8 KiB
Architecture
This document describes high-level architecture of rust-analyzer. If you want to familiarize yourself with the code base, you are just in the right place!
The Big Picture
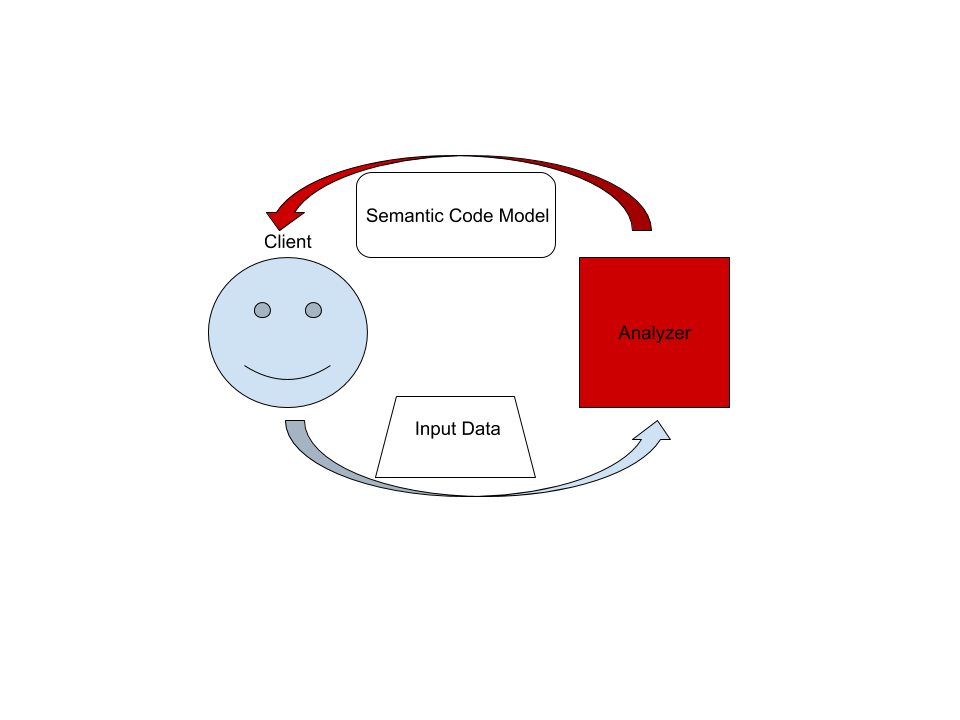
On the highest level, rust-analyzer is a thing which accepts input source code from the client and produces a structured semantic model of the code.
More specifically, input data consists of a set of test files ((PathBuf, String) pairs) and an information about project structure, the so called
CrateGraph. Crate graph specifies which files are crate roots, which cfg flags
are specified for each crate (TODO: actually implement this) and what are
dependencies between the crate. The analyzer keeps all these input data in
memory and never does any IO. Because the input data is source code, which
typically measures in tens of megabytes at most, keeping all input data in
memory is OK.
A "structured semantic model" is basically an object-oriented representation of modules, functions and types which appear in the source code. This representation is fully "resolved": all expressions have types, all references are bound to declarations, etc.
The client can submit a small delta of input data (typically, a change to a single file) and get a fresh code model which accounts for changes.
Underlying engine makes sure that model is computed lazily (on-demand) and can be quickly updated for small modifications.
Code generation
Some of the components of this repository are generated through automatic processes. These are outlined below:
gen-syntax: The kinds of tokens are reused in several places, so a generator is used. We use tera templates to generate the files listed below, based on the grammar described in grammar.ron:- ast/generated.rs in
ra_syntaxbased on ast/generated.tera.rs - syntax_kinds/generated.rs in
ra_syntaxbased on syntax_kinds/generated.tera.rs
- ast/generated.rs in
Code Walk-Through
crates/ra_syntax
Rust syntax tree structure and parser. See RFC for some design notes.
- rowan library is used for constructing syntax trees.
grammarmodule is the actual parser. It is a hand-written recursive descent parsers, which produces a sequence of events like "start node X", "finish not Y". It works similarly to kotlin parser, which is a good source for inspiration for dealing with syntax errors and incomplete input. Original libsyntax parser is what we use for the definition of the Rust language.parser_api/parser_implbridges the tree-agnostic parser fromgrammarwithrowantrees. This is the thing that turns a flat list of events into a tree (seeEventProcessor)asta type safe API on top of the rawrowantree.grammar.ronRON description of the grammar, which is used to generatesyntax_kindsandastmodules, usingcargo gen-syntaxcommand.algo: generic tree algorithms, includingwalkfor O(1) stack space tree traversal (this is cool) andvisitfor type-driven visiting the nodes (this is double plus cool, if you understand howVisitorworks, you understand rust-analyzer).
Test for ra_syntax are mostly data-driven: tests/data/parser contains a bunch of .rs
(test vectors) and .txt files with corresponding syntax trees. During testing, we check
.rs against .txt. If the .txt file is missing, it is created (this is how you update
tests). Additionally, running cargo gen-tests will walk the grammar module and collect
all //test test_name comments into files inside tests/data directory.
See #93 for an example PR which fixes a bug in the grammar.
crates/ra_db
We use the salsa crate for incremental and
on-demand computation. Roughly, you can think of salsa as a key-value store, but
it also can compute derived values using specified functions. The ra_db crate
provides a basic infrastructure for interacting with salsa. Crucially, it
defines most of the "input" queries: facts supplied by the client of the
analyzer. Reading the docs of the ra_db::input module should be useful:
everything else is strictly derived from those inputs.
crates/ra_hir
HIR provides high-level "object oriented" access to Rust code.
The principal difference between HIR and syntax trees is that HIR is bound to a
particular crate instance. That is, it has cfg flags and features applied (in
theory, in practice this is to be implemented). So, the relation between
syntax and HIR is many-to-one. The source_binder modules is responsible for
guessing a HIR for a particular source position.
Underneath, HIR works on top of salsa, using a HirDatabase trait.
crates/ra_analysis
A stateful library for analyzing many Rust files as they change.
AnalysisHost is a mutable entity (clojure's atom) which holds the
current state, incorporates changes and handles out Analysis --- an
immutable and consistent snapshot of world state at a point in time, which
actually powers analysis.
One interesting aspect of analysis is its support for cancellation. When a change
is applied to AnalysisHost, first all currently active snapshots are
cancelled. Only after all snapshots are dropped the change actually affects the
database.
crates/ra_lsp_server
An LSP implementation which uses ra_analysis for managing state and
ra_editor for actually doing useful stuff.
See #79 as an
example of PR which adds a new feature to ra_editor and exposes it
to ra_lsp_server.
crates/ra_editor
All IDE features which can be implemented if you only have access to a
single file. ra_editor could be used to enhance editing of Rust code
without the need to fiddle with build-systems, file
synchronization and such.
In a sense, ra_editor is just a bunch of pure functions which take a
syntax tree as input.
The tests for ra_editor are #[cfg(test)] mod tests unit-tests spread
throughout its modules.
crates/gen_lsp_server
A language server scaffold, exposing a synchronous crossbeam-channel based API. This crate handles protocol handshaking and parsing messages, while you control the message dispatch loop yourself.
Run with RUST_LOG=sync_lsp_server=debug to see all the messages.
crates/ra_cli
A CLI interface to rust-analyzer.
crate/tools
Custom Cargo tasks used to develop rust-analyzer:
cargo gen-syntax-- generateastandsyntax_kindscargo gen-tests-- collect inline tests from grammarcargo install-code-- build and install VS Code extension and server
editors/code
VS Code plugin
Common workflows
To try out VS Code extensions, run cargo install-code. This installs both the
ra_lsp_server binary and VS Code extension. To install only the binary, use
cargo install --path crates/ra_lsp_server --force
To see logs from the language server, set RUST_LOG=info env variable. To see
all communication between the server and the client, use
RUST_LOG=gen_lsp_server=debug (will print quite a bit of stuff).
To run tests, just cargo test.
To work on VS Code extension, launch code inside editors/code and use F5 to
launch/debug. To automatically apply formatter and linter suggestions, use npm run fix.