13 KiB
Exploiting a debuggeable application
Learn AWS hacking from zero to hero with htARTE (HackTricks AWS Red Team Expert)!
Other ways to support HackTricks:
- If you want to see your company advertised in HackTricks or download HackTricks in PDF Check the SUBSCRIPTION PLANS!
- Get the official PEASS & HackTricks swag
- Discover The PEASS Family, our collection of exclusive NFTs
- Join the 💬 Discord group or the telegram group or follow me on Twitter 🐦 @carlospolopm.
- Share your hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the HackTricks and HackTricks Cloud github repos.
Bypassing root and debuggeable checks
This section of the post is a summary from the post https://medium.com/@shubhamsonani/hacking-with-precision-bypass-techniques-via-debugger-in-android-apps-27fd562b2cc0
Make the app debuggeable and execute it waiting for a debugger
Step 1 — Decompile the APK using APK-GUI tool. Edit the android-manifest file and add android:debuggable=true, to make the application debuggable. Recompile, sign and zipalign the application.
Step 2 — Install the application via -
adb install <application_name>.
Step 3 — Get the package name using -
adb shell pm list packages –3 (to list the 3rd party applications.
Step 4 — Now make the application wait for debugger via this command — adb shell am setup-debug-app –w <package_name>.
Note — You will require to run this command every time, before you start the application, so that application waits for debugger.
To make it persistent you can use –
adb shell am setup-debug-app –w -–persistent <package_name>.
To clear all the flags –
adb shell am clear-debug-app <package_name>.
Step 5 — Open the Android Studio -> File -> Open Profile or APK -> Open the recompiled APK.
Step 6 — Add breakpoints to the java files
- MainActivity.java — onCreate method, b.java, ContextWrapper.java
Bypass checks
At tome point the app will get information about the app to check if it's debuggeable and will also search for some binaries to see if the mobile is rooted. Using the debugger it's possible to change the app info to unset the debuggeable bit and change also the searched binaries names so those checks are bypassed. For example for the debuggeable check:
Step 1 — Under the variable section of the debugger console, navigate to “this mLoadedAPK -> mApplicationInfo -> flags = 814267974”
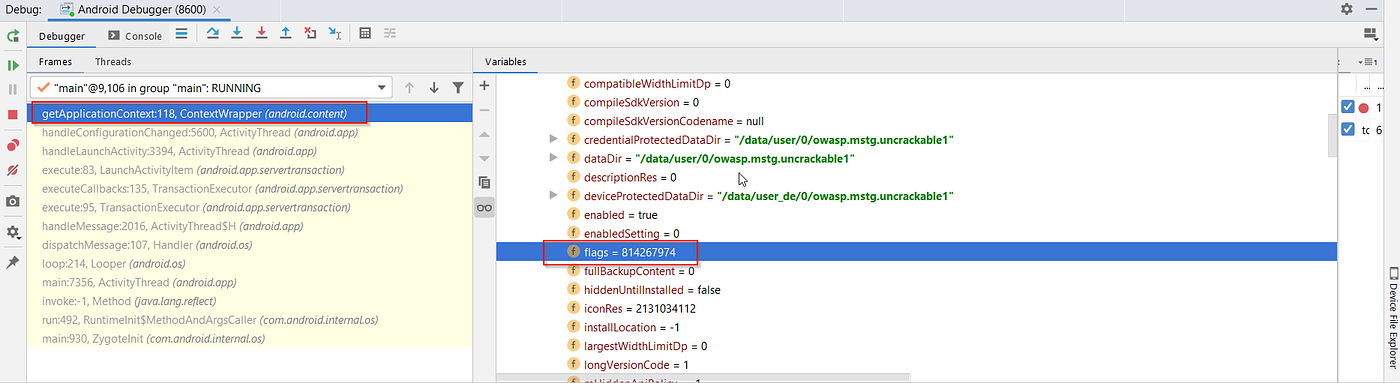
screenshot 9
Note: flags = 814267974 in binary bits is 11000011100111011110. This means “Flag_debuggable” is set.
Step 2 — Change the flag value to 814267972. Binary bits conversion — 110000101101000000100010100.
Exploiting a vuln
The following part of the post was copied from https://resources.infosecinstitute.com/android-hacking-security-part-6-exploiting-debuggable-android-applications/#article
To make this article more interesting, I have developed a vulnerable application for demonstration purposes, which has a “button” and a “textview“.
Fill out the form below to download the code associated with this article.
If we launch the application, it shows the message “Crack Me“.
Figure 1
If we click the button, it says “Try Again“. Now, our goal is to change the message “Try Again” to “Hacked” without modifying the application’s source code. To be precise, we have to change it at runtime.
Required tools
- Emulator
- adb – Android Debug Bridge
- jdb – Java Debugger
In my case, to make the installations easier, I am using Android Tamer since all the above required tools are pre-installed.
Topics Involved
- Checking for Vulnerability.
- Getting Ready with the Setup.
- Runtime Code Injection.
Let’s begin the game.
Checking for vulnerability
In fact, this is the easiest part of the entire article.
- Decompile the application using
apktoolto get theAndroidManifest.xmlfile using the following command.
apktool d <vulnerableapp>.apk
- Inspect
Androidmanifest.xmlfile for the following line.
android_debuggable="true"
If you find the above line in the AndroidManifest.xml file, the application is debuggable and it can be exploited.
Note: We used apktool to see whether the app is debuggable or not. We won’t touch or modify any piece of code as mentioned earlier.
Getting ready with the setup
In this step, we will set up all the required things to inject code in to the app during its execution. As mentioned in the previous article, we will use remote debugging in this article.
- Start Your Emulator
- Install the vulnerable application
- Open up your terminal and run the following command to see the Dalvik VM ports listening on the emulator.
adb jdwp
The above command displays all the ports on which we can connect and debug as shown below.
Figure 2
Note: JDWP stands for Java Debug Wire Protocol. If an application running in its VM is debuggable, it exposes a unique port on which we can connect to it using JDB. This is possible in Dalvik Virtual Machines with the support of JDWP.
- Now, launch our target application and run the same command to see the listening port associated with our target application. It looks as shown below.
Figure 2
If we observe the difference between Figure 2 and Figure 3, there is one extra port 543 listening after launching the target application in Figure 3. We will attach JDB to the application using this port, since this is our target.
- Before attaching to the application, we need to port forward using adb since we are using remote debugging. This is shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4
- Now, let’s attach JDB to the application as shown in the following figure.
Figure 5
Runtime code injection
In this step, we will actually exploit the vulnerable application by modifying its behavior at runtime.
To modify the application’s behavior at runtime, we need to set up breakpoints and control the flow. But, we don’t know what classes and methods are used in the application. So, let’s use the following commands to find out the classes and methods used in the application.
To find the classes: “classes”
Figure 6.1
Since I have too many classes listed, I am listing only a few classes. But if you still scroll down, you will see some interesting user defined classes as shown in the figure below.
Figure 6.2
Now, let us see the methods associated with MainActivity$1 class using the following command.
“methods com.example.debug.MainActivity$1”
This is shown in figure 7.
Figure 7
Now, let’s set up a breakpoint at onClick method and control the execution of the app as shown in Figure 8.
“stop in com.example.debug.MainActivity$1.onClick(android.view.View)”
Figure 8
To hit the breakpoint, we will have to manually click the button in the application. Once after clicking the button, the breakpoint will be hit and it appears as shown in Figure 9.
Figure 9
From here onwards, we will be able to control and see the sensitive values, method arguments, etc. using various commands.
Just to understand what’s happening in the background, I am following the code associated with the onClick method, which is shown in Figure 10.
Figure 10
Before proceeding further, let’s see if there are any local variables at this point in time using the command “locals“.
Figure 11
As we can see, there is no interesting information for us.
So, let’s execute the next line using the “next” command as shown below.
Figure 12
Let’s again try executing the command “locals” to see what happened in the previous command.
Figure 13
It’s pretty clear that TextView has been loaded into method arguments. If we look at the source code provided in Figure 10, the line associated with TextView instantiation has been executed.
Let’s now execute the next lines by executing the “next” command, and check the local variables as shown in the figure below.
Figure 14
As we can see, all the local variables have been displayed. The string “secret” looks interesting. The value “Try Again” is what is going to be printed when we click the button.
From Figure 10, it is very clear that the method setText is getting executed to print the value “Try Again“. So, let’s use the “step” command to get into the definition of the “setText” method and dynamically modify the text to be printed.
Figure 15
Let’s see the local variables inside the definition using “locals“.
Figure 16
Now, let’s change the value of “text” from “Try Again” to “Hacked” using “set” command.
Figure 17
We cannot see any changes in the application, since we haven’t executed the modified code.
So, let’s run the application using the “run” command as shown below, and see the application’s output on its screen.
Figure 18
Let’s look at the application running in the emulator.
Figure 19
We have successfully modified the output of the application at runtime. This is just an example to show how an application’s behavior can be modified if the application is debuggable. We can perform various other things including “Getting a shell” on the device in the context of the vulnerable application.
Learn AWS hacking from zero to hero with htARTE (HackTricks AWS Red Team Expert)!
Other ways to support HackTricks:
- If you want to see your company advertised in HackTricks or download HackTricks in PDF Check the SUBSCRIPTION PLANS!
- Get the official PEASS & HackTricks swag
- Discover The PEASS Family, our collection of exclusive NFTs
- Join the 💬 Discord group or the telegram group or follow me on Twitter 🐦 @carlospolopm.
- Share your hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the HackTricks and HackTricks Cloud github repos.



















