mirror of
https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks
synced 2024-12-25 12:33:39 +00:00
5 KiB
5 KiB
unlink
{% hint style="success" %}
Aprenda e pratique Hacking AWS: HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
Aprenda e pratique Hacking GCP:  HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Support HackTricks
- Confira os planos de assinatura!
- Junte-se ao 💬 grupo do Discord ou ao grupo do telegram ou siga-nos no Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live.
- Compartilhe truques de hacking enviando PRs para os HackTricks e HackTricks Cloud repositórios do github.
Código
// From https://github.com/bminor/glibc/blob/master/malloc/malloc.c
/* Take a chunk off a bin list. */
static void
unlink_chunk (mstate av, mchunkptr p)
{
if (chunksize (p) != prev_size (next_chunk (p)))
malloc_printerr ("corrupted size vs. prev_size");
mchunkptr fd = p->fd;
mchunkptr bk = p->bk;
if (__builtin_expect (fd->bk != p || bk->fd != p, 0))
malloc_printerr ("corrupted double-linked list");
fd->bk = bk;
bk->fd = fd;
if (!in_smallbin_range (chunksize_nomask (p)) && p->fd_nextsize != NULL)
{
if (p->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize != p
|| p->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize != p)
malloc_printerr ("corrupted double-linked list (not small)");
// Added: If the FD is not in the nextsize list
if (fd->fd_nextsize == NULL)
{
if (p->fd_nextsize == p)
fd->fd_nextsize = fd->bk_nextsize = fd;
else
// Link the nexsize list in when removing the new chunk
{
fd->fd_nextsize = p->fd_nextsize;
fd->bk_nextsize = p->bk_nextsize;
p->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize = fd;
p->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = fd;
}
}
else
{
p->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize = p->bk_nextsize;
p->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = p->fd_nextsize;
}
}
}
Explicação Gráfica
Confira esta ótima explicação gráfica do processo unlink:
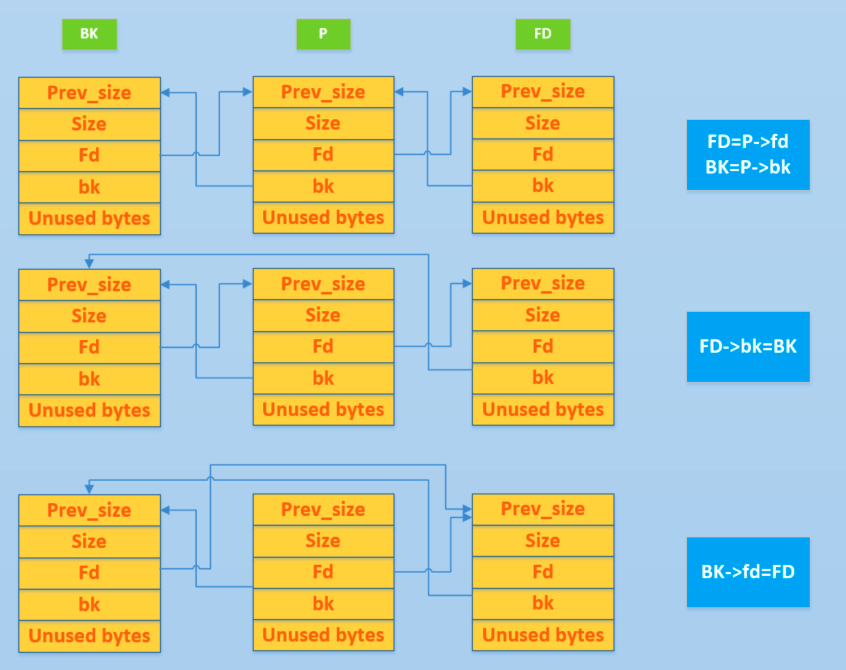
https://ctf-wiki.mahaloz.re/pwn/linux/glibc-heap/implementation/figure/unlink_smallbin_intro.png
Verificações de Segurança
- Verifique se o tamanho indicado do chunk é o mesmo que o prev_size indicado no próximo chunk
- Verifique também se
P->fd->bk == PeP->bk->fw == P - Se o chunk não for pequeno, verifique se
P->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize == PeP->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize == P
Vazamentos
Um chunk não vinculado não limpa os endereços alocados, então tendo acesso a ele, é possível vazar alguns endereços interessantes:
Vazamentos de Libc:
- Se P estiver localizado na cabeça da lista duplamente encadeada,
bkestará apontando paramalloc_statena libc - Se P estiver localizado no final da lista duplamente encadeada,
fdestará apontando paramalloc_statena libc - Quando a lista duplamente encadeada contém apenas um chunk livre, P está na lista duplamente encadeada, e tanto
fdquantobkpodem vazar o endereço dentro demalloc_state.
Vazamentos de Heap:
- Se P estiver localizado na cabeça da lista duplamente encadeada,
fdestará apontando para um chunk disponível no heap - Se P estiver localizado no final da lista duplamente encadeada,
bkestará apontando para um chunk disponível no heap - Se P estiver na lista duplamente encadeada, tanto
fdquantobkestarão apontando para um chunk disponível no heap
{% hint style="success" %}
Learn & practice AWS Hacking: HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
Learn & practice GCP Hacking:  HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Support HackTricks
- Check the subscription plans!
- Join the 💬 Discord group or the telegram group or follow us on Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live.
- Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the HackTricks and HackTricks Cloud github repos.