Bind unused parameter assistant
This PR introduces a new **Bind unused parameter assistant**.
While we do have a QuickFix from `rustc` (prefixing the parameter with an underscore), it's sometimes more convenient to suppress the warning using the following approach:
```rust
fn some_function(unused: i32) {}
```
->
```rust
fn some_function(unused: i32) {
let _ = unused;
}
```
minor : use crate name for `CARGO_CRATE_NAME`
fixes#15572 . Until now we used the package name as a replacement of crate name. With this PR r-a first sets all the env variables it set before and on top of those it tries to set `CARGO_CRATE_NAME` to crates name, following envvar's naming convention.
Replace format-args parser with upstream fork
Turns out we can't bump rustc_abi right now because it got its generics removed accidentally https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/107163
On type format '(', by adding closing ')' automatically
If I understand right, `()` can surround pretty much the same `{}` can, so add another on type formatting pair for convenience: sometimes it's not that pleasant to write parenthesis in `Some(2).map(|i| (i, i+1))` cases and I would prefer r-a to do that for me.
One note: currently, b06503b6ec/crates/rust-analyzer/src/handlers/request.rs (L357) fires always.
Should we remove the assertion entirely now, since apparently things work in release despite that check?
Implement `write_via_move` intrinsic for mir-eval
Required for getting `write!`ing to work again. we fail with an odd type mimsatch eval error after this change though
Implement builtin#format_args, using rustc's format_args parser
`format_args!` now expands to `builtin#format_args(template, args...)`, the actual expansion now instead happens in lowering where we desugar this expression by using lang paths.
As a bonus, we no longer need to evaluate `format_args` as an eager macro which means less macro expansions overall -> less cache thrashing!
Fixes https://github.com/rust-lang/rust-analyzer/issues/15082
Add a few more `db.unwind_if_cancelled()` calls
Judging from a profile sent by a friend, the borrowck query took up a significant amount of time in their project which might be the cause for some unresponsiveness as nothing in the mir stack currently unwinds on cancellation
Shuffle some locking around
The main thread is still occasionally blocking on something and I am unsure what the cause might be. This will hopefully help somewhat
Editor itself is able to invalidate hints after edits, and /refresh was
sent after editor reports changes to the language server.
This forces the editor to either query & invalidate the hints twice
after every edit, or wait for /refresh to come before querying the
hints.
Both options are rather useless, so instead, send a request on server
startup only: client editors do not know when the server actually starts
up, this will help to query the initial hints after editor was open and
the server was still starting up.
Fix cargo handle logging in flycheck
This PR has two commits, so it's probably easier to review them separately:
(1) Rename `CargoHandle` to `CommandHandle`, as the command may not be a cargo command.
(2) Logging should format the current command, rather than calling `check_command()` again. This ensures that any later configuration changes don't cause us to log incorrect information.
proc-macro-test: Pass target to cargo invocation
When cross compiling macos → dragonfly the dist build fails in the proc-maro-test-impl crate with the following error:
`ld: unknown option: -z\nclang: error: linker command failed with exit code 1 (use -v to see invocation)`
This appears to be a wart stemming from using an Apple host for cross compiling. Passing the target along to cargo allows it to pick up a linker that it understands and DTRT.
Previously this was hard coded to "0.1". The SCIP protocol allows this
to be an arbitrary string:
```
message ToolInfo {
// Name of the indexer that produced this index.
string name = 1;
// Version of the indexer that produced this index.
string version = 2;
// Command-line arguments that were used to invoke this indexer.
repeated string arguments = 3;
}
```
so use the same string reported by `rust-analyzer --version`.
Warn on elided lifetimes in associated constants (`ELIDED_LIFETIMES_IN_ASSOCIATED_CONSTANT`)
Elided lifetimes in associated constants (in impls) erroneously resolve to fresh lifetime parameters on the impl since #97313. This is not correct behavior (see #38831).
I originally opened #114716 to fix this, but given the time that has passed, the crater results seem pretty bad: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/114716#issuecomment-1682091952
This PR alternatively implements a lint against this behavior, and I'm hoping to bump this to deny in a few versions.
Warn on elided lifetimes in associated constants (`ELIDED_LIFETIMES_IN_ASSOCIATED_CONSTANT`)
Elided lifetimes in associated constants (in impls) erroneously resolve to fresh lifetime parameters on the impl since #97313. This is not correct behavior (see #38831).
I originally opened #114716 to fix this, but given the time that has passed, the crater results seem pretty bad: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/pull/114716#issuecomment-1682091952
This PR alternatively implements a lint against this behavior, and I'm hoping to bump this to deny in a few versions.
fix help text for rust-analyzer.check.invocation{Strategy,Location}
I highly doubt that `check.invocationLocation` only has an effect if `cargo.buildScripts.overrideCommand` is set -- looks like a copy-paste mistake from `buildScripts.invocationLocation` to me.
minor : Deunwrap generate_derive
#15398 subtask 1. Since the editing closure has arms, I did something *experimental* ( in this case just a clever term for bad code ) to bypass creating an `Option` but I am ready to change this.
internal: Record import origins in ItemScope and PerNS
This records the import items definitions come from in the module scope (as well as what an import resolves to in an ItemScope). It does ignore glob imports as thats a lot more work for little to no gain, glob imports act as if the importing items are "inlined" into the scope which suffices for almost all use cases I believe (to my knowledge, attributes on them have little effect).
There is still a lot of work needed to make this available to the IDE layer, but this lays out the ground work for havin IDE layer support.
cc https://github.com/rust-lang/rust-analyzer/issues/14079
fix: start hovering default values of generic constants
It's just a kind of a postscriptum for [my last PR](https://github.com/rust-lang/rust-analyzer/pull/15179) adding default values of const generics to `hir::ConstParamData`. Here I patch other pieces of code which used to ignore const default values and which I managed to find (you're welcome to show me more)
the "add missing members" assists: implemented substitution of default values of const params
To achieve this, I've made `hir::ConstParamData` store the default values
internal : rewrite DeMorgan assist
fixes#15239 , #15240 . This PR is a rewrite of the DeMorgan assist that essentially rids of all the string manipulation and modifies syntax trees to apply demorgan on a binary expr. The main reason for the rewrite is that I wanted to use `Expr::needs_parens_in` method to see if the expr on which the assist is applied would still need the parens it had once the parent expression's operator had equal precedence with that of the expression. I used `.clone_(subtree|for_update)` left and right and probably more than I should have, so I would also be happy to hear how I could have prevented redundant cloning.
Suggest type completions for type arguments and constant completions for constant arguments
When determining completions for generic arguments, suggest only types or only constants if the corresponding generic parameter is a type parameter or constant parameter.
Closes#12568
Fix signature help of methods from macros
Currently the receiver type is copied from AST instead re-formatting through `HirDisplay`. Macro generated functions seem to have no spaces and their signature help are rendered like `fn foo(&'amutself)` instead of `fn foo(&'a mut self)`.
Fix pinned version of lsp-types
lsp-types published a new patch version that breaks semver with the proposed feature set (this is intended and documented), we unfortunately forgot to specify the patch version for the pinned version so this breaks us.
Similar to prior support added for the mips430, avr, and x86 targets
this change implements the rough equivalent of clang's
[`__attribute__((interrupt))`][clang-attr] for riscv targets, enabling
e.g.
```rust
static mut CNT: usize = 0;
pub extern "riscv-interrupt-m" fn isr_m() {
unsafe {
CNT += 1;
}
}
```
to produce highly effective assembly like:
```asm
pub extern "riscv-interrupt-m" fn isr_m() {
420003a0: 1141 addi sp,sp,-16
unsafe {
CNT += 1;
420003a2: c62a sw a0,12(sp)
420003a4: c42e sw a1,8(sp)
420003a6: 3fc80537 lui a0,0x3fc80
420003aa: 63c52583 lw a1,1596(a0) # 3fc8063c <_ZN12esp_riscv_rt3CNT17hcec3e3a214887d53E.0>
420003ae: 0585 addi a1,a1,1
420003b0: 62b52e23 sw a1,1596(a0)
}
}
420003b4: 4532 lw a0,12(sp)
420003b6: 45a2 lw a1,8(sp)
420003b8: 0141 addi sp,sp,16
420003ba: 30200073 mret
```
(disassembly via `riscv64-unknown-elf-objdump -C -S --disassemble ./esp32c3-hal/target/riscv32imc-unknown-none-elf/release/examples/gpio_interrupt`)
This outcome is superior to hand-coded interrupt routines which, lacking
visibility into any non-assembly body of the interrupt handler, have to
be very conservative and save the [entire CPU state to the stack
frame][full-frame-save]. By instead asking LLVM to only save the
registers that it uses, we defer the decision to the tool with the best
context: it can more accurately account for the cost of spills if it
knows that every additional register used is already at the cost of an
implicit spill.
At the LLVM level, this is apparently [implemented by] marking every
register as "[callee-save]," matching the semantics of an interrupt
handler nicely (it has to leave the CPU state just as it found it after
its `{m|s}ret`).
This approach is not suitable for every interrupt handler, as it makes
no attempt to e.g. save the state in a user-accessible stack frame. For
a full discussion of those challenges and tradeoffs, please refer to
[the interrupt calling conventions RFC][rfc].
Inside rustc, this implementation differs from prior art because LLVM
does not expose the "all-saved" function flavor as a calling convention
directly, instead preferring to use an attribute that allows for
differentiating between "machine-mode" and "superivsor-mode" interrupts.
Finally, some effort has been made to guide those who may not yet be
aware of the differences between machine-mode and supervisor-mode
interrupts as to why no `riscv-interrupt` calling convention is exposed
through rustc, and similarly for why `riscv-interrupt-u` makes no
appearance (as it would complicate future LLVM upgrades).
[clang-attr]: https://clang.llvm.org/docs/AttributeReference.html#interrupt-risc-v
[full-frame-save]: 9281af2ecf/src/lib.rs (L440-L469)
[implemented by]: b7fb2a3fec/llvm/lib/Target/RISCV/RISCVRegisterInfo.cpp (L61-L67)
[callee-save]: 973f1fe7a8/llvm/lib/Target/RISCV/RISCVCallingConv.td (L30-L37)
[rfc]: https://github.com/rust-lang/rfcs/pull/3246
Similar to prior support added for the mips430, avr, and x86 targets
this change implements the rough equivalent of clang's
[`__attribute__((interrupt))`][clang-attr] for riscv targets, enabling
e.g.
```rust
static mut CNT: usize = 0;
pub extern "riscv-interrupt-m" fn isr_m() {
unsafe {
CNT += 1;
}
}
```
to produce highly effective assembly like:
```asm
pub extern "riscv-interrupt-m" fn isr_m() {
420003a0: 1141 addi sp,sp,-16
unsafe {
CNT += 1;
420003a2: c62a sw a0,12(sp)
420003a4: c42e sw a1,8(sp)
420003a6: 3fc80537 lui a0,0x3fc80
420003aa: 63c52583 lw a1,1596(a0) # 3fc8063c <_ZN12esp_riscv_rt3CNT17hcec3e3a214887d53E.0>
420003ae: 0585 addi a1,a1,1
420003b0: 62b52e23 sw a1,1596(a0)
}
}
420003b4: 4532 lw a0,12(sp)
420003b6: 45a2 lw a1,8(sp)
420003b8: 0141 addi sp,sp,16
420003ba: 30200073 mret
```
(disassembly via `riscv64-unknown-elf-objdump -C -S --disassemble ./esp32c3-hal/target/riscv32imc-unknown-none-elf/release/examples/gpio_interrupt`)
This outcome is superior to hand-coded interrupt routines which, lacking
visibility into any non-assembly body of the interrupt handler, have to
be very conservative and save the [entire CPU state to the stack
frame][full-frame-save]. By instead asking LLVM to only save the
registers that it uses, we defer the decision to the tool with the best
context: it can more accurately account for the cost of spills if it
knows that every additional register used is already at the cost of an
implicit spill.
At the LLVM level, this is apparently [implemented by] marking every
register as "[callee-save]," matching the semantics of an interrupt
handler nicely (it has to leave the CPU state just as it found it after
its `{m|s}ret`).
This approach is not suitable for every interrupt handler, as it makes
no attempt to e.g. save the state in a user-accessible stack frame. For
a full discussion of those challenges and tradeoffs, please refer to
[the interrupt calling conventions RFC][rfc].
Inside rustc, this implementation differs from prior art because LLVM
does not expose the "all-saved" function flavor as a calling convention
directly, instead preferring to use an attribute that allows for
differentiating between "machine-mode" and "superivsor-mode" interrupts.
Finally, some effort has been made to guide those who may not yet be
aware of the differences between machine-mode and supervisor-mode
interrupts as to why no `riscv-interrupt` calling convention is exposed
through rustc, and similarly for why `riscv-interrupt-u` makes no
appearance (as it would complicate future LLVM upgrades).
[clang-attr]: https://clang.llvm.org/docs/AttributeReference.html#interrupt-risc-v
[full-frame-save]: 9281af2ecf/src/lib.rs (L440-L469)
[implemented by]: b7fb2a3fec/llvm/lib/Target/RISCV/RISCVRegisterInfo.cpp (L61-L67)
[callee-save]: 973f1fe7a8/llvm/lib/Target/RISCV/RISCVCallingConv.td (L30-L37)
[rfc]: https://github.com/rust-lang/rfcs/pull/3246
internal: use `Cast::cast()` instead of explicit interning
I firmly believe that we should generally use `cast()` instead of interning `GenericArgData` to construct `GenericArg` because it's less verbose and more readable.
Support doc links that resolve to fields
Fixes#15331
Also removes `Resolver::resolve_module_path_in_trait_assoc_items()` and reimplements it in hir with other `Resolver` methods to decouple things a bit.
Handle `#[cfg]`s on generic parameters
Records attributes on generic parameters in the item tree and filters out generic parameters disabled by `#[cfg]`s in `generic_params_query`.
Closes#11756
internal: Turn unresolved proc macro expansions into missing expressions
Reduces the amount of type related errors one gets when proc macro expansion is disabled.
SCIP requires symbols to be unique, but multiple functions may have a
parameter with the same name. Qualify parameters according to the
containing function.
When cross compiling macos → dragonfly the dist build fails in the
proc-maro-test-impl crate with the following error:
ld: unknown option: -z\nclang: error: linker command failed with
exit code 1 (use -v to see invocation)
This appears to be a wart stemming from using an Apple host for cross
compiling. Passing the target along to cargo allows it to pick up
a linker that it understands and DTRT.
Exclude non-identifier aliases from completion filtering text
When building `CompletionItem`s, this excludes aliases that aren't valid identifiers from the "lookup" text used to filter completions in the LSP client. Including them results in weird completion filtering behavior e.g. `Partial>` matching a completion for the `PartialOrd` trait because it has a doc alias of ">".
Closes#14692
Add ExternCrateDecl to HIR
Adding these doesn't really require much design effort as they represent a single import, unlike use trees which are one item that represent 0 or more imports.
We only resolve to this definition when actually resolving on the name or alias of an `extern crate name as alias` item, not usages yet as that requires far more changes that won't lead anywhere without giving it more thought. Nevertheless the changes slightly improve IDE things, an example being hover on the decl showing the merged doc comments for example.
cc https://github.com/rust-lang/rust-analyzer/issues/14079
Added remove unused imports assist
This resolves the most important part of #5131. I needed to make a couple of cosmetic changes to the search infrastructure to do this.
A few open questions:
* Should imports that don't resolve to anything be considered unused? I figured probably not, but it would be a trivial change to make if we want it.
* Is there a cleaner way to make the edits to the use list?
* Is there a cleaner way to get the list of uses that intersect the current selection?
* Is the performance acceptable? When testing this on itself, it takes a good couple seconds to perform the assist.
* Is there a way to hide the rustc diagnostics that overlap with this functionality?
internal: Defer structured snippet rendering to allow escaping snippet bits
Since we know exactly where snippets are, we can transparently escape snippet bits to the exact text edits that need it, and not have to do it for anything other text edits.
Also will eventually fix#11006 once all assists are migrated. This comes as a side-effect of text edits that don't have snippets get marked as having no insert formatting at all.
Don't provide `add_missing_match_arms` assist when upmapping match arm list failed
Fixes#15310
We shouldn't provide the assist when we fail to find the original match arm list.
Note that this PR will temporarily make the assist not applicable when attribute macro operates on the match expression in question, just like the case in #15310, for most of the current stable toolchain users. This is because the sysroot-abi proc-macro-srv on the current stable [discards] spans for `Group` delimiters in some code paths, which the popular `proc-macro2` crate almost always calls, and it makes the identity of match arm list's brackets lost, leading to the upmapping failure. This has been fixed by #14960, which will land in the next stable, 1.71.
[discards]: 8ede3aae28/src/tools/rust-analyzer/crates/proc-macro-srv/src/abis/abi_sysroot/ra_server.rs (L231)
bugfix : skip doc(hidden) default members
fixes #14957 . I have two questions :
1. I am definitely looking for a more idiomatic way for the things I added in `crates/ide-assists/src/utils.rs`. See `FIXME` in that file.
2. Would it be actually better to change `DefaultMethods` to something like
```rust
enum DefaultMethods {
Only( IgnoreHidden ( bool ) ) ,
None
}
```
instead of adding a boolean to every function that calls `crates/ide-assists/src/utils.rs::filter_assoc_items`
fix: Expand eager macros to delimited comma separated expression list
Prior to this, we were just parsing it as an expression which works fine for `()` and `[]` calls as those are tuple and array expressions respectively, but if tails for `{}` calls which with my recent changes reported errors for such eager macro invocations.
Fixup path fragments upon MBE transcription
Fixes#14367
There are roughly two types of paths: paths in expression context, where a separator `::` between an identifier and its following generic argument list is mandatory, and paths in type context, where `::` can be omitted.
Unlike rustc, we need to transform the parsed fragments back into tokens during transcription. When the matched path fragment is a type-context path and is transcribed as an expression-context path, verbatim transcription would cause a syntax error.
This PR fixes up path fragments by inserting `::` to make sure they are syntactically correct in all contexts. Note that this works because expression-context paths are a strict superset of type-context paths.
Add manual implementation of clone for tuples in mir interpreter
And some other minor changes.
Clone for tuple is not implemented in the std and it is magically implemented by the compiler, so we need this.
Properly infer types with type casts
This PR reenables `Expectation::Castable` (previous attempt at #14104, reverted by #14120) and implements type cast checks, which enable us to infer a bit more.
Castable expectations are relatively weak -- they only influence the inference if we cannot infer the types by other means. Therefore, we need to defer possible type unification with the casted type until we type check all expressions of the body. This PR adds a struct and slots in `InferenceContext` for the deferred cast checks (c.f. [`CastCheck`] in `rustc_hir_typeck`).
I only implemented the bits that affect the inference result. It should be possible to return type adjustments for well-formed casts and report diagnostics for invalid casts, but I'm leaving them for future work for now.
Fixes#11571Fixes#15246
[`CastCheck`]: da1d099f91/compiler/rustc_hir_typeck/src/cast.rs (L55)
Normalize expected ty in call arguments
fix#15321
I'm not sure if we should do this, or add a normalize in the beginning of `infer_expr_inner`, or somewhere else. r? `@lowr`
Report `incorrect-ident-case` for inner items
Fixes#15319
Although we have been collecting the diagnostics for inner items within function bodies, we were discarding them and never reported to the users. This PR makes sure that they are all reported and additionally collects the diagnostics for inner items within const bodies, static bodies, and enum variant bodies.
Pass `TraitEnvironment` into `layout_ty` and `const_eval`
We need to do either this or get rid of trait environment in `normalize_ty`. Let's go with this for now.
rust-lang/rust#113695 makes the dylib metadata uncompressed for perf
reasons. This commit allows reading both the current compressed and
future uncompressed dylib metadata.
Make fields of mir::Terminator public
When trying to use the RA crate, I am unable to access the fields in `hir_def::mir::Terminator`.
I don't see any reason, why these should be private, especially as the fields of `hir_def::mir::Statement` are `pub`.
I am not sure if the fields in `hir_def::mir::SwitchTargets` should be made `pub` too, but at least they are read-accessible via some public methods..
Sorry if I missed something, this is my first PR.
Mark test for MIR execution limit as slow test
The test for MIR execution limit accounts for ~2/3 of total execution time of non-slow hir-ty tests. It significantly slows down edit-and-run-test type of workflow. Can we mark it as a slow test?
internal: Migrate assists to the structured snippet API, part 3
Continuing from #15231
Migrates the following assists:
- `add_missing_match_arms`
- `fix_visibility`
- `promote_local_to_const`
The `add_missing_match_arms` changes are best reviewed commit-by-commit since they're relatively big changes compared to the rest of the commits.
Structured snippets precisely track which text edits need to be marked
as snippet text edits, but the cases where structured snippets aren't
used but snippets are still present are for simple single text-edit
changes, so it's perfectly fine to mark all one of them as being a
snippet text edit
`clone_for_update` is relatively cheap in comparison, since making a
node require parsing an entire source text
Adds a test to make sure that it doesn't crash when multiple uses are
present.
Skip building subtrees for builtin derives
This is a waste of resources, we go from node to subtree just to go from subtree to node in the expander impl. We can skip the subtree building and only build the tokenmap instead.
internal: Migrate more assists to use the structured snippet API
Continuing from #14979
Migrates the following assists:
- `generate_derive`
- `wrap_return_type_in_result`
- `generate_delegate_methods`
As a bonus, `generate_delegate_methods` now generates the function and impl block at the correct indentation 🎉.
`does_not_fill_wildcard_with_wildcard`
and `does_not_fill_wildcard_with_partial_wildcard_and_wildcard`
both made no modifications to the code,
which is a problem for mutable ast porting as it generates a best-effort
minimal set of text edits,
and assists require at least one text edit.
# Overview
Extracting a match arm value that has type unit into a function, when a
comma already follows the match arm value, results in an invalid (syntax
error) semicolon added between the newly generated function's generated
call and the comma.
# Example
Running this extraction
```rust
fn main() {
match () {
_ => $0()$0,
};
}
```
would lead to
```rust
fn main() {
match () {
_ => fun_name();,
};
}
fn fun_name() {
}
```
# Issue / Fix details
This happens because when there is no comma, rust-analyzer would simply
add the comma and wouldn't even try to evaluate whether it needs to add
a semicolon. But when the comma is there, it proceeds to evaluate
whether it needs to add a semicolon and it looks like the evaluation
logic erroneously ignores the possibility that we're in a match arm.
IIUC it never makes sense to add a semicolon when we're extracting from
a match arm value, so I've adjusted the logic to always decide against
adding a semicolon when we're in a match arm
Can actually split out adding the functions from getting the impl to
update or create thanks to being able to refer to the impl ast node.
FIXME Context:
Unfortunately we can't adjust the indentation of the newly added function
inside of `ast::AssocItemList::add_item` since for some reason the `todo!()`
placeholder generated by `add_missing_impl_members` and
`replace_derive_with_manual_impl` gets indented weirdly.
Implement recursion in mir interpreter without recursion
This enables interpreting functions with deep stack + profiling. I also applied some changes to make it faster based on the profiling result.
Unify getter and setter assists
This PR combines what previously have been two different files into a single file. I want to talk about the reasons why I did this. The issue that prompted this PR ( and before I forget : this pr fixes#15080 ) mentions an interesting behavior. We combine these two assists into an assist group and the order in which the assists are listed in this group changes depending on the text range of the selected area. The reason for that is that VSCode prioritizes actions that have a bigger impact in a smaller area and until now generate setter assist was only possible to be invoked for a single field whereas you could generate multiple getters for the getter assist. So I used the latter's infra to make former applicable to multiple fields, hence the unification. So this PR solves in essence
1. Make `generate setter` applicable to multiple fields
2. Provide a consistent order of the said assists in listing.
Don't show `unresolved-field` diagnostic for missing names
I don't think reporting ``"no field `[missing name]` on type `SomeType`"`` makes much sense because it's a syntax error rather than a semantic error. We already report a syntax error for it and I find it sufficient.
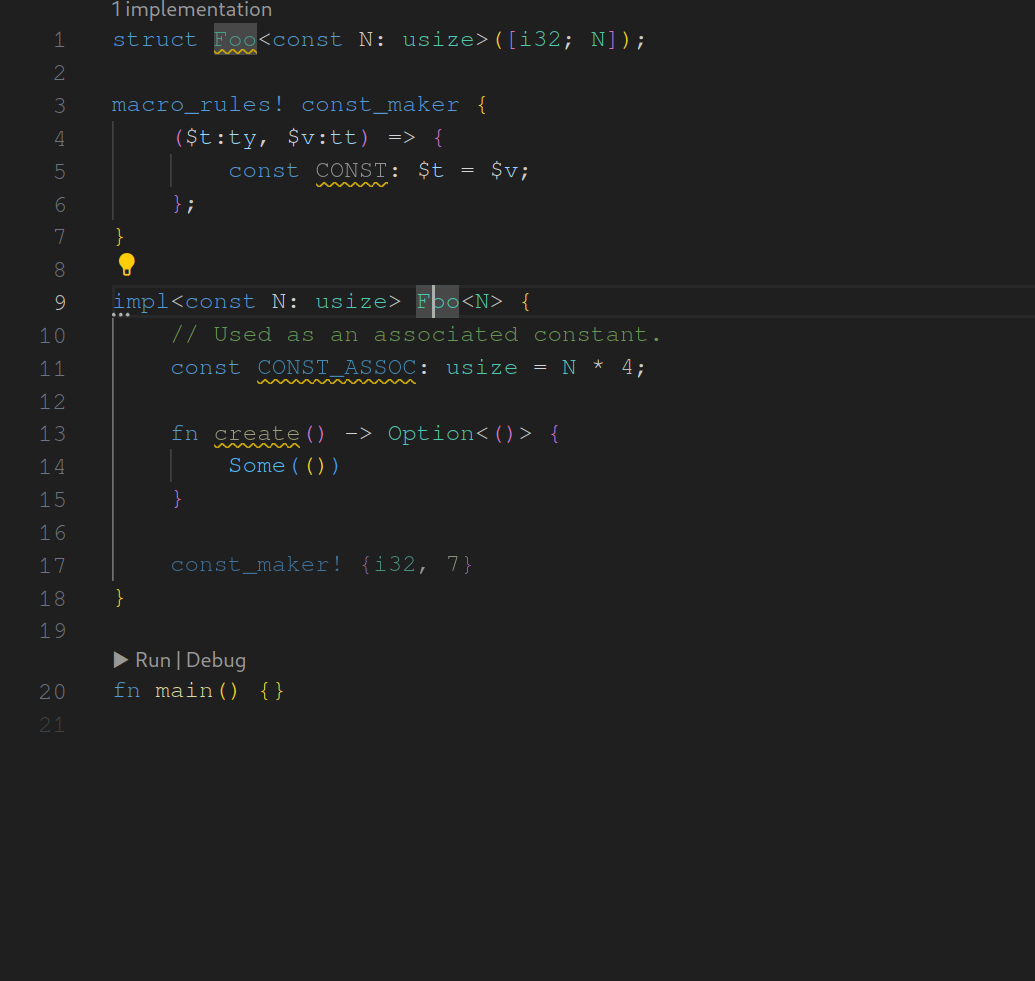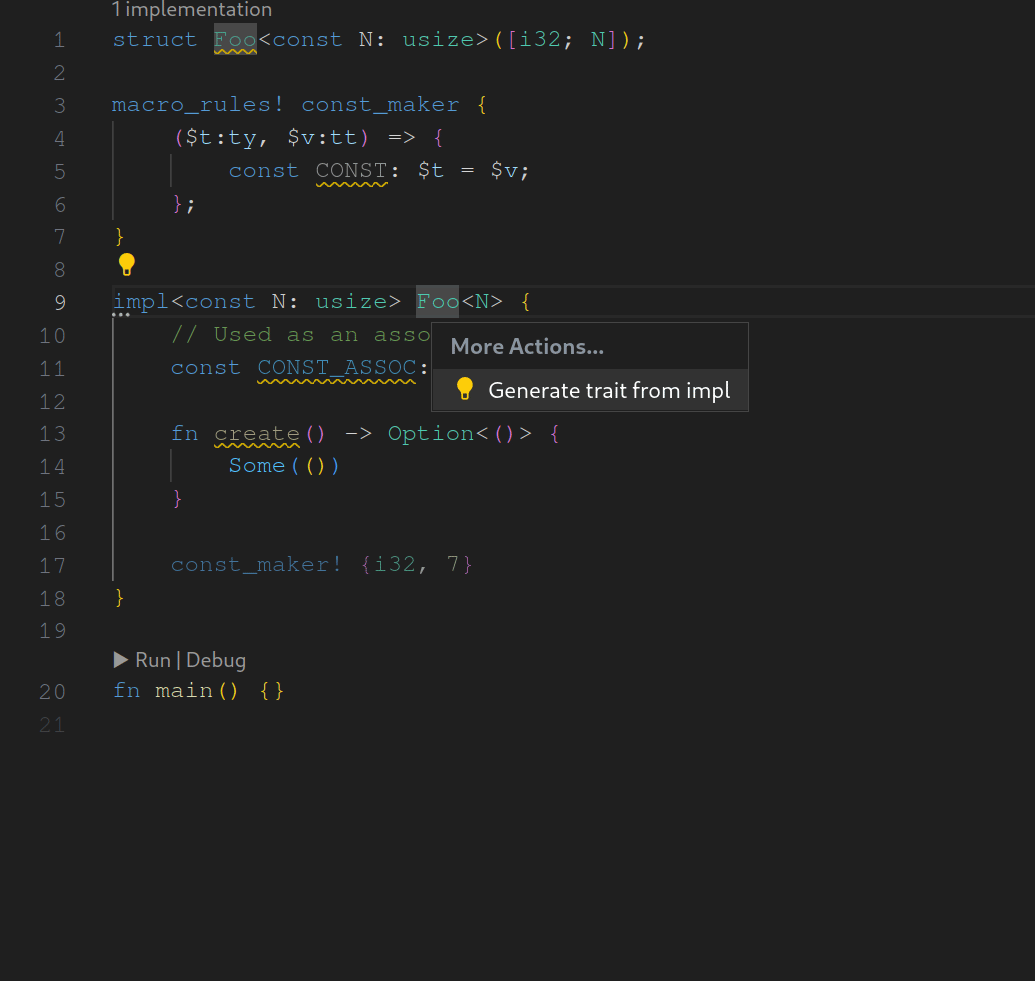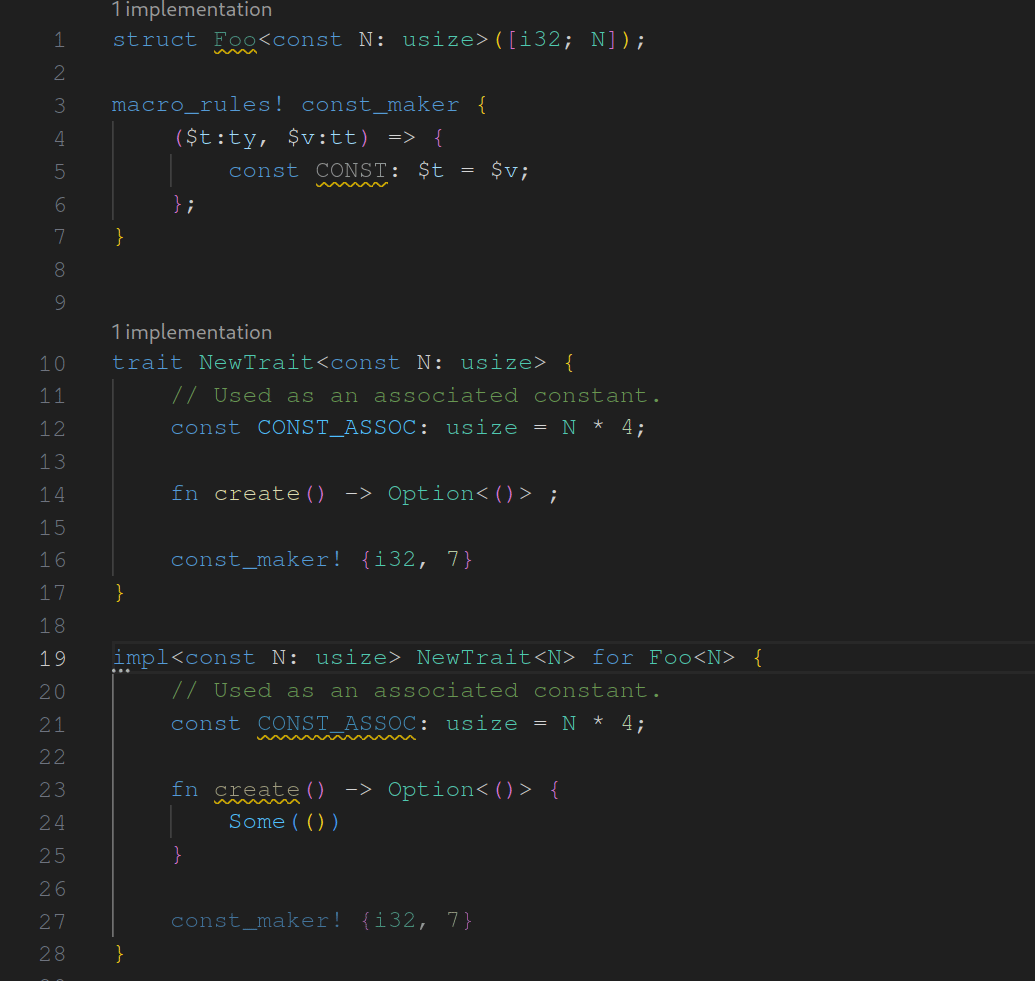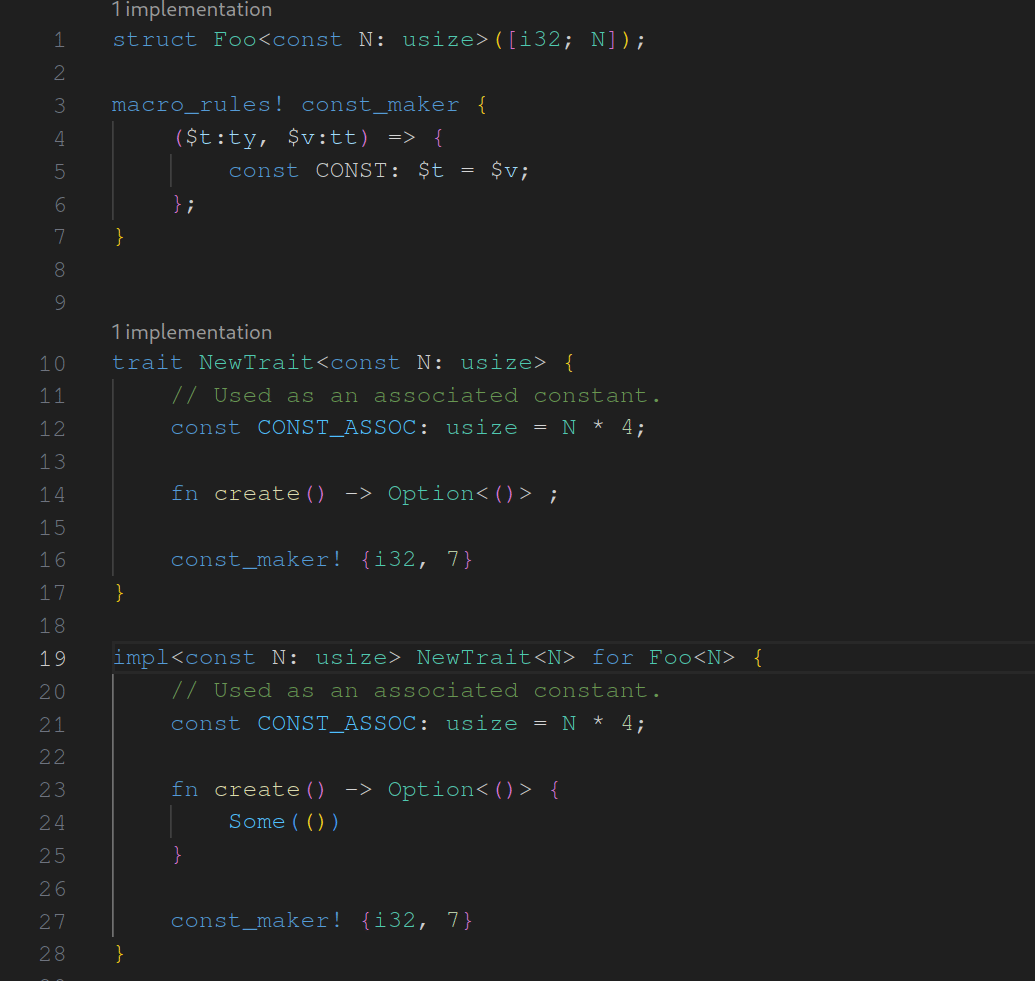
assist : generate trait from impl
fixes#14987 . As the name suggests this assist is used to generate traits from inherent impls while adapting the original impl to fit to the newly generated trait. I made some decisions regarding when the assist should be applicable. These are surely open to discussion. I looking forward to any feedback.
Disable remove unnecessary braces diagnotics for self imports
Disable `remove unnecessary braces` diagnostic if the there is a `self` inside the bracketed `use`
Fix#15191
Support GATs in bounds for associated types
Chalk has a dedicated IR for bounds on trait associated type: `rust_ir::InlineBound`. We have been failing to convert GATs inside those bounds from our IR to chalk IR. This PR provides an easy fix for it: properly take GATs into account during the conversion.
Map our diagnostics to rustc and clippy's ones
And control their severity by lint attributes `#[allow]`, `#[deny]` and ... .
It doesn't work with proc macros and I would like to fix that before merge but I don't know how to do it.
internal: Format let-else
As nightly finally got support for it I went ahead and formatted r-a with the latest nightly, then with the latest stable (in case other stuff changed)
Split out project loading capabilities from rust-analyzer crate
External tools currently depend on the entire lsp infra for no good reason so let's lift that out so those tools have something better to depend on
Clean up `ImportMap`
There are several things in `hir_def::import_map` that are never used. This PR removes them and restructures the code. Namely:
- Removes `Query::name_only`, because it's *always* true.
- Because of this, we never took advantage of storing items' full path. This PR removes `ImportPath` and changes `ImportInfo` to only store items' name, which should reduce the memory consumption to some extent.
- Removes `SearchMode::Contains` for `Query` because it's never used.
- Merges `Query::assoc_items_only` and `Query::exclude_import_kinds` into `Query::assoc_mode`, because the latter is never used besides filtering associated items out.
Best reviewed one commit at a time. I made sure each commit passes full test suite. I can squash the first three commits if needed.
Use anonymous lifetime where possible
Because anonymous lifetimes are *super* cool.
More seriously, I believe anonymous lifetimes, especially those in impl headers, reduce cognitive load to a certain extent because they usually signify that they are not relevant in the signature of the methods within (or that we can apply the usual lifetime elision rules even if they are relevant).
Fix runnable detection for `#[tokio::test]`
fix#15141
It is hacky, and it wouldn't work for e.g. this case:
```Rust
use ::core::prelude;
#[prelude::v1::test]
fn foo() {
}
```
But it works for the tokio case. We should use the name resolution here somehow, and after that we should probably also get rid of the ast based `test_related_attribute` function.
internal: add `library` fixture meta
Currently, there is no way to specify `CrateOrigin` of a file fixture ([this] might be a bug?). This PR adds `library` meta to explicitly specify the fixture to be `CrateOrigin::Library` and also makes sure crates that belong to a library source root are set `CrateOrigin::Library`.
(`library` isn't really the best name. It essentially means that the crate is outside workspace but `non_workspace_member` feels a bit too long. Suggestions for the better name would be appreciated)
Additionally:
- documents the fixture meta syntax as thoroughly as possible
- refactors relevant code
[this]: 4b06d3c595/crates/base-db/src/fixture.rs (L450)
Fix `self` and `super` path resolution in block modules
This PR fixes `self` and `super` path resolution with block modules involved.
Previously, we were just going up the module tree count-of-`super` times without considering block modules in the way, and then if we ended up in a block `DefMap`, we adjust "to the containing crate-rooted module". While this seems to work in most real-world cases, we failed to resolve them within peculiar module structures.
`self` and `super` should actually be resolved to the nearest non-block module, and the paths don't necessarily resolve to a crate-rooted module. This PR makes sure every `self` and `super` segment in paths are resolved to a non-block module.
internal: support `#[rustc_coinductive]`
rust-lang/rust#100386 changed the trait solver so that `Sized` is treated as coinductive trait, just like auto traits. This is now controlled by the perma-unstable `#[rustc_coinductive]` attribute (rust-lang/rust#108033), which this PR adds support for.
In practice, I don't think this matters much if at all. Currently we don't give chalk enough information so chalk cannot precisely (dis)prove `Sized` bounds.
internal: Add run-tests command
This command is similar to `cargo test` except that it uses r-a to run tests instead of compiling and running them with rustc. This is slower than `cargo test` and it is only useful for me to see a bird view of what needs to be fixed. The current output is:
```
48 passed, 5028 failed, 2 ignored
All tests 174.74s, 648ginstr
```
48 is very low, but higher than what I originally thought.
Now that there is some passing tests, I can show the plan:
https://github.com/rust-lang/rust-analyzer/assets/45197576/76d7d777-1843-4ca4-b7fe-e463bdade6cb
That is, at the end, I want to be able to immediately re run every test after every change. (0.5s is not really immediate, but it's not finished yet, and it is way better than 8s that running a typical test in r-a will take on my system)
Change comparsion for checking if number is negative to include 128
The last byte in Little-Endian representation of negative integers start at 128 (Ox80) till 255 (OxFF). The comparison before the fix didn't check for 128 which made is_negative variable as false.
Potentially fixes#15096
Added a test near positive extermes and two test near negative
extermes as well one for 0.
Added a test using the `as` cast and one with comparison with 0.
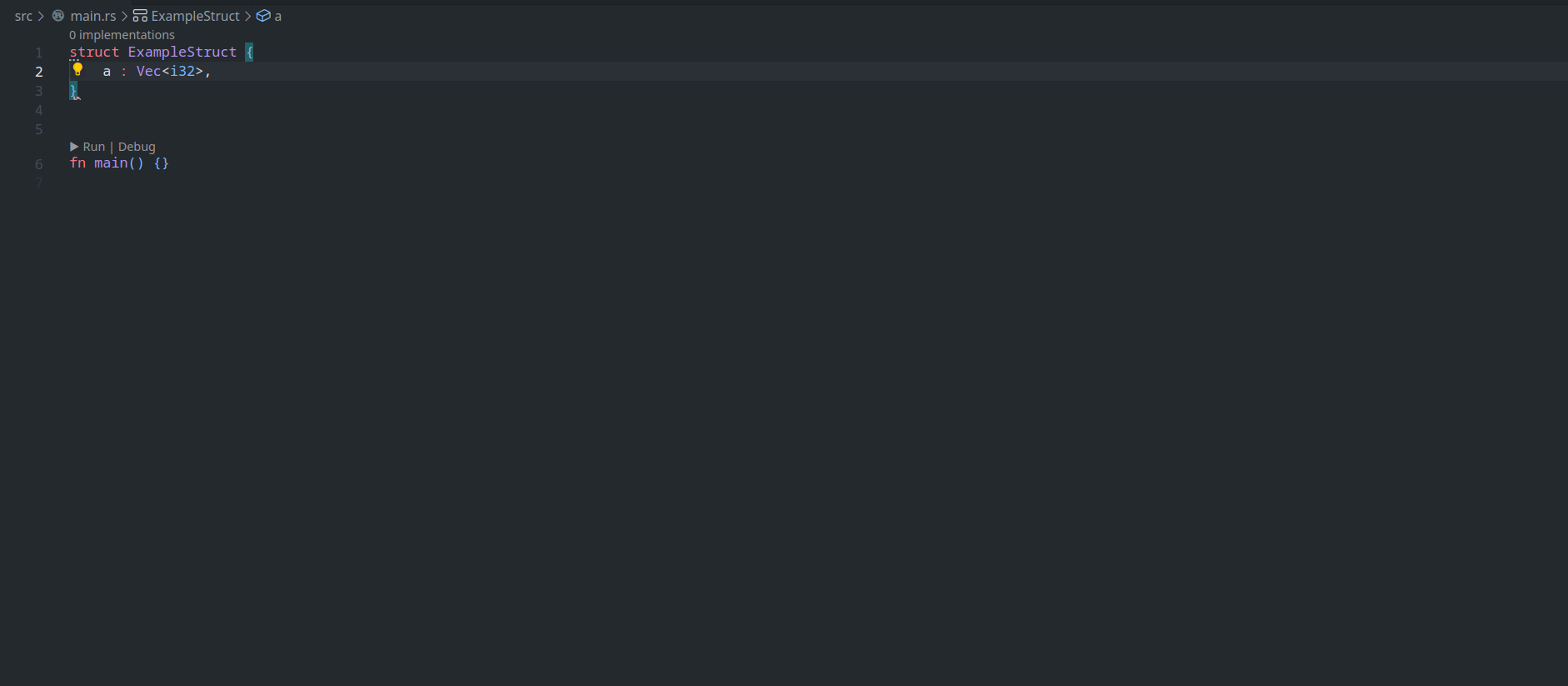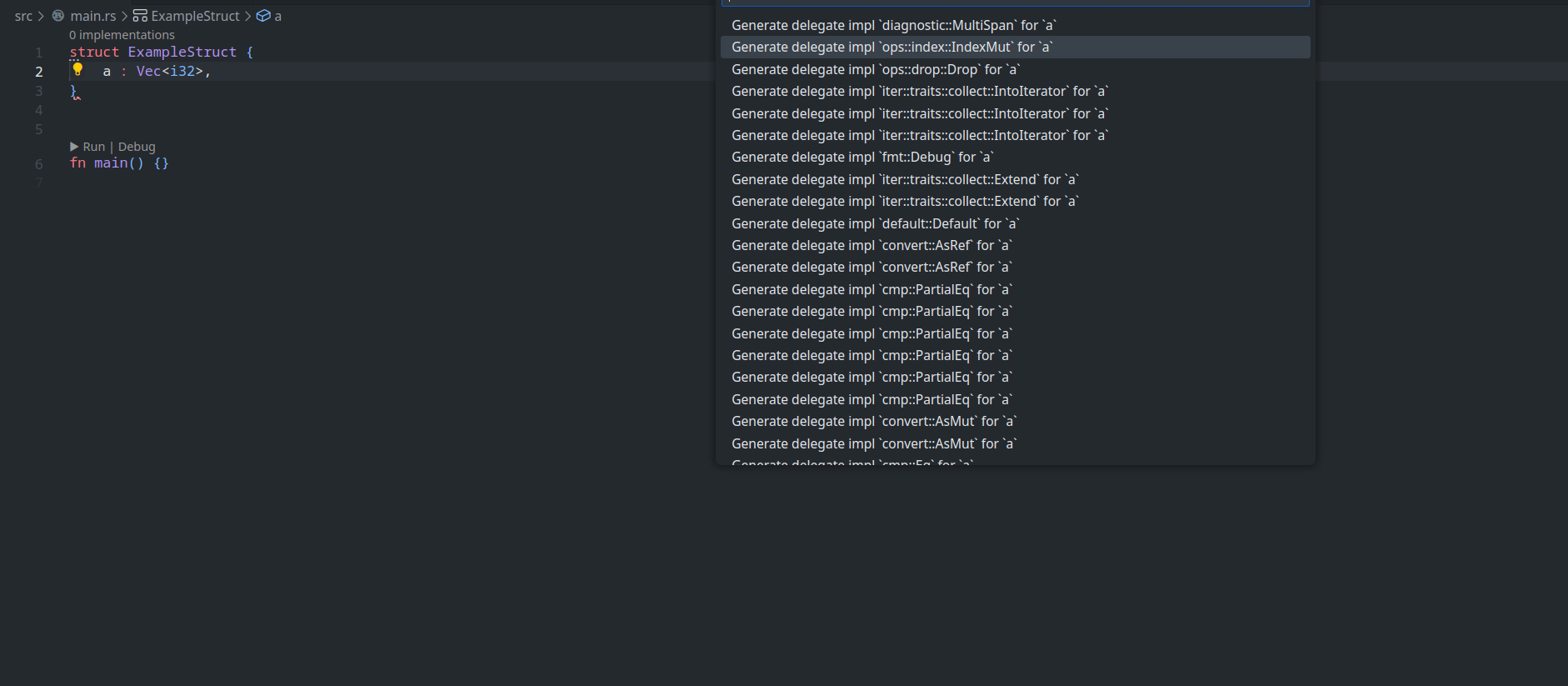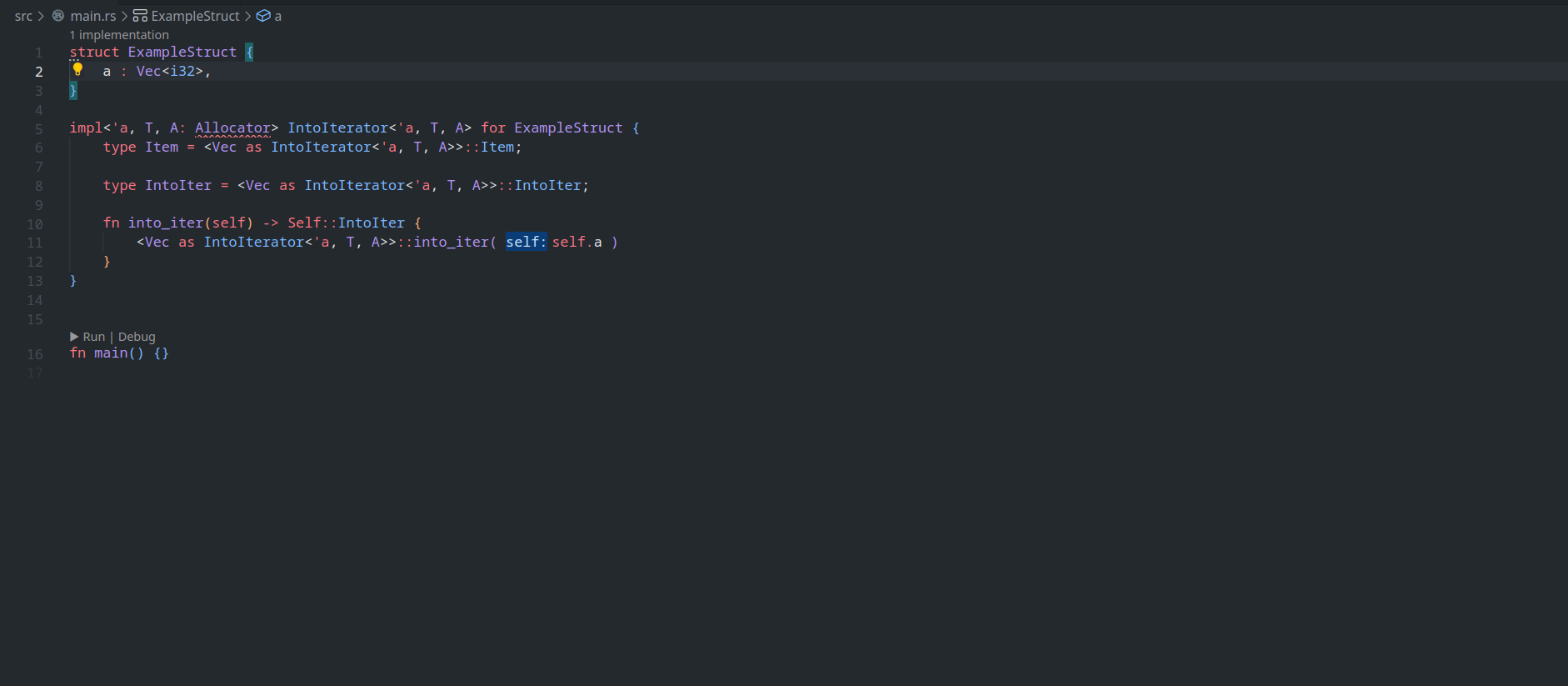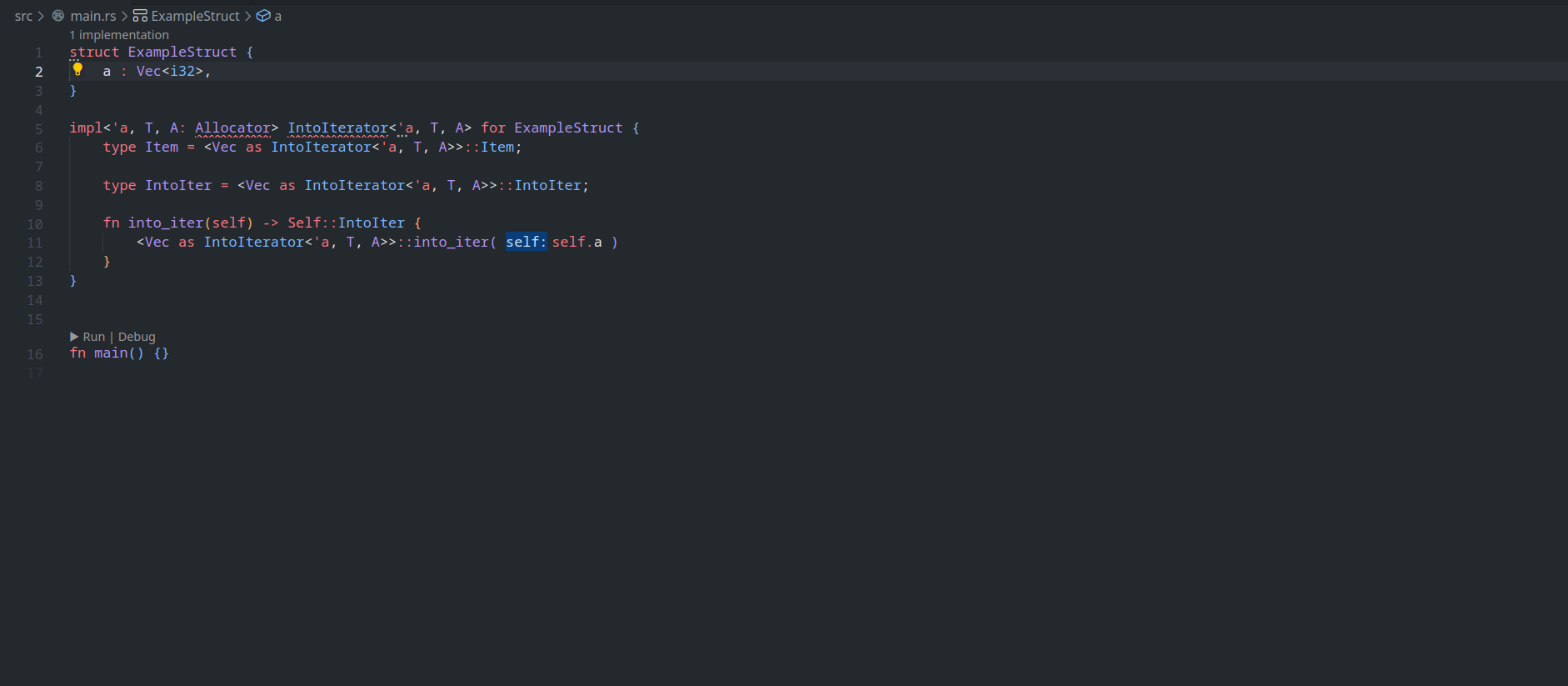
feature : assist delegate impl
This PR ( fixes#14386 ) introduces a new IDE assist that generates a trait impl for a struct that delegates a field. This is a draft because the current `ide_db::path_transform::PathTransform` produces some unwanted results when it deals with extern crates, an example of which I attach as a GIF.
GIFs :
1. A general case
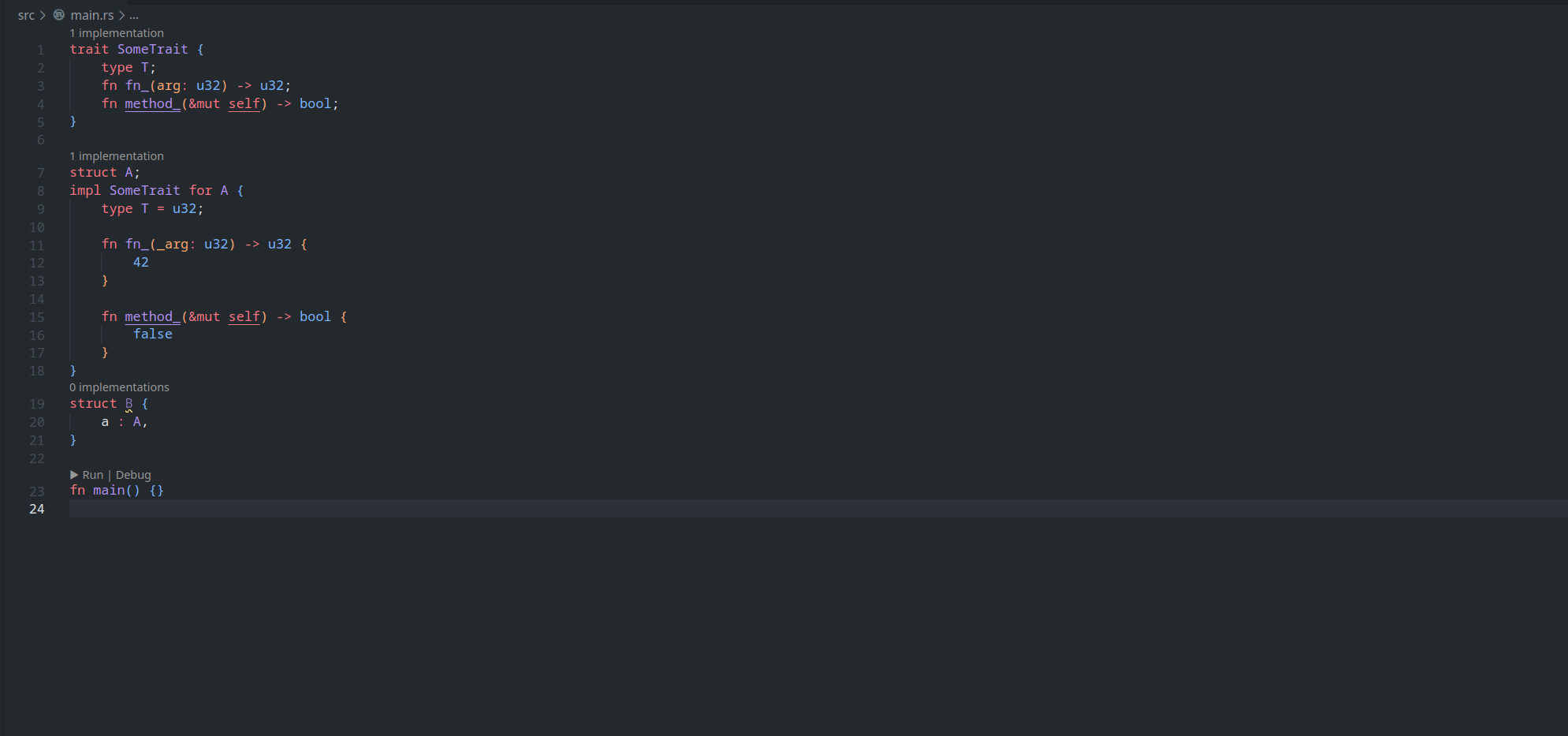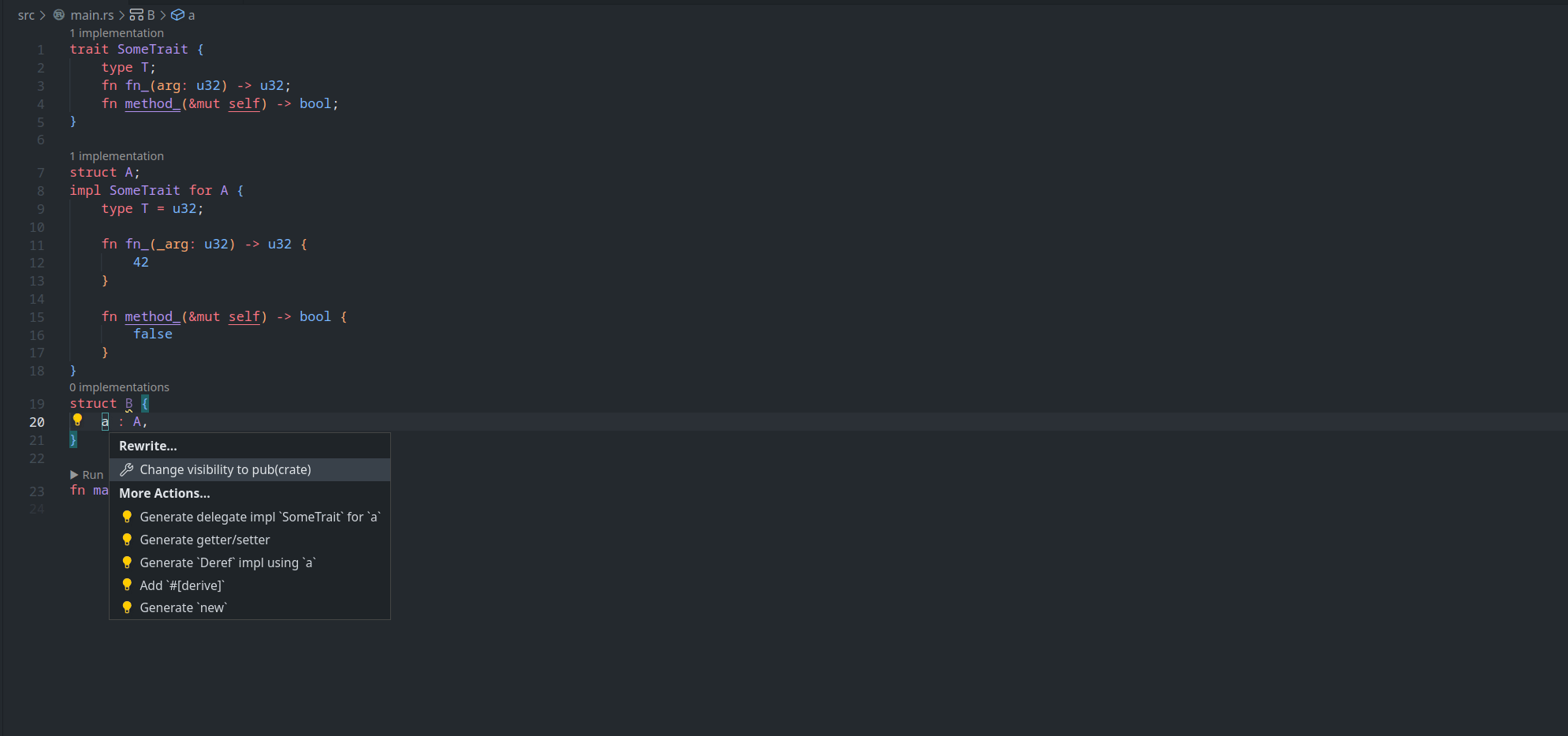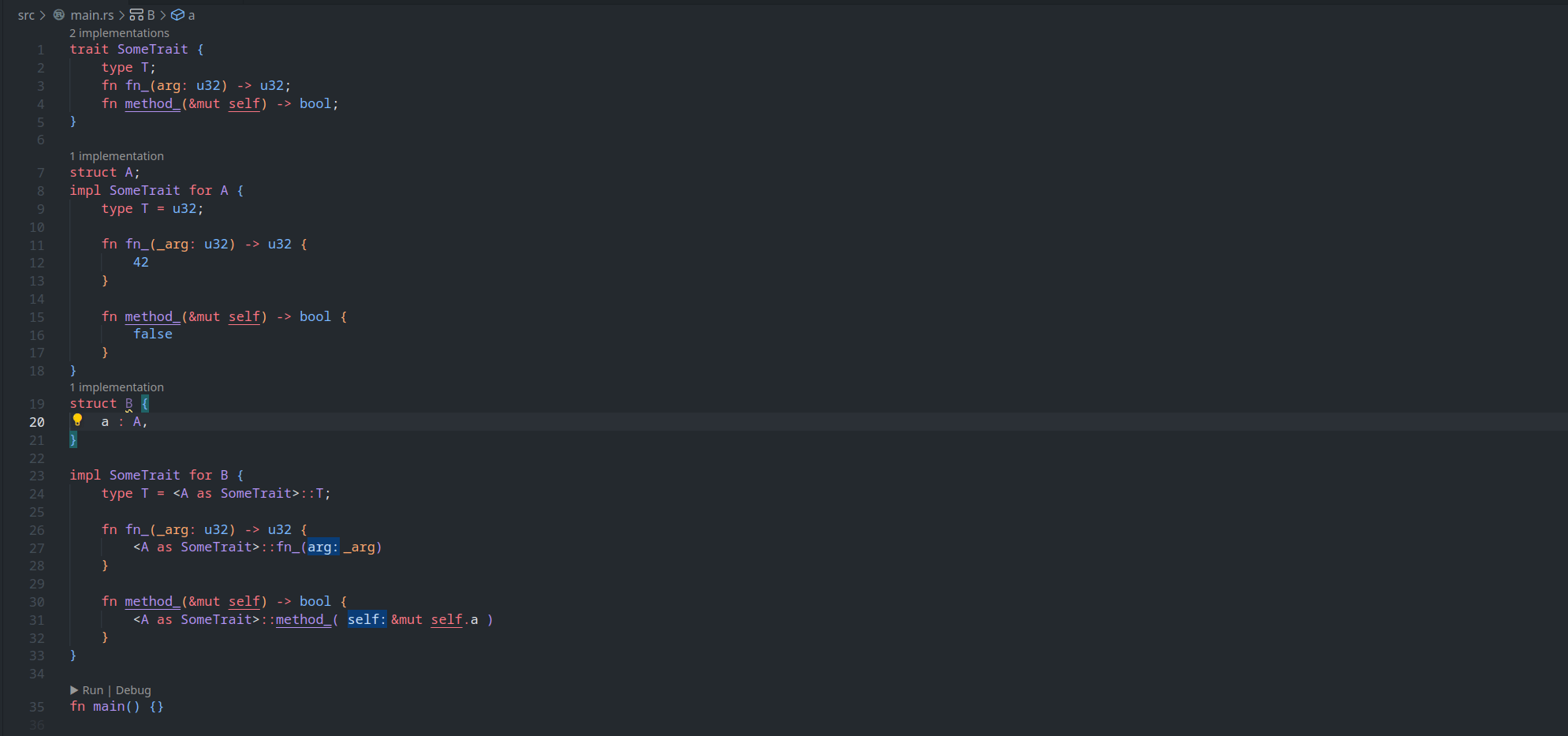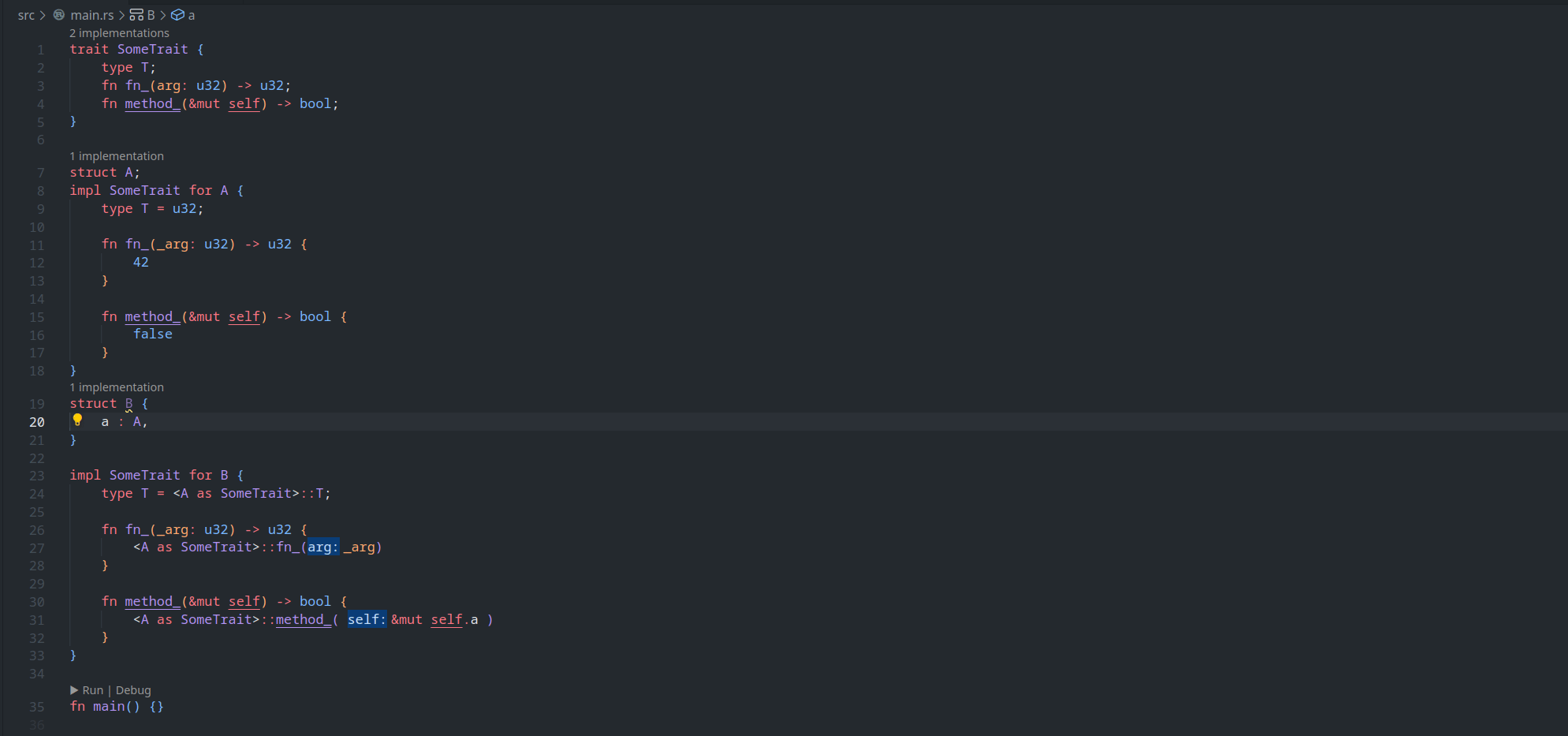
2. A case where `ide_db::path_transform::PathTransform` fails to correctly resolve a property ( take `Allocator` as an example ) to its full path, thus causing an error to occur. ( Not to even mention that resolving this causes another error `use of unstable library feature 'allocator_api'` to occur
Reason: The last byte in Little Endian representation of negative
integers start at 128 (Ox80) till 255 (OxFF). The comparison before
the fix didn't check for 128 which made is_negative variable as false.
internal: remove spurious regex dependency
- replace tokio's env-filter with a smaller&simpler targets filter
- reshuffle logging infra a bit to make sure there's only a single place where we read environmental variables
- use anyhow::Result in rust-analyzer binary
- replace tokio's env-filter with a smaller&simpler targets filter
- reshuffle logging infra a bit to make sure there's only a single place
where we read environmental variables
- use anyhow::Result in rust-analyzer binary
Remove scope_for_def calls as the definition have been removed entirely.
As a result of this change the problem with false path resolutions has been solved.