
let reflect_deserializer =
UntypedReflectDeserializer::new_dynamic(®istry);
let mut deserializer = ron:🇩🇪:Deserializer::from_str(input)?;
// OLD
let output: DynamicStruct = reflect_deserializer.deserialize(&mut
deserializer)?.take()?;
// NEW
let output: SomeStruct = reflect_deserializer.deserialize(&mut
deserializer)?.take()?;
```
Alternatively, if this behavior isn't desired, use the
`TypedReflectDeserializer::new_dynamic` and
`UntypedReflectDeserializer::new_dynamic` methods instead:
```rust
// OLD
let reflect_deserializer = UntypedReflectDeserializer::new(®istry);
// NEW
let reflect_deserializer =
UntypedReflectDeserializer::new_dynamic(®istry);
```
</details>
---------
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
Title. This is necessary in order to update
[`bevy-trait-query`](https://crates.io/crates/bevy-trait-query) to Bevy
0.11.
---
## Changelog
Added the unsafe function `UnsafeWorldCell::storages`, which provides
unchecked access to the internal data stores of a `World`.
# Objective
`World::entity`, `World::entity_mut` and `Commands::entity` should be
marked with `track_caller` to display where (in user code) the call with
the invalid `Entity` was made. `Commands::entity` already has the
attibute, but it does nothing due to the call to `unwrap_or_else`.
## Solution
- Apply the `track_caller` attribute to the `World::entity_mut` and
`World::entity`.
- Remove the call to `unwrap_or_else` which makes the `track_caller`
attribute useless (because `unwrap_or_else` is not `track_caller`
itself). The avoid eager evaluation of the panicking branch it is never
inlined.
---------
Co-authored-by: Giacomo Stevanato <giaco.stevanato@gmail.com>
# Objective
Partially address #5504. Fix#4278. Provide "whole entity" access in
queries. This can be useful when you don't know at compile time what
you're accessing (i.e. reflection via `ReflectComponent`).
## Solution
Implement `WorldQuery` for `EntityRef`.
- This provides read-only access to the entire entity, and supports
anything that `EntityRef` can normally do.
- It matches all archetypes and tables and will densely iterate when
possible.
- It marks all of the ArchetypeComponentIds of a matched archetype as
read.
- Adding it to a query will cause it to panic if used in conjunction
with any other mutable access.
- Expanded the docs on Query to advertise this feature.
- Added tests to ensure the panics were working as intended.
- Added `EntityRef` to the ECS prelude.
To make this safe, `EntityRef::world` was removed as it gave potential
`UnsafeCell`-like access to other parts of the `World` including aliased
mutable access to the components it would otherwise read safely.
## Performance
Not great beyond the additional parallelization opportunity over
exclusive systems. The `EntityRef` is fetched from `Entities` like any
other call to `World::entity`, which can be very random access heavy.
This could be simplified if `ArchetypeRow` is available in
`WorldQuery::fetch`'s arguments, but that's likely not something we
should optimize for.
## Future work
An equivalent API where it gives mutable access to all components on a
entity can be done with a scoped version of `EntityMut` where it does
not provide `&mut World` access nor allow for structural changes to the
entity is feasible as well. This could be done as a safe alternative to
exclusive system when structural mutation isn't required or the target
set of entities is scoped.
---
## Changelog
Added: `Access::has_any_write`
Added: `EntityRef` now implements `WorldQuery`. Allows read-only access
to the entire entity, incompatible with any other mutable access, can be
mixed with `With`/`Without` filters for more targeted use.
Added: `EntityRef` to `bevy::ecs::prelude`.
Removed: `EntityRef::world`
## Migration Guide
TODO
---------
Co-authored-by: Carter Weinberg <weinbergcarter@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Jakob Hellermann <jakob.hellermann@protonmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Use `AppTypeRegistry` on API defined in `bevy_ecs`
(https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/8895#discussion_r1234748418)
A lot of the API on `Reflect` depends on a registry. When it comes to
the ECS. We should use `AppTypeRegistry` in the general case.
This is however impossible in `bevy_ecs`, since `AppTypeRegistry` is
defined in `bevy_app`.
## Solution
- Move `AppTypeRegistry` resource definition from `bevy_app` to
`bevy_ecs`
- Still add the resource in the `App` plugin, since bevy_ecs itself
doesn't know of plugins
Note that `bevy_ecs` is a dependency of `bevy_app`, so nothing
revolutionary happens.
## Alternative
- Define the API as a trait in `bevy_app` over `bevy_ecs`. (though this
prevents us from using bevy_ecs internals)
- Do not rely on `AppTypeRegistry` for the API in question, requring
users to extract themselves the resource and pass it to the API methods.
---
## Changelog
- Moved `AppTypeRegistry` resource definition from `bevy_app` to
`bevy_ecs`
## Migration Guide
- If you were **not** using a `prelude::*` to import `AppTypeRegistry`,
you should update your imports:
```diff
- use bevy::app::AppTypeRegistry;
+ use bevy::ecs::reflect::AppTypeRegistry
```
# Objective
`WorldQuery::Fetch` is a type used to optimize the implementation of
queries. These types are hidden and not intended to be outside of the
engine, so there is no need to provide type aliases to make it easier to
refer to them. If a user absolutely needs to refer to one of these
types, they can always just refer to the associated type directly.
## Solution
Deprecate these type aliases.
---
## Changelog
- Deprecated the type aliases `QueryFetch` and `ROQueryFetch`.
## Migration Guide
The type aliases `bevy_ecs::query::QueryFetch` and `ROQueryFetch` have
been deprecated. If you need to refer to a `WorldQuery` struct's fetch
type, refer to the associated type defined on `WorldQuery` directly:
```rust
// Before:
type MyFetch<'w> = QueryFetch<'w, MyQuery>;
type MyFetchReadOnly<'w> = ROQueryFetch<'w, MyQuery>;
// After:
type MyFetch<'w> = <MyQuery as WorldQuery>::Fetch;
type MyFetchReadOnly<'w> = <<MyQuery as WorldQuery>::ReadOnly as WorldQuery>::Fetch;
```