| .. | ||
| clone-a-website.md | ||
| detecting-phising.md | ||
| phishing-documents.md | ||
| README.md | ||
Phishing Methodology
{% hint style="success" %}
Learn & practice AWS Hacking: HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
Learn & practice GCP Hacking:  HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Support HackTricks
- Check the subscription plans!
- Join the 💬 Discord group or the telegram group or follow us on Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live.
- Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the HackTricks and HackTricks Cloud github repos.
Methodology
- Recon the victim
- Select the victim domain.
- Perform some basic web enumeration searching for login portals used by the victim and decide which one you will impersonate.
- Use some OSINT to find emails.
- Prepare the environment
- Buy the domain you are going to use for the phishing assessment
- Configure the email service related records (SPF, DMARC, DKIM, rDNS)
- Configure the VPS with gophish
- Prepare the campaign
- Prepare the email template
- Prepare the web page to steal the credentials
- Launch the campaign!
Generate similar domain names or buy a trusted domain
Domain Name Variation Techniques
- Keyword: The domain name contains an important keyword of the original domain (e.g., zelster.com-management.com).
- hypened subdomain: Change the dot for a hyphen of a subdomain (e.g., www-zelster.com).
- New TLD: Same domain using a new TLD (e.g., zelster.org)
- Homoglyph: It replaces a letter in the domain name with letters that look similar (e.g., zelfser.com).
- Transposition: It swaps two letters within the domain name (e.g., zelsetr.com).
- Singularization/Pluralization: Adds or removes “s” at the end of the domain name (e.g., zeltsers.com).
- Omission: It removes one of the letters from the domain name (e.g., zelser.com).
- Repetition: It repeats one of the letters in the domain name (e.g., zeltsser.com).
- Replacement: Like homoglyph but less stealthy. It replaces one of the letters in the domain name, perhaps with a letter in proximity of the original letter on the keyboard (e.g, zektser.com).
- Subdomained: Introduce a dot inside the domain name (e.g., ze.lster.com).
- Insertion: It inserts a letter into the domain name (e.g., zerltser.com).
- Missing dot: Append the TLD to the domain name. (e.g., zelstercom.com)
Automatic Tools
Websites
- https://dnstwist.it/
- https://dnstwister.report/
- https://www.internetmarketingninjas.com/tools/free-tools/domain-typo-generator/
Bitflipping
There is a possibility that one of some bits stored or in communication might get automatically flipped due to various factors like solar flares, cosmic rays, or hardware errors.
When this concept is applied to DNS requests, it is possible that the domain received by the DNS server is not the same as the domain initially requested.
For example, a single bit modification in the domain "windows.com" can change it to "windnws.com."
Attackers may take advantage of this by registering multiple bit-flipping domains that are similar to the victim's domain. Their intention is to redirect legitimate users to their own infrastructure.
For more information read https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/hijacking-traffic-to-microsoft-s-windowscom-with-bitflipping/
Buy a trusted domain
You can search in https://www.expireddomains.net/ for a expired domain that you could use.
In order to make sure that the expired domain that you are going to buy has already a good SEO you could search how is it categorized in:
Discovering Emails
- https://github.com/laramies/theHarvester (100% free)
- https://phonebook.cz/ (100% free)
- https://maildb.io/
- https://hunter.io/
- https://anymailfinder.com/
In order to discover more valid email addresses or verify the ones you have already discovered you can check if you can brute-force them smtp servers of the victim. Learn how to verify/discover email address here.
Moreover, don't forget that if the users use any web portal to access their mails, you can check if it's vulnerable to username brute force, and exploit the vulnerability if possible.
Configuring GoPhish
Installation
You can download it from https://github.com/gophish/gophish/releases/tag/v0.11.0
Download and decompress it inside /opt/gophish and execute /opt/gophish/gophish
You will be given a password for the admin user in port 3333 in the output. Therefore, access that port and use those credentials to change the admin password. You may need to tunnel that port to local:
ssh -L 3333:127.0.0.1:3333 <user>@<ip>
Configuration
TLS certificate configuration
Before this step you should have already bought the domain you are going to use and it must be pointing to the IP of the VPS where you are configuring gophish.
DOMAIN="<domain>"
wget https://dl.eff.org/certbot-auto
chmod +x certbot-auto
sudo apt install snapd
sudo snap install core
sudo snap refresh core
sudo apt-get remove certbot
sudo snap install --classic certbot
sudo ln -s /snap/bin/certbot /usr/bin/certbot
certbot certonly --standalone -d "$DOMAIN"
mkdir /opt/gophish/ssl_keys
cp "/etc/letsencrypt/live/$DOMAIN/privkey.pem" /opt/gophish/ssl_keys/key.pem
cp "/etc/letsencrypt/live/$DOMAIN/fullchain.pem" /opt/gophish/ssl_keys/key.crt
Mail configuration
Start installing: apt-get install postfix
Then add the domain to the following files:
- /etc/postfix/virtual_domains
- /etc/postfix/transport
- /etc/postfix/virtual_regexp
Change also the values of the following variables inside /etc/postfix/main.cf
myhostname = <domain>
mydestination = $myhostname, <domain>, localhost.com, localhost
Finally modify the files /etc/hostname and /etc/mailname to your domain name and restart your VPS.
Now, create a DNS A record of mail.<domain> pointing to the ip address of the VPS and a DNS MX record pointing to mail.<domain>
Now lets test to send an email:
apt install mailutils
echo "This is the body of the email" | mail -s "This is the subject line" test@email.com
Gophish configuration
Stop the execution of gophish and lets configure it.
Modify /opt/gophish/config.json to the following (note the use of https):
{
"admin_server": {
"listen_url": "127.0.0.1:3333",
"use_tls": true,
"cert_path": "gophish_admin.crt",
"key_path": "gophish_admin.key"
},
"phish_server": {
"listen_url": "0.0.0.0:443",
"use_tls": true,
"cert_path": "/opt/gophish/ssl_keys/key.crt",
"key_path": "/opt/gophish/ssl_keys/key.pem"
},
"db_name": "sqlite3",
"db_path": "gophish.db",
"migrations_prefix": "db/db_",
"contact_address": "",
"logging": {
"filename": "",
"level": ""
}
}
Configure gophish service
In order to create the gophish service so it can be started automatically and managed a service you can create the file /etc/init.d/gophish with the following content:
#!/bin/bash
# /etc/init.d/gophish
# initialization file for stop/start of gophish application server
#
# chkconfig: - 64 36
# description: stops/starts gophish application server
# processname:gophish
# config:/opt/gophish/config.json
# From https://github.com/gophish/gophish/issues/586
# define script variables
processName=Gophish
process=gophish
appDirectory=/opt/gophish
logfile=/var/log/gophish/gophish.log
errfile=/var/log/gophish/gophish.error
start() {
echo 'Starting '${processName}'...'
cd ${appDirectory}
nohup ./$process >>$logfile 2>>$errfile &
sleep 1
}
stop() {
echo 'Stopping '${processName}'...'
pid=$(/bin/pidof ${process})
kill ${pid}
sleep 1
}
status() {
pid=$(/bin/pidof ${process})
if [["$pid" != ""| "$pid" != "" ]]; then
echo ${processName}' is running...'
else
echo ${processName}' is not running...'
fi
}
case $1 in
start|stop|status) "$1" ;;
esac
Finish configuring the service and checking it doing:
mkdir /var/log/gophish
chmod +x /etc/init.d/gophish
update-rc.d gophish defaults
#Check the service
service gophish start
service gophish status
ss -l | grep "3333\|443"
service gophish stop
Configuring mail server and domain
Wait & be legit
The older a domain is the less probable it's going to be caught as spam. Then you should wait as much time as possible (at least 1week) before the phishing assessment. moreover, if you put a page about a reputational sector the reputation obtained will be better.
Note that even if you have to wait a week you can finish configuring everything now.
Configure Reverse DNS (rDNS) record
Set a rDNS (PTR) record that resolves the IP address of the VPS to the domain name.
Sender Policy Framework (SPF) Record
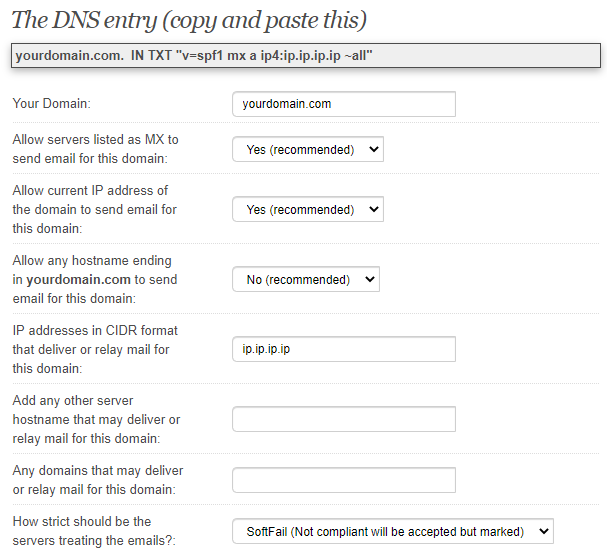
You must configure a SPF record for the new domain. If you don't know what is a SPF record read this page.
You can use https://www.spfwizard.net/ to generate your SPF policy (use the IP of the VPS machine)
This is the content that must be set inside a TXT record inside the domain:
v=spf1 mx a ip4:ip.ip.ip.ip ?all
Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance (DMARC) Record
You must configure a DMARC record for the new domain. If you don't know what is a DMARC record read this page.
You have to create a new DNS TXT record pointing the hostname _dmarc.<domain> with the following content:
v=DMARC1; p=none
DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM)
You must configure a DKIM for the new domain. If you don't know what is a DMARC record read this page.
This tutorial is based on: https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/how-to-install-and-configure-dkim-with-postfix-on-debian-wheezy
{% hint style="info" %} You need to concatenate both B64 values that the DKIM key generates:
v=DKIM1; h=sha256; k=rsa; p=MIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEA0wPibdqPtzYk81njjQCrChIcHzxOp8a1wjbsoNtka2X9QXCZs+iXkvw++QsWDtdYu3q0Ofnr0Yd/TmG/Y2bBGoEgeE+YTUG2aEgw8Xx42NLJq2D1pB2lRQPW4IxefROnXu5HfKSm7dyzML1gZ1U0pR5X4IZCH0wOPhIq326QjxJZm79E1nTh3xj" "Y9N/Dt3+fVnIbMupzXE216TdFuifKM6Tl6O/axNsbswMS1TH812euno8xRpsdXJzFlB9q3VbMkVWig4P538mHolGzudEBg563vv66U8D7uuzGYxYT4WS8NVm3QBMg0QKPWZaKp+bADLkOSB9J2nUpk4Aj9KB5swIDAQAB
{% endhint %}
Test your email configuration score
You can do that using https://www.mail-tester.com/
Just access the page and send an email to the address they give you:
echo "This is the body of the email" | mail -s "This is the subject line" test-iimosa79z@srv1.mail-tester.com
You can also check your email configuration sending an email to check-auth@verifier.port25.com and reading the response (for this you will need to open port 25 and see the response in the file /var/mail/root if you send the email a as root).
Check that you pass all the tests:
==========================================================
Summary of Results
==========================================================
SPF check: pass
DomainKeys check: neutral
DKIM check: pass
Sender-ID check: pass
SpamAssassin check: ham
You could also send message to a Gmail under your control, and check the email’s headers in your Gmail inbox, dkim=pass should be present in the Authentication-Results header field.
Authentication-Results: mx.google.com;
spf=pass (google.com: domain of contact@example.com designates --- as permitted sender) smtp.mail=contact@example.com;
dkim=pass header.i=@example.com;
Removing from Spamhouse Blacklist
The page www.mail-tester.com can indicate you if you your domain is being blocked by spamhouse. You can request your domain/IP to be removed at: https://www.spamhaus.org/lookup/
Removing from Microsoft Blacklist
You can request your domain/IP to be removed at https://sender.office.com/.
Create & Launch GoPhish Campaign
Sending Profile
- Set some name to identify the sender profile
- Decide from which account are you going to send the phishing emails. Suggestions: noreply, support, servicedesk, salesforce...
- You can leave blank the username and password, but make sure to check the Ignore Certificate Errors
{% hint style="info" %}
It's recommended to use the "Send Test Email" functionality to test that everything is working.
I would recommend to send the test emails to 10min mails addresses in order to avoid getting blacklisted making tests.
{% endhint %}
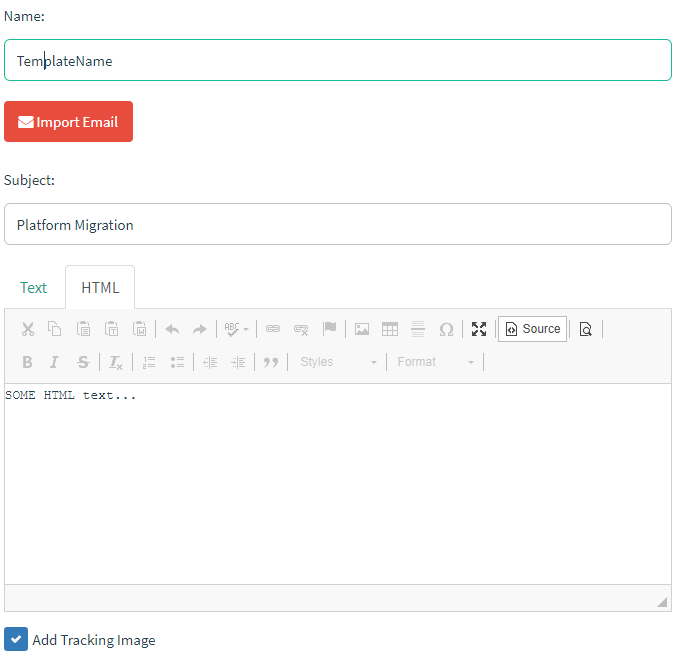
Email Template
- Set some name to identify the template
- Then write a subject (nothing estrange, just something you could expect to read in a regular email)
- Make sure you have checked "Add Tracking Image"
- Write the email template (you can use variables like in the following example):
<html>
<head>
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<p class="MsoNormal"><span style="font-size:10.0pt;font-family:"Verdana",sans-serif;color:black">Dear {{.FirstName}} {{.LastName}},</span></p>
<br />
Note: We require all user to login an a very suspicios page before the end of the week, thanks!<br />
<br />
Regards,</span></p>
WRITE HERE SOME SIGNATURE OF SOMEONE FROM THE COMPANY
<p>{{.Tracker}}</p>
</body>
</html>
Note that in order to increase the credibility of the email, it's recommended to use some signature from an email from the client. Suggestions:
- Send an email to a non existent address and check if the response has any signature.
- Search for public emails like info@ex.com or press@ex.com or public@ex.com and send them an email and wait for the response.
- Try to contact some valid discovered email and wait for the response
{% hint style="info" %} The Email Template also allows to attach files to send. If you would also like to steal NTLM challenges using some specially crafted files/documents read this page. {% endhint %}
Landing Page
- Write a name
- Write the HTML code of the web page. Note that you can import web pages.
- Mark Capture Submitted Data and Capture Passwords
- Set a redirection
{% hint style="info" %}
Usually you will need to modify the HTML code of the page and make some tests in local (maybe using some Apache server) until you like the results. Then, write that HTML code in the box.
Note that if you need to use some static resources for the HTML (maybe some CSS and JS pages) you can save them in /opt/gophish/static/endpoint and then access them from /static/<filename>
{% endhint %}
{% hint style="info" %} For the redirection you could redirect the users to the legit main web page of the victim, or redirect them to /static/migration.html for example, put some spinning wheel (https://loading.io/) for 5 seconds and then indicate that the process was successful. {% endhint %}
Users & Groups
- Set a name
- Import the data (note that in order to use the template for the example you need the firstname, last name and email address of each user)
Campaign
Finally, create a campaign selecting a name, the email template, the landing page, the URL, the sending profile and the group. Note that the URL will be the link sent to the victims
Note that the Sending Profile allow to send a test email to see how will the final phishing email looks like:
{% hint style="info" %} I would recommend to send the test emails to 10min mails addresses in order to avoid getting blacklisted making tests. {% endhint %}
Once everything is ready, just launch the campaign!
Website Cloning
If for any reason you want to clone the website check the following page:
{% content-ref url="clone-a-website.md" %} clone-a-website.md {% endcontent-ref %}
Backdoored Documents & Files
In some phishing assessments (mainly for Red Teams) you will want to also send files containing some kind of backdoor (maybe a C2 or maybe just something that will trigger an authentication).
Check out the following page for some examples:
{% content-ref url="phishing-documents.md" %} phishing-documents.md {% endcontent-ref %}
Phishing MFA
Via Proxy MitM
The previous attack is pretty clever as you are faking a real website and gathering the information set by the user. Unfortunately, if the user didn't put the correct password or if the application you faked is configured with 2FA, this information won't allow you to impersonate the tricked user.
This is where tools like evilginx2, CredSniper and muraena are useful. This tool will allow you to generate a MitM like attack. Basically, the attacks works in the following way:
- You impersonate the login form of the real webpage.
- The user send his credentials to your fake page and the tool send those to the real webpage, checking if the credentials work.
- If the account is configured with 2FA, the MitM page will ask for it and once the user introduces it the tool will send it to the real web page.
- Once the user is authenticated you (as attacker) will have captured the credentials, the 2FA, the cookie and any information of every interaction your while the tool is performing a MitM.
Via VNC
What if instead of sending the victim to a malicious page with the same looks as the original one, you send him to a VNC session with a browser connected to the real web page? You will be able to see what he does, steal the password, the MFA used, the cookies...
You can do this with EvilnVNC
Detecting the detection
Obviously one of the best ways to know if you have been busted is to search your domain inside blacklists. If it appears listed, somehow your domain was detected as suspicions.
One easy way to check if you domain appears in any blacklist is to use https://malwareworld.com/
However, there are other ways to know if the victim is actively looking for suspicions phishing activity in the wild as explained in:
{% content-ref url="detecting-phising.md" %} detecting-phising.md {% endcontent-ref %}
You can buy a domain with a very similar name to the victims domain and/or generate a certificate for a subdomain of a domain controlled by you containing the keyword of the victim's domain. If the victim perform any kind of DNS or HTTP interaction with them, you will know that he is actively looking for suspicious domains and you will need to be very stealth.
Evaluate the phishing
Use Phishious to evaluate if your email is going to end in the spam folder or if it's going to be blocked or successful.
References
- https://zeltser.com/domain-name-variations-in-phishing/
- https://0xpatrik.com/phishing-domains/
- https://darkbyte.net/robando-sesiones-y-bypasseando-2fa-con-evilnovnc/
- https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/how-to-install-and-configure-dkim-with-postfix-on-debian-wheezy
{% hint style="success" %}
Learn & practice AWS Hacking: HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
Learn & practice GCP Hacking:  HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Support HackTricks
- Check the subscription plans!
- Join the 💬 Discord group or the telegram group or follow us on Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live.
- Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the HackTricks and HackTricks Cloud github repos.