20 KiB
Astuces JS diverses et informations pertinentes
☁️ HackTricks Cloud ☁️ -🐦 Twitter 🐦 - 🎙️ Twitch 🎙️ - 🎥 Youtube 🎥
- Travaillez-vous dans une entreprise de cybersécurité ? Voulez-vous voir votre entreprise annoncée dans HackTricks ? ou voulez-vous avoir accès à la dernière version de PEASS ou télécharger HackTricks en PDF ? Consultez les PLANS D'ABONNEMENT !
- Découvrez The PEASS Family, notre collection exclusive de NFTs
- Obtenez le swag officiel PEASS & HackTricks
- Rejoignez le 💬 groupe Discord ou le groupe telegram ou suivez moi sur Twitter 🐦@carlospolopm.
- Partagez vos astuces de piratage en soumettant des PR au repo hacktricks et au repo hacktricks-cloud.
Fuzzing Javascript
Caractères de commentaire JS valides
//This is a 1 line comment
/* This is a multiline comment*/
#!This is a 1 line comment, but "#!" must to be at the beggining of the line
-->This is a 1 line comment, but "-->" must to be at the beggining of the line
for (let j = 0; j < 128; j++) {
for (let k = 0; k < 128; k++) {
for (let l = 0; l < 128; l++) {
if (j == 34 || k ==34 || l ==34)
continue;
if (j == 0x0a || k ==0x0a || l ==0x0a)
continue;
if (j == 0x0d || k ==0x0d || l ==0x0d)
continue;
if (j == 0x3c || k ==0x3c || l ==0x3c)
continue;
if (
(j == 47 && k == 47)
||(k == 47 && l == 47)
)
continue;
try {
var cmd = String.fromCharCode(j) + String.fromCharCode(k) + String.fromCharCode(l) + 'a.orange.ctf"';
eval(cmd);
} catch(e) {
var err = e.toString().split('\n')[0].split(':')[0];
if (err === 'SyntaxError' || err === "ReferenceError")
continue
err = e.toString().split('\n')[0]
}
console.log(err,cmd);
}
}
}
//From: https://balsn.tw/ctf_writeup/20191012-hitconctfquals/#bounty-pl33z
// From: Heyes, Gareth. JavaScript for hackers: Learn to think like a hacker (p. 43). Kindle Edition.
log=[];
for(let i=0;i<=0xff;i++){
for(let j=0;j<=0xfff;j++){
try {
eval(`${String.fromCodePoint(i,j)}%$£234$`)
log.push([i,j])
}catch(e){}
}
}
console.log(log)//[35,33],[47,47]
Caractères de saut de ligne JS valides
//Javascript interpret as new line these chars:
String.fromCharCode(10) //0x0a
String.fromCharCode(13) //0x0d
String.fromCharCode(8232) //0xe2 0x80 0xa8
String.fromCharCode(8233) //0xe2 0x80 0xa8
for (let j = 0; j < 65536; j++) {
try {
var cmd = '"aaaaa";'+String.fromCharCode(j) + '-->a.orange.ctf"';
eval(cmd);
} catch(e) {
var err = e.toString().split('\n')[0].split(':')[0];
if (err === 'SyntaxError' || err === "ReferenceError")
continue;
err = e.toString().split('\n')[0]
}
console.log(`[${err}]`,j,cmd);
}
//From: https://balsn.tw/ctf_writeup/20191012-hitconctfquals/#bounty-pl33z
Espaces JS valides dans l'appel de fonction
// Heyes, Gareth. JavaScript for hackers: Learn to think like a hacker (pp. 40-41). Kindle Edition.
// Check chars that can be put in between in func name and the ()
function x(){}
log=[];
for(let i=0;i<=0x10ffff;i++){
try {
eval(`x${String.fromCodePoint(i)}()`)
log.push(i)
}catch(e){}
}
console.log(log)v//9,10,11,12,13,32,160,5760,8192,8193,8194,8195,8196,8197,8198,8199,8200,8201,8202,813 232,8233,8239,8287,12288,65279
Caractères valides pour générer des chaînes de caractères
// Heyes, Gareth. JavaScript for hackers: Learn to think like a hacker (pp. 41-42). Kindle Edition.
// Check which pairs of chars can make something be a valid string
log=[];
for(let i=0;i<=0x10ffff;i++){
try {
eval(`${String.fromCodePoint(i)}%$£234${String.fromCodePoint(i)}`)
log.push(i)
}catch(e){}
}
console.log(log) //34,39,47,96
//single quote, quotes, backticks & // (regex)
Surrogate Pairs BF
Cette technique ne sera pas très utile pour XSS, mais elle pourrait être utile pour contourner les protections WAF. Ce code python reçoit en entrée 2 octets et recherche des paires de substitution qui ont le premier octet comme dernier octet de la paire de substitution haute et le dernier octet comme dernier octet de la paire de substitution basse.
def unicode(findHex):
for i in range(0,0xFFFFF):
H = hex(int(((i - 0x10000) / 0x400) + 0xD800))
h = chr(int(H[-2:],16))
L = hex(int(((i - 0x10000) % 0x400 + 0xDC00)))
l = chr(int(L[-2:],16))
if(h == findHex[0]) and (l == findHex[1]):
print(H.replace("0x","\\u")+L.replace("0x","\\u"))
Fuzzing du protocole javascript{}:
Le protocole javascript{}: est utilisé pour exécuter du code JavaScript dans l'URL. Il peut être utilisé pour lancer des attaques de type XSS. Pour effectuer une attaque de type XSS, un attaquant peut utiliser le protocole javascript{}: pour exécuter du code malveillant sur le navigateur de la victime.
Le fuzzing du protocole javascript{}: peut être effectué en utilisant des caractères Unicode et des encodages différents pour contourner les filtres de sécurité. Les caractères Unicode peuvent être utilisés pour représenter des caractères spéciaux qui peuvent être utilisés pour contourner les filtres de sécurité. Les encodages différents peuvent être utilisés pour encoder le code malveillant de différentes manières pour éviter la détection.
Pour plus d'informations sur les caractères Unicode et les encodages, vous pouvez consulter les liens suivants :
- https://github.com/dreadlocked/ctf-writeups/blob/master/nn8ed/README.md
- https://mathiasbynens.be/notes/javascript-unicode https://mathiasbynens.be/notes/javascript-encoding
// Heyes, Gareth. JavaScript for hackers: Learn to think like a hacker (p. 34). Kindle Edition.
log=[];
let anchor = document.createElement('a');
for(let i=0;i<=0x10ffff;i++){
anchor.href = `javascript${String.fromCodePoint(i)}:`;
if(anchor.protocol === 'javascript:') {
log.push(i);
}
}
console.log(log)//9,10,13,58
// Note that you could BF also other possitions of the use of multiple chars
// Test one option
let anchor = document.createElement('a');
anchor.href = `javascript${String.fromCodePoint(58)}:alert(1337)`;
anchor.append('Click me')
document.body.append(anchor)
// Another way to test
<a href="javascript:alert(1337)">Test</a>
Fuzzing d'URL
// Heyes, Gareth. JavaScript for hackers: Learn to think like a hacker (pp. 36-37). Kindle Edition.
// Before the protocol
a=document.createElement('a');
log=[];
for(let i=0;i<=0x10ffff;i++){
a.href = `${String.fromCodePoint(i)}https://hacktricks.xyz`;
if(a.hostname === 'hacktricks.xyz'){
log.push(i);
}
}
console.log(log) //0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32
// Between the slashes
a=document.createElement('a');
log=[];
for(let i=0;i<=0x10ffff;i++){
a.href = `/${String.fromCodePoint(i)}/hacktricks.xyz`;
if(a.hostname === 'hacktricks.xyz'){
log.push(i);
}
}
console.log(log) //9,10,13,47,92
Fuzzing HTML
// Heyes, Gareth. JavaScript for hackers: Learn to think like a hacker (p. 38). Kindle Edition.
// Fuzzing chars that can close an HTML comment
let log=[];
let div = document.createElement('div');
for(let i=0;i<=0x10ffff;i++){
div.innerHTML=`<!----${String.fromCodePoint(i)}><span></span>-->`;
if(div.querySelector('span')){
log.push(i);
}
}
console.log(log)//33,45,62
Analyse des attributs
L'outil Hackability inspector de Portswigger aide à analyser les attributs d'un objet javascript. Vérifiez: https://portswigger-labs.net/hackability/inspector/?input=x.contentWindow&html=%3Ciframe%20src=//subdomain1.portswigger-labs.net%20id=x%3E
Fichiers .map js
- Astuce pour télécharger les fichiers .map js: https://medium.com/@bitthebyte/javascript-for-bug-bounty-hunters-part-2-f82164917e7
- Vous pouvez utiliser cet outil pour analyser ces fichiers https://github.com/paazmaya/shuji
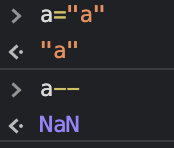
Affectation "--"
L'opérateur de décrémentation -- est également une affectation. Cet opérateur prend une valeur et la décrémente de un. Si cette valeur n'est pas un nombre, elle sera définie sur NaN. Cela peut être utilisé pour supprimer le contenu des variables de l'environnement.
Astuces de fonctions
.call et .apply
La méthode .call d'une fonction est utilisée pour exécuter la fonction.
Le premier argument qu'elle attend par défaut est la valeur de this et si rien n'est fourni, window sera cette valeur (sauf si le mode strict est utilisé).
function test_call(){
console.log(this.value); //baz
}
new_this={value:"hey!"}
test_call.call(new_this);
// To pass more arguments, just pass then inside .call()
function test_call() {
console.log(arguments[0]); //"arg1"
console.log(arguments[1]); //"arg2"
console.log(this); //[object Window]
}
test_call.call(null, "arg1", "arg2")
// If you use the "use strict" directive "this" will be null instead of window:
function test_call() {
"use strict";
console.log(this); //null
}
test_call.call(null)
//The apply function is pretty much exactly the same as the call function with one important difference, you can supply an array of arguments in the second argument:
function test_apply() {
console.log(arguments[0]); //"arg1"
console.log(arguments[1]); //"arg2"
console.log(this); //[object Window]
}
test_apply.apply(null, ["arg1", "arg2"])
Fonctions fléchées
Les fonctions fléchées vous permettent de générer des fonctions en une seule ligne plus facilement (si vous les comprenez).
// Traditional
function (a){ return a + 1; }
// Arrow forms
a => a + 100;
a => {a + 100};
// Traditional
function (a, b){ return a + b + 1; }
// Arrow
(a, b) => a + b + 100;
// Tradictional no args
let a = 4;
let b = 2;
function (){ return a + b + 1; }
// Arrow
let a = 4;
let b = 2;
() => a + b + 1;
Donc, la plupart des fonctions précédentes sont en fait inutiles car nous ne les enregistrons nulle part pour les sauvegarder et les appeler. Par exemple, la création de la fonction plusone:
// Traductional
function plusone (a){ return a + 1; }
//Arrow
plusone = a => a + 100;
Fonction Bind
La fonction Bind permet de créer une copie d'une fonction en modifiant l'objet this et les paramètres donnés.
//This will use the this object and print "Hello World"
var fn = function ( param1, param2 ) {
console.info( this, param1, param2 );
}
fn('Hello', 'World')
//This will still use the this object and print "Hello World"
var copyFn = fn.bind();
copyFn('Hello', 'World')
//This will use the "console" object as "this" object inside the function and print "fixingparam1 Hello"
var bindFn_change = fn.bind(console, "fixingparam1");
bindFn_change('Hello', 'World')
//This will still use the this object and print "fixingparam1 Hello"
var bindFn_thisnull = fn.bind(null, "fixingparam1");
bindFn_change('Hello', 'World')
//This will still use the this object and print "fixingparam1 Hello"
var bindFn_this = fn.bind(this, "fixingparam1");
bindFn_change('Hello', 'World')
{% hint style="info" %}
Notez qu'en utilisant bind, vous pouvez manipuler l'objet this qui sera utilisé lors de l'appel de la fonction.
{% endhint %}
Fuite de code de fonction
Si vous pouvez accéder à l'objet d'une fonction, vous pouvez obtenir le code de cette fonction.
function afunc(){
return 1+1;
}
console.log(afunc.toString()); //This will print the code of the function
console.log(String(afunc)); //This will print the code of the function
console.log(this.afunc.toString()); //This will print the code of the function
console.log(global.afunc.toString()); //This will print the code of the function
Dans les cas où la fonction n'a pas de nom, vous pouvez toujours imprimer le code de la fonction à partir de l'intérieur :
(function (){ return arguments.callee.toString(); })()
(function (){ return arguments[0]; })("arg0")
Voici quelques façons aléatoires d'extraire le code d'une fonction (y compris les commentaires) à partir d'une autre fonction :
(function (){ return retFunc => String(arguments[0]) })(a=>{/* Hidden commment */})()
(function (){ return retFunc => Array(arguments[0].toString()) })(a=>{/* Hidden commment */})()
(function (){ return String(this)}).bind(()=>{ /* Hidden commment */ })()
(u=>(String(u)))(_=>{ /* Hidden commment */ })
(u=>_=>(String(u)))(_=>{ /* Hidden commment */ })()
Évasion de bac à sable - Récupération de l'objet window
L'objet Window permet d'accéder aux fonctions définies globalement telles que alert ou eval.
{% code overflow="wrap" %}
// Some ways to access window
window.eval("alert(1)")
frames
globalThis
parent
self
top //If inside a frame, this is top most window
// Access window from document
document.defaultView.alert(1)
// Access document from a node object
node = document.createElement('div')
node.ownerDocument.defaultView.alert(1)
// There is a path property on each error event whose last element is the window
<img src onerror=event.path.pop().alert(1337)>
// In other browsers the method is
<img src onerror=event.composedPath().pop().alert(1337)>
// In case of svg, the "event" object is called "evt"
<svg><image href=1 onerror=evt.composedPath().pop().alert(1337)>
// Abusing Error.prepareStackTrace to get Window back
Error.prepareStackTrace=function(error, callSites){
2 callSites.shift().getThis().alert(1337);
3 };
4 new Error().stack
// From an HTML event
// Events from HTML are executed in this context
with(document) {
with(element) {
//executed event
}
}
// Because of that with(document) it's possible to access properties of document like:
<img src onerror=defaultView.alert(1337)>
<img src onerror=s=createElement('script');s.append('alert(1337)');appendChild(s)>
{% endcode %}
Point d'arrêt sur l'accès à une valeur
// Stop when a property in sessionStorage or localStorage is set/get
// via getItem or setItem functions
sessionStorage.getItem = localStorage.getItem = function(prop) {
debugger;
return sessionStorage[prop];
}
localStorage.setItem = function(prop, val) {
debugger;
localStorage[prop] = val;
}
// Stop when anyone sets or gets the property "ppmap" in any object
// For example sessionStorage.ppmap
// "123".ppmap
// Useful to find where weird properties are being set or accessed
// or to find where prototype pollutions are occurring
function debugAccess(obj, prop, debugGet=true){
var origValue = obj[prop];
Object.defineProperty(obj, prop, {
get: function () {
if ( debugGet )
debugger;
return origValue;
},
set: function(val) {
debugger;
origValue = val;
}
});
};
debugAccess(Object.prototype, 'ppmap')
Accès automatique du navigateur pour tester les charges utiles
//Taken from https://github.com/svennergr/writeups/blob/master/inti/0621/README.md
const puppeteer = require("puppeteer");
const realPasswordLength = 3000;
async function sleep(ms) {
return new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, ms));
}
(async () => {
const browser = await puppeteer.launch();
const page = await browser.newPage();
//Loop to iterate through different values
for (let i = 0; i < 10000; i += 100) {
console.log(`Run number ${i}`);
const input = `${"0".repeat(i)}${realPasswordLength}`;
console.log(` https://challenge-0621.intigriti.io/passgen.php?passwordLength=${input}&allowNumbers=true&allowSymbols=true×tamp=1624556811000`);
//Go to the page
await page.goto(
`https://challenge-0621.intigriti.io/passgen.php?passwordLength=${input}&allowNumbers=true&allowSymbols=true×tamp=1624556811000`
);
//Call function "generate()" inside the page
await page.evaluate("generate()");
//Get node inner text from an HTML element
const passwordContent = await page.$$eval(
".alert .page-content",
(node) => node[0].innerText
);
//Transform the content and print it in console
const plainPassword = passwordContent.replace("Your password is: ", "");
if (plainPassword.length != realPasswordLength) {
console.log(i, plainPassword.length, plainPassword);
}
await sleep(1000);
}
await browser.close();
})();
☁️ HackTricks Cloud ☁️ -🐦 Twitter 🐦 - 🎙️ Twitch 🎙️ - 🎥 Youtube 🎥
- Travaillez-vous dans une entreprise de cybersécurité ? Voulez-vous voir votre entreprise annoncée dans HackTricks ? ou voulez-vous avoir accès à la dernière version de PEASS ou télécharger HackTricks en PDF ? Consultez les PLANS D'ABONNEMENT !
- Découvrez The PEASS Family, notre collection exclusive de NFTs
- Obtenez le swag officiel PEASS & HackTricks
- Rejoignez le 💬 groupe Discord ou le groupe telegram ou suivez moi sur Twitter 🐦@carlospolopm.
- Partagez vos astuces de piratage en soumettant des PR au repo hacktricks et au repo hacktricks-cloud.