# Objective
- Fix the environment map shader not working under webgl due to textureNumLevels() not being supported
- Fixes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/7722
## Solution
- Instead of using textureNumLevels(), put an extra field in the GpuLights uniform to store the mip count
# Objective
Splits tone mapping from https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/6677 into a separate PR.
Address https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/2264.
Adds tone mapping options:
- None: Bypasses tonemapping for instances where users want colors output to match those set.
- Reinhard
- Reinhard Luminance: Bevy's exiting tonemapping
- [ACES](https://github.com/TheRealMJP/BakingLab/blob/master/BakingLab/ACES.hlsl) (Fitted version, based on the same implementation that Godot 4 uses) see https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/2264
- [AgX](https://github.com/sobotka/AgX)
- SomewhatBoringDisplayTransform
- TonyMcMapface
- Blender Filmic
This PR also adds support for EXR images so they can be used to compare tonemapping options with reference images.
## Migration Guide
- Tonemapping is now an enum with NONE and the various tonemappers.
- The DebandDither is now a separate component.
Co-authored-by: JMS55 <47158642+JMS55@users.noreply.github.com>
# Objective
Allow for creating pipelines that use push constants. To be able to use push constants. Fixes#4825
As of right now, trying to call `RenderPass::set_push_constants` will trigger the following error:
```
thread 'main' panicked at 'wgpu error: Validation Error
Caused by:
In a RenderPass
note: encoder = `<CommandBuffer-(0, 59, Vulkan)>`
In a set_push_constant command
provided push constant is for stage(s) VERTEX | FRAGMENT | VERTEX_FRAGMENT, however the pipeline layout has no push constant range for the stage(s) VERTEX | FRAGMENT | VERTEX_FRAGMENT
```
## Solution
Add a field push_constant_ranges to` RenderPipelineDescriptor` and `ComputePipelineDescriptor`.
This PR supersedes #4908 which now contains merge conflicts due to significant changes to `bevy_render`.
Meanwhile, this PR also made the `layout` field of `RenderPipelineDescriptor` and `ComputePipelineDescriptor` non-optional. If the user do not need to specify the bind group layouts, they can simply supply an empty vector here. No need for it to be optional.
---
## Changelog
- Add a field push_constant_ranges to RenderPipelineDescriptor and ComputePipelineDescriptor
- Made the `layout` field of RenderPipelineDescriptor and ComputePipelineDescriptor non-optional.
## Migration Guide
- Add push_constant_ranges: Vec::new() to every `RenderPipelineDescriptor` and `ComputePipelineDescriptor`
- Unwrap the optional values on the `layout` field of `RenderPipelineDescriptor` and `ComputePipelineDescriptor`. If the descriptor has no layout, supply an empty vector.
Co-authored-by: Zhixing Zhang <me@neoto.xin>
# Objective
We have a few old system labels that are now system sets but are still named or documented as labels. Documentation also generally mentioned system labels in some places.
## Solution
- Clean up naming and documentation regarding system sets
## Migration Guide
`PrepareAssetLabel` is now called `PrepareAssetSet`
fixes#6799
# Objective
We should be able to reuse the `Globals` or `View` shader struct definitions from anywhere (including third party plugins) without needing to worry about defining unrelated shader defs.
Also we'd like to refactor these structs to not be repeatedly defined.
## Solution
Refactor both `Globals` and `View` into separate importable shaders.
Use the imports throughout.
Co-authored-by: Torstein Grindvik <52322338+torsteingrindvik@users.noreply.github.com>
Huge thanks to @maniwani, @devil-ira, @hymm, @cart, @superdump and @jakobhellermann for the help with this PR.
# Objective
- Followup #6587.
- Minimal integration for the Stageless Scheduling RFC: https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/pull/45
## Solution
- [x] Remove old scheduling module
- [x] Migrate new methods to no longer use extension methods
- [x] Fix compiler errors
- [x] Fix benchmarks
- [x] Fix examples
- [x] Fix docs
- [x] Fix tests
## Changelog
### Added
- a large number of methods on `App` to work with schedules ergonomically
- the `CoreSchedule` enum
- `App::add_extract_system` via the `RenderingAppExtension` trait extension method
- the private `prepare_view_uniforms` system now has a public system set for scheduling purposes, called `ViewSet::PrepareUniforms`
### Removed
- stages, and all code that mentions stages
- states have been dramatically simplified, and no longer use a stack
- `RunCriteriaLabel`
- `AsSystemLabel` trait
- `on_hierarchy_reports_enabled` run criteria (now just uses an ad hoc resource checking run condition)
- systems in `RenderSet/Stage::Extract` no longer warn when they do not read data from the main world
- `RunCriteriaLabel`
- `transform_propagate_system_set`: this was a nonstandard pattern that didn't actually provide enough control. The systems are already `pub`: the docs have been updated to ensure that the third-party usage is clear.
### Changed
- `System::default_labels` is now `System::default_system_sets`.
- `App::add_default_labels` is now `App::add_default_sets`
- `CoreStage` and `StartupStage` enums are now `CoreSet` and `StartupSet`
- `App::add_system_set` was renamed to `App::add_systems`
- The `StartupSchedule` label is now defined as part of the `CoreSchedules` enum
- `.label(SystemLabel)` is now referred to as `.in_set(SystemSet)`
- `SystemLabel` trait was replaced by `SystemSet`
- `SystemTypeIdLabel<T>` was replaced by `SystemSetType<T>`
- The `ReportHierarchyIssue` resource now has a public constructor (`new`), and implements `PartialEq`
- Fixed time steps now use a schedule (`CoreSchedule::FixedTimeStep`) rather than a run criteria.
- Adding rendering extraction systems now panics rather than silently failing if no subapp with the `RenderApp` label is found.
- the `calculate_bounds` system, with the `CalculateBounds` label, is now in `CoreSet::Update`, rather than in `CoreSet::PostUpdate` before commands are applied.
- `SceneSpawnerSystem` now runs under `CoreSet::Update`, rather than `CoreStage::PreUpdate.at_end()`.
- `bevy_pbr::add_clusters` is no longer an exclusive system
- the top level `bevy_ecs::schedule` module was replaced with `bevy_ecs::scheduling`
- `tick_global_task_pools_on_main_thread` is no longer run as an exclusive system. Instead, it has been replaced by `tick_global_task_pools`, which uses a `NonSend` resource to force running on the main thread.
## Migration Guide
- Calls to `.label(MyLabel)` should be replaced with `.in_set(MySet)`
- Stages have been removed. Replace these with system sets, and then add command flushes using the `apply_system_buffers` exclusive system where needed.
- The `CoreStage`, `StartupStage, `RenderStage` and `AssetStage` enums have been replaced with `CoreSet`, `StartupSet, `RenderSet` and `AssetSet`. The same scheduling guarantees have been preserved.
- Systems are no longer added to `CoreSet::Update` by default. Add systems manually if this behavior is needed, although you should consider adding your game logic systems to `CoreSchedule::FixedTimestep` instead for more reliable framerate-independent behavior.
- Similarly, startup systems are no longer part of `StartupSet::Startup` by default. In most cases, this won't matter to you.
- For example, `add_system_to_stage(CoreStage::PostUpdate, my_system)` should be replaced with
- `add_system(my_system.in_set(CoreSet::PostUpdate)`
- When testing systems or otherwise running them in a headless fashion, simply construct and run a schedule using `Schedule::new()` and `World::run_schedule` rather than constructing stages
- Run criteria have been renamed to run conditions. These can now be combined with each other and with states.
- Looping run criteria and state stacks have been removed. Use an exclusive system that runs a schedule if you need this level of control over system control flow.
- For app-level control flow over which schedules get run when (such as for rollback networking), create your own schedule and insert it under the `CoreSchedule::Outer` label.
- Fixed timesteps are now evaluated in a schedule, rather than controlled via run criteria. The `run_fixed_timestep` system runs this schedule between `CoreSet::First` and `CoreSet::PreUpdate` by default.
- Command flush points introduced by `AssetStage` have been removed. If you were relying on these, add them back manually.
- Adding extract systems is now typically done directly on the main app. Make sure the `RenderingAppExtension` trait is in scope, then call `app.add_extract_system(my_system)`.
- the `calculate_bounds` system, with the `CalculateBounds` label, is now in `CoreSet::Update`, rather than in `CoreSet::PostUpdate` before commands are applied. You may need to order your movement systems to occur before this system in order to avoid system order ambiguities in culling behavior.
- the `RenderLabel` `AppLabel` was renamed to `RenderApp` for clarity
- `App::add_state` now takes 0 arguments: the starting state is set based on the `Default` impl.
- Instead of creating `SystemSet` containers for systems that run in stages, simply use `.on_enter::<State::Variant>()` or its `on_exit` or `on_update` siblings.
- `SystemLabel` derives should be replaced with `SystemSet`. You will also need to add the `Debug`, `PartialEq`, `Eq`, and `Hash` traits to satisfy the new trait bounds.
- `with_run_criteria` has been renamed to `run_if`. Run criteria have been renamed to run conditions for clarity, and should now simply return a bool.
- States have been dramatically simplified: there is no longer a "state stack". To queue a transition to the next state, call `NextState::set`
## TODO
- [x] remove dead methods on App and World
- [x] add `App::add_system_to_schedule` and `App::add_systems_to_schedule`
- [x] avoid adding the default system set at inappropriate times
- [x] remove any accidental cycles in the default plugins schedule
- [x] migrate benchmarks
- [x] expose explicit labels for the built-in command flush points
- [x] migrate engine code
- [x] remove all mentions of stages from the docs
- [x] verify docs for States
- [x] fix uses of exclusive systems that use .end / .at_start / .before_commands
- [x] migrate RenderStage and AssetStage
- [x] migrate examples
- [x] ensure that transform propagation is exported in a sufficiently public way (the systems are already pub)
- [x] ensure that on_enter schedules are run at least once before the main app
- [x] re-enable opt-in to execution order ambiguities
- [x] revert change to `update_bounds` to ensure it runs in `PostUpdate`
- [x] test all examples
- [x] unbreak directional lights
- [x] unbreak shadows (see 3d_scene, 3d_shape, lighting, transparaency_3d examples)
- [x] game menu example shows loading screen and menu simultaneously
- [x] display settings menu is a blank screen
- [x] `without_winit` example panics
- [x] ensure all tests pass
- [x] SubApp doc test fails
- [x] runs_spawn_local tasks fails
- [x] [Fix panic_when_hierachy_cycle test hanging](https://github.com/alice-i-cecile/bevy/pull/120)
## Points of Difficulty and Controversy
**Reviewers, please give feedback on these and look closely**
1. Default sets, from the RFC, have been removed. These added a tremendous amount of implicit complexity and result in hard to debug scheduling errors. They're going to be tackled in the form of "base sets" by @cart in a followup.
2. The outer schedule controls which schedule is run when `App::update` is called.
3. I implemented `Label for `Box<dyn Label>` for our label types. This enables us to store schedule labels in concrete form, and then later run them. I ran into the same set of problems when working with one-shot systems. We've previously investigated this pattern in depth, and it does not appear to lead to extra indirection with nested boxes.
4. `SubApp::update` simply runs the default schedule once. This sucks, but this whole API is incomplete and this was the minimal changeset.
5. `time_system` and `tick_global_task_pools_on_main_thread` no longer use exclusive systems to attempt to force scheduling order
6. Implemetnation strategy for fixed timesteps
7. `AssetStage` was migrated to `AssetSet` without reintroducing command flush points. These did not appear to be used, and it's nice to remove these bottlenecks.
8. Migration of `bevy_render/lib.rs` and pipelined rendering. The logic here is unusually tricky, as we have complex scheduling requirements.
## Future Work (ideally before 0.10)
- Rename schedule_v3 module to schedule or scheduling
- Add a derive macro to states, and likely a `EnumIter` trait of some form
- Figure out what exactly to do with the "systems added should basically work by default" problem
- Improve ergonomics for working with fixed timesteps and states
- Polish FixedTime API to match Time
- Rebase and merge #7415
- Resolve all internal ambiguities (blocked on better tools, especially #7442)
- Add "base sets" to replace the removed default sets.
# Objective
allow negatively-scaled mesh2ds to render correctly by disabling back-face culling. this brings the mesh2d pipeline into line with the sprite pipeline. i don't see any cases where backface-culling would be useful for 2d meshes.
# Objective
Update Bevy to wgpu 0.15.
## Changelog
- Update to wgpu 0.15, wgpu-hal 0.15.1, and naga 0.11
- Users can now use the [DirectX Shader Compiler](https://github.com/microsoft/DirectXShaderCompiler) (DXC) on Windows with DX12 for faster shader compilation and ShaderModel 6.0+ support (requires `dxcompiler.dll` and `dxil.dll`, which are included in DXC downloads from [here](https://github.com/microsoft/DirectXShaderCompiler/releases/latest))
## Migration Guide
### WGSL Top-Level `let` is now `const`
All top level constants are now declared with `const`, catching up with the wgsl spec.
`let` is no longer allowed at the global scope, only within functions.
```diff
-let SOME_CONSTANT = 12.0;
+const SOME_CONSTANT = 12.0;
```
#### `TextureDescriptor` and `SurfaceConfiguration` now requires a `view_formats` field
The new `view_formats` field in the `TextureDescriptor` is used to specify a list of formats the texture can be re-interpreted to in a texture view. Currently only changing srgb-ness is allowed (ex. `Rgba8Unorm` <=> `Rgba8UnormSrgb`). You should set `view_formats` to `&[]` (empty) unless you have a specific reason not to.
#### The DirectX Shader Compiler (DXC) is now supported on DX12
DXC is now the default shader compiler when using the DX12 backend. DXC is Microsoft's replacement for their legacy FXC compiler, and is faster, less buggy, and allows for modern shader features to be used (ShaderModel 6.0+). DXC requires `dxcompiler.dll` and `dxil.dll` to be available, otherwise it will log a warning and fall back to FXC.
You can get `dxcompiler.dll` and `dxil.dll` by downloading the latest release from [Microsoft's DirectXShaderCompiler github repo](https://github.com/microsoft/DirectXShaderCompiler/releases/latest) and copying them into your project's root directory. These must be included when you distribute your Bevy game/app/etc if you plan on supporting the DX12 backend and are using DXC.
`WgpuSettings` now has a `dx12_shader_compiler` field which can be used to choose between either FXC or DXC (if you pass None for the paths for DXC, it will check for the .dlls in the working directory).
# Objective
Fixes#6931
Continues #6954 by squashing `Msaa` to a flat enum
Helps out #7215
# Solution
```
pub enum Msaa {
Off = 1,
#[default]
Sample4 = 4,
}
```
# Changelog
- Modified
- `Msaa` is now enum
- Defaults to 4 samples
- Uses `.samples()` method to get the sample number as `u32`
# Migration Guide
```
let multi = Msaa { samples: 4 }
// is now
let multi = Msaa::Sample4
multi.samples
// is now
multi.samples()
```
Co-authored-by: Sjael <jakeobrien44@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Allow rendering queue systems to use a `Res<PipelineCache>` even for queueing up new rendering pipelines. This is part of unblocking parallel execution queue systems.
## Solution
- Make `PipelineCache` internally mutable w.r.t to queueing new pipelines. Pipelines are no longer immediately updated into the cache state, but rather queued into a Vec. The Vec of pending new pipelines is then later processed at the same time we actually create the queued pipelines on the GPU device.
---
## Changelog
`PipelineCache` no longer requires mutable access in order to queue render / compute pipelines.
## Migration Guide
* Most usages of `resource_mut::<PipelineCache>` and `ResMut<PipelineCache>` can be changed to `resource::<PipelineCache>` and `Res<PipelineCache>` as long as they don't use any methods requiring mutability - the only public method requiring it is `process_queue`.
# Objective
Pipelines can be customized by wrapping an existing pipeline in a newtype and adding custom logic to its implementation of `SpecializedMeshPipeline::specialize`. To make that easier, the wrapped pipeline type needs to implement `Clone`.
For example, the current non-cloneable pipelines require wrapper pipelines to pull apart the wrapped pipeline like this:
```rust
impl FromWorld for Wireframe2dPipeline {
fn from_world(world: &mut World) -> Self {
let p = &world.resource::<Material2dPipeline<ColorMaterial>>();
Self {
mesh2d_pipeline: p.mesh2d_pipeline.clone(),
material2d_layout: p.material2d_layout.clone(),
vertex_shader: p.vertex_shader.clone(),
fragment_shader: p.fragment_shader.clone(),
}
}
}
```
## Solution
Derive or implement `Clone` on all built-in pipeline types. This is easy to do since they mostly just contain cheaply clonable reference-counted types.
---
## Changelog
Implement `Clone` for all pipeline types.
# Objective
Speed up the render phase of rendering. Simplify the trait structure for render commands.
## Solution
- Merge `EntityPhaseItem` into `PhaseItem` (`EntityPhaseItem::entity` -> `PhaseItem::entity`)
- Merge `EntityRenderCommand` into `RenderCommand`.
- Add two associated types to `RenderCommand`: `RenderCommand::ViewWorldQuery` and `RenderCommand::WorldQuery`.
- Use the new associated types to construct two `QueryStates`s for `RenderCommandState`.
- Hoist any `SQuery<T>` fetches in `EntityRenderCommand`s into the aformentioned two queries. Batch fetch them all at once.
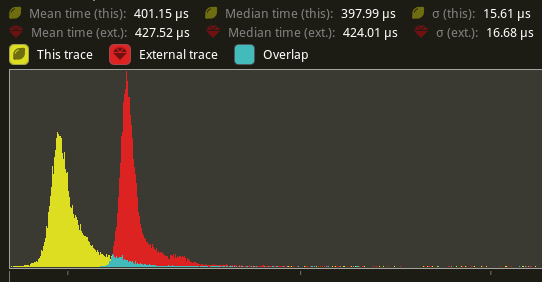
## Performance
`main_opaque_pass_3d` is slightly faster on `many_foxes` (427.52us -> 401.15us)
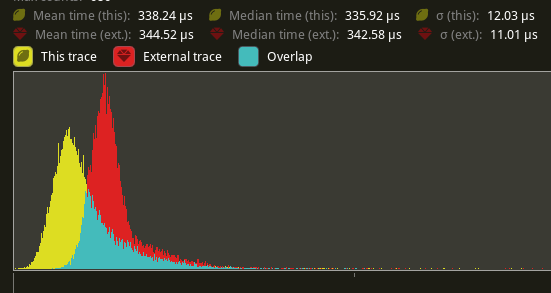
The shadow pass node is also slightly faster (344.52 -> 338.24us)
## Future Work
- Can we hoist the view level queries out of the core loop?
---
## Changelog
Added: `PhaseItem::entity`
Added: `RenderCommand::ViewWorldQuery` associated type.
Added: `RenderCommand::ItemorldQuery` associated type.
Added: `Draw<T>::prepare` optional trait function.
Removed: `EntityPhaseItem` trait
## Migration Guide
TODO
# Objective
- Every usage of `DrawFunctionsInternals::get_id()` was followed by a `.unwrap()`. which just adds boilerplate.
## Solution
- Introduce a fallible version of `DrawFunctionsInternals::get_id()` and use it where possible.
- I also took the opportunity to improve the error message a little in the case where it fails.
---
## Changelog
- Added `DrawFunctionsInternals::id()`
# Objective
- shaders defs can now have a `bool` or `int` value
- `#if SHADER_DEF <operator> 3`
- ok if `SHADER_DEF` is defined, has the correct type and pass the comparison
- `==`, `!=`, `>=`, `>`, `<`, `<=` supported
- `#SHADER_DEF` or `#{SHADER_DEF}`
- will be replaced by the value in the shader code
---
## Migration Guide
- replace `shader_defs.push(String::from("NAME"));` by `shader_defs.push("NAME".into());`
- if you used shader def `NO_STORAGE_BUFFERS_SUPPORT`, check how `AVAILABLE_STORAGE_BUFFER_BINDINGS` is now used in Bevy default shaders
# Objective
- Closes#5262
- Fix color banding caused by quantization.
## Solution
- Adds dithering to the tonemapping node from #3425.
- This is inspired by Godot's default "debanding" shader: https://gist.github.com/belzecue/
- Unlike Godot:
- debanding happens after tonemapping. My understanding is that this is preferred, because we are running the debanding at the last moment before quantization (`[f32, f32, f32, f32]` -> `f32`). This ensures we aren't biasing the dithering strength by applying it in a different (linear) color space.
- This code instead uses and reference the origin source, Valve at GDC 2015
## Additional Notes
Real time rendering to standard dynamic range outputs is limited to 8 bits of depth per color channel. Internally we keep everything in full 32-bit precision (`vec4<f32>`) inside passes and 16-bit between passes until the image is ready to be displayed, at which point the GPU implicitly converts our `vec4<f32>` into a single 32bit value per pixel, with each channel (rgba) getting 8 of those 32 bits.
### The Problem
8 bits of color depth is simply not enough precision to make each step invisible - we only have 256 values per channel! Human vision can perceive steps in luma to about 14 bits of precision. When drawing a very slight gradient, the transition between steps become visible because with a gradient, neighboring pixels will all jump to the next "step" of precision at the same time.
### The Solution
One solution is to simply output in HDR - more bits of color data means the transition between bands will become smaller. However, not everyone has hardware that supports 10+ bit color depth. Additionally, 10 bit color doesn't even fully solve the issue, banding will result in coherent bands on shallow gradients, but the steps will be harder to perceive.
The solution in this PR adds noise to the signal before it is "quantized" or resampled from 32 to 8 bits. Done naively, it's easy to add unneeded noise to the image. To ensure dithering is correct and absolutely minimal, noise is adding *within* one step of the output color depth. When converting from the 32bit to 8bit signal, the value is rounded to the nearest 8 bit value (0 - 255). Banding occurs around the transition from one value to the next, let's say from 50-51. Dithering will never add more than +/-0.5 bits of noise, so the pixels near this transition might round to 50 instead of 51 but will never round more than one step. This means that the output image won't have excess variance:
- in a gradient from 49 to 51, there will be a step between each band at 49, 50, and 51.
- Done correctly, the modified image of this gradient will never have a adjacent pixels more than one step (0-255) from each other.
- I.e. when scanning across the gradient you should expect to see:
```
|-band-| |-band-| |-band-|
Baseline: 49 49 49 50 50 50 51 51 51
Dithered: 49 50 49 50 50 51 50 51 51
Dithered (wrong): 49 50 51 49 50 51 49 51 50
```


You can see from above how correct dithering "fuzzes" the transition between bands to reduce distinct steps in color, without adding excess noise.
### HDR
The previous section (and this PR) assumes the final output is to an 8-bit texture, however this is not always the case. When Bevy adds HDR support, the dithering code will need to take the per-channel depth into account instead of assuming it to be 0-255. Edit: I talked with Rob about this and it seems like the current solution is okay. We may need to revisit once we have actual HDR final image output.
---
## Changelog
### Added
- All pipelines now support deband dithering. This is enabled by default in 3D, and can be toggled in the `Tonemapping` component in camera bundles. Banding is a graphical artifact created when the rendered image is crunched from high precision (f32 per color channel) down to the final output (u8 per channel in SDR). This results in subtle gradients becoming blocky due to the reduced color precision. Deband dithering applies a small amount of noise to the signal before it is "crunched", which breaks up the hard edges of blocks (bands) of color. Note that this does not add excess noise to the image, as the amount of noise is less than a single step of a color channel - just enough to break up the transition between color blocks in a gradient.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Fixes#4019
- Fix lighting of double-sided materials when using a negative scale
- The FlightHelmet.gltf model's hose uses a double-sided material. Loading the model with a uniform scale of -1.0, and comparing against Blender, it was identified that negating the world-space tangent, bitangent, and interpolated normal produces incorrect lighting. Discussion with Morten Mikkelsen clarified that this is both incorrect and unnecessary.
## Solution
- Remove the code that negates the T, B, and N vectors (the interpolated world-space tangent, calculated world-space bitangent, and interpolated world-space normal) when seeing the back face of a double-sided material with negative scale.
- Negate the world normal for a double-sided back face only when not using normal mapping
### Before, on `main`, flipping T, B, and N
<img width="932" alt="Screenshot 2022-08-22 at 15 11 53" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/302146/185965366-f776ff2c-cfa1-46d1-9c84-fdcb399c273c.png">
### After, on this PR
<img width="932" alt="Screenshot 2022-08-22 at 15 12 11" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/302146/185965420-8be493e2-3b1a-4188-bd13-fd6b17a76fe7.png">
### Double-sided material without normal maps
https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/302146/185988113-44a384e7-0b55-4946-9b99-20f8c803ab7e.mp4
---
## Changelog
- Fixed: Lighting of normal-mapped, double-sided materials applied to models with negative scale
- Fixed: Lighting and shadowing of back faces with no normal-mapping and a double-sided material
## Migration Guide
`prepare_normal` from the `bevy_pbr::pbr_functions` shader import has been reworked.
Before:
```rust
pbr_input.world_normal = in.world_normal;
pbr_input.N = prepare_normal(
pbr_input.material.flags,
in.world_normal,
#ifdef VERTEX_TANGENTS
#ifdef STANDARDMATERIAL_NORMAL_MAP
in.world_tangent,
#endif
#endif
in.uv,
in.is_front,
);
```
After:
```rust
pbr_input.world_normal = prepare_world_normal(
in.world_normal,
(material.flags & STANDARD_MATERIAL_FLAGS_DOUBLE_SIDED_BIT) != 0u,
in.is_front,
);
pbr_input.N = apply_normal_mapping(
pbr_input.material.flags,
pbr_input.world_normal,
#ifdef VERTEX_TANGENTS
#ifdef STANDARDMATERIAL_NORMAL_MAP
in.world_tangent,
#endif
#endif
in.uv,
);
```
# Objective
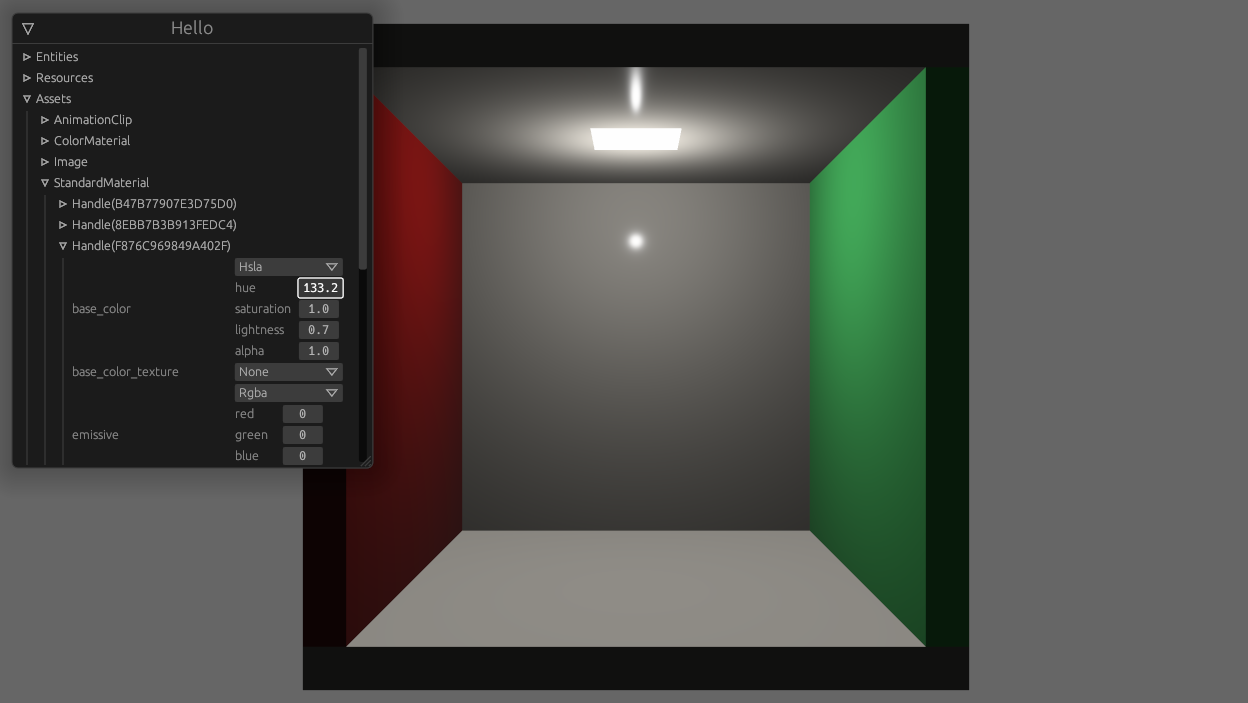
^ enable this
Concretely, I need to
- list all handle ids for an asset type
- fetch the asset as `dyn Reflect`, given a `HandleUntyped`
- when encountering a `Handle<T>`, find out what asset type that handle refers to (`T`'s type id) and turn the handle into a `HandleUntyped`
## Solution
- add `ReflectAsset` type containing function pointers for working with assets
```rust
pub struct ReflectAsset {
type_uuid: Uuid,
assets_resource_type_id: TypeId, // TypeId of the `Assets<T>` resource
get: fn(&World, HandleUntyped) -> Option<&dyn Reflect>,
get_mut: fn(&mut World, HandleUntyped) -> Option<&mut dyn Reflect>,
get_unchecked_mut: unsafe fn(&World, HandleUntyped) -> Option<&mut dyn Reflect>,
add: fn(&mut World, &dyn Reflect) -> HandleUntyped,
set: fn(&mut World, HandleUntyped, &dyn Reflect) -> HandleUntyped,
len: fn(&World) -> usize,
ids: for<'w> fn(&'w World) -> Box<dyn Iterator<Item = HandleId> + 'w>,
remove: fn(&mut World, HandleUntyped) -> Option<Box<dyn Reflect>>,
}
```
- add `ReflectHandle` type relating the handle back to the asset type and providing a way to create a `HandleUntyped`
```rust
pub struct ReflectHandle {
type_uuid: Uuid,
asset_type_id: TypeId,
downcast_handle_untyped: fn(&dyn Any) -> Option<HandleUntyped>,
}
```
- add the corresponding `FromType` impls
- add a function `app.register_asset_reflect` which is supposed to be called after `.add_asset` and registers `ReflectAsset` and `ReflectHandle` in the type registry
---
## Changelog
- add `ReflectAsset` and `ReflectHandle` types, which allow code to use reflection to manipulate arbitrary assets without knowing their types at compile time
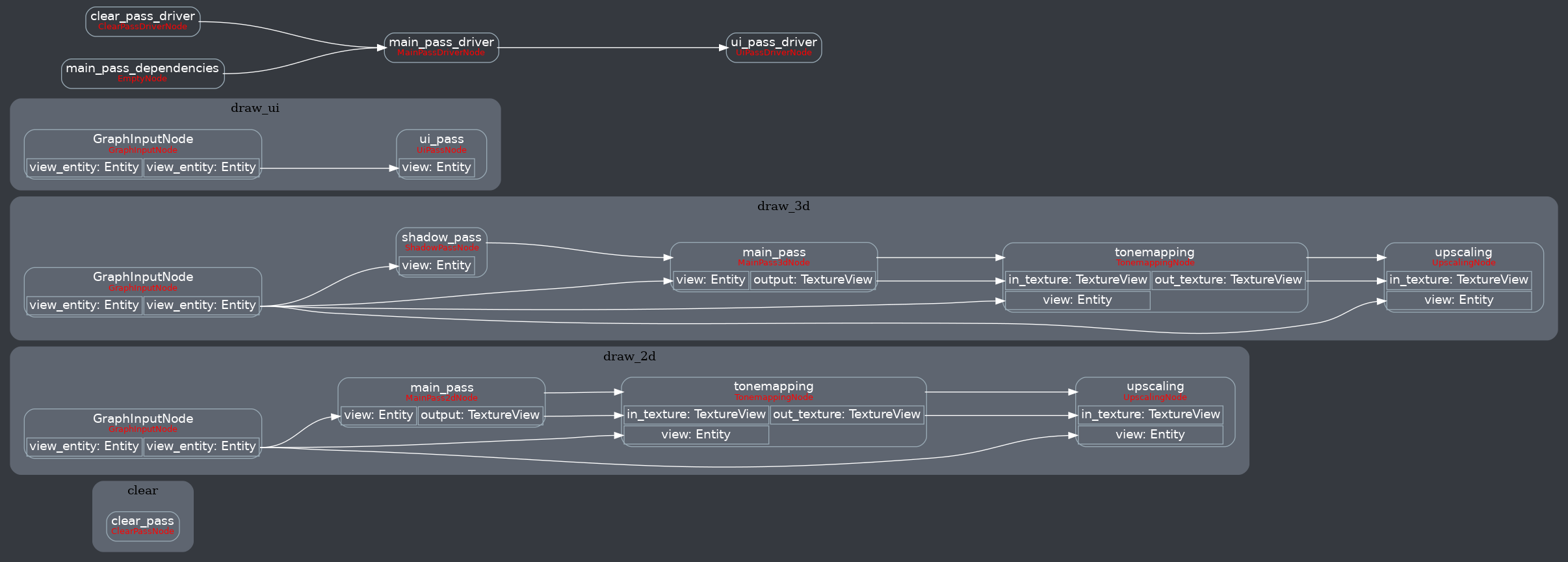
Attempt to make features like bloom https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/2876 easier to implement.
**This PR:**
- Moves the tonemapping from `pbr.wgsl` into a separate pass
- also add a separate upscaling pass after the tonemapping which writes to the swap chain (enables resolution-independant rendering and post-processing after tonemapping)
- adds a `hdr` bool to the camera which controls whether the pbr and sprite shaders render into a `Rgba16Float` texture
**Open questions:**
- ~should the 2d graph work the same as the 3d one?~ it is the same now
- ~The current solution is a bit inflexible because while you can add a post processing pass that writes to e.g. the `hdr_texture`, you can't write to a separate `user_postprocess_texture` while reading the `hdr_texture` and tell the tone mapping pass to read from the `user_postprocess_texture` instead. If the tonemapping and upscaling render graph nodes were to take in a `TextureView` instead of the view entity this would almost work, but the bind groups for their respective input textures are already created in the `Queue` render stage in the hardcoded order.~ solved by creating bind groups in render node
**New render graph:**
<details>
<summary>Before</summary>
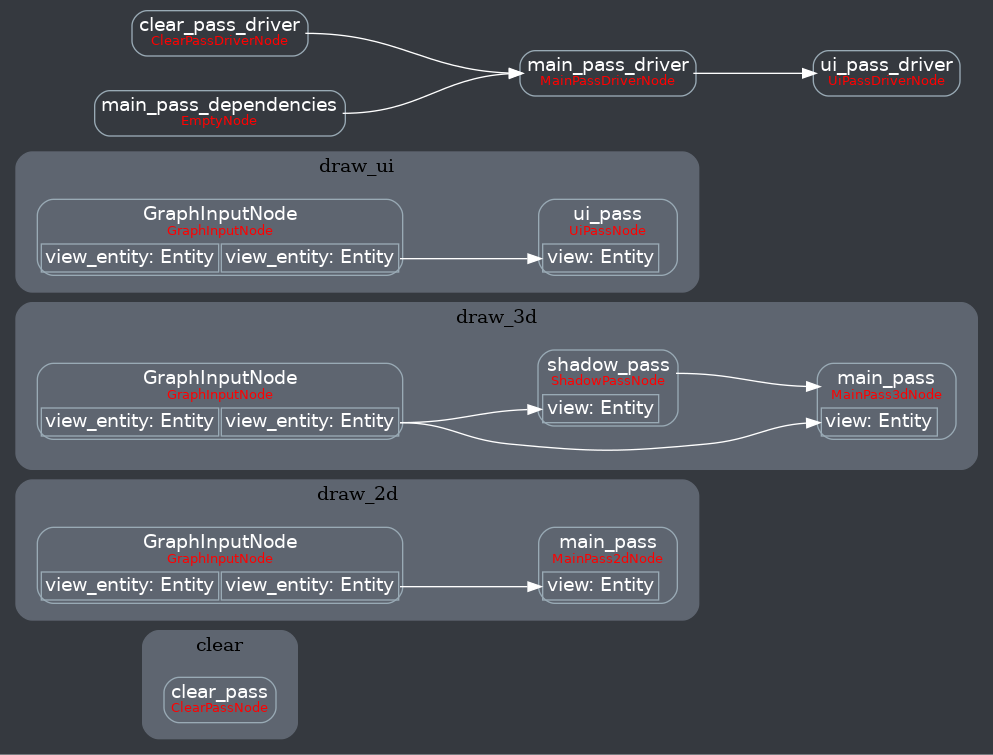
</details>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
See commit message.
I noticed I couldn't use `globals.time` when using `Material2d`.
I copied the solution from 8073362039 , and now `Material2d` works for me.
Perhaps some of these struct definitions could be shared in the future, but for now I've just copy pasted it (it looked like the `View` struct was done that way).
Ping @IceSentry , I saw a comment on the linked commit that you intended to do this work at some point in the future.
# Objective
- It's possible to create a mesh without positions or normals, but currently bevy forces these attributes to be present on any mesh.
## Solution
- Don't assume these attributes are present and add a shader defs for each attributes
- I updated 2d and 3d meshes to use the same logic.
---
## Changelog
- Meshes don't require any attributes
# Notes
I didn't update the pbr.wgsl shader because I'm not sure how to handle it. It doesn't really make sense to use it without positions or normals.
# Objective
There is no Srgb support on some GPU and display protocols with `winit` (for example, Nvidia's GPUs with Wayland). Thus `TextureFormat::bevy_default()` which returns `Rgba8UnormSrgb` or `Bgra8UnormSrgb` will cause panics on such platforms. This patch will resolve this problem. Fix https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/3897.
## Solution
Make `initialize_renderer` expose `wgpu::Adapter` and `first_available_texture_format`, use the `first_available_texture_format` by default.
## Changelog
* Fixed https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/3897.
# Objective
Allow `Mesh2d` shaders to work with meshes that have vertex tangents
## Solution
Correctly pass `mesh.model` into `mesh2d_tangent_local_to_world`
# Objective
The [Stageless RFC](https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/pull/45) involves allowing exclusive systems to be referenced and ordered relative to parallel systems. We've agreed that unifying systems under `System` is the right move.
This is an alternative to #4166 (see rationale in the comments I left there). Note that this builds on the learnings established there (and borrows some patterns).
## Solution
This unifies parallel and exclusive systems under the shared `System` trait, removing the old `ExclusiveSystem` trait / impls. This is accomplished by adding a new `ExclusiveFunctionSystem` impl similar to `FunctionSystem`. It is backed by `ExclusiveSystemParam`, which is similar to `SystemParam`. There is a new flattened out SystemContainer api (which cuts out a lot of trait and type complexity).
This means you can remove all cases of `exclusive_system()`:
```rust
// before
commands.add_system(some_system.exclusive_system());
// after
commands.add_system(some_system);
```
I've also implemented `ExclusiveSystemParam` for `&mut QueryState` and `&mut SystemState`, which makes this possible in exclusive systems:
```rust
fn some_exclusive_system(
world: &mut World,
transforms: &mut QueryState<&Transform>,
state: &mut SystemState<(Res<Time>, Query<&Player>)>,
) {
for transform in transforms.iter(world) {
println!("{transform:?}");
}
let (time, players) = state.get(world);
for player in players.iter() {
println!("{player:?}");
}
}
```
Note that "exclusive function systems" assume `&mut World` is present (and the first param). I think this is a fair assumption, given that the presence of `&mut World` is what defines the need for an exclusive system.
I added some targeted SystemParam `static` constraints, which removed the need for this:
``` rust
fn some_exclusive_system(state: &mut SystemState<(Res<'static, Time>, Query<&'static Player>)>) {}
```
## Related
- #2923
- #3001
- #3946
## Changelog
- `ExclusiveSystem` trait (and implementations) has been removed in favor of sharing the `System` trait.
- `ExclusiveFunctionSystem` and `ExclusiveSystemParam` were added, enabling flexible exclusive function systems
- `&mut SystemState` and `&mut QueryState` now implement `ExclusiveSystemParam`
- Exclusive and parallel System configuration is now done via a unified `SystemDescriptor`, `IntoSystemDescriptor`, and `SystemContainer` api.
## Migration Guide
Calling `.exclusive_system()` is no longer required (or supported) for converting exclusive system functions to exclusive systems:
```rust
// Old (0.8)
app.add_system(some_exclusive_system.exclusive_system());
// New (0.9)
app.add_system(some_exclusive_system);
```
Converting "normal" parallel systems to exclusive systems is done by calling the exclusive ordering apis:
```rust
// Old (0.8)
app.add_system(some_system.exclusive_system().at_end());
// New (0.9)
app.add_system(some_system.at_end());
```
Query state in exclusive systems can now be cached via ExclusiveSystemParams, which should be preferred for clarity and performance reasons:
```rust
// Old (0.8)
fn some_system(world: &mut World) {
let mut transforms = world.query::<&Transform>();
for transform in transforms.iter(world) {
}
}
// New (0.9)
fn some_system(world: &mut World, transforms: &mut QueryState<&Transform>) {
for transform in transforms.iter(world) {
}
}
```
# Objective
Now that we can consolidate Bundles and Components under a single insert (thanks to #2975 and #6039), almost 100% of world spawns now look like `world.spawn().insert((Some, Tuple, Here))`. Spawning an entity without any components is an extremely uncommon pattern, so it makes sense to give spawn the "first class" ergonomic api. This consolidated api should be made consistent across all spawn apis (such as World and Commands).
## Solution
All `spawn` apis (`World::spawn`, `Commands:;spawn`, `ChildBuilder::spawn`, and `WorldChildBuilder::spawn`) now accept a bundle as input:
```rust
// before:
commands
.spawn()
.insert((A, B, C));
world
.spawn()
.insert((A, B, C);
// after
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
world.spawn((A, B, C));
```
All existing instances of `spawn_bundle` have been deprecated in favor of the new `spawn` api. A new `spawn_empty` has been added, replacing the old `spawn` api.
By allowing `world.spawn(some_bundle)` to replace `world.spawn().insert(some_bundle)`, this opened the door to removing the initial entity allocation in the "empty" archetype / table done in `spawn()` (and subsequent move to the actual archetype in `.insert(some_bundle)`).
This improves spawn performance by over 10%:

To take this measurement, I added a new `world_spawn` benchmark.
Unfortunately, optimizing `Commands::spawn` is slightly less trivial, as Commands expose the Entity id of spawned entities prior to actually spawning. Doing the optimization would (naively) require assurances that the `spawn(some_bundle)` command is applied before all other commands involving the entity (which would not necessarily be true, if memory serves). Optimizing `Commands::spawn` this way does feel possible, but it will require careful thought (and maybe some additional checks), which deserves its own PR. For now, it has the same performance characteristics of the current `Commands::spawn_bundle` on main.
**Note that 99% of this PR is simple renames and refactors. The only code that needs careful scrutiny is the new `World::spawn()` impl, which is relatively straightforward, but it has some new unsafe code (which re-uses battle tested BundlerSpawner code path).**
---
## Changelog
- All `spawn` apis (`World::spawn`, `Commands:;spawn`, `ChildBuilder::spawn`, and `WorldChildBuilder::spawn`) now accept a bundle as input
- All instances of `spawn_bundle` have been deprecated in favor of the new `spawn` api
- World and Commands now have `spawn_empty()`, which is equivalent to the old `spawn()` behavior.
## Migration Guide
```rust
// Old (0.8):
commands
.spawn()
.insert_bundle((A, B, C));
// New (0.9)
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
// Old (0.8):
commands.spawn_bundle((A, B, C));
// New (0.9)
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
// Old (0.8):
let entity = commands.spawn().id();
// New (0.9)
let entity = commands.spawn_empty().id();
// Old (0.8)
let entity = world.spawn().id();
// New (0.9)
let entity = world.spawn_empty();
```
# Objective
Implement `IntoIterator` for `&Extract<P>` if the system parameter it wraps implements `IntoIterator`.
Enables the use of `IntoIterator` with an extracted query.
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
# Objective
fixes#5946
## Solution
adjust cluster index calculation for viewport origin.
from reading point 2 of the rasterization algorithm description in https://gpuweb.github.io/gpuweb/#rasterization, it looks like framebuffer space (and so @bulitin(position)) is not meant to be adjusted for viewport origin, so we need to subtract that to get the right cluster index.
- add viewport origin to rust `ExtractedView` and wgsl `View` structs
- subtract from frag coord for cluster index calculation
# Objective
This PR changes it possible to use vertex colors without a texture using the bevy_sprite ColorMaterial.
Fixes#5679
## Solution
- Made multiplication of the output color independent of the COLOR_MATERIAL_FLAGS_TEXTURE_BIT bit
- Extended mesh2d_vertex_color_texture example to show off both vertex colors and tinting
Not sure if extending the existing example was the right call but it seems to be reasonable to me.
I couldn't find any tests for the shaders and I think adding shader testing would be beyond the scope of this PR. So no tests in this PR. 😬
Co-authored-by: Jonas Wagner <jonas@29a.ch>
*This PR description is an edited copy of #5007, written by @alice-i-cecile.*
# Objective
Follow-up to https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/2254. The `Resource` trait currently has a blanket implementation for all types that meet its bounds.
While ergonomic, this results in several drawbacks:
* it is possible to make confusing, silent mistakes such as inserting a function pointer (Foo) rather than a value (Foo::Bar) as a resource
* it is challenging to discover if a type is intended to be used as a resource
* we cannot later add customization options (see the [RFC](https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/blob/main/rfcs/27-derive-component.md) for the equivalent choice for Component).
* dependencies can use the same Rust type as a resource in invisibly conflicting ways
* raw Rust types used as resources cannot preserve privacy appropriately, as anyone able to access that type can read and write to internal values
* we cannot capture a definitive list of possible resources to display to users in an editor
## Notes to reviewers
* Review this commit-by-commit; there's effectively no back-tracking and there's a lot of churn in some of these commits.
*ira: My commits are not as well organized :')*
* I've relaxed the bound on Local to Send + Sync + 'static: I don't think these concerns apply there, so this can keep things simple. Storing e.g. a u32 in a Local is fine, because there's a variable name attached explaining what it does.
* I think this is a bad place for the Resource trait to live, but I've left it in place to make reviewing easier. IMO that's best tackled with https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/4981.
## Changelog
`Resource` is no longer automatically implemented for all matching types. Instead, use the new `#[derive(Resource)]` macro.
## Migration Guide
Add `#[derive(Resource)]` to all types you are using as a resource.
If you are using a third party type as a resource, wrap it in a tuple struct to bypass orphan rules. Consider deriving `Deref` and `DerefMut` to improve ergonomics.
`ClearColor` no longer implements `Component`. Using `ClearColor` as a component in 0.8 did nothing.
Use the `ClearColorConfig` in the `Camera3d` and `Camera2d` components instead.
Co-authored-by: Alice <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
View mesh2d_view_types.wgsl was missing a couple of fields present in bevy::render::ViewUniform, causing rendering issues for shaders using later fields.
## Solution
Solved by adding the fields in question
# Objective
I've found there is a duplicated line, probably left after some copy paste.
## Solution
- removed it
---
Co-authored-by: adsick <vadimgangsta73@gmail.com>
Port changes made to Material in #5053 to Material2d as well.
This is more or less an exact copy of the implementation in bevy_pbr; I
simply pretended the API existed, then copied stuff over until it
started building and the shapes example was working again.
# Objective
The changes in #5053 makes it possible to add custom materials with a lot less boiler plate. However, the implementation isn't shared with Material 2d as it's a kind of fork of the bevy_pbr version. It should be possible to use AsBindGroup on the 2d version as well.
## Solution
This makes the same kind of changes in Material2d in bevy_sprite.
This makes the following work:
```rust
//! Draws a circular purple bevy in the middle of the screen using a custom shader
use bevy::{
prelude::*,
reflect::TypeUuid,
render::render_resource::{AsBindGroup, ShaderRef},
sprite::{Material2d, Material2dPlugin, MaterialMesh2dBundle},
};
fn main() {
App::new()
.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins)
.add_plugin(Material2dPlugin::<CustomMaterial>::default())
.add_startup_system(setup)
.run();
}
/// set up a simple 2D scene
fn setup(
mut commands: Commands,
mut meshes: ResMut<Assets<Mesh>>,
mut materials: ResMut<Assets<CustomMaterial>>,
asset_server: Res<AssetServer>,
) {
commands.spawn_bundle(MaterialMesh2dBundle {
mesh: meshes.add(shape::Circle::new(50.).into()).into(),
material: materials.add(CustomMaterial {
color: Color::PURPLE,
color_texture: Some(asset_server.load("branding/icon.png")),
}),
transform: Transform::from_translation(Vec3::new(-100., 0., 0.)),
..default()
});
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle::default());
}
/// The Material2d trait is very configurable, but comes with sensible defaults for all methods.
/// You only need to implement functions for features that need non-default behavior. See the Material api docs for details!
impl Material2d for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"shaders/custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
// This is the struct that will be passed to your shader
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
# Objective
Fixes#4907. Fixes#838. Fixes#5089.
Supersedes #5146. Supersedes #2087. Supersedes #865. Supersedes #5114
Visibility is currently entirely local. Set a parent entity to be invisible, and the children are still visible. This makes it hard for users to hide entire hierarchies of entities.
Additionally, the semantics of `Visibility` vs `ComputedVisibility` are inconsistent across entity types. 3D meshes use `ComputedVisibility` as the "definitive" visibility component, with `Visibility` being just one data source. Sprites just use `Visibility`, which means they can't feed off of `ComputedVisibility` data, such as culling information, RenderLayers, and (added in this pr) visibility inheritance information.
## Solution
Splits `ComputedVisibilty::is_visible` into `ComputedVisibilty::is_visible_in_view` and `ComputedVisibilty::is_visible_in_hierarchy`. For each visible entity, `is_visible_in_hierarchy` is computed by propagating visibility down the hierarchy. The `ComputedVisibility::is_visible()` function combines these two booleans for the canonical "is this entity visible" function.
Additionally, all entities that have `Visibility` now also have `ComputedVisibility`. Sprites, Lights, and UI entities now use `ComputedVisibility` when appropriate.
This means that in addition to visibility inheritance, everything using Visibility now also supports RenderLayers. Notably, Sprites (and other 2d objects) now support `RenderLayers` and work properly across multiple views.
Also note that this does increase the amount of work done per sprite. Bevymark with 100,000 sprites on `main` runs in `0.017612` seconds and this runs in `0.01902`. That is certainly a gap, but I believe the api consistency and extra functionality this buys us is worth it. See [this thread](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/5146#issuecomment-1182783452) for more info. Note that #5146 in combination with #5114 _are_ a viable alternative to this PR and _would_ perform better, but that comes at the cost of api inconsistencies and doing visibility calculations in the "wrong" place. The current visibility system does have potential for performance improvements. I would prefer to evolve that one system as a whole rather than doing custom hacks / different behaviors for each feature slice.
Here is a "split screen" example where the left camera uses RenderLayers to filter out the blue sprite.
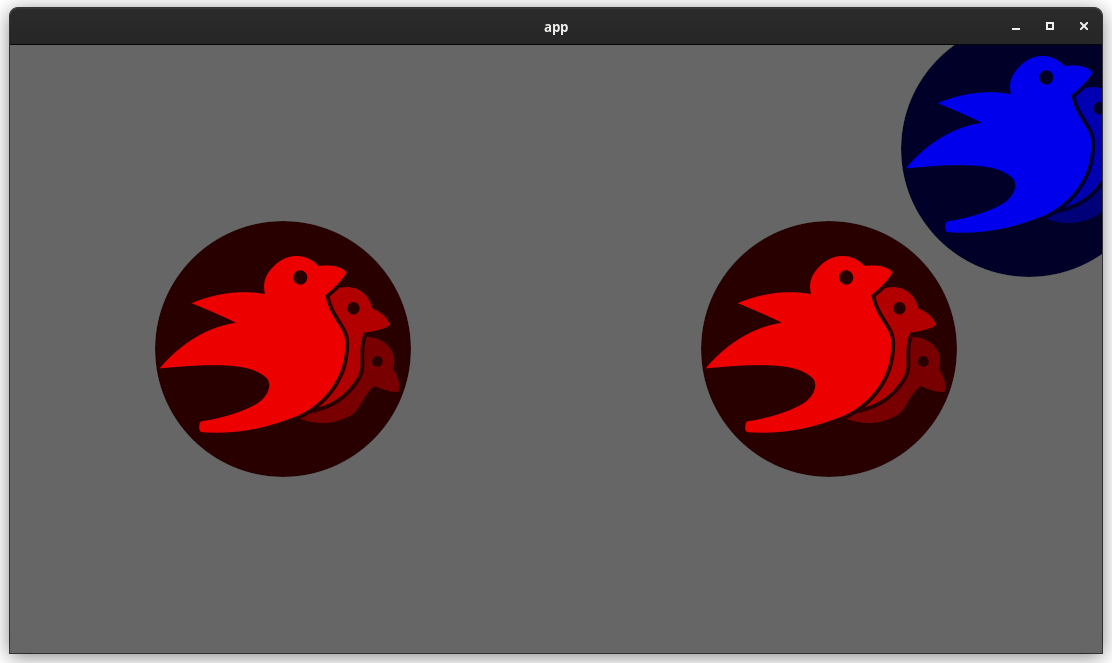

Note that this builds directly on #5146 and that @james7132 deserves the credit for the baseline visibility inheritance work. This pr moves the inherited visibility field into `ComputedVisibility`, then does the additional work of porting everything to `ComputedVisibility`. See my [comments here](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/5146#issuecomment-1182783452) for rationale.
## Follow up work
* Now that lights use ComputedVisibility, VisibleEntities now includes "visible lights" in the entity list. Functionally not a problem as we use queries to filter the list down in the desired context. But we should consider splitting this out into a separate`VisibleLights` collection for both clarity and performance reasons. And _maybe_ even consider scoping `VisibleEntities` down to `VisibleMeshes`?.
* Investigate alternative sprite rendering impls (in combination with visibility system tweaks) that avoid re-generating a per-view fixedbitset of visible entities every frame, then checking each ExtractedEntity. This is where most of the performance overhead lives. Ex: we could generate ExtractedEntities per-view using the VisibleEntities list, avoiding the need for the bitset.
* Should ComputedVisibility use bitflags under the hood? This would cut down on the size of the component, potentially speed up the `is_visible()` function, and allow us to cheaply expand ComputedVisibility with more data (ex: split out local visibility and parent visibility, add more culling classes, etc).
---
## Changelog
* ComputedVisibility now takes hierarchy visibility into account.
* 2D, UI and Light entities now use the ComputedVisibility component.
## Migration Guide
If you were previously reading `Visibility::is_visible` as the "actual visibility" for sprites or lights, use `ComputedVisibilty::is_visible()` instead:
```rust
// before (0.7)
fn system(query: Query<&Visibility>) {
for visibility in query.iter() {
if visibility.is_visible {
log!("found visible entity");
}
}
}
// after (0.8)
fn system(query: Query<&ComputedVisibility>) {
for visibility in query.iter() {
if visibility.is_visible() {
log!("found visible entity");
}
}
}
```
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
Remove unnecessary calls to `iter()`/`iter_mut()`.
Mainly updates the use of queries in our code, docs, and examples.
```rust
// From
for _ in list.iter() {
for _ in list.iter_mut() {
// To
for _ in &list {
for _ in &mut list {
```
We already enable the pedantic lint [clippy::explicit_iter_loop](https://rust-lang.github.io/rust-clippy/stable/) inside of Bevy. However, this only warns for a few known types from the standard library.
## Note for reviewers
As you can see the additions and deletions are exactly equal.
Maybe give it a quick skim to check I didn't sneak in a crypto miner, but you don't have to torture yourself by reading every line.
I already experienced enough pain making this PR :)
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Currently, the `Extract` `RenderStage` is executed on the main world, with the render world available as a resource.
- However, when needing access to resources in the render world (e.g. to mutate them), the only way to do so was to get exclusive access to the whole `RenderWorld` resource.
- This meant that effectively only one extract which wrote to resources could run at a time.
- We didn't previously make `Extract`ing writing to the world a non-happy path, even though we want to discourage that.
## Solution
- Move the extract stage to run on the render world.
- Add the main world as a `MainWorld` resource.
- Add an `Extract` `SystemParam` as a convenience to access a (read only) `SystemParam` in the main world during `Extract`.
## Future work
It should be possible to avoid needing to use `get_or_spawn` for the render commands, since now the `Commands`' `Entities` matches up with the world being executed on.
We need to determine how this interacts with https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/3519
It's theoretically possible to remove the need for the `value` method on `Extract`. However, that requires slightly changing the `SystemParam` interface, which would make it more complicated. That would probably mess up the `SystemState` api too.
## Todo
I still need to add doc comments to `Extract`.
---
## Changelog
### Changed
- The `Extract` `RenderStage` now runs on the render world (instead of the main world as before).
You must use the `Extract` `SystemParam` to access the main world during the extract phase.
Resources on the render world can now be accessed using `ResMut` during extract.
### Removed
- `Commands::spawn_and_forget`. Use `Commands::get_or_spawn(e).insert_bundle(bundle)` instead
## Migration Guide
The `Extract` `RenderStage` now runs on the render world (instead of the main world as before).
You must use the `Extract` `SystemParam` to access the main world during the extract phase. `Extract` takes a single type parameter, which is any system parameter (such as `Res`, `Query` etc.). It will extract this from the main world, and returns the result of this extraction when `value` is called on it.
For example, if previously your extract system looked like:
```rust
fn extract_clouds(mut commands: Commands, clouds: Query<Entity, With<Cloud>>) {
for cloud in clouds.iter() {
commands.get_or_spawn(cloud).insert(Cloud);
}
}
```
the new version would be:
```rust
fn extract_clouds(mut commands: Commands, mut clouds: Extract<Query<Entity, With<Cloud>>>) {
for cloud in clouds.value().iter() {
commands.get_or_spawn(cloud).insert(Cloud);
}
}
```
The diff is:
```diff
--- a/src/clouds.rs
+++ b/src/clouds.rs
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
-fn extract_clouds(mut commands: Commands, clouds: Query<Entity, With<Cloud>>) {
- for cloud in clouds.iter() {
+fn extract_clouds(mut commands: Commands, mut clouds: Extract<Query<Entity, With<Cloud>>>) {
+ for cloud in clouds.value().iter() {
commands.get_or_spawn(cloud).insert(Cloud);
}
}
```
You can now also access resources from the render world using the normal system parameters during `Extract`:
```rust
fn extract_assets(mut render_assets: ResMut<MyAssets>, source_assets: Extract<Res<MyAssets>>) {
*render_assets = source_assets.clone();
}
```
Please note that all existing extract systems need to be updated to match this new style; even if they currently compile they will not run as expected. A warning will be emitted on a best-effort basis if this is not met.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
Make it easier to create pipelines derived from the `Material2dPipeline`. Currently this is made difficult because the fields of `Material2dKey` are private.
## Solution
Make the fields public.
Removed `const_vec2`/`const_vec3`
and replaced with equivalent `.from_array`.
# Objective
Fixes#5112
## Solution
- `encase` needs to update to `glam` as well. See teoxoy/encase#4 on progress on that.
- `hexasphere` also needs to be updated, see OptimisticPeach/hexasphere#12.
# Objective
- Add reusable shader functions for transforming positions / normals / tangents between local and world / clip space for 2D and 3D so that they are done in a simple and correct way
- The next step in #3969 so check there for more details.
## Solution
- Add `bevy_pbr::mesh_functions` and `bevy_sprite::mesh2d_functions` shader imports
- These contain `mesh_` and `mesh2d_` versions of the following functions:
- `mesh_position_local_to_world`
- `mesh_position_world_to_clip`
- `mesh_position_local_to_clip`
- `mesh_normal_local_to_world`
- `mesh_tangent_local_to_world`
- Use them everywhere where it is appropriate
- Notably not in the sprite and UI shaders where `mesh2d_position_world_to_clip` could have been used, but including all the functions depends on the mesh binding so I chose to not use the function there
- NOTE: The `mesh_` and `mesh2d_` functions are currently identical. However, if I had defined only `bevy_pbr::mesh_functions` and used that in bevy_sprite, then bevy_sprite would have a runtime dependency on bevy_pbr, which seems undesirable. I also expect that when we have a proper 2D rendering API, these functions will diverge between 2D and 3D.
---
## Changelog
- Added: `bevy_pbr::mesh_functions` and `bevy_sprite::mesh2d_functions` shader imports containing `mesh_` and `mesh2d_` versions of the following functions:
- `mesh_position_local_to_world`
- `mesh_position_world_to_clip`
- `mesh_position_local_to_clip`
- `mesh_normal_local_to_world`
- `mesh_tangent_local_to_world`
## Migration Guide
- The `skin_tangents` function from the `bevy_pbr::skinning` shader import has been replaced with the `mesh_tangent_local_to_world` function from the `bevy_pbr::mesh_functions` shader import
# Objective
Fix#4958
There was 4 issues:
- this is not true in WASM and on macOS: f28b921209/examples/3d/split_screen.rs (L90)
- ~~I made sure the system was running at least once~~
- I'm sending the event on window creation
- in webgl, setting a viewport has impacts on other render passes
- only in webgl and when there is a custom viewport, I added a render pass without a custom viewport
- shaderdef NO_ARRAY_TEXTURES_SUPPORT was not used by the 2d pipeline
- webgl feature was used but not declared in bevy_sprite, I added it to the Cargo.toml
- shaderdef NO_STORAGE_BUFFERS_SUPPORT was not used by the 2d pipeline
- I added it based on the BufferBindingType
The last commit changes the two last fixes to add the shaderdefs in the shader cache directly instead of needing to do it in each pipeline
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
# Objective
- Closes#4464
## Solution
- Specify default mag and min filter types for `Image` instead of using `wgpu`'s defaults.
---
## Changelog
### Changed
- Default `Image` filtering changed from `Nearest` to `Linear`.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
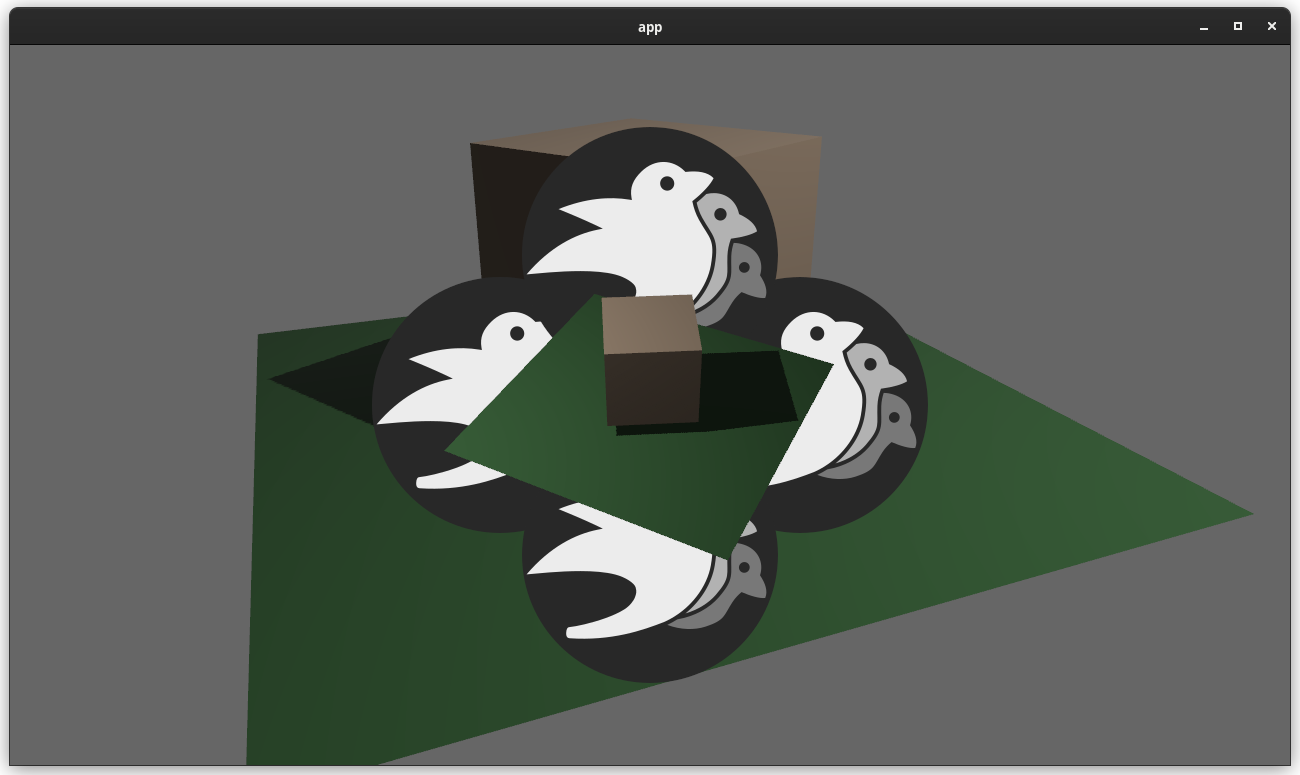
This adds "high level camera driven rendering" to Bevy. The goal is to give users more control over what gets rendered (and where) without needing to deal with render logic. This will make scenarios like "render to texture", "multiple windows", "split screen", "2d on 3d", "3d on 2d", "pass layering", and more significantly easier.
Here is an [example of a 2d render sandwiched between two 3d renders (each from a different perspective)](https://gist.github.com/cart/4fe56874b2e53bc5594a182fc76f4915):

Users can now spawn a camera, point it at a RenderTarget (a texture or a window), and it will "just work".
Rendering to a second window is as simple as spawning a second camera and assigning it to a specific window id:
```rust
// main camera (main window)
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle::default());
// second camera (other window)
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle {
camera: Camera {
target: RenderTarget::Window(window_id),
..default()
},
..default()
});
```
Rendering to a texture is as simple as pointing the camera at a texture:
```rust
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle {
camera: Camera {
target: RenderTarget::Texture(image_handle),
..default()
},
..default()
});
```
Cameras now have a "render priority", which controls the order they are drawn in. If you want to use a camera's output texture as a texture in the main pass, just set the priority to a number lower than the main pass camera (which defaults to `0`).
```rust
// main pass camera with a default priority of 0
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle::default());
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle {
camera: Camera {
target: RenderTarget::Texture(image_handle.clone()),
priority: -1,
..default()
},
..default()
});
commands.spawn_bundle(SpriteBundle {
texture: image_handle,
..default()
})
```
Priority can also be used to layer to cameras on top of each other for the same RenderTarget. This is what "2d on top of 3d" looks like in the new system:
```rust
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle::default());
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle {
camera: Camera {
// this will render 2d entities "on top" of the default 3d camera's render
priority: 1,
..default()
},
..default()
});
```
There is no longer the concept of a global "active camera". Resources like `ActiveCamera<Camera2d>` and `ActiveCamera<Camera3d>` have been replaced with the camera-specific `Camera::is_active` field. This does put the onus on users to manage which cameras should be active.
Cameras are now assigned a single render graph as an "entry point", which is configured on each camera entity using the new `CameraRenderGraph` component. The old `PerspectiveCameraBundle` and `OrthographicCameraBundle` (generic on camera marker components like Camera2d and Camera3d) have been replaced by `Camera3dBundle` and `Camera2dBundle`, which set 3d and 2d default values for the `CameraRenderGraph` and projections.
```rust
// old 3d perspective camera
commands.spawn_bundle(PerspectiveCameraBundle::default())
// new 3d perspective camera
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle::default())
```
```rust
// old 2d orthographic camera
commands.spawn_bundle(OrthographicCameraBundle::new_2d())
// new 2d orthographic camera
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera2dBundle::default())
```
```rust
// old 3d orthographic camera
commands.spawn_bundle(OrthographicCameraBundle::new_3d())
// new 3d orthographic camera
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle {
projection: OrthographicProjection {
scale: 3.0,
scaling_mode: ScalingMode::FixedVertical,
..default()
}.into(),
..default()
})
```
Note that `Camera3dBundle` now uses a new `Projection` enum instead of hard coding the projection into the type. There are a number of motivators for this change: the render graph is now a part of the bundle, the way "generic bundles" work in the rust type system prevents nice `..default()` syntax, and changing projections at runtime is much easier with an enum (ex for editor scenarios). I'm open to discussing this choice, but I'm relatively certain we will all come to the same conclusion here. Camera2dBundle and Camera3dBundle are much clearer than being generic on marker components / using non-default constructors.
If you want to run a custom render graph on a camera, just set the `CameraRenderGraph` component:
```rust
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle {
camera_render_graph: CameraRenderGraph::new(some_render_graph_name),
..default()
})
```
Just note that if the graph requires data from specific components to work (such as `Camera3d` config, which is provided in the `Camera3dBundle`), make sure the relevant components have been added.
Speaking of using components to configure graphs / passes, there are a number of new configuration options:
```rust
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle {
camera_3d: Camera3d {
// overrides the default global clear color
clear_color: ClearColorConfig::Custom(Color::RED),
..default()
},
..default()
})
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle {
camera_3d: Camera3d {
// disables clearing
clear_color: ClearColorConfig::None,
..default()
},
..default()
})
```
Expect to see more of the "graph configuration Components on Cameras" pattern in the future.
By popular demand, UI no longer requires a dedicated camera. `UiCameraBundle` has been removed. `Camera2dBundle` and `Camera3dBundle` now both default to rendering UI as part of their own render graphs. To disable UI rendering for a camera, disable it using the CameraUi component:
```rust
commands
.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle::default())
.insert(CameraUi {
is_enabled: false,
..default()
})
```
## Other Changes
* The separate clear pass has been removed. We should revisit this for things like sky rendering, but I think this PR should "keep it simple" until we're ready to properly support that (for code complexity and performance reasons). We can come up with the right design for a modular clear pass in a followup pr.
* I reorganized bevy_core_pipeline into Core2dPlugin and Core3dPlugin (and core_2d / core_3d modules). Everything is pretty much the same as before, just logically separate. I've moved relevant types (like Camera2d, Camera3d, Camera3dBundle, Camera2dBundle) into their relevant modules, which is what motivated this reorganization.
* I adapted the `scene_viewer` example (which relied on the ActiveCameras behavior) to the new system. I also refactored bits and pieces to be a bit simpler.
* All of the examples have been ported to the new camera approach. `render_to_texture` and `multiple_windows` are now _much_ simpler. I removed `two_passes` because it is less relevant with the new approach. If someone wants to add a new "layered custom pass with CameraRenderGraph" example, that might fill a similar niche. But I don't feel much pressure to add that in this pr.
* Cameras now have `target_logical_size` and `target_physical_size` fields, which makes finding the size of a camera's render target _much_ simpler. As a result, the `Assets<Image>` and `Windows` parameters were removed from `Camera::world_to_screen`, making that operation much more ergonomic.
* Render order ambiguities between cameras with the same target and the same priority now produce a warning. This accomplishes two goals:
1. Now that there is no "global" active camera, by default spawning two cameras will result in two renders (one covering the other). This would be a silent performance killer that would be hard to detect after the fact. By detecting ambiguities, we can provide a helpful warning when this occurs.
2. Render order ambiguities could result in unexpected / unpredictable render results. Resolving them makes sense.
## Follow Up Work
* Per-Camera viewports, which will make it possible to render to a smaller area inside of a RenderTarget (great for something like splitscreen)
* Camera-specific MSAA config (should use the same "overriding" pattern used for ClearColor)
* Graph Based Camera Ordering: priorities are simple, but they make complicated ordering constraints harder to express. We should consider adopting a "graph based" camera ordering model with "before" and "after" relationships to other cameras (or build it "on top" of the priority system).
* Consider allowing graphs to run subgraphs from any nest level (aka a global namespace for graphs). Right now the 2d and 3d graphs each need their own UI subgraph, which feels "fine" in the short term. But being able to share subgraphs between other subgraphs seems valuable.
* Consider splitting `bevy_core_pipeline` into `bevy_core_2d` and `bevy_core_3d` packages. Theres a shared "clear color" dependency here, which would need a new home.
# Objective
- Split PBR and 2D mesh shaders into types and bindings to prepare the shaders to be more reusable.
- See #3969 for details. I'm doing this in multiple steps to make review easier.
---
## Changelog
- Changed: 2D and PBR mesh shaders are now split into types and bindings, the following shader imports are available: `bevy_pbr::mesh_view_types`, `bevy_pbr::mesh_view_bindings`, `bevy_pbr::mesh_types`, `bevy_pbr::mesh_bindings`, `bevy_sprite::mesh2d_view_types`, `bevy_sprite::mesh2d_view_bindings`, `bevy_sprite::mesh2d_types`, `bevy_sprite::mesh2d_bindings`
## Migration Guide
- In shaders for 3D meshes:
- `#import bevy_pbr::mesh_view_bind_group` -> `#import bevy_pbr::mesh_view_bindings`
- `#import bevy_pbr::mesh_struct` -> `#import bevy_pbr::mesh_types`
- NOTE: If you are using the mesh bind group at bind group index 2, you can remove those binding statements in your shader and just use `#import bevy_pbr::mesh_bindings` which itself imports the mesh types needed for the bindings.
- In shaders for 2D meshes:
- `#import bevy_sprite::mesh2d_view_bind_group` -> `#import bevy_sprite::mesh2d_view_bindings`
- `#import bevy_sprite::mesh2d_struct` -> `#import bevy_sprite::mesh2d_types`
- NOTE: If you are using the mesh2d bind group at bind group index 2, you can remove those binding statements in your shader and just use `#import bevy_sprite::mesh2d_bindings` which itself imports the mesh2d types needed for the bindings.
# Objective
- Add an `ExtractResourcePlugin` for convenience and consistency
## Solution
- Add an `ExtractResourcePlugin` similar to `ExtractComponentPlugin` but for ECS `Resource`s. The system that is executed simply clones the main world resource into a render world resource, if and only if the main world resource was either added or changed since the last execution of the system.
- Add an `ExtractResource` trait with a `fn extract_resource(res: &Self) -> Self` function. This is used by the `ExtractResourcePlugin` to extract the resource
- Add a derive macro for `ExtractResource` on a `Resource` with the `Clone` trait, that simply returns `res.clone()`
- Use `ExtractResourcePlugin` wherever both possible and appropriate
# Objective
- Add Vertex Color support to 2D meshes and ColorMaterial. This extends the work from #4528 (which in turn builds on the excellent tangent handling).
## Solution
- Added `#ifdef` wrapped support for vertex colors in the 2D mesh shader and `ColorMaterial` shader.
- Added an example, `mesh2d_vertex_color_texture` to demonstrate it in action.

---
## Changelog
- Added optional (ifdef wrapped) vertex color support to the 2dmesh and color material systems.