
Camera Driven Viewports (#4898)
# Objective
Users should be able to render cameras to specific areas of a render target, which enables scenarios like split screen, minimaps, etc.
Builds on the new Camera Driven Rendering added here: #4745
Fixes: #202
Alternative to #1389 and #3626 (which are incompatible with the new Camera Driven Rendering)
## Solution
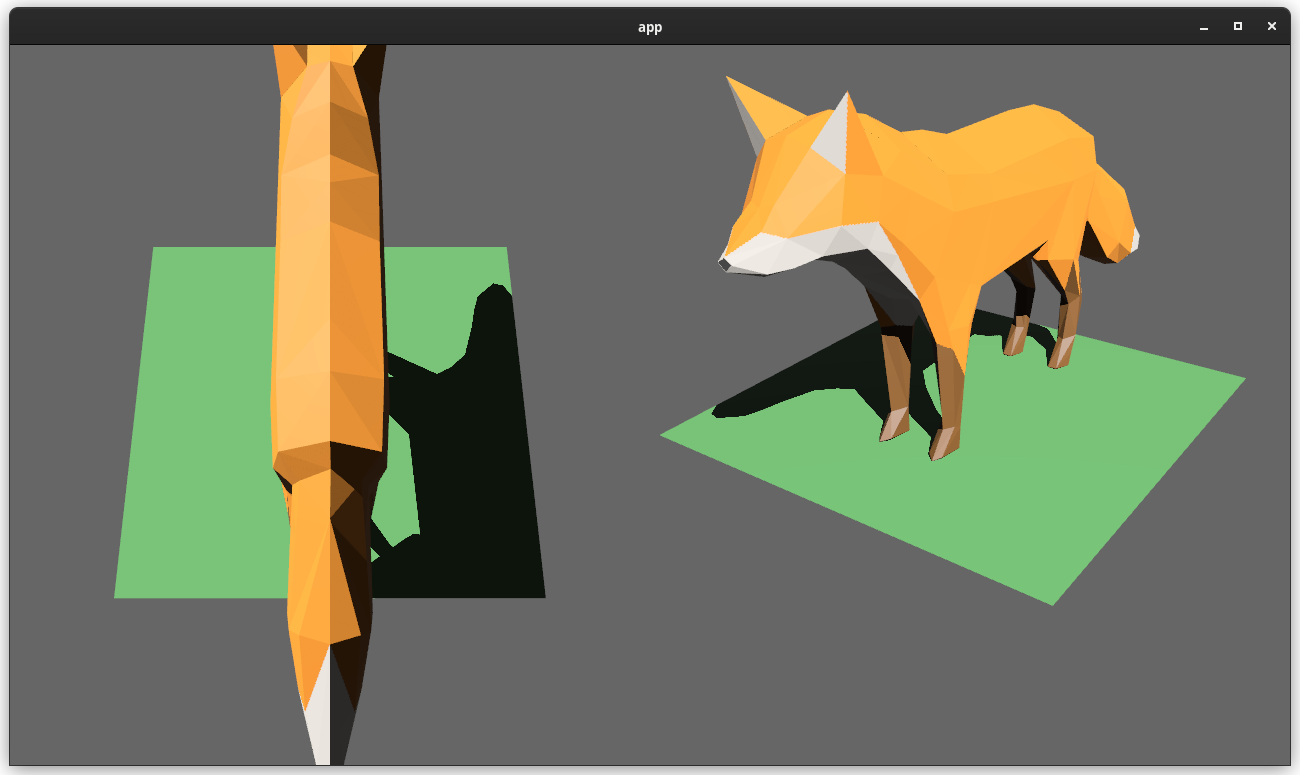
Cameras can now configure an optional "viewport", which defines a rectangle within their render target to draw to. If a `Viewport` is defined, the camera's `CameraProjection`, `View`, and visibility calculations will use the viewport configuration instead of the full render target.
```rust
// This camera will render to the first half of the primary window (on the left side).
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle {
camera: Camera {
viewport: Some(Viewport {
physical_position: UVec2::new(0, 0),
physical_size: UVec2::new(window.physical_width() / 2, window.physical_height()),
depth: 0.0..1.0,
}),
..default()
},
..default()
});
```
To account for this, the `Camera` component has received a few adjustments:
* `Camera` now has some new getter functions:
* `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, `projection_matrix`
* All computed camera values are now private and live on the `ComputedCameraValues` field (logical/physical width/height, the projection matrix). They are now exposed on `Camera` via getters/setters This wasn't _needed_ for viewports, but it was long overdue.
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `Camera` components now have a `viewport` field, which can be set to draw to a portion of a render target instead of the full target.
* `Camera` component has some new functions: `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, and `projection_matrix`
* Added a new split_screen example illustrating how to render two cameras to the same scene
## Migration Guide
`Camera::projection_matrix` is no longer a public field. Use the new `Camera::projection_matrix()` method instead:
```rust
// Bevy 0.7
let projection = camera.projection_matrix;
// Bevy 0.8
let projection = camera.projection_matrix();
```
2022-06-05 00:27:49 +00:00
|
|
|
//! Renders two cameras to the same window to accomplish "split screen".
|
|
|
|
|
|
2022-08-30 19:52:11 +00:00
|
|
|
use std::f32::consts::PI;
|
|
|
|
|
|

Camera Driven Viewports (#4898)
# Objective
Users should be able to render cameras to specific areas of a render target, which enables scenarios like split screen, minimaps, etc.
Builds on the new Camera Driven Rendering added here: #4745
Fixes: #202
Alternative to #1389 and #3626 (which are incompatible with the new Camera Driven Rendering)
## Solution

Cameras can now configure an optional "viewport", which defines a rectangle within their render target to draw to. If a `Viewport` is defined, the camera's `CameraProjection`, `View`, and visibility calculations will use the viewport configuration instead of the full render target.
```rust
// This camera will render to the first half of the primary window (on the left side).
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle {
camera: Camera {
viewport: Some(Viewport {
physical_position: UVec2::new(0, 0),
physical_size: UVec2::new(window.physical_width() / 2, window.physical_height()),
depth: 0.0..1.0,
}),
..default()
},
..default()
});
```
To account for this, the `Camera` component has received a few adjustments:
* `Camera` now has some new getter functions:
* `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, `projection_matrix`
* All computed camera values are now private and live on the `ComputedCameraValues` field (logical/physical width/height, the projection matrix). They are now exposed on `Camera` via getters/setters This wasn't _needed_ for viewports, but it was long overdue.
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `Camera` components now have a `viewport` field, which can be set to draw to a portion of a render target instead of the full target.
* `Camera` component has some new functions: `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, and `projection_matrix`
* Added a new split_screen example illustrating how to render two cameras to the same scene
## Migration Guide
`Camera::projection_matrix` is no longer a public field. Use the new `Camera::projection_matrix()` method instead:
```rust
// Bevy 0.7
let projection = camera.projection_matrix;
// Bevy 0.8
let projection = camera.projection_matrix();
```
2022-06-05 00:27:49 +00:00
|
|
|
use bevy::{
|
2024-03-05 22:19:59 -07:00
|
|
|
pbr::CascadeShadowConfigBuilder, prelude::*, render::camera::Viewport, window::WindowResized,
|

Camera Driven Viewports (#4898)
# Objective
Users should be able to render cameras to specific areas of a render target, which enables scenarios like split screen, minimaps, etc.
Builds on the new Camera Driven Rendering added here: #4745
Fixes: #202
Alternative to #1389 and #3626 (which are incompatible with the new Camera Driven Rendering)
## Solution

Cameras can now configure an optional "viewport", which defines a rectangle within their render target to draw to. If a `Viewport` is defined, the camera's `CameraProjection`, `View`, and visibility calculations will use the viewport configuration instead of the full render target.
```rust
// This camera will render to the first half of the primary window (on the left side).
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle {
camera: Camera {
viewport: Some(Viewport {
physical_position: UVec2::new(0, 0),
physical_size: UVec2::new(window.physical_width() / 2, window.physical_height()),
depth: 0.0..1.0,
}),
..default()
},
..default()
});
```
To account for this, the `Camera` component has received a few adjustments:
* `Camera` now has some new getter functions:
* `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, `projection_matrix`
* All computed camera values are now private and live on the `ComputedCameraValues` field (logical/physical width/height, the projection matrix). They are now exposed on `Camera` via getters/setters This wasn't _needed_ for viewports, but it was long overdue.
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `Camera` components now have a `viewport` field, which can be set to draw to a portion of a render target instead of the full target.
* `Camera` component has some new functions: `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, and `projection_matrix`
* Added a new split_screen example illustrating how to render two cameras to the same scene
## Migration Guide
`Camera::projection_matrix` is no longer a public field. Use the new `Camera::projection_matrix()` method instead:
```rust
// Bevy 0.7
let projection = camera.projection_matrix;
// Bevy 0.8
let projection = camera.projection_matrix();
```
2022-06-05 00:27:49 +00:00
|
|
|
};
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
fn main() {
|
|
|
|
|
App::new()
|
|
|
|
|
.add_plugins(DefaultPlugins)
|
2023-03-17 18:45:34 -07:00
|
|
|
.add_systems(Startup, setup)
|
2024-01-16 01:39:10 +01:00
|
|
|
.add_systems(Update, (set_camera_viewports, button_system))
|

Camera Driven Viewports (#4898)
# Objective
Users should be able to render cameras to specific areas of a render target, which enables scenarios like split screen, minimaps, etc.
Builds on the new Camera Driven Rendering added here: #4745
Fixes: #202
Alternative to #1389 and #3626 (which are incompatible with the new Camera Driven Rendering)
## Solution

Cameras can now configure an optional "viewport", which defines a rectangle within their render target to draw to. If a `Viewport` is defined, the camera's `CameraProjection`, `View`, and visibility calculations will use the viewport configuration instead of the full render target.
```rust
// This camera will render to the first half of the primary window (on the left side).
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle {
camera: Camera {
viewport: Some(Viewport {
physical_position: UVec2::new(0, 0),
physical_size: UVec2::new(window.physical_width() / 2, window.physical_height()),
depth: 0.0..1.0,
}),
..default()
},
..default()
});
```
To account for this, the `Camera` component has received a few adjustments:
* `Camera` now has some new getter functions:
* `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, `projection_matrix`
* All computed camera values are now private and live on the `ComputedCameraValues` field (logical/physical width/height, the projection matrix). They are now exposed on `Camera` via getters/setters This wasn't _needed_ for viewports, but it was long overdue.
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `Camera` components now have a `viewport` field, which can be set to draw to a portion of a render target instead of the full target.
* `Camera` component has some new functions: `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, and `projection_matrix`
* Added a new split_screen example illustrating how to render two cameras to the same scene
## Migration Guide
`Camera::projection_matrix` is no longer a public field. Use the new `Camera::projection_matrix()` method instead:
```rust
// Bevy 0.7
let projection = camera.projection_matrix;
// Bevy 0.8
let projection = camera.projection_matrix();
```
2022-06-05 00:27:49 +00:00
|
|
|
.run();
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/// set up a simple 3D scene
|
|
|
|
|
fn setup(
|
|
|
|
|
mut commands: Commands,
|
|
|
|
|
asset_server: Res<AssetServer>,
|
|
|
|
|
mut meshes: ResMut<Assets<Mesh>>,
|
|
|
|
|
mut materials: ResMut<Assets<StandardMaterial>>,
|
|
|
|
|
) {
|
|
|
|
|
// plane
|

Spawn now takes a Bundle (#6054)
# Objective
Now that we can consolidate Bundles and Components under a single insert (thanks to #2975 and #6039), almost 100% of world spawns now look like `world.spawn().insert((Some, Tuple, Here))`. Spawning an entity without any components is an extremely uncommon pattern, so it makes sense to give spawn the "first class" ergonomic api. This consolidated api should be made consistent across all spawn apis (such as World and Commands).
## Solution
All `spawn` apis (`World::spawn`, `Commands:;spawn`, `ChildBuilder::spawn`, and `WorldChildBuilder::spawn`) now accept a bundle as input:
```rust
// before:
commands
.spawn()
.insert((A, B, C));
world
.spawn()
.insert((A, B, C);
// after
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
world.spawn((A, B, C));
```
All existing instances of `spawn_bundle` have been deprecated in favor of the new `spawn` api. A new `spawn_empty` has been added, replacing the old `spawn` api.
By allowing `world.spawn(some_bundle)` to replace `world.spawn().insert(some_bundle)`, this opened the door to removing the initial entity allocation in the "empty" archetype / table done in `spawn()` (and subsequent move to the actual archetype in `.insert(some_bundle)`).
This improves spawn performance by over 10%:

To take this measurement, I added a new `world_spawn` benchmark.
Unfortunately, optimizing `Commands::spawn` is slightly less trivial, as Commands expose the Entity id of spawned entities prior to actually spawning. Doing the optimization would (naively) require assurances that the `spawn(some_bundle)` command is applied before all other commands involving the entity (which would not necessarily be true, if memory serves). Optimizing `Commands::spawn` this way does feel possible, but it will require careful thought (and maybe some additional checks), which deserves its own PR. For now, it has the same performance characteristics of the current `Commands::spawn_bundle` on main.
**Note that 99% of this PR is simple renames and refactors. The only code that needs careful scrutiny is the new `World::spawn()` impl, which is relatively straightforward, but it has some new unsafe code (which re-uses battle tested BundlerSpawner code path).**
---
## Changelog
- All `spawn` apis (`World::spawn`, `Commands:;spawn`, `ChildBuilder::spawn`, and `WorldChildBuilder::spawn`) now accept a bundle as input
- All instances of `spawn_bundle` have been deprecated in favor of the new `spawn` api
- World and Commands now have `spawn_empty()`, which is equivalent to the old `spawn()` behavior.
## Migration Guide
```rust
// Old (0.8):
commands
.spawn()
.insert_bundle((A, B, C));
// New (0.9)
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
// Old (0.8):
commands.spawn_bundle((A, B, C));
// New (0.9)
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
// Old (0.8):
let entity = commands.spawn().id();
// New (0.9)
let entity = commands.spawn_empty().id();
// Old (0.8)
let entity = world.spawn().id();
// New (0.9)
let entity = world.spawn_empty();
```
2022-09-23 19:55:54 +00:00
|
|
|
commands.spawn(PbrBundle {
|
2024-02-08 20:01:34 +02:00
|
|
|
mesh: meshes.add(Plane3d::default().mesh().size(100.0, 100.0)),
|

Migrate from `LegacyColor` to `bevy_color::Color` (#12163)
# Objective
- As part of the migration process we need to a) see the end effect of
the migration on user ergonomics b) check for serious perf regressions
c) actually migrate the code
- To accomplish this, I'm going to attempt to migrate all of the
remaining user-facing usages of `LegacyColor` in one PR, being careful
to keep a clean commit history.
- Fixes #12056.
## Solution
I've chosen to use the polymorphic `Color` type as our standard
user-facing API.
- [x] Migrate `bevy_gizmos`.
- [x] Take `impl Into<Color>` in all `bevy_gizmos` APIs
- [x] Migrate sprites
- [x] Migrate UI
- [x] Migrate `ColorMaterial`
- [x] Migrate `MaterialMesh2D`
- [x] Migrate fog
- [x] Migrate lights
- [x] Migrate StandardMaterial
- [x] Migrate wireframes
- [x] Migrate clear color
- [x] Migrate text
- [x] Migrate gltf loader
- [x] Register color types for reflection
- [x] Remove `LegacyColor`
- [x] Make sure CI passes
Incidental improvements to ease migration:
- added `Color::srgba_u8`, `Color::srgba_from_array` and friends
- added `set_alpha`, `is_fully_transparent` and `is_fully_opaque` to the
`Alpha` trait
- add and immediately deprecate (lol) `Color::rgb` and friends in favor
of more explicit and consistent `Color::srgb`
- standardized on white and black for most example text colors
- added vector field traits to `LinearRgba`: ~~`Add`, `Sub`,
`AddAssign`, `SubAssign`,~~ `Mul<f32>` and `Div<f32>`. Multiplications
and divisions do not scale alpha. `Add` and `Sub` have been cut from
this PR.
- added `LinearRgba` and `Srgba` `RED/GREEN/BLUE`
- added `LinearRgba_to_f32_array` and `LinearRgba::to_u32`
## Migration Guide
Bevy's color types have changed! Wherever you used a
`bevy::render::Color`, a `bevy::color::Color` is used instead.
These are quite similar! Both are enums storing a color in a specific
color space (or to be more precise, using a specific color model).
However, each of the different color models now has its own type.
TODO...
- `Color::rgba`, `Color::rgb`, `Color::rbga_u8`, `Color::rgb_u8`,
`Color::rgb_from_array` are now `Color::srgba`, `Color::srgb`,
`Color::srgba_u8`, `Color::srgb_u8` and `Color::srgb_from_array`.
- `Color::set_a` and `Color::a` is now `Color::set_alpha` and
`Color::alpha`. These are part of the `Alpha` trait in `bevy_color`.
- `Color::is_fully_transparent` is now part of the `Alpha` trait in
`bevy_color`
- `Color::r`, `Color::set_r`, `Color::with_r` and the equivalents for
`g`, `b` `h`, `s` and `l` have been removed due to causing silent
relatively expensive conversions. Convert your `Color` into the desired
color space, perform your operations there, and then convert it back
into a polymorphic `Color` enum.
- `Color::hex` is now `Srgba::hex`. Call `.into` or construct a
`Color::Srgba` variant manually to convert it.
- `WireframeMaterial`, `ExtractedUiNode`, `ExtractedDirectionalLight`,
`ExtractedPointLight`, `ExtractedSpotLight` and `ExtractedSprite` now
store a `LinearRgba`, rather than a polymorphic `Color`
- `Color::rgb_linear` and `Color::rgba_linear` are now
`Color::linear_rgb` and `Color::linear_rgba`
- The various CSS color constants are no longer stored directly on
`Color`. Instead, they're defined in the `Srgba` color space, and
accessed via `bevy::color::palettes::css`. Call `.into()` on them to
convert them into a `Color` for quick debugging use, and consider using
the much prettier `tailwind` palette for prototyping.
- The `LIME_GREEN` color has been renamed to `LIMEGREEN` to comply with
the standard naming.
- Vector field arithmetic operations on `Color` (add, subtract, multiply
and divide by a f32) have been removed. Instead, convert your colors
into `LinearRgba` space, and perform your operations explicitly there.
This is particularly relevant when working with emissive or HDR colors,
whose color channel values are routinely outside of the ordinary 0 to 1
range.
- `Color::as_linear_rgba_f32` has been removed. Call
`LinearRgba::to_f32_array` instead, converting if needed.
- `Color::as_linear_rgba_u32` has been removed. Call
`LinearRgba::to_u32` instead, converting if needed.
- Several other color conversion methods to transform LCH or HSL colors
into float arrays or `Vec` types have been removed. Please reimplement
these externally or open a PR to re-add them if you found them
particularly useful.
- Various methods on `Color` such as `rgb` or `hsl` to convert the color
into a specific color space have been removed. Convert into
`LinearRgba`, then to the color space of your choice.
- Various implicitly-converting color value methods on `Color` such as
`r`, `g`, `b` or `h` have been removed. Please convert it into the color
space of your choice, then check these properties.
- `Color` no longer implements `AsBindGroup`. Store a `LinearRgba`
internally instead to avoid conversion costs.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecil@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Afonso Lage <lage.afonso@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Rob Parrett <robparrett@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Zachary Harrold <zac@harrold.com.au>
2024-02-29 14:35:12 -05:00
|
|
|
material: materials.add(Color::srgb(0.3, 0.5, 0.3)),
|

Camera Driven Viewports (#4898)
# Objective
Users should be able to render cameras to specific areas of a render target, which enables scenarios like split screen, minimaps, etc.
Builds on the new Camera Driven Rendering added here: #4745
Fixes: #202
Alternative to #1389 and #3626 (which are incompatible with the new Camera Driven Rendering)
## Solution

Cameras can now configure an optional "viewport", which defines a rectangle within their render target to draw to. If a `Viewport` is defined, the camera's `CameraProjection`, `View`, and visibility calculations will use the viewport configuration instead of the full render target.
```rust
// This camera will render to the first half of the primary window (on the left side).
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle {
camera: Camera {
viewport: Some(Viewport {
physical_position: UVec2::new(0, 0),
physical_size: UVec2::new(window.physical_width() / 2, window.physical_height()),
depth: 0.0..1.0,
}),
..default()
},
..default()
});
```
To account for this, the `Camera` component has received a few adjustments:
* `Camera` now has some new getter functions:
* `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, `projection_matrix`
* All computed camera values are now private and live on the `ComputedCameraValues` field (logical/physical width/height, the projection matrix). They are now exposed on `Camera` via getters/setters This wasn't _needed_ for viewports, but it was long overdue.
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `Camera` components now have a `viewport` field, which can be set to draw to a portion of a render target instead of the full target.
* `Camera` component has some new functions: `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, and `projection_matrix`
* Added a new split_screen example illustrating how to render two cameras to the same scene
## Migration Guide
`Camera::projection_matrix` is no longer a public field. Use the new `Camera::projection_matrix()` method instead:
```rust
// Bevy 0.7
let projection = camera.projection_matrix;
// Bevy 0.8
let projection = camera.projection_matrix();
```
2022-06-05 00:27:49 +00:00
|
|
|
..default()
|
|
|
|
|
});
|
|
|
|
|
|

Spawn now takes a Bundle (#6054)
# Objective
Now that we can consolidate Bundles and Components under a single insert (thanks to #2975 and #6039), almost 100% of world spawns now look like `world.spawn().insert((Some, Tuple, Here))`. Spawning an entity without any components is an extremely uncommon pattern, so it makes sense to give spawn the "first class" ergonomic api. This consolidated api should be made consistent across all spawn apis (such as World and Commands).
## Solution
All `spawn` apis (`World::spawn`, `Commands:;spawn`, `ChildBuilder::spawn`, and `WorldChildBuilder::spawn`) now accept a bundle as input:
```rust
// before:
commands
.spawn()
.insert((A, B, C));
world
.spawn()
.insert((A, B, C);
// after
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
world.spawn((A, B, C));
```
All existing instances of `spawn_bundle` have been deprecated in favor of the new `spawn` api. A new `spawn_empty` has been added, replacing the old `spawn` api.
By allowing `world.spawn(some_bundle)` to replace `world.spawn().insert(some_bundle)`, this opened the door to removing the initial entity allocation in the "empty" archetype / table done in `spawn()` (and subsequent move to the actual archetype in `.insert(some_bundle)`).
This improves spawn performance by over 10%:

To take this measurement, I added a new `world_spawn` benchmark.
Unfortunately, optimizing `Commands::spawn` is slightly less trivial, as Commands expose the Entity id of spawned entities prior to actually spawning. Doing the optimization would (naively) require assurances that the `spawn(some_bundle)` command is applied before all other commands involving the entity (which would not necessarily be true, if memory serves). Optimizing `Commands::spawn` this way does feel possible, but it will require careful thought (and maybe some additional checks), which deserves its own PR. For now, it has the same performance characteristics of the current `Commands::spawn_bundle` on main.
**Note that 99% of this PR is simple renames and refactors. The only code that needs careful scrutiny is the new `World::spawn()` impl, which is relatively straightforward, but it has some new unsafe code (which re-uses battle tested BundlerSpawner code path).**
---
## Changelog
- All `spawn` apis (`World::spawn`, `Commands:;spawn`, `ChildBuilder::spawn`, and `WorldChildBuilder::spawn`) now accept a bundle as input
- All instances of `spawn_bundle` have been deprecated in favor of the new `spawn` api
- World and Commands now have `spawn_empty()`, which is equivalent to the old `spawn()` behavior.
## Migration Guide
```rust
// Old (0.8):
commands
.spawn()
.insert_bundle((A, B, C));
// New (0.9)
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
// Old (0.8):
commands.spawn_bundle((A, B, C));
// New (0.9)
commands.spawn((A, B, C));
// Old (0.8):
let entity = commands.spawn().id();
// New (0.9)
let entity = commands.spawn_empty().id();
// Old (0.8)
let entity = world.spawn().id();
// New (0.9)
let entity = world.spawn_empty();
```
2022-09-23 19:55:54 +00:00
|
|
|
commands.spawn(SceneBundle {
|
2024-06-01 01:25:57 +02:00
|
|
|
scene: asset_server.load(GltfAssetLabel::Scene(0).from_asset("models/animated/Fox.glb")),
|
2022-06-09 20:34:09 +00:00
|
|
|
..default()
|
|
|
|
|
});
|

Camera Driven Viewports (#4898)
# Objective
Users should be able to render cameras to specific areas of a render target, which enables scenarios like split screen, minimaps, etc.
Builds on the new Camera Driven Rendering added here: #4745
Fixes: #202
Alternative to #1389 and #3626 (which are incompatible with the new Camera Driven Rendering)
## Solution

Cameras can now configure an optional "viewport", which defines a rectangle within their render target to draw to. If a `Viewport` is defined, the camera's `CameraProjection`, `View`, and visibility calculations will use the viewport configuration instead of the full render target.
```rust
// This camera will render to the first half of the primary window (on the left side).
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle {
camera: Camera {
viewport: Some(Viewport {
physical_position: UVec2::new(0, 0),
physical_size: UVec2::new(window.physical_width() / 2, window.physical_height()),
depth: 0.0..1.0,
}),
..default()
},
..default()
});
```
To account for this, the `Camera` component has received a few adjustments:
* `Camera` now has some new getter functions:
* `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, `projection_matrix`
* All computed camera values are now private and live on the `ComputedCameraValues` field (logical/physical width/height, the projection matrix). They are now exposed on `Camera` via getters/setters This wasn't _needed_ for viewports, but it was long overdue.
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `Camera` components now have a `viewport` field, which can be set to draw to a portion of a render target instead of the full target.
* `Camera` component has some new functions: `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, and `projection_matrix`
* Added a new split_screen example illustrating how to render two cameras to the same scene
## Migration Guide
`Camera::projection_matrix` is no longer a public field. Use the new `Camera::projection_matrix()` method instead:
```rust
// Bevy 0.7
let projection = camera.projection_matrix;
// Bevy 0.8
let projection = camera.projection_matrix();
```
2022-06-05 00:27:49 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
// Light
|
2024-10-01 06:20:43 +03:00
|
|
|
commands.spawn((
|
|
|
|
|
Transform::from_rotation(Quat::from_euler(EulerRot::ZYX, 0.0, 1.0, -PI / 4.)),
|
|
|
|
|
DirectionalLight {
|

Camera Driven Viewports (#4898)
# Objective
Users should be able to render cameras to specific areas of a render target, which enables scenarios like split screen, minimaps, etc.
Builds on the new Camera Driven Rendering added here: #4745
Fixes: #202
Alternative to #1389 and #3626 (which are incompatible with the new Camera Driven Rendering)
## Solution

Cameras can now configure an optional "viewport", which defines a rectangle within their render target to draw to. If a `Viewport` is defined, the camera's `CameraProjection`, `View`, and visibility calculations will use the viewport configuration instead of the full render target.
```rust
// This camera will render to the first half of the primary window (on the left side).
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle {
camera: Camera {
viewport: Some(Viewport {
physical_position: UVec2::new(0, 0),
physical_size: UVec2::new(window.physical_width() / 2, window.physical_height()),
depth: 0.0..1.0,
}),
..default()
},
..default()
});
```
To account for this, the `Camera` component has received a few adjustments:
* `Camera` now has some new getter functions:
* `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, `projection_matrix`
* All computed camera values are now private and live on the `ComputedCameraValues` field (logical/physical width/height, the projection matrix). They are now exposed on `Camera` via getters/setters This wasn't _needed_ for viewports, but it was long overdue.
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `Camera` components now have a `viewport` field, which can be set to draw to a portion of a render target instead of the full target.
* `Camera` component has some new functions: `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, and `projection_matrix`
* Added a new split_screen example illustrating how to render two cameras to the same scene
## Migration Guide
`Camera::projection_matrix` is no longer a public field. Use the new `Camera::projection_matrix()` method instead:
```rust
// Bevy 0.7
let projection = camera.projection_matrix;
// Bevy 0.8
let projection = camera.projection_matrix();
```
2022-06-05 00:27:49 +00:00
|
|
|
shadows_enabled: true,
|
|
|
|
|
..default()
|
|
|
|
|
},
|
2024-10-01 06:20:43 +03:00
|
|
|
CascadeShadowConfigBuilder {
|
2024-08-04 22:57:22 +09:00
|
|
|
num_cascades: if cfg!(all(
|
|
|
|
|
feature = "webgl2",
|
|
|
|
|
target_arch = "wasm32",
|
|
|
|
|
not(feature = "webgpu")
|
|
|
|
|
)) {
|
|
|
|
|
// Limited to 1 cascade in WebGL
|
|
|
|
|
1
|
|
|
|
|
} else {
|
|
|
|
|
2
|
|
|
|
|
},
|
2023-02-05 08:06:32 +00:00
|
|
|
first_cascade_far_bound: 200.0,
|
|
|
|
|
maximum_distance: 280.0,
|
|
|
|
|
..default()
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
2024-10-01 06:20:43 +03:00
|
|
|
.build(),
|
|
|
|
|
));
|

Camera Driven Viewports (#4898)
# Objective
Users should be able to render cameras to specific areas of a render target, which enables scenarios like split screen, minimaps, etc.
Builds on the new Camera Driven Rendering added here: #4745
Fixes: #202
Alternative to #1389 and #3626 (which are incompatible with the new Camera Driven Rendering)
## Solution

Cameras can now configure an optional "viewport", which defines a rectangle within their render target to draw to. If a `Viewport` is defined, the camera's `CameraProjection`, `View`, and visibility calculations will use the viewport configuration instead of the full render target.
```rust
// This camera will render to the first half of the primary window (on the left side).
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle {
camera: Camera {
viewport: Some(Viewport {
physical_position: UVec2::new(0, 0),
physical_size: UVec2::new(window.physical_width() / 2, window.physical_height()),
depth: 0.0..1.0,
}),
..default()
},
..default()
});
```
To account for this, the `Camera` component has received a few adjustments:
* `Camera` now has some new getter functions:
* `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, `projection_matrix`
* All computed camera values are now private and live on the `ComputedCameraValues` field (logical/physical width/height, the projection matrix). They are now exposed on `Camera` via getters/setters This wasn't _needed_ for viewports, but it was long overdue.
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `Camera` components now have a `viewport` field, which can be set to draw to a portion of a render target instead of the full target.
* `Camera` component has some new functions: `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, and `projection_matrix`
* Added a new split_screen example illustrating how to render two cameras to the same scene
## Migration Guide
`Camera::projection_matrix` is no longer a public field. Use the new `Camera::projection_matrix()` method instead:
```rust
// Bevy 0.7
let projection = camera.projection_matrix;
// Bevy 0.8
let projection = camera.projection_matrix();
```
2022-06-05 00:27:49 +00:00
|
|
|
|
2024-02-20 22:15:44 +00:00
|
|
|
// Cameras and their dedicated UI
|
|
|
|
|
for (index, (camera_name, camera_pos)) in [
|
|
|
|
|
("Player 1", Vec3::new(0.0, 200.0, -150.0)),
|
|
|
|
|
("Player 2", Vec3::new(150.0, 150., 50.0)),
|
|
|
|
|
("Player 3", Vec3::new(100.0, 150., -150.0)),
|
|
|
|
|
("Player 4", Vec3::new(-100.0, 80., 150.0)),
|
|
|
|
|
]
|
|
|
|
|
.iter()
|
|
|
|
|
.enumerate()
|
|
|
|
|
{
|
|
|
|
|
let camera = commands
|
|
|
|
|
.spawn((
|
|
|
|
|
Camera3dBundle {
|
|
|
|
|
transform: Transform::from_translation(*camera_pos)
|
|
|
|
|
.looking_at(Vec3::ZERO, Vec3::Y),
|
|
|
|
|
camera: Camera {
|
|
|
|
|
// Renders cameras with different priorities to prevent ambiguities
|
|
|
|
|
order: index as isize,
|
|
|
|
|
..default()
|
|
|
|
|
},
|
2024-01-16 01:39:10 +01:00
|
|
|
..default()
|
|
|
|
|
},
|
2024-02-20 22:15:44 +00:00
|
|
|
CameraPosition {
|
|
|
|
|
pos: UVec2::new((index % 2) as u32, (index / 2) as u32),
|
2024-01-16 01:39:10 +01:00
|
|
|
},
|
2024-02-20 22:15:44 +00:00
|
|
|
))
|
|
|
|
|
.id();
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
// Set up UI
|
|
|
|
|
commands
|
|
|
|
|
.spawn((
|
|
|
|
|
TargetCamera(camera),
|
|
|
|
|
NodeBundle {
|
|
|
|
|
style: Style {
|
|
|
|
|
width: Val::Percent(100.),
|
|
|
|
|
height: Val::Percent(100.),
|
|
|
|
|
..default()
|
|
|
|
|
},
|
2024-01-16 01:39:10 +01:00
|
|
|
..default()
|
|
|
|
|
},
|
2024-02-20 22:15:44 +00:00
|
|
|
))
|
|
|
|
|
.with_children(|parent| {
|
2024-07-20 10:17:14 -07:00
|
|
|
parent.spawn(
|
|
|
|
|
TextBundle::from_section(*camera_name, TextStyle::default()).with_style(
|
|
|
|
|
Style {
|
|
|
|
|
position_type: PositionType::Absolute,
|
|
|
|
|
top: Val::Px(12.),
|
|
|
|
|
left: Val::Px(12.),
|
|
|
|
|
..default()
|
|
|
|
|
},
|
|
|
|
|
),
|
|
|
|
|
);
|
2024-02-20 22:15:44 +00:00
|
|
|
buttons_panel(parent);
|
|
|
|
|
});
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
2024-01-16 01:39:10 +01:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
fn buttons_panel(parent: &mut ChildBuilder) {
|
|
|
|
|
parent
|
|
|
|
|
.spawn(NodeBundle {
|
|
|
|
|
style: Style {
|
|
|
|
|
position_type: PositionType::Absolute,
|
|
|
|
|
width: Val::Percent(100.),
|
|
|
|
|
height: Val::Percent(100.),
|
|
|
|
|
display: Display::Flex,
|
|
|
|
|
flex_direction: FlexDirection::Row,
|
|
|
|
|
justify_content: JustifyContent::SpaceBetween,
|
|
|
|
|
align_items: AlignItems::Center,
|
|
|
|
|
padding: UiRect::all(Val::Px(20.)),
|
|
|
|
|
..default()
|
|
|
|
|
},
|
|
|
|
|
..default()
|
|
|
|
|
})
|
|
|
|
|
.with_children(|parent| {
|
|
|
|
|
rotate_button(parent, "<", Direction::Left);
|
|
|
|
|
rotate_button(parent, ">", Direction::Right);
|
|
|
|
|
});
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
fn rotate_button(parent: &mut ChildBuilder, caption: &str, direction: Direction) {
|
|
|
|
|
parent
|
|
|
|
|
.spawn((
|
|
|
|
|
RotateCamera(direction),
|
|
|
|
|
ButtonBundle {
|
|
|
|
|
style: Style {
|
|
|
|
|
width: Val::Px(40.),
|
|
|
|
|
height: Val::Px(40.),
|
|
|
|
|
border: UiRect::all(Val::Px(2.)),
|
|
|
|
|
justify_content: JustifyContent::Center,
|
|
|
|
|
align_items: AlignItems::Center,
|
|
|
|
|
..default()
|
|
|
|
|
},
|

Migrate from `LegacyColor` to `bevy_color::Color` (#12163)
# Objective
- As part of the migration process we need to a) see the end effect of
the migration on user ergonomics b) check for serious perf regressions
c) actually migrate the code
- To accomplish this, I'm going to attempt to migrate all of the
remaining user-facing usages of `LegacyColor` in one PR, being careful
to keep a clean commit history.
- Fixes #12056.
## Solution
I've chosen to use the polymorphic `Color` type as our standard
user-facing API.
- [x] Migrate `bevy_gizmos`.
- [x] Take `impl Into<Color>` in all `bevy_gizmos` APIs
- [x] Migrate sprites
- [x] Migrate UI
- [x] Migrate `ColorMaterial`
- [x] Migrate `MaterialMesh2D`
- [x] Migrate fog
- [x] Migrate lights
- [x] Migrate StandardMaterial
- [x] Migrate wireframes
- [x] Migrate clear color
- [x] Migrate text
- [x] Migrate gltf loader
- [x] Register color types for reflection
- [x] Remove `LegacyColor`
- [x] Make sure CI passes
Incidental improvements to ease migration:
- added `Color::srgba_u8`, `Color::srgba_from_array` and friends
- added `set_alpha`, `is_fully_transparent` and `is_fully_opaque` to the
`Alpha` trait
- add and immediately deprecate (lol) `Color::rgb` and friends in favor
of more explicit and consistent `Color::srgb`
- standardized on white and black for most example text colors
- added vector field traits to `LinearRgba`: ~~`Add`, `Sub`,
`AddAssign`, `SubAssign`,~~ `Mul<f32>` and `Div<f32>`. Multiplications
and divisions do not scale alpha. `Add` and `Sub` have been cut from
this PR.
- added `LinearRgba` and `Srgba` `RED/GREEN/BLUE`
- added `LinearRgba_to_f32_array` and `LinearRgba::to_u32`
## Migration Guide
Bevy's color types have changed! Wherever you used a
`bevy::render::Color`, a `bevy::color::Color` is used instead.
These are quite similar! Both are enums storing a color in a specific
color space (or to be more precise, using a specific color model).
However, each of the different color models now has its own type.
TODO...
- `Color::rgba`, `Color::rgb`, `Color::rbga_u8`, `Color::rgb_u8`,
`Color::rgb_from_array` are now `Color::srgba`, `Color::srgb`,
`Color::srgba_u8`, `Color::srgb_u8` and `Color::srgb_from_array`.
- `Color::set_a` and `Color::a` is now `Color::set_alpha` and
`Color::alpha`. These are part of the `Alpha` trait in `bevy_color`.
- `Color::is_fully_transparent` is now part of the `Alpha` trait in
`bevy_color`
- `Color::r`, `Color::set_r`, `Color::with_r` and the equivalents for
`g`, `b` `h`, `s` and `l` have been removed due to causing silent
relatively expensive conversions. Convert your `Color` into the desired
color space, perform your operations there, and then convert it back
into a polymorphic `Color` enum.
- `Color::hex` is now `Srgba::hex`. Call `.into` or construct a
`Color::Srgba` variant manually to convert it.
- `WireframeMaterial`, `ExtractedUiNode`, `ExtractedDirectionalLight`,
`ExtractedPointLight`, `ExtractedSpotLight` and `ExtractedSprite` now
store a `LinearRgba`, rather than a polymorphic `Color`
- `Color::rgb_linear` and `Color::rgba_linear` are now
`Color::linear_rgb` and `Color::linear_rgba`
- The various CSS color constants are no longer stored directly on
`Color`. Instead, they're defined in the `Srgba` color space, and
accessed via `bevy::color::palettes::css`. Call `.into()` on them to
convert them into a `Color` for quick debugging use, and consider using
the much prettier `tailwind` palette for prototyping.
- The `LIME_GREEN` color has been renamed to `LIMEGREEN` to comply with
the standard naming.
- Vector field arithmetic operations on `Color` (add, subtract, multiply
and divide by a f32) have been removed. Instead, convert your colors
into `LinearRgba` space, and perform your operations explicitly there.
This is particularly relevant when working with emissive or HDR colors,
whose color channel values are routinely outside of the ordinary 0 to 1
range.
- `Color::as_linear_rgba_f32` has been removed. Call
`LinearRgba::to_f32_array` instead, converting if needed.
- `Color::as_linear_rgba_u32` has been removed. Call
`LinearRgba::to_u32` instead, converting if needed.
- Several other color conversion methods to transform LCH or HSL colors
into float arrays or `Vec` types have been removed. Please reimplement
these externally or open a PR to re-add them if you found them
particularly useful.
- Various methods on `Color` such as `rgb` or `hsl` to convert the color
into a specific color space have been removed. Convert into
`LinearRgba`, then to the color space of your choice.
- Various implicitly-converting color value methods on `Color` such as
`r`, `g`, `b` or `h` have been removed. Please convert it into the color
space of your choice, then check these properties.
- `Color` no longer implements `AsBindGroup`. Store a `LinearRgba`
internally instead to avoid conversion costs.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <alice.i.cecil@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Afonso Lage <lage.afonso@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Rob Parrett <robparrett@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Zachary Harrold <zac@harrold.com.au>
2024-02-29 14:35:12 -05:00
|
|
|
border_color: Color::WHITE.into(),
|

Make default behavior for `BackgroundColor` and `BorderColor` more intuitive (#14017)
# Objective
In Bevy 0.13, `BackgroundColor` simply tinted the image of any
`UiImage`. This was confusing: in every other case (e.g. Text), this
added a solid square behind the element. #11165 changed this, but
removed `BackgroundColor` from `ImageBundle` to avoid confusion, since
the semantic meaning had changed.
However, this resulted in a serious UX downgrade / inconsistency, as
this behavior was no longer part of the bundle (unlike for `TextBundle`
or `NodeBundle`), leaving users with a relatively frustrating upgrade
path.
Additionally, adding both `BackgroundColor` and `UiImage` resulted in a
bizarre effect, where the background color was seemingly ignored as it
was covered by a solid white placeholder image.
Fixes #13969.
## Solution
Per @viridia's design:
> - if you don't specify a background color, it's transparent.
> - if you don't specify an image color, it's white (because it's a
multiplier).
> - if you don't specify an image, no image is drawn.
> - if you specify both a background color and an image color, they are
independent.
> - the background color is drawn behind the image (in whatever pixels
are transparent)
As laid out by @benfrankel, this involves:
1. Changing the default `UiImage` to use a transparent texture but a
pure white tint.
2. Adding `UiImage::solid_color` to quickly set placeholder images.
3. Changing the default `BorderColor` and `BackgroundColor` to
transparent.
4. Removing the default overrides for these values in the other assorted
UI bundles.
5. Adding `BackgroundColor` back to `ImageBundle` and `ButtonBundle`.
6. Adding a 1x1 `Image::transparent`, which can be accessed from
`Assets<Image>` via the `TRANSPARENT_IMAGE_HANDLE` constant.
Huge thanks to everyone who helped out with the design in the linked
issue and [the Discord
thread](https://discord.com/channels/691052431525675048/1255209923890118697/1255209999278280844):
this was very much a joint design.
@cart helped me figure out how to set the UiImage's default texture to a
transparent 1x1 image, which is a much nicer fix.
## Testing
I've checked the examples modified by this PR, and the `ui` example as
well just to be sure.
## Migration Guide
- `BackgroundColor` no longer tints the color of images in `ImageBundle`
or `ButtonBundle`. Set `UiImage::color` to tint images instead.
- The default texture for `UiImage` is now a transparent white square.
Use `UiImage::solid_color` to quickly draw debug images.
- The default value for `BackgroundColor` and `BorderColor` is now
transparent. Set the color to white manually to return to previous
behavior.
2024-06-25 17:50:41 -04:00
|
|
|
background_color: Color::srgb(0.25, 0.25, 0.25).into(),
|
2024-01-16 01:39:10 +01:00
|
|
|
..default()
|
|
|
|
|
},
|
|
|
|
|
))
|
|
|
|
|
.with_children(|parent| {
|
2024-05-31 13:41:27 -03:00
|
|
|
parent.spawn(TextBundle::from_section(caption, TextStyle::default()));
|
2024-01-16 01:39:10 +01:00
|
|
|
});
|
|
|
|
|
}
|

Camera Driven Viewports (#4898)
# Objective
Users should be able to render cameras to specific areas of a render target, which enables scenarios like split screen, minimaps, etc.
Builds on the new Camera Driven Rendering added here: #4745
Fixes: #202
Alternative to #1389 and #3626 (which are incompatible with the new Camera Driven Rendering)
## Solution

Cameras can now configure an optional "viewport", which defines a rectangle within their render target to draw to. If a `Viewport` is defined, the camera's `CameraProjection`, `View`, and visibility calculations will use the viewport configuration instead of the full render target.
```rust
// This camera will render to the first half of the primary window (on the left side).
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle {
camera: Camera {
viewport: Some(Viewport {
physical_position: UVec2::new(0, 0),
physical_size: UVec2::new(window.physical_width() / 2, window.physical_height()),
depth: 0.0..1.0,
}),
..default()
},
..default()
});
```
To account for this, the `Camera` component has received a few adjustments:
* `Camera` now has some new getter functions:
* `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, `projection_matrix`
* All computed camera values are now private and live on the `ComputedCameraValues` field (logical/physical width/height, the projection matrix). They are now exposed on `Camera` via getters/setters This wasn't _needed_ for viewports, but it was long overdue.
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `Camera` components now have a `viewport` field, which can be set to draw to a portion of a render target instead of the full target.
* `Camera` component has some new functions: `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, and `projection_matrix`
* Added a new split_screen example illustrating how to render two cameras to the same scene
## Migration Guide
`Camera::projection_matrix` is no longer a public field. Use the new `Camera::projection_matrix()` method instead:
```rust
// Bevy 0.7
let projection = camera.projection_matrix;
// Bevy 0.8
let projection = camera.projection_matrix();
```
2022-06-05 00:27:49 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[derive(Component)]
|
2024-02-20 22:15:44 +00:00
|
|
|
struct CameraPosition {
|
|
|
|
|
pos: UVec2,
|
|
|
|
|
}
|

Camera Driven Viewports (#4898)
# Objective
Users should be able to render cameras to specific areas of a render target, which enables scenarios like split screen, minimaps, etc.
Builds on the new Camera Driven Rendering added here: #4745
Fixes: #202
Alternative to #1389 and #3626 (which are incompatible with the new Camera Driven Rendering)
## Solution

Cameras can now configure an optional "viewport", which defines a rectangle within their render target to draw to. If a `Viewport` is defined, the camera's `CameraProjection`, `View`, and visibility calculations will use the viewport configuration instead of the full render target.
```rust
// This camera will render to the first half of the primary window (on the left side).
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle {
camera: Camera {
viewport: Some(Viewport {
physical_position: UVec2::new(0, 0),
physical_size: UVec2::new(window.physical_width() / 2, window.physical_height()),
depth: 0.0..1.0,
}),
..default()
},
..default()
});
```
To account for this, the `Camera` component has received a few adjustments:
* `Camera` now has some new getter functions:
* `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, `projection_matrix`
* All computed camera values are now private and live on the `ComputedCameraValues` field (logical/physical width/height, the projection matrix). They are now exposed on `Camera` via getters/setters This wasn't _needed_ for viewports, but it was long overdue.
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `Camera` components now have a `viewport` field, which can be set to draw to a portion of a render target instead of the full target.
* `Camera` component has some new functions: `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, and `projection_matrix`
* Added a new split_screen example illustrating how to render two cameras to the same scene
## Migration Guide
`Camera::projection_matrix` is no longer a public field. Use the new `Camera::projection_matrix()` method instead:
```rust
// Bevy 0.7
let projection = camera.projection_matrix;
// Bevy 0.8
let projection = camera.projection_matrix();
```
2022-06-05 00:27:49 +00:00
|
|
|
|
2024-01-16 01:39:10 +01:00
|
|
|
#[derive(Component)]
|
|
|
|
|
struct RotateCamera(Direction);
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
enum Direction {
|
|
|
|
|
Left,
|
|
|
|
|
Right,
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|

Camera Driven Viewports (#4898)
# Objective
Users should be able to render cameras to specific areas of a render target, which enables scenarios like split screen, minimaps, etc.
Builds on the new Camera Driven Rendering added here: #4745
Fixes: #202
Alternative to #1389 and #3626 (which are incompatible with the new Camera Driven Rendering)
## Solution

Cameras can now configure an optional "viewport", which defines a rectangle within their render target to draw to. If a `Viewport` is defined, the camera's `CameraProjection`, `View`, and visibility calculations will use the viewport configuration instead of the full render target.
```rust
// This camera will render to the first half of the primary window (on the left side).
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle {
camera: Camera {
viewport: Some(Viewport {
physical_position: UVec2::new(0, 0),
physical_size: UVec2::new(window.physical_width() / 2, window.physical_height()),
depth: 0.0..1.0,
}),
..default()
},
..default()
});
```
To account for this, the `Camera` component has received a few adjustments:
* `Camera` now has some new getter functions:
* `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, `projection_matrix`
* All computed camera values are now private and live on the `ComputedCameraValues` field (logical/physical width/height, the projection matrix). They are now exposed on `Camera` via getters/setters This wasn't _needed_ for viewports, but it was long overdue.
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `Camera` components now have a `viewport` field, which can be set to draw to a portion of a render target instead of the full target.
* `Camera` component has some new functions: `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, and `projection_matrix`
* Added a new split_screen example illustrating how to render two cameras to the same scene
## Migration Guide
`Camera::projection_matrix` is no longer a public field. Use the new `Camera::projection_matrix()` method instead:
```rust
// Bevy 0.7
let projection = camera.projection_matrix;
// Bevy 0.8
let projection = camera.projection_matrix();
```
2022-06-05 00:27:49 +00:00
|
|
|
fn set_camera_viewports(
|
2023-01-19 00:38:28 +00:00
|
|
|
windows: Query<&Window>,
|

Camera Driven Viewports (#4898)
# Objective
Users should be able to render cameras to specific areas of a render target, which enables scenarios like split screen, minimaps, etc.
Builds on the new Camera Driven Rendering added here: #4745
Fixes: #202
Alternative to #1389 and #3626 (which are incompatible with the new Camera Driven Rendering)
## Solution

Cameras can now configure an optional "viewport", which defines a rectangle within their render target to draw to. If a `Viewport` is defined, the camera's `CameraProjection`, `View`, and visibility calculations will use the viewport configuration instead of the full render target.
```rust
// This camera will render to the first half of the primary window (on the left side).
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle {
camera: Camera {
viewport: Some(Viewport {
physical_position: UVec2::new(0, 0),
physical_size: UVec2::new(window.physical_width() / 2, window.physical_height()),
depth: 0.0..1.0,
}),
..default()
},
..default()
});
```
To account for this, the `Camera` component has received a few adjustments:
* `Camera` now has some new getter functions:
* `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, `projection_matrix`
* All computed camera values are now private and live on the `ComputedCameraValues` field (logical/physical width/height, the projection matrix). They are now exposed on `Camera` via getters/setters This wasn't _needed_ for viewports, but it was long overdue.
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `Camera` components now have a `viewport` field, which can be set to draw to a portion of a render target instead of the full target.
* `Camera` component has some new functions: `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, and `projection_matrix`
* Added a new split_screen example illustrating how to render two cameras to the same scene
## Migration Guide
`Camera::projection_matrix` is no longer a public field. Use the new `Camera::projection_matrix()` method instead:
```rust
// Bevy 0.7
let projection = camera.projection_matrix;
// Bevy 0.8
let projection = camera.projection_matrix();
```
2022-06-05 00:27:49 +00:00
|
|
|
mut resize_events: EventReader<WindowResized>,
|
2024-02-20 22:15:44 +00:00
|
|
|
mut query: Query<(&CameraPosition, &mut Camera)>,
|

Camera Driven Viewports (#4898)
# Objective
Users should be able to render cameras to specific areas of a render target, which enables scenarios like split screen, minimaps, etc.
Builds on the new Camera Driven Rendering added here: #4745
Fixes: #202
Alternative to #1389 and #3626 (which are incompatible with the new Camera Driven Rendering)
## Solution

Cameras can now configure an optional "viewport", which defines a rectangle within their render target to draw to. If a `Viewport` is defined, the camera's `CameraProjection`, `View`, and visibility calculations will use the viewport configuration instead of the full render target.
```rust
// This camera will render to the first half of the primary window (on the left side).
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle {
camera: Camera {
viewport: Some(Viewport {
physical_position: UVec2::new(0, 0),
physical_size: UVec2::new(window.physical_width() / 2, window.physical_height()),
depth: 0.0..1.0,
}),
..default()
},
..default()
});
```
To account for this, the `Camera` component has received a few adjustments:
* `Camera` now has some new getter functions:
* `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, `projection_matrix`
* All computed camera values are now private and live on the `ComputedCameraValues` field (logical/physical width/height, the projection matrix). They are now exposed on `Camera` via getters/setters This wasn't _needed_ for viewports, but it was long overdue.
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `Camera` components now have a `viewport` field, which can be set to draw to a portion of a render target instead of the full target.
* `Camera` component has some new functions: `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, and `projection_matrix`
* Added a new split_screen example illustrating how to render two cameras to the same scene
## Migration Guide
`Camera::projection_matrix` is no longer a public field. Use the new `Camera::projection_matrix()` method instead:
```rust
// Bevy 0.7
let projection = camera.projection_matrix;
// Bevy 0.8
let projection = camera.projection_matrix();
```
2022-06-05 00:27:49 +00:00
|
|
|
) {
|
|
|
|
|
// We need to dynamically resize the camera's viewports whenever the window size changes
|
|
|
|
|
// so then each camera always takes up half the screen.
|
|
|
|
|
// A resize_event is sent when the window is first created, allowing us to reuse this system for initial setup.
|
2023-08-30 10:20:03 -04:00
|
|
|
for resize_event in resize_events.read() {
|
2023-01-19 00:38:28 +00:00
|
|
|
let window = windows.get(resize_event.window).unwrap();
|
2024-03-01 17:28:37 -05:00
|
|
|
let size = window.physical_size() / 2;
|
2024-02-20 22:15:44 +00:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
for (camera_position, mut camera) in &mut query {
|
|
|
|
|
camera.viewport = Some(Viewport {
|
|
|
|
|
physical_position: camera_position.pos * size,
|
|
|
|
|
physical_size: size,
|
|
|
|
|
..default()
|
|
|
|
|
});
|
|
|
|
|
}
|

Camera Driven Viewports (#4898)
# Objective
Users should be able to render cameras to specific areas of a render target, which enables scenarios like split screen, minimaps, etc.
Builds on the new Camera Driven Rendering added here: #4745
Fixes: #202
Alternative to #1389 and #3626 (which are incompatible with the new Camera Driven Rendering)
## Solution

Cameras can now configure an optional "viewport", which defines a rectangle within their render target to draw to. If a `Viewport` is defined, the camera's `CameraProjection`, `View`, and visibility calculations will use the viewport configuration instead of the full render target.
```rust
// This camera will render to the first half of the primary window (on the left side).
commands.spawn_bundle(Camera3dBundle {
camera: Camera {
viewport: Some(Viewport {
physical_position: UVec2::new(0, 0),
physical_size: UVec2::new(window.physical_width() / 2, window.physical_height()),
depth: 0.0..1.0,
}),
..default()
},
..default()
});
```
To account for this, the `Camera` component has received a few adjustments:
* `Camera` now has some new getter functions:
* `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, `projection_matrix`
* All computed camera values are now private and live on the `ComputedCameraValues` field (logical/physical width/height, the projection matrix). They are now exposed on `Camera` via getters/setters This wasn't _needed_ for viewports, but it was long overdue.
---
## Changelog
### Added
* `Camera` components now have a `viewport` field, which can be set to draw to a portion of a render target instead of the full target.
* `Camera` component has some new functions: `logical_viewport_size`, `physical_viewport_size`, `logical_target_size`, `physical_target_size`, and `projection_matrix`
* Added a new split_screen example illustrating how to render two cameras to the same scene
## Migration Guide
`Camera::projection_matrix` is no longer a public field. Use the new `Camera::projection_matrix()` method instead:
```rust
// Bevy 0.7
let projection = camera.projection_matrix;
// Bevy 0.8
let projection = camera.projection_matrix();
```
2022-06-05 00:27:49 +00:00
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
2024-01-16 01:39:10 +01:00
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#[allow(clippy::type_complexity)]
|
|
|
|
|
fn button_system(
|
|
|
|
|
interaction_query: Query<
|
|
|
|
|
(&Interaction, &TargetCamera, &RotateCamera),
|
|
|
|
|
(Changed<Interaction>, With<Button>),
|
|
|
|
|
>,
|
|
|
|
|
mut camera_query: Query<&mut Transform, With<Camera>>,
|
|
|
|
|
) {
|
|
|
|
|
for (interaction, target_camera, RotateCamera(direction)) in &interaction_query {
|
|
|
|
|
if let Interaction::Pressed = *interaction {
|
|
|
|
|
// Since TargetCamera propagates to the children, we can use it to find
|
|
|
|
|
// which side of the screen the button is on.
|
|
|
|
|
if let Ok(mut camera_transform) = camera_query.get_mut(target_camera.entity()) {
|
|
|
|
|
let angle = match direction {
|
|
|
|
|
Direction::Left => -0.1,
|
|
|
|
|
Direction::Right => 0.1,
|
|
|
|
|
};
|
|
|
|
|
camera_transform.rotate_around(Vec3::ZERO, Quat::from_axis_angle(Vec3::Y, angle));
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
}
|