2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
use crate::{
|
2023-03-02 22:44:10 +00:00
|
|
|
render, AlphaMode, DrawMesh, DrawPrepass, EnvironmentMapLight, MeshPipeline, MeshPipelineKey,
|
2023-03-03 15:08:54 +00:00
|
|
|
MeshUniform, PrepassPipelinePlugin, PrepassPlugin, RenderLightSystems, SetMeshBindGroup,
|
|
|
|
|
SetMeshViewBindGroup, Shadow,
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
};
|
2023-02-24 18:33:55 +00:00
|
|
|
use bevy_app::{App, IntoSystemAppConfig, Plugin};
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
use bevy_asset::{AddAsset, AssetEvent, AssetServer, Assets, Handle};
|
2022-10-26 20:13:59 +00:00
|
|
|
use bevy_core_pipeline::{
|
|
|
|
|
core_3d::{AlphaMask3d, Opaque3d, Transparent3d},
|
2023-02-19 20:38:13 +00:00
|
|
|
tonemapping::{DebandDither, Tonemapping},
|
2022-10-26 20:13:59 +00:00
|
|
|
};
|

Make `Resource` trait opt-in, requiring `#[derive(Resource)]` V2 (#5577)
*This PR description is an edited copy of #5007, written by @alice-i-cecile.*
# Objective
Follow-up to https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/2254. The `Resource` trait currently has a blanket implementation for all types that meet its bounds.
While ergonomic, this results in several drawbacks:
* it is possible to make confusing, silent mistakes such as inserting a function pointer (Foo) rather than a value (Foo::Bar) as a resource
* it is challenging to discover if a type is intended to be used as a resource
* we cannot later add customization options (see the [RFC](https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/blob/main/rfcs/27-derive-component.md) for the equivalent choice for Component).
* dependencies can use the same Rust type as a resource in invisibly conflicting ways
* raw Rust types used as resources cannot preserve privacy appropriately, as anyone able to access that type can read and write to internal values
* we cannot capture a definitive list of possible resources to display to users in an editor
## Notes to reviewers
* Review this commit-by-commit; there's effectively no back-tracking and there's a lot of churn in some of these commits.
*ira: My commits are not as well organized :')*
* I've relaxed the bound on Local to Send + Sync + 'static: I don't think these concerns apply there, so this can keep things simple. Storing e.g. a u32 in a Local is fine, because there's a variable name attached explaining what it does.
* I think this is a bad place for the Resource trait to live, but I've left it in place to make reviewing easier. IMO that's best tackled with https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/4981.
## Changelog
`Resource` is no longer automatically implemented for all matching types. Instead, use the new `#[derive(Resource)]` macro.
## Migration Guide
Add `#[derive(Resource)]` to all types you are using as a resource.
If you are using a third party type as a resource, wrap it in a tuple struct to bypass orphan rules. Consider deriving `Deref` and `DerefMut` to improve ergonomics.
`ClearColor` no longer implements `Component`. Using `ClearColor` as a component in 0.8 did nothing.
Use the `ClearColorConfig` in the `Camera3d` and `Camera2d` components instead.
Co-authored-by: Alice <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
2022-08-08 21:36:35 +00:00
|
|
|
use bevy_derive::{Deref, DerefMut};
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
use bevy_ecs::{
|

Migrate engine to Schedule v3 (#7267)
Huge thanks to @maniwani, @devil-ira, @hymm, @cart, @superdump and @jakobhellermann for the help with this PR.
# Objective
- Followup #6587.
- Minimal integration for the Stageless Scheduling RFC: https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/pull/45
## Solution
- [x] Remove old scheduling module
- [x] Migrate new methods to no longer use extension methods
- [x] Fix compiler errors
- [x] Fix benchmarks
- [x] Fix examples
- [x] Fix docs
- [x] Fix tests
## Changelog
### Added
- a large number of methods on `App` to work with schedules ergonomically
- the `CoreSchedule` enum
- `App::add_extract_system` via the `RenderingAppExtension` trait extension method
- the private `prepare_view_uniforms` system now has a public system set for scheduling purposes, called `ViewSet::PrepareUniforms`
### Removed
- stages, and all code that mentions stages
- states have been dramatically simplified, and no longer use a stack
- `RunCriteriaLabel`
- `AsSystemLabel` trait
- `on_hierarchy_reports_enabled` run criteria (now just uses an ad hoc resource checking run condition)
- systems in `RenderSet/Stage::Extract` no longer warn when they do not read data from the main world
- `RunCriteriaLabel`
- `transform_propagate_system_set`: this was a nonstandard pattern that didn't actually provide enough control. The systems are already `pub`: the docs have been updated to ensure that the third-party usage is clear.
### Changed
- `System::default_labels` is now `System::default_system_sets`.
- `App::add_default_labels` is now `App::add_default_sets`
- `CoreStage` and `StartupStage` enums are now `CoreSet` and `StartupSet`
- `App::add_system_set` was renamed to `App::add_systems`
- The `StartupSchedule` label is now defined as part of the `CoreSchedules` enum
- `.label(SystemLabel)` is now referred to as `.in_set(SystemSet)`
- `SystemLabel` trait was replaced by `SystemSet`
- `SystemTypeIdLabel<T>` was replaced by `SystemSetType<T>`
- The `ReportHierarchyIssue` resource now has a public constructor (`new`), and implements `PartialEq`
- Fixed time steps now use a schedule (`CoreSchedule::FixedTimeStep`) rather than a run criteria.
- Adding rendering extraction systems now panics rather than silently failing if no subapp with the `RenderApp` label is found.
- the `calculate_bounds` system, with the `CalculateBounds` label, is now in `CoreSet::Update`, rather than in `CoreSet::PostUpdate` before commands are applied.
- `SceneSpawnerSystem` now runs under `CoreSet::Update`, rather than `CoreStage::PreUpdate.at_end()`.
- `bevy_pbr::add_clusters` is no longer an exclusive system
- the top level `bevy_ecs::schedule` module was replaced with `bevy_ecs::scheduling`
- `tick_global_task_pools_on_main_thread` is no longer run as an exclusive system. Instead, it has been replaced by `tick_global_task_pools`, which uses a `NonSend` resource to force running on the main thread.
## Migration Guide
- Calls to `.label(MyLabel)` should be replaced with `.in_set(MySet)`
- Stages have been removed. Replace these with system sets, and then add command flushes using the `apply_system_buffers` exclusive system where needed.
- The `CoreStage`, `StartupStage, `RenderStage` and `AssetStage` enums have been replaced with `CoreSet`, `StartupSet, `RenderSet` and `AssetSet`. The same scheduling guarantees have been preserved.
- Systems are no longer added to `CoreSet::Update` by default. Add systems manually if this behavior is needed, although you should consider adding your game logic systems to `CoreSchedule::FixedTimestep` instead for more reliable framerate-independent behavior.
- Similarly, startup systems are no longer part of `StartupSet::Startup` by default. In most cases, this won't matter to you.
- For example, `add_system_to_stage(CoreStage::PostUpdate, my_system)` should be replaced with
- `add_system(my_system.in_set(CoreSet::PostUpdate)`
- When testing systems or otherwise running them in a headless fashion, simply construct and run a schedule using `Schedule::new()` and `World::run_schedule` rather than constructing stages
- Run criteria have been renamed to run conditions. These can now be combined with each other and with states.
- Looping run criteria and state stacks have been removed. Use an exclusive system that runs a schedule if you need this level of control over system control flow.
- For app-level control flow over which schedules get run when (such as for rollback networking), create your own schedule and insert it under the `CoreSchedule::Outer` label.
- Fixed timesteps are now evaluated in a schedule, rather than controlled via run criteria. The `run_fixed_timestep` system runs this schedule between `CoreSet::First` and `CoreSet::PreUpdate` by default.
- Command flush points introduced by `AssetStage` have been removed. If you were relying on these, add them back manually.
- Adding extract systems is now typically done directly on the main app. Make sure the `RenderingAppExtension` trait is in scope, then call `app.add_extract_system(my_system)`.
- the `calculate_bounds` system, with the `CalculateBounds` label, is now in `CoreSet::Update`, rather than in `CoreSet::PostUpdate` before commands are applied. You may need to order your movement systems to occur before this system in order to avoid system order ambiguities in culling behavior.
- the `RenderLabel` `AppLabel` was renamed to `RenderApp` for clarity
- `App::add_state` now takes 0 arguments: the starting state is set based on the `Default` impl.
- Instead of creating `SystemSet` containers for systems that run in stages, simply use `.on_enter::<State::Variant>()` or its `on_exit` or `on_update` siblings.
- `SystemLabel` derives should be replaced with `SystemSet`. You will also need to add the `Debug`, `PartialEq`, `Eq`, and `Hash` traits to satisfy the new trait bounds.
- `with_run_criteria` has been renamed to `run_if`. Run criteria have been renamed to run conditions for clarity, and should now simply return a bool.
- States have been dramatically simplified: there is no longer a "state stack". To queue a transition to the next state, call `NextState::set`
## TODO
- [x] remove dead methods on App and World
- [x] add `App::add_system_to_schedule` and `App::add_systems_to_schedule`
- [x] avoid adding the default system set at inappropriate times
- [x] remove any accidental cycles in the default plugins schedule
- [x] migrate benchmarks
- [x] expose explicit labels for the built-in command flush points
- [x] migrate engine code
- [x] remove all mentions of stages from the docs
- [x] verify docs for States
- [x] fix uses of exclusive systems that use .end / .at_start / .before_commands
- [x] migrate RenderStage and AssetStage
- [x] migrate examples
- [x] ensure that transform propagation is exported in a sufficiently public way (the systems are already pub)
- [x] ensure that on_enter schedules are run at least once before the main app
- [x] re-enable opt-in to execution order ambiguities
- [x] revert change to `update_bounds` to ensure it runs in `PostUpdate`
- [x] test all examples
- [x] unbreak directional lights
- [x] unbreak shadows (see 3d_scene, 3d_shape, lighting, transparaency_3d examples)
- [x] game menu example shows loading screen and menu simultaneously
- [x] display settings menu is a blank screen
- [x] `without_winit` example panics
- [x] ensure all tests pass
- [x] SubApp doc test fails
- [x] runs_spawn_local tasks fails
- [x] [Fix panic_when_hierachy_cycle test hanging](https://github.com/alice-i-cecile/bevy/pull/120)
## Points of Difficulty and Controversy
**Reviewers, please give feedback on these and look closely**
1. Default sets, from the RFC, have been removed. These added a tremendous amount of implicit complexity and result in hard to debug scheduling errors. They're going to be tackled in the form of "base sets" by @cart in a followup.
2. The outer schedule controls which schedule is run when `App::update` is called.
3. I implemented `Label for `Box<dyn Label>` for our label types. This enables us to store schedule labels in concrete form, and then later run them. I ran into the same set of problems when working with one-shot systems. We've previously investigated this pattern in depth, and it does not appear to lead to extra indirection with nested boxes.
4. `SubApp::update` simply runs the default schedule once. This sucks, but this whole API is incomplete and this was the minimal changeset.
5. `time_system` and `tick_global_task_pools_on_main_thread` no longer use exclusive systems to attempt to force scheduling order
6. Implemetnation strategy for fixed timesteps
7. `AssetStage` was migrated to `AssetSet` without reintroducing command flush points. These did not appear to be used, and it's nice to remove these bottlenecks.
8. Migration of `bevy_render/lib.rs` and pipelined rendering. The logic here is unusually tricky, as we have complex scheduling requirements.
## Future Work (ideally before 0.10)
- Rename schedule_v3 module to schedule or scheduling
- Add a derive macro to states, and likely a `EnumIter` trait of some form
- Figure out what exactly to do with the "systems added should basically work by default" problem
- Improve ergonomics for working with fixed timesteps and states
- Polish FixedTime API to match Time
- Rebase and merge #7415
- Resolve all internal ambiguities (blocked on better tools, especially #7442)
- Add "base sets" to replace the removed default sets.
2023-02-06 02:04:50 +00:00
|
|
|
prelude::*,
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
system::{
|
2023-01-04 01:13:30 +00:00
|
|
|
lifetimeless::{Read, SRes},
|

Migrate engine to Schedule v3 (#7267)
Huge thanks to @maniwani, @devil-ira, @hymm, @cart, @superdump and @jakobhellermann for the help with this PR.
# Objective
- Followup #6587.
- Minimal integration for the Stageless Scheduling RFC: https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/pull/45
## Solution
- [x] Remove old scheduling module
- [x] Migrate new methods to no longer use extension methods
- [x] Fix compiler errors
- [x] Fix benchmarks
- [x] Fix examples
- [x] Fix docs
- [x] Fix tests
## Changelog
### Added
- a large number of methods on `App` to work with schedules ergonomically
- the `CoreSchedule` enum
- `App::add_extract_system` via the `RenderingAppExtension` trait extension method
- the private `prepare_view_uniforms` system now has a public system set for scheduling purposes, called `ViewSet::PrepareUniforms`
### Removed
- stages, and all code that mentions stages
- states have been dramatically simplified, and no longer use a stack
- `RunCriteriaLabel`
- `AsSystemLabel` trait
- `on_hierarchy_reports_enabled` run criteria (now just uses an ad hoc resource checking run condition)
- systems in `RenderSet/Stage::Extract` no longer warn when they do not read data from the main world
- `RunCriteriaLabel`
- `transform_propagate_system_set`: this was a nonstandard pattern that didn't actually provide enough control. The systems are already `pub`: the docs have been updated to ensure that the third-party usage is clear.
### Changed
- `System::default_labels` is now `System::default_system_sets`.
- `App::add_default_labels` is now `App::add_default_sets`
- `CoreStage` and `StartupStage` enums are now `CoreSet` and `StartupSet`
- `App::add_system_set` was renamed to `App::add_systems`
- The `StartupSchedule` label is now defined as part of the `CoreSchedules` enum
- `.label(SystemLabel)` is now referred to as `.in_set(SystemSet)`
- `SystemLabel` trait was replaced by `SystemSet`
- `SystemTypeIdLabel<T>` was replaced by `SystemSetType<T>`
- The `ReportHierarchyIssue` resource now has a public constructor (`new`), and implements `PartialEq`
- Fixed time steps now use a schedule (`CoreSchedule::FixedTimeStep`) rather than a run criteria.
- Adding rendering extraction systems now panics rather than silently failing if no subapp with the `RenderApp` label is found.
- the `calculate_bounds` system, with the `CalculateBounds` label, is now in `CoreSet::Update`, rather than in `CoreSet::PostUpdate` before commands are applied.
- `SceneSpawnerSystem` now runs under `CoreSet::Update`, rather than `CoreStage::PreUpdate.at_end()`.
- `bevy_pbr::add_clusters` is no longer an exclusive system
- the top level `bevy_ecs::schedule` module was replaced with `bevy_ecs::scheduling`
- `tick_global_task_pools_on_main_thread` is no longer run as an exclusive system. Instead, it has been replaced by `tick_global_task_pools`, which uses a `NonSend` resource to force running on the main thread.
## Migration Guide
- Calls to `.label(MyLabel)` should be replaced with `.in_set(MySet)`
- Stages have been removed. Replace these with system sets, and then add command flushes using the `apply_system_buffers` exclusive system where needed.
- The `CoreStage`, `StartupStage, `RenderStage` and `AssetStage` enums have been replaced with `CoreSet`, `StartupSet, `RenderSet` and `AssetSet`. The same scheduling guarantees have been preserved.
- Systems are no longer added to `CoreSet::Update` by default. Add systems manually if this behavior is needed, although you should consider adding your game logic systems to `CoreSchedule::FixedTimestep` instead for more reliable framerate-independent behavior.
- Similarly, startup systems are no longer part of `StartupSet::Startup` by default. In most cases, this won't matter to you.
- For example, `add_system_to_stage(CoreStage::PostUpdate, my_system)` should be replaced with
- `add_system(my_system.in_set(CoreSet::PostUpdate)`
- When testing systems or otherwise running them in a headless fashion, simply construct and run a schedule using `Schedule::new()` and `World::run_schedule` rather than constructing stages
- Run criteria have been renamed to run conditions. These can now be combined with each other and with states.
- Looping run criteria and state stacks have been removed. Use an exclusive system that runs a schedule if you need this level of control over system control flow.
- For app-level control flow over which schedules get run when (such as for rollback networking), create your own schedule and insert it under the `CoreSchedule::Outer` label.
- Fixed timesteps are now evaluated in a schedule, rather than controlled via run criteria. The `run_fixed_timestep` system runs this schedule between `CoreSet::First` and `CoreSet::PreUpdate` by default.
- Command flush points introduced by `AssetStage` have been removed. If you were relying on these, add them back manually.
- Adding extract systems is now typically done directly on the main app. Make sure the `RenderingAppExtension` trait is in scope, then call `app.add_extract_system(my_system)`.
- the `calculate_bounds` system, with the `CalculateBounds` label, is now in `CoreSet::Update`, rather than in `CoreSet::PostUpdate` before commands are applied. You may need to order your movement systems to occur before this system in order to avoid system order ambiguities in culling behavior.
- the `RenderLabel` `AppLabel` was renamed to `RenderApp` for clarity
- `App::add_state` now takes 0 arguments: the starting state is set based on the `Default` impl.
- Instead of creating `SystemSet` containers for systems that run in stages, simply use `.on_enter::<State::Variant>()` or its `on_exit` or `on_update` siblings.
- `SystemLabel` derives should be replaced with `SystemSet`. You will also need to add the `Debug`, `PartialEq`, `Eq`, and `Hash` traits to satisfy the new trait bounds.
- `with_run_criteria` has been renamed to `run_if`. Run criteria have been renamed to run conditions for clarity, and should now simply return a bool.
- States have been dramatically simplified: there is no longer a "state stack". To queue a transition to the next state, call `NextState::set`
## TODO
- [x] remove dead methods on App and World
- [x] add `App::add_system_to_schedule` and `App::add_systems_to_schedule`
- [x] avoid adding the default system set at inappropriate times
- [x] remove any accidental cycles in the default plugins schedule
- [x] migrate benchmarks
- [x] expose explicit labels for the built-in command flush points
- [x] migrate engine code
- [x] remove all mentions of stages from the docs
- [x] verify docs for States
- [x] fix uses of exclusive systems that use .end / .at_start / .before_commands
- [x] migrate RenderStage and AssetStage
- [x] migrate examples
- [x] ensure that transform propagation is exported in a sufficiently public way (the systems are already pub)
- [x] ensure that on_enter schedules are run at least once before the main app
- [x] re-enable opt-in to execution order ambiguities
- [x] revert change to `update_bounds` to ensure it runs in `PostUpdate`
- [x] test all examples
- [x] unbreak directional lights
- [x] unbreak shadows (see 3d_scene, 3d_shape, lighting, transparaency_3d examples)
- [x] game menu example shows loading screen and menu simultaneously
- [x] display settings menu is a blank screen
- [x] `without_winit` example panics
- [x] ensure all tests pass
- [x] SubApp doc test fails
- [x] runs_spawn_local tasks fails
- [x] [Fix panic_when_hierachy_cycle test hanging](https://github.com/alice-i-cecile/bevy/pull/120)
## Points of Difficulty and Controversy
**Reviewers, please give feedback on these and look closely**
1. Default sets, from the RFC, have been removed. These added a tremendous amount of implicit complexity and result in hard to debug scheduling errors. They're going to be tackled in the form of "base sets" by @cart in a followup.
2. The outer schedule controls which schedule is run when `App::update` is called.
3. I implemented `Label for `Box<dyn Label>` for our label types. This enables us to store schedule labels in concrete form, and then later run them. I ran into the same set of problems when working with one-shot systems. We've previously investigated this pattern in depth, and it does not appear to lead to extra indirection with nested boxes.
4. `SubApp::update` simply runs the default schedule once. This sucks, but this whole API is incomplete and this was the minimal changeset.
5. `time_system` and `tick_global_task_pools_on_main_thread` no longer use exclusive systems to attempt to force scheduling order
6. Implemetnation strategy for fixed timesteps
7. `AssetStage` was migrated to `AssetSet` without reintroducing command flush points. These did not appear to be used, and it's nice to remove these bottlenecks.
8. Migration of `bevy_render/lib.rs` and pipelined rendering. The logic here is unusually tricky, as we have complex scheduling requirements.
## Future Work (ideally before 0.10)
- Rename schedule_v3 module to schedule or scheduling
- Add a derive macro to states, and likely a `EnumIter` trait of some form
- Figure out what exactly to do with the "systems added should basically work by default" problem
- Improve ergonomics for working with fixed timesteps and states
- Polish FixedTime API to match Time
- Rebase and merge #7415
- Resolve all internal ambiguities (blocked on better tools, especially #7442)
- Add "base sets" to replace the removed default sets.
2023-02-06 02:04:50 +00:00
|
|
|
SystemParamItem,
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
},
|
|
|
|
|
};
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
use bevy_reflect::TypeUuid;
|
2021-12-14 03:58:23 +00:00
|
|
|
use bevy_render::{
|
2022-05-30 18:36:03 +00:00
|
|
|
extract_component::ExtractComponentPlugin,
|

Mesh vertex buffer layouts (#3959)
This PR makes a number of changes to how meshes and vertex attributes are handled, which the goal of enabling easy and flexible custom vertex attributes:
* Reworks the `Mesh` type to use the newly added `VertexAttribute` internally
* `VertexAttribute` defines the name, a unique `VertexAttributeId`, and a `VertexFormat`
* `VertexAttributeId` is used to produce consistent sort orders for vertex buffer generation, replacing the more expensive and often surprising "name based sorting"
* Meshes can be used to generate a `MeshVertexBufferLayout`, which defines the layout of the gpu buffer produced by the mesh. `MeshVertexBufferLayouts` can then be used to generate actual `VertexBufferLayouts` according to the requirements of a specific pipeline. This decoupling of "mesh layout" vs "pipeline vertex buffer layout" is what enables custom attributes. We don't need to standardize _mesh layouts_ or contort meshes to meet the needs of a specific pipeline. As long as the mesh has what the pipeline needs, it will work transparently.
* Mesh-based pipelines now specialize on `&MeshVertexBufferLayout` via the new `SpecializedMeshPipeline` trait (which behaves like `SpecializedPipeline`, but adds `&MeshVertexBufferLayout`). The integrity of the pipeline cache is maintained because the `MeshVertexBufferLayout` is treated as part of the key (which is fully abstracted from implementers of the trait ... no need to add any additional info to the specialization key).
* Hashing `MeshVertexBufferLayout` is too expensive to do for every entity, every frame. To make this scalable, I added a generalized "pre-hashing" solution to `bevy_utils`: `Hashed<T>` keys and `PreHashMap<K, V>` (which uses `Hashed<T>` internally) . Why didn't I just do the quick and dirty in-place "pre-compute hash and use that u64 as a key in a hashmap" that we've done in the past? Because its wrong! Hashes by themselves aren't enough because two different values can produce the same hash. Re-hashing a hash is even worse! I decided to build a generalized solution because this pattern has come up in the past and we've chosen to do the wrong thing. Now we can do the right thing! This did unfortunately require pulling in `hashbrown` and using that in `bevy_utils`, because avoiding re-hashes requires the `raw_entry_mut` api, which isn't stabilized yet (and may never be ... `entry_ref` has favor now, but also isn't available yet). If std's HashMap ever provides the tools we need, we can move back to that. Note that adding `hashbrown` doesn't increase our dependency count because it was already in our tree. I will probably break these changes out into their own PR.
* Specializing on `MeshVertexBufferLayout` has one non-obvious behavior: it can produce identical pipelines for two different MeshVertexBufferLayouts. To optimize the number of active pipelines / reduce re-binds while drawing, I de-duplicate pipelines post-specialization using the final `VertexBufferLayout` as the key. For example, consider a pipeline that needs the layout `(position, normal)` and is specialized using two meshes: `(position, normal, uv)` and `(position, normal, other_vec2)`. If both of these meshes result in `(position, normal)` specializations, we can use the same pipeline! Now we do. Cool!
To briefly illustrate, this is what the relevant section of `MeshPipeline`'s specialization code looks like now:
```rust
impl SpecializedMeshPipeline for MeshPipeline {
type Key = MeshPipelineKey;
fn specialize(
&self,
key: Self::Key,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
) -> RenderPipelineDescriptor {
let mut vertex_attributes = vec![
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL.at_shader_location(1),
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_UV_0.at_shader_location(2),
];
let mut shader_defs = Vec::new();
if layout.contains(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_TANGENT) {
shader_defs.push(String::from("VERTEX_TANGENTS"));
vertex_attributes.push(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_TANGENT.at_shader_location(3));
}
let vertex_buffer_layout = layout
.get_layout(&vertex_attributes)
.expect("Mesh is missing a vertex attribute");
```
Notice that this is _much_ simpler than it was before. And now any mesh with any layout can be used with this pipeline, provided it has vertex postions, normals, and uvs. We even got to remove `HAS_TANGENTS` from MeshPipelineKey and `has_tangents` from `GpuMesh`, because that information is redundant with `MeshVertexBufferLayout`.
This is still a draft because I still need to:
* Add more docs
* Experiment with adding error handling to mesh pipeline specialization (which would print errors at runtime when a mesh is missing a vertex attribute required by a pipeline). If it doesn't tank perf, we'll keep it.
* Consider breaking out the PreHash / hashbrown changes into a separate PR.
* Add an example illustrating this change
* Verify that the "mesh-specialized pipeline de-duplication code" works properly
Please dont yell at me for not doing these things yet :) Just trying to get this in peoples' hands asap.
Alternative to #3120
Fixes #3030
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
2022-02-23 23:21:13 +00:00
|
|
|
mesh::{Mesh, MeshVertexBufferLayout},
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
prelude::Image,
|
2023-02-14 21:46:07 +00:00
|
|
|
render_asset::{PrepareAssetSet, RenderAssets},
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
render_phase::{
|
2023-01-04 01:13:30 +00:00
|
|
|
AddRenderCommand, DrawFunctions, PhaseItem, RenderCommand, RenderCommandResult,
|
|
|
|
|
RenderPhase, SetItemPipeline, TrackedRenderPass,
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
},
|
2021-12-23 22:49:12 +00:00
|
|
|
render_resource::{
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
AsBindGroup, AsBindGroupError, BindGroup, BindGroupLayout, OwnedBindingResource,
|
|
|
|
|
PipelineCache, RenderPipelineDescriptor, Shader, ShaderRef, SpecializedMeshPipeline,
|
|
|
|
|
SpecializedMeshPipelineError, SpecializedMeshPipelines,
|
2021-12-23 22:49:12 +00:00
|
|
|
},
|
2021-12-14 03:58:23 +00:00
|
|
|
renderer::RenderDevice,
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
texture::FallbackImage,
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
view::{ExtractedView, Msaa, VisibleEntities},
|

Migrate engine to Schedule v3 (#7267)
Huge thanks to @maniwani, @devil-ira, @hymm, @cart, @superdump and @jakobhellermann for the help with this PR.
# Objective
- Followup #6587.
- Minimal integration for the Stageless Scheduling RFC: https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/pull/45
## Solution
- [x] Remove old scheduling module
- [x] Migrate new methods to no longer use extension methods
- [x] Fix compiler errors
- [x] Fix benchmarks
- [x] Fix examples
- [x] Fix docs
- [x] Fix tests
## Changelog
### Added
- a large number of methods on `App` to work with schedules ergonomically
- the `CoreSchedule` enum
- `App::add_extract_system` via the `RenderingAppExtension` trait extension method
- the private `prepare_view_uniforms` system now has a public system set for scheduling purposes, called `ViewSet::PrepareUniforms`
### Removed
- stages, and all code that mentions stages
- states have been dramatically simplified, and no longer use a stack
- `RunCriteriaLabel`
- `AsSystemLabel` trait
- `on_hierarchy_reports_enabled` run criteria (now just uses an ad hoc resource checking run condition)
- systems in `RenderSet/Stage::Extract` no longer warn when they do not read data from the main world
- `RunCriteriaLabel`
- `transform_propagate_system_set`: this was a nonstandard pattern that didn't actually provide enough control. The systems are already `pub`: the docs have been updated to ensure that the third-party usage is clear.
### Changed
- `System::default_labels` is now `System::default_system_sets`.
- `App::add_default_labels` is now `App::add_default_sets`
- `CoreStage` and `StartupStage` enums are now `CoreSet` and `StartupSet`
- `App::add_system_set` was renamed to `App::add_systems`
- The `StartupSchedule` label is now defined as part of the `CoreSchedules` enum
- `.label(SystemLabel)` is now referred to as `.in_set(SystemSet)`
- `SystemLabel` trait was replaced by `SystemSet`
- `SystemTypeIdLabel<T>` was replaced by `SystemSetType<T>`
- The `ReportHierarchyIssue` resource now has a public constructor (`new`), and implements `PartialEq`
- Fixed time steps now use a schedule (`CoreSchedule::FixedTimeStep`) rather than a run criteria.
- Adding rendering extraction systems now panics rather than silently failing if no subapp with the `RenderApp` label is found.
- the `calculate_bounds` system, with the `CalculateBounds` label, is now in `CoreSet::Update`, rather than in `CoreSet::PostUpdate` before commands are applied.
- `SceneSpawnerSystem` now runs under `CoreSet::Update`, rather than `CoreStage::PreUpdate.at_end()`.
- `bevy_pbr::add_clusters` is no longer an exclusive system
- the top level `bevy_ecs::schedule` module was replaced with `bevy_ecs::scheduling`
- `tick_global_task_pools_on_main_thread` is no longer run as an exclusive system. Instead, it has been replaced by `tick_global_task_pools`, which uses a `NonSend` resource to force running on the main thread.
## Migration Guide
- Calls to `.label(MyLabel)` should be replaced with `.in_set(MySet)`
- Stages have been removed. Replace these with system sets, and then add command flushes using the `apply_system_buffers` exclusive system where needed.
- The `CoreStage`, `StartupStage, `RenderStage` and `AssetStage` enums have been replaced with `CoreSet`, `StartupSet, `RenderSet` and `AssetSet`. The same scheduling guarantees have been preserved.
- Systems are no longer added to `CoreSet::Update` by default. Add systems manually if this behavior is needed, although you should consider adding your game logic systems to `CoreSchedule::FixedTimestep` instead for more reliable framerate-independent behavior.
- Similarly, startup systems are no longer part of `StartupSet::Startup` by default. In most cases, this won't matter to you.
- For example, `add_system_to_stage(CoreStage::PostUpdate, my_system)` should be replaced with
- `add_system(my_system.in_set(CoreSet::PostUpdate)`
- When testing systems or otherwise running them in a headless fashion, simply construct and run a schedule using `Schedule::new()` and `World::run_schedule` rather than constructing stages
- Run criteria have been renamed to run conditions. These can now be combined with each other and with states.
- Looping run criteria and state stacks have been removed. Use an exclusive system that runs a schedule if you need this level of control over system control flow.
- For app-level control flow over which schedules get run when (such as for rollback networking), create your own schedule and insert it under the `CoreSchedule::Outer` label.
- Fixed timesteps are now evaluated in a schedule, rather than controlled via run criteria. The `run_fixed_timestep` system runs this schedule between `CoreSet::First` and `CoreSet::PreUpdate` by default.
- Command flush points introduced by `AssetStage` have been removed. If you were relying on these, add them back manually.
- Adding extract systems is now typically done directly on the main app. Make sure the `RenderingAppExtension` trait is in scope, then call `app.add_extract_system(my_system)`.
- the `calculate_bounds` system, with the `CalculateBounds` label, is now in `CoreSet::Update`, rather than in `CoreSet::PostUpdate` before commands are applied. You may need to order your movement systems to occur before this system in order to avoid system order ambiguities in culling behavior.
- the `RenderLabel` `AppLabel` was renamed to `RenderApp` for clarity
- `App::add_state` now takes 0 arguments: the starting state is set based on the `Default` impl.
- Instead of creating `SystemSet` containers for systems that run in stages, simply use `.on_enter::<State::Variant>()` or its `on_exit` or `on_update` siblings.
- `SystemLabel` derives should be replaced with `SystemSet`. You will also need to add the `Debug`, `PartialEq`, `Eq`, and `Hash` traits to satisfy the new trait bounds.
- `with_run_criteria` has been renamed to `run_if`. Run criteria have been renamed to run conditions for clarity, and should now simply return a bool.
- States have been dramatically simplified: there is no longer a "state stack". To queue a transition to the next state, call `NextState::set`
## TODO
- [x] remove dead methods on App and World
- [x] add `App::add_system_to_schedule` and `App::add_systems_to_schedule`
- [x] avoid adding the default system set at inappropriate times
- [x] remove any accidental cycles in the default plugins schedule
- [x] migrate benchmarks
- [x] expose explicit labels for the built-in command flush points
- [x] migrate engine code
- [x] remove all mentions of stages from the docs
- [x] verify docs for States
- [x] fix uses of exclusive systems that use .end / .at_start / .before_commands
- [x] migrate RenderStage and AssetStage
- [x] migrate examples
- [x] ensure that transform propagation is exported in a sufficiently public way (the systems are already pub)
- [x] ensure that on_enter schedules are run at least once before the main app
- [x] re-enable opt-in to execution order ambiguities
- [x] revert change to `update_bounds` to ensure it runs in `PostUpdate`
- [x] test all examples
- [x] unbreak directional lights
- [x] unbreak shadows (see 3d_scene, 3d_shape, lighting, transparaency_3d examples)
- [x] game menu example shows loading screen and menu simultaneously
- [x] display settings menu is a blank screen
- [x] `without_winit` example panics
- [x] ensure all tests pass
- [x] SubApp doc test fails
- [x] runs_spawn_local tasks fails
- [x] [Fix panic_when_hierachy_cycle test hanging](https://github.com/alice-i-cecile/bevy/pull/120)
## Points of Difficulty and Controversy
**Reviewers, please give feedback on these and look closely**
1. Default sets, from the RFC, have been removed. These added a tremendous amount of implicit complexity and result in hard to debug scheduling errors. They're going to be tackled in the form of "base sets" by @cart in a followup.
2. The outer schedule controls which schedule is run when `App::update` is called.
3. I implemented `Label for `Box<dyn Label>` for our label types. This enables us to store schedule labels in concrete form, and then later run them. I ran into the same set of problems when working with one-shot systems. We've previously investigated this pattern in depth, and it does not appear to lead to extra indirection with nested boxes.
4. `SubApp::update` simply runs the default schedule once. This sucks, but this whole API is incomplete and this was the minimal changeset.
5. `time_system` and `tick_global_task_pools_on_main_thread` no longer use exclusive systems to attempt to force scheduling order
6. Implemetnation strategy for fixed timesteps
7. `AssetStage` was migrated to `AssetSet` without reintroducing command flush points. These did not appear to be used, and it's nice to remove these bottlenecks.
8. Migration of `bevy_render/lib.rs` and pipelined rendering. The logic here is unusually tricky, as we have complex scheduling requirements.
## Future Work (ideally before 0.10)
- Rename schedule_v3 module to schedule or scheduling
- Add a derive macro to states, and likely a `EnumIter` trait of some form
- Figure out what exactly to do with the "systems added should basically work by default" problem
- Improve ergonomics for working with fixed timesteps and states
- Polish FixedTime API to match Time
- Rebase and merge #7415
- Resolve all internal ambiguities (blocked on better tools, especially #7442)
- Add "base sets" to replace the removed default sets.
2023-02-06 02:04:50 +00:00
|
|
|
Extract, ExtractSchedule, RenderApp, RenderSet,
|
2021-12-14 03:58:23 +00:00
|
|
|
};
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
use bevy_utils::{tracing::error, HashMap, HashSet};
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
use std::hash::Hash;
|
|
|
|
|
use std::marker::PhantomData;
|
2020-02-11 17:31:49 +00:00
|
|
|
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
/// Materials are used alongside [`MaterialPlugin`] and [`MaterialMeshBundle`](crate::MaterialMeshBundle)
|
|
|
|
|
/// to spawn entities that are rendered with a specific [`Material`] type. They serve as an easy to use high level
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
/// way to render [`Mesh`] entities with custom shader logic.
|
|
|
|
|
///
|
|
|
|
|
/// Materials must implement [`AsBindGroup`] to define how data will be transferred to the GPU and bound in shaders.
|
|
|
|
|
/// [`AsBindGroup`] can be derived, which makes generating bindings straightforward. See the [`AsBindGroup`] docs for details.
|
|
|
|
|
///
|
|
|
|
|
/// Materials must also implement [`TypeUuid`] so they can be treated as an [`Asset`](bevy_asset::Asset).
|
|
|
|
|
///
|
|
|
|
|
/// # Example
|
|
|
|
|
///
|
|
|
|
|
/// Here is a simple Material implementation. The [`AsBindGroup`] derive has many features. To see what else is available,
|
|
|
|
|
/// check out the [`AsBindGroup`] documentation.
|
|
|
|
|
/// ```
|
|
|
|
|
/// # use bevy_pbr::{Material, MaterialMeshBundle};
|
|
|
|
|
/// # use bevy_ecs::prelude::*;
|
|
|
|
|
/// # use bevy_reflect::TypeUuid;
|
|
|
|
|
/// # use bevy_render::{render_resource::{AsBindGroup, ShaderRef}, texture::Image, color::Color};
|
|
|
|
|
/// # use bevy_asset::{Handle, AssetServer, Assets};
|
|
|
|
|
///
|
|
|
|
|
/// #[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
|
|
|
|
|
/// #[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
|
|
|
|
|
/// pub struct CustomMaterial {
|
|
|
|
|
/// // Uniform bindings must implement `ShaderType`, which will be used to convert the value to
|
|
|
|
|
/// // its shader-compatible equivalent. Most core math types already implement `ShaderType`.
|
|
|
|
|
/// #[uniform(0)]
|
|
|
|
|
/// color: Color,
|
|
|
|
|
/// // Images can be bound as textures in shaders. If the Image's sampler is also needed, just
|
|
|
|
|
/// // add the sampler attribute with a different binding index.
|
|
|
|
|
/// #[texture(1)]
|
|
|
|
|
/// #[sampler(2)]
|
|
|
|
|
/// color_texture: Handle<Image>,
|
|
|
|
|
/// }
|
|
|
|
|
///
|
|
|
|
|
/// // All functions on `Material` have default impls. You only need to implement the
|
|
|
|
|
/// // functions that are relevant for your material.
|
|
|
|
|
/// impl Material for CustomMaterial {
|
|
|
|
|
/// fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
|
|
|
|
|
/// "shaders/custom_material.wgsl".into()
|
|
|
|
|
/// }
|
|
|
|
|
/// }
|
|
|
|
|
///
|
|
|
|
|
/// // Spawn an entity using `CustomMaterial`.
|
|
|
|
|
/// fn setup(mut commands: Commands, mut materials: ResMut<Assets<CustomMaterial>>, asset_server: Res<AssetServer>) {
|

Spawn now takes a Bundle (#6054)
# Objective
Now that we can consolidate Bundles and Components under a single insert (thanks to #2975 and #6039), almost 100% of world spawns now look like `world.spawn().insert((Some, Tuple, Here))`. Spawning an entity without any components is an extremely uncommon pattern, so it makes sense to give spawn the "first class" ergonomic api. This consolidated api should be made consistent across all spawn apis (such as World and Commands).
## Solution
All `spawn` apis (`World::spawn`, `Commands:;spawn`, `ChildBuilder::spawn`, and `WorldChildBuilder::spawn`) now accept a bundle as input:
```rust
// before:
commands
.spawn()
.insert((A, B, C));
world
.spawn()
.insert((A, B, C);
// after
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
world.spawn((A, B, C));
```
All existing instances of `spawn_bundle` have been deprecated in favor of the new `spawn` api. A new `spawn_empty` has been added, replacing the old `spawn` api.
By allowing `world.spawn(some_bundle)` to replace `world.spawn().insert(some_bundle)`, this opened the door to removing the initial entity allocation in the "empty" archetype / table done in `spawn()` (and subsequent move to the actual archetype in `.insert(some_bundle)`).
This improves spawn performance by over 10%:

To take this measurement, I added a new `world_spawn` benchmark.
Unfortunately, optimizing `Commands::spawn` is slightly less trivial, as Commands expose the Entity id of spawned entities prior to actually spawning. Doing the optimization would (naively) require assurances that the `spawn(some_bundle)` command is applied before all other commands involving the entity (which would not necessarily be true, if memory serves). Optimizing `Commands::spawn` this way does feel possible, but it will require careful thought (and maybe some additional checks), which deserves its own PR. For now, it has the same performance characteristics of the current `Commands::spawn_bundle` on main.
**Note that 99% of this PR is simple renames and refactors. The only code that needs careful scrutiny is the new `World::spawn()` impl, which is relatively straightforward, but it has some new unsafe code (which re-uses battle tested BundlerSpawner code path).**
---
## Changelog
- All `spawn` apis (`World::spawn`, `Commands:;spawn`, `ChildBuilder::spawn`, and `WorldChildBuilder::spawn`) now accept a bundle as input
- All instances of `spawn_bundle` have been deprecated in favor of the new `spawn` api
- World and Commands now have `spawn_empty()`, which is equivalent to the old `spawn()` behavior.
## Migration Guide
```rust
// Old (0.8):
commands
.spawn()
.insert_bundle((A, B, C));
// New (0.9)
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
// Old (0.8):
commands.spawn_bundle((A, B, C));
// New (0.9)
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
// Old (0.8):
let entity = commands.spawn().id();
// New (0.9)
let entity = commands.spawn_empty().id();
// Old (0.8)
let entity = world.spawn().id();
// New (0.9)
let entity = world.spawn_empty();
```
2022-09-23 19:55:54 +00:00
|
|
|
/// commands.spawn(MaterialMeshBundle {
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
/// material: materials.add(CustomMaterial {
|
|
|
|
|
/// color: Color::RED,
|
|
|
|
|
/// color_texture: asset_server.load("some_image.png"),
|
|
|
|
|
/// }),
|
|
|
|
|
/// ..Default::default()
|
|
|
|
|
/// });
|
|
|
|
|
/// }
|
|
|
|
|
/// ```
|
|
|
|
|
/// In WGSL shaders, the material's binding would look like this:
|
|
|
|
|
///
|
|
|
|
|
/// ```wgsl
|
2022-07-14 21:17:16 +00:00
|
|
|
/// @group(1) @binding(0)
|
2022-11-28 13:15:03 +00:00
|
|
|
/// var<uniform> color: vec4<f32>;
|
2022-07-14 21:17:16 +00:00
|
|
|
/// @group(1) @binding(1)
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
/// var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
|
2022-07-14 21:17:16 +00:00
|
|
|
/// @group(1) @binding(2)
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
/// var color_sampler: sampler;
|
|
|
|
|
/// ```
|
|
|
|
|
pub trait Material: AsBindGroup + Send + Sync + Clone + TypeUuid + Sized + 'static {
|
|
|
|
|
/// Returns this material's vertex shader. If [`ShaderRef::Default`] is returned, the default mesh vertex shader
|
|
|
|
|
/// will be used.
|
|
|
|
|
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
|
|
|
|
|
ShaderRef::Default
|
2020-02-11 17:31:49 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
2020-08-01 00:10:29 +00:00
|
|
|
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
/// Returns this material's fragment shader. If [`ShaderRef::Default`] is returned, the default mesh fragment shader
|
|
|
|
|
/// will be used.
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
#[allow(unused_variables)]
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
|
|
|
|
|
ShaderRef::Default
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/// Returns this material's [`AlphaMode`]. Defaults to [`AlphaMode::Opaque`].
|
|
|
|
|
#[inline]
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
|
|
|
|
|
AlphaMode::Opaque
|
2020-08-01 00:10:29 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|

Mesh vertex buffer layouts (#3959)
This PR makes a number of changes to how meshes and vertex attributes are handled, which the goal of enabling easy and flexible custom vertex attributes:
* Reworks the `Mesh` type to use the newly added `VertexAttribute` internally
* `VertexAttribute` defines the name, a unique `VertexAttributeId`, and a `VertexFormat`
* `VertexAttributeId` is used to produce consistent sort orders for vertex buffer generation, replacing the more expensive and often surprising "name based sorting"
* Meshes can be used to generate a `MeshVertexBufferLayout`, which defines the layout of the gpu buffer produced by the mesh. `MeshVertexBufferLayouts` can then be used to generate actual `VertexBufferLayouts` according to the requirements of a specific pipeline. This decoupling of "mesh layout" vs "pipeline vertex buffer layout" is what enables custom attributes. We don't need to standardize _mesh layouts_ or contort meshes to meet the needs of a specific pipeline. As long as the mesh has what the pipeline needs, it will work transparently.
* Mesh-based pipelines now specialize on `&MeshVertexBufferLayout` via the new `SpecializedMeshPipeline` trait (which behaves like `SpecializedPipeline`, but adds `&MeshVertexBufferLayout`). The integrity of the pipeline cache is maintained because the `MeshVertexBufferLayout` is treated as part of the key (which is fully abstracted from implementers of the trait ... no need to add any additional info to the specialization key).
* Hashing `MeshVertexBufferLayout` is too expensive to do for every entity, every frame. To make this scalable, I added a generalized "pre-hashing" solution to `bevy_utils`: `Hashed<T>` keys and `PreHashMap<K, V>` (which uses `Hashed<T>` internally) . Why didn't I just do the quick and dirty in-place "pre-compute hash and use that u64 as a key in a hashmap" that we've done in the past? Because its wrong! Hashes by themselves aren't enough because two different values can produce the same hash. Re-hashing a hash is even worse! I decided to build a generalized solution because this pattern has come up in the past and we've chosen to do the wrong thing. Now we can do the right thing! This did unfortunately require pulling in `hashbrown` and using that in `bevy_utils`, because avoiding re-hashes requires the `raw_entry_mut` api, which isn't stabilized yet (and may never be ... `entry_ref` has favor now, but also isn't available yet). If std's HashMap ever provides the tools we need, we can move back to that. Note that adding `hashbrown` doesn't increase our dependency count because it was already in our tree. I will probably break these changes out into their own PR.
* Specializing on `MeshVertexBufferLayout` has one non-obvious behavior: it can produce identical pipelines for two different MeshVertexBufferLayouts. To optimize the number of active pipelines / reduce re-binds while drawing, I de-duplicate pipelines post-specialization using the final `VertexBufferLayout` as the key. For example, consider a pipeline that needs the layout `(position, normal)` and is specialized using two meshes: `(position, normal, uv)` and `(position, normal, other_vec2)`. If both of these meshes result in `(position, normal)` specializations, we can use the same pipeline! Now we do. Cool!
To briefly illustrate, this is what the relevant section of `MeshPipeline`'s specialization code looks like now:
```rust
impl SpecializedMeshPipeline for MeshPipeline {
type Key = MeshPipelineKey;
fn specialize(
&self,
key: Self::Key,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
) -> RenderPipelineDescriptor {
let mut vertex_attributes = vec![
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL.at_shader_location(1),
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_UV_0.at_shader_location(2),
];
let mut shader_defs = Vec::new();
if layout.contains(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_TANGENT) {
shader_defs.push(String::from("VERTEX_TANGENTS"));
vertex_attributes.push(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_TANGENT.at_shader_location(3));
}
let vertex_buffer_layout = layout
.get_layout(&vertex_attributes)
.expect("Mesh is missing a vertex attribute");
```
Notice that this is _much_ simpler than it was before. And now any mesh with any layout can be used with this pipeline, provided it has vertex postions, normals, and uvs. We even got to remove `HAS_TANGENTS` from MeshPipelineKey and `has_tangents` from `GpuMesh`, because that information is redundant with `MeshVertexBufferLayout`.
This is still a draft because I still need to:
* Add more docs
* Experiment with adding error handling to mesh pipeline specialization (which would print errors at runtime when a mesh is missing a vertex attribute required by a pipeline). If it doesn't tank perf, we'll keep it.
* Consider breaking out the PreHash / hashbrown changes into a separate PR.
* Add an example illustrating this change
* Verify that the "mesh-specialized pipeline de-duplication code" works properly
Please dont yell at me for not doing these things yet :) Just trying to get this in peoples' hands asap.
Alternative to #3120
Fixes #3030
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
2022-02-23 23:21:13 +00:00
|
|
|
|
2022-05-31 02:02:49 +00:00
|
|
|
#[inline]
|
|
|
|
|
/// Add a bias to the view depth of the mesh which can be used to force a specific render order
|
|
|
|
|
/// for meshes with equal depth, to avoid z-fighting.
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
fn depth_bias(&self) -> f32 {
|
2022-05-31 02:02:49 +00:00
|
|
|
0.0
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
2023-01-19 22:11:13 +00:00
|
|
|
/// Returns this material's prepass vertex shader. If [`ShaderRef::Default`] is returned, the default prepass vertex shader
|
|
|
|
|
/// will be used.
|
|
|
|
|
fn prepass_vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
|
|
|
|
|
ShaderRef::Default
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/// Returns this material's prepass fragment shader. If [`ShaderRef::Default`] is returned, the default prepass fragment shader
|
|
|
|
|
/// will be used.
|
|
|
|
|
#[allow(unused_variables)]
|
|
|
|
|
fn prepass_fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
|
|
|
|
|
ShaderRef::Default
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
/// Customizes the default [`RenderPipelineDescriptor`] for a specific entity using the entity's
|
|
|
|
|
/// [`MaterialPipelineKey`] and [`MeshVertexBufferLayout`] as input.
|

Mesh vertex buffer layouts (#3959)
This PR makes a number of changes to how meshes and vertex attributes are handled, which the goal of enabling easy and flexible custom vertex attributes:
* Reworks the `Mesh` type to use the newly added `VertexAttribute` internally
* `VertexAttribute` defines the name, a unique `VertexAttributeId`, and a `VertexFormat`
* `VertexAttributeId` is used to produce consistent sort orders for vertex buffer generation, replacing the more expensive and often surprising "name based sorting"
* Meshes can be used to generate a `MeshVertexBufferLayout`, which defines the layout of the gpu buffer produced by the mesh. `MeshVertexBufferLayouts` can then be used to generate actual `VertexBufferLayouts` according to the requirements of a specific pipeline. This decoupling of "mesh layout" vs "pipeline vertex buffer layout" is what enables custom attributes. We don't need to standardize _mesh layouts_ or contort meshes to meet the needs of a specific pipeline. As long as the mesh has what the pipeline needs, it will work transparently.
* Mesh-based pipelines now specialize on `&MeshVertexBufferLayout` via the new `SpecializedMeshPipeline` trait (which behaves like `SpecializedPipeline`, but adds `&MeshVertexBufferLayout`). The integrity of the pipeline cache is maintained because the `MeshVertexBufferLayout` is treated as part of the key (which is fully abstracted from implementers of the trait ... no need to add any additional info to the specialization key).
* Hashing `MeshVertexBufferLayout` is too expensive to do for every entity, every frame. To make this scalable, I added a generalized "pre-hashing" solution to `bevy_utils`: `Hashed<T>` keys and `PreHashMap<K, V>` (which uses `Hashed<T>` internally) . Why didn't I just do the quick and dirty in-place "pre-compute hash and use that u64 as a key in a hashmap" that we've done in the past? Because its wrong! Hashes by themselves aren't enough because two different values can produce the same hash. Re-hashing a hash is even worse! I decided to build a generalized solution because this pattern has come up in the past and we've chosen to do the wrong thing. Now we can do the right thing! This did unfortunately require pulling in `hashbrown` and using that in `bevy_utils`, because avoiding re-hashes requires the `raw_entry_mut` api, which isn't stabilized yet (and may never be ... `entry_ref` has favor now, but also isn't available yet). If std's HashMap ever provides the tools we need, we can move back to that. Note that adding `hashbrown` doesn't increase our dependency count because it was already in our tree. I will probably break these changes out into their own PR.
* Specializing on `MeshVertexBufferLayout` has one non-obvious behavior: it can produce identical pipelines for two different MeshVertexBufferLayouts. To optimize the number of active pipelines / reduce re-binds while drawing, I de-duplicate pipelines post-specialization using the final `VertexBufferLayout` as the key. For example, consider a pipeline that needs the layout `(position, normal)` and is specialized using two meshes: `(position, normal, uv)` and `(position, normal, other_vec2)`. If both of these meshes result in `(position, normal)` specializations, we can use the same pipeline! Now we do. Cool!
To briefly illustrate, this is what the relevant section of `MeshPipeline`'s specialization code looks like now:
```rust
impl SpecializedMeshPipeline for MeshPipeline {
type Key = MeshPipelineKey;
fn specialize(
&self,
key: Self::Key,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
) -> RenderPipelineDescriptor {
let mut vertex_attributes = vec![
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL.at_shader_location(1),
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_UV_0.at_shader_location(2),
];
let mut shader_defs = Vec::new();
if layout.contains(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_TANGENT) {
shader_defs.push(String::from("VERTEX_TANGENTS"));
vertex_attributes.push(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_TANGENT.at_shader_location(3));
}
let vertex_buffer_layout = layout
.get_layout(&vertex_attributes)
.expect("Mesh is missing a vertex attribute");
```
Notice that this is _much_ simpler than it was before. And now any mesh with any layout can be used with this pipeline, provided it has vertex postions, normals, and uvs. We even got to remove `HAS_TANGENTS` from MeshPipelineKey and `has_tangents` from `GpuMesh`, because that information is redundant with `MeshVertexBufferLayout`.
This is still a draft because I still need to:
* Add more docs
* Experiment with adding error handling to mesh pipeline specialization (which would print errors at runtime when a mesh is missing a vertex attribute required by a pipeline). If it doesn't tank perf, we'll keep it.
* Consider breaking out the PreHash / hashbrown changes into a separate PR.
* Add an example illustrating this change
* Verify that the "mesh-specialized pipeline de-duplication code" works properly
Please dont yell at me for not doing these things yet :) Just trying to get this in peoples' hands asap.
Alternative to #3120
Fixes #3030
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
2022-02-23 23:21:13 +00:00
|
|
|
#[allow(unused_variables)]
|
|
|
|
|
#[inline]
|
|
|
|
|
fn specialize(
|
2022-04-07 16:16:35 +00:00
|
|
|
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
|

Mesh vertex buffer layouts (#3959)
This PR makes a number of changes to how meshes and vertex attributes are handled, which the goal of enabling easy and flexible custom vertex attributes:
* Reworks the `Mesh` type to use the newly added `VertexAttribute` internally
* `VertexAttribute` defines the name, a unique `VertexAttributeId`, and a `VertexFormat`
* `VertexAttributeId` is used to produce consistent sort orders for vertex buffer generation, replacing the more expensive and often surprising "name based sorting"
* Meshes can be used to generate a `MeshVertexBufferLayout`, which defines the layout of the gpu buffer produced by the mesh. `MeshVertexBufferLayouts` can then be used to generate actual `VertexBufferLayouts` according to the requirements of a specific pipeline. This decoupling of "mesh layout" vs "pipeline vertex buffer layout" is what enables custom attributes. We don't need to standardize _mesh layouts_ or contort meshes to meet the needs of a specific pipeline. As long as the mesh has what the pipeline needs, it will work transparently.
* Mesh-based pipelines now specialize on `&MeshVertexBufferLayout` via the new `SpecializedMeshPipeline` trait (which behaves like `SpecializedPipeline`, but adds `&MeshVertexBufferLayout`). The integrity of the pipeline cache is maintained because the `MeshVertexBufferLayout` is treated as part of the key (which is fully abstracted from implementers of the trait ... no need to add any additional info to the specialization key).
* Hashing `MeshVertexBufferLayout` is too expensive to do for every entity, every frame. To make this scalable, I added a generalized "pre-hashing" solution to `bevy_utils`: `Hashed<T>` keys and `PreHashMap<K, V>` (which uses `Hashed<T>` internally) . Why didn't I just do the quick and dirty in-place "pre-compute hash and use that u64 as a key in a hashmap" that we've done in the past? Because its wrong! Hashes by themselves aren't enough because two different values can produce the same hash. Re-hashing a hash is even worse! I decided to build a generalized solution because this pattern has come up in the past and we've chosen to do the wrong thing. Now we can do the right thing! This did unfortunately require pulling in `hashbrown` and using that in `bevy_utils`, because avoiding re-hashes requires the `raw_entry_mut` api, which isn't stabilized yet (and may never be ... `entry_ref` has favor now, but also isn't available yet). If std's HashMap ever provides the tools we need, we can move back to that. Note that adding `hashbrown` doesn't increase our dependency count because it was already in our tree. I will probably break these changes out into their own PR.
* Specializing on `MeshVertexBufferLayout` has one non-obvious behavior: it can produce identical pipelines for two different MeshVertexBufferLayouts. To optimize the number of active pipelines / reduce re-binds while drawing, I de-duplicate pipelines post-specialization using the final `VertexBufferLayout` as the key. For example, consider a pipeline that needs the layout `(position, normal)` and is specialized using two meshes: `(position, normal, uv)` and `(position, normal, other_vec2)`. If both of these meshes result in `(position, normal)` specializations, we can use the same pipeline! Now we do. Cool!
To briefly illustrate, this is what the relevant section of `MeshPipeline`'s specialization code looks like now:
```rust
impl SpecializedMeshPipeline for MeshPipeline {
type Key = MeshPipelineKey;
fn specialize(
&self,
key: Self::Key,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
) -> RenderPipelineDescriptor {
let mut vertex_attributes = vec![
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL.at_shader_location(1),
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_UV_0.at_shader_location(2),
];
let mut shader_defs = Vec::new();
if layout.contains(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_TANGENT) {
shader_defs.push(String::from("VERTEX_TANGENTS"));
vertex_attributes.push(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_TANGENT.at_shader_location(3));
}
let vertex_buffer_layout = layout
.get_layout(&vertex_attributes)
.expect("Mesh is missing a vertex attribute");
```
Notice that this is _much_ simpler than it was before. And now any mesh with any layout can be used with this pipeline, provided it has vertex postions, normals, and uvs. We even got to remove `HAS_TANGENTS` from MeshPipelineKey and `has_tangents` from `GpuMesh`, because that information is redundant with `MeshVertexBufferLayout`.
This is still a draft because I still need to:
* Add more docs
* Experiment with adding error handling to mesh pipeline specialization (which would print errors at runtime when a mesh is missing a vertex attribute required by a pipeline). If it doesn't tank perf, we'll keep it.
* Consider breaking out the PreHash / hashbrown changes into a separate PR.
* Add an example illustrating this change
* Verify that the "mesh-specialized pipeline de-duplication code" works properly
Please dont yell at me for not doing these things yet :) Just trying to get this in peoples' hands asap.
Alternative to #3120
Fixes #3030
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
2022-02-23 23:21:13 +00:00
|
|
|
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
|
|
|
|
|
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
|

Mesh vertex buffer layouts (#3959)
This PR makes a number of changes to how meshes and vertex attributes are handled, which the goal of enabling easy and flexible custom vertex attributes:
* Reworks the `Mesh` type to use the newly added `VertexAttribute` internally
* `VertexAttribute` defines the name, a unique `VertexAttributeId`, and a `VertexFormat`
* `VertexAttributeId` is used to produce consistent sort orders for vertex buffer generation, replacing the more expensive and often surprising "name based sorting"
* Meshes can be used to generate a `MeshVertexBufferLayout`, which defines the layout of the gpu buffer produced by the mesh. `MeshVertexBufferLayouts` can then be used to generate actual `VertexBufferLayouts` according to the requirements of a specific pipeline. This decoupling of "mesh layout" vs "pipeline vertex buffer layout" is what enables custom attributes. We don't need to standardize _mesh layouts_ or contort meshes to meet the needs of a specific pipeline. As long as the mesh has what the pipeline needs, it will work transparently.
* Mesh-based pipelines now specialize on `&MeshVertexBufferLayout` via the new `SpecializedMeshPipeline` trait (which behaves like `SpecializedPipeline`, but adds `&MeshVertexBufferLayout`). The integrity of the pipeline cache is maintained because the `MeshVertexBufferLayout` is treated as part of the key (which is fully abstracted from implementers of the trait ... no need to add any additional info to the specialization key).
* Hashing `MeshVertexBufferLayout` is too expensive to do for every entity, every frame. To make this scalable, I added a generalized "pre-hashing" solution to `bevy_utils`: `Hashed<T>` keys and `PreHashMap<K, V>` (which uses `Hashed<T>` internally) . Why didn't I just do the quick and dirty in-place "pre-compute hash and use that u64 as a key in a hashmap" that we've done in the past? Because its wrong! Hashes by themselves aren't enough because two different values can produce the same hash. Re-hashing a hash is even worse! I decided to build a generalized solution because this pattern has come up in the past and we've chosen to do the wrong thing. Now we can do the right thing! This did unfortunately require pulling in `hashbrown` and using that in `bevy_utils`, because avoiding re-hashes requires the `raw_entry_mut` api, which isn't stabilized yet (and may never be ... `entry_ref` has favor now, but also isn't available yet). If std's HashMap ever provides the tools we need, we can move back to that. Note that adding `hashbrown` doesn't increase our dependency count because it was already in our tree. I will probably break these changes out into their own PR.
* Specializing on `MeshVertexBufferLayout` has one non-obvious behavior: it can produce identical pipelines for two different MeshVertexBufferLayouts. To optimize the number of active pipelines / reduce re-binds while drawing, I de-duplicate pipelines post-specialization using the final `VertexBufferLayout` as the key. For example, consider a pipeline that needs the layout `(position, normal)` and is specialized using two meshes: `(position, normal, uv)` and `(position, normal, other_vec2)`. If both of these meshes result in `(position, normal)` specializations, we can use the same pipeline! Now we do. Cool!
To briefly illustrate, this is what the relevant section of `MeshPipeline`'s specialization code looks like now:
```rust
impl SpecializedMeshPipeline for MeshPipeline {
type Key = MeshPipelineKey;
fn specialize(
&self,
key: Self::Key,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
) -> RenderPipelineDescriptor {
let mut vertex_attributes = vec![
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL.at_shader_location(1),
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_UV_0.at_shader_location(2),
];
let mut shader_defs = Vec::new();
if layout.contains(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_TANGENT) {
shader_defs.push(String::from("VERTEX_TANGENTS"));
vertex_attributes.push(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_TANGENT.at_shader_location(3));
}
let vertex_buffer_layout = layout
.get_layout(&vertex_attributes)
.expect("Mesh is missing a vertex attribute");
```
Notice that this is _much_ simpler than it was before. And now any mesh with any layout can be used with this pipeline, provided it has vertex postions, normals, and uvs. We even got to remove `HAS_TANGENTS` from MeshPipelineKey and `has_tangents` from `GpuMesh`, because that information is redundant with `MeshVertexBufferLayout`.
This is still a draft because I still need to:
* Add more docs
* Experiment with adding error handling to mesh pipeline specialization (which would print errors at runtime when a mesh is missing a vertex attribute required by a pipeline). If it doesn't tank perf, we'll keep it.
* Consider breaking out the PreHash / hashbrown changes into a separate PR.
* Add an example illustrating this change
* Verify that the "mesh-specialized pipeline de-duplication code" works properly
Please dont yell at me for not doing these things yet :) Just trying to get this in peoples' hands asap.
Alternative to #3120
Fixes #3030
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
2022-02-23 23:21:13 +00:00
|
|
|
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
|
|
|
|
|
Ok(())
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
2020-08-01 00:10:29 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
/// Adds the necessary ECS resources and render logic to enable rendering entities using the given [`Material`]
|
|
|
|
|
/// asset type.
|
2023-01-19 22:11:13 +00:00
|
|
|
pub struct MaterialPlugin<M: Material> {
|
|
|
|
|
/// Controls if the prepass is enabled for the Material.
|
|
|
|
|
/// For more information about what a prepass is, see the [`bevy_core_pipeline::prepass`] docs.
|
|
|
|
|
///
|
|
|
|
|
/// When it is enabled, it will automatically add the [`PrepassPlugin`]
|
|
|
|
|
/// required to make the prepass work on this Material.
|
|
|
|
|
pub prepass_enabled: bool,
|
|
|
|
|
pub _marker: PhantomData<M>,
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
2021-12-14 03:58:23 +00:00
|
|
|
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
impl<M: Material> Default for MaterialPlugin<M> {
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
fn default() -> Self {
|
2023-01-19 22:11:13 +00:00
|
|
|
Self {
|
|
|
|
|
prepass_enabled: true,
|
|
|
|
|
_marker: Default::default(),
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
impl<M: Material> Plugin for MaterialPlugin<M>
|
|
|
|
|
where
|
|
|
|
|
M::Data: PartialEq + Eq + Hash + Clone,
|
|
|
|
|
{
|
2021-12-14 03:58:23 +00:00
|
|
|
fn build(&self, app: &mut App) {
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
app.add_asset::<M>()
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
.add_plugin(ExtractComponentPlugin::<Handle<M>>::extract_visible());
|
2023-01-19 22:11:13 +00:00
|
|
|
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
if let Ok(render_app) = app.get_sub_app_mut(RenderApp) {
|
|
|
|
|
render_app
|
2023-03-02 08:21:21 +00:00
|
|
|
.init_resource::<DrawFunctions<Shadow>>()
|
|
|
|
|
.add_render_command::<Shadow, DrawPrepass<M>>()
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
.add_render_command::<Transparent3d, DrawMaterial<M>>()
|
|
|
|
|
.add_render_command::<Opaque3d, DrawMaterial<M>>()
|
|
|
|
|
.add_render_command::<AlphaMask3d, DrawMaterial<M>>()
|
|
|
|
|
.init_resource::<MaterialPipeline<M>>()
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
.init_resource::<ExtractedMaterials<M>>()
|
|
|
|
|
.init_resource::<RenderMaterials<M>>()
|

Mesh vertex buffer layouts (#3959)
This PR makes a number of changes to how meshes and vertex attributes are handled, which the goal of enabling easy and flexible custom vertex attributes:
* Reworks the `Mesh` type to use the newly added `VertexAttribute` internally
* `VertexAttribute` defines the name, a unique `VertexAttributeId`, and a `VertexFormat`
* `VertexAttributeId` is used to produce consistent sort orders for vertex buffer generation, replacing the more expensive and often surprising "name based sorting"
* Meshes can be used to generate a `MeshVertexBufferLayout`, which defines the layout of the gpu buffer produced by the mesh. `MeshVertexBufferLayouts` can then be used to generate actual `VertexBufferLayouts` according to the requirements of a specific pipeline. This decoupling of "mesh layout" vs "pipeline vertex buffer layout" is what enables custom attributes. We don't need to standardize _mesh layouts_ or contort meshes to meet the needs of a specific pipeline. As long as the mesh has what the pipeline needs, it will work transparently.
* Mesh-based pipelines now specialize on `&MeshVertexBufferLayout` via the new `SpecializedMeshPipeline` trait (which behaves like `SpecializedPipeline`, but adds `&MeshVertexBufferLayout`). The integrity of the pipeline cache is maintained because the `MeshVertexBufferLayout` is treated as part of the key (which is fully abstracted from implementers of the trait ... no need to add any additional info to the specialization key).
* Hashing `MeshVertexBufferLayout` is too expensive to do for every entity, every frame. To make this scalable, I added a generalized "pre-hashing" solution to `bevy_utils`: `Hashed<T>` keys and `PreHashMap<K, V>` (which uses `Hashed<T>` internally) . Why didn't I just do the quick and dirty in-place "pre-compute hash and use that u64 as a key in a hashmap" that we've done in the past? Because its wrong! Hashes by themselves aren't enough because two different values can produce the same hash. Re-hashing a hash is even worse! I decided to build a generalized solution because this pattern has come up in the past and we've chosen to do the wrong thing. Now we can do the right thing! This did unfortunately require pulling in `hashbrown` and using that in `bevy_utils`, because avoiding re-hashes requires the `raw_entry_mut` api, which isn't stabilized yet (and may never be ... `entry_ref` has favor now, but also isn't available yet). If std's HashMap ever provides the tools we need, we can move back to that. Note that adding `hashbrown` doesn't increase our dependency count because it was already in our tree. I will probably break these changes out into their own PR.
* Specializing on `MeshVertexBufferLayout` has one non-obvious behavior: it can produce identical pipelines for two different MeshVertexBufferLayouts. To optimize the number of active pipelines / reduce re-binds while drawing, I de-duplicate pipelines post-specialization using the final `VertexBufferLayout` as the key. For example, consider a pipeline that needs the layout `(position, normal)` and is specialized using two meshes: `(position, normal, uv)` and `(position, normal, other_vec2)`. If both of these meshes result in `(position, normal)` specializations, we can use the same pipeline! Now we do. Cool!
To briefly illustrate, this is what the relevant section of `MeshPipeline`'s specialization code looks like now:
```rust
impl SpecializedMeshPipeline for MeshPipeline {
type Key = MeshPipelineKey;
fn specialize(
&self,
key: Self::Key,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
) -> RenderPipelineDescriptor {
let mut vertex_attributes = vec![
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL.at_shader_location(1),
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_UV_0.at_shader_location(2),
];
let mut shader_defs = Vec::new();
if layout.contains(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_TANGENT) {
shader_defs.push(String::from("VERTEX_TANGENTS"));
vertex_attributes.push(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_TANGENT.at_shader_location(3));
}
let vertex_buffer_layout = layout
.get_layout(&vertex_attributes)
.expect("Mesh is missing a vertex attribute");
```
Notice that this is _much_ simpler than it was before. And now any mesh with any layout can be used with this pipeline, provided it has vertex postions, normals, and uvs. We even got to remove `HAS_TANGENTS` from MeshPipelineKey and `has_tangents` from `GpuMesh`, because that information is redundant with `MeshVertexBufferLayout`.
This is still a draft because I still need to:
* Add more docs
* Experiment with adding error handling to mesh pipeline specialization (which would print errors at runtime when a mesh is missing a vertex attribute required by a pipeline). If it doesn't tank perf, we'll keep it.
* Consider breaking out the PreHash / hashbrown changes into a separate PR.
* Add an example illustrating this change
* Verify that the "mesh-specialized pipeline de-duplication code" works properly
Please dont yell at me for not doing these things yet :) Just trying to get this in peoples' hands asap.
Alternative to #3120
Fixes #3030
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
2022-02-23 23:21:13 +00:00
|
|
|
.init_resource::<SpecializedMeshPipelines<MaterialPipeline<M>>>()
|
2023-02-24 18:33:55 +00:00
|
|
|
.add_system(extract_materials::<M>.in_schedule(ExtractSchedule))
|
2023-02-10 03:32:54 +00:00
|
|
|
.add_system(
|
|
|
|
|
prepare_materials::<M>
|
|
|
|
|
.in_set(RenderSet::Prepare)
|
2023-02-14 21:46:07 +00:00
|
|
|
.after(PrepareAssetSet::PreAssetPrepare),
|
2023-02-10 03:32:54 +00:00
|
|
|
)
|
2023-03-02 08:21:21 +00:00
|
|
|
.add_system(render::queue_shadows::<M>.in_set(RenderLightSystems::QueueShadows))
|

Migrate engine to Schedule v3 (#7267)
Huge thanks to @maniwani, @devil-ira, @hymm, @cart, @superdump and @jakobhellermann for the help with this PR.
# Objective
- Followup #6587.
- Minimal integration for the Stageless Scheduling RFC: https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/pull/45
## Solution
- [x] Remove old scheduling module
- [x] Migrate new methods to no longer use extension methods
- [x] Fix compiler errors
- [x] Fix benchmarks
- [x] Fix examples
- [x] Fix docs
- [x] Fix tests
## Changelog
### Added
- a large number of methods on `App` to work with schedules ergonomically
- the `CoreSchedule` enum
- `App::add_extract_system` via the `RenderingAppExtension` trait extension method
- the private `prepare_view_uniforms` system now has a public system set for scheduling purposes, called `ViewSet::PrepareUniforms`
### Removed
- stages, and all code that mentions stages
- states have been dramatically simplified, and no longer use a stack
- `RunCriteriaLabel`
- `AsSystemLabel` trait
- `on_hierarchy_reports_enabled` run criteria (now just uses an ad hoc resource checking run condition)
- systems in `RenderSet/Stage::Extract` no longer warn when they do not read data from the main world
- `RunCriteriaLabel`
- `transform_propagate_system_set`: this was a nonstandard pattern that didn't actually provide enough control. The systems are already `pub`: the docs have been updated to ensure that the third-party usage is clear.
### Changed
- `System::default_labels` is now `System::default_system_sets`.
- `App::add_default_labels` is now `App::add_default_sets`
- `CoreStage` and `StartupStage` enums are now `CoreSet` and `StartupSet`
- `App::add_system_set` was renamed to `App::add_systems`
- The `StartupSchedule` label is now defined as part of the `CoreSchedules` enum
- `.label(SystemLabel)` is now referred to as `.in_set(SystemSet)`
- `SystemLabel` trait was replaced by `SystemSet`
- `SystemTypeIdLabel<T>` was replaced by `SystemSetType<T>`
- The `ReportHierarchyIssue` resource now has a public constructor (`new`), and implements `PartialEq`
- Fixed time steps now use a schedule (`CoreSchedule::FixedTimeStep`) rather than a run criteria.
- Adding rendering extraction systems now panics rather than silently failing if no subapp with the `RenderApp` label is found.
- the `calculate_bounds` system, with the `CalculateBounds` label, is now in `CoreSet::Update`, rather than in `CoreSet::PostUpdate` before commands are applied.
- `SceneSpawnerSystem` now runs under `CoreSet::Update`, rather than `CoreStage::PreUpdate.at_end()`.
- `bevy_pbr::add_clusters` is no longer an exclusive system
- the top level `bevy_ecs::schedule` module was replaced with `bevy_ecs::scheduling`
- `tick_global_task_pools_on_main_thread` is no longer run as an exclusive system. Instead, it has been replaced by `tick_global_task_pools`, which uses a `NonSend` resource to force running on the main thread.
## Migration Guide
- Calls to `.label(MyLabel)` should be replaced with `.in_set(MySet)`
- Stages have been removed. Replace these with system sets, and then add command flushes using the `apply_system_buffers` exclusive system where needed.
- The `CoreStage`, `StartupStage, `RenderStage` and `AssetStage` enums have been replaced with `CoreSet`, `StartupSet, `RenderSet` and `AssetSet`. The same scheduling guarantees have been preserved.
- Systems are no longer added to `CoreSet::Update` by default. Add systems manually if this behavior is needed, although you should consider adding your game logic systems to `CoreSchedule::FixedTimestep` instead for more reliable framerate-independent behavior.
- Similarly, startup systems are no longer part of `StartupSet::Startup` by default. In most cases, this won't matter to you.
- For example, `add_system_to_stage(CoreStage::PostUpdate, my_system)` should be replaced with
- `add_system(my_system.in_set(CoreSet::PostUpdate)`
- When testing systems or otherwise running them in a headless fashion, simply construct and run a schedule using `Schedule::new()` and `World::run_schedule` rather than constructing stages
- Run criteria have been renamed to run conditions. These can now be combined with each other and with states.
- Looping run criteria and state stacks have been removed. Use an exclusive system that runs a schedule if you need this level of control over system control flow.
- For app-level control flow over which schedules get run when (such as for rollback networking), create your own schedule and insert it under the `CoreSchedule::Outer` label.
- Fixed timesteps are now evaluated in a schedule, rather than controlled via run criteria. The `run_fixed_timestep` system runs this schedule between `CoreSet::First` and `CoreSet::PreUpdate` by default.
- Command flush points introduced by `AssetStage` have been removed. If you were relying on these, add them back manually.
- Adding extract systems is now typically done directly on the main app. Make sure the `RenderingAppExtension` trait is in scope, then call `app.add_extract_system(my_system)`.
- the `calculate_bounds` system, with the `CalculateBounds` label, is now in `CoreSet::Update`, rather than in `CoreSet::PostUpdate` before commands are applied. You may need to order your movement systems to occur before this system in order to avoid system order ambiguities in culling behavior.
- the `RenderLabel` `AppLabel` was renamed to `RenderApp` for clarity
- `App::add_state` now takes 0 arguments: the starting state is set based on the `Default` impl.
- Instead of creating `SystemSet` containers for systems that run in stages, simply use `.on_enter::<State::Variant>()` or its `on_exit` or `on_update` siblings.
- `SystemLabel` derives should be replaced with `SystemSet`. You will also need to add the `Debug`, `PartialEq`, `Eq`, and `Hash` traits to satisfy the new trait bounds.
- `with_run_criteria` has been renamed to `run_if`. Run criteria have been renamed to run conditions for clarity, and should now simply return a bool.
- States have been dramatically simplified: there is no longer a "state stack". To queue a transition to the next state, call `NextState::set`
## TODO
- [x] remove dead methods on App and World
- [x] add `App::add_system_to_schedule` and `App::add_systems_to_schedule`
- [x] avoid adding the default system set at inappropriate times
- [x] remove any accidental cycles in the default plugins schedule
- [x] migrate benchmarks
- [x] expose explicit labels for the built-in command flush points
- [x] migrate engine code
- [x] remove all mentions of stages from the docs
- [x] verify docs for States
- [x] fix uses of exclusive systems that use .end / .at_start / .before_commands
- [x] migrate RenderStage and AssetStage
- [x] migrate examples
- [x] ensure that transform propagation is exported in a sufficiently public way (the systems are already pub)
- [x] ensure that on_enter schedules are run at least once before the main app
- [x] re-enable opt-in to execution order ambiguities
- [x] revert change to `update_bounds` to ensure it runs in `PostUpdate`
- [x] test all examples
- [x] unbreak directional lights
- [x] unbreak shadows (see 3d_scene, 3d_shape, lighting, transparaency_3d examples)
- [x] game menu example shows loading screen and menu simultaneously
- [x] display settings menu is a blank screen
- [x] `without_winit` example panics
- [x] ensure all tests pass
- [x] SubApp doc test fails
- [x] runs_spawn_local tasks fails
- [x] [Fix panic_when_hierachy_cycle test hanging](https://github.com/alice-i-cecile/bevy/pull/120)
## Points of Difficulty and Controversy
**Reviewers, please give feedback on these and look closely**
1. Default sets, from the RFC, have been removed. These added a tremendous amount of implicit complexity and result in hard to debug scheduling errors. They're going to be tackled in the form of "base sets" by @cart in a followup.
2. The outer schedule controls which schedule is run when `App::update` is called.
3. I implemented `Label for `Box<dyn Label>` for our label types. This enables us to store schedule labels in concrete form, and then later run them. I ran into the same set of problems when working with one-shot systems. We've previously investigated this pattern in depth, and it does not appear to lead to extra indirection with nested boxes.
4. `SubApp::update` simply runs the default schedule once. This sucks, but this whole API is incomplete and this was the minimal changeset.
5. `time_system` and `tick_global_task_pools_on_main_thread` no longer use exclusive systems to attempt to force scheduling order
6. Implemetnation strategy for fixed timesteps
7. `AssetStage` was migrated to `AssetSet` without reintroducing command flush points. These did not appear to be used, and it's nice to remove these bottlenecks.
8. Migration of `bevy_render/lib.rs` and pipelined rendering. The logic here is unusually tricky, as we have complex scheduling requirements.
## Future Work (ideally before 0.10)
- Rename schedule_v3 module to schedule or scheduling
- Add a derive macro to states, and likely a `EnumIter` trait of some form
- Figure out what exactly to do with the "systems added should basically work by default" problem
- Improve ergonomics for working with fixed timesteps and states
- Polish FixedTime API to match Time
- Rebase and merge #7415
- Resolve all internal ambiguities (blocked on better tools, especially #7442)
- Add "base sets" to replace the removed default sets.
2023-02-06 02:04:50 +00:00
|
|
|
.add_system(queue_material_meshes::<M>.in_set(RenderSet::Queue));
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
2023-01-19 22:11:13 +00:00
|
|
|
|
2023-03-03 15:08:54 +00:00
|
|
|
// PrepassPipelinePlugin is required for shadow mapping and the optional PrepassPlugin
|
|
|
|
|
app.add_plugin(PrepassPipelinePlugin::<M>::default());
|
|
|
|
|
|
2023-01-19 22:11:13 +00:00
|
|
|
if self.prepass_enabled {
|
|
|
|
|
app.add_plugin(PrepassPlugin::<M>::default());
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
2021-12-14 03:58:23 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
/// A key uniquely identifying a specialized [`MaterialPipeline`].
|
|
|
|
|
pub struct MaterialPipelineKey<M: Material> {
|
2022-04-18 10:11:14 +00:00
|
|
|
pub mesh_key: MeshPipelineKey,
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
pub bind_group_data: M::Data,
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
impl<M: Material> Eq for MaterialPipelineKey<M> where M::Data: PartialEq {}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
impl<M: Material> PartialEq for MaterialPipelineKey<M>
|
|
|
|
|
where
|
|
|
|
|
M::Data: PartialEq,
|
|
|
|
|
{
|
|
|
|
|
fn eq(&self, other: &Self) -> bool {
|
|
|
|
|
self.mesh_key == other.mesh_key && self.bind_group_data == other.bind_group_data
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
impl<M: Material> Clone for MaterialPipelineKey<M>
|
|
|
|
|
where
|
|
|
|
|
M::Data: Clone,
|
|
|
|
|
{
|
|
|
|
|
fn clone(&self) -> Self {
|
|
|
|
|
Self {
|
|
|
|
|
mesh_key: self.mesh_key,
|
|
|
|
|
bind_group_data: self.bind_group_data.clone(),
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
impl<M: Material> Hash for MaterialPipelineKey<M>
|
|
|
|
|
where
|
|
|
|
|
M::Data: Hash,
|
|
|
|
|
{
|
|
|
|
|
fn hash<H: std::hash::Hasher>(&self, state: &mut H) {
|
|
|
|
|
self.mesh_key.hash(state);
|
|
|
|
|
self.bind_group_data.hash(state);
|
|
|
|
|
}
|

Mesh vertex buffer layouts (#3959)
This PR makes a number of changes to how meshes and vertex attributes are handled, which the goal of enabling easy and flexible custom vertex attributes:
* Reworks the `Mesh` type to use the newly added `VertexAttribute` internally
* `VertexAttribute` defines the name, a unique `VertexAttributeId`, and a `VertexFormat`
* `VertexAttributeId` is used to produce consistent sort orders for vertex buffer generation, replacing the more expensive and often surprising "name based sorting"
* Meshes can be used to generate a `MeshVertexBufferLayout`, which defines the layout of the gpu buffer produced by the mesh. `MeshVertexBufferLayouts` can then be used to generate actual `VertexBufferLayouts` according to the requirements of a specific pipeline. This decoupling of "mesh layout" vs "pipeline vertex buffer layout" is what enables custom attributes. We don't need to standardize _mesh layouts_ or contort meshes to meet the needs of a specific pipeline. As long as the mesh has what the pipeline needs, it will work transparently.
* Mesh-based pipelines now specialize on `&MeshVertexBufferLayout` via the new `SpecializedMeshPipeline` trait (which behaves like `SpecializedPipeline`, but adds `&MeshVertexBufferLayout`). The integrity of the pipeline cache is maintained because the `MeshVertexBufferLayout` is treated as part of the key (which is fully abstracted from implementers of the trait ... no need to add any additional info to the specialization key).
* Hashing `MeshVertexBufferLayout` is too expensive to do for every entity, every frame. To make this scalable, I added a generalized "pre-hashing" solution to `bevy_utils`: `Hashed<T>` keys and `PreHashMap<K, V>` (which uses `Hashed<T>` internally) . Why didn't I just do the quick and dirty in-place "pre-compute hash and use that u64 as a key in a hashmap" that we've done in the past? Because its wrong! Hashes by themselves aren't enough because two different values can produce the same hash. Re-hashing a hash is even worse! I decided to build a generalized solution because this pattern has come up in the past and we've chosen to do the wrong thing. Now we can do the right thing! This did unfortunately require pulling in `hashbrown` and using that in `bevy_utils`, because avoiding re-hashes requires the `raw_entry_mut` api, which isn't stabilized yet (and may never be ... `entry_ref` has favor now, but also isn't available yet). If std's HashMap ever provides the tools we need, we can move back to that. Note that adding `hashbrown` doesn't increase our dependency count because it was already in our tree. I will probably break these changes out into their own PR.
* Specializing on `MeshVertexBufferLayout` has one non-obvious behavior: it can produce identical pipelines for two different MeshVertexBufferLayouts. To optimize the number of active pipelines / reduce re-binds while drawing, I de-duplicate pipelines post-specialization using the final `VertexBufferLayout` as the key. For example, consider a pipeline that needs the layout `(position, normal)` and is specialized using two meshes: `(position, normal, uv)` and `(position, normal, other_vec2)`. If both of these meshes result in `(position, normal)` specializations, we can use the same pipeline! Now we do. Cool!
To briefly illustrate, this is what the relevant section of `MeshPipeline`'s specialization code looks like now:
```rust
impl SpecializedMeshPipeline for MeshPipeline {
type Key = MeshPipelineKey;
fn specialize(
&self,
key: Self::Key,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
) -> RenderPipelineDescriptor {
let mut vertex_attributes = vec![
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL.at_shader_location(1),
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_UV_0.at_shader_location(2),
];
let mut shader_defs = Vec::new();
if layout.contains(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_TANGENT) {
shader_defs.push(String::from("VERTEX_TANGENTS"));
vertex_attributes.push(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_TANGENT.at_shader_location(3));
}
let vertex_buffer_layout = layout
.get_layout(&vertex_attributes)
.expect("Mesh is missing a vertex attribute");
```
Notice that this is _much_ simpler than it was before. And now any mesh with any layout can be used with this pipeline, provided it has vertex postions, normals, and uvs. We even got to remove `HAS_TANGENTS` from MeshPipelineKey and `has_tangents` from `GpuMesh`, because that information is redundant with `MeshVertexBufferLayout`.
This is still a draft because I still need to:
* Add more docs
* Experiment with adding error handling to mesh pipeline specialization (which would print errors at runtime when a mesh is missing a vertex attribute required by a pipeline). If it doesn't tank perf, we'll keep it.
* Consider breaking out the PreHash / hashbrown changes into a separate PR.
* Add an example illustrating this change
* Verify that the "mesh-specialized pipeline de-duplication code" works properly
Please dont yell at me for not doing these things yet :) Just trying to get this in peoples' hands asap.
Alternative to #3120
Fixes #3030
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
2022-02-23 23:21:13 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
/// Render pipeline data for a given [`Material`].
|

Make `Resource` trait opt-in, requiring `#[derive(Resource)]` V2 (#5577)
*This PR description is an edited copy of #5007, written by @alice-i-cecile.*
# Objective
Follow-up to https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/2254. The `Resource` trait currently has a blanket implementation for all types that meet its bounds.
While ergonomic, this results in several drawbacks:
* it is possible to make confusing, silent mistakes such as inserting a function pointer (Foo) rather than a value (Foo::Bar) as a resource
* it is challenging to discover if a type is intended to be used as a resource
* we cannot later add customization options (see the [RFC](https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/blob/main/rfcs/27-derive-component.md) for the equivalent choice for Component).
* dependencies can use the same Rust type as a resource in invisibly conflicting ways
* raw Rust types used as resources cannot preserve privacy appropriately, as anyone able to access that type can read and write to internal values
* we cannot capture a definitive list of possible resources to display to users in an editor
## Notes to reviewers
* Review this commit-by-commit; there's effectively no back-tracking and there's a lot of churn in some of these commits.
*ira: My commits are not as well organized :')*
* I've relaxed the bound on Local to Send + Sync + 'static: I don't think these concerns apply there, so this can keep things simple. Storing e.g. a u32 in a Local is fine, because there's a variable name attached explaining what it does.
* I think this is a bad place for the Resource trait to live, but I've left it in place to make reviewing easier. IMO that's best tackled with https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/4981.
## Changelog
`Resource` is no longer automatically implemented for all matching types. Instead, use the new `#[derive(Resource)]` macro.
## Migration Guide
Add `#[derive(Resource)]` to all types you are using as a resource.
If you are using a third party type as a resource, wrap it in a tuple struct to bypass orphan rules. Consider deriving `Deref` and `DerefMut` to improve ergonomics.
`ClearColor` no longer implements `Component`. Using `ClearColor` as a component in 0.8 did nothing.
Use the `ClearColorConfig` in the `Camera3d` and `Camera2d` components instead.
Co-authored-by: Alice <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
2022-08-08 21:36:35 +00:00
|
|
|
#[derive(Resource)]
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
pub struct MaterialPipeline<M: Material> {
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
pub mesh_pipeline: MeshPipeline,
|
|
|
|
|
pub material_layout: BindGroupLayout,
|
|
|
|
|
pub vertex_shader: Option<Handle<Shader>>,
|
|
|
|
|
pub fragment_shader: Option<Handle<Shader>>,
|
|
|
|
|
marker: PhantomData<M>,
|
2021-12-14 03:58:23 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
2023-01-14 18:33:38 +00:00
|
|
|
impl<M: Material> Clone for MaterialPipeline<M> {
|
|
|
|
|
fn clone(&self) -> Self {
|
|
|
|
|
Self {
|
|
|
|
|
mesh_pipeline: self.mesh_pipeline.clone(),
|
|
|
|
|
material_layout: self.material_layout.clone(),
|
|
|
|
|
vertex_shader: self.vertex_shader.clone(),
|
|
|
|
|
fragment_shader: self.fragment_shader.clone(),
|
|
|
|
|
marker: PhantomData,
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
impl<M: Material> SpecializedMeshPipeline for MaterialPipeline<M>
|
|
|
|
|
where
|
|
|
|
|
M::Data: PartialEq + Eq + Hash + Clone,
|
|
|
|
|
{
|
|
|
|
|
type Key = MaterialPipelineKey<M>;
|
2021-12-14 03:58:23 +00:00
|
|
|
|

Mesh vertex buffer layouts (#3959)
This PR makes a number of changes to how meshes and vertex attributes are handled, which the goal of enabling easy and flexible custom vertex attributes:
* Reworks the `Mesh` type to use the newly added `VertexAttribute` internally
* `VertexAttribute` defines the name, a unique `VertexAttributeId`, and a `VertexFormat`
* `VertexAttributeId` is used to produce consistent sort orders for vertex buffer generation, replacing the more expensive and often surprising "name based sorting"
* Meshes can be used to generate a `MeshVertexBufferLayout`, which defines the layout of the gpu buffer produced by the mesh. `MeshVertexBufferLayouts` can then be used to generate actual `VertexBufferLayouts` according to the requirements of a specific pipeline. This decoupling of "mesh layout" vs "pipeline vertex buffer layout" is what enables custom attributes. We don't need to standardize _mesh layouts_ or contort meshes to meet the needs of a specific pipeline. As long as the mesh has what the pipeline needs, it will work transparently.
* Mesh-based pipelines now specialize on `&MeshVertexBufferLayout` via the new `SpecializedMeshPipeline` trait (which behaves like `SpecializedPipeline`, but adds `&MeshVertexBufferLayout`). The integrity of the pipeline cache is maintained because the `MeshVertexBufferLayout` is treated as part of the key (which is fully abstracted from implementers of the trait ... no need to add any additional info to the specialization key).
* Hashing `MeshVertexBufferLayout` is too expensive to do for every entity, every frame. To make this scalable, I added a generalized "pre-hashing" solution to `bevy_utils`: `Hashed<T>` keys and `PreHashMap<K, V>` (which uses `Hashed<T>` internally) . Why didn't I just do the quick and dirty in-place "pre-compute hash and use that u64 as a key in a hashmap" that we've done in the past? Because its wrong! Hashes by themselves aren't enough because two different values can produce the same hash. Re-hashing a hash is even worse! I decided to build a generalized solution because this pattern has come up in the past and we've chosen to do the wrong thing. Now we can do the right thing! This did unfortunately require pulling in `hashbrown` and using that in `bevy_utils`, because avoiding re-hashes requires the `raw_entry_mut` api, which isn't stabilized yet (and may never be ... `entry_ref` has favor now, but also isn't available yet). If std's HashMap ever provides the tools we need, we can move back to that. Note that adding `hashbrown` doesn't increase our dependency count because it was already in our tree. I will probably break these changes out into their own PR.
* Specializing on `MeshVertexBufferLayout` has one non-obvious behavior: it can produce identical pipelines for two different MeshVertexBufferLayouts. To optimize the number of active pipelines / reduce re-binds while drawing, I de-duplicate pipelines post-specialization using the final `VertexBufferLayout` as the key. For example, consider a pipeline that needs the layout `(position, normal)` and is specialized using two meshes: `(position, normal, uv)` and `(position, normal, other_vec2)`. If both of these meshes result in `(position, normal)` specializations, we can use the same pipeline! Now we do. Cool!
To briefly illustrate, this is what the relevant section of `MeshPipeline`'s specialization code looks like now:
```rust
impl SpecializedMeshPipeline for MeshPipeline {
type Key = MeshPipelineKey;
fn specialize(
&self,
key: Self::Key,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
) -> RenderPipelineDescriptor {
let mut vertex_attributes = vec![
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL.at_shader_location(1),
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_UV_0.at_shader_location(2),
];
let mut shader_defs = Vec::new();
if layout.contains(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_TANGENT) {
shader_defs.push(String::from("VERTEX_TANGENTS"));
vertex_attributes.push(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_TANGENT.at_shader_location(3));
}
let vertex_buffer_layout = layout
.get_layout(&vertex_attributes)
.expect("Mesh is missing a vertex attribute");
```
Notice that this is _much_ simpler than it was before. And now any mesh with any layout can be used with this pipeline, provided it has vertex postions, normals, and uvs. We even got to remove `HAS_TANGENTS` from MeshPipelineKey and `has_tangents` from `GpuMesh`, because that information is redundant with `MeshVertexBufferLayout`.
This is still a draft because I still need to:
* Add more docs
* Experiment with adding error handling to mesh pipeline specialization (which would print errors at runtime when a mesh is missing a vertex attribute required by a pipeline). If it doesn't tank perf, we'll keep it.
* Consider breaking out the PreHash / hashbrown changes into a separate PR.
* Add an example illustrating this change
* Verify that the "mesh-specialized pipeline de-duplication code" works properly
Please dont yell at me for not doing these things yet :) Just trying to get this in peoples' hands asap.
Alternative to #3120
Fixes #3030
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
2022-02-23 23:21:13 +00:00
|
|
|
fn specialize(
|
|
|
|
|
&self,
|
|
|
|
|
key: Self::Key,
|
|
|
|
|
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
|
|
|
|
|
) -> Result<RenderPipelineDescriptor, SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
|
|
|
|
|
let mut descriptor = self.mesh_pipeline.specialize(key.mesh_key, layout)?;
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
if let Some(vertex_shader) = &self.vertex_shader {
|
|
|
|
|
descriptor.vertex.shader = vertex_shader.clone();
|
2021-12-14 03:58:23 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
if let Some(fragment_shader) = &self.fragment_shader {
|
|
|
|
|
descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap().shader = fragment_shader.clone();
|
2021-12-14 03:58:23 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
2022-03-29 18:31:13 +00:00
|
|
|
|
2023-02-17 06:20:16 +00:00
|
|
|
descriptor.layout.insert(1, self.material_layout.clone());
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
M::specialize(self, &mut descriptor, layout, key)?;
|

Mesh vertex buffer layouts (#3959)
This PR makes a number of changes to how meshes and vertex attributes are handled, which the goal of enabling easy and flexible custom vertex attributes:
* Reworks the `Mesh` type to use the newly added `VertexAttribute` internally
* `VertexAttribute` defines the name, a unique `VertexAttributeId`, and a `VertexFormat`
* `VertexAttributeId` is used to produce consistent sort orders for vertex buffer generation, replacing the more expensive and often surprising "name based sorting"
* Meshes can be used to generate a `MeshVertexBufferLayout`, which defines the layout of the gpu buffer produced by the mesh. `MeshVertexBufferLayouts` can then be used to generate actual `VertexBufferLayouts` according to the requirements of a specific pipeline. This decoupling of "mesh layout" vs "pipeline vertex buffer layout" is what enables custom attributes. We don't need to standardize _mesh layouts_ or contort meshes to meet the needs of a specific pipeline. As long as the mesh has what the pipeline needs, it will work transparently.
* Mesh-based pipelines now specialize on `&MeshVertexBufferLayout` via the new `SpecializedMeshPipeline` trait (which behaves like `SpecializedPipeline`, but adds `&MeshVertexBufferLayout`). The integrity of the pipeline cache is maintained because the `MeshVertexBufferLayout` is treated as part of the key (which is fully abstracted from implementers of the trait ... no need to add any additional info to the specialization key).
* Hashing `MeshVertexBufferLayout` is too expensive to do for every entity, every frame. To make this scalable, I added a generalized "pre-hashing" solution to `bevy_utils`: `Hashed<T>` keys and `PreHashMap<K, V>` (which uses `Hashed<T>` internally) . Why didn't I just do the quick and dirty in-place "pre-compute hash and use that u64 as a key in a hashmap" that we've done in the past? Because its wrong! Hashes by themselves aren't enough because two different values can produce the same hash. Re-hashing a hash is even worse! I decided to build a generalized solution because this pattern has come up in the past and we've chosen to do the wrong thing. Now we can do the right thing! This did unfortunately require pulling in `hashbrown` and using that in `bevy_utils`, because avoiding re-hashes requires the `raw_entry_mut` api, which isn't stabilized yet (and may never be ... `entry_ref` has favor now, but also isn't available yet). If std's HashMap ever provides the tools we need, we can move back to that. Note that adding `hashbrown` doesn't increase our dependency count because it was already in our tree. I will probably break these changes out into their own PR.
* Specializing on `MeshVertexBufferLayout` has one non-obvious behavior: it can produce identical pipelines for two different MeshVertexBufferLayouts. To optimize the number of active pipelines / reduce re-binds while drawing, I de-duplicate pipelines post-specialization using the final `VertexBufferLayout` as the key. For example, consider a pipeline that needs the layout `(position, normal)` and is specialized using two meshes: `(position, normal, uv)` and `(position, normal, other_vec2)`. If both of these meshes result in `(position, normal)` specializations, we can use the same pipeline! Now we do. Cool!
To briefly illustrate, this is what the relevant section of `MeshPipeline`'s specialization code looks like now:
```rust
impl SpecializedMeshPipeline for MeshPipeline {
type Key = MeshPipelineKey;
fn specialize(
&self,
key: Self::Key,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
) -> RenderPipelineDescriptor {
let mut vertex_attributes = vec![
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL.at_shader_location(1),
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_UV_0.at_shader_location(2),
];
let mut shader_defs = Vec::new();
if layout.contains(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_TANGENT) {
shader_defs.push(String::from("VERTEX_TANGENTS"));
vertex_attributes.push(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_TANGENT.at_shader_location(3));
}
let vertex_buffer_layout = layout
.get_layout(&vertex_attributes)
.expect("Mesh is missing a vertex attribute");
```
Notice that this is _much_ simpler than it was before. And now any mesh with any layout can be used with this pipeline, provided it has vertex postions, normals, and uvs. We even got to remove `HAS_TANGENTS` from MeshPipelineKey and `has_tangents` from `GpuMesh`, because that information is redundant with `MeshVertexBufferLayout`.
This is still a draft because I still need to:
* Add more docs
* Experiment with adding error handling to mesh pipeline specialization (which would print errors at runtime when a mesh is missing a vertex attribute required by a pipeline). If it doesn't tank perf, we'll keep it.
* Consider breaking out the PreHash / hashbrown changes into a separate PR.
* Add an example illustrating this change
* Verify that the "mesh-specialized pipeline de-duplication code" works properly
Please dont yell at me for not doing these things yet :) Just trying to get this in peoples' hands asap.
Alternative to #3120
Fixes #3030
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
2022-02-23 23:21:13 +00:00
|
|
|
Ok(descriptor)
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
impl<M: Material> FromWorld for MaterialPipeline<M> {
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
fn from_world(world: &mut World) -> Self {
|
2022-02-27 22:37:18 +00:00
|
|
|
let asset_server = world.resource::<AssetServer>();
|
|
|
|
|
let render_device = world.resource::<RenderDevice>();
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MaterialPipeline {
|
2022-02-27 22:37:18 +00:00
|
|
|
mesh_pipeline: world.resource::<MeshPipeline>().clone(),
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
material_layout: M::bind_group_layout(render_device),
|
|
|
|
|
vertex_shader: match M::vertex_shader() {
|
|
|
|
|
ShaderRef::Default => None,
|
|
|
|
|
ShaderRef::Handle(handle) => Some(handle),
|
|
|
|
|
ShaderRef::Path(path) => Some(asset_server.load(path)),
|
|
|
|
|
},
|
|
|
|
|
fragment_shader: match M::fragment_shader() {
|
|
|
|
|
ShaderRef::Default => None,
|
|
|
|
|
ShaderRef::Handle(handle) => Some(handle),
|
|
|
|
|
ShaderRef::Path(path) => Some(asset_server.load(path)),
|
|
|
|
|
},
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
marker: PhantomData,
|
2021-12-14 03:58:23 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
type DrawMaterial<M> = (
|
|
|
|
|
SetItemPipeline,
|
|
|
|
|
SetMeshViewBindGroup<0>,
|
|
|
|
|
SetMaterialBindGroup<M, 1>,
|
|
|
|
|
SetMeshBindGroup<2>,
|
|
|
|
|
DrawMesh,
|
|
|
|
|
);
|
|
|
|
|
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
/// Sets the bind group for a given [`Material`] at the configured `I` index.
|
|
|
|
|
pub struct SetMaterialBindGroup<M: Material, const I: usize>(PhantomData<M>);
|
2023-01-04 01:13:30 +00:00
|
|
|
impl<P: PhaseItem, M: Material, const I: usize> RenderCommand<P> for SetMaterialBindGroup<M, I> {
|
|
|
|
|
type Param = SRes<RenderMaterials<M>>;
|
|
|
|
|
type ViewWorldQuery = ();
|
|
|
|
|
type ItemWorldQuery = Read<Handle<M>>;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[inline]
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
fn render<'w>(
|
2023-01-04 01:13:30 +00:00
|
|
|
_item: &P,
|
|
|
|
|
_view: (),
|
|
|
|
|
material_handle: &'_ Handle<M>,
|
|
|
|
|
materials: SystemParamItem<'w, '_, Self::Param>,
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
pass: &mut TrackedRenderPass<'w>,
|
|
|
|
|
) -> RenderCommandResult {
|
|
|
|
|
let material = materials.into_inner().get(material_handle).unwrap();
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
pass.set_bind_group(I, &material.bind_group, &[]);
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
RenderCommandResult::Success
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[allow(clippy::too_many_arguments)]
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
pub fn queue_material_meshes<M: Material>(
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
opaque_draw_functions: Res<DrawFunctions<Opaque3d>>,
|
|
|
|
|
alpha_mask_draw_functions: Res<DrawFunctions<AlphaMask3d>>,
|
|
|
|
|
transparent_draw_functions: Res<DrawFunctions<Transparent3d>>,
|
|
|
|
|
material_pipeline: Res<MaterialPipeline<M>>,
|

Mesh vertex buffer layouts (#3959)
This PR makes a number of changes to how meshes and vertex attributes are handled, which the goal of enabling easy and flexible custom vertex attributes:
* Reworks the `Mesh` type to use the newly added `VertexAttribute` internally
* `VertexAttribute` defines the name, a unique `VertexAttributeId`, and a `VertexFormat`
* `VertexAttributeId` is used to produce consistent sort orders for vertex buffer generation, replacing the more expensive and often surprising "name based sorting"
* Meshes can be used to generate a `MeshVertexBufferLayout`, which defines the layout of the gpu buffer produced by the mesh. `MeshVertexBufferLayouts` can then be used to generate actual `VertexBufferLayouts` according to the requirements of a specific pipeline. This decoupling of "mesh layout" vs "pipeline vertex buffer layout" is what enables custom attributes. We don't need to standardize _mesh layouts_ or contort meshes to meet the needs of a specific pipeline. As long as the mesh has what the pipeline needs, it will work transparently.
* Mesh-based pipelines now specialize on `&MeshVertexBufferLayout` via the new `SpecializedMeshPipeline` trait (which behaves like `SpecializedPipeline`, but adds `&MeshVertexBufferLayout`). The integrity of the pipeline cache is maintained because the `MeshVertexBufferLayout` is treated as part of the key (which is fully abstracted from implementers of the trait ... no need to add any additional info to the specialization key).
* Hashing `MeshVertexBufferLayout` is too expensive to do for every entity, every frame. To make this scalable, I added a generalized "pre-hashing" solution to `bevy_utils`: `Hashed<T>` keys and `PreHashMap<K, V>` (which uses `Hashed<T>` internally) . Why didn't I just do the quick and dirty in-place "pre-compute hash and use that u64 as a key in a hashmap" that we've done in the past? Because its wrong! Hashes by themselves aren't enough because two different values can produce the same hash. Re-hashing a hash is even worse! I decided to build a generalized solution because this pattern has come up in the past and we've chosen to do the wrong thing. Now we can do the right thing! This did unfortunately require pulling in `hashbrown` and using that in `bevy_utils`, because avoiding re-hashes requires the `raw_entry_mut` api, which isn't stabilized yet (and may never be ... `entry_ref` has favor now, but also isn't available yet). If std's HashMap ever provides the tools we need, we can move back to that. Note that adding `hashbrown` doesn't increase our dependency count because it was already in our tree. I will probably break these changes out into their own PR.
* Specializing on `MeshVertexBufferLayout` has one non-obvious behavior: it can produce identical pipelines for two different MeshVertexBufferLayouts. To optimize the number of active pipelines / reduce re-binds while drawing, I de-duplicate pipelines post-specialization using the final `VertexBufferLayout` as the key. For example, consider a pipeline that needs the layout `(position, normal)` and is specialized using two meshes: `(position, normal, uv)` and `(position, normal, other_vec2)`. If both of these meshes result in `(position, normal)` specializations, we can use the same pipeline! Now we do. Cool!
To briefly illustrate, this is what the relevant section of `MeshPipeline`'s specialization code looks like now:
```rust
impl SpecializedMeshPipeline for MeshPipeline {
type Key = MeshPipelineKey;
fn specialize(
&self,
key: Self::Key,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
) -> RenderPipelineDescriptor {
let mut vertex_attributes = vec![
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL.at_shader_location(1),
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_UV_0.at_shader_location(2),
];
let mut shader_defs = Vec::new();
if layout.contains(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_TANGENT) {
shader_defs.push(String::from("VERTEX_TANGENTS"));
vertex_attributes.push(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_TANGENT.at_shader_location(3));
}
let vertex_buffer_layout = layout
.get_layout(&vertex_attributes)
.expect("Mesh is missing a vertex attribute");
```
Notice that this is _much_ simpler than it was before. And now any mesh with any layout can be used with this pipeline, provided it has vertex postions, normals, and uvs. We even got to remove `HAS_TANGENTS` from MeshPipelineKey and `has_tangents` from `GpuMesh`, because that information is redundant with `MeshVertexBufferLayout`.
This is still a draft because I still need to:
* Add more docs
* Experiment with adding error handling to mesh pipeline specialization (which would print errors at runtime when a mesh is missing a vertex attribute required by a pipeline). If it doesn't tank perf, we'll keep it.
* Consider breaking out the PreHash / hashbrown changes into a separate PR.
* Add an example illustrating this change
* Verify that the "mesh-specialized pipeline de-duplication code" works properly
Please dont yell at me for not doing these things yet :) Just trying to get this in peoples' hands asap.
Alternative to #3120
Fixes #3030
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
2022-02-23 23:21:13 +00:00
|
|
|
mut pipelines: ResMut<SpecializedMeshPipelines<MaterialPipeline<M>>>,
|
2023-01-16 15:41:14 +00:00
|
|
|
pipeline_cache: Res<PipelineCache>,
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
msaa: Res<Msaa>,
|
|
|
|
|
render_meshes: Res<RenderAssets<Mesh>>,
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
render_materials: Res<RenderMaterials<M>>,
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
material_meshes: Query<(&Handle<M>, &Handle<Mesh>, &MeshUniform)>,
|

EnvironmentMapLight, BRDF Improvements (#7051)
(Before)

(After)

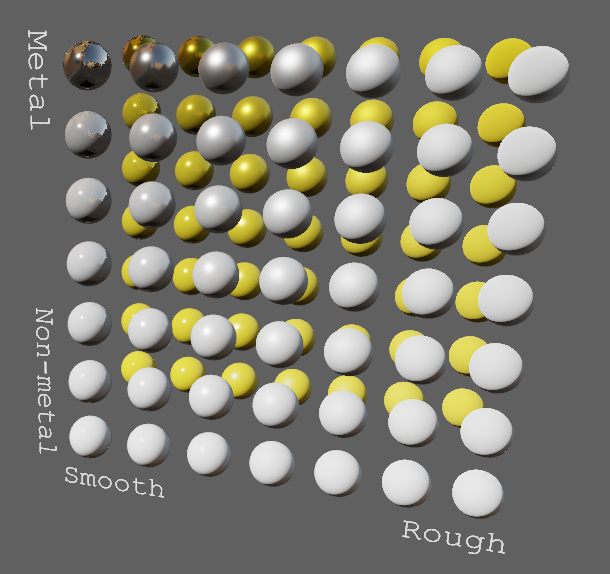
# Objective
- Improve lighting; especially reflections.
- Closes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/4581.
## Solution
- Implement environment maps, providing better ambient light.
- Add microfacet multibounce approximation for specular highlights from Filament.
- Occlusion is no longer incorrectly applied to direct lighting. It now only applies to diffuse indirect light. Unsure if it's also supposed to apply to specular indirect light - the glTF specification just says "indirect light". In the case of ambient occlusion, for instance, that's usually only calculated as diffuse though. For now, I'm choosing to apply this just to indirect diffuse light, and not specular.
- Modified the PBR example to use an environment map, and have labels.
- Added `FallbackImageCubemap`.
## Implementation
- IBL technique references can be found in environment_map.wgsl.
- It's more accurate to use a LUT for the scale/bias. Filament has a good reference on generating this LUT. For now, I just used an analytic approximation.
- For now, environment maps must first be prefiltered outside of bevy using a 3rd party tool. See the `EnvironmentMap` documentation.
- Eventually, we should have our own prefiltering code, so that we can have dynamically changing environment maps, as well as let users drop in an HDR image and use asset preprocessing to create the needed textures using only bevy.
---
## Changelog
- Added an `EnvironmentMapLight` camera component that adds additional ambient light to a scene.
- StandardMaterials will now appear brighter and more saturated at high roughness, due to internal material changes. This is more physically correct.
- Fixed StandardMaterial occlusion being incorrectly applied to direct lighting.
- Added `FallbackImageCubemap`.
Co-authored-by: IceSentry <c.giguere42@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: James Liu <contact@jamessliu.com>
Co-authored-by: Rob Parrett <robparrett@gmail.com>
2023-02-09 16:46:32 +00:00
|
|
|
images: Res<RenderAssets<Image>>,
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
mut views: Query<(
|
|
|
|
|
&ExtractedView,
|
|
|
|
|
&VisibleEntities,
|
2022-10-26 20:13:59 +00:00
|
|
|
Option<&Tonemapping>,
|
2023-02-19 20:38:13 +00:00
|
|
|
Option<&DebandDither>,
|

EnvironmentMapLight, BRDF Improvements (#7051)
(Before)

(After)


# Objective
- Improve lighting; especially reflections.
- Closes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/4581.
## Solution
- Implement environment maps, providing better ambient light.
- Add microfacet multibounce approximation for specular highlights from Filament.
- Occlusion is no longer incorrectly applied to direct lighting. It now only applies to diffuse indirect light. Unsure if it's also supposed to apply to specular indirect light - the glTF specification just says "indirect light". In the case of ambient occlusion, for instance, that's usually only calculated as diffuse though. For now, I'm choosing to apply this just to indirect diffuse light, and not specular.
- Modified the PBR example to use an environment map, and have labels.
- Added `FallbackImageCubemap`.
## Implementation
- IBL technique references can be found in environment_map.wgsl.
- It's more accurate to use a LUT for the scale/bias. Filament has a good reference on generating this LUT. For now, I just used an analytic approximation.
- For now, environment maps must first be prefiltered outside of bevy using a 3rd party tool. See the `EnvironmentMap` documentation.
- Eventually, we should have our own prefiltering code, so that we can have dynamically changing environment maps, as well as let users drop in an HDR image and use asset preprocessing to create the needed textures using only bevy.
---
## Changelog
- Added an `EnvironmentMapLight` camera component that adds additional ambient light to a scene.
- StandardMaterials will now appear brighter and more saturated at high roughness, due to internal material changes. This is more physically correct.
- Fixed StandardMaterial occlusion being incorrectly applied to direct lighting.
- Added `FallbackImageCubemap`.
Co-authored-by: IceSentry <c.giguere42@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: James Liu <contact@jamessliu.com>
Co-authored-by: Rob Parrett <robparrett@gmail.com>
2023-02-09 16:46:32 +00:00
|
|
|
Option<&EnvironmentMapLight>,
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
&mut RenderPhase<Opaque3d>,
|
|
|
|
|
&mut RenderPhase<AlphaMask3d>,
|
|
|
|
|
&mut RenderPhase<Transparent3d>,
|
|
|
|
|
)>,
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
) where
|
|
|
|
|
M::Data: PartialEq + Eq + Hash + Clone,
|
|
|
|
|
{
|
2022-10-26 20:13:59 +00:00
|
|
|
for (
|
|
|
|
|
view,
|
|
|
|
|
visible_entities,
|
|
|
|
|
tonemapping,
|
2023-02-19 20:38:13 +00:00
|
|
|
dither,
|

EnvironmentMapLight, BRDF Improvements (#7051)
(Before)

(After)


# Objective
- Improve lighting; especially reflections.
- Closes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/4581.
## Solution
- Implement environment maps, providing better ambient light.
- Add microfacet multibounce approximation for specular highlights from Filament.
- Occlusion is no longer incorrectly applied to direct lighting. It now only applies to diffuse indirect light. Unsure if it's also supposed to apply to specular indirect light - the glTF specification just says "indirect light". In the case of ambient occlusion, for instance, that's usually only calculated as diffuse though. For now, I'm choosing to apply this just to indirect diffuse light, and not specular.
- Modified the PBR example to use an environment map, and have labels.
- Added `FallbackImageCubemap`.
## Implementation
- IBL technique references can be found in environment_map.wgsl.
- It's more accurate to use a LUT for the scale/bias. Filament has a good reference on generating this LUT. For now, I just used an analytic approximation.
- For now, environment maps must first be prefiltered outside of bevy using a 3rd party tool. See the `EnvironmentMap` documentation.
- Eventually, we should have our own prefiltering code, so that we can have dynamically changing environment maps, as well as let users drop in an HDR image and use asset preprocessing to create the needed textures using only bevy.
---
## Changelog
- Added an `EnvironmentMapLight` camera component that adds additional ambient light to a scene.
- StandardMaterials will now appear brighter and more saturated at high roughness, due to internal material changes. This is more physically correct.
- Fixed StandardMaterial occlusion being incorrectly applied to direct lighting.
- Added `FallbackImageCubemap`.
Co-authored-by: IceSentry <c.giguere42@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: James Liu <contact@jamessliu.com>
Co-authored-by: Rob Parrett <robparrett@gmail.com>
2023-02-09 16:46:32 +00:00
|
|
|
environment_map,
|
2022-10-26 20:13:59 +00:00
|
|
|
mut opaque_phase,
|
|
|
|
|
mut alpha_mask_phase,
|
|
|
|
|
mut transparent_phase,
|
|
|
|
|
) in &mut views
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
{
|
2022-11-28 13:54:13 +00:00
|
|
|
let draw_opaque_pbr = opaque_draw_functions.read().id::<DrawMaterial<M>>();
|
|
|
|
|
let draw_alpha_mask_pbr = alpha_mask_draw_functions.read().id::<DrawMaterial<M>>();
|
|
|
|
|
let draw_transparent_pbr = transparent_draw_functions.read().id::<DrawMaterial<M>>();
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
|
2023-01-20 14:25:21 +00:00
|
|
|
let mut view_key = MeshPipelineKey::from_msaa_samples(msaa.samples())
|
|
|
|
|
| MeshPipelineKey::from_hdr(view.hdr);
|
2022-10-26 20:13:59 +00:00
|
|
|
|

EnvironmentMapLight, BRDF Improvements (#7051)
(Before)

(After)


# Objective
- Improve lighting; especially reflections.
- Closes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/4581.
## Solution
- Implement environment maps, providing better ambient light.
- Add microfacet multibounce approximation for specular highlights from Filament.
- Occlusion is no longer incorrectly applied to direct lighting. It now only applies to diffuse indirect light. Unsure if it's also supposed to apply to specular indirect light - the glTF specification just says "indirect light". In the case of ambient occlusion, for instance, that's usually only calculated as diffuse though. For now, I'm choosing to apply this just to indirect diffuse light, and not specular.
- Modified the PBR example to use an environment map, and have labels.
- Added `FallbackImageCubemap`.
## Implementation
- IBL technique references can be found in environment_map.wgsl.
- It's more accurate to use a LUT for the scale/bias. Filament has a good reference on generating this LUT. For now, I just used an analytic approximation.
- For now, environment maps must first be prefiltered outside of bevy using a 3rd party tool. See the `EnvironmentMap` documentation.
- Eventually, we should have our own prefiltering code, so that we can have dynamically changing environment maps, as well as let users drop in an HDR image and use asset preprocessing to create the needed textures using only bevy.
---
## Changelog
- Added an `EnvironmentMapLight` camera component that adds additional ambient light to a scene.
- StandardMaterials will now appear brighter and more saturated at high roughness, due to internal material changes. This is more physically correct.
- Fixed StandardMaterial occlusion being incorrectly applied to direct lighting.
- Added `FallbackImageCubemap`.
Co-authored-by: IceSentry <c.giguere42@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: James Liu <contact@jamessliu.com>
Co-authored-by: Rob Parrett <robparrett@gmail.com>
2023-02-09 16:46:32 +00:00
|
|
|
let environment_map_loaded = match environment_map {
|
|
|
|
|
Some(environment_map) => environment_map.is_loaded(&images),
|
|
|
|
|
None => false,
|
|
|
|
|
};
|
|
|
|
|
if environment_map_loaded {
|
|
|
|
|
view_key |= MeshPipelineKey::ENVIRONMENT_MAP;
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
2023-02-19 20:38:13 +00:00
|
|
|
if !view.hdr {
|
|
|
|
|
if let Some(tonemapping) = tonemapping {
|
2022-10-26 20:13:59 +00:00
|
|
|
view_key |= MeshPipelineKey::TONEMAP_IN_SHADER;
|
2023-02-19 20:38:13 +00:00
|
|
|
view_key |= match tonemapping {
|
|
|
|
|
Tonemapping::None => MeshPipelineKey::TONEMAP_METHOD_NONE,
|
|
|
|
|
Tonemapping::Reinhard => MeshPipelineKey::TONEMAP_METHOD_REINHARD,
|
|
|
|
|
Tonemapping::ReinhardLuminance => {
|
|
|
|
|
MeshPipelineKey::TONEMAP_METHOD_REINHARD_LUMINANCE
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
Tonemapping::AcesFitted => MeshPipelineKey::TONEMAP_METHOD_ACES_FITTED,
|
|
|
|
|
Tonemapping::AgX => MeshPipelineKey::TONEMAP_METHOD_AGX,
|
|
|
|
|
Tonemapping::SomewhatBoringDisplayTransform => {
|
|
|
|
|
MeshPipelineKey::TONEMAP_METHOD_SOMEWHAT_BORING_DISPLAY_TRANSFORM
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
Tonemapping::TonyMcMapface => MeshPipelineKey::TONEMAP_METHOD_TONY_MC_MAPFACE,
|
|
|
|
|
Tonemapping::BlenderFilmic => MeshPipelineKey::TONEMAP_METHOD_BLENDER_FILMIC,
|
|
|
|
|
};
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
if let Some(DebandDither::Enabled) = dither {
|
|
|
|
|
view_key |= MeshPipelineKey::DEBAND_DITHER;
|
2022-10-26 20:13:59 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
|

EnvironmentMapLight, BRDF Improvements (#7051)
(Before)

(After)


# Objective
- Improve lighting; especially reflections.
- Closes https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/4581.
## Solution
- Implement environment maps, providing better ambient light.
- Add microfacet multibounce approximation for specular highlights from Filament.
- Occlusion is no longer incorrectly applied to direct lighting. It now only applies to diffuse indirect light. Unsure if it's also supposed to apply to specular indirect light - the glTF specification just says "indirect light". In the case of ambient occlusion, for instance, that's usually only calculated as diffuse though. For now, I'm choosing to apply this just to indirect diffuse light, and not specular.
- Modified the PBR example to use an environment map, and have labels.
- Added `FallbackImageCubemap`.
## Implementation
- IBL technique references can be found in environment_map.wgsl.
- It's more accurate to use a LUT for the scale/bias. Filament has a good reference on generating this LUT. For now, I just used an analytic approximation.
- For now, environment maps must first be prefiltered outside of bevy using a 3rd party tool. See the `EnvironmentMap` documentation.
- Eventually, we should have our own prefiltering code, so that we can have dynamically changing environment maps, as well as let users drop in an HDR image and use asset preprocessing to create the needed textures using only bevy.
---
## Changelog
- Added an `EnvironmentMapLight` camera component that adds additional ambient light to a scene.
- StandardMaterials will now appear brighter and more saturated at high roughness, due to internal material changes. This is more physically correct.
- Fixed StandardMaterial occlusion being incorrectly applied to direct lighting.
- Added `FallbackImageCubemap`.
Co-authored-by: IceSentry <c.giguere42@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: James Liu <contact@jamessliu.com>
Co-authored-by: Rob Parrett <robparrett@gmail.com>
2023-02-09 16:46:32 +00:00
|
|
|
let rangefinder = view.rangefinder3d();
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
for visible_entity in &visible_entities.entities {
|
|
|
|
|
if let Ok((material_handle, mesh_handle, mesh_uniform)) =
|
|
|
|
|
material_meshes.get(*visible_entity)
|
|
|
|
|
{
|
2023-02-13 19:33:51 +00:00
|
|
|
if let (Some(mesh), Some(material)) = (
|
|
|
|
|
render_meshes.get(mesh_handle),
|
|
|
|
|
render_materials.get(material_handle),
|
|
|
|
|
) {
|
|
|
|
|
let mut mesh_key =
|
|
|
|
|
MeshPipelineKey::from_primitive_topology(mesh.primitive_topology)
|
|
|
|
|
| view_key;
|
|
|
|
|
let alpha_mode = material.properties.alpha_mode;
|
|
|
|
|
if let AlphaMode::Blend | AlphaMode::Premultiplied | AlphaMode::Add = alpha_mode
|
|
|
|
|
{
|
|
|
|
|
// Blend, Premultiplied and Add all share the same pipeline key
|
|
|
|
|
// They're made distinct in the PBR shader, via `premultiply_alpha()`
|
|
|
|
|
mesh_key |= MeshPipelineKey::BLEND_PREMULTIPLIED_ALPHA;
|
|
|
|
|
} else if let AlphaMode::Multiply = alpha_mode {
|
|
|
|
|
mesh_key |= MeshPipelineKey::BLEND_MULTIPLY;
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
|
2023-02-13 19:33:51 +00:00
|
|
|
let pipeline_id = pipelines.specialize(
|
|
|
|
|
&pipeline_cache,
|
|
|
|
|
&material_pipeline,
|
|
|
|
|
MaterialPipelineKey {
|
|
|
|
|
mesh_key,
|
|
|
|
|
bind_group_data: material.key.clone(),
|
|
|
|
|
},
|
|
|
|
|
&mesh.layout,
|
|
|
|
|
);
|
|
|
|
|
let pipeline_id = match pipeline_id {
|
|
|
|
|
Ok(id) => id,
|
|
|
|
|
Err(err) => {
|
|
|
|
|
error!("{}", err);
|
|
|
|
|
continue;
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
};
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
let distance = rangefinder.distance(&mesh_uniform.transform)
|
|
|
|
|
+ material.properties.depth_bias;
|
|
|
|
|
match alpha_mode {
|
|
|
|
|
AlphaMode::Opaque => {
|
|
|
|
|
opaque_phase.add(Opaque3d {
|
|
|
|
|
entity: *visible_entity,
|
|
|
|
|
draw_function: draw_opaque_pbr,
|
|
|
|
|
pipeline: pipeline_id,
|
|
|
|
|
distance,
|
|
|
|
|
});
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
AlphaMode::Mask(_) => {
|
|
|
|
|
alpha_mask_phase.add(AlphaMask3d {
|
|
|
|
|
entity: *visible_entity,
|
|
|
|
|
draw_function: draw_alpha_mask_pbr,
|
|
|
|
|
pipeline: pipeline_id,
|
|
|
|
|
distance,
|
|
|
|
|
});
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
AlphaMode::Blend
|
|
|
|
|
| AlphaMode::Premultiplied
|
|
|
|
|
| AlphaMode::Add
|
|
|
|
|
| AlphaMode::Multiply => {
|
|
|
|
|
transparent_phase.add(Transparent3d {
|
|
|
|
|
entity: *visible_entity,
|
|
|
|
|
draw_function: draw_transparent_pbr,
|
|
|
|
|
pipeline: pipeline_id,
|
|
|
|
|
distance,
|
|
|
|
|
});
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
2021-12-14 03:58:23 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
2021-12-25 21:45:43 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
2021-12-14 03:58:23 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/// Common [`Material`] properties, calculated for a specific material instance.
|
|
|
|
|
pub struct MaterialProperties {
|
|
|
|
|
/// The [`AlphaMode`] of this material.
|
|
|
|
|
pub alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
|
|
|
|
|
/// Add a bias to the view depth of the mesh which can be used to force a specific render order
|
|
|
|
|
/// for meshes with equal depth, to avoid z-fighting.
|
|
|
|
|
pub depth_bias: f32,
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/// Data prepared for a [`Material`] instance.
|
|
|
|
|
pub struct PreparedMaterial<T: Material> {
|
|
|
|
|
pub bindings: Vec<OwnedBindingResource>,
|
|
|
|
|
pub bind_group: BindGroup,
|
|
|
|
|
pub key: T::Data,
|
|
|
|
|
pub properties: MaterialProperties,
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|

Make `Resource` trait opt-in, requiring `#[derive(Resource)]` V2 (#5577)
*This PR description is an edited copy of #5007, written by @alice-i-cecile.*
# Objective
Follow-up to https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/2254. The `Resource` trait currently has a blanket implementation for all types that meet its bounds.
While ergonomic, this results in several drawbacks:
* it is possible to make confusing, silent mistakes such as inserting a function pointer (Foo) rather than a value (Foo::Bar) as a resource
* it is challenging to discover if a type is intended to be used as a resource
* we cannot later add customization options (see the [RFC](https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/blob/main/rfcs/27-derive-component.md) for the equivalent choice for Component).
* dependencies can use the same Rust type as a resource in invisibly conflicting ways
* raw Rust types used as resources cannot preserve privacy appropriately, as anyone able to access that type can read and write to internal values
* we cannot capture a definitive list of possible resources to display to users in an editor
## Notes to reviewers
* Review this commit-by-commit; there's effectively no back-tracking and there's a lot of churn in some of these commits.
*ira: My commits are not as well organized :')*
* I've relaxed the bound on Local to Send + Sync + 'static: I don't think these concerns apply there, so this can keep things simple. Storing e.g. a u32 in a Local is fine, because there's a variable name attached explaining what it does.
* I think this is a bad place for the Resource trait to live, but I've left it in place to make reviewing easier. IMO that's best tackled with https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/4981.
## Changelog
`Resource` is no longer automatically implemented for all matching types. Instead, use the new `#[derive(Resource)]` macro.
## Migration Guide
Add `#[derive(Resource)]` to all types you are using as a resource.
If you are using a third party type as a resource, wrap it in a tuple struct to bypass orphan rules. Consider deriving `Deref` and `DerefMut` to improve ergonomics.
`ClearColor` no longer implements `Component`. Using `ClearColor` as a component in 0.8 did nothing.
Use the `ClearColorConfig` in the `Camera3d` and `Camera2d` components instead.
Co-authored-by: Alice <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
2022-08-08 21:36:35 +00:00
|
|
|
#[derive(Resource)]
|
2023-02-13 19:33:51 +00:00
|
|
|
pub struct ExtractedMaterials<M: Material> {
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
extracted: Vec<(Handle<M>, M)>,
|
|
|
|
|
removed: Vec<Handle<M>>,
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
impl<M: Material> Default for ExtractedMaterials<M> {
|
|
|
|
|
fn default() -> Self {
|
|
|
|
|
Self {
|
|
|
|
|
extracted: Default::default(),
|
|
|
|
|
removed: Default::default(),
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/// Stores all prepared representations of [`Material`] assets for as long as they exist.
|

Make `Resource` trait opt-in, requiring `#[derive(Resource)]` V2 (#5577)
*This PR description is an edited copy of #5007, written by @alice-i-cecile.*
# Objective
Follow-up to https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/2254. The `Resource` trait currently has a blanket implementation for all types that meet its bounds.
While ergonomic, this results in several drawbacks:
* it is possible to make confusing, silent mistakes such as inserting a function pointer (Foo) rather than a value (Foo::Bar) as a resource
* it is challenging to discover if a type is intended to be used as a resource
* we cannot later add customization options (see the [RFC](https://github.com/bevyengine/rfcs/blob/main/rfcs/27-derive-component.md) for the equivalent choice for Component).
* dependencies can use the same Rust type as a resource in invisibly conflicting ways
* raw Rust types used as resources cannot preserve privacy appropriately, as anyone able to access that type can read and write to internal values
* we cannot capture a definitive list of possible resources to display to users in an editor
## Notes to reviewers
* Review this commit-by-commit; there's effectively no back-tracking and there's a lot of churn in some of these commits.
*ira: My commits are not as well organized :')*
* I've relaxed the bound on Local to Send + Sync + 'static: I don't think these concerns apply there, so this can keep things simple. Storing e.g. a u32 in a Local is fine, because there's a variable name attached explaining what it does.
* I think this is a bad place for the Resource trait to live, but I've left it in place to make reviewing easier. IMO that's best tackled with https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/issues/4981.
## Changelog
`Resource` is no longer automatically implemented for all matching types. Instead, use the new `#[derive(Resource)]` macro.
## Migration Guide
Add `#[derive(Resource)]` to all types you are using as a resource.
If you are using a third party type as a resource, wrap it in a tuple struct to bypass orphan rules. Consider deriving `Deref` and `DerefMut` to improve ergonomics.
`ClearColor` no longer implements `Component`. Using `ClearColor` as a component in 0.8 did nothing.
Use the `ClearColorConfig` in the `Camera3d` and `Camera2d` components instead.
Co-authored-by: Alice <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecile@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: devil-ira <justthecooldude@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
2022-08-08 21:36:35 +00:00
|
|
|
#[derive(Resource, Deref, DerefMut)]
|
|
|
|
|
pub struct RenderMaterials<T: Material>(pub HashMap<Handle<T>, PreparedMaterial<T>>);
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
impl<T: Material> Default for RenderMaterials<T> {
|
|
|
|
|
fn default() -> Self {
|
|
|
|
|
Self(Default::default())
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/// This system extracts all created or modified assets of the corresponding [`Material`] type
|
|
|
|
|
/// into the "render world".
|
2023-02-13 19:33:51 +00:00
|
|
|
pub fn extract_materials<M: Material>(
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
mut commands: Commands,
|

Make `RenderStage::Extract` run on the render world (#4402)
# Objective
- Currently, the `Extract` `RenderStage` is executed on the main world, with the render world available as a resource.
- However, when needing access to resources in the render world (e.g. to mutate them), the only way to do so was to get exclusive access to the whole `RenderWorld` resource.
- This meant that effectively only one extract which wrote to resources could run at a time.
- We didn't previously make `Extract`ing writing to the world a non-happy path, even though we want to discourage that.
## Solution
- Move the extract stage to run on the render world.
- Add the main world as a `MainWorld` resource.
- Add an `Extract` `SystemParam` as a convenience to access a (read only) `SystemParam` in the main world during `Extract`.
## Future work
It should be possible to avoid needing to use `get_or_spawn` for the render commands, since now the `Commands`' `Entities` matches up with the world being executed on.
We need to determine how this interacts with https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/3519
It's theoretically possible to remove the need for the `value` method on `Extract`. However, that requires slightly changing the `SystemParam` interface, which would make it more complicated. That would probably mess up the `SystemState` api too.
## Todo
I still need to add doc comments to `Extract`.
---
## Changelog
### Changed
- The `Extract` `RenderStage` now runs on the render world (instead of the main world as before).
You must use the `Extract` `SystemParam` to access the main world during the extract phase.
Resources on the render world can now be accessed using `ResMut` during extract.
### Removed
- `Commands::spawn_and_forget`. Use `Commands::get_or_spawn(e).insert_bundle(bundle)` instead
## Migration Guide
The `Extract` `RenderStage` now runs on the render world (instead of the main world as before).
You must use the `Extract` `SystemParam` to access the main world during the extract phase. `Extract` takes a single type parameter, which is any system parameter (such as `Res`, `Query` etc.). It will extract this from the main world, and returns the result of this extraction when `value` is called on it.
For example, if previously your extract system looked like:
```rust
fn extract_clouds(mut commands: Commands, clouds: Query<Entity, With<Cloud>>) {
for cloud in clouds.iter() {
commands.get_or_spawn(cloud).insert(Cloud);
}
}
```
the new version would be:
```rust
fn extract_clouds(mut commands: Commands, mut clouds: Extract<Query<Entity, With<Cloud>>>) {
for cloud in clouds.value().iter() {
commands.get_or_spawn(cloud).insert(Cloud);
}
}
```
The diff is:
```diff
--- a/src/clouds.rs
+++ b/src/clouds.rs
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
-fn extract_clouds(mut commands: Commands, clouds: Query<Entity, With<Cloud>>) {
- for cloud in clouds.iter() {
+fn extract_clouds(mut commands: Commands, mut clouds: Extract<Query<Entity, With<Cloud>>>) {
+ for cloud in clouds.value().iter() {
commands.get_or_spawn(cloud).insert(Cloud);
}
}
```
You can now also access resources from the render world using the normal system parameters during `Extract`:
```rust
fn extract_assets(mut render_assets: ResMut<MyAssets>, source_assets: Extract<Res<MyAssets>>) {
*render_assets = source_assets.clone();
}
```
Please note that all existing extract systems need to be updated to match this new style; even if they currently compile they will not run as expected. A warning will be emitted on a best-effort basis if this is not met.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
2022-07-08 23:56:33 +00:00
|
|
|
mut events: Extract<EventReader<AssetEvent<M>>>,
|
|
|
|
|
assets: Extract<Res<Assets<M>>>,
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
) {
|
|
|
|
|
let mut changed_assets = HashSet::default();
|
|
|
|
|
let mut removed = Vec::new();
|
|
|
|
|
for event in events.iter() {
|
|
|
|
|
match event {
|
|
|
|
|
AssetEvent::Created { handle } | AssetEvent::Modified { handle } => {
|

Make `RenderStage::Extract` run on the render world (#4402)
# Objective
- Currently, the `Extract` `RenderStage` is executed on the main world, with the render world available as a resource.
- However, when needing access to resources in the render world (e.g. to mutate them), the only way to do so was to get exclusive access to the whole `RenderWorld` resource.
- This meant that effectively only one extract which wrote to resources could run at a time.
- We didn't previously make `Extract`ing writing to the world a non-happy path, even though we want to discourage that.
## Solution
- Move the extract stage to run on the render world.
- Add the main world as a `MainWorld` resource.
- Add an `Extract` `SystemParam` as a convenience to access a (read only) `SystemParam` in the main world during `Extract`.
## Future work
It should be possible to avoid needing to use `get_or_spawn` for the render commands, since now the `Commands`' `Entities` matches up with the world being executed on.
We need to determine how this interacts with https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/3519
It's theoretically possible to remove the need for the `value` method on `Extract`. However, that requires slightly changing the `SystemParam` interface, which would make it more complicated. That would probably mess up the `SystemState` api too.
## Todo
I still need to add doc comments to `Extract`.
---
## Changelog
### Changed
- The `Extract` `RenderStage` now runs on the render world (instead of the main world as before).
You must use the `Extract` `SystemParam` to access the main world during the extract phase.
Resources on the render world can now be accessed using `ResMut` during extract.
### Removed
- `Commands::spawn_and_forget`. Use `Commands::get_or_spawn(e).insert_bundle(bundle)` instead
## Migration Guide
The `Extract` `RenderStage` now runs on the render world (instead of the main world as before).
You must use the `Extract` `SystemParam` to access the main world during the extract phase. `Extract` takes a single type parameter, which is any system parameter (such as `Res`, `Query` etc.). It will extract this from the main world, and returns the result of this extraction when `value` is called on it.
For example, if previously your extract system looked like:
```rust
fn extract_clouds(mut commands: Commands, clouds: Query<Entity, With<Cloud>>) {
for cloud in clouds.iter() {
commands.get_or_spawn(cloud).insert(Cloud);
}
}
```
the new version would be:
```rust
fn extract_clouds(mut commands: Commands, mut clouds: Extract<Query<Entity, With<Cloud>>>) {
for cloud in clouds.value().iter() {
commands.get_or_spawn(cloud).insert(Cloud);
}
}
```
The diff is:
```diff
--- a/src/clouds.rs
+++ b/src/clouds.rs
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
-fn extract_clouds(mut commands: Commands, clouds: Query<Entity, With<Cloud>>) {
- for cloud in clouds.iter() {
+fn extract_clouds(mut commands: Commands, mut clouds: Extract<Query<Entity, With<Cloud>>>) {
+ for cloud in clouds.value().iter() {
commands.get_or_spawn(cloud).insert(Cloud);
}
}
```
You can now also access resources from the render world using the normal system parameters during `Extract`:
```rust
fn extract_assets(mut render_assets: ResMut<MyAssets>, source_assets: Extract<Res<MyAssets>>) {
*render_assets = source_assets.clone();
}
```
Please note that all existing extract systems need to be updated to match this new style; even if they currently compile they will not run as expected. A warning will be emitted on a best-effort basis if this is not met.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
2022-07-08 23:56:33 +00:00
|
|
|
changed_assets.insert(handle.clone_weak());
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
AssetEvent::Removed { handle } => {
|
|
|
|
|
changed_assets.remove(handle);
|
|
|
|
|
removed.push(handle.clone_weak());
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
let mut extracted_assets = Vec::new();
|
|
|
|
|
for handle in changed_assets.drain() {
|

Make `RenderStage::Extract` run on the render world (#4402)
# Objective
- Currently, the `Extract` `RenderStage` is executed on the main world, with the render world available as a resource.
- However, when needing access to resources in the render world (e.g. to mutate them), the only way to do so was to get exclusive access to the whole `RenderWorld` resource.
- This meant that effectively only one extract which wrote to resources could run at a time.
- We didn't previously make `Extract`ing writing to the world a non-happy path, even though we want to discourage that.
## Solution
- Move the extract stage to run on the render world.
- Add the main world as a `MainWorld` resource.
- Add an `Extract` `SystemParam` as a convenience to access a (read only) `SystemParam` in the main world during `Extract`.
## Future work
It should be possible to avoid needing to use `get_or_spawn` for the render commands, since now the `Commands`' `Entities` matches up with the world being executed on.
We need to determine how this interacts with https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/pull/3519
It's theoretically possible to remove the need for the `value` method on `Extract`. However, that requires slightly changing the `SystemParam` interface, which would make it more complicated. That would probably mess up the `SystemState` api too.
## Todo
I still need to add doc comments to `Extract`.
---
## Changelog
### Changed
- The `Extract` `RenderStage` now runs on the render world (instead of the main world as before).
You must use the `Extract` `SystemParam` to access the main world during the extract phase.
Resources on the render world can now be accessed using `ResMut` during extract.
### Removed
- `Commands::spawn_and_forget`. Use `Commands::get_or_spawn(e).insert_bundle(bundle)` instead
## Migration Guide
The `Extract` `RenderStage` now runs on the render world (instead of the main world as before).
You must use the `Extract` `SystemParam` to access the main world during the extract phase. `Extract` takes a single type parameter, which is any system parameter (such as `Res`, `Query` etc.). It will extract this from the main world, and returns the result of this extraction when `value` is called on it.
For example, if previously your extract system looked like:
```rust
fn extract_clouds(mut commands: Commands, clouds: Query<Entity, With<Cloud>>) {
for cloud in clouds.iter() {
commands.get_or_spawn(cloud).insert(Cloud);
}
}
```
the new version would be:
```rust
fn extract_clouds(mut commands: Commands, mut clouds: Extract<Query<Entity, With<Cloud>>>) {
for cloud in clouds.value().iter() {
commands.get_or_spawn(cloud).insert(Cloud);
}
}
```
The diff is:
```diff
--- a/src/clouds.rs
+++ b/src/clouds.rs
@@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
-fn extract_clouds(mut commands: Commands, clouds: Query<Entity, With<Cloud>>) {
- for cloud in clouds.iter() {
+fn extract_clouds(mut commands: Commands, mut clouds: Extract<Query<Entity, With<Cloud>>>) {
+ for cloud in clouds.value().iter() {
commands.get_or_spawn(cloud).insert(Cloud);
}
}
```
You can now also access resources from the render world using the normal system parameters during `Extract`:
```rust
fn extract_assets(mut render_assets: ResMut<MyAssets>, source_assets: Extract<Res<MyAssets>>) {
*render_assets = source_assets.clone();
}
```
Please note that all existing extract systems need to be updated to match this new style; even if they currently compile they will not run as expected. A warning will be emitted on a best-effort basis if this is not met.
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <mcanders1@gmail.com>
2022-07-08 23:56:33 +00:00
|
|
|
if let Some(asset) = assets.get(&handle) {
|
|
|
|
|
extracted_assets.push((handle, asset.clone()));
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
commands.insert_resource(ExtractedMaterials {
|
|
|
|
|
extracted: extracted_assets,
|
|
|
|
|
removed,
|
|
|
|
|
});
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/// All [`Material`] values of a given type that should be prepared next frame.
|
|
|
|
|
pub struct PrepareNextFrameMaterials<M: Material> {
|
|
|
|
|
assets: Vec<(Handle<M>, M)>,
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
impl<M: Material> Default for PrepareNextFrameMaterials<M> {
|
|
|
|
|
fn default() -> Self {
|
|
|
|
|
Self {
|
|
|
|
|
assets: Default::default(),
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/// This system prepares all assets of the corresponding [`Material`] type
|
|
|
|
|
/// which where extracted this frame for the GPU.
|
2023-02-13 19:33:51 +00:00
|
|
|
pub fn prepare_materials<M: Material>(
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
mut prepare_next_frame: Local<PrepareNextFrameMaterials<M>>,
|
|
|
|
|
mut extracted_assets: ResMut<ExtractedMaterials<M>>,
|
|
|
|
|
mut render_materials: ResMut<RenderMaterials<M>>,
|
|
|
|
|
render_device: Res<RenderDevice>,
|
|
|
|
|
images: Res<RenderAssets<Image>>,
|
|
|
|
|
fallback_image: Res<FallbackImage>,
|
|
|
|
|
pipeline: Res<MaterialPipeline<M>>,
|
|
|
|
|
) {
|
2022-11-06 01:42:15 +00:00
|
|
|
let queued_assets = std::mem::take(&mut prepare_next_frame.assets);
|
|
|
|
|
for (handle, material) in queued_assets.into_iter() {
|

Better Materials: AsBindGroup trait and derive, simpler Material trait (#5053)
# Objective
This PR reworks Bevy's Material system, making the user experience of defining Materials _much_ nicer. Bevy's previous material system leaves a lot to be desired:
* Materials require manually implementing the `RenderAsset` trait, which involves manually generating the bind group, handling gpu buffer data transfer, looking up image textures, etc. Even the simplest single-texture material involves writing ~80 unnecessary lines of code. This was never the long term plan.
* There are two material traits, which is confusing, hard to document, and often redundant: `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial`. `Material` implicitly implements `SpecializedMaterial`, and `SpecializedMaterial` is used in most high level apis to support both use cases. Most users shouldn't need to think about specialization at all (I consider it a "power-user tool"), so the fact that `SpecializedMaterial` is front-and-center in our apis is a miss.
* Implementing either material trait involves a lot of "type soup". The "prepared asset" parameter is particularly heinous: `&<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset`. Defining vertex and fragment shaders is also more verbose than it needs to be.
## Solution
Say hello to the new `Material` system:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
```
Thats it! This same material would have required [~80 lines of complicated "type heavy" code](https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/blob/v0.7.0/examples/shader/shader_material.rs) in the old Material system. Now it is just 14 lines of simple, readable code.
This is thanks to a new consolidated `Material` trait and the new `AsBindGroup` trait / derive.
### The new `Material` trait
The old "split" `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been removed in favor of a new consolidated `Material` trait. All of the functions on the trait are optional.
The difficulty of implementing `Material` has been reduced by simplifying dataflow and removing type complexity:
```rust
// Old
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn alpha_mode(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> AlphaMode {
render_asset.alpha_mode
}
}
// New
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn alpha_mode(&self) -> AlphaMode {
self.alpha_mode
}
}
```
Specialization is still supported, but it is hidden by default under the `specialize()` function (more on this later).
### The `AsBindGroup` trait / derive
The `Material` trait now requires the `AsBindGroup` derive. This can be implemented manually relatively easily, but deriving it will almost always be preferable.
Field attributes like `uniform` and `texture` are used to define which fields should be bindings,
what their binding type is, and what index they should be bound at:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding looks like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
[[group(1), binding(1)]]
var color_texture: texture_2d<f32>;
[[group(1), binding(2)]]
var color_sampler: sampler;
```
Note that the "group" index is determined by the usage context. It is not defined in `AsBindGroup`. Bevy material bind groups are bound to group 1.
The following field-level attributes are supported:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX)`
* The field will be converted to a shader-compatible type using the `ShaderType` trait, written to a `Buffer`, and bound as a uniform. It can also be derived for custom structs.
* `texture(BINDING_INDEX)`
* This field's `Handle<Image>` will be used to look up the matching `Texture` gpu resource, which will be bound as a texture in shaders. The field will be assumed to implement `Into<Option<Handle<Image>>>`. In practice, most fields should be a `Handle<Image>` or `Option<Handle<Image>>`. If the value of an `Option<Handle<Image>>` is `None`, the new `FallbackImage` resource will be used instead. This attribute can be used in conjunction with a `sampler` binding attribute (with a different binding index).
* `sampler(BINDING_INDEX)`
* Behaves exactly like the `texture` attribute, but sets the Image's sampler binding instead of the texture.
Note that fields without field-level binding attributes will be ignored.
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
this_field_is_ignored: String,
}
```
As mentioned above, `Option<Handle<Image>>` is also supported:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
}
```
This is useful if you want a texture to be optional. When the value is `None`, the `FallbackImage` will be used for the binding instead, which defaults to "pure white".
Field uniforms with the same binding index will be combined into a single binding:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[uniform(0)]
roughness: f32,
}
```
In WGSL shaders, the binding would look like this:
```wgsl
struct CoolMaterial {
color: vec4<f32>;
roughness: f32;
};
[[group(1), binding(0)]]
var<uniform> material: CoolMaterial;
```
Some less common scenarios will require "struct-level" attributes. These are the currently supported struct-level attributes:
* `uniform(BINDING_INDEX, ConvertedShaderType)`
* Similar to the field-level `uniform` attribute, but instead the entire `AsBindGroup` value is converted to `ConvertedShaderType`, which must implement `ShaderType`. This is useful if more complicated conversion logic is required.
* `bind_group_data(DataType)`
* The `AsBindGroup` type will be converted to some `DataType` using `Into<DataType>` and stored as `AsBindGroup::Data` as part of the `AsBindGroup::as_bind_group` call. This is useful if data needs to be stored alongside the generated bind group, such as a unique identifier for a material's bind group. The most common use case for this attribute is "shader pipeline specialization".
The previous `CoolMaterial` example illustrating "combining multiple field-level uniform attributes with the same binding index" can
also be equivalently represented with a single struct-level uniform attribute:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
#[uniform(0, CoolMaterialUniform)]
struct CoolMaterial {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
#[derive(ShaderType)]
struct CoolMaterialUniform {
color: Color,
roughness: f32,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialUniform {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialUniform {
CoolMaterialUniform {
color: material.color,
roughness: material.roughness,
}
}
}
```
### Material Specialization
Material shader specialization is now _much_ simpler:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
#[bind_group_data(CoolMaterialKey)]
struct CoolMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
is_red: bool,
}
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Hash, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: bool,
}
impl From<&CoolMaterial> for CoolMaterialKey {
fn from(material: &CoolMaterial) -> CoolMaterialKey {
CoolMaterialKey {
is_red: material.is_red,
}
}
}
impl Material for CoolMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"cool_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
if key.bind_group_data.is_red {
let fragment = descriptor.fragment.as_mut().unwrap();
fragment.shader_defs.push("IS_RED".to_string());
}
Ok(())
}
}
```
Setting `bind_group_data` is not required for specialization (it defaults to `()`). Scenarios like "custom vertex attributes" also benefit from this system:
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn vertex_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
fn specialize(
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<Self>,
descriptor: &mut RenderPipelineDescriptor,
layout: &MeshVertexBufferLayout,
key: MaterialPipelineKey<Self>,
) -> Result<(), SpecializedMeshPipelineError> {
let vertex_layout = layout.get_layout(&[
Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION.at_shader_location(0),
ATTRIBUTE_BLEND_COLOR.at_shader_location(1),
])?;
descriptor.vertex.buffers = vec![vertex_layout];
Ok(())
}
}
```
### Ported `StandardMaterial` to the new `Material` system
Bevy's built-in PBR material uses the new Material system (including the AsBindGroup derive):
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup, Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "7494888b-c082-457b-aacf-517228cc0c22"]
#[bind_group_data(StandardMaterialKey)]
#[uniform(0, StandardMaterialUniform)]
pub struct StandardMaterial {
pub base_color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
pub base_color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
/* other fields omitted for brevity */
```
### Ported Bevy examples to the new `Material` system
The overall complexity of Bevy's "custom shader examples" has gone down significantly. Take a look at the diffs if you want a dopamine spike.
Please note that while this PR has a net increase in "lines of code", most of those extra lines come from added documentation. There is a significant reduction
in the overall complexity of the code (even accounting for the new derive logic).
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `AsBindGroup` trait and derive, which make it much easier to transfer data to the gpu and generate bind groups for a given type.
### Changed
* The old `Material` and `SpecializedMaterial` traits have been replaced by a consolidated (much simpler) `Material` trait. Materials no longer implement `RenderAsset`.
* `StandardMaterial` was ported to the new material system. There are no user-facing api changes to the `StandardMaterial` struct api, but it now implements `AsBindGroup` and `Material` instead of `RenderAsset` and `SpecializedMaterial`.
## Migration Guide
The Material system has been reworked to be much simpler. We've removed a lot of boilerplate with the new `AsBindGroup` derive and the `Material` trait is simpler as well!
### Bevy 0.7 (old)
```rust
#[derive(Debug, Clone, TypeUuid)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
#[derive(Clone)]
pub struct GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: Buffer,
bind_group: BindGroup,
}
impl RenderAsset for CustomMaterial {
type ExtractedAsset = CustomMaterial;
type PreparedAsset = GpuCustomMaterial;
type Param = (SRes<RenderDevice>, SRes<MaterialPipeline<Self>>);
fn extract_asset(&self) -> Self::ExtractedAsset {
self.clone()
}
fn prepare_asset(
extracted_asset: Self::ExtractedAsset,
(render_device, material_pipeline): &mut SystemParamItem<Self::Param>,
) -> Result<Self::PreparedAsset, PrepareAssetError<Self::ExtractedAsset>> {
let color = Vec4::from_slice(&extracted_asset.color.as_linear_rgba_f32());
let byte_buffer = [0u8; Vec4::SIZE.get() as usize];
let mut buffer = encase::UniformBuffer::new(byte_buffer);
buffer.write(&color).unwrap();
let buffer = render_device.create_buffer_with_data(&BufferInitDescriptor {
contents: buffer.as_ref(),
label: None,
usage: BufferUsages::UNIFORM | BufferUsages::COPY_DST,
});
let (texture_view, texture_sampler) = if let Some(result) = material_pipeline
.mesh_pipeline
.get_image_texture(gpu_images, &Some(extracted_asset.color_texture.clone()))
{
result
} else {
return Err(PrepareAssetError::RetryNextUpdate(extracted_asset));
};
let bind_group = render_device.create_bind_group(&BindGroupDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: buffer.as_entire_binding(),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 0,
resource: BindingResource::TextureView(texture_view),
},
BindGroupEntry {
binding: 1,
resource: BindingResource::Sampler(texture_sampler),
},
],
label: None,
layout: &material_pipeline.material_layout,
});
Ok(GpuCustomMaterial {
_buffer: buffer,
bind_group,
})
}
}
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader(asset_server: &AssetServer) -> Option<Handle<Shader>> {
Some(asset_server.load("custom_material.wgsl"))
}
fn bind_group(render_asset: &<Self as RenderAsset>::PreparedAsset) -> &BindGroup {
&render_asset.bind_group
}
fn bind_group_layout(render_device: &RenderDevice) -> BindGroupLayout {
render_device.create_bind_group_layout(&BindGroupLayoutDescriptor {
entries: &[
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 0,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Buffer {
ty: BufferBindingType::Uniform,
has_dynamic_offset: false,
min_binding_size: Some(Vec4::min_size()),
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 1,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Texture {
multisampled: false,
sample_type: TextureSampleType::Float { filterable: true },
view_dimension: TextureViewDimension::D2Array,
},
count: None,
},
BindGroupLayoutEntry {
binding: 2,
visibility: ShaderStages::FRAGMENT,
ty: BindingType::Sampler(SamplerBindingType::Filtering),
count: None,
},
],
label: None,
})
}
}
```
### Bevy 0.8 (new)
```rust
impl Material for CustomMaterial {
fn fragment_shader() -> ShaderRef {
"custom_material.wgsl".into()
}
}
#[derive(AsBindGroup, TypeUuid, Debug, Clone)]
#[uuid = "f690fdae-d598-45ab-8225-97e2a3f056e0"]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform(0)]
color: Color,
#[texture(1)]
#[sampler(2)]
color_texture: Handle<Image>,
}
```
## Future Work
* Add support for more binding types (cubemaps, buffers, etc). This PR intentionally includes a bare minimum number of binding types to keep "reviewability" in check.
* Consider optionally eliding binding indices using binding names. `AsBindGroup` could pass in (optional?) reflection info as a "hint".
* This would make it possible for the derive to do this:
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[uniform]
color: Color,
#[texture]
#[sampler]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or this
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
#[binding]
color: Color,
#[binding]
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* Or even this (if we flip to "include bindings by default")
```rust
#[derive(AsBindGroup)]
pub struct CustomMaterial {
color: Color,
color_texture: Option<Handle<Image>>,
#[binding(ignore)]
alpha_mode: AlphaMode,
}
```
* If we add the option to define custom draw functions for materials (which could be done in a type-erased way), I think that would be enough to support extra non-material bindings. Worth considering!
2022-06-30 23:48:46 +00:00
|
|
|
match prepare_material(
|
|
|
|
|
&material,
|
|
|
|
|
&render_device,
|
|
|
|
|
&images,
|
|
|
|
|
&fallback_image,
|
|
|
|
|
&pipeline,
|
|
|
|
|
) {
|
|
|
|
|
Ok(prepared_asset) => {
|
|
|
|
|
render_materials.insert(handle, prepared_asset);
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
Err(AsBindGroupError::RetryNextUpdate) => {
|
|
|
|
|
prepare_next_frame.assets.push((handle, material));
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
for removed in std::mem::take(&mut extracted_assets.removed) {
|
|
|
|
|
render_materials.remove(&removed);
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
for (handle, material) in std::mem::take(&mut extracted_assets.extracted) {
|
|
|
|
|
match prepare_material(
|
|
|
|
|
&material,
|
|
|
|
|
&render_device,
|
|
|
|
|
&images,
|
|
|
|
|
&fallback_image,
|
|
|
|
|
&pipeline,
|
|
|
|
|
) {
|
|
|
|
|
Ok(prepared_asset) => {
|
|
|
|
|
render_materials.insert(handle, prepared_asset);
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
Err(AsBindGroupError::RetryNextUpdate) => {
|
|
|
|
|
prepare_next_frame.assets.push((handle, material));
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
fn prepare_material<M: Material>(
|
|
|
|
|
material: &M,
|
|
|
|
|
render_device: &RenderDevice,
|
|
|
|
|
images: &RenderAssets<Image>,
|
|
|
|
|
fallback_image: &FallbackImage,
|
|
|
|
|
pipeline: &MaterialPipeline<M>,
|
|
|
|
|
) -> Result<PreparedMaterial<M>, AsBindGroupError> {
|
|
|
|
|
let prepared = material.as_bind_group(
|
|
|
|
|
&pipeline.material_layout,
|
|
|
|
|
render_device,
|
|
|
|
|
images,
|
|
|
|
|
fallback_image,
|
|
|
|
|
)?;
|
|
|
|
|
Ok(PreparedMaterial {
|
|
|
|
|
bindings: prepared.bindings,
|
|
|
|
|
bind_group: prepared.bind_group,
|
|
|
|
|
key: prepared.data,
|
|
|
|
|
properties: MaterialProperties {
|
|
|
|
|
alpha_mode: material.alpha_mode(),
|
|
|
|
|
depth_bias: material.depth_bias(),
|
|
|
|
|
},
|
|
|
|
|
})
|
|
|
|
|
}
|