13 KiB
21 - Pentesting FTP
{% hint style="success" %}
Learn & practice AWS Hacking: HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
Learn & practice GCP Hacking:  HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Support HackTricks
- Check the subscription plans!
- Join the 💬 Discord group or the telegram group or follow us on Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live.
- Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the HackTricks and HackTricks Cloud github repos.
Basic Information
The File Transfer Protocol (FTP) serves as a standard protocol for file transfer across a computer network between a server and a client.
It is a plain-text protocol that uses as new line character 0x0d 0x0a so sometimes you need to connect using telnet or nc -C.
Default Port: 21
PORT STATE SERVICE
21/tcp open ftp
Connections Active & Passive
In Active FTP the FTP client first initiates the control connection from its port N to FTP Servers command port – port 21. The client then listens to port N+1 and sends the port N+1 to FTP Server. FTP Server then initiates the data connection, from its port M to the port N+1 of the FTP Client.
But, if the FTP Client has a firewall setup that controls the incoming data connections from outside, then active FTP may be a problem. And, a feasible solution for that is Passive FTP.
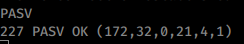
In Passive FTP, the client initiates the control connection from its port N to the port 21 of FTP Server. After this, the client issues a passv comand. The server then sends the client one of its port number M. And the client initiates the data connection from its port P to port M of the FTP Server.
Source: https://www.thesecuritybuddy.com/vulnerabilities/what-is-ftp-bounce-attack/
Connection debugging
The FTP commands debug and trace can be used to see how is the communication occurring.
Enumeration
Banner Grabbing
nc -vn <IP> 21
openssl s_client -connect crossfit.htb:21 -starttls ftp #Get certificate if any
Connect to FTP using starttls
lftp
lftp :~> set ftp:ssl-force true
lftp :~> set ssl:verify-certificate no
lftp :~> connect 10.10.10.208
lftp 10.10.10.208:~> login
Usage: login <user|URL> [<pass>]
lftp 10.10.10.208:~> login username Password
Unauth enum
With nmap
sudo nmap -sV -p21 -sC -A 10.10.10.10
You can us the commands HELP and FEAT to obtain some information of the FTP server:
HELP
214-The following commands are recognized (* =>'s unimplemented):
214-CWD XCWD CDUP XCUP SMNT* QUIT PORT PASV
214-EPRT EPSV ALLO* RNFR RNTO DELE MDTM RMD
214-XRMD MKD XMKD PWD XPWD SIZE SYST HELP
214-NOOP FEAT OPTS AUTH CCC* CONF* ENC* MIC*
214-PBSZ PROT TYPE STRU MODE RETR STOR STOU
214-APPE REST ABOR USER PASS ACCT* REIN* LIST
214-NLST STAT SITE MLSD MLST
214 Direct comments to root@drei.work
FEAT
211-Features:
PROT
CCC
PBSZ
AUTH TLS
MFF modify;UNIX.group;UNIX.mode;
REST STREAM
MLST modify*;perm*;size*;type*;unique*;UNIX.group*;UNIX.mode*;UNIX.owner*;
UTF8
EPRT
EPSV
LANG en-US
MDTM
SSCN
TVFS
MFMT
SIZE
211 End
STAT
#Info about the FTP server (version, configs, status...)
Anonymous login
anonymous : anonymous
anonymous :
ftp : ftp
ftp <IP>
>anonymous
>anonymous
>ls -a # List all files (even hidden) (yes, they could be hidden)
>binary #Set transmission to binary instead of ascii
>ascii #Set transmission to ascii instead of binary
>bye #exit
Brute force
Here you can find a nice list with default ftp credentials: https://github.com/danielmiessler/SecLists/blob/master/Passwords/Default-Credentials/ftp-betterdefaultpasslist.txt
Automated
Anon login and bounce FTP checks are perform by default by nmap with -sC option or:
nmap --script ftp-* -p 21 <ip>
Browser connection
You can connect to a FTP server using a browser (like Firefox) using a URL like:
ftp://anonymous:anonymous@10.10.10.98
Note that if a web application is sending data controlled by a user directly to a FTP server you can send double URL encode %0d%0a (in double URL encode this is %250d%250a) bytes and make the FTP server perform arbitrary actions. One of this possible arbitrary actions is to download content from a users controlled server, perform port scanning or try to talk to other plain-text based services (like http).
Download all files from FTP
wget -m ftp://anonymous:anonymous@10.10.10.98 #Donwload all
wget -m --no-passive ftp://anonymous:anonymous@10.10.10.98 #Download all
If your user/password has special characters, the following command can be used:
wget -r --user="USERNAME" --password="PASSWORD" ftp://server.com/
Some FTP commands
USER usernamePASS passwordHELPThe server indicates which commands are supported- **
PORT 127,0,0,1,0,80**This will indicate the FTP server to establish a connection with the IP 127.0.0.1 in port 80 (you need to put the 5th char as "0" and the 6th as the port in decimal or use the 5th and 6th to express the port in hex). - **
EPRT |2|127.0.0.1|80|**This will indicate the FTP server to establish a TCP connection (indicated by "2") with the IP 127.0.0.1 in port 80. This command supports IPv6. LISTThis will send the list of files in current folderLIST -RList recursively (if allowed by the server)
APPE /path/something.txtThis will indicate the FTP to store the data received from a passive connection or from a PORT/EPRT connection to a file. If the filename exists, it will append the data.STOR /path/something.txtLikeAPPEbut it will overwrite the filesSTOU /path/something.txtLikeAPPE, but if exists it won't do anything.RETR /path/to/fileA passive or a port connection must be establish. Then, the FTP server will send the indicated file through that connectionREST 6This will indicate the server that next time it send something usingRETRit should start in the 6th byte.TYPE iSet transfer to binaryPASVThis will open a passive connection and will indicate the user were he can connectsPUT /tmp/file.txtUpload indicated file to the FTP
FTPBounce attack
Some FTP servers allow the command PORT. This command can be used to indicate to the server that you wants to connect to other FTP server at some port. Then, you can use this to scan which ports of a host are open through a FTP server.
Learn here how to abuse a FTP server to scan ports.
You could also abuse this behaviour to make a FTP server interact with other protocols. You could upload a file containing an HTTP request and make the vulnerable FTP server send it to an arbitrary HTTP server (maybe to add a new admin user?) or even upload a FTP request and make the vulnerable FTP server download a file for a different FTP server.
The theory is easy:
- Upload the request (inside a text file) to the vulnerable server. Remember that if you want to talk with another HTTP or FTP server you need to change lines with
0x0d 0x0a - Use
REST Xto avoid sending the characters you don't want to send (maybe to upload the request inside the file you needed to put some image header at the beginning) - Use
PORTto connect to the arbitrary server and service - Use
RETRto send the saved request to the server.
Its highly probably that this will throw an error like Socket not writable because the connection doesn't last enough to send the data with RETR. Suggestions to try to avoid that are:
- If you are sending an HTTP request, put the same request one after another until ~0.5MB at least. Like this:
{% file src="../../.gitbook/assets/posts.txt" %} posts.txt {% endfile %}
- Try to fill the request with "junk" data relative to the protocol (talking to FTP maybe just junk commands or repeating the
RETRinstruction to get the file) - Just fill the request with a lot of null characters or others (divided on lines or not)
Anyway, here you have an old example about how to abuse this to make a FTP server download a file from a different FTP server.
Filezilla Server Vulnerability
FileZilla usually binds to local an Administrative service for the FileZilla-Server (port 14147). If you can create a tunnel from your machine to access this port, you can connect to it using a blank password and create a new user for the FTP service.
Config files
ftpusers
ftp.conf
proftpd.conf
vsftpd.conf
Post-Exploitation
The default configuration of vsFTPd can be found in /etc/vsftpd.conf. In here, you could find some dangerous settings:
anonymous_enable=YESanon_upload_enable=YESanon_mkdir_write_enable=YESanon_root=/home/username/ftp- Directory for anonymous.chown_uploads=YES- Change ownership of anonymously uploaded fileschown_username=username- User who is given ownership of anonymously uploaded fileslocal_enable=YES- Enable local users to loginno_anon_password=YES- Do not ask anonymous for passwordwrite_enable=YES- Allow commands: STOR, DELE, RNFR, RNTO, MKD, RMD, APPE, and SITE
Shodan
ftpport:21
HackTricks Automatic Commands
Protocol_Name: FTP #Protocol Abbreviation if there is one.
Port_Number: 21 #Comma separated if there is more than one.
Protocol_Description: File Transfer Protocol #Protocol Abbreviation Spelled out
Entry_1:
Name: Notes
Description: Notes for FTP
Note: |
Anonymous Login
-bi <<< so that your put is done via binary
wget --mirror 'ftp://ftp_user:UTDRSCH53c"$6hys@10.10.10.59'
^^to download all dirs and files
wget --no-passive-ftp --mirror 'ftp://anonymous:anonymous@10.10.10.98'
if PASV transfer is disabled
https://book.hacktricks.xyz/pentesting/pentesting-ftp
Entry_2:
Name: Banner Grab
Description: Grab FTP Banner via telnet
Command: telnet -n {IP} 21
Entry_3:
Name: Cert Grab
Description: Grab FTP Certificate if existing
Command: openssl s_client -connect {IP}:21 -starttls ftp
Entry_4:
Name: nmap ftp
Description: Anon login and bounce FTP checks are performed
Command: nmap --script ftp-* -p 21 {IP}
Entry_5:
Name: Browser Connection
Description: Connect with Browser
Note: ftp://anonymous:anonymous@{IP}
Entry_6:
Name: Hydra Brute Force
Description: Need Username
Command: hydra -t 1 -l {Username} -P {Big_Passwordlist} -vV {IP} ftp
Entry_7:
Name: consolesless mfs enumeration ftp
Description: FTP enumeration without the need to run msfconsole
Note: sourced from https://github.com/carlospolop/legion
Command: msfconsole -q -x 'use auxiliary/scanner/ftp/anonymous; set RHOSTS {IP}; set RPORT 21; run; exit' && msfconsole -q -x 'use auxiliary/scanner/ftp/ftp_version; set RHOSTS {IP}; set RPORT 21; run; exit' && msfconsole -q -x 'use auxiliary/scanner/ftp/bison_ftp_traversal; set RHOSTS {IP}; set RPORT 21; run; exit' && msfconsole -q -x 'use auxiliary/scanner/ftp/colorado_ftp_traversal; set RHOSTS {IP}; set RPORT 21; run; exit' && msfconsole -q -x 'use auxiliary/scanner/ftp/titanftp_xcrc_traversal; set RHOSTS {IP}; set RPORT 21; run; exit'
{% hint style="success" %}
Learn & practice AWS Hacking: HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
Learn & practice GCP Hacking:  HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Support HackTricks
- Check the subscription plans!
- Join the 💬 Discord group or the telegram group or follow us on Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live.
- Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the HackTricks and HackTricks Cloud github repos.