15 KiB
macOS通用二进制文件和Mach-O格式
☁️ HackTricks云 ☁️ -🐦 推特 🐦 - 🎙️ Twitch 🎙️ - 🎥 YouTube 🎥
- 你在一家网络安全公司工作吗?想要在HackTricks中看到你的公司广告吗?或者你想要获取PEASS的最新版本或下载PDF格式的HackTricks吗?请查看订阅计划!
- 发现我们的独家NFT收藏品The PEASS Family
- 获取官方PEASS和HackTricks周边产品
- 加入💬 Discord群组 或 Telegram群组 或 关注我在Twitter上的🐦@carlospolopm。
- 通过向hacktricks repo 和hacktricks-cloud repo 提交PR来分享你的黑客技巧。
基本信息
Mac OS二进制文件通常被编译为通用二进制文件。通用二进制文件可以在同一个文件中支持多个架构。
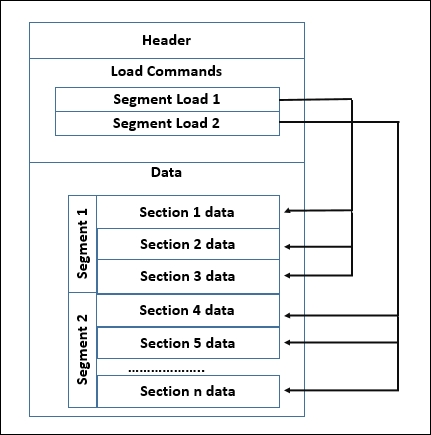
这些二进制文件遵循Mach-O结构,基本上由以下部分组成:
- 头部(Header)
- 载入命令(Load Commands)
- 数据(Data)
Fat Header
使用以下命令搜索文件:mdfind fat.h | grep -i mach-o | grep -E "fat.h$"
#define FAT_MAGIC 0xcafebabe
#define FAT_CIGAM 0xbebafeca /* NXSwapLong(FAT_MAGIC) */
struct fat_header {
uint32_t magic; /* FAT_MAGIC or FAT_MAGIC_64 */
uint32_t nfat_arch; /* 后面跟随的结构体数量 */
};
struct fat_arch {
cpu_type_t cputype; /* CPU类型(int) */
cpu_subtype_t cpusubtype; /* 机器类型(int) */
uint32_t offset; /* 该目标文件的文件偏移量 */
uint32_t size; /* 该目标文件的大小 */
uint32_t align; /* 2的幂次方对齐 */
};
头部包含魔数(magic)字节,后面是文件包含的架构数量(nfat_arch),每个架构都有一个fat_arch结构体。
使用以下命令进行检查:
% file /bin/ls
/bin/ls: Mach-O universal binary with 2 architectures: [x86_64:Mach-O 64-bit executable x86_64] [arm64e:Mach-O 64-bit executable arm64e]
/bin/ls (for architecture x86_64): Mach-O 64-bit executable x86_64
/bin/ls (for architecture arm64e): Mach-O 64-bit executable arm64e
% otool -f -v /bin/ls
Fat headers
fat_magic FAT_MAGIC
nfat_arch 2
architecture x86_64
cputype CPU_TYPE_X86_64
cpusubtype CPU_SUBTYPE_X86_64_ALL
capabilities 0x0
offset 16384
size 72896
align 2^14 (16384)
architecture arm64e
cputype CPU_TYPE_ARM64
cpusubtype CPU_SUBTYPE_ARM64E
capabilities PTR_AUTH_VERSION USERSPACE 0
offset 98304
size 88816
align 2^14 (16384)
或者使用Mach-O View工具:
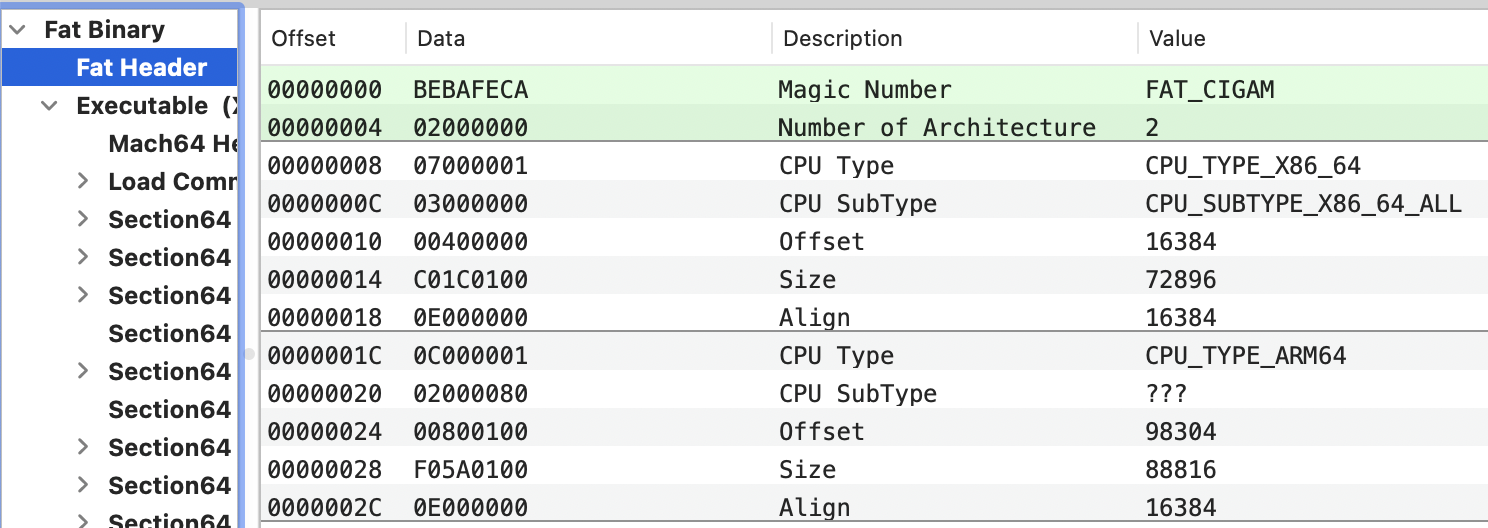
正如你可能想到的,通常编译为2个架构的通用二进制文件会使文件大小增加一倍,相比只编译为1个架构的文件。
Mach-O Header
头部包含文件的基本信息,例如魔数字节以识别它为Mach-O文件,以及有关目标架构的信息。你可以在以下位置找到它:mdfind loader.h | grep -i mach-o | grep -E "loader.h$"
#define MH_MAGIC 0xfeedface /* the mach magic number */
#define MH_CIGAM 0xcefaedfe /* NXSwapInt(MH_MAGIC) */
struct mach_header {
uint32_t magic; /* mach magic number identifier */
cpu_type_t cputype; /* cpu specifier (e.g. I386) */
cpu_subtype_t cpusubtype; /* machine specifier */
uint32_t filetype; /* type of file (usage and alignment for the file) */
uint32_t ncmds; /* number of load commands */
uint32_t sizeofcmds; /* the size of all the load commands */
uint32_t flags; /* flags */
};
#define MH_MAGIC_64 0xfeedfacf /* the 64-bit mach magic number */
#define MH_CIGAM_64 0xcffaedfe /* NXSwapInt(MH_MAGIC_64) */
struct mach_header_64 {
uint32_t magic; /* mach magic number identifier */
int32_t cputype; /* cpu specifier */
int32_t cpusubtype; /* machine specifier */
uint32_t filetype; /* type of file */
uint32_t ncmds; /* number of load commands */
uint32_t sizeofcmds; /* the size of all the load commands */
uint32_t flags; /* flags */
uint32_t reserved; /* reserved */
};
文件类型:
- MH_EXECUTE (0x2):标准的 Mach-O 可执行文件
- MH_DYLIB (0x6):Mach-O 动态链接库(即 .dylib)
- MH_BUNDLE (0x8):Mach-O bundle(即 .bundle)
# Checking the mac header of a binary
otool -arch arm64e -hv /bin/ls
Mach header
magic cputype cpusubtype caps filetype ncmds sizeofcmds flags
MH_MAGIC_64 ARM64 E USR00 EXECUTE 19 1728 NOUNDEFS DYLDLINK TWOLEVEL PIE
或者使用Mach-O View:

Mach-O 加载命令
这指定了文件在内存中的布局。它包含了符号表的位置,执行开始时的主线程上下文,以及所需的共享库。
这些命令基本上指示动态加载器**(dyld)如何将二进制文件加载到内存中**。
加载命令都以load_command结构开始,该结构在之前提到的**loader.h**中定义:
struct load_command {
uint32_t cmd; /* type of load command */
uint32_t cmdsize; /* total size of command in bytes */
};
大约有50种不同类型的加载命令,系统会以不同方式处理它们。最常见的类型有:LC_SEGMENT_64、LC_LOAD_DYLINKER、LC_MAIN、LC_LOAD_DYLIB和LC_CODE_SIGNATURE。
LC_SEGMENT/LC_SEGMENT_64
{% hint style="success" %} 基本上,这种类型的加载命令定义了在执行二进制文件时如何加载存储在DATA中的段。 {% endhint %}
这些命令定义了在执行过程中映射到进程的虚拟内存空间中的段。
有不同类型的段,比如保存程序可执行代码的**__TEXT段,以及包含进程使用的数据的__DATA**段。这些段位于Mach-O文件的数据部分中。
每个段可以进一步划分为多个区块。加载命令结构包含了有关各个段内部的这些区块的信息。
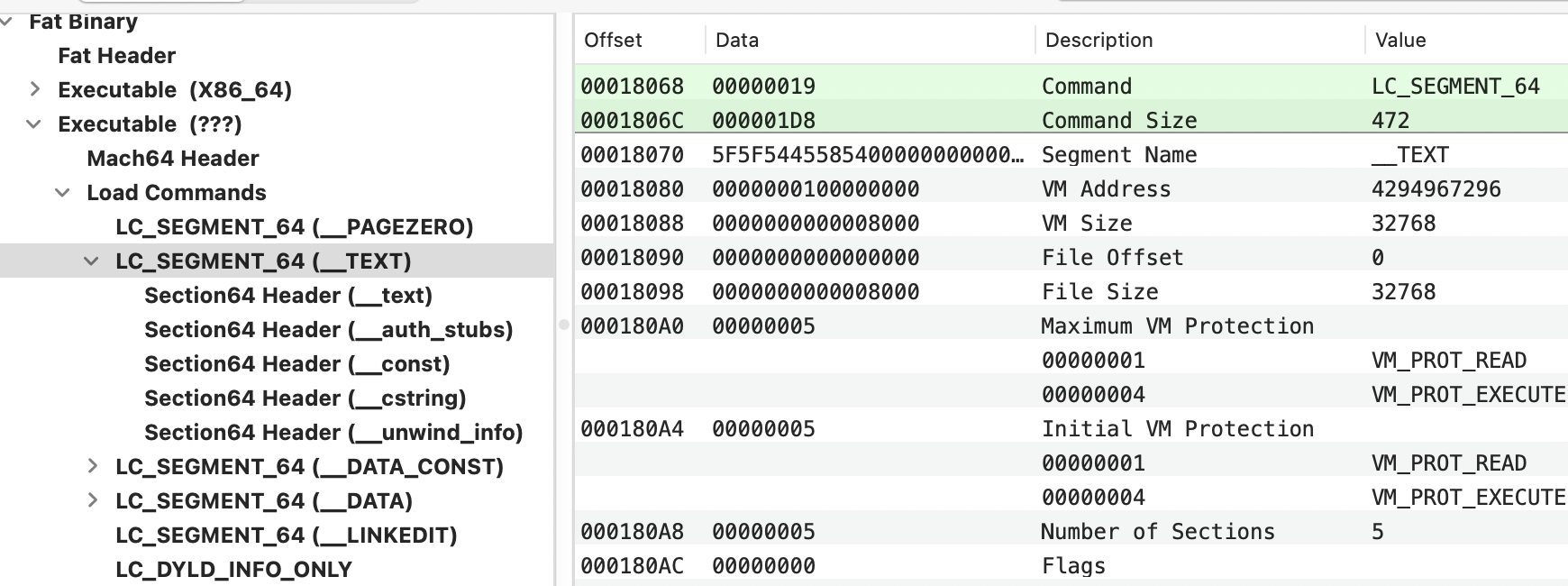
在头部中首先找到段头:
struct segment_command_64 { /* for 64-bit architectures */
uint32_t cmd; /* LC_SEGMENT_64 */
uint32_t cmdsize; /* includes sizeof section_64 structs */
char segname[16]; /* segment name */
uint64_t vmaddr; /* memory address of this segment */
uint64_t vmsize; /* memory size of this segment */
uint64_t fileoff; /* file offset of this segment */
uint64_t filesize; /* amount to map from the file */
int32_t maxprot; /* maximum VM protection */
int32_t initprot; /* initial VM protection */
uint32_t nsects; /* number of sections in segment */
uint32_t flags; /* flags */
};
段头的示例:
该头部定义了在其后出现的区块头的数量:
struct section_64 { /* for 64-bit architectures */
char sectname[16]; /* name of this section */
char segname[16]; /* segment this section goes in */
uint64_t addr; /* memory address of this section */
uint64_t size; /* size in bytes of this section */
uint32_t offset; /* file offset of this section */
uint32_t align; /* section alignment (power of 2) */
uint32_t reloff; /* file offset of relocation entries */
uint32_t nreloc; /* number of relocation entries */
uint32_t flags; /* flags (section type and attributes)*/
uint32_t reserved1; /* reserved (for offset or index) */
uint32_t reserved2; /* reserved (for count or sizeof) */
uint32_t reserved3; /* reserved */
};
示例的章节标题:
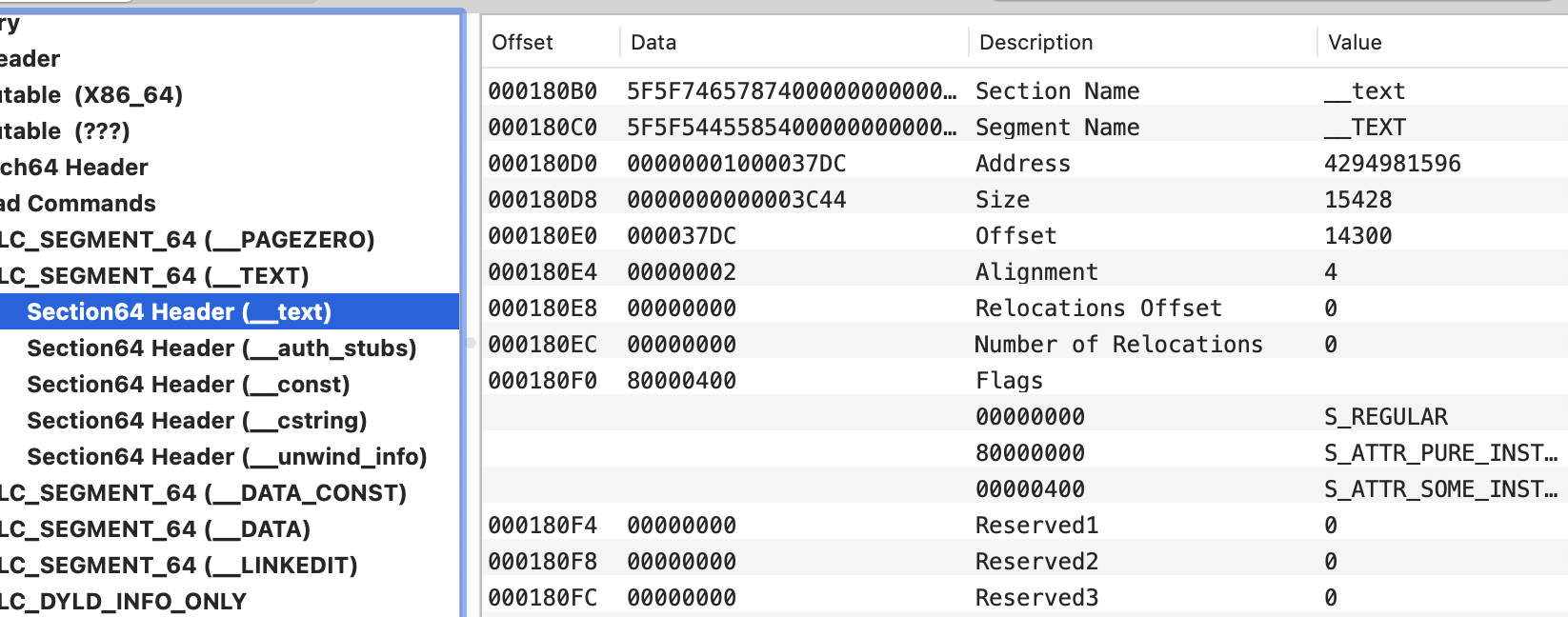
如果你添加了章节偏移量(0x37DC)+ arch开始的偏移量,在这个例子中是0x18000 --> 0x37DC + 0x18000 = 0x1B7DC

也可以通过命令行获取头部信息:
otool -lv /bin/ls
以下是关于MacOS文件、文件夹和二进制文件的内容。
加载的常见段:
__PAGEZERO:它指示内核将地址零映射到不可读取、写入或执行的位置。结构中的maxprot和minprot变量设置为零,表示该页面没有读写执行权限。这种分配对于减轻空指针解引用漏洞非常重要。__TEXT:包含可执行代码和只读数据。该段的常见部分有:__text:编译的二进制代码__const:常量数据__cstring:字符串常量__stubs和__stubs_helper:在动态库加载过程中使用__DATA:包含可写数据。__data:全局变量(已初始化)__bss:静态变量(未初始化)__objc_*(__objc_classlist,__objc_protolist等):Objective-C运行时使用的信息- **
__LINKEDIT:**包含链接器(dyld)的信息,如“符号、字符串和重定位表项”。 - **
__OBJC:**包含Objective-C运行时使用的信息。尽管此信息也可以在__DATA段中找到,但位于各种__objc_*部分中。
LC_MAIN
包含entryoff属性中的入口点。在加载时,dyld只需将此值添加到(内存中的)二进制文件的基址,然后跳转到此指令以开始执行二进制文件的代码。
LC_CODE_SIGNATURE
包含有关Macho-O文件的代码签名的信息。它只包含一个指向签名块的偏移量。这通常位于文件的末尾。
但是,您可以在此博客文章和此gists中找到有关此部分的一些信息。
LC_LOAD_DYLINKER
包含将共享库映射到进程地址空间的动态链接器可执行文件的路径。该值始终设置为/usr/lib/dyld。重要的是要注意,在macOS中,dylib映射发生在用户模式而不是内核模式中。
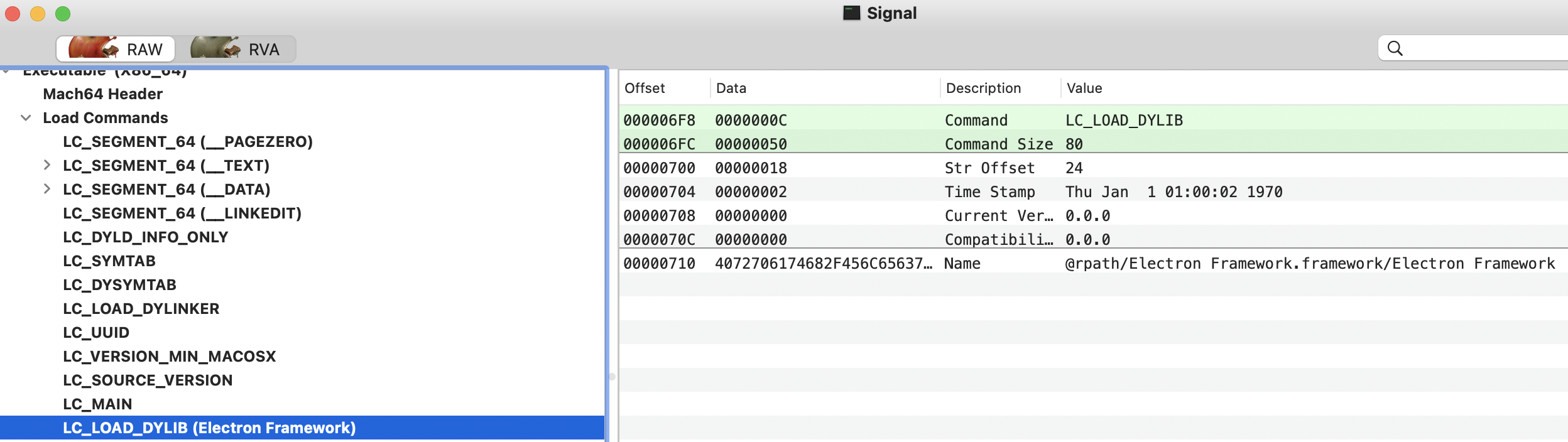
LC_LOAD_DYLIB
此加载命令描述了一个动态库依赖项,它指示加载器(dyld)加载和链接该库。Mach-O二进制文件所需的每个库都有一个LC_LOAD_DYLIB加载命令。
- 此加载命令是**
dylib_command**类型的结构(其中包含描述实际依赖动态库的struct dylib):
struct dylib_command {
uint32_t cmd; /* LC_LOAD_{,WEAK_}DYLIB */
uint32_t cmdsize; /* includes pathname string */
struct dylib dylib; /* the library identification */
};
struct dylib {
union lc_str name; /* library's path name */
uint32_t timestamp; /* library's build time stamp */
uint32_t current_version; /* library's current version number */
uint32_t compatibility_version; /* library's compatibility vers number*/
};
您也可以使用命令行界面获取此信息:
otool -L /bin/ls
/bin/ls:
/usr/lib/libutil.dylib (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 1.0.0)
/usr/lib/libncurses.5.4.dylib (compatibility version 5.4.0, current version 5.4.0)
/usr/lib/libSystem.B.dylib (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 1319.0.0)
一些潜在的与恶意软件相关的库包括:
- DiskArbitration:监控USB驱动器
- AVFoundation:捕获音频和视频
- CoreWLAN:Wifi扫描。
{% hint style="info" %} Mach-O二进制文件可以包含一个或多个构造函数,这些函数将在LC_MAIN指定的地址之前执行。任何构造函数的偏移量都保存在**__DATA_CONST段的__mod_init_func**部分中。 {% endhint %}
Mach-O数据
文件的核心是最后一个区域,即数据区域,它由加载命令区域中的多个段组成。每个段可以包含多个数据段。每个数据段都包含一种特定类型的代码或数据。
{% hint style="success" %} 数据基本上是包含由加载命令LC_SEGMENTS_64加载的所有信息的部分。 {% endhint %}
这包括:
- 函数表:保存有关程序函数的信息。
- 符号表:包含二进制文件使用的外部函数的信息
- 它还可以包含内部函数、变量名等等。
您可以使用Mach-O View工具来检查:
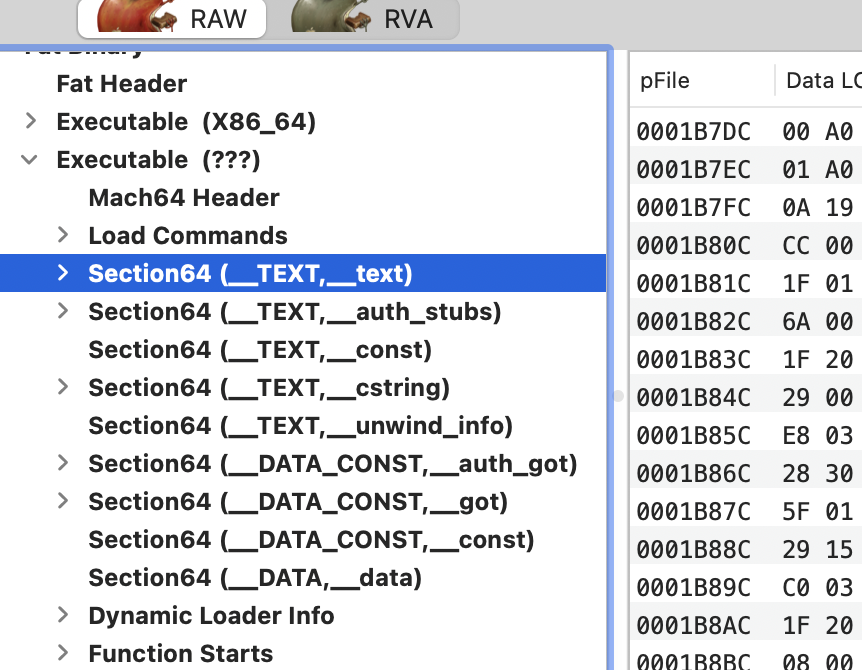
或者使用命令行:
size -m /bin/ls
☁️ HackTricks 云 ☁️ -🐦 推特 🐦 - 🎙️ Twitch 🎙️ - 🎥 Youtube 🎥
- 你在一家网络安全公司工作吗?想要在 HackTricks 中宣传你的公司吗?或者你想要获取最新版本的 PEASS 或下载 HackTricks 的 PDF吗?请查看订阅计划!
- 发现我们的独家NFTs收藏品——The PEASS Family
- 获取官方 PEASS & HackTricks 商品
- 加入 💬 Discord 群组 或 Telegram 群组,或者关注我在推特上的🐦@carlospolopm。
- 通过向 hacktricks 仓库 和 hacktricks-cloud 仓库 提交 PR 来分享你的黑客技巧。