16 KiB
53 - Pentesting DNS
{% hint style="success" %}
Learn & practice AWS Hacking: HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
Learn & practice GCP Hacking:  HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
Support HackTricks
- Check the subscription plans!
- Join the 💬 Discord group or the telegram group or follow us on Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_live.
- Share hacking tricks by submitting PRs to the HackTricks and HackTricks Cloud github repos.
あなたのウェブアプリ、ネットワーク、クラウドに対するハッカーの視点を得る
実際のビジネスに影響を与える重大で悪用可能な脆弱性を見つけて報告します。 20以上のカスタムツールを使用して攻撃面をマッピングし、特権を昇格させるセキュリティ問題を見つけ、自動化されたエクスプロイトを使用して重要な証拠を収集し、あなたの努力を説得力のある報告書に変えます。
{% embed url="https://pentest-tools.com/?utm_term=jul2024&utm_medium=link&utm_source=hacktricks&utm_campaign=spons" %}
基本情報
ドメインネームシステム (DNS) はインターネットのディレクトリとして機能し、ユーザーがgoogle.comやfacebook.comのような覚えやすいドメイン名を通じてウェブサイトにアクセスできるようにします。これにより、数値のインターネットプロトコル (IP) アドレスの代わりに、ドメイン名をIPアドレスに変換することで、DNSはウェブブラウザがインターネットリソースを迅速に読み込むことを保証し、オンライン世界のナビゲートを簡素化します。
デフォルトポート: 53
PORT STATE SERVICE REASON
53/tcp open domain Microsoft DNS 6.1.7601 (1DB15D39) (Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1)
5353/udp open zeroconf udp-response
53/udp open domain Microsoft DNS 6.1.7601 (1DB15D39) (Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1)
Different DNS Servers
- DNS Root Servers: これらはDNS階層の最上部にあり、トップレベルドメインを管理し、下位サーバーが応答しない場合にのみ介入します。インターネット名称と番号割り当て機関(ICANN)がその運営を監督しており、世界中で13のサーバーがあります。
- Authoritative Nameservers: これらのサーバーは、指定されたゾーン内のクエリに対して最終的な回答を持ち、明確な答えを提供します。応答できない場合、クエリはルートサーバーにエスカレーションされます。
- Non-authoritative Nameservers: DNSゾーンに対する所有権がないこれらのサーバーは、他のサーバーへのクエリを通じてドメイン情報を収集します。
- Caching DNS Server: このタイプのサーバーは、将来のリクエストの応答時間を短縮するために、以前のクエリの回答を一定の時間記憶します。キャッシュの期間は権威あるサーバーによって決定されます。
- Forwarding Server: 単純な役割を果たすフォワーディングサーバーは、クエリを別のサーバーに中継するだけです。
- Resolver: コンピュータやルーターに統合されているリゾルバーは、ローカルで名前解決を実行し、権威あるものとは見なされません。
Enumeration
Banner Grabbing
DNSにはバナーはありませんが、version.bind. CHAOS TXTのマジッククエリを取得できます。これはほとんどのBINDネームサーバーで機能します。
このクエリはdigを使用して実行できます:
dig version.bind CHAOS TXT @DNS
さらに、ツール fpdns はサーバーのフィンガープリンティングも行うことができます。
nmap スクリプトを使用してバナーを取得することも可能です:
--script dns-nsid
Any record
レコード ANY は、DNSサーバーに 返す ように要求し、開示する意志のある すべての エントリ を取得します。
dig any victim.com @<DNS_IP>
ゾーン転送
この手順は Asynchronous Full Transfer Zone (AXFR) と略されます。
dig axfr @<DNS_IP> #Try zone transfer without domain
dig axfr @<DNS_IP> <DOMAIN> #Try zone transfer guessing the domain
fierce --domain <DOMAIN> --dns-servers <DNS_IP> #Will try toperform a zone transfer against every authoritative name server and if this doesn'twork, will launch a dictionary attack
さらに詳しい情報
dig ANY @<DNS_IP> <DOMAIN> #Any information
dig A @<DNS_IP> <DOMAIN> #Regular DNS request
dig AAAA @<DNS_IP> <DOMAIN> #IPv6 DNS request
dig TXT @<DNS_IP> <DOMAIN> #Information
dig MX @<DNS_IP> <DOMAIN> #Emails related
dig NS @<DNS_IP> <DOMAIN> #DNS that resolves that name
dig -x 192.168.0.2 @<DNS_IP> #Reverse lookup
dig -x 2a00:1450:400c:c06::93 @<DNS_IP> #reverse IPv6 lookup
#Use [-p PORT] or -6 (to use ivp6 address of dns)
自動化
for sub in $(cat <WORDLIST>);do dig $sub.<DOMAIN> @<DNS_IP> | grep -v ';\|SOA' | sed -r '/^\s*$/d' | grep $sub | tee -a subdomains.txt;done
dnsenum --dnsserver <DNS_IP> --enum -p 0 -s 0 -o subdomains.txt -f <WORDLIST> <DOMAIN>
nslookupの使用
nslookup
> SERVER <IP_DNS> #Select dns server
> 127.0.0.1 #Reverse lookup of 127.0.0.1, maybe...
> <IP_MACHINE> #Reverse lookup of a machine, maybe...
有用なMetasploitモジュール
auxiliary/gather/enum_dns #Perform enumeration actions
有用なnmapスクリプト
#Perform enumeration actions
nmap -n --script "(default and *dns*) or fcrdns or dns-srv-enum or dns-random-txid or dns-random-srcport" <IP>
DNS - リバースBF
dnsrecon -r 127.0.0.0/24 -n <IP_DNS> #DNS reverse of all of the addresses
dnsrecon -r 127.0.1.0/24 -n <IP_DNS> #DNS reverse of all of the addresses
dnsrecon -r <IP_DNS>/24 -n <IP_DNS> #DNS reverse of all of the addresses
dnsrecon -d active.htb -a -n <IP_DNS> #Zone transfer
{% hint style="info" %} 内部IPアドレスに解決するサブドメインを見つけることができた場合、そのIP範囲を要求するドメインのNSに対してリバースDNSブルートフォースを実行してみてください。 {% endhint %}
別のツールはこちら: https://github.com/amine7536/reverse-scan
リバースIP範囲をクエリできます: https://bgp.he.net/net/205.166.76.0/24#_dns (このツールはBGPにも役立ちます)。
DNS - サブドメインブルートフォース
dnsenum --dnsserver <IP_DNS> --enum -p 0 -s 0 -o subdomains.txt -f subdomains-1000.txt <DOMAIN>
dnsrecon -D subdomains-1000.txt -d <DOMAIN> -n <IP_DNS>
dnscan -d <domain> -r -w subdomains-1000.txt #Bruteforce subdomains in recursive way, https://github.com/rbsec/dnscan
Active Directoryサーバー
dig -t _gc._tcp.lab.domain.com
dig -t _ldap._tcp.lab.domain.com
dig -t _kerberos._tcp.lab.domain.com
dig -t _kpasswd._tcp.lab.domain.com
nslookup -type=srv _kerberos._tcp.<CLIENT_DOMAIN>
nslookup -type=srv _kerberos._tcp.domain.com
nmap --script dns-srv-enum --script-args "dns-srv-enum.domain='domain.com'"
DNSSec
#Query paypal subdomains to ns3.isc-sns.info
nmap -sSU -p53 --script dns-nsec-enum --script-args dns-nsec-enum.domains=paypal.com ns3.isc-sns.info
IPv6
サブドメインのIPv6を収集するために「AAAA」リクエストを使用したブルートフォース。
dnsdict6 -s -t <domain>
IPv6アドレスを使用した逆DNSのブルートフォース
dnsrevenum6 pri.authdns.ripe.net 2001:67c:2e8::/48 #Will use the dns pri.authdns.ripe.net
DNS再帰DDoS
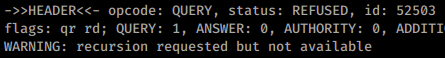
もしDNS再帰が有効であれば、攻撃者はUDPパケットの起源を偽装してDNSが被害者サーバーに応答を送信するようにすることができます。攻撃者はANYまたはDNSSECレコードタイプを悪用することができ、これらはより大きな応答を持つためです。
DNSが再帰をサポートしているかどうかを確認する方法は、ドメイン名をクエリし、フラグ "ra"(再帰利用可能)が応答に含まれているかを確認することです:
dig google.com A @<IP>
非利用可能:
利用可能:
ウェブアプリ、ネットワーク、クラウドに対するハッカーの視点を得る
実際のビジネスに影響を与える重大で悪用可能な脆弱性を見つけて報告します。 攻撃面をマッピングし、特権を昇格させるセキュリティ問題を見つけるために、20以上のカスタムツールを使用し、自動化されたエクスプロイトを利用して重要な証拠を収集し、あなたの努力を説得力のある報告書に変えます。
{% embed url="https://pentest-tools.com/?utm_term=jul2024&utm_medium=link&utm_source=hacktricks&utm_campaign=spons" %}
存在しないアカウントへのメール
ターゲットドメイン内の無効なアドレスに送信されたメールによってトリガーされた配信不能通知(NDN)を調査することで、貴重な内部ネットワークの詳細がしばしば開示されます。
提供された配信不能報告には以下の情報が含まれています:
- 生成サーバーは
server.example.comとして特定されました。 user@example.comに対する失敗通知がエラーコード#550 5.1.1 RESOLVER.ADR.RecipNotFound; not foundと共に返されました。- 元のメッセージヘッダーに内部IPアドレスとホスト名が開示されました。
The original message headers were modified for anonymity and now present randomized data:
Generating server: server.example.com
user@example.com
#550 5.1.1 RESOLVER.ADR.RecipNotFound; not found ##
Original message headers:
Received: from MAILSERVER01.domain.example.com (192.168.1.1) by
mailserver02.domain.example.com (192.168.2.2) with Microsoft SMTP Server (TLS)
id 14.3.174.1; Mon, 25 May 2015 14:52:22 -0700
Received: from filter.example.com (203.0.113.1) by
MAILSERVER01.domain.example.com (192.168.1.1) with Microsoft SMTP Server (TLS)
id 14.3.174.1; Mon, 25 May 2015 14:51:22 -0700
X-ASG-Debug-ID: 1432576343-0614671716190e0d0001-zOQ9WJ
Received: from gateway.domainhost.com (gateway.domainhost.com [198.51.100.37]) by
filter.example.com with ESMTP id xVNPkwaqGgdyH5Ag for user@example.com; Mon,
25 May 2015 14:52:13 -0700 (PDT)
X-Envelope-From: sender@anotherdomain.org
X-Apparent-Source-IP: 198.51.100.37
設定ファイル
host.conf
/etc/resolv.conf
/etc/bind/named.conf
/etc/bind/named.conf.local
/etc/bind/named.conf.options
/etc/bind/named.conf.log
/etc/bind/*
危険な設定をBindサーバーを構成する際に:
| オプション | 説明 |
|---|---|
allow-query |
DNSサーバーにリクエストを送信できるホストを定義します。 |
allow-recursion |
DNSサーバーに再帰的リクエストを送信できるホストを定義します。 |
allow-transfer |
DNSサーバーからゾーントランスファーを受信できるホストを定義します。 |
zone-statistics |
ゾーンの統計データを収集します。 |
参考文献
- https://www.myrasecurity.com/en/knowledge-hub/dns/
- 書籍: Network Security Assessment 3rd edition
HackTricks 自動コマンド
Protocol_Name: DNS #Protocol Abbreviation if there is one.
Port_Number: 53 #Comma separated if there is more than one.
Protocol_Description: Domain Name Service #Protocol Abbreviation Spelled out
Entry_1:
Name: Notes
Description: Notes for DNS
Note: |
#These are the commands I run every time I see an open DNS port
dnsrecon -r 127.0.0.0/24 -n {IP} -d {Domain_Name}
dnsrecon -r 127.0.1.0/24 -n {IP} -d {Domain_Name}
dnsrecon -r {Network}{CIDR} -n {IP} -d {Domain_Name}
dig axfr @{IP}
dig axfr {Domain_Name} @{IP}
nslookup
SERVER {IP}
127.0.0.1
{IP}
Domain_Name
exit
https://book.hacktricks.xyz/pentesting/pentesting-dns
Entry_2:
Name: Banner Grab
Description: Grab DNS Banner
Command: dig version.bind CHAOS TXT @DNS
Entry_3:
Name: Nmap Vuln Scan
Description: Scan for Vulnerabilities with Nmap
Command: nmap -n --script "(default and *dns*) or fcrdns or dns-srv-enum or dns-random-txid or dns-random-srcport" {IP}
Entry_4:
Name: Zone Transfer
Description: Three attempts at forcing a zone transfer
Command: dig axfr @{IP} && dix axfr @{IP} {Domain_Name} && fierce --dns-servers {IP} --domain {Domain_Name}
Entry_5:
Name: Active Directory
Description: Eunuerate a DC via DNS
Command: dig -t _gc._{Domain_Name} && dig -t _ldap._{Domain_Name} && dig -t _kerberos._{Domain_Name} && dig -t _kpasswd._{Domain_Name} && nmap --script dns-srv-enum --script-args "dns-srv-enum.domain={Domain_Name}"
Entry_6:
Name: consolesless mfs enumeration
Description: DNS enumeration without the need to run msfconsole
Note: sourced from https://github.com/carlospolop/legion
Command: msfconsole -q -x 'use auxiliary/scanner/dns/dns_amp; set RHOSTS {IP}; set RPORT 53; run; exit' && msfconsole -q -x 'use auxiliary/gather/enum_dns; set RHOSTS {IP}; set RPORT 53; run; exit'
ウェブアプリ、ネットワーク、クラウドに対するハッカーの視点を得る
実際のビジネスに影響を与える重大で悪用可能な脆弱性を見つけて報告します。 20以上のカスタムツールを使用して攻撃面をマッピングし、特権を昇格させるセキュリティ問題を見つけ、自動化されたエクスプロイトを使用して重要な証拠を収集し、あなたの努力を説得力のある報告書に変えます。
{% embed url="https://pentest-tools.com/?utm_term=jul2024&utm_medium=link&utm_source=hacktricks&utm_campaign=spons" %}
{% hint style="success" %}
AWSハッキングを学び、実践する: HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
HackTricks Training AWS Red Team Expert (ARTE)
GCPハッキングを学び、実践する: HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
HackTricks Training GCP Red Team Expert (GRTE)
HackTricksをサポートする
- サブスクリプションプランを確認してください!
- **💬 Discordグループまたはテレグラムグループに参加するか、Twitter 🐦 @hacktricks_liveをフォローしてください。
- ハッキングのトリックを共有するために、HackTricksとHackTricks CloudのGitHubリポジトリにPRを提出してください。