7.3 KiB
Exploiting a debuggeable application
{% hint style="success" %}
Learn & practice AWS Hacking: HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
Learn & practice GCP Hacking:  HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Support HackTricks
- Check the subscription plans!
- Join the 💬 Discord group or the telegram group or follow us on Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live.
- Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the HackTricks and HackTricks Cloud github repos.
Bypassing root and debuggeable checks
This section of the post is a summary from the post https://medium.com/@shubhamsonani/hacking-with-precision-bypass-techniques-via-debugger-in-android-apps-27fd562b2cc0
Steps to Make an Android App Debuggable and Bypass Checks
Making the App Debuggable
Content based on https://medium.com/@shubhamsonani/hacking-with-precision-bypass-techniques-via-debugger-in-android-apps-27fd562b2cc0
-
Decompile the APK:
- Utilize the APK-GUI tool for decompiling the APK.
- In the android-manifest file, insert
android:debuggable=trueto enable debugging mode. - Recompile, sign, and zipalign the modified application.
-
Install the Modified Application:
- Use the command:
adb install <application_name>.
- Use the command:
-
Retrieve the Package Name:
- Execute
adb shell pm list packages –3to list third-party applications and find the package name.
- Execute
-
Set the App to Await Debugger Connection:
- Command:
adb shell am setup-debug-app –w <package_name>. - Note: This command must be run each time before starting the application to ensure it waits for the debugger.
- For persistence, use
adb shell am setup-debug-app –w -–persistent <package_name>. - To remove all flags, use
adb shell am clear-debug-app <package_name>.
- Command:
-
Prepare for Debugging in Android Studio:
- Navigate in Android Studio to File -> Open Profile or APK.
- Open the recompiled APK.
-
Set Breakpoints in Key Java Files:
- Place breakpoints in
MainActivity.java(specifically in theonCreatemethod),b.java, andContextWrapper.java.
- Place breakpoints in
Bypassing Checks
The application, at certain points, will verify if it is debuggable and will also check for binaries indicating a rooted device. The debugger can be used to modify app info, unset the debuggable bit, and alter the names of searched binaries to bypass these checks.
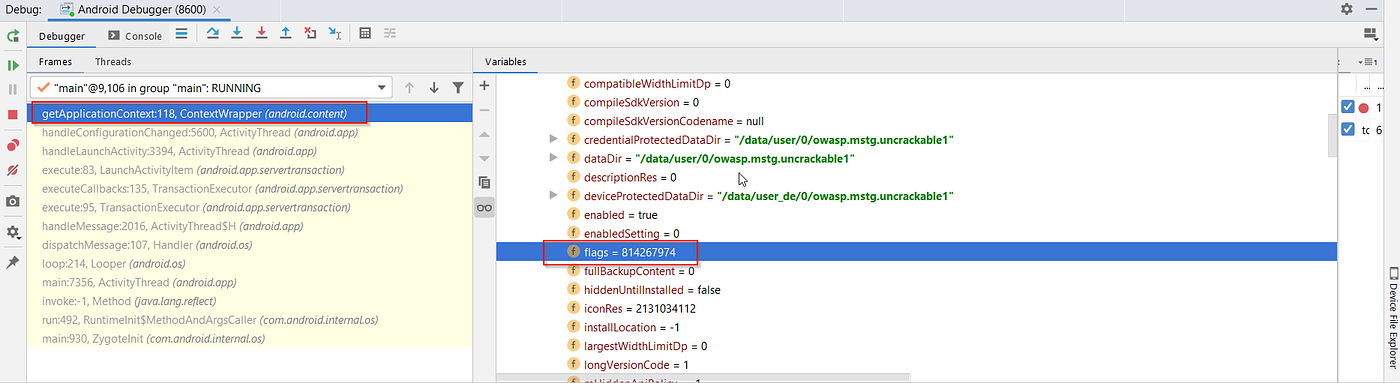
For the debuggable check:
- Modify Flag Settings:
- In the debugger console's variable section, navigate to:
this mLoadedAPK -> mApplicationInfo -> flags = 814267974. - Note: The binary representation of
flags = 814267974is11000011100111011110, indicating that the "Flag_debuggable" is active.
- In the debugger console's variable section, navigate to:
These steps collectively ensure that the application can be debugged and that certain security checks can be bypassed using the debugger, facilitating a more in-depth analysis or modification of the application's behavior.
Step 2 involves changing a flag value to 814267972, which is represented in binary as 110000101101000000100010100.
Exploiting a Vulnerability
A demonstration was provided using a vulnerable application containing a button and a textview. Initially, the application displays "Crack Me". The aim is to alter the message from "Try Again" to "Hacked" at runtime, without modifying the source code.
Checking for Vulnerability
- The application was decompiled using
apktoolto access theAndroidManifest.xmlfile. - The presence of
android_debuggable="true"in the AndroidManifest.xml indicates the application is debuggable and susceptible to exploitation. - It's worth noting that
apktoolis employed solely to check the debuggable status without altering any code.
Preparing the Setup
- The process involved initiating an emulator, installing the vulnerable application, and using
adb jdwpto identify Dalvik VM ports that are listening. - The JDWP (Java Debug Wire Protocol) allows debugging of an application running in a VM by exposing a unique port.
- Port forwarding was necessary for remote debugging, followed by attaching JDB to the target application.
Injecting Code at Runtime
- The exploitation was carried out by setting breakpoints and controlling the application flow.
- Commands like
classesandmethods <class_name>were used to uncover the application’s structure. - A breakpoint was set at the
onClickmethod, and its execution was controlled. - The
locals,next, andsetcommands were utilized to inspect and modify local variables, particularly changing the "Try Again" message to "Hacked". - The modified code was executed using the
runcommand, successfully altering the application’s output in real-time.
This example demonstrated how the behavior of a debuggable application can be manipulated, highlighting the potential for more complex exploits like gaining shell access on the device in the application's context.
References
- https://medium.com/@shubhamsonani/hacking-with-precision-bypass-techniques-via-debugger-in-android-apps-27fd562b2cc0
- https://resources.infosecinstitute.com/android-hacking-security-part-6-exploiting-debuggable-android-applications
{% hint style="success" %}
Learn & practice AWS Hacking: HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
Learn & practice GCP Hacking:  HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Support HackTricks
- Check the subscription plans!
- Join the 💬 Discord group or the telegram group or follow us on Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live.
- Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the HackTricks and HackTricks Cloud github repos.