9.6 KiB
安装Burp证书
从零开始学习AWS黑客技术,成为专家 htARTE(HackTricks AWS Red Team Expert)!
支持HackTricks的其他方式:
- 如果您想看到您的公司在HackTricks中做广告或下载PDF格式的HackTricks,请查看订阅计划!
- 获取官方PEASS & HackTricks周边产品
- 探索PEASS家族,我们的独家NFTs
- 加入 💬 Discord群 或 电报群 或 关注我们的Twitter 🐦 @carlospolopm。
- 通过向HackTricks和HackTricks Cloud github仓库提交PR来分享您的黑客技巧。
在虚拟机上
首先,您需要从Burp中下载Der证书。您可以在_代理_ --> 选项 --> 导入/导出CA证书 中执行此操作
以Der格式导出证书,然后将其转换为Android能够理解的形式。请注意,为了在AVD中配置Burp证书,您需要使用**-writable-system选项运行**此虚拟机。
例如,您可以这样运行它:
{% code overflow="wrap" %}
C:\Users\<UserName>\AppData\Local\Android\Sdk\tools\emulator.exe -avd "AVD9" -http-proxy 192.168.1.12:8080 -writable-system
{% endcode %}
然后,配置Burp证书:
{% code overflow="wrap" %}
openssl x509 -inform DER -in burp_cacert.der -out burp_cacert.pem
CERTHASHNAME="`openssl x509 -inform PEM -subject_hash_old -in burp_cacert.pem | head -1`.0"
mv burp_cacert.pem $CERTHASHNAME #Correct name
adb root && sleep 2 && adb remount #Allow to write on /syste
adb push $CERTHASHNAME /sdcard/ #Upload certificate
adb shell mv /sdcard/$CERTHASHNAME /system/etc/security/cacerts/ #Move to correct location
adb shell chmod 644 /system/etc/security/cacerts/$CERTHASHNAME #Assign privileges
adb reboot #Now, reboot the machine
{% endcode %}
一旦机器完成重新启动,Burp证书将被其使用!
使用Magisc
如果您使用Magisc(可能是模拟器)对设备进行了root处理,并且由于文件系统是只读的且无法将其重新挂载为可写状态,因此无法按照之前的步骤安装Burp证书,那么还有另一种方法。
在此视频中有详细说明,您需要:
- 安装CA证书:只需将DER Burp证书拖放到移动设备上,将扩展名更改为
.crt,以便将其存储在下载文件夹中,然后转到安装证书->CA证书
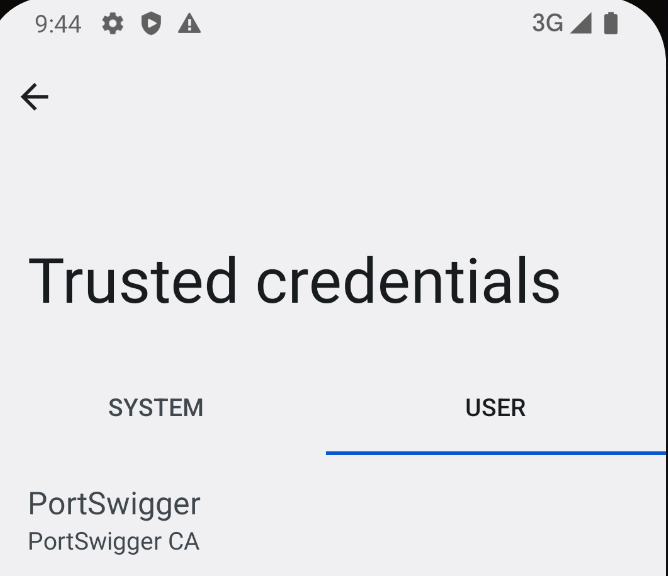
- 检查证书是否正确存储,转到
受信任的凭据->用户

- 使其成为系统信任的证书:下载Magisc模块MagiskTrustUserCerts(一个.zip文件),将其拖放到手机中,在手机中打开Magics应用,转到**
模块部分,点击从存储安装,选择.zip模块,安装后重新启动**手机:

- 重新启动后,转到
受信任的凭据->系统,检查Postswigger证书是否存在

Android 14后
在最新的Android 14版本中,观察到了系统信任的证书颁发机构(CA)证书处理方式的重大变化。以前,这些证书存储在**/system/etc/security/cacerts/中,用户可以使用root权限访问和修改,从而可以立即应用于整个系统。然而,随着Android 14的推出,存储位置已经移至/apex/com.android.conscrypt/cacerts,这是/apex**路径内的一个目录,具有不可变性。
尝试将APEX cacerts路径重新挂载为可写会失败,因为系统不允许此类操作。即使尝试卸载或使用临时文件系统(tmpfs)覆盖该目录也无法绕过不可变性;应用程序仍然会访问原始证书数据,而不考虑文件系统级别的更改。这种韧性是由于**/apex挂载配置为私有传播,确保/apex**目录内的任何修改不会影响其他进程。
Android的初始化涉及init进程,该进程在启动操作系统时还会启动Zygote进程。该进程负责使用包含私有**/apex**挂载的新挂载命名空间启动应用程序进程,从而将对该目录的更改与其他进程隔离开来。
然而,对于需要修改**/apex目录内系统信任的CA证书的人来说,存在一种解决方法。这涉及手动重新挂载/apex以去除私有传播,从而使其可写。该过程包括将/apex/com.android.conscrypt的内容复制到另一个位置,卸载/apex/com.android.conscrypt目录以消除只读约束,然后将内容恢复到/apex**内的原始位置。这种方法需要迅速行动以避免系统崩溃。为了确保这些更改在整个系统范围内应用,建议重新启动system_server,这将有效地重新启动所有应用程序并使系统处于一致状态。
# Create a separate temp directory, to hold the current certificates
# Otherwise, when we add the mount we can't read the current certs anymore.
mkdir -p -m 700 /data/local/tmp/tmp-ca-copy
# Copy out the existing certificates
cp /apex/com.android.conscrypt/cacerts/* /data/local/tmp/tmp-ca-copy/
# Create the in-memory mount on top of the system certs folder
mount -t tmpfs tmpfs /system/etc/security/cacerts
# Copy the existing certs back into the tmpfs, so we keep trusting them
mv /data/local/tmp/tmp-ca-copy/* /system/etc/security/cacerts/
# Copy our new cert in, so we trust that too
mv $CERTIFICATE_PATH /system/etc/security/cacerts/
# Update the perms & selinux context labels
chown root:root /system/etc/security/cacerts/*
chmod 644 /system/etc/security/cacerts/*
chcon u:object_r:system_file:s0 /system/etc/security/cacerts/*
# Deal with the APEX overrides, which need injecting into each namespace:
# First we get the Zygote process(es), which launch each app
ZYGOTE_PID=$(pidof zygote || true)
ZYGOTE64_PID=$(pidof zygote64 || true)
# N.b. some devices appear to have both!
# Apps inherit the Zygote's mounts at startup, so we inject here to ensure
# all newly started apps will see these certs straight away:
for Z_PID in "$ZYGOTE_PID" "$ZYGOTE64_PID"; do
if [ -n "$Z_PID" ]; then
nsenter --mount=/proc/$Z_PID/ns/mnt -- \
/bin/mount --bind /system/etc/security/cacerts /apex/com.android.conscrypt/cacerts
fi
done
# Then we inject the mount into all already running apps, so they
# too see these CA certs immediately:
# Get the PID of every process whose parent is one of the Zygotes:
APP_PIDS=$(
echo "$ZYGOTE_PID $ZYGOTE64_PID" | \
xargs -n1 ps -o 'PID' -P | \
grep -v PID
)
# Inject into the mount namespace of each of those apps:
for PID in $APP_PIDS; do
nsenter --mount=/proc/$PID/ns/mnt -- \
/bin/mount --bind /system/etc/security/cacerts /apex/com.android.conscrypt/cacerts &
done
wait # Launched in parallel - wait for completion here
echo "System certificate injected"
通过 NSEnter 进行绑定挂载
- 设置可写目录:首先,通过在现有非 APEX 系统证书目录上挂载
tmpfs来建立一个可写目录。使用以下命令实现:
mount -t tmpfs tmpfs /system/etc/security/cacerts
- 准备 CA 证书:在可写目录设置完成后,应将打算使用的 CA 证书复制到该目录中。这可能涉及从
/apex/com.android.conscrypt/cacerts/复制默认证书。必须相应地调整这些证书的权限和 SELinux 标签。 - 为 Zygote 进行绑定挂载:利用
nsenter,进入 Zygote 的挂载命名空间。Zygote 是负责启动 Android 应用程序的进程,需要执行此步骤以确保此后启动的所有应用程序都使用新配置的 CA 证书。使用的命令为:
nsenter --mount=/proc/$ZYGOTE_PID/ns/mnt -- /bin/mount --bind /system/etc/security/cacerts /apex/com.android.conscrypt/cacerts
这将确保每个新启动的应用程序都遵守更新后的 CA 证书设置。
- 将更改应用于正在运行的应用程序:要将更改应用于已经运行的应用程序,再次使用
nsenter逐个进入每个应用程序的命名空间,并执行类似的绑定挂载。必要的命令是:
nsenter --mount=/proc/$APP_PID/ns/mnt -- /bin/mount --bind /system/etc/security/cacerts /apex/com.android.conscrypt/cacerts
- 替代方法 - 软重启:另一种方法涉及在
init进程(PID 1)上执行绑定挂载,然后使用stop && start命令对操作系统进行软重启。这种方法将在所有命名空间中传播更改,避免了需要单独处理每个运行中的应用程序的需求。然而,由于重新启动的不便,通常不太受欢迎。
