8.9 KiB
Radio
SigDigger
****SigDigger is a free digital signal analyzer for GNU/Linux and macOS, designed to extract information of unknown radio signals. It supports a variety of SDR devices through SoapySDR, and allows adjustable demodulation of FSK, PSK and ASK signals, decode analog video, analyze bursty signals and listen to analog voice channels (all in real time).
Basic Config
After installing there are a few things that you could consider configuring.
In settings (the second tab button) you can select the SDR device or select a file to read and which frequency to syntonise and the Sample rate (recommended to up to 2.56Msps if your PC support it)\
In the GUI behaviour it's recommended to enable a few things if your PC support it:
{% hint style="info" %} If you realise that your PC is not capturing things try to disable OpenGL and lowering the sample rate. {% endhint %}
Synchronize with radio channel
With SigDigger synchronize with the channel you want to hear, configure "Baseband audio preview" option, configure the bandwith to get all the info being sent and then set the Tuner to the level before the noise is really starting to increase:
Interesting tricks
- When a device is sending bursts of information, usually the first part is going to be a preamble so you don't need to worry if you don't find information in there or if there are some errors there.
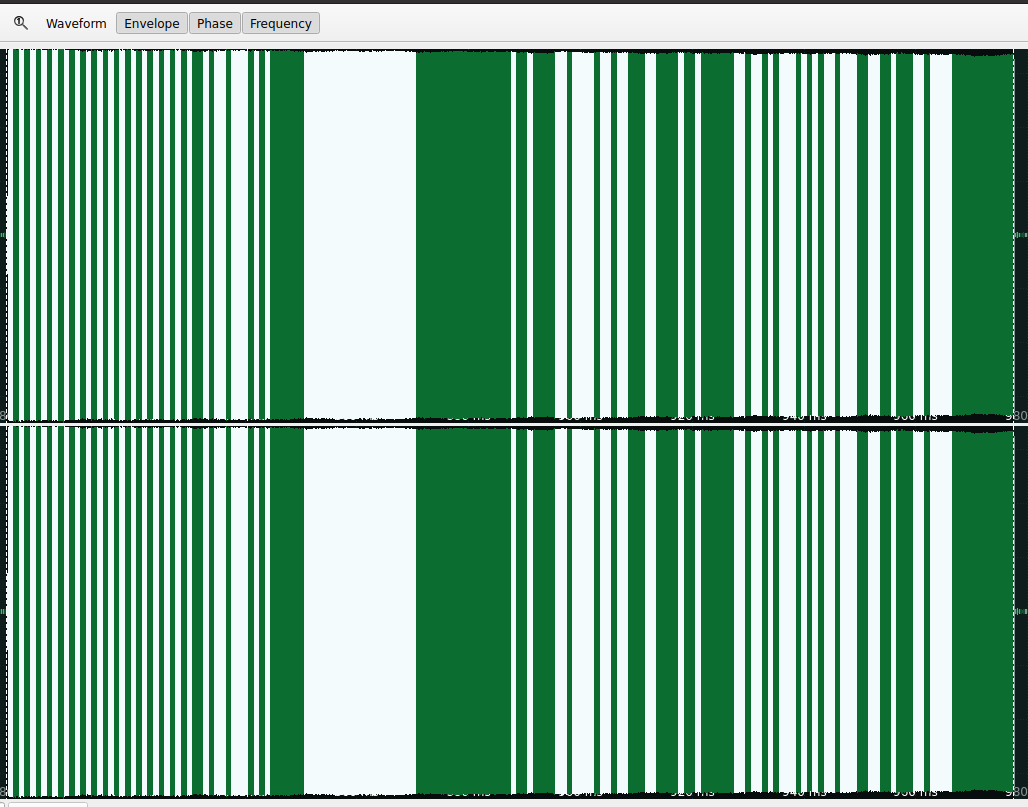
- In frames of information you usually should find different frames well aligned between them:
- After recovering the bytes you might need to process them someway. For example, in Manchester codification a up+down will be a 1 or 0 and a down+up will be the other one. So pairs of 1s and 0s (ups and downs) will be a real 1 or a real 0.
Uncovering modulation type with IQ
There are 3 ways to store information in signals: Modulating the amplitude, frequency or phase.
If you are checking a signal there are different ways to try to figure out what is being used to store information (fin more ways below) but a good one is to check the IQ graph.
- Detecting AM: If in the IQ graph appears for example 2 circles (probably one in 0 and other in a different amplitude), it could means that this is an AM signal. This is because in the IQ graph the distance between the 0 and the circle is the amplitude of the signal, so it's easy to visualize different amplitudes being used.
- Detecting PM: Like in the previous image, if you find small circles not related between them it probably means that a phase modulation is used. This is because in the IQ graph, the angle between the point and the 0,0 is the phase of the signal, so that means that 4 different phases are used.
AM Example
Uncovering AM
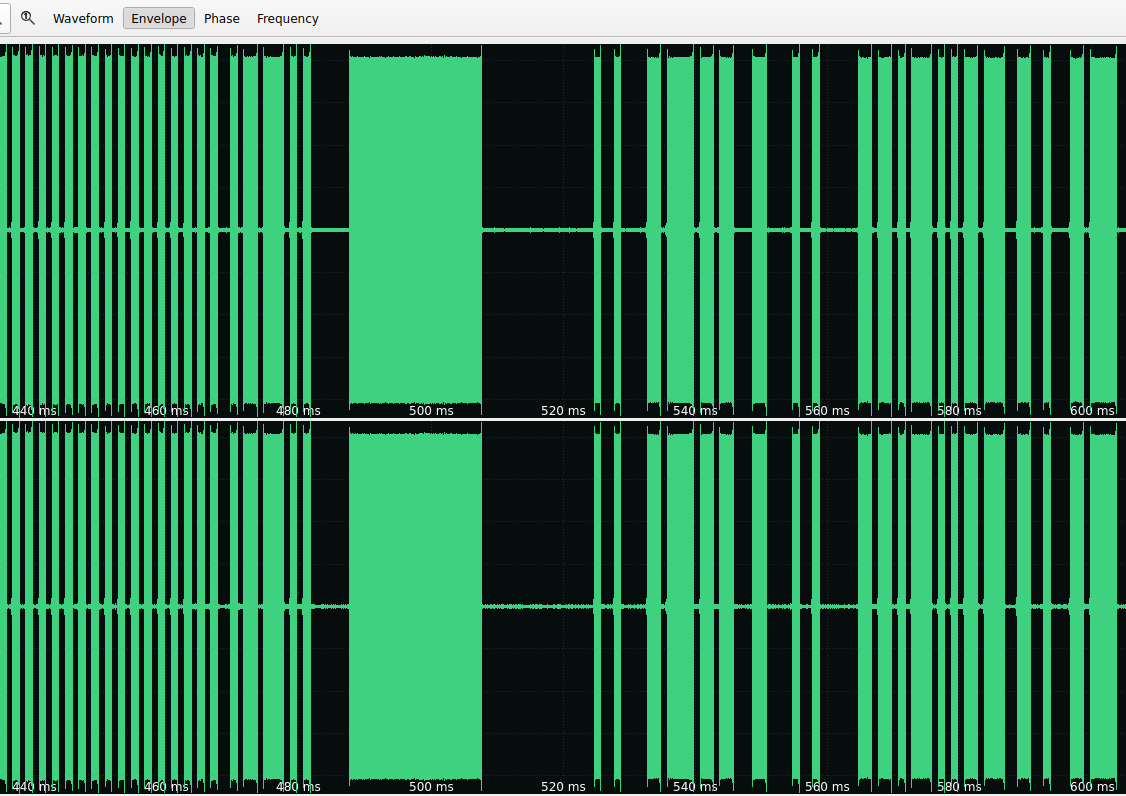
Checking the envelope
Checking AM info with SigDigger and just looking at the envelop you can see different clear amplitude levels. The used signal is sending pulses with information in AM, this is how one pulse looks like:
And this is how part of the symbol looks like with the waveform:
Checking the Histogram
You can select the whole signal where information is located, select Amplitude mode and Selection and click on Histogram. You can observer that 2 clear levels are only found
For example, if you select Frequency instead of Amplitude in this AM signal you find just 1 frequency (no way information modulated in frequency is just using 1 freq).
If you find a lot of frequencies potentially this won't be a FM, probably the signal frequency was just modified because of the channel.
With IQ
In this example you can see how there is a big circle but also a lot of points in the centre.
Get Symbol Rate
With one symbol
Select the smallest symbol you can find (so you are sure it's just 1) and check the "Selection freq". I this case it would be 1.013kHz (so 1kHz).
With a group of symbols
You can also indicate the number of symbols you are going to select and SigDigger will calculate the frequency of 1 symbol (the more symbols selected the better probably). In this scenario I selected 10 symbols and the "Selection freq" is 1.004 Khz:
Get Bits
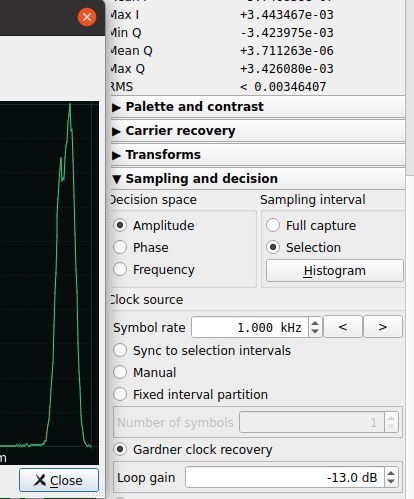
Having found this is an AM modulated signal and the symbol rate (and knowing that in this case something up means 1 and something down means 0), it's very easy to obtain the bits encoded in the signal. So, select the signal with info and configure the sampling and decision and press sample (check that Amplitude is selected, the discovered Symbol rate is configured and the Gadner clock recovery is selected):
- Sync to selection intervals means that if you previously selected intervals to find the symbol rate, that symbol rate will be used.
- Manual means that the indicated symbol rate is going to be used
- In Fixed interval selection you indicate the number of intervals that should be selected and it calculates the symbol rate from it
- Gadner clock recovery is usually the best option, but you still need to indicate some approximate symbol rate.
Pressing sample this appears:
Now, to make SigDigger understand where is the range of the level carrying information you need to click on the lower level and maintain clicked until the biggest level:
If there would have been for example 4 different levels of amplitude, you should have need to configure the Bits per symbol to 2 and select from the smallest to the biggest.
Finally increasing the Zoom and changing the Row size you can see the bits (and you can select all and copy to get all the bits):
If the signal has more than 1 bit per symbol (for example 2), SigDigger has no way to know which symbol is 00, 01, 10, 11, so it will use different grey scales the represent each (and if you copy the bits it will use numbers from 0 to 3, you will need to treat them).
Also, use codifications such as Manchester, and up+down can be 1 or 0 and an down+up can be a 1 or 0. In those cases you need to treat the obtained ups (1) and downs (0) to substitute the pairs of 01 or 10 as 0s or 1s.
FM Example
Uncovering FM
Checking the frequencies and waveform
Signal example sending information modulated in FM:
In the previous image you can observe pretty good that 2 frequencies are used but if you observe the waveform you might not be able to identify correctly the 2 different frequencies:
This is because I capture the signal in booth frequencies, therefore one is approximately the other in negative:
If the synchronized frequency is closer to one frequency than to the other you can easily see the 2 different frequencies:
Checking the histogram
Checking the frequency histogram of the signal with information you can easily see 2 different signals:
In this case if you check the Amplitude histogram you will find only one amplitude, so it cannot be AM (if you find a lot of amplitudes it might be because the signal has been losing power along the channel):
And this is would be phase histogram (which makes very clear the signal is not modulated in phase):
With IQ
IQ doesn't have a field to identify frequencies (distance to centre is amplitude and angle is phase).
Therefore, to identify FM, you should only see basically a circle in this graph.
Moreover,
Get Symbol Rate
You can use the same technique as the one used in the AM example to get the symbol rate once you have found the frequencies carrying symbols.
Get Bits
You can use the same technique as the one used in the AM example to get the bits once you have found the signal is modulated in frequency and the symbol rate.